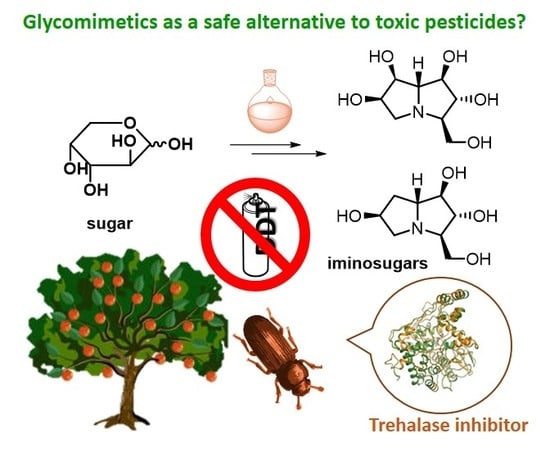
New Frontiers on Human Safe Insecticides and Fungicides: An Opinion on Trehalase Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Carbohydrate- and Carbocyclic-Based Inhibitors
| Compound | Silkworm (B. mori), IC50 (Ki) | Tobacco Cutworm (S. litura), IC50 (Ki) | R. solani, IC50 (Ki) | Porcine Kidney, IC50 (Ki) | Porcine Intestine, IC50 (Ki) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | n.d. | 370 nM [19] | 72 µM [18] | 250 µM [21] | 420 nM [19] |
| 3a | n.d. | 48 nM [19] (43 nM) [20] | 140 nM (1.9 nM) [18] | 2.4 nM [21] | 14 nM [19] |
| 4 | 8.3 µM [31] | n.d. | n.d. | (0.18 µM) [30] | n.d. |
| 5b,c | 49 nM [36] 52 nM [35] (10 nM) [35] | n.d. | 66 nM [42] | 15.5 nM [39] d (2.1 nM) [39] | n.d. |
| 8a | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 83.0 nM [39] (30.4 nM) [39] | n.d. |
3. Iminosugar-Based Inhibitors
3.1. Monocyclic Iminosugars and Their Derivatives
| Compound | C. riparius, IC50 (Ki) | Porcine Kidney, IC50 (Ki) | Selectivity a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 2.83 μM [54] (1.39 μM) [54] | 5.96 μM [54] b (2.98 μM) [54] | |
| 13 | 55 μM [48] | n.i. [50] | 18.2 |
| 15 | 19 μM [54] (9.3 μM) [54] | 4.8 μM [50] c (5.3 μM) [54] | - |
| 16 | 10 μM [52] d | n.i. [52] | 100 |
| 19 | 9.7 μM [55] | 109 μM [55] | 11.2 |
| 20 | 11 μM [56] | 76 μM [56] | 6.9 |
3.2. Bicyclic Iminosugars and Their Glycosyl Derivatives
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elbein, A.D. The metabolism of α,α-trehalose. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 1974, 30, 227–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbein, A.D.; Pan, Y.T.; Pastuszak, I.; Carroll, D. New insights on trehalose: A multifunctional molecule. Glycobiology 2003, 13, 17R–27R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunn, J.E.; Delorge, I.; Figueroa, C.M.; Van Dijck, P.; Stitt, M. Trehalose metabolism in plants. Plant J. 2014, 79, 544–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, J.H. Trehalose as a “chemical chaperone”: Fact and fantasy. In Molecular Aspects of the Stress Response: Chaperones, Membranes and Networks; Csermely, P., Vígh, L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 594, pp. 143–158. ISBN 978-0-387-39975-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.K.; Roy, I. Effect of trehalose on protein structure. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.N. Trehalose—The insect “blood” sugar. In Advances in Insect Physiology; Simpson, S.J., Ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2003; Volume 31, pp. 205–285. ISBN 0-12-024231-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defaye, J.; Driguez, H.; Henrissat, B.; Bar-Guilloux, E. Stereochemistry of the hydrolysis of α,α-trehalose by trehalase, determined by using a labelled substrate. Carbohydr. Res. 1983, 124, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Schlöder, P.; Steele, J.E.; Wegener, G. The regulation of trehalose metabolism in insects. Experentia 1996, 52, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneyama, Y.; Lever, J.E. Apical trehalase expression associated with cell patterning after inducer treatment of LLC-PK1 monolayers. J. Cell Physiol. 1987, 131, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlqvist, A. Assay of intestinal disaccharides. Anal. Biochem. 1968, 22, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevelein, J.M. Regulation of trehalose metabolism in fungi. Microbiol. Rev. 1984, 48, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bini, D.; Cardona, F.; Gabrielli, L.; Russo, L.; Cipolla, L. Trehalose mimetics as inhibitors of trehalose processing enzymes. In Carbohydrate Chemistry Chemical and Biological Approaches; Rauter, A.M., Lidhorst, T., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2012; Volume 37, pp. 259–302. ISBN 978-1-84973-154-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, G.; Tschiedel, V.; Schlöder, P.; Ando, O. The toxic and lethal effects of the trehalase inhibitor trehazolin in locusts are caused by hypoglycaemia. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Compain, P.; Martin, O.R. Iminosugars: From Synthesis to Therapeutic Applications; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-0-470-03391-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, T.; Higashide, E.; Yamamoto, H.; Shibata, M. Studies on validamycins, new antibiotics. II. Production and biological properties of validamycins A and B. J. Antibiot. 1971, 24, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horii, S.; Kameda, Y.; Kawahara, K. Studies on validamycins, new antibiotics. VIII. Isolation and characterization of validamycins C, D, E and F. J. Antibiot. 1972, 25, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kameda, Y.; Asano, N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Matsui, K.; Horii, S.; Fukase, H. Validamycin G and validoxylamine G, new members of the validamycins. J. Antibiot. 1986, 39, 1491–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kameda, Y.; Matsui, K. Effect of Validamycins on Glycohydrolases of Rhizoctonia Solani. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kameda, Y.; Asano, N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Matsui, K. Validoxylamines as trehalase inhibitors. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asano, N.; Takeuchi, M.; Kameda, Y.; Matsui, K.; Kono, Y. Trehalase inhibitors, validoxylamine A and related compounds as insecticides. J. Antibiot. 1990, 43, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyosseva, S.V.; Kyossev, Z.N.; Elbein, A.D. Inhibitors of pig kidney trehalase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1995, 316, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salleh, H.M.; Honek, J.F. Time-dependent inhibition of porcine kidney trehalase by aminosugars. FEBS Lett. 1990, 262, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, L.-Q.; Zheng, Y.-G. Inhibitory effects of validamycin compounds on the termites trehalase. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 2009, 95, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, S.; Kono, Y.; Kameda, Y. Induction of non-diapause eggs in Bombyx mori by a trehalase inhibitor. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1988, 46, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, Y.; Takeda, S.; Kameda, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Matsushita, K.; Nishina, M.; Hori, E. Lethal activity of trehalase inhibitor, validoxylamine A, and its influence on the blood sugar level in Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1993, 28, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kono, Y.; Takeda, S.; Kameda, Y. Lethal activity of a trehalase inhibitor, validoxylamine A, against Mamestra brassicae and Spodoptera litura. J. Pestic. Sci. 1994, 19, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kono, Y.; Takeda, S.; Kameda, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Matsushita, K.; Nishina, M.; Hori, E. NMR analysis of the effect of validoxylamine A, a trehalase inhibitor, on the larvae of the cabbage armyworm. J. Pestic. Sci. 1995, 20, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kono, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Matsushita, K.; Nishina, M.; Kameda, Y.; Hori, E. Inhibition of flight in Periplaneta americana (Linn.) by a trehalase inhibitor, validoxylamine A. J. Insect Physiol. 1994, 40, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Mihara, M.; Matsushita, K.; Nishina, M.; Kameda, Y. Effect of a Trehalase Inhibitor, Validoxylamine A, on Oocyte Development and Ootheca Formation in Periplaneta americana (Blattodea, Blattidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1997, 32, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vértesy, L.; Fehlhaber, H.-W.; Schulz, A. The Trehalase Inhibitor Salbostatin, a Novel Metabolite from Streptomyces albus, ATCC21838. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1994, 33, 1844–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, T.; Uchida, C.; Ogawa, S. Total Synthesis of Trehalase Inhibitor Salbostatin. Chem. Eur. J. 1995, 9, 634–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, O.; Satake, H.; Itoi, K.; Sato, A.; Nakajima, M.; Takahashi, S.; Haruyama, H.; Ohkuma, Y.; Kinoshita, T.; Enokita, R. Trehazolin, a new trehalase inhibitor. J. Antibiot. 1991, 44, 1165–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ando, O.; Nakajima, M.; Hamano, K.; Itoi, K.; Takahashi, S.; Takamatsu, A.; Sato, A.; Enokita, R.; Okazaki, T.; Haruyama, H.; et al. Isolation on trehalamine, the aglycon of trehazolin, from microbial broths and characterization of trehazolin related compounds. J. Antibiot. 1993, 46, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Nemr, A.; El Ashry, E.H. Chapter 3—Potential trehalase inhibitors: Syntheses of trehazolin and its analogues. In Advances in Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biochemistry; Horton, D., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 65, pp. 45–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, O.; Nakajima, M.; Kifune, M.; Fang, H.; Tanzawa, K. Trehazolin, a slow, tight-binding inhibitor of silkworm trehalase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1244, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, C.; Yamagashi, T.; Kitahashi, H.; Iwaisaki, Y.; Ogawa, S. Further chemical modification of trehalase inhibitor trehazolin: Structure and inhibitory-activity relationship of the inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1995, 3, 1605–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berecibar, A.; Grandjean, A.; Siriwardena, A. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Natural Aminocyclopentitol Glycosidase Inhibitors: Mannostatins, Trehazolin, Allosamidins, and Their Analogues. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 779–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y. Chemistry and biology of trehazolins. Carbohydr. Res. 1999, 315, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiara, J.L.; Storch de Gracia, I.; García, Á.; Bastida, Á.; Bobo, S.; Martín-Ortega, M.D. Synthesis, inhibition properties, and theoretical study of the new nanomolar trehalase inhibitor 1-thiatrehazolin: Towards a structural understanding of trehazolin inhibition. ChemBioChem 2005, 6, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibson, R.P.; Gloster, T.M.; Roberts, S.; Warren, R.A.J.; Storch de Gracia, I.; García, Á.; Chiara, J.L.; Davies, G.J. Molecular Basis for Trehalase Inhibition Revealed by the Structure of Trehalase in Complex with Potent Inhibitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4115–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, N.; Kato, A.; Matsui, K. Two Subsites on the Active Center of Pig Kidney Trehalase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 240, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, O.; Kifune, M.; Nakajima, M. Effects of Trehazolin, a Potent Trehalase Inhibitor, on Bombyx mori and Plant Pathogenic Fungi. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1995, 59, 711–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, G.; Macho, C.; Schlöder, P.; Kamp, G.; Ando, O. Long-term effects of the trehalase inhibitor trehazolin on trehalase activity in locust flight muscles. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 3852–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Song, G. Synthesis and Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships of Fluorine-Containing 4,4-Dihydroxylmethyl-2-aryliminooxazo(thiazo)lidines as Trehalase inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5279–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Song, G.; Li, Z. Syntheses and activities as trehalase inhibitors of N-arylglycosylamines derived from fluorinated anilines. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 336, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, T.; Inouye, S.; Tsuruoka, T.; Koaze, Y.; Niida, T. “Nojirimycin” as a potent inhibitor of glucosidase. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1970, 34, 966–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.D.; Frommer, W.; Muller, L.; Trusheit, E. Glucosidase-inhibitoren aus Bazillen. Naturwissenschaften 1979, 66, 584–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.V.; Fellows, L.E.; Bell, E.A. Glucosidase and trehalase inhibition by 1,5-dideoxy-1,5-imino-d-mannitol, a cyclic amino alditol from Lonchocarpus sericeus. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 768–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murao, S.; Miyata, S. Isolation and characterization of a new trehalase inhibitor, S-GI. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1980, 44, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, N.; Oseki, K.; Kizu, H.; Matsui, K. Nitrogen-in-the-ring pyranoses and furanoses: Structural basis of inhibition of mammalian glycosidases. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 3701–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzeveno, P.B.; Creemer, L.J.; Daniel, L.K.; King, C.H.R.; Liu, P.S. A facile, practical synthesis of 2,6-dideoxy-2,6-imino-7-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-d-glycero-l-gulo-heptitol (MDL 25,637). J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 2539–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Kato, H.; Nagayama, K.; Abe, H. Isolation of 2R,SR-Dihydroxymethyl-3R,4R- dihydroxypyrrolidine (DMDP) from the Fermentation broth of Streptomyces sp. KSC-S791. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1995, 59, 936–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, D.; Forcella, M.; Cipolla, L.; Fusi, P.; Matassini, C.; Cardona, F. Synthesis of Novel Iminosugar-Based Trehalase Inhibitors by Cross-Metathesis Reactions. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 3995–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcella, M.; Cardona, F.; Goti, A.; Parmeggiani, C.; Cipolla, L.; Gregori, M.; Schirone, R.; Fusi, P.; Parenti, P. A membrane-bound trehalase from Chironomus riparius larvae: Purification and sensitivity to inhibition. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bini, D.; Cardona, F.; Forcella, M.; Parmeggiani, C.; Parenti, P.; Nicotra, F.; Cipolla, L. Synthesis and biological evaluation of nojirimycin- and pyrrolidine-based trehalase inhibitors. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cipolla, L.; Sgambato, A.; Forcella, M.; Fusi, P.; Parenti, P.; Cardona, F.; Bini, D. N-Bridged 1-deoxynojirimycin dimers as selective insect trehalase inhibitors. Carbohydr. Res. 2014, 389, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cendret, V.; Legigan, T.; Mingot, A.; Thibaudeau, S.; Adachi, I.; Forcella, M.; Parenti, P.; Bertrand, J.; Becq, F.; Norez, C.; et al. Synthetic deoxynojirimycin derivatives bearing a thiolated, fluorinated or unsaturated N-alkyl chain: Identification of potent α-glucosidase and trehalase inhibitors as well as F508del-CFTR correctors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 10734–10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konno, K.; Ono, H.; Nakamura, M.; Tateishi, K.; Hirayama, C.; Tamura, Y.; Hattori, M.; Koyama, A.; Kohno, K. Mulberry latex rich in anti-diabetic sugar-mimic alkaloids forces dieting on caterpillars. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirayama, C.; Konno, K.; Wasano, N.; Nakamura, M. Differential effects of sugar-mimic alkaloids in mulberry latex on sugar metabolism and disaccharidases of Eri and domesticated silkworms: Enzymatic adaptation of Bombyx mori to mulberry defense. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, N.; Kato, A.; Kizu, H.; Matsui, K.; Watson, A.A.; Nash, R.J. Calystegine B4, a novel trehalase inhibitor from Scopolia japonica. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 293, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaaanderup, P.R.; Madsen, R. Short syntheses of enantiopure calystegine B2, B3, and B4. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1106–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaaanderup, P.R.; Madsen, R. A Short Synthetic Route to the Calystegine Alkaloids. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosophon, P.; Baird, M.C.; Kanokmedhakul, S.; Pyne, S.G. Total Synthesis of Calystegine B4. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 3337–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, R.J.; Fellows, L.E.; Dring, J.V.; Fleet, G.W.J.; Derome, A.E.; Hamor, T.A.; Scofield, A.M.; Watkin, D.J. Isolation from alexia leiopetala and X-ray crystal structure of alexine, (1r,2r,3r,7s,8s)-3-hydroxymethyl-1,2,7-trihydroxypyrrolizidine[(2r,3r,4r,5s,6s)-2-hydroxymethyl-1-azabicyclo[3.3.0]octan-3,4,6-triol], a unique pyrrolizidine alkaloid. Tetrahedron Lett. 1988, 29, 2487–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, J.T. Chapter 7 Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids. In The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Pharmacology; Brossi, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 26, pp. 327–385. ISBN 9780080865508. [Google Scholar]
- Robins, D.J. Chapter 1 Biosynthesis of Pyrrolizidine and Quinolizidine Alkaloids. In The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Pharmacology; Cordell, G.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 46, pp. 1–61. ISBN 978-0-12-469546-7. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, R.J.; Thomas, P.I.; Waigh, R.D.; Fleet, G.W.J.; Wormald, M.R.; Lilley, P.M.d.Q.; Watkin, D.J. Casuarine: A very highly oxygenated pyrrolizidine alkaloid. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 7849–7852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, R.N.; Nayar, S.L.; Chopra, I.C. Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants; Council of Scientific and Industrial Research: New Delhi, India, 1956; ISBN 8172360487. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, R.B.; Santhakumari, G. Anti–Diabetic Activity of the Seed Kernel of Syzygium Cumini Linn. Anc. Sci. Life 1986, 6, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grover, J.K.; Yadav, S.; Vats, V. Medicinal plants of India with anti-diabetic potential. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 81, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentreddy, S.R. Medicinal plant species with potential antidiabetic properties. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2007, 87, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormald, M.R.; Nash, R.J.; Watson, A.A.; Bhadoria, B.K.; Langford, R.; Sims, M.; Fleet, G.W.J. Casuarine-6-α-d-glucoside from Casuarina equisetifolia and Eugenia jambolana. Carbohydr. Lett. 1996, 2, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, A.; Kano, E.; Adachi, I.; Molyneux, R.J.; Watson, A.A.; Nash, R.J.; Fleet, G.W.J.; Wormald, M.R.; Kizu, H.; Ikeda, K.; et al. Australine and related alkaloids: Easy structural confirmation by 13C NMR spectral data and biological activities. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2003, 14, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, N.; Yamauchi, T.; Kagamifuchi, K.; Shimizu, N.; Takahashi, S.; Takatsuka, H.; Ikeda, K.; Kizu, H.; Chuakul, W.; Kettawan, A.; et al. Iminosugar-Producing Thai Medicinal Plants. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoda, H.; Katoh, H.; Takabe, K. Asymmetric total synthesis of natural pyrrolizidine alkaloid, (+)-alexine. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 7661–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressel, M.; Restorp, P.; Somfai, P. Total Synthesis of (+)-Alexine by Utilizing a Highly Stereoselective [3 + 2] Annulation Reaction of an N-Tosyl-α-Amino Aldehyde and a 1,3-Bis(silyl)propene. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 3072–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Maehara, T.; Sengoku, T.; Fujita, N.; Takabe, K.; Yoda, H. New asymmetric strategy for the total synthesis of naturally occurring (+)-alexine and (−)-7-epi-alexine. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 5254–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Somfai, P. Enantioselective synthesis of anti-3-alkenyl-2- amido-3-hydroxy esters: Application to the total synthesis of (+)-alexine. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2799–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myeong, I.-S.; Jung, C.; Ham, W.-H. Total Syntheses of (−)-7-epi-Alexine and (+)-Alexine Using Stereoselective Allylation. Synthesis 2019, 51, 3471–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denmark, S.E.; Hurd, A.R. Synthesis of (+)-Casuarine. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 1311–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denmark, S.E.; Hurd, A.R. Synthesis of (+)-Casuarine. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 2875–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, I.; Plaz, M.T.; Tamayo, J.A. Polyhydroxylated pyrrolizidines. Part 6: A new and concise stereoselective synthesis of (+)-casuarine and its 6,7-diepi isomer, from DMDP. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 6527–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritthiwigrom, T.; Willis, A.C.; Pyne, S.G. Total Synthesis of Uniflorine A, Casuarine, Australine, 3-epi-Australine, and 3,7-Di-epi-australine from a Common Precursor. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parmeggiani, C.; Cardona, F.; Giusti, L.; Reissig, H.-U.; Goti, A. Stereocomplementary Routes to Hydroxylated Nitrogen Heterocycles: Total Syntheses of Casuarine, Australine, and 7-epi-Australine. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 10595–10604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, F.; Parmeggiani, C.; Faggi, E.; Bonaccini, C.; Gratteri, P.; Sim, L.; Gloster, T.M.; Roberts, S.; Davies, G.J.; Rose, D.R.; et al. Total Synthesis of Casuarine and Its 6-O-α-Glucoside: Complementary Inhibition towards Glycoside Hydrolases of the GH31 and GH37 Families. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccini, C.; Chioccioli, M.; Parmeggiani, C.; Cardona, F.; Lo Re, D.; Soldaini, G.; Vogel, P.; Bello, C.; Goti, A.; Gratteri, P. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Docking Studies of Casuarine Analogues: Effects of Structural Modifications at Ring B on Inhibitory Activity Towards Glucoamylase. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 5574–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, F.; Goti, A.; Parmeggiani, C.; Parenti, P.; Forcella, M.; Fusi, P.; Cipolla, L.; Roberts, S.M.; Davies, G.J.; Gloster, T.M. Casuarina-6-O-α-d-glucoside and its analogues are tight binding inhibitors of insect and bacterial trehalases. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 2629–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, T.; Kasai, M.; Hayashi, T.; Arisawa, M.; Momose, Y.; Arai, I.; Amagaya, S.; Komatsu, Y. a-glucosidase Inhibitors from Paraguayan natural medicine, Ñangapiry, the leaves of Eugenia uniflora. Pharm. Biol. 2000, 38, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.S.; Pyne, S.G.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H. Synthesis of Putative Uniflorine A. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 3139–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritthiwigrom, T.; Pyne, S.G. Synthesis of (+)-Uniflorine A: A Structural Reassignment and a Configurational Assignment. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 2769–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmeggiani, C.; Martella, D.; Cardona, F.; Goti, A. Total Synthesis of (−)-Uniflorine A. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2058–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-K.; Qiu, S.; Xiang, Y.-G.; Ruan, Y.-P.; Zheng, X.; Huang, P.-Q. SmI2-Mediated Radical Cross-Couplings of α-Hydroxylated Aza-hemiacetals and N,S-Acetals with α,β-Unsaturated Compounds: Asymmetric Synthesis of (+)-Hyacinthacine A2, (−)-Uniflorine A, and (+)-7-epi-Casuarine. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 4952–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Adamio, G.; Sgambato, A.; Forcella, M.; Caccia, S.; Parmeggiani, C.; Casartelli, M.; Parenti, P.; Bini, D.; Cipolla, L.; Fusi, P.; et al. New Synthesis and biological evaluation of uniflorine A derivatives: Towards specific insect trehalase inhibitors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Adamio, G.; Forcella, M.; Fusi, P.; Parenti, P.; Matassini, C.; Ferhati, X.; Vanni, C.; Cardona, F. Probing the Influence of Linker Length and Flexibility in the Design and Synthesis of New Trehalase Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Compound | Porcine Kidney, Ki | E. coli Tre37A, Ki | C. riparius, Ki |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 12 μM [73] a | 17 μM [85] | 0.12 μM [54] |
| 26 | 11 nM [87] | 12 nM [87] | 0.66 nM [87] |
| 27 | 138 nM [87] | 86 nM [87] | 22 nM [87] |
| 28 | >10 μM [87] | 2.8 μM [87] | 157 nM [87] |
| Compound | Porcine Kidney, IC50 | C. riparius, IC50 | Selectivity a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 29 | >1 mM [93] | 177 ± 18 nM [93] | >5649 |
| 30 | 20.6 ± 2.2 μM [93] | 1.22 ± 0.08 μM [93] | 17 |
| 31 | >1 mM [93] | 175 ± 12 nM [93] | >5714 |
| 27 | 479 ± 45 nM [93] | 44 ± 1.0 nM [93] | 10 |
| 32 | 190.60 ± 34.14 μM [94] | 29.49 ± 7.26 μM [94] | 6 |
| 33 α,β | 7.67 ± 3.91 μM [94] | 2.30 ± 0.13 μM [94] | 3 |
| 33 α | 27.64 ± 5.35 μM [94] | 9.36 ± 1.49 μM [94] | 3 |
| 33 β | 5.84 ± 0.26 μM [94] | 0.784 ± 0.059 μM [94] | 7 |
| 34 α,β | n.d. | >1 mM | - |
| 35 α,β | n.d. | >1 mM | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matassini, C.; Parmeggiani, C.; Cardona, F. New Frontiers on Human Safe Insecticides and Fungicides: An Opinion on Trehalase Inhibitors. Molecules 2020, 25, 3013. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133013
Matassini C, Parmeggiani C, Cardona F. New Frontiers on Human Safe Insecticides and Fungicides: An Opinion on Trehalase Inhibitors. Molecules. 2020; 25(13):3013. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133013
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatassini, Camilla, Camilla Parmeggiani, and Francesca Cardona. 2020. "New Frontiers on Human Safe Insecticides and Fungicides: An Opinion on Trehalase Inhibitors" Molecules 25, no. 13: 3013. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133013
APA StyleMatassini, C., Parmeggiani, C., & Cardona, F. (2020). New Frontiers on Human Safe Insecticides and Fungicides: An Opinion on Trehalase Inhibitors. Molecules, 25(13), 3013. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133013