Development of Porous Pt Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction and Evolution Reactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
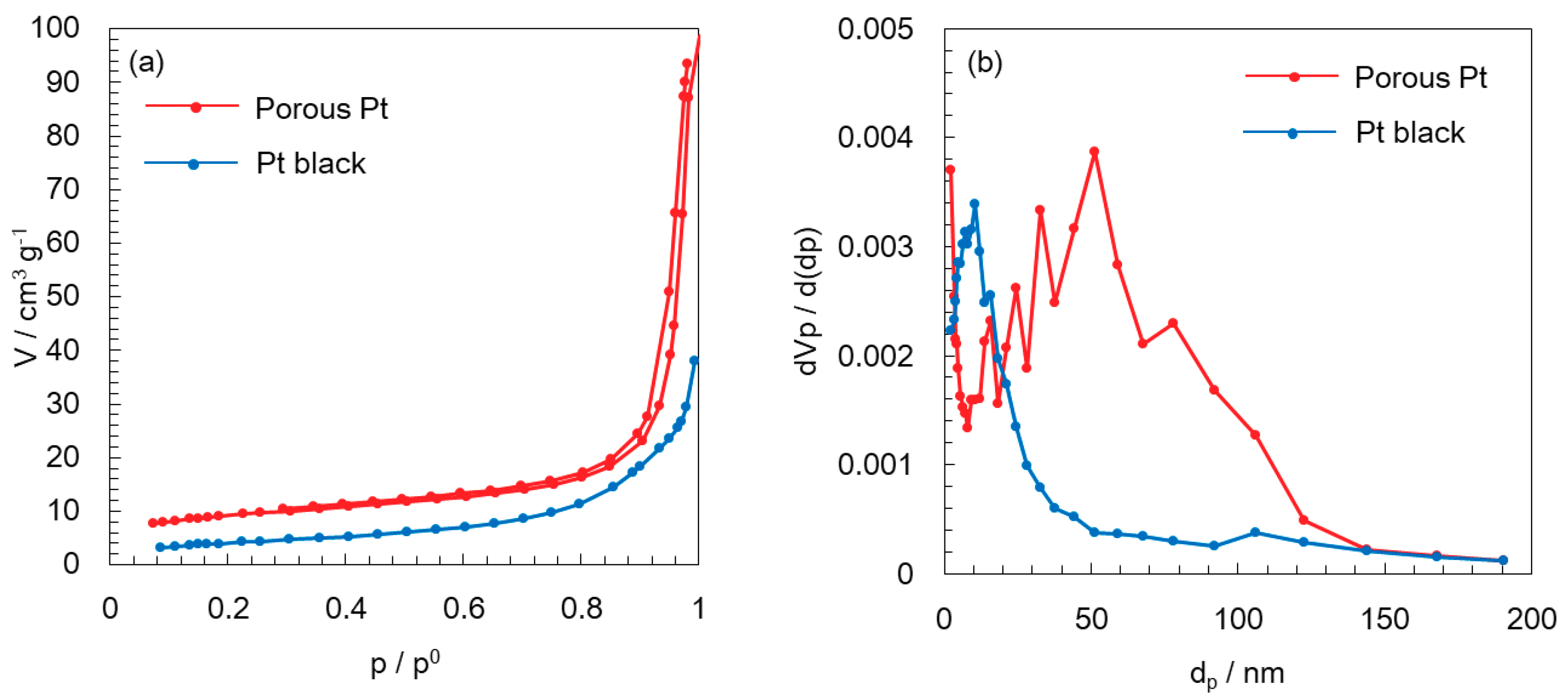
2.1. Heat Treatment and Characterization of Porous Pt
2.2. Electrochemical Analyses of Oxygen Reduction and Evolution Reactions
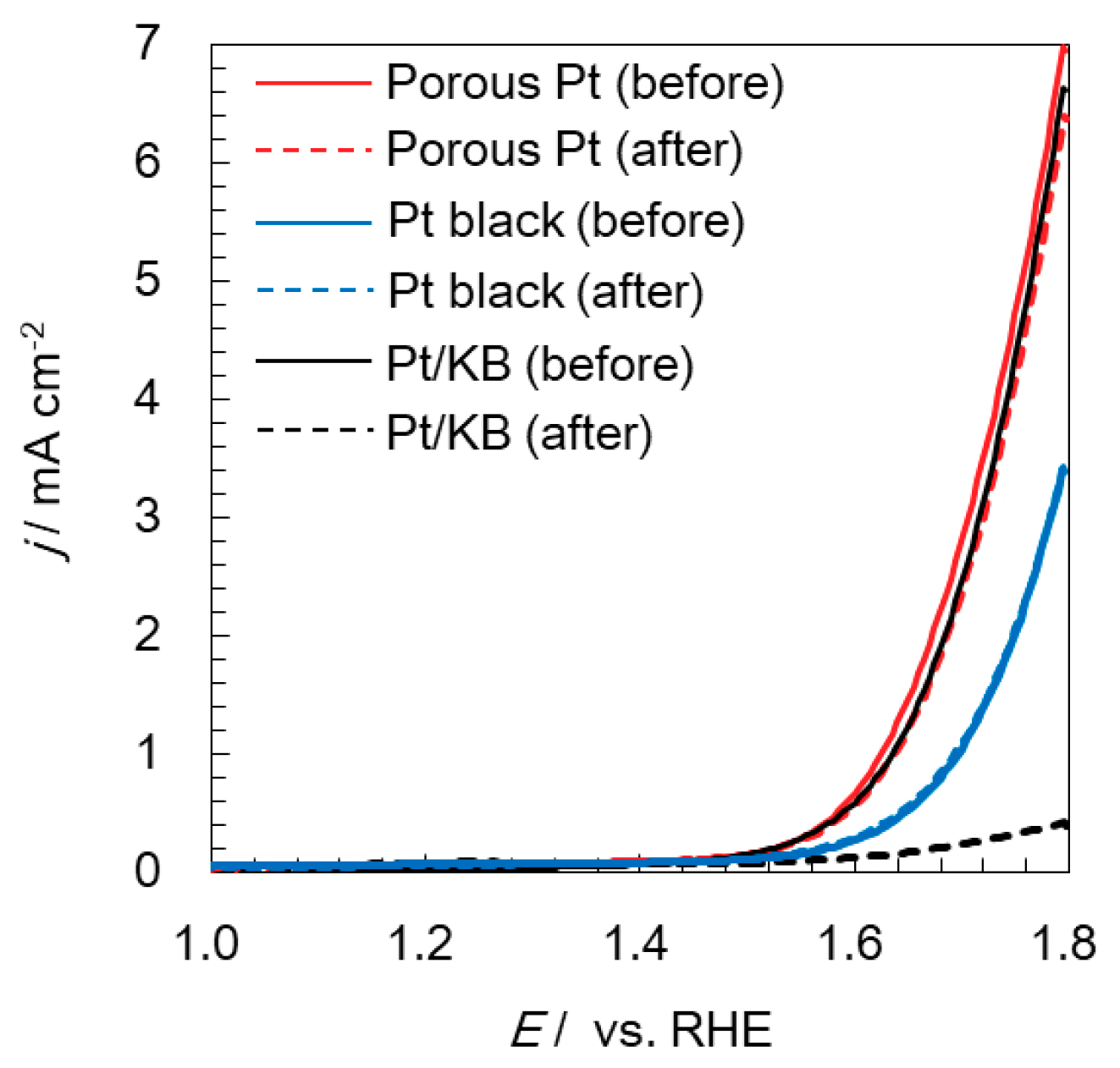
2.3. Electrochemical Durability of Catalysts at a High Potential
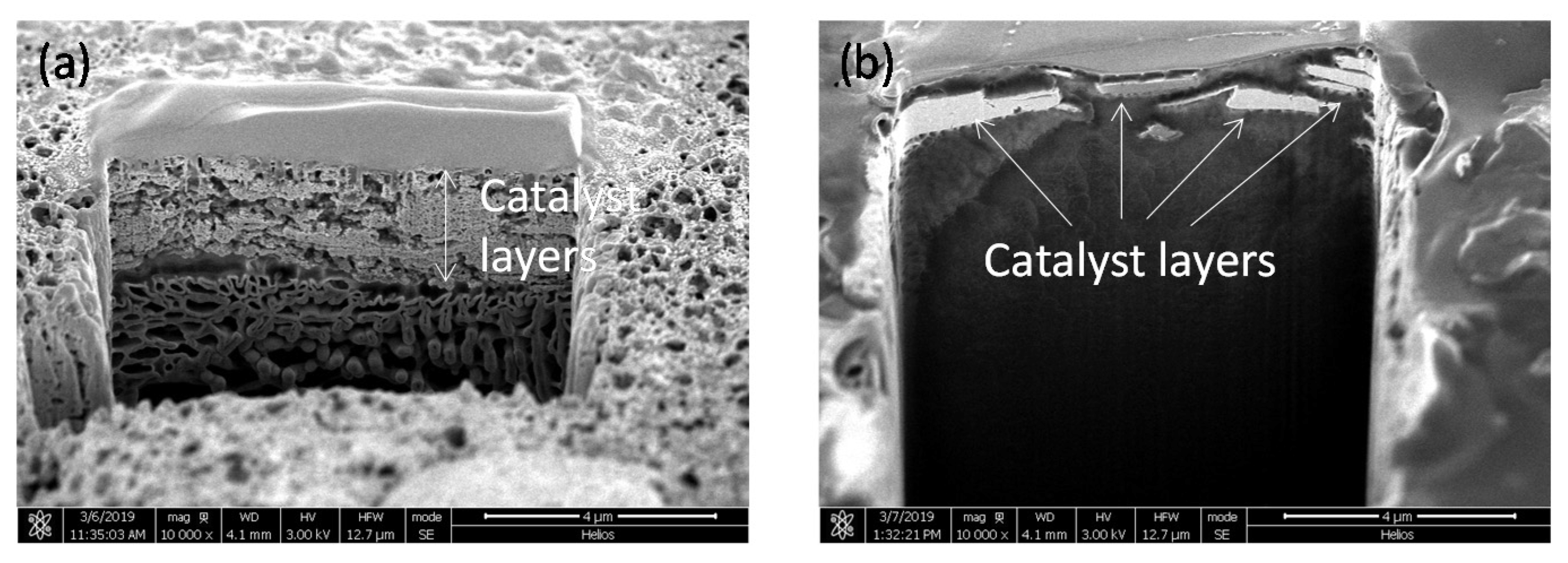
2.4. Evaluation of Catalyst Layers
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Porous Pt
3.3. Material Characterization
3.4. Electrochemical Analyses
3.5. Evaluation of Catalyst Layers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kinoshita, K.; Bett, J.A.S. Potentiodynamic analysis of surface oxides on carbon blacks. Carbon 1973, 11, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babic, U.; Tarik, M.; Schmidt, T.J.; Gubler, L. Understanding the effects of material properties and operating conditions on component aging in polymer electrolyte water electrolyzers. J. Power Sources 2020, 451, 227778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borup, R.; Meyers, J.; Pivovar, B.; Kim, Y.S.; Mukundan, R.; Garland, N.; Myers, D.; Wilson, M.; Garzon, F.; Wood, D.; et al. Scientific aspects of polymer electrolyte fuel cell durability and degradation. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3904–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohma, A.; Shinohara, K.; Iliyama, A.; Yoshida, T.; Daimaru, A. Membrane and catalyst performance targets for automotive fuel cells by FCCJ membrane, catalyst, MEA. WG. ECS Trans. 2011, 41, 775. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, D.; Li, B.; Zhang, C. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell reversal: A review. Catalysts 2016, 6, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao-Horn, Y.; Sheng, W.C.; Chen, S.; Ferreira, P.J.; Holby, E.F.; Morgan, D. Instability of supported platinum nanoparticles in low-Temperature fuel cells. Top Catal. 2007, 46, 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasten, E.; Hagen, G.; Tunol, R. Electrocatalysis in water electrolysis with solid polymer electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 3945–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lirong, M.; Sui, S.; Zhai, Y. Investigations on high performance proton exchange membrane water electrolyzer. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 678–684. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.-Y.; Ganesan, P.; Park, S.; Popov, B.N. Development of a titanium dioxide-Supported platinum catalyst with ultrahigh stability for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13898–13899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakinuma, K.; Chino, Y.; Senoo, Y.; Uchida, M.; Kamino, T.; Uchida, H.; Deki, S.; Watanabe, M. Characterization of Pt catalysts on Nb-doped and Sb-doped SnO2 support materials with aggregated structure by rotating disk electrode and fuel cell measurements. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 110, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Gu, J.; Su, L.; Cheng, L. An overview of metal oxide materials as electrocatalysts and supports for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2535–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Xu, J.; Li, Q.; Jensen, J.O.; Huang, Y.; Cleemann, L.N.; Bjerrum, N.J.; Xing, W. Highly active and stable Pt electrocatalysts promoted by antimony-doped SnO2 supports for oxygen reduction reactions. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 144, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioroi, T.; Yasuda, K. PEM-type water electrolysis/fuel cell reversible cell with low PGM catalyst loadings. ECS Trans. 2015, 69, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, F.; Peppley, B.A. Metal carbide and oxide supports for iridium-Based oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalysts for polymer-Electrolyte-Membrane water electrolysis. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 246, 654–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawy, E.N.E.; Birss, V.I. Nano-Porous iridium and iridium oxide thin films formed by high efficiency electrodeposition. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8244–8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Beasley, C.A.; Murray, R.W. Efficient electro-Oxidation of water near its reversible potential by a mesoporous IrOx nanoparticle film. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 12958–12961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, T.; Kuroki, H.; Ogura, S.; Fuchigami, T.; Kitamoto, Y.; Yamaguchi, T. Connected nanoparticle catalysts possessing a porous, hollow capsule structure as carbon-free electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3545–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, G.C.; Perini, N.; Ticianelli, E.A. Effect of temperature on the activities and stabilities of hydrothermally prepared IrOx nanocatalyst layers for the oxygen evolution reaction. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 218, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debe, M.K. Tutorial on the fundamental characteristics and practical properties of nanostructured thin film (NSTF) catalysts. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, F522–F534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Notsu, H.; Kimijima, K.; Miyamoto, J.; Yagi, I. Preparation of Pt/mesoporous carbon (MC) electrode catalyst and its reactivity toward oxygen reduction. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 6117–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Kimijima, K.; Miyamoto, J.; Yagi, I. Oxygen transfer and storage processes inside the mesopores of platinum-Deposited mesoporous carbon catalyst thin-Layer electrode. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 12149–12153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Kimijima, K.; Miyamoto, J.; Yagi, I. Direct observation of well-Dispersed Pt nanoparticles inside the pores of mesoporous carbon through the cross section of Pt/mesoporous carbon particles. Chem. Lett. 2009, 38, 346–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamida, Y.; Noda, Z.; Hyashi, A.; Sasaki, K. Development of MEAs with Pt/Mesoporous carbon as a cathode catalyst. ECS Trans. 2014, 64, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoda, Y.; Hayashi, A.; Minamida, Y.; Matsuda, J.; Akiba, E. Nanostructure control of porous carbon materials through changing acidity with a soft-Template method. Chem. Lett. 2015, 44, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Minamida, Y.; Noda, Z.; Sasaki, K.; Hayashi, A. Development of MEAs by controlling carbon structures in cathode layers. ECS Trans. 2016, 75, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B.; Ma, Y.; Tao, H.; Yu, L.; Jian, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Hu, Z. CNx nanotubes as catalyst support to immobilize platinum nanoparticles for methanol oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 1747–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakisaka, M.; Mitsui, S.; Hirose, Y.; Kawashima, K.; Uchida, H.; Watanabe, M. Electronic structures of Pt-Co and Pt-Ru alloys for CO-tolerant anode catalysts in polymer electrolyte fuel cells studied by EC-XPS. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 23489–23496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhong, H.; Song, S.; Ma, H. A novel bifunctional electrocatalyst for unitized regenerative fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, K.; Zack, J.W.; Pylypenko, S.; Pivovar, B.S.; Kocha, S.S. Oxygen reduction reaction measurements on platinum electrocatalysts utilizing rotating disk electrode technique II. Influence of ink formulation, catalyst layer uniformity and thickness. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, F1384–F1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garsany, Y.; Ge, J.; St-Pierre, J.; Rocheleau, R.; Swider-Lyons, K.E. Analytical procedure for accurate comparison of rotating disk electrode results for the oxygen reduction activity of Pt/C. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, F628–F640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, G.W.; Jensen, A.W.; Brüser, V.; Arenz, M.; Escudero-Escribano, M. Sputtered platinum thin-films for oxygen reduction in gas diffusion electrodes: A Model System for Studies under Realistic Reaction Conditions. Surfaces 2019, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Hayashi, A.; Noda, Z.; Kimijima, K.; Yagi, I.; Sasaki, K. Evaluation of change in nanostructure through the heat treatment of carbon materials and their durability for the start/stop operation of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 97, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garsany, Y.; Baturina, O.A.; Swider-Lyons, K.E.; Kocha, S.S. Experimental Methods for Quantifying the Activity of Platinum Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6321–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reier, T.; Oezaslan, M.; Strasser, P. Electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction (OER) on Ru, Ir, and Pt catalysts: A comparative study of nanoparticles and bulk materials. ACS Catal 2012, 2, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yu, H.; Song, W.; Dou, M.; Li, Y.; Shao, Z.; Yi, B. A hard-Template method for the preparation of IrO2, and its performance in a solid-Polymer-Electrolyte water electrolyzer. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dastafkan, K.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Han, L.; Zhao, C. Enhanced surface wettability and innate activity of an iron borate catalyst for efficient oxygen evolution and gas bubble detachment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 15252–15261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusano, S.; Baglio, V.; Di Blasi, A.; Briguglio, N.; Stassi, A.; Ornelas, R.; Trifoni, E.; Antonucci, V.; Arico, A.S. Electrochemical characterization of single cell and short stack PEM electrolyzers based on a nanosized IrO2 anode electrocatalyst. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 5558–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Carmo, M.; Bender, G.; Everwand, A.; Lickert, T.; Young, J.L.; Smolinka, T.; Stolten, D.; Lehnert, W. Performance enhancement of PEM electrolyzers through iridium-Coated titanium porous transport layers. Electrochem. Commun. 2018, 97, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Uchida, M.; Tryk, D.A.; Uchida, H.; Watanabe, M. The effectiveness of platinum/carbon electrocatalysts: Dependence on catalyst layer thickness and Pt alloy catalytic effects. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 4783–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds porous Pt is available from the authors. |



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muto, M.; Nagayama, M.; Sasaki, K.; Hayashi, A. Development of Porous Pt Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction and Evolution Reactions. Molecules 2020, 25, 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102398
Muto M, Nagayama M, Sasaki K, Hayashi A. Development of Porous Pt Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction and Evolution Reactions. Molecules. 2020; 25(10):2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102398
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuto, Marika, Mayumi Nagayama, Kazunari Sasaki, and Akari Hayashi. 2020. "Development of Porous Pt Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction and Evolution Reactions" Molecules 25, no. 10: 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102398
APA StyleMuto, M., Nagayama, M., Sasaki, K., & Hayashi, A. (2020). Development of Porous Pt Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction and Evolution Reactions. Molecules, 25(10), 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102398




