Size and Shape-Dependent Antimicrobial Activities of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles: A Model Study as Potential Fungicides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of LTP-Derived AgNPs and AuNPs
2.2. Toxicity of LTP-AgNPs on Fungi
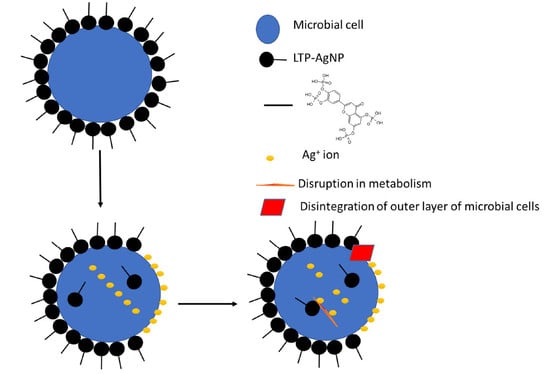
2.3. Toxicity of LTP-AgNPs on Bacteria
2.4. Cytotoxicity of LTP-AgNPs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis and Physicochemical Characterization of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles
4.2. Antifungal Studies
Turbidity/Agar Studies
4.3. Antibacterial Studies
4.3.1. Turbidity Studies
4.3.2. Bacterial Growth Kinetics in Response to Nanoparticle Treatment
4.4. Cytotoxicity of the LTP-AgNPs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franci, G.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S.; Palomba, L.; Rai, M.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 8856–88742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulit, J.; Banach, M.; Szczygłowska, R.; Bryk, M. Nanosilver against fungi. Silver nanoparticles as an effective biocidal factor. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2013, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahverdi, A.R.; Fakhimi, A.; Shahverdi, H.R.; Minaian, S. Synthesis and effect of silver nanoparticles on the antibacterial activity of different antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, N.; Shamaila, S.; Nazir, J.; Sharif, R.; Rafique, M.S.; Ul-Hasan, J.; Ammara, S.; Khalid, H. Antibacterial action of chemically synthesized and laser generated silver nanoparticles against human pathogenic bacteria. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.D. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: Enzymatic degradation and modification. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2005, 57, 1451–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soenen, S.J.; Manshian, B.; Montenegro, J.M.; Amin, F.; Meermann, B.; Thiron, T.; Cornelissen, M.; Vanhaecke, F.; Doak, S.; Parak, W.J. Cytotoxic effects of gold nanoparticles: A multiparametric study. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5767–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Hung, Y.-C.; Liau, I.; Huang, G.S. Assessment of the in vivo toxicity of gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindhu, M.R.; Umadevi, M. Antibacterial activities of green synthesized gold nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2014, 120, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hurt, R.H. Ion release kinetics and particle persistence in aqueous nano-silver colloids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidy, B.; Haase, A.; Luch, A.; Dawson, K.A.; Lynch, I. Mechanisms of silver nanoparticle release, transformation and toxicity: A critical review of current knowledge and recommendations for future studies and applications. Materials 2013, 6, 2295–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ouay, B.; Stellacci, F. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: A surface science insight. Nano today 2015, 10, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakirdere, S.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Tornuk, F.; Keyf, S.; Yilmaz, A.; Sagdic, O.; Kocabas, B. Molecular characterization of silver–stearate nanoparticles (AgStNPs): A hydrophobic and antimicrobial material against foodborne pathogens. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, M.A.; Kanwal, Z.; Rauf, A.; Sabri, A.N.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Size-and shape-dependent antibacterial studies of silver nanoparticles synthesized by wet chemical routes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, D.; Jung, K.-H.; Zhang, H.; Nannapaneni, S.; Wang, X.; Amin, A.R.; Chen, Z.; Shin, D.M. Luteolin nanoparticle in chemoprevention: In vitro and in vivo anticancer activity. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.M.; Ha, J.H.; Park, S.N. Cytoprotective effects against UVA and physical properties of luteolin-loaded cationic solid lipid nanoparticle. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 35, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xie, M. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of Luteolin on Staphylococcus aureus. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao = Acta Microbiologica Sinica 2010, 50, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Eumkeb, G.; Siriwong, S.; Thumanu, K. Synergistic activity of luteolin and amoxicillin combination against amoxicillin-resistant Escherichia coli and mode of action. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2012, 117, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osonga, F.J.; Le, P.; Luther, D.; Sakhaee, L.; Sadik, O.A. Water-based synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles with cuboidal and spherical shapes using luteolin tetraphosphate at room temperature. Environ. Sci. 2018, 5, 917–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.S.; Rai, A.; Ankamwar, B.; Singh, A.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Biological synthesis of triangular gold nanoprisms. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osonga, F.J.; Yazgan, I.; Kariuki, V.; Luther, D.; Jimenez, A.; Le, P.; Sadik, O.A. Greener synthesis and characterization, antimicrobial and cytotoxicity studies of gold nanoparticles of novel shapes and sizes. RSC. Advances 2016, 6, 2302–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindhu, M.R.; Umadevi, M. Silver and gold nanoparticles for sensor and antibacterial applications. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2014, 128, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Du, Y.; Li, D.; Lv, Z.; Wang, E. One-step synthesized silver micro-dendrites used as novel separation mediums and their applications in multi-DNA analysis. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10581–10583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, D. Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using Hibiscus rosa sinensis. Physica E 2010, 42, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osonga, F.J.; Kariuki, V.M.; Yazgan, I.; Jimenez, A.; Luther, D.; Schulte, J.; Sadik, O.A. Synthesis and antibacterial characterization of sustainable nanosilver using naturally-derived macromolecules. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Sharma, S.; Alam, M.K.; Singh, V.; Shamsi, S.; Mehta, B.; Fatma, A. Rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles using dried medicinal plant of basil. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 81, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jeong, S.; Moon, J. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the polyol process and the influence of precursor injection. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4019–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, M.; Mir, N.; Mousavi-Kamazani, M.; Bagheri, S.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles prepared from two novel natural precursors by facile thermal decomposition methods. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Mukherjee, P.; Singla, S.K.; Guturu, P.; Frost, M.C.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Shah, V.H.; Patra, C.R. Fabrication and characterization of an inorganic gold and silica nanoparticle mediated drug delivery system for nitric oxide. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 305102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeshehy, E.; Elazzazy, A.; Aggelis, G. Silver nanoparticles synthesis mediated by new isolates of Bacillus spp., nanoparticle characterization and their activity against Bean Yellow Mosaic Virus and human pathogens. Front Microbiol. 2015, 6, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, K.; Kim, S.W.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y.S. application of silver nanoparticles for the control of Colletotrichum species in vitro and pepper anthracnose disease in field. Mycobiology 2011, 39, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Rong, K.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, R. Size-dependent antibacterial activities of silver nanoparticles against oral anaerobic pathogenic bacteria. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Durán, M.; De Jesus, M.B.; Seabra, A.B.; Fávaro, W.J.; Nakazato, G. Silver nanoparticles: A new view on mechanistic aspects on antimicrobial activity. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, S.; Cheng, T.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhi, F. Somatostatin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced tight junction damage via the ERK–MAPK pathway in caco2 cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 93, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeckx, K.; Cotter, P.; López-Expósito, I.; Kleiveland, C.; Lea, T.; Mackie, A.; Requena, T.; Swiatecka, D.; Wichers, H. The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: In vitro and Ex Vivo Models; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ciftci, H.; TÜRK, M.; TAMER, U.; Karahan, S.; Menemen, Y. Silver nanoparticles: Cytotoxic, apoptotic, and necrotic effects on MCF-7 cells. Turkish J. Biol. 2013, 37, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sonshine, D.A.; Shervani, S.; Hurt, R.H. Controlled release of biologically active silver from nanosilver surfaces. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6903–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliga, A.R.; Skoglund, S.; Wallinder, I.O.; Fadeel, B.; Karlsson, H.L. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human lung cells: The role of cellular uptake, agglomeration and Ag release. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemire, J.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, A.; Herman, A.P. Nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: Their toxicity and mechanisms of action. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamaila, S.; Zafar, N.; Riaz, S.; Sharif, R.; Nazir, J.; Naseem, S. Gold nanoparticles: An efficient antimicrobial agent against enteric bacterial human pathogen. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalishwaralal, K.; BarathManiKanth, S.; Pandian, S.R.K.; Deepak, V.; Gurunathan, S. Silver nanoparticles impede the biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 79, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barapatre, A.; Aadil, K.R.; Jha, H. Synergistic antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized by lignin-degrading fungus. Bioresources Bioprocess 2016, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, I.A.; Ahmad, T. Size and shape dependant antifungal activity of gold nanoparticles: A case study of Candida. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 101, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutaj, K.; Szlazak, R.; Szalapata, K.; Starzyk, J.; Luchowski, R.; Grudzinski, W.; Osinska-Jaroszuk, M.; Jarosz-Wilkolazka, A.; Szuster-Ciesielska, A.; Gruszecki, W.I. Amphotericin B-silver hybrid nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties and antifungal activity. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.G.; Fernández-Baldo, M.A.; Berni, E.; Camí, G.; Durán, N.; Raba, J.; Sanz, M.I. Production of silver nanoparticles using yeasts and evaluation of their antifungal activity against phytopathogenic fungi. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogar, A.; Tylko, G.; Turnau, K. Antifungal properties of silver nanoparticles against indoor mould growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.-K.; Ma, Q.-H.; Li, S.-Y.; Zhang, D.-Q.; Cong, L.; Tian, Y.-L.; Yang, R.-Y. The antifungal effect of silver nanoparticles on Trichosporon asahii. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infection 2016, 49, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, N.; OuYang, Q.; Jia, L. Citral inhibits mycelial growth of Penicillium italicum by a membrane damage mechanism. Food Control 2014, 41, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, S.; bin Abdullah, M.S.; Dash, G.; Nanda, A. Facile and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Penicillium italicum and its antimicrobial property in combination with Sparfloxacin. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Osonga, F.J.; Akgul, A.; Yazgan, I.; Akgul, A.; Ontman, R.; Kariuki, V.M.; Eshun, G.B.; Sadik, O.A. Flavonoid-derived anisotropic silver nanoparticles inhibit growth and change the expression of virulence genes in Escherichia coli SM10. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4649–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osonga, F.J.; Onyango, J.O.; Mwilu, S.K.; Noah, N.M.; Schulte, J.; An, M.; Sadik, O.A. Synthesis and characterization of novel flavonoid derivatives via sequential phosphorylation of quercetin. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |










| Types of NP | Day 2 (mm) | Day 4 (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 12.5 | 18 |
| LTP-AgNP1 | 0 | 0 |
| LTP-AgNP2 | 8 | 13 |
| LTP-AgNP3 | 9 | 14 |
| LTP-AgNP4 | 12 | 17 |
| LTP-AgNP5 | 0 | 0 |
| LTP-AgNP6 | 7 | 12 |
| LTP-AgNP7 | 11 | 15 |
| Parameters of NP | LTP- AgNPs | LTP-AuNPs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shape | Spherical | Quasi-spherical | Spherical | Cubic |
| Sizes (nm) | 9, 16, 30, 35 | 21, 37, 21 | 8, 9, 10 | 16, 20, 372, 510 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osonga, F.J.; Akgul, A.; Yazgan, I.; Akgul, A.; Eshun, G.B.; Sakhaee, L.; Sadik, O.A. Size and Shape-Dependent Antimicrobial Activities of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles: A Model Study as Potential Fungicides. Molecules 2020, 25, 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112682
Osonga FJ, Akgul A, Yazgan I, Akgul A, Eshun GB, Sakhaee L, Sadik OA. Size and Shape-Dependent Antimicrobial Activities of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles: A Model Study as Potential Fungicides. Molecules. 2020; 25(11):2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112682
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsonga, Francis J., Ali Akgul, Idris Yazgan, Ayfer Akgul, Gaddi B. Eshun, Laura Sakhaee, and Omowunmi A. Sadik. 2020. "Size and Shape-Dependent Antimicrobial Activities of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles: A Model Study as Potential Fungicides" Molecules 25, no. 11: 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112682
APA StyleOsonga, F. J., Akgul, A., Yazgan, I., Akgul, A., Eshun, G. B., Sakhaee, L., & Sadik, O. A. (2020). Size and Shape-Dependent Antimicrobial Activities of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles: A Model Study as Potential Fungicides. Molecules, 25(11), 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112682