Deuterium-Depleted Water as Adjuvant Therapeutic Agent for Treatment of Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Somatometric and Nutritional Parameters in Control and DIO Rats that Consumed either MilliQ Water or DDW
2.2. Biochemical Parameters at the End of the Experiment in Control and DIO Rats that Consumed either MilliQ Water or DDW
2.3. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in Serum at the End of the Experiment in Control and DIO Rats that Consumed either MilliQ Water or DDW
2.4. Serum Cytokine Profile at the End of the Experiment in Control and DIO Rats that Consumed either MilliQ Water or DDW
2.5. End of Experiment Levels of Tryptophan and Serotonin in the Brains of Control and DIO Rats that had Consumed MilliQ Water or DDW
2.6. End of Experiment Levels of Certain Heavy Metals in the Livers of Control and DIO Rats that had Consumed either MilliQ Water or DDW
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Physicochemical Analysis of Water with Different Deuterium Ratios
4.2. Animals and Housing Conditions
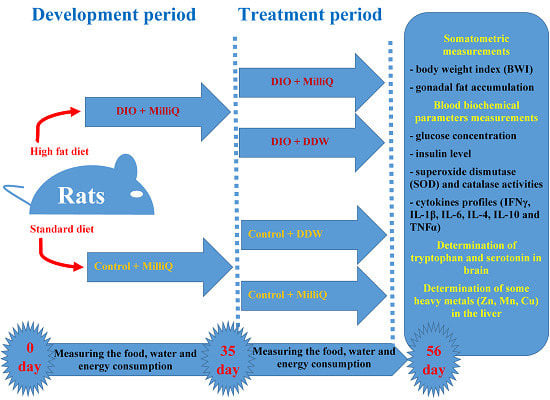
4.3. Experimental Design
4.4. Somatometric and Nutritional Assessments
4.5. Biochemical Analysis
4.6. Heavy Metal Analysis in Rat Liver
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic. Available online: http://www.who.int/nutrition/publications/obesity/WHO_TRS_894/en/ (accessed on 10 February 2016).
- Qatanani, M.; Lazar, M.A. Mechanisms of obesity-associated insulin resistance: Many choices on the menu. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Golay, A.; Ybarra, J. Link between obesity and type 2 diabetes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 19, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novelli, E.L.B.; Fernandes, A.; Campos, K.; Diniz, Y.; Almeida, J.; Ribas, B.O. The adverse effects of a high-energy dense diet on cardiac tissue. J. Nutr. Environ. Med. 2002, 12, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, F.; Kaaks, R.; Vainiuo, H. Overweight, obesity and cancer risk. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafort, T.T.; Rufino, R.; Costa, C.H.; Lopes, A.J. Obesity: Systemic and pulmonary complications, biochemical abnormalities, and impairment of lung function. Multidiscip. Resp. Med. 2016, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowen, G.J.; Winter, D.A.; Spero, H.J.; Zierenberg, R.A.; Reeder, M.D.; Cerling, T.E.; Ehleringer, J.R. Stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios of bottled waters of the world. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 3442–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharuk, V.V.; Lapshin, V.B.; Burdeynaya, T.N.; Pleteneva, T.V.; Chernopyatko, A.S.; Atamanenko, I.D.; Ul’yantsev, A.S.; Uspenskaya, E.V.; Samsoni-Todorov, A.O.; Taranov, V.V.; et al. Physico-chemical properties and biological activity of water, lean on heavy isotope. Chem. Technol. Water. 2011, 33, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, G.N. Biology of heavy water. Nature 1934, 133, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobyshev, V.N.; Kalinichenko, L.P. Isotopic Effects in Biological Systems; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1978. (In Russia) [Google Scholar]
- Cleland, W.W. The use of isotope effects to determine enzyme mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 51975–51984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ignatov, I.I.; Mosin, O.V. Isotopic Composition of Water and the Longevity. Water Hyg. Ecolog. 2013, 3, 22–32. (In Russia) [Google Scholar]
- Strekalova, T.; Evansa, M.; Chernopiatko, A.; Coucha, Y.; Costa-Nunes, J.; Cespuglio, R.; Chesson, L.; Vignisse, J.; Steinbusch, H.W.; Anthony, D.C.; et al. Deuterium content of water increases depression susceptibility: The potential role of a serotonin-related mechanism. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cărpinişan, L.; Petcu, M.D.; Petrovici, S.; Chiş, C.; Ghişe, A.; Zehan, R. The Influence of deuterium depleted water on the hematocrit and the leukocyte formula in rats intoxicated with chromium. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 43, 464–468. [Google Scholar]
- Olariu, L.; Petcu, M.; Cuna, S.; Scurtu, M.; Tulcan, C.; Brudiu, I. The role of deuterium depleted water (ddw) administration in blood deuterium concentration in Cr (VI) intoxicated rats. Lucr. Stiinłifice Med. Vet. 2010, 43, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, D.S.; Somlyai, G.; Somlyai, I.; Aschner, M. Antiaging effects of deuterium depletion on Mn-induced toxicity in a C.elegans model. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 211, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goncharuk, V.V.; Syroeshkin, A.V.; Zlatskiy, I.A.; Uspenskaya, E.V.; Orekhova, A.V.; Levitskaya, O.V.; Dobrovolskiy, V.I.; Pleteneva, T. Quasi-chemical description of the kinetics of cell death Spirostomum ambiguum biosensor for biological activity of aqueous solutions. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2017, 39, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syroeshkin, A.V.; Pleteneva, T.V.; Uspenskaya, E.V.; Zlatskiy, I.A.; Antipova, N.V.; Grebennikova, T.V.; Levitskaya, O.V. D/H control of chemical kinetics in water solutions under low deuterium concentrations. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 377, 119827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somlyai, G. Use of deuterium depleted water for the treatment of insulin resistance. CA Patent CA2805313A1, 12 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lobyshev, V.I.; Kirkina, A.A. Influence of variations in the isotopic composition of water on its biological activity. In Proceedings of the VI Int Congr «Weak and superweak fields and radiations in biology and medicine», St. Petersburg, Russia, 2–6 July 2012; pp. 1–38. (In Russia). [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Changgong, M. Method for production of deuterium depleted potable water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 378–381. [Google Scholar]
- Somlyai, G. Defeating cancer. In The Biological Effects of Deuterium Depletion; Author House: Bloomington, IN, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Atzrodt, J.; Derdau, V.; William, J.; Reid, M. Deuterium- and Tritium-Labelled Compounds: Applications in the Life Sciences. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1758–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gyöngyi, Z.; Budán, F.; Szabó, I. Deuterium Depleted Water Effects on Survival of Lung Cancer Patients and Expression of Kras, Bcl2, and Myc Genes in Mouse Lung. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basov, A.; Fedulova, L.; Baryshev, M.; Dzhimak, S. Deuterium-Depleted Water Influence on the Isotope 2H/1H Regulation in Body and Individual Adaptation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boros, L.G.; D’Agostino, D.P.; Katz, H.E. Submolecular regulation of cell transformation by deuterium depleting water exchange reactions in the tricarboxylic acid substrate cycle. Med. Hypotheses 2016, 87, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlatska, O.V.; Zubov, D.O.; Vasyliev, R.G.; Syroeshkin, A.V.; Zlatskiy, I.A. Deuterium Effect on Proliferation and Clonogenic Potential of Human Dermal Fibroblasts In Vitro. Probl. Cryobiol. Cryomed. 2018, 28, 049–053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goncharuk, V.V.; Pleteneva, T.V.; Grebennikova, T.V.; Syroeshkin, A.V.; Uspenskaya, E.V.; Antipova, N.V.; Kovalenko, V.F.; Saprykina, M.N.; Skil’skaya, M.D.; Zlatskiy, I.A. Determination of Biological Activity of Water Having a Different Isotope Ratio of Protium and Deuterium. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2018, 40, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syroeshkin, A.V.; Antipova, N.V.; Zlatska, A.V.; Zlatskiy, I.A.; Skylska, M.D.; Grebennikova, T.V.; Goncharuk, V.V. The effect of the deuterium depleted water on the biological activity of the eukaryotic cells. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 50, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatska, A.; Gordiienko, I.; Vasyliev, R.; Zubov, D.; Gubar, O.; Rodnichenko, A.; Syroeshkin, A.; Zlatskiy, I. In Vitro study of deuterium effect on biological properties of human cultured adipose-derived stem cells. Sci. World J. 2018, 2018, 4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hang, M.; Huynh, V.; Meyer, T.J. Colossal kinetic isotope effects in proton-coupled electron transfer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13138–13141. [Google Scholar]
- Dzhimak, S.S.; Basov, A.A.; Baryshev, M.G. Content of Deuterium in Biological fluids and organs: Influence of deuterium depleted water on D/H gradient and the process of adaptation biochemistry. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2015, 465, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomytkin, I.A.; Kolesova, O.E. Relationship between Natural concentration of heavy water isotopologs and rate of H2O2 generation by mitochondria. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2006, 142, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halenova, T.; Raksha, N.; Vovk, T.; Savchuk, O.; Ostapchenko, L.; Prylutskyy, Y.; Kyzyma, O.; Ritter, U.; Scharff, P. Effect of C60 fullerene nanoparticles on the diet-induced obesity in rats. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiganis, T. Reactive oxygen species and insulin resistance: The good, the bad and the ugly. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konukoğlu, D.; Serin, O.; Ercan, M.; Turhan, M.S. Plasma homocysteine levels in obese and non-obese subjects with or without hypertension; its relationship with oxidative stress and copper. Clin. Biochem. 2003, 36, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halenova, T.; Savchuk, O.; Ostapchenko, L.; Chursov, A.; Fridlyand, N.; Komissarov, A.B.; Venanzi, F.; Kolesnikov, S.I.; Sufianov, A.A.; Sherman, M.Y.; et al. P62 plasmid can alleviate diet-induced obesity and metabolic dysfunctions. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56030–56040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, R.W.; Dixit, V.D. Adipose tissue as an immunological organ. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2015, 23, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Saltiel, A.R. Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2111–21117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Youm, Y.H.; Vandanmagsar, B. Obesity increases the production of proinflammatory mediators from adipose tissue T cells and compromises TCR repertoire diversity: Implications for systemic inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1836–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voigt, J.P.; Fink, H. Serotonin controlling feeding and satiety. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.M.; Park, S.; Kim, H. Serotonin as a new therapeutic target for diabetes mellitus and obesity. Diabetes Metab. J. 2016, 40, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skolarczyk, J.; Pekar, J.; Łabądź, D.; Skórzyńska-Dziduszko, K. Role of heavy metals in the development of obesity: A review of research. J. Elem. 2018, 23, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkanlou, K.; Bibak, B.; Abbaspour, A.; Abdi, H.; Saleh Moghaddam, M.; Tayefi, M.; Mohammadzadeh, E.; Safarian Bana, H.; Aghasizade, M.; Ferns, G.A.; et al. Reduced serum levels of zinc and superoxide dismutase in obese individuals. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 69, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.L.; Zheng, Y.L.; Cong, F.S. Research progress of biological effects of deuterium-depleted water. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Med Sci.) 2018, 38, 467–471. [Google Scholar]
- Robins, R.J.; Remaud, G.S.; Billault, I. Natural mechanisms by which deuterium depletion occurs in specific positions in metabolites. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2012, 1, 39–40. [Google Scholar]
- Basov, A.A.; Elkina, A.A.; Samkov, A.A.; Volchenko, N.N.; Moiseev, A.V.; Fedulova, L.V.; Baryshev, M.G.; Dzhimak, S.S. Influence of Deuterium-Depleted Water on the Isotope D/H Composition of Liver Tissue and Morphological Development of Rats at Different Periods of Ontogenesis. Iran Biomed. J. 2018, 23, 129–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Toki, H.; Fujita, Y.; Ma, M.; Chang, L.; Qu, Y.; Harada, S.; Nemoto, T.; Mizuno-Yasuhira, A.; Yamaguchi, J.I.; et al. Lack of deuterium isotope effects in the antidepressant effects of (R)-ketamine in a chronic social defeat stress model. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 3177–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farthing, D.E.; Buxbaum, N.P.; Lucas, P.J.; Maglakelidze, N.; Oliver, B.; Wang, J.; Hu, K.; Castro, E.; Bare, C.V.; Gress, R.R. Comparing DNA enrichment of proliferating cells following administration of different stable isotopes of heavy water. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charidemou, E.; Ashmore, T.; Griffin, J.L. The use of stable isotopes in the study of human pathophysiology. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 93, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.J.; Park, H.-J.; Cho, N.; Kim, H.P. Aquaporin 11-Dependent Inhibition of Proliferation by Deuterium Oxide in Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, X.H.; Tang, Q.Y.; Huang, J.; Cai, W. Vitamin E regulates adipocytokine expression in a rat model of dietary-induced obesity. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2010, 235, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, A.N.; Struve, M.F.; Mueller, R.A.; Lee, M.B.; Kissebah, A.H. Glucose metabolism in obesity: Influence of body fat distribution. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1988, 67, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, A.N.; Mueller, R.A.; Smith, G.A.; Struve, M.F.; Kissebah, A.H. Splanchnic insulin metabolism in obesity. Influ. Body Fat Distrib. J. Clin. Invest. 1986, 78, 1648–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, C.J.; Hodson, L. The influence of dietary fat on liver fat accumulation. Nutrients 2014, 6, 5018–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhimak, S.; Basov, A.; Fedulova, L.; Kotenkova, E. Influence of deuterium depleted water on indicators of prooxidant-antioxidant and detoxifying systems in experimental diabetes. Life Sci. 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehakova, R.; Klimentova, J.; Cebova, M.; Barta, A.; Matuskova, Z.; Labas, P.; Pechanova, O. Effect of Deuterium-Depleted Water on Selected Cardiometabolic Parameters in Fructose-Treated Rats. Physiol. Res. 2016, 65 (Suppl. 3), S401–S407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boros, L.; Lee, P.; Brandes, J.; Cascante, M.; Muscarella, P.; Schirmer, W.; Melvin, W.; Ellison, E. Nonoxidative pentose phosphate pathways and their direct role in ribose synthesis in tumors: Is cancer a disease of cellular glucose metabolism? Med. Hypotheses 1998, 50, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.S.; King, J.C.; Lowe, N. A review of dietary zinc recommendations. Food Nutr. Bull. 2016, 30, S108–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Chen, C.; Nie, X.; Han, B.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Y.; Xia, F.; Cang, Z.; et al. Blood lead level and its association with body mass index and obesity in China—Results from SPECT-China study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Bu, J. Relationship between selected serum metallic elements and obesity in children and adolescent in the U.S. Nutrients 2017, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy-Bushrow, A.E.; Havstad, S.; Basu, N.; Ownby, D.R.; Park, S.K.; Ownby, D.R.; Johnson, C.C.; Wegienka, G. Detectable blood lead level and body size in early childhood. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 171, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Błażewicz, A.; Klatka, M.; Astel, A.; Partyka, M.; Kocjan, R. Differences in trace metal con-centrations (Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, Zn, Cd and Ni) in whole blood, plasma, and urine of obese and nonobese children. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 55, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Zubarev, R.A. On the Effect of Planetary Stable Isotope Compositions on Growth and Survival of Terrestrial Organisms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, K.; Kooshesh, L. Deuterium Depleted Water Inhibits the Proliferation of Human MCF7 Breast Cancer Cell Lines by Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest. Nutr. Cancer 2019, 71, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacey, D.C.; Achuthan, A.; Fleetwood, A.J. Defining GM-CSF- and macrophage-CSF-dependent macrophage responses by in vitro models. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 5752–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, R.W.; White, A.E.; Metcalf, M.D. Systemic inflammation and insulin sensitivity in obese IFN-gamma knockout mice. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pollard, K.M.; Cauvi, D.M.; Toomey, C.B.; Morris, K.V.; Kono, D.H. Interferon-gamma and systemic autoimmunity. Discov. Med. 2013, 16, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Negrin, K.A.; Roth Flach, R.J.; DiStefano, M.T. IL-1 signaling in obesity-induced hepatic lipogenesis and steatosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donath, M.Y.; Storling, J.; Berchtold, L.A.; Billestrup, N.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Cytokines and ß-cell biology: From concept to clinical translation. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrigan, C.; Pang, K. Obesity market overview. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpovets, T.P.; Savchuk, O.M.; Ostapchenko, L.I. Serotonin metabolism system as a potential target for correction of metabolic imbalance under development obesity. Biopharm. J. 2014, 6, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Young, S.N. How to increase serotonin in the human brain without drugs. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2007, 32, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, C. Serotonin in Pain and Pain Control. In Handbook of the Behavioral Neurobiology of Serotonin, 1st ed.; Jacobs, C.P., Müller, B., Eds.; Academic: London, UK, 2009; pp. 457–460. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, P.W.; Bharwani, A.; Lee, K.R.; Fox, M.; Thomson, J.A. Is serotonin an upper or a downer? The evolution of the serotonergic system and its role in depression and the antidepressant response. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 51, 164–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, L.G.; Collins, T.Q.; Somlyai, G. What to eat or what not to eat - that is still the question. Neuro. Oncol. 2017, 19, 595–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Novelli, E.L.; Diniz, Y.S.; Galhardi, C.M.; Ebaid, G.M.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Mani, F.; Fernandes, A.A.; Cicogna, A.C.; Novelli Filho, J.L. Anthropometrical parameters and markers of obesity in rats Laboratory Animals Ltd. Lab Anim. 2007, 41, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sirota, T.V. A novel approach to study the reaction of adrenaline autooxidation: A possibility for polarographic determination of superoxide dismutase activity and antioxidant properties of various preparations. Biochemistry 2011, 5, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolyuk, M.A.; Ivanova, L.I.; Maiorova, I.G.; Tokarev, V.E. Method for determining the activity of catalase. Lab Delo 1988, 1, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximenko, E.; Savchenko, V. The level of tryptophan and serotonin in terms of seizure activity in the brain. J. VN Karazin Kharkiv Natl. Univ. Med. 2000, 494, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, J.W.; Skelly, E.; George, M. Undergraduate Instrumental Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 441–505. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: The experimental data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request. |




| Parameters | Experimental Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control + MilliQ | Control + DDW | DIO + MilliQ | DIO + DDW | |
| Biochemical Parameters | ||||
| Glucose (blood), | 4.5 ± 0.4 | 4.2 ± 0.3 | 6.5 ± 0.8 * | 4.9 ± 0.03 |
| Insulin (serum), rel. un/mL of total protein | 0.312 ± 0.066 | 0.298 ± 0.029 # | 0.141 ± 0.011 * | 0.120 ± 0.024 * |
| Catalase activities (serum), µmol Н2О2∙mg−1∙min−1 | 5.68 ± 0.87 | 7.00 ± 0.26 # | 2.43 ± 0.33 * | 6.18 ± 1.21 # |
| SOD activities (serum), c.u./mg∙min | 27.44 ± 2.41 | 15.62 ± 3.24 *,# | 4.78 ± 0.99 * | 10.77 ± 2.18 *,# |
| Tryptophan (brain), µg∙g−1 tissue | 9.57 ± 1.98 | 8.74 ± 1.57 # | 4.89 ± 0.83 * | 6.89 ± 1.89 # |
| Serotonin (brain), µg∙g−1 tissue | 1.23 ± 0.27 | 1.06 ± 0.24 | 0.64 ± 0.16 * | 1.16 ± 0.45 |
| Heavy Metals (liver) | ||||
| Zn, µg∙g−1 tissue | 36.024 ± 3.822 | 32.205 ± 3.767 # | 25.080 ± 3.128 * | 35.195 ± 3.038 # |
| Mn, µg∙g−1 tissue | 2.204 ± 0.246 | 1.910 ± 0.137 # | 1.586 ± 0.102 * | 1.773 ± 0.205 |
| Cu, µg∙g−1 tissue | 3.184 ± 0.265 | 3.059 ± 0.314 | 3.521 ± 0.483 | 3.480 ± 0.337 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halenova, T.; Zlatskiy, I.; Syroeshkin, A.; Maximova, T.; Pleteneva, T. Deuterium-Depleted Water as Adjuvant Therapeutic Agent for Treatment of Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats. Molecules 2020, 25, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010023
Halenova T, Zlatskiy I, Syroeshkin A, Maximova T, Pleteneva T. Deuterium-Depleted Water as Adjuvant Therapeutic Agent for Treatment of Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats. Molecules. 2020; 25(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalenova, Tetiana, Igor Zlatskiy, Anton Syroeshkin, Tatiana Maximova, and Tatiana Pleteneva. 2020. "Deuterium-Depleted Water as Adjuvant Therapeutic Agent for Treatment of Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats" Molecules 25, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010023
APA StyleHalenova, T., Zlatskiy, I., Syroeshkin, A., Maximova, T., & Pleteneva, T. (2020). Deuterium-Depleted Water as Adjuvant Therapeutic Agent for Treatment of Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats. Molecules, 25(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010023