Microbial Shelf-Life, Starch Physicochemical Properties, and In Vitro Digestibility of Pigeon Pea Milk Altered by High Pressure Processing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HPP Conditions
2.2. Microbial Shelf-Life
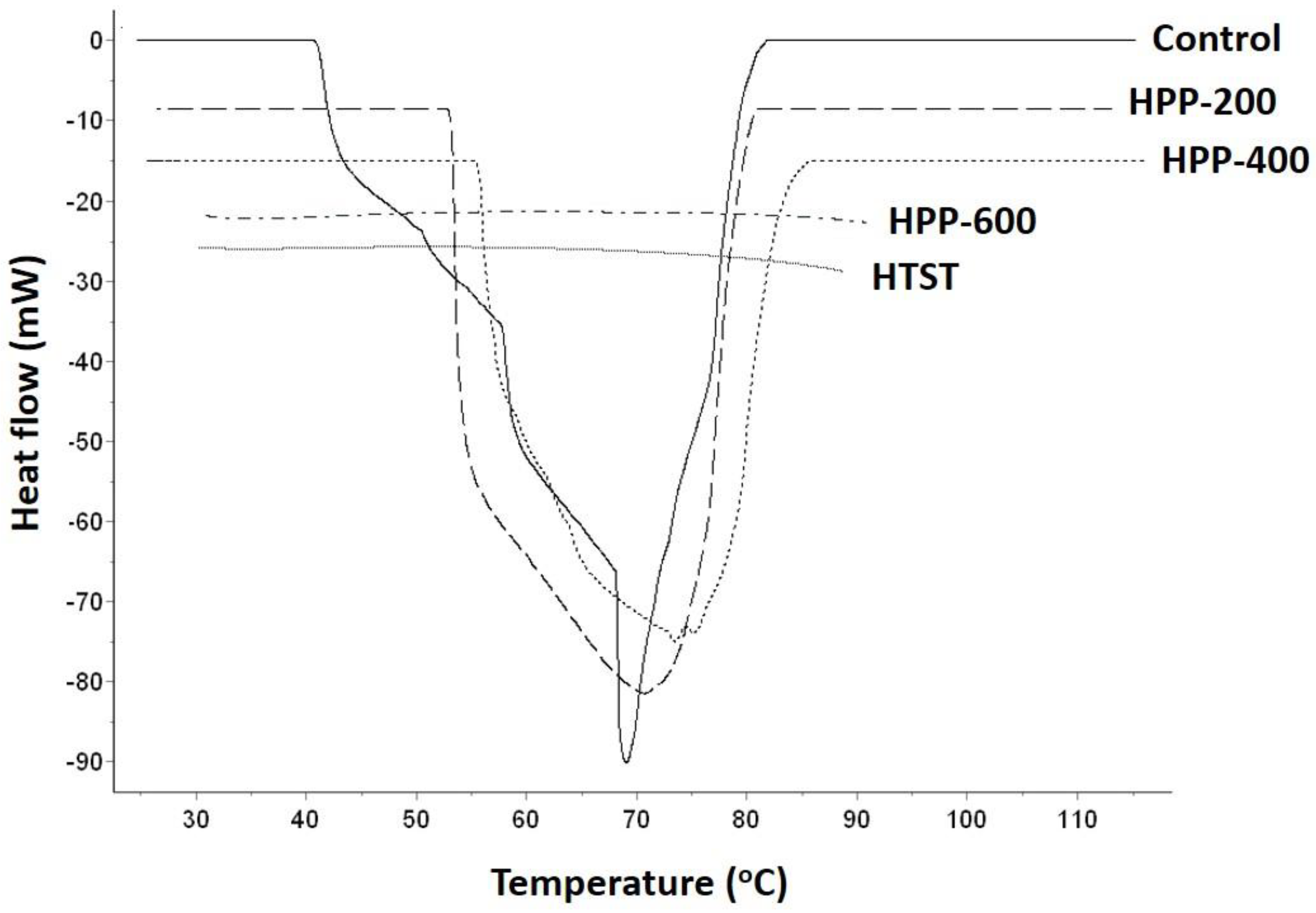
2.3. Starch Gelatinization Characteristics
2.4. In Vitro Digestibility Experiment
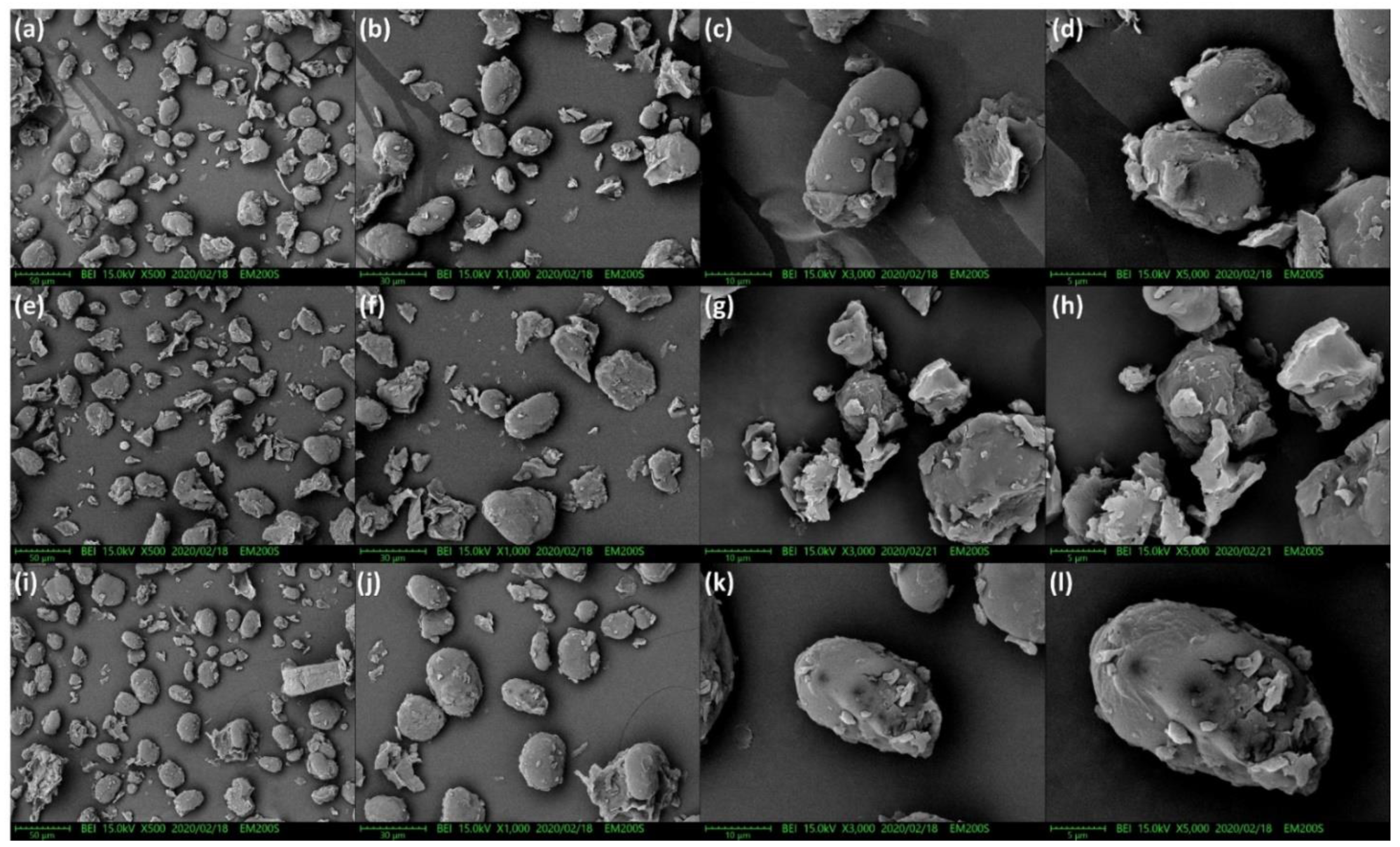
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Pigeon Pea Milk Preparation
4.2. HPP
4.3. HPP and HTST Pasteurization
4.4. Degree of Gelatinization
4.5. In Vitro Digestibility Experiment
4.6. Electron Microscopy
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, N.; Fu, K.; Fu, Y.J.; Zu, Y.G.; Chang, F.R.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, X.L.; Kong, Y.; Liu, W.; Gu, C.B. Antioxidant activities of extracts and main components of Pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.] leaves. Molecules 2009, 14, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nix, A.; Paull, C.A.; Colgrave, M. The flavonoid profile of pigeonpea, Cajanus cajan: A review. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.K.; Bhutani, K.K. Pinostrobin and Cajanus lactone isolated from Cajanus cajan (L.) leaves inhibits TNF-α and IL-1β production: In vitro and in vivo experimentation. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Fu, Y.J.; Zu, Y.G.; Chang, F.R.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, X.L.; Stelten, J.; Schiebel, H.M. Cajanuslactone, a new coumarin with anti-bacterial activity from pigeon pea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.] leaves. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Lai, Y.S.; Wu, S.C. Antioxidation, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition activity, nattokinase, and antihypertension of Bacillus subtilis (natto)-fermented pigeon pea. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariviani, S.; Affandi, D.R.; Listyaningsih, E.; Handajani, S. The potential of pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) beverage as an anti-diabetic functional drink. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 102, 01254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.J.; Hsu, W.H.; Huang, J.J.; Wu, S.C. Effect of pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan L.) on high-fat diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in hamsters. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Q.F.; Sun, L.; Si, J.Y.; Chen, D.H. Hypocholesterolemic effect of stilbenes containing extract-fraction from Cajanus cajan L. on diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in mice. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 932–939. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.W.; Wu, S.J.; Lu, J.K.; Shyu, Y.T.; Wang, C.Y. Current status and future trends of high-pressure processing in food industry. Food Control. 2017, 72, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, V.M.; Martinez-Monteagudo, S.I.; Gupta, R. Principles and application of high pressure-based technologies in the food industry. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 435–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.; Mendonca, A.; Jung, S. Impact of high-pressure processing on microbial shelf-life and protein stability of refrigerated soymilk. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés, V.; Villanueva, M.J.; Tenorio, M.D. Influence of high pressure processing on microbial shelf life, sensory profile, soluble sugars, organic acids, and mineral content of milk- and soy-smoothies. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, V.; Mateo-Vivaracho, L.; Guillamón, L.; Villanueva, M.J.; Tenorio, M.D. High hydrostatic pressure treatment and storage of soy-smoothies: Colour, bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuonye, J.C.; Ndaliman, M.; Elizabeh, O.U.; Yakubu, M.C. Effect of blending on the composition and acceptability of blends of unripe banana and pigeon pea flours. Nigerian Food J. 2012, 30, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hassan, H.A.; Mustafa, A.I.; Ahmed, A.R. Utilization of decorticated pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan L.) with wheat (Triticum aestivum) flours in bread making. Adv. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 3, 413–417. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, B.S.; Yadav, R.B.; Kumar, M. Suitability of pigeon pea and rice starches and their blends for noodle making. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Murphy, P.A.; Sala, I. Isoflavone profiles of soymilk as affected by high-pressure treatments of soymilk and soybeans. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.J.; Cheng, M.C.; Chen, B.Y.; Wang, C.Y. Effect of high-pressure processing on immunoreactivity, microbial and physicochemical properties of hazelnut milk. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tian, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Wu, G.; Zheng, J.; Ouyang, S.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, G. High pressure induced gelatinization of red adzuki bean starch and its effects on starch physicochemical and structural properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Fan, H.; Wang, M. In vitro digestibility and changes in physicochemical and textural properties of tartary buckwheat starch under high hydrostatic pressure. J. Food Eng. 2016, 189, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fan, H.; Cao, R.; Blanchard, C.; Wang, M. Physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of sorghumstarch altered by high hydrostatic pressure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narina, S.S.; Xu, Y.; Hamama, A.A.; Phatak, S.C.; Bhardwaj, H.L. Effect of cultivar and planting time on resistant starch accumulation in pigeon pea grown in Virginia. ISRN Agron. 2012, 2012, 576471. [Google Scholar]
- Kasote, D.M.; Nilegaonkar, S.S.; Agte, V.V. Effect of different processing methods on resistant starch content and in vitro starch digestibility of some common Indian pulses. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2014, 73, 541–546. [Google Scholar]
- Leite, T.S.; de Jesus, A.L.T.; Schmiele, M.; Tribst, A.A.L.; Cristianini, M. High pressure processing (HPP) of pea starch: Effect on the gelatinization properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, K.; Takahashi, K.; Shirai, K.; Kawamura, A. differential thermal analysis (DTA) applied to examining gelatinization of starches in foods. J. Food Sci. 1979, 44, 1366–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englyst, H.N.; Kingman, S.M.; Cummings, J.H. Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 46, S33–S50. [Google Scholar]
- Goñi, I.; Garcia-Alonso, A.; Saura-Calixto, F. A starch hydrolysis procedure to estimate glycemic index. Nutr. Res. 1997, 17, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |

| Treatment | Time (Days) | ||||||
| 0† | 0‡ | 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | ||
| TAB (log CFU/mL) | Control | 1.65 ± 0.23Ad | - | 2.82 ± 0.34Ac | 4.12 ± 0.27Ab | 5.57 ± 0.34Aa | 5.42 ± 0.28Aa |
| HPP-200 | 1.48 ± 0.28Aa | ND | 0.31 ± 0.08Be | 0.59 ± 0.11Bd | 0.71 ± 0.14Bc | 1.12 ± 0.21Bb | |
| HPP-400 | 1.72 ± 0.19Aa | ND | ND | 0.27 ± 0.09Bd | 0.46 ± 0.10Bc | 0.78 ± 0.15Bb | |
| HPP-600 | 1.55 ± 0.14Aa | ND | 0.23 ± 0.09Be | 0.44 ± 0.17Bd | 0.69 ± 0.13Bc | 0.92 ± 0.12Bb | |
| HTST | 1.51 ± 0.16Aa | ND | ND | ND | 0.41 ± 0.15Bc | 0.63 ± 0.11Bb | |
| Psychrotrophs (log CFU/mL) | Control | 1.34 ± 0.24Ae | - | 2.15 ± 0.21Ad | 2.33 ± 0.17Ac | 3.21 ± 0.14Ab | 3.82 ± 0.37Aa |
| HPP-200 | 1.60 ± 0.27Aa | ND | ND | 0.38 ± 0.10Bc | 0.59 ± 0.11Bb | 0.66 ± 0.17Bb | |
| HPP-400 | 1.46 ± 0.21Aa | ND | ND | 0.22 ± 0.14Bc | 0.64 ± 0.11Bb | 0.77 ± 0.09Bb | |
| HPP-600 | 1.59 ± 0.17Aa | ND | ND | 0.30 ± 0.08Bd | 0.77 ± 0.17Bc | 0.92 ± 0.18Bb | |
| HTST | 1.52 ± 0.29Aa | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.72 ± 0.11Bb | |
| E. coli/Coliforms (log CFU/mL) | Control | 0.35 ± 0.16Ae | - | 0.51 ± 0.29Ad | 0.47 ± 0.12Ac | 0.89 ± 0.15Ab | 1.77 ± 0.24Aa |
| HPP-200 | 0.47 ± 0.17Aa | ND | ND | ND | 0.33 ± 0.07Bb | 0.65 ± 0.11Ba | |
| HPP-400 | 0.39 ± 0.09Aa | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.48 ± 0.13Ba | |
| HPP-600 | 0.45 ± 0.11Aa | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.57 ± 0.08Ba | |
| HTST | 0.38 ± 0.12Aa | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| Treatments | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ∆Tr (°C) | ∆H (J/g) | % G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 39.54 ± 1.21b | 70.09 ± 1.50b | 80.20 ± 1.31b | 41.65 | 645.53 ± 46.64a | 0 |
| HPP-200 | 51.83 ± 1.63a | 70.81 ± 0.25b | 84.52 ± 0.38a | 31.18 | 490.84 ± 25.38b | 23.9 |
| HPP-400 | 54.34 ± 1.34a | 75.70 ± 1.73a | 84.77 ± 0.61a | 30.59 | 526.73 ± 53.18b | 18.4 |
| HPP-600 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 100 |
| HTST | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 100 |
| Treatment | RS (%) | RDS (%) | SDS (%) | HI | GI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 43.1 ± 0.4c | 7.7 ± 0.7d | 15.3 ± 0.3b | 19.5 ± 0.4b | 50.4 ± 0.4b |
| HPP-200 | 44.1 ± 0.5b | 11.5 ± 0.1c | 17.6 ± 0.5a | 18.2 ± 0.4c | 49.7 ± 0.3ab |
| HPP-400 | 47.3 ± 0.6a | 11.1 ± 0.2c | 17.8 ± 0.6a | 17.1 ± 0.5d | 49.1 ± 0.4c |
| HPP-600 | 17.5 ± 0.1e | 20.2 ± 1.3a | 9.2 ± 0.4d | 29.1 ± 0.6a | 55.7 ± 0.5a |
| HTST | 22.7 ± 0.1d | 19.8 ± 0.6b | 11.5 ± 0.4c | 28.4 ± 0.4a | 55.3 ± 0.3a |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsiao, Y.-T.; Wang, C.-Y. Microbial Shelf-Life, Starch Physicochemical Properties, and In Vitro Digestibility of Pigeon Pea Milk Altered by High Pressure Processing. Molecules 2020, 25, 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112516
Hsiao Y-T, Wang C-Y. Microbial Shelf-Life, Starch Physicochemical Properties, and In Vitro Digestibility of Pigeon Pea Milk Altered by High Pressure Processing. Molecules. 2020; 25(11):2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112516
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsiao, Yun-Ting, and Chung-Yi Wang. 2020. "Microbial Shelf-Life, Starch Physicochemical Properties, and In Vitro Digestibility of Pigeon Pea Milk Altered by High Pressure Processing" Molecules 25, no. 11: 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112516
APA StyleHsiao, Y.-T., & Wang, C.-Y. (2020). Microbial Shelf-Life, Starch Physicochemical Properties, and In Vitro Digestibility of Pigeon Pea Milk Altered by High Pressure Processing. Molecules, 25(11), 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112516







