Taurine and Ginsenoside Rf Induce BDNF Expression in SH-SY5Y Cells: A Potential Role of BDNF in Corticosterone-Triggered Cellular Damage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
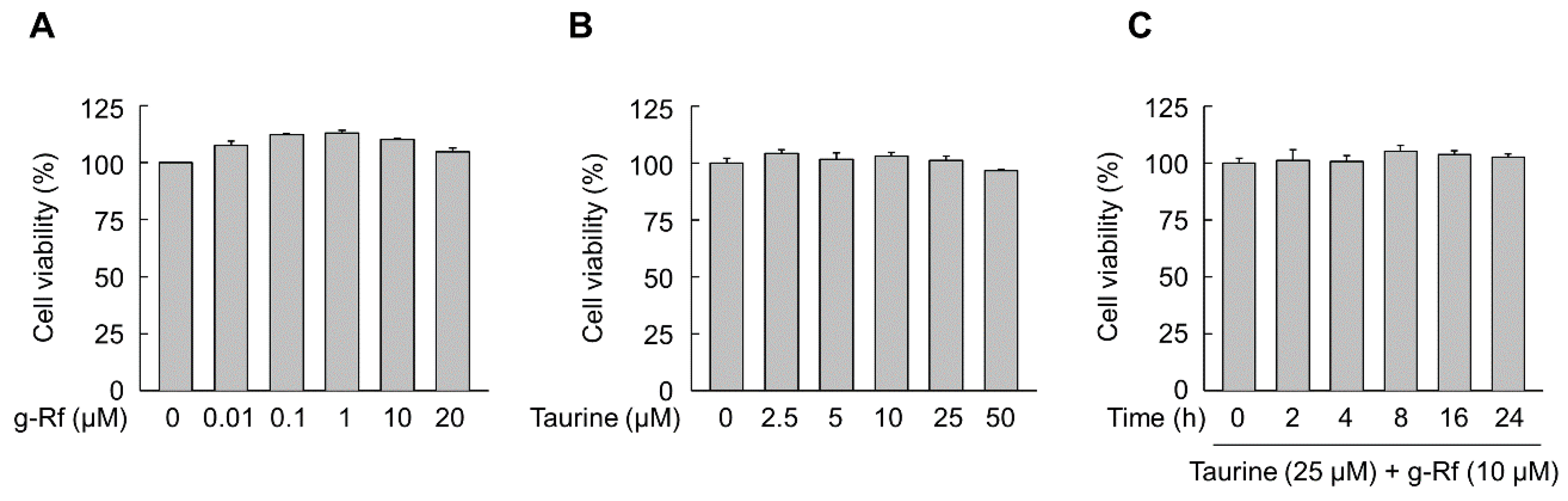
2.1. g-Rf and Taurine Induce BDNF Expression
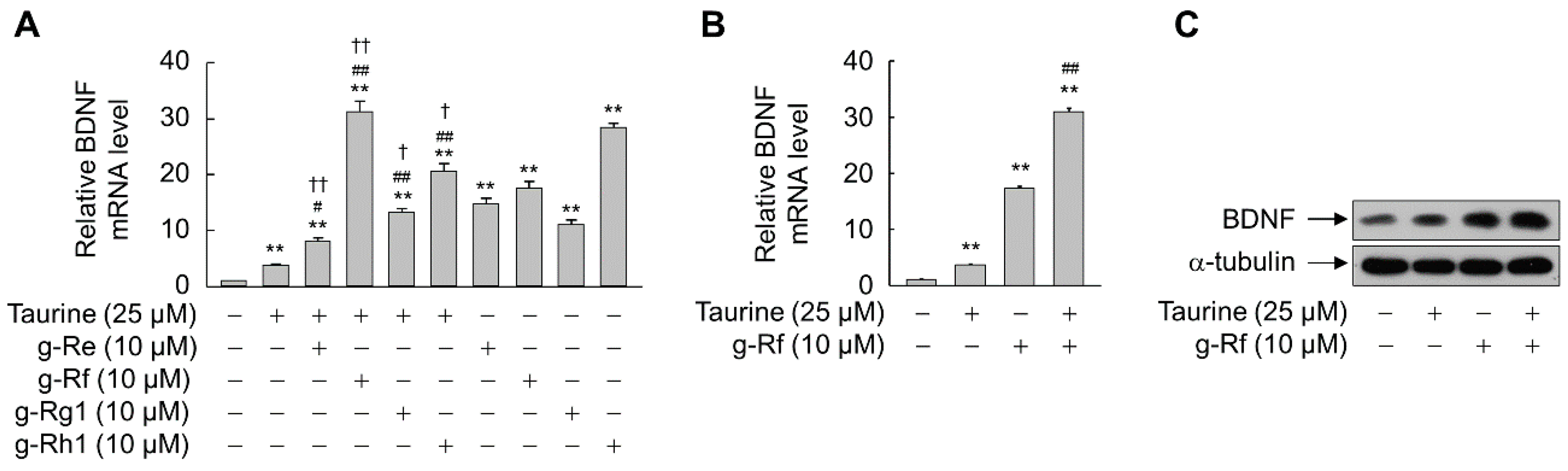
2.2. Ginsenosides and Taurine Synergistically Induce BDNF Expression
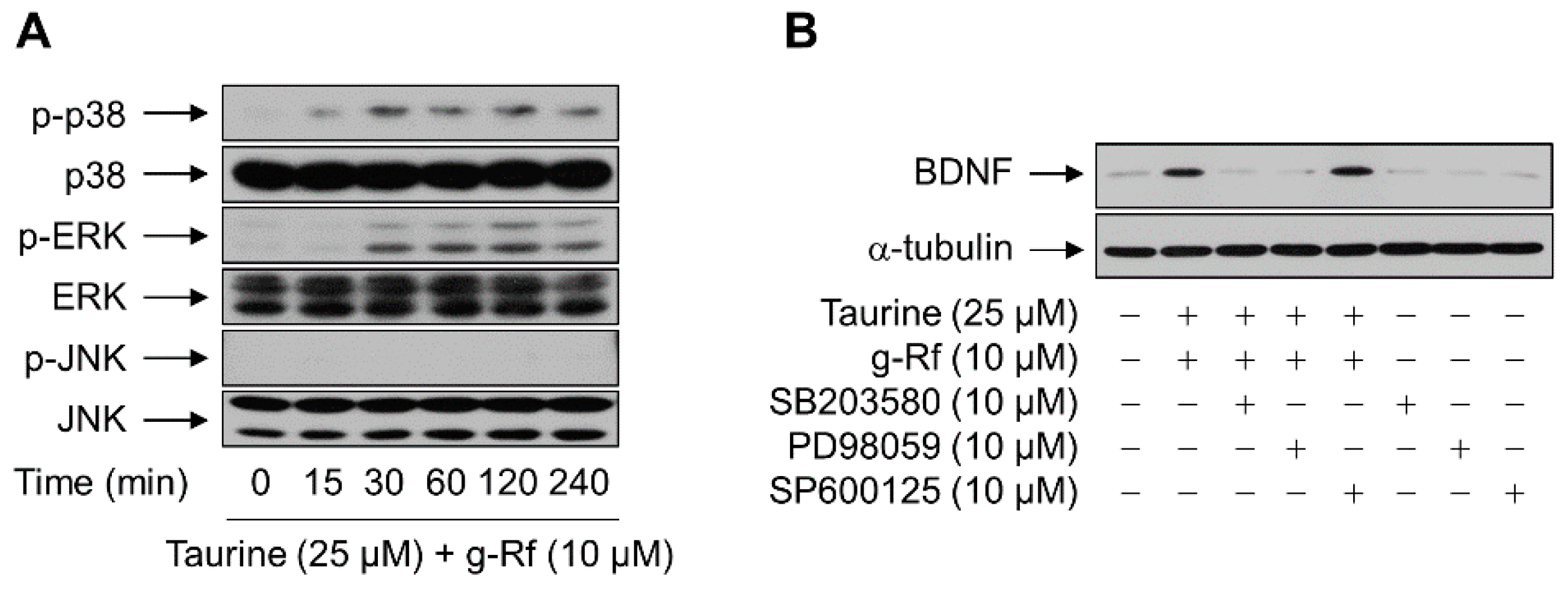
2.3. g-Rf and Taurine Upregulate BDNF Expression via MAP Kinases
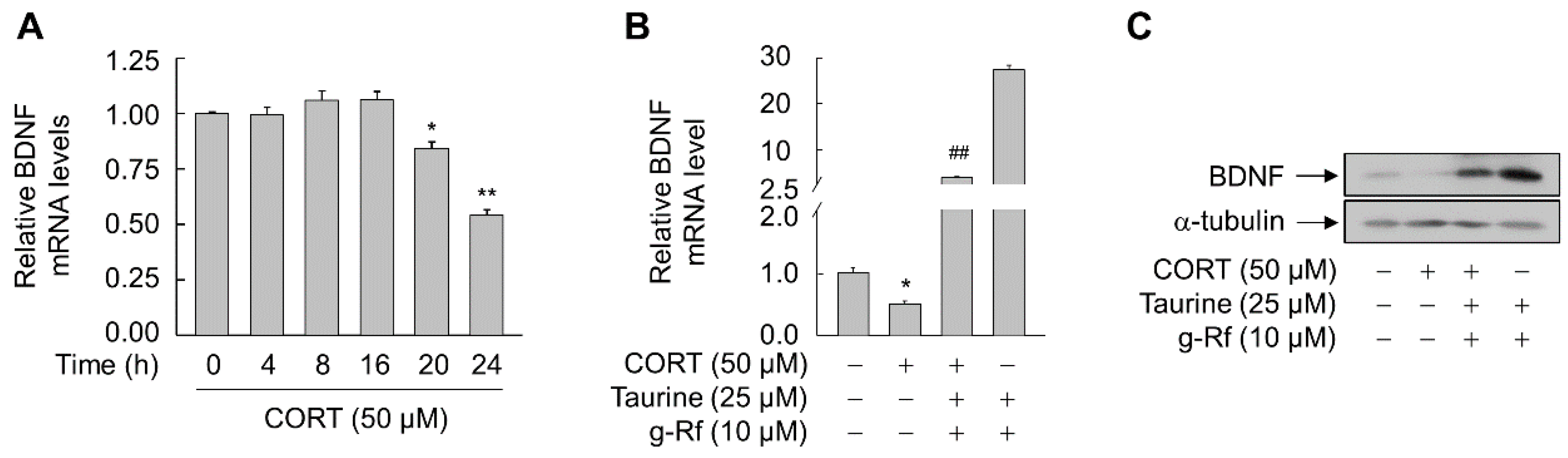
2.4. g-Rf and Taurine Protect against Corticosterone (CORT)-Induced Cellular Damage
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.4. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Analysis
4.5. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albrecht, J.; Schousboe, A. Taurine interaction with neurotransmitter receptors in the CNS: An update. Neurochem. Res. 2005, 30, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, I.H.; Kristensen, D.M.; Holm, J.B.; Mortensen, O.H. Physiological role of taurine—from organism to organelle. Acta Physiol. (Oxf) 2015, 213, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Maraghi, E.F.; Abdel-Fattah, K.I.; Soliman, S.M.; El-Sayed, W.M. Taurine provides a time-dependent amelioration of the brain damage induced by γ-irradiation in rats. J. Hazard Mater. 2018, 359, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Prentice, H.; Price, A.L.; Wu, J.Y. Beneficial effect of taurine on hypoxia- and glutamate-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways in primary neuronal culture. Amino Acids. 2012, 43, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, H.; Pan, C.; Gharibani, P.M.; Ma, Z.; Price, A.L.; Giraldo, G.S.; Retz, H.M.; Gupta, A.; Chen, P.C.; Chiu, H.; et al. Analysis of Neuroprotection by Taurine and Taurine Combinations in Primary Neuronal Cultures and in Neuronal Cell Lines Exposed to Glutamate Excitotoxicity and to Hypoxia/Re-oxygenation. In Taurine 10, 1st ed.; Lee, D.-H., Schaffer, S.W., Park, E., Kim, H.W., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 975, pp. 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, D.G.; Chang, Y.L.; Chou, C.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Chiang, C.C.; Chang, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Preventive effects of taurine against d-galactose-induced cognitive dysfunction and brain damage. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, S.H.; Lee, D.S. Taurine Chloramine Prevents Neuronal HT22 Cell Damage Through Nrf2-Related Heme Oxygenase-1. In Taurine 10, 1st ed.; Lee, D.-H., Schaffer, S.W., Park, E., Kim, H.W., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 975, pp. 145–157. [Google Scholar]
- Pasantes-Morales, H.; Ramos-Mandujano, G.; Hernández-Benítez, R. Taurine enhances proliferation and promotes neuronal specification of murine and human neural stem/progenitor cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 803, 457–472. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Benítez, R.; Vangipuram, S.D.; Ramos-Mandujano, G.; Lyman, W.D.; Pasantes-Morales, H. Taurine enhances the growth of neural precursors derived from fetal human brain and promotes neuronal specification. Dev. Neurosci. 2013, 35, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Y.; Zeng, J.Z.; Wong, A.S.T. Chemical Structures and Pharmacological Profiles of Ginseng Saponins. Molecules 2019, 24, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Guo, Y.; Yang, W.; Zheng, P.; Zeng, J.; Tong, W. Involvement of Connexin40 in the Protective Effects of Ginsenoside Rb1 Against Traumatic Brain Injury. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hata, R.; Zhu, P.; Sato, K.; Wen, T.C.; Yang, L.; Fujita, H.; Mitsuda, N.; Tanaka, J.; Samukawa, K.; et al. Prevention of ischemic neuronal death by intravenous infusion of a ginseng saponin, ginsenoside Rb(1), that upregulates Bcl-x(L) expression. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2006, 26, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, T.; Liu, G.; Ma, H.; Lu, B.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Ge, P.; Liang, J. Inhibition of autophagy via activation of PI3K/Akt pathway contributes to the protection of ginsenoside Rb1 against neuronal death caused by ischemic insults. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 15426–15442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, D.W.; Jung, B.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.; Hwang, G.S.; Kang, K.S.; Lee, J.W. Ginsenoside Rb2 suppresses the glutamate-mediated oxidative stress and neuronal cell death in HT22 cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Song, Q.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Yu, S.Y. Neuroprotective Effects of Ginsenoside-Rg1 Against Depression-Like Behaviors via Suppressing Glial Activation, Synaptic Deficits, and Neuronal Apoptosis in Rats. Front Immunol. 2018, 9, 2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Fan, C.; Yang, L.; Yu, S.; Song, Q.; Wang, P.; Mao, X. Ginsenoside Rg1 Prevents Chronic Stress-Induced Depression-Like Behaviors and Neuronal Structural Plasticity in Rats. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 2470–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Jing, G.; Cai, H. Ginsenoside Rg1 suppressed inflammation and neuron apoptosis by activating PPARγ/HO-1 in hippocampus in rat model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 2484–2494. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Xue, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, W. Ginsenoside Rg3 and Rh2 protect trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity via prevention on neuronal apoptosis and neuroinflammation. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Alam, A.; San, C.Y.; Eguchi, S.; Chen, Q.; Lian, Q.; Ma, D. Molecular mechanisms of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neuro-protection: Recent developments. Brain Res. 2017, 1665, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yu, Y.; Tang, L.J.; Kong, L.; Zhang, C.H.; Chu, H.Y.; Yin, L.W.; Ma, H.Y. Neural stem cells over-expressing brain-derived neurotrophic factor promote neuronal survival and cytoskeletal protein expression in traumatic brain injury sites. Neural. Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 433–439. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Yu, B.; Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y. Neural stem cells over-expressing brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) stimulate synaptic protein expression and promote functional recovery following transplantation in rat model of traumatic brain injury. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkholm, C.; Monteggia, L.M. BDNF—a key transducer of antidepressant effects. Neuropharmacology 2016, 102, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, T.; Li, N.; Wu, L.; Gu, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, C.; Liu, W.; Shan, L.; Yu, P.; et al. Tetramethylpyrazine nitrone activates the BDNF/Akt/CREB pathway to promote post-ischaemic neuroregeneration and recovery of neurological functions in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Yang, T.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, L.; Bai, G.; Li, D.; Li, Q.; Wang, W. Dexamethasone and vitamin B(12) synergistically promote peripheral nerve regeneration in rats by upregulating the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Arch. Med. Sci. 2012, 8, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Xiong, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.L.; Wang, F.; Chen, J.G. Antidepressant-like effects of ginsenoside Rg1 are due to activation of the BDNF signalling pathway and neurogenesis in the hippocampus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 1872–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.Q.; Yang, C.X.; Chen, G.J.; Wang, G.Y.; Chen, B.; Tan, S.K.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Q.L. Ginsenoside Rb1 regulates the expressions of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and caspase-3 and induces neurogenesis in rats with experimental cerebral ischemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 132, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Z.J.; Sun, T.; Xia, F.; Zhao, G.; Wu, Y.M. Ginsenoside Reduces Cognitive Impairment During Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion Through Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Regulated by Epigenetic Modulation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Hong, W.; Xie, K.; Tang, H.; Tang, J.; Luo, S.; Geng, W.; Jia, D. Ginsenoside Rb1 pretreatment reverses hippocampal changes in BDNF/TrkB mRNA and protein in rats subjected to acute immobilization stress. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 2127–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Kim, S.O.; Lee, M.; Park, Y.; Kim, D.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, E.H. Effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on the stress-induced changes of BDNF and HSP70 expression in rat hippocampus. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 38, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, X.; Fan, C.; Yu, S.Y. The effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on chronic stress induced depression-like behaviors, BDNF expression and the phosphorylation of PKA and CREB in rats. Neuroscience 2016, 322, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, C.; Zhao, W.; Gao, S.; Cui, Z. Antidepressant-like effects of ginsenoside Rg5 in mice: Involving of hippocampus BDNF signaling pathway. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 645, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Yao, Q.; Shen, J.; Gu, Z.; Xu, H.; Wu, Z.; Chen, C.; Li, L. Antidepressant-like effects of ginsenoside Rg3 in mice via activation of the hippocampal BDNF signaling cascade. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gite, S.; Ross, R.P.; Kirke, D.; Guihéneuf, F.; Aussant, J.; Stengel, D.B.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Stanton, C. Nutraceuticals to promote neuronal plasticity in response to corticosterone-induced stress in human neuroblastoma cells. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 551–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, A.; Corey-Bloom, J.; Thomas, E.A.; Desplats, P. Evaluation of Biochemical and Epigenetic Measures of Peripheral Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a Biomarker in Huntington’s Disease Patients. Front Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 12, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiao, Y.; Palmgren, B.; Novozhilova, E.; Englund Johansson, U.; Spieles-Engemann, A.L.; Kale, A.; Stupp, S.I.; Olivius, P. BDNF increases survival and neuronal differentiation of human neural precursor cells cotransplanted with a nanofiber gel to the auditory nerve in a rat model of neuronal damage. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 356415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Park, J.H.; Yoo, K.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Hwang, I.K.; Ryu, P.D.; Kim, D.H.; Kwon, Y.G.; Kim, Y.M.; Won, M.H. Pre- and post-treatments with escitalopram protect against experimental ischemic neuronal damage via regulation of BDNF expression and oxidative stress. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 229, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capibaribe, V.C.C.; Vasconcelos Mallmann, A.S.; Lopes, I.S.; Oliveira, I.C.M.; de Oliveira, N.F.; Chaves, R.C.; Fernandes, M.L.; de Araujo, M.A.; da Silva, D.M.A.; Valentim, J.T.; et al. Thymol reverses depression-like behaviour and upregulates hippocampal BDNF levels in chronic corticosterone-induced depression model in female mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1774–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.Y.; Luo, S.Y.; Al-Hawwas, M.; Herselman, M.F.; Zhou, X.F.; Bobrovskaya, L. The Long-Term Effects of Ethanol and Corticosterone on the Mood-Related Behaviours and the Balance Between Mature BDNF and proBDNF in Mice. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 69, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Song, J.; Meng, D.; Chang, Q. TPPU, a sEH Inhibitor, Attenuates Corticosterone-Induced PC12 Cell Injury by Modulation of BDNF-TrkB Pathway. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 67, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, S.; Jiang, C. Ginsenoside Rf relieves mechanical hypersensitivity, depression-like behavior, and inflammatory reactions in chronic constriction injury rats. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.W.; Almeida, F.B.; Bandiera, S.; Pulcinelli, R.R.; Fragoso, A.L.R.; Schneider, R.J.; Barros, H.M.T.; Gomez, R. Taurine restores the exploratory behavior following alcohol withdrawal and decreases BDNF mRNA expression in the frontal cortex of chronic alcohol-treated rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2017, 161, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, J.M.; Liao, X.B.; Hu, Y.R.; Shang, B.P.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Yuan, L.Q.; Xie, H.; Sheng, Z.F.; Tang, H.; et al. Taurine suppresses osteoblastic differentiation of aortic valve interstitial cells induced by beta-glycerophosphate disodium, dexamethasone and ascorbic acid via the ERK pathway. Amino. Acids. 2012, 43, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Joe, S.G.; Kim, G.B.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, N.S.; Hong, C.U.; Kim, S.Z.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Taurine increases cell proliferation and generates an increase in [Mg2+]i accompanied by ERK 1/2 activation in human osteoblast cells. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 5929–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.; Ding, X.; Liu, C.; Pei, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, W. Mechanism of taurine in alleviating myocardial oxidative stress in rats after burn through p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Minerva Med. 2019, 110, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, C.; Kim, J.; Quan, H.; Yin, M.; Jeong, S.; Choi, J.I.; Jang, E.A.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, D.H.; Bae, H.B. Ginsenoside Rg3 promotes Fc gamma receptor-mediated phagocytosis of bacteria by macrophages via an extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mechanism. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 77, 105945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Yi, P.F.; Shen, H.Q.; Zhang, L.Y.; Dong, H.B.; Wu, S.C.; Xia, F.; Guo, X.; Wei, X.B.; Fu, B.D. Ginsenoside Rh2-B1 stimulates cell proliferation and IFN-γ production by activating the p38 MAPK and ERK-dependent signaling pathways in CTLL-2 cells. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2014, 36, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Fu, M.; Wang, Y.T.; Dong, Z. Neuroprotective Effects of Ginsenoside Rf on Amyloid-β-Induced Neurotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, W.J.; Lee, G.H.; Hur, J.; Lee, H.G.; Kim, E.; Won, J.P.; Cho, Y.; Choi, M.-J.; Seo, H.G. Taurine and Ginsenoside Rf Induce BDNF Expression in SH-SY5Y Cells: A Potential Role of BDNF in Corticosterone-Triggered Cellular Damage. Molecules 2020, 25, 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122819
Lee WJ, Lee GH, Hur J, Lee HG, Kim E, Won JP, Cho Y, Choi M-J, Seo HG. Taurine and Ginsenoside Rf Induce BDNF Expression in SH-SY5Y Cells: A Potential Role of BDNF in Corticosterone-Triggered Cellular Damage. Molecules. 2020; 25(12):2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122819
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Won Jin, Gyeong Hee Lee, Jinwoo Hur, Hyuk Gyoon Lee, Eunsu Kim, Jun Pil Won, Youngjae Cho, Mi-Jung Choi, and Han Geuk Seo. 2020. "Taurine and Ginsenoside Rf Induce BDNF Expression in SH-SY5Y Cells: A Potential Role of BDNF in Corticosterone-Triggered Cellular Damage" Molecules 25, no. 12: 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122819
APA StyleLee, W. J., Lee, G. H., Hur, J., Lee, H. G., Kim, E., Won, J. P., Cho, Y., Choi, M. -J., & Seo, H. G. (2020). Taurine and Ginsenoside Rf Induce BDNF Expression in SH-SY5Y Cells: A Potential Role of BDNF in Corticosterone-Triggered Cellular Damage. Molecules, 25(12), 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122819





