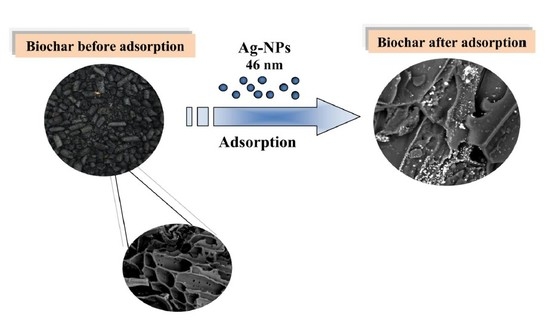
Purification of Aqueous Media by Biochars: Feedstock Type Effect on Silver Nanoparticles Removal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characteristic of Ag-NPs
2.2. Biochar Characteristics
2.3. Kinetics of Ag-NPs Adsorption on Biochar
2.4. Equilibrium Adsorption of Ag-NPs on Biochar
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Specific Surface Area
3.2. Ag-NPs Synthesis
3.3. The Average Size of Ag-NPs
3.4. Quantitative Determination of Surface Functional Groups
3.5. Determination of the Distribution of the Surface Negative Charge and Dissociation Constants of Functional Groups
3.6. Qualitative Determination of Surface Functional Groups—FTIR Spectroscopy
3.7. SEM Analysis
3.8. Batch Adsorption Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stensberg, M.C.; Wei, Q.; McLamore, E.S.; Porterfield, D.M.; Wei, A.; Sepulveda, M.S. Toxicological studies on silver nanoparticles: Challenges, opportunities in assessment, monitoring and imaging. Nanomedicine 2012, 6, 879–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jo, H.J.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, S.W. Acute toxicity of Ag and CuO nanoparticle suspensions against Daphnia magna: The importance of their dissolved fraction varying with preparation methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227–228, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Tian, S. Acute toxicities of six manufactured nanomaterial suspensions to Daphnia magna. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyżewska, I.; Kyzioł-Komosińska, J.; Rosik-Dulewska, C.; Czupioł, J.; Antoszczyszyn-Szpicka, P. Inorganic nanomaterials in the aquatic environment: Behavior, toxicity, and interaction with environmental elements. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2016, 42, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syberg, K.; Hansen, S.F. Environmental risk assessment of chemicals and nanomaterial-The best foundation for regulatory decision-making. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samarajeewa, A.D.; Velicogna, J.R.; Princz, J.I.; Subasinghe, R.M.; Scroggins, R.P. Effect of silver Nanoparticles on soil microbial growth, activity and community diversity in a sandy loam soil. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 220, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, F.; Ort, C.; Scholz, R.W.; Nowack, B. Engineered nanomaterials in rivers—Exposure scenarios for Switzerland at high spatial and temporal resolution. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3439–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicho, R.C.; Santos, F.C.F.; Scott-Fordsmand, J.J.; Amorim, M.J.B. Effects of copper oxide nanomaterials (CuONMs) are life stage dependent-full life cycle in Enchytraeus crypticus. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlich, K.; Beule, L.; Hund-Rinke, K. Single versus repeated applications of CuO and Ag nanomaterials and their effect on soil microflora. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimiya, M.; Pignatello, J.J.; White, J.C.; Hu, S.-L.; Ferreira, P.J. Surface interactions between gold nanoparticles and biochar. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Syafiuddin, A.; Fulazzaky, M.A.; Salmiati, S.; Kueh, A.; Fulazzaky, M.; Salim, M.R. Silver nanoparticles adsorption by the synthetic and natural adsorbent materials: An exclusive review. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2020, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gicheva, G.; Yordanov, G. Removal of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles from aqueous dispersions by using activated carbon. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 431, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach, M.; Bukała, A.; Pulit-Prociak, J.; Staroń, P. Equilibrium and kinetics of nanosilver sorption from aqueous solutions. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 7898–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.X.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, J.F. Highly efficient removal of silver-containing nanoparticles in waters by aged iron oxide magnetic particles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5468–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Baltazar, A.; Reyes-López, S.Y.; Tellez-Vasquez, O.; Esparza, R.; Rosas, G.; Pérez, R. Analysis for the sorption kinetics of Ag nanoparticles on natural clinoptilolite. Adv. Condens. Matter. Phys. 2015, 284518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padil, V.V.T.; Stuchlík, M.; Černík, M. Plasma modified nanofibres based on gum kondagogu and their use for collection of nanoparticulate silver, gold and platinum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhandayuthapani, B.; Mallampati, R.; Sriramulu, D.; Dsouza, R.F.; Valiyaveettil, S. PVA/gluten hybrid nanofibers for removal of nanoparticles from water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallampati, R.; Valiyaveettil, S. Biomimetic metal oxides for the extraction of nanoparticles from water. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3395–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R. Novel ligand functionalized composite material for efficient copper (II) capturing from wastewater sample. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 172, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malińska, K. Biowęgiel odpowiedzią na aktualne problem ochrony środowiska. Inż. Ochr. Środ. 2012, 15, 387–403. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, K.; Quicker, P. Properties of biochar. Fuel 2018, 217, 240–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for Environmental Management: Science and Technology; Earthscan: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Shao, D.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Li, J. Removal of U (VI) from aqueous solution by amino functionalized flake graphite prepared by plasma treatment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4073–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Mena, L.E.; Pécora, A.A.B.; Beraldo, A.L. Slow pyrolysis of bamboo biomass: Analysis of biochar properties. AIDIC 2014, 37, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zielińska, A.; Skwarek, E.; Zaleska, A.; Gazda, M.; Hupka, J. Preparation of silver nanoparticles with controlled particle size. Proc. Chem. 2009, 1, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, S.; Yao, P.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, T.; Gong, G. Removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solutions by Phytolacca americana L. biomass as a low cost biosorbent. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raveendran, K.; Ganesh, A. Adsorption characteristic and pore-development of biomass pyrolysis char. Fuel 1998, 77, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.; Boguta, P.; Sokołowska, Z. Biochar efficiency in Cu removal from Haplic soils. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 4899–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; He, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Gu, L.; Zhao, Y. Mixed heavy metal removal from wastewater by using discarded mushroom-stick biochar: Adsorption properties and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumaraj; Xiong, Z.; Sarmah, A.K.; Padhye, L.P. Acidic surface functional groups control chemisorption of ammonium onto carbon materials in aqueous media. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second-order model for sorption process. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczuk-Karpisz, K.; Nowicki, P.; Sokołowska, Z.; Pietrzak, R. Hay-based activated biochars obtained using two different heating methods as effective low-cost sorbents: Solid surface characteristics, adsorptive properties and aggregation in the mixed Cu(II)/PAM system. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołodyńska, D.; Wnętrzak, R.; Leahy, J.J.; Kwapiński, W.; Hayes, M.H.B.; Hubicki, Z. Kinetic and adsorptive characterization of biochar in metal ions removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewu, D.D.; Boakye, P.; Woo, S.H. Highly efficient adsorption of cationic dye by biochar produced with Korean cabbage waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elhamid, A.I.; Emran, M.; El-Sadek, M.H.; El-Shanshory, A.A.; Soliman, H.M.A.; Akl, M.A.; Rashad, M. Enhanced removal of cationic dye by eco-friendly activated biochar derived from rice straw. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, B.; Chen, L.; Que, C.; Yang, K.; Deng, F.; Deng, X.; Shi, G.; Xu, G.; Wang, M. Adsorption of Antibiotics on Graphene and Biochar in Aqueous Solutions Induced by π-π Interactions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, J.; Du, Q.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Y. Antibiotic removal by agricultural waste biochars with different forms of iron oxide. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14143–14153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anasonye, F.; Tammeorg, P.; Parshintsev, J.; Riekkola, M.J.; Tuomela, M. Role of biochar and fungi on PAH sorption to soil rich in organic matter. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ukalska-Jaruga, A.; Debaene, G.; Smreczak, B. Dissipation and sorption processes of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) to organic matter in soils amended by exogenous rich-carbon material. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deal, C.; Brewer, C.E.; Brown, R.C.; Okure, M.A.; Amoding, A. Comparison of kiln-derived and gasifier-derived biochars as soil amendments in the humid tropics. Biomass Bioenerg. 2012, 37, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönherr, J.; Buchheim, J.R.; Sholz, P.; Adelhelm, P. Boehm titration revisited (Part I): Practical aspects for achieving a high precision in quantifying oxygen-containing surface groups on carbon materials. Carbon 2018, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Józefaciuk, G. Effect of acid and alkali treatments on surface-charge properties of selected minerals. Clay Miner. 2002, 50, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe. Kunglinga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich, H.M. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. A 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Sips, R. On the structure of a Catalyst Surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1950, 18, 1024–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |





| Type Biochar | Q [cmol/kg] | Carboxylic Groups [cmol/kg] | Lactonic Groups [cmol/kg] | Phenolic Groups [cmol/kg] | SBET [m2/g] | Vt [cm3/g] | Vm [cm3/g] | M [%] | D [nm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BV | 99.7 | 26.7 | 34.9 | 104.1 | 98.96 | 0.049 | 0.037 | 75.5 | 2.02 |
| BP | 66.7 | 13.8 | 9.8 | 92.3 | 83.97 | 0.041 | 0.034 | 82.9 | 1.96 |
| BT | 48.6 | 6.9 | 23.8 | 20.7 | 1.92 | 0.0096 | 0.0015 | 15.6 | 19.94 |
| Pseudo First-Order (Lagergren) | Pseudo Second-Order (Ho and Mckay) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1·10−2 [1/min] | qe [mg/g] | R2 | k2·10−2 [g/mg·min] | qe [mg/g] | R2 | |
| BV | 2.1 | 45.2 | 0.69 | 0.44 | 88.9 | 0.99 |
| BP | 1.9 | 41.2 | 0.51 | 0.24 | 75.2 | 0.99 |
| BT | 1.5 | 30.3 | 0.84 | 0.10 | 72.5 | 0.98 |
| Freundlich Isotherm | Langmuir Isotherm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KF [mg/g(L/mg]1/n | 1/n | R2 | KL [L/mg] | Qm [mg/g] | R2 | |
| BV | 0.46 | 0.41 | 0.97 | 5.98·10−3 | 114.94 | 0.90 |
| BP | 1.69·10−6 | 0.72 | 0.98 | 2.74·10−5 | 12.97 | 0.69 |
| BT | 6.01·10−9 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 3.39·10−7 | 4.6 | 0.95 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomczyk, A.; Szewczuk-Karpisz, K.; Sokołowska, Z.; Kercheva, M.; Dimitrov, E. Purification of Aqueous Media by Biochars: Feedstock Type Effect on Silver Nanoparticles Removal. Molecules 2020, 25, 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122930
Tomczyk A, Szewczuk-Karpisz K, Sokołowska Z, Kercheva M, Dimitrov E. Purification of Aqueous Media by Biochars: Feedstock Type Effect on Silver Nanoparticles Removal. Molecules. 2020; 25(12):2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122930
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomczyk, Agnieszka, Katarzyna Szewczuk-Karpisz, Zofia Sokołowska, Milena Kercheva, and Emil Dimitrov. 2020. "Purification of Aqueous Media by Biochars: Feedstock Type Effect on Silver Nanoparticles Removal" Molecules 25, no. 12: 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122930
APA StyleTomczyk, A., Szewczuk-Karpisz, K., Sokołowska, Z., Kercheva, M., & Dimitrov, E. (2020). Purification of Aqueous Media by Biochars: Feedstock Type Effect on Silver Nanoparticles Removal. Molecules, 25(12), 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122930