Abstract
Much has been written on the physiological benefits of Korean Red Ginseng (KRG). Among its various components, ginsenosides have been widely investigated for their various pharmacological effects. However, polysaccharides are a major KRG component that has not received scrutiny similar to that of ginsenosides. The present study aims to fill that gap in the existing literature and to investigate the possible functions of polysaccharide in KRG. The researchers evaluated proteomic changes in non-saponin fractions with rich polysaccharides (NFP) in KRG. Based on the serum analysis, proteomics analysis of the liver and the spleen was additionally conducted to identify related functions. We validated the suggested functions of NFP with the galactosamine-induced liver injury model and the cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression model. Then, we evaluated the antimetastatic potential of NFP in the lungs. Further proteomics analysis of the spleen and liver after ingestion confirmed functions related to immunity, cancer, hepatoprotection, and others. Then, we validated the suggested corresponding functions of the NFP in vivo model. NFP showed immune-enhancing effects, inhibited melanoma cell metastasis in the lung, and decreased liver damage. The results show that using the proteomic approach uncovers the potential effects of polysaccharides in KRG, which include enhancing the immune system and protecting the liver.
1. Introduction
Korean Red Ginseng (KRG) is processed Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer), a representative indigenous plant. KRG has been safely used as herbal medicine to normalize and strengthen body functions for a long time [1], making it a functional food. The representative activities of KRG are the boosting of immune function, helping in fatigue recovery, supporting blood circulation, acting as an antioxidant, improving memory function, and alleviating menopause symptoms [2]. The diverse pharmacological effects of KRG have been reported in both clinical and experimental research. These effects were the result of a combination of diverse components in KRG, namely, ginsenoside, non-saponin components such as polysaccharides, polyphenols, flavonoids, and others [3]. Among these components, ginsenosides have been well researched for various pharmacological activities. However, the activities of polysaccharides as major components of KRG have not been as deeply investigated as ginsenoside activities [4], because ginsenosides seemed easier to isolate and characterize in terms of chemical structure. For this reason, polysaccharides have been less explored, in terms of evaluating all their possible functions individually.
A proteomic research strategy presents comprehensive biological data from changes in related proteins, suggesting their interrelationships [5]. In a previous study, we demonstrated a proteomics research tool to study the bioactivity and biomarkers of KRG [6]. Currently, multiomics strategy systems are applied in the field of natural product studies [7,8,9,10].
The present study aims to investigate and identify the effects of polysaccharides in KRG. We evaluated proteomic changes in non-saponin fractions with rich polysaccharide (NFP) in KRG between a blank group (control group) and an NFP-treated group, in order to investigate how polysaccharides work in KRG. A label-free global proteomic analysis was employed to compare proteins between the groups in serum, in order to identify NFP’s effects on human physiology. Based on these results, the possible effects of NFP were identified and selected for testing in relation to organ efficiency. Then, we investigated several effects of the NFP in order to validate the suggested functions of the NFP in vivo model.
2. Results
2.1. Protein Identification for Serum Proteins
The researchers performed a proteomic analysis of rat sera to identify differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) in the first step. The representative protein identification process and spectra are provided in Figure 1. We compared the total identified protein list at 1% false discovery rate (FDR) level (Supplemental Table S1), and selected proteins with the following criteria to identify the proteins under a stringent level of evaluation: p < 0.05 (T-test), and p < 0.025 (PLGEM p-value), as shown in Table 1. PLGEM here is the power law global error model.
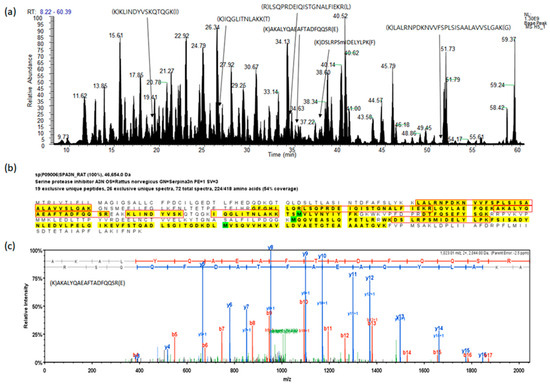
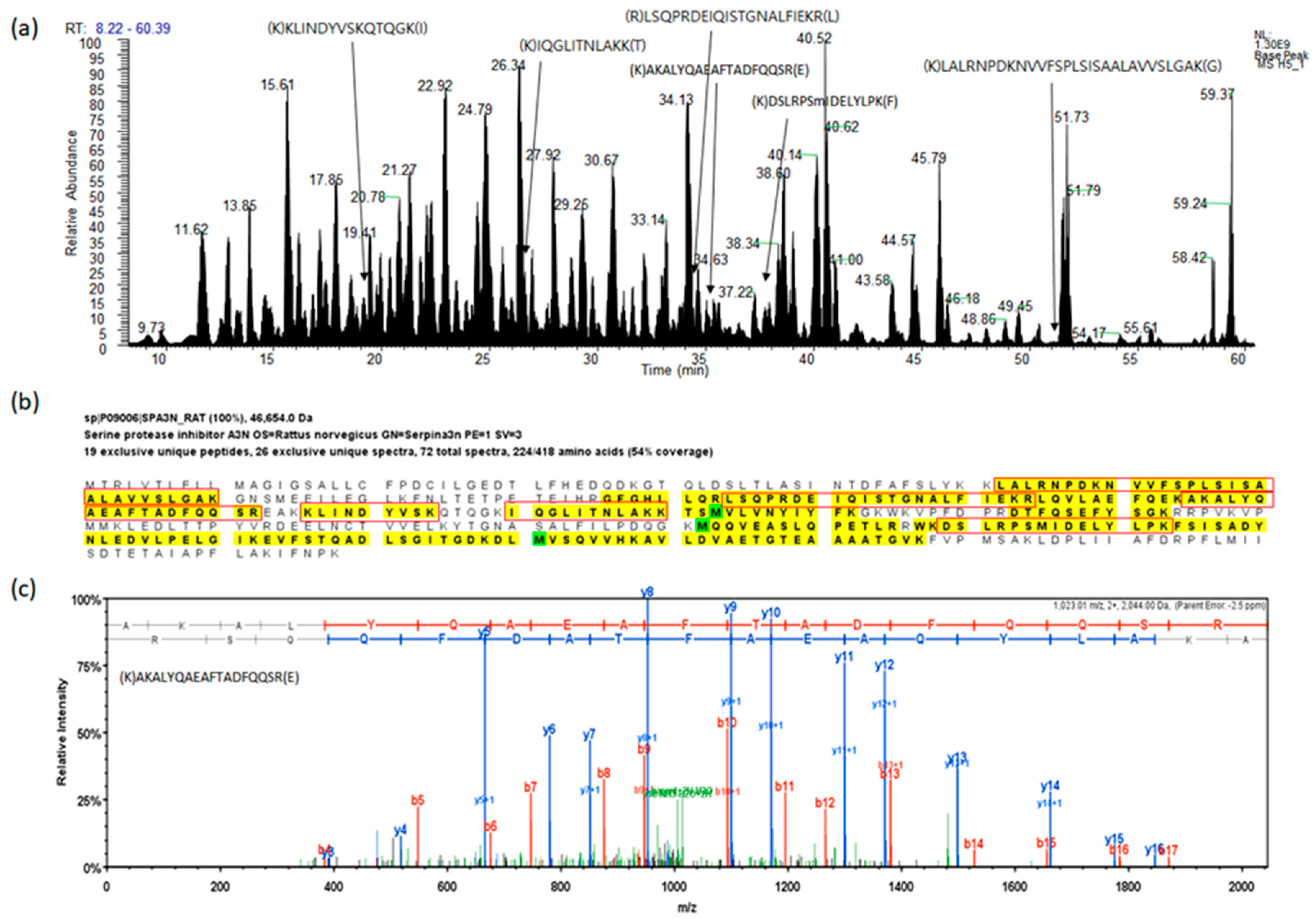
Figure 1.
A representative example of the analysis for fractionated serum protein digest by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). (a) Base peak chromatogram based on total ion chromatography, the peptides indicate identified peptides of SPA3N. (b) The sequence of SPA3N, the peptides in the red boxes indicate peptides found by MS/MS. (c) The experimental MS/MS spectrum for the SPA3N doubly charged tryptic peptide sequence AKALYQAEAFTADFQQSR among the identified peptides by matching a peptide fragmentation pattern.

Table 1.
Selected biosignature candidate proteins identified in the serum of the aged rat treated with non-saponin fractions with rich polysaccharide (NFP).
Then, we performed enrichment analysis using the Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) for functional annotation, to estimate the relevant biological function. For example, Gstm1, Gstm2, and Gsta3 as upregulated proteins showed a function associated with glutathione and redoxin metabolism. Meanwhile, proteins related to hepatitis B, viral carcinogenesis, and platelet aggregation were all shown to have decreased. In the next step, we enlarged the total pool of proteins (protein: probability > 99.9%; peptide: probability > 95%) (Supplemental Table S3) for bioinformatics evaluation, using an Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) tool in three different conditions: (1) all organs and cell lines for the overall changes; (2) focusing on cancer-related functions and cell lines, because cancer-related bio functions were mainly identified via existing criteria; and (3) other organs and cell lines except cancer-related functions. Our particular interest was to identify all the possible effects of NFP, including new functions. As a result, the overall upregulated functions we identified were related to the activation of cells (phagocytes and macrophages), and the number of cells (Table 2). Meanwhile, various cancers, brain diseases, viral infections, and the synthesis of reactive oxygen species were downregulated. In the cancer-specific evaluation (criteria 2), the IPA analysis showed that the proteins were related to cancer types and anticancer functions, like metastasis, cell spreading, and angiogenesis. Based on the results from the IPA analysis, we further evaluated organs, like the spleen, for immunity and cancer, as well as the liver for antioxidants and liver protection.

Table 2.
Identified possible functions of NFP in the serum of the rat treated with NFP by Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA).
2.2. Protein Identification: Spleen and Liver as Select Target Organs
Based on the analysis of serum proteins, we selected the liver and the spleen as primary candidate organs. In the next step, we further compared the proteomic profiles between control and NFP. A total of 4656 unique proteins were identified by the MS analysis of the spleen, and 3583 for the liver (protein: probability > 99%; peptide: probability > 95%) (Supplemental Table S3).
Among the DEP pool (p < 0.001), between the normal and the NFP, we selected the DEPs whose changes showed top upregulated/downregulated proteins in Table 3.

Table 3.
Selected biosignature candidate proteins identified in the spleen and liver of the aged rat treated with NFP.
The DEPs in the spleen showed a function associated with innate immune response, biosynthesis of antibiotics, mitochondria, and amoebiasis derived using DAVID. At the same time, the liver DEPs were related to the glutathione metabolic process and wound healing. Then, we integrated the DEPs into the context of biological processes, using the same approach as that used for the IPA in the serum analysis. Our analysis of the results from the IPA tool revealed that the movement of immune cells was upregulated in the analysis of the spleen. In contrast, the cell death of hepatocytes, liver necrosis, and inflammation were downregulated in the liver (Table 4).

Table 4.
Selected Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) and IPA functional analysis of the identified proteins in the spleen and liver of the aged rat treated with NFP.
2.3. A More Detailed Function Analysis of the Proteins
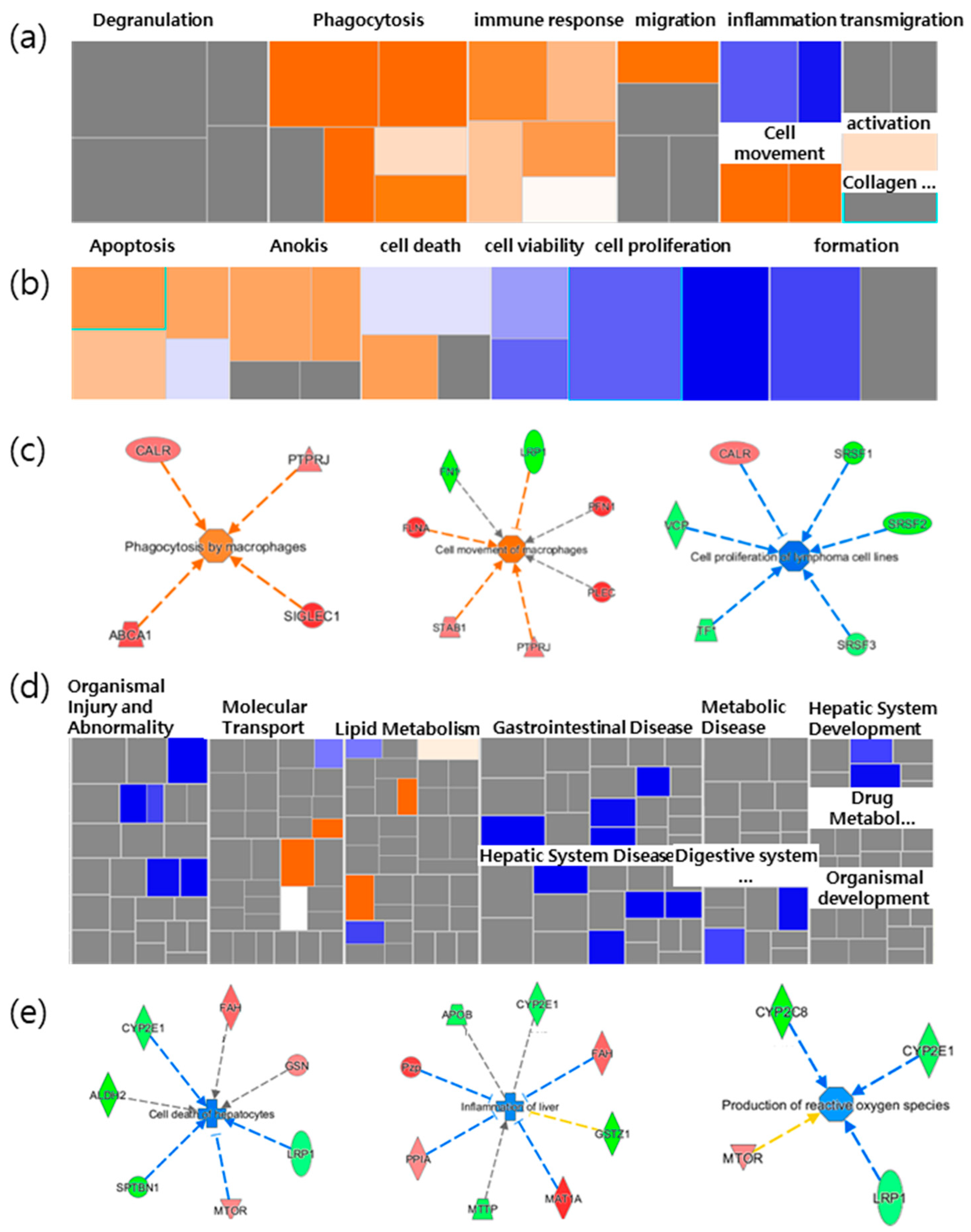
Based on the results from the IPA, we focused on the main bio functions related to both the spleen immune function and the liver-protective function. The DEPs of the spleen were mainly related to cancer, and inflammatory responses related to immune functions. A more detailed analysis of the inflammatory response-related immune functions revealed that movement, migration, and phagocytosis increased with immune cells, as shown in Figure 1a. For the functions associated with cell death and the survival of cancer, the apoptosis of tumor cells and carcinomas, anoikis, and cell death were all shown to increase. In contrast, cancer cell proliferation decreased (Figure 2b). Thus, the results showed that NFP was involved in cancer cell proliferation while increasing the immune response (Figure 2c).
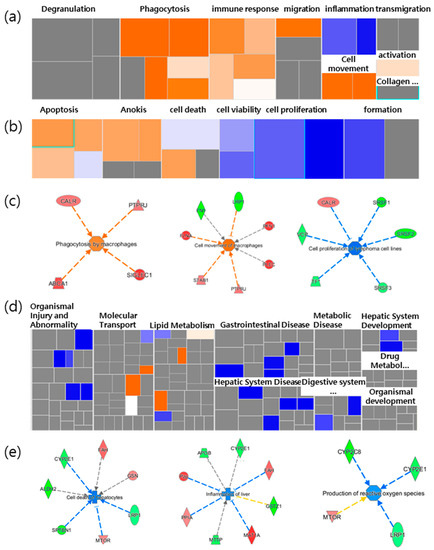
Figure 2.
Heatmap analysis of selected functions related to spleen and liver. The heatmap showed (a) inflammatory response related to immunological functions and (b) cell death and survival related to cancer in the spleen. (c) Selected increased immunological functions, and the cell death and survival function of cancer in the spleen. (d) The heatmap panel shows hepatic functions in the liver. (e) Selected decreased typical function in the liver led to cell death of hepatocytes, inflammation of the liver, and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the liver. Each box represents a biological process or disease. The color of the box (a,b,d) and the proteins (c,e) indicates the predicted increase or decrease. Orange boxes represent biological processes or diseases that are trending toward an increase. Blue boxes represent biological processes or diseases that are trending toward a decrease. Grey boxes represent biological processes or diseases that are not predictable (currently ineligible for a prediction). NFP is a non-saponin fraction with rich polysaccharide.
Concerning hepatic functions, it was mostly gastrointestinal disease that was downregulated (Figure 1d). The cell death of hepatocytes and inflammation were reduced, while reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid synthesis were also slightly decreased. For example, the fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (Fah) gene increased, and Cype2e1 decreased, in relation to both the cell death and inflammation functions. In addition, there was a decrease in Stopn1 and low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (Lrp1), and increases in the pregnancy zone protein (Pzp), peptidylprolyl isomerase A (Ppia) and methionine adenosyltransferase 1A (Mat1a), which were associated with decreases in inflammation (Figure 1e). These results implied that the NFP has a protective effect on liver tissue and cells. Based on the results, we evaluated the effects of the enhanced immune function of immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibody-producing cells, the antimetastatic potential in the lungs, as well as liver protection and antioxidants, with the in vivo model as the validation target.
2.4. IgM Antibody-Producing Cells in the Spleen
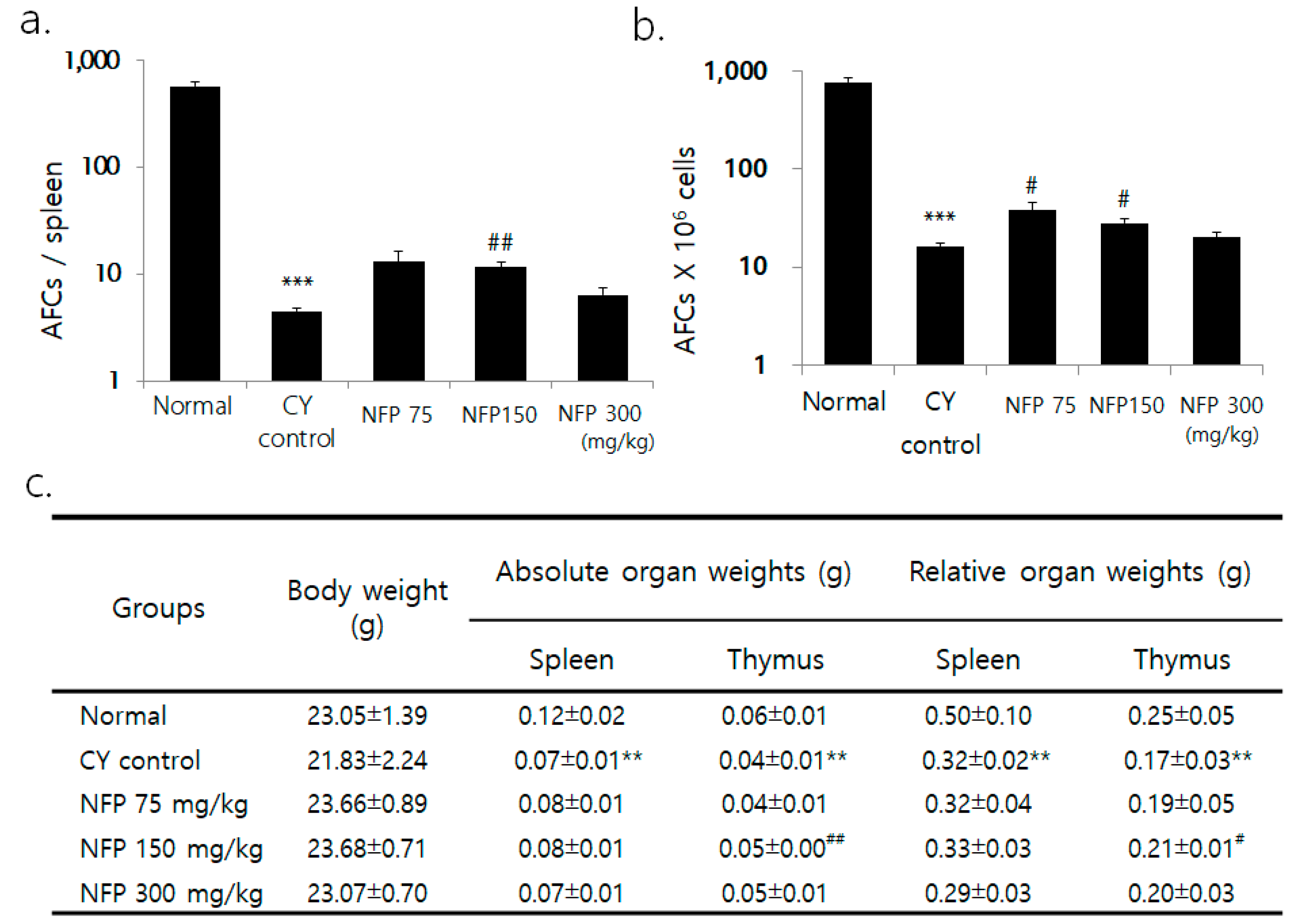
Although the researchers observed no significant difference in body weight between the groups, the weight of the spleen and thymus decreased in the cyclophosphamide (CY) group for immunosuppression, compared to the normal group (Figure 3c). Compared to the CY control, the thymus weight was greater in the group administered with 150 mg/kg of NFP (p < 0.01). Across all splenic cells, the count of plasma cells significantly decreased in the CY control compared to the normal group, confirming CY-induced immunosuppression (p < 0.001). NFP administration resulted in a trend of increased plasma cell count, especially with the administration of 150 mg/kg, with a statistical significance (p < 0.01), as in Figure 3a. The plasma cell count per 1 × 106 splenic cells significantly decreased in the CY control, compared to the normal group. Meanwhile, 75-mg/kg and 150-mg/kg of NFP resulted in an increased plasma cell count, with statistical significance (p < 0.05), as in Figure 3b.
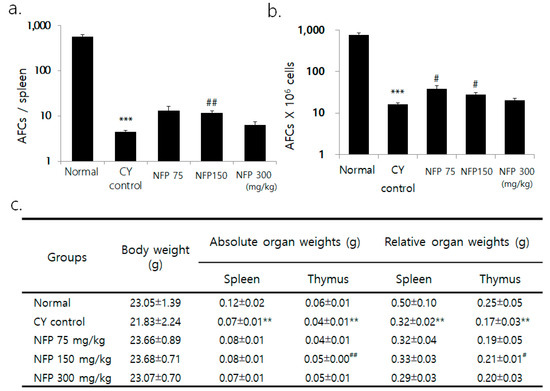
Figure 3.
Effects of NFP on antibody-forming cells (AFCs) and splenic subpopulation in Bagg Albino (BALB/c) mice treated with cyclophosphamide (CY). (a) Decrease in AFCs/spleen from the normal group at *** p < 0.001, increase in AFCs/spleen in the NFP 150 mg/kg groups compared with the CY control at ## p < 0.01. (b) Decrease in AFCs (× 106) cells from the normal group at *** p < 0.001, increase in AFCs (× 106)/spleen in the NFP 75, 150 mg/kg-treated groups compared with the CY control at #p < 0.05. (c) Comparing the normal group and the CY control group shows a decrease of **p < 0.01. However, in the NFP group administered with 150 mg/kg, the absolute organ weight (## p < 0.01) and relative organ weight (# p < 0.05) of the thymus increased. The data represent means ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (n = 8).
2.5. Evaluation for the Antimetastatic Potential of NFP in the Lungs
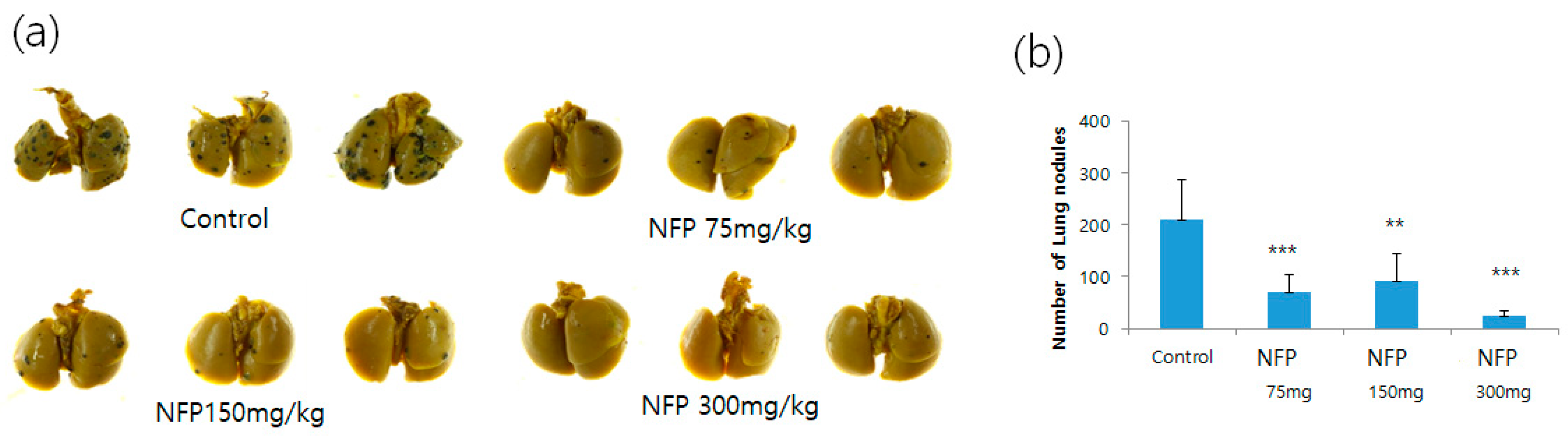
NFP was orally administered to mice intravenously injected with B16F10 cells, to confirm that NFP could inhibit the formation of distant metastasis in vivo. The NFP treatment for mice intravenously injected with B16F10 cells resulted in increased inhibition of lung metastasis, compared with the vehicle control (Figure 4a).
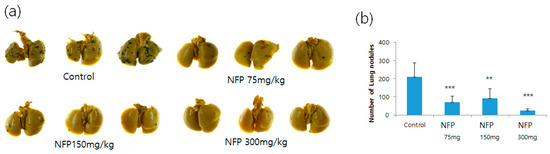
Figure 4.
Effects of NFP on the lung metastasis of B16F10 melanoma cells in vivo. (a) Photographs of lung colonization in C57BL/6 mice orally administered with NFP at doses of 75, 150 and 300 mg/kg/day, compared with the vehicle control group. (b) Quantitative analysis of lung nodules of B16F10 melanoma cells. Data represent the mean-standard deviation (SD) (n = 6). Statistical significance of differences between the vehicle control and NFP treatment groups was evaluated using Student’s t-test (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001).
As shown in Figure 4b, the number of metastatic colonies was counted. In the vehicle control without the NFP treatment, 210 ± 77 metastatic colonies were generated. In contrast, the corresponding colony numbers in mice orally administered with 75, 150 and 300 mg/kg/day of NFP were 70 ± 33 (p < 0.001), 91 ± 52 (p < 0.01) and 23 ± 10 (p < 0.001), respectively.
2.6. Galactosamine (GalN)-Induced Rat for Liver Injury Model
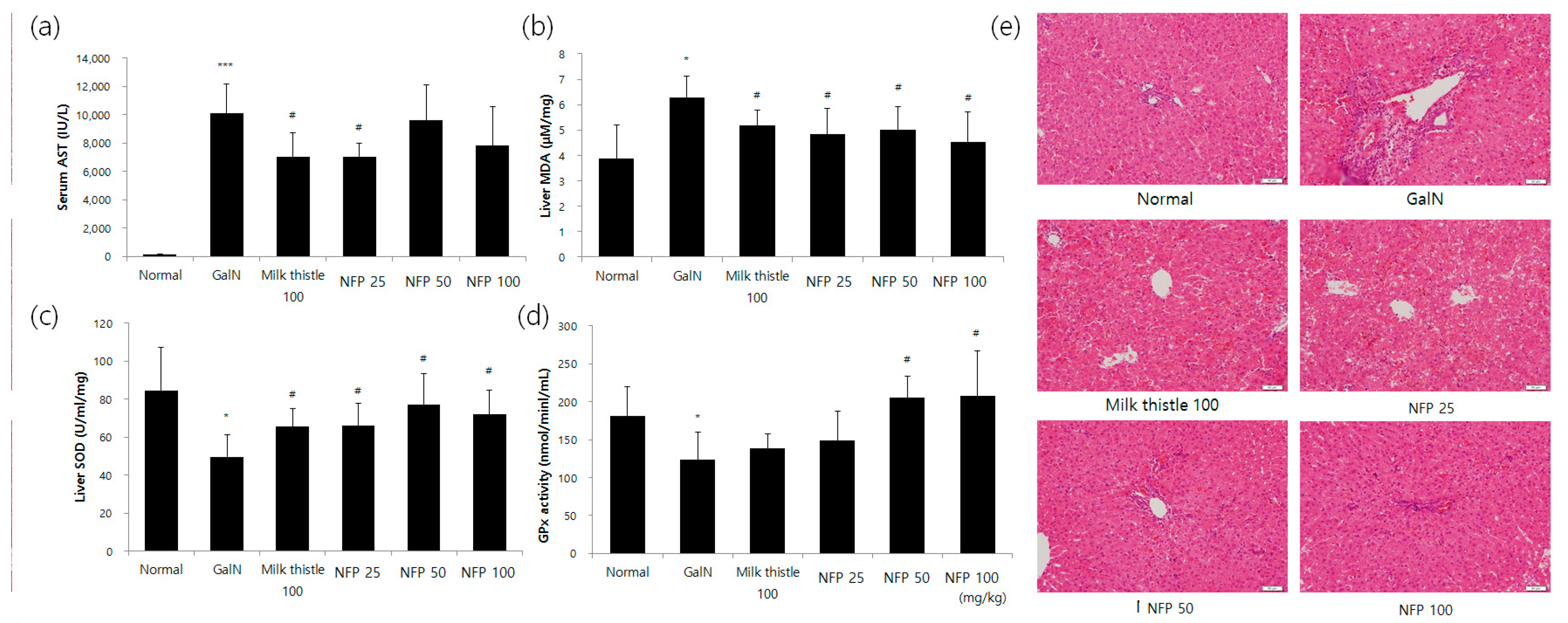
The results regarding serum aspartate transaminase (AST) levels are shown in Figure 5. In the GalN-treated group, serum AST levels were significantly increased, compared with those in the normal group. The AST levels seemingly tended to decrease with the concentration of NFP treatment. The alanine transaminase (ALT) level was reduced via treatment using 25 mg/kg NFP, with significance (p < 0.05) similar to that of the milk thistle, which was used as a positive control (Figure 5a). Hepatic malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activities were measured to evaluate the antioxidant activity of the liver. Treatment with NFP of 25, 50 or 100 mg/kg, and milk thistle (100 mg/kg), significantly recovered MDA and SOD levels as the antioxidant parameters of liver damage (p < 0.05), as shown Figure 5b,c.
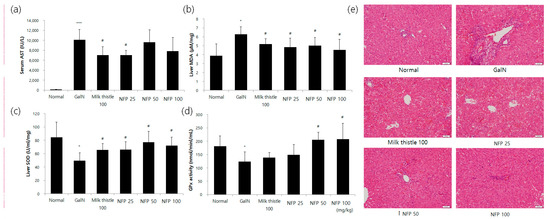
Figure 5.
Effects of NFP on liver functions, oxidative stress markers, and histopathological changes (GalN, 400 mg/kg, single intraosseous (IP) dose). (a) Decreased aspartate transaminase (AST) activity in the NFP 25 mg/kg groups compared with the GalN control at # p < 0.05, *** p< 0.001. (b) Decrease in the lipid peroxidation product malondialdehyde (MDA) in the NFP 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg groups, compared with the GalN control at # p < 0.05. (c, d) Increase in the superoxide dismutase (SOD) (25, 50, and 100 mg/kg) and GPx (50 and 100 mg/kg) levels in the NFP groups compared with the GalN control at # p < 0.05. (e) NFP showed an absence of ballooning, inflammatory cells, regeneration of hepatocytes around the central vein, and also a slight congestion in the central vein. Data represent means ±SD (n = 8). Magnification: 20×, Scale bar: 50 μm.
The NFP showed an increasing pattern of GPx activity (Figure 5d). The NFP treatments with 50 and 100 mg/kg were shown to increase the GPx activity with statistical significance (p < 0.05). For histopathological examination, we performed the hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining study in the different treatment groups. Compared with the control group, the GalN-challenged group showed an inflammatory response. The NSP showed the absence of ballooning and inflammatory cell infiltration (Figure 5e).
3. Discussion
Many KRG-related articles look at its active components, like ginsenoside and polysaccharide, but polysaccharides have not been as deeply investigated when compared with ginsenosides [4]. With this in mind, this study aimed to fill this gap in the literature. In the present study, we prepared an NFP of KRG. It is widely accepted that older adults are more susceptible to various diseases compared to young adults [11] because biological aging comes with increased morbidity and multiple function decline [12]. Thus, aged animal models seemed suitable for assessing the diverse activity of NFP.
The researchers performed a comprehensive serum proteomic analysis to compare proteins between the NFP-treated groups and the nontreated group in old rats, using bioinformatic interpretation to identify the potential activities of NFP. As a result, a variety of functions were identified that are related to the activation of immune cells, brain disease, viral infection, liver-related functions, synthesis of reactive oxygen species, and other effects (Table 2). In addition, the cancer-specific analysis showed that the proteins were related to types of anticancer, anticancer functions (including metastasis), cell spreading, and angiogenesis. Based on the results, we performed an additional analysis of the spleen to test the NFP’s effect in relation to immune function and cancer, and another analysis of the liver in relation to antioxidants and liver protection.
Proteomic analysis of the spleen suggested that the NFP increases immune cell activity by increasing cell movement and migration. In addition, it is thought to increase innate immunity by increasing phagocytosis and internalization. In terms of anticancer activity, NFP is expected to induce apoptosis and carcinoma death, while downregulating the proliferation and survival rate of cancer cells. The top regulated DEPs in the spleen are listed in Table 3 and Table 4. Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectins (Siglecs) are cell-surface proteins that bind sialic acid, which, in turn, binds the proteins of type A and B influenza viruses [13]. It has been reported that Siglecs are involved in the phagocytosis of bacteria, while some Siglecs are capable of phagocytosing pathogens that express cell-surface sialic acid moieties. Siglec1 is a member of the Siglec family, expressed on a number of macrophage populations. Siglec1 has been reported to mediate phagocytosis of the Gram-negative bacteria [13,14]. Fn1 (fibronectin) is a component of the extracellular matrix that binds to integrins, and plays important roles in cell adhesion, migration, growth and differentiation [15]. Fn1 was also reported as a major component during wound healing [16]. Plec is a protein that acts as a cytoskeletal linker protein, which plays an important role in maintaining tissues, cell integrity, coordinating dynamic alterations in cell shape, and cytoarchitecture [17,18]. Plec was also reported as essential to the integrity of muscle cells in epithelial cells [19], and vital to the crosslinking of actin filaments and microtubules in the nervous system [20]. The protein serine and arginine-rich splicing factor 1 (Srsf1) is a proto-oncogene [21] that can act as an oncoprotein, and is an important target for cancer therapy, as it is overexpressed in many tumors [22]. Extracellular matrix molecules, including fibronectin, have been identified as activators of the toll-like receptors that function as regulators of the innate immune system in response to pathogens and damaged tissue [23]. Filamin alpha (Flna) is a multifunctional protein that binds to integrins and couples them to the actin cytoskeleton [24]. Flna plays an important role in infection by viral pathogens [25,26]. However, little is known about its interactions with components of the host’s innate immune response [27].
Based on the results, we evaluated the NFP’s effect on immunity using IgM antibody-producing cells in the spleen. NFP significantly increased the number of antibody-forming cells in the spleen of the CY model. Therefore, we confirmed that NFP exhibited immunity-enhancing effects. For the immune functions of the polysaccharides, it was reported that polysaccharides from ginseng or red ginseng could activate macrophage functions through toll-like receptor 2 (Tlr2) and stimulate macrophages to produce Th1 and Th2 cytokines. Furthermore, polysaccharides stimulate the dendritic-cell-enhancing production of interferon-γ, thereby promoting the production of cytotoxic cells against tumors. The present study also reported that KRG polysaccharides enhance the phagocytic activity of macrophages, which was consistent with our analysis [28,29].
In addition, we evaluated the effects of NFP on the lung metastasis of B16F10 melanoma cells in vivo. The results showed that NFP significantly inhibited melanoma cell metastasis in the lungs. It was reported that lung metastasis in B16-F10 melanoma-bearing mice was reduced significantly by intraosseous (IP) [30] and per os (PO) [31] administration of red ginseng acidic polysaccharide.
Liver disease is regarded as a global health problem [32]. One of the solutions that researchers have looked into is the possible beneficial effects of KRG on liver disease. Some studies have reported that KRG has hepatoprotective effects against hepatotoxins like hydrogen peroxide, alcohol, carbon tetrachloride, aflatoxin B1, diethylnitrosamine, viruses, and inflammation. Moreover, KRG has antioxidative effects in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [33]. Most studies have been conducted with ginsenosides, and only a few have studied the effects of polysaccharides on CCl4-induced hepatic injury [34] and hepatocellular carcinoma [35]. Some studies reported that there are correlations between NAFLD and obesity, dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome [36,37]. Thus, the present study looked into the hepatoprotective effects of KRG polysaccharides and their beneficial effects on various liver-related diseases.
A detailed liver proteomic analysis of the IPA function showed the possibility of NFP reducing hepatocyte cell death and liver inflammation, and inhibiting ROS production and synthesis. The top regulated DEPs in the liver are listed in Table 3 and Table 4. Glutathione, as an endogenous antioxidant, plays a key role in the maintenance of the intracellular redox balance, and the detoxification of xenobiotics [38]. The DAVID analysis showed that glutathione peroxidase 1 (Gpx1), Glutathione S-transferase alpha 1 (Gsta1), Glutathione S-transferase Mu 2 (Gstm2) and hemoglobin subunit beta (Hbb) are glutathione metabolic process proteins. Gpx1, as an antioxidant enzyme counteracting oxidative stress, is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues, where it plays an important role in modulating intracellular ROS [39]. HBB is a globin protein, along with alpha globin (Hba). Its functions involve oxygen transport from the lungs to various peripheral tissues [40]. Meanwhile, Aldh2 is a mitochondrial enzyme that is highly expressed in the liver, and plays a crucial role in the detoxification of reactive acetaldehydes [41]. Methionine adenosyltransferase (Mat) is the enzyme responsible for the synthesis of S-adenosyl-L-methionine, a biological methyl donor required for methylation [42]. There are three types of genes that encode protein products: Mat1a, Mat2a and Mat2b [43]. Mat1a is expressed only in adult hepatocytes, whereas Mat2a shows a wider distribution [44]. There are also reports linking Mat and liver dysfunction, which detailed that patients with advanced NAFLD exhibit Mat1a hypermethylation and lower Mat1a mRNA levels, compared to patients with mild NAFLD and normal subjects [45]. In addition, the livers of Mat1a-deficient mice exhibit increased oxidative stress caused by low glutathione levels [46]. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects were confirmed in the GalN-induced rat for the liver injury model.
We plan to analyze brain-related functions, one area of the suggested functions in serum proteomics. In this research, we suggested the overall potential activities of polysaccharides in KRG. Among these activities, we confirmed how polysaccharides, or NFP, have immunity-enhancing and liver-protective effects.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of the KRG Water Extract and General Chemicals
The KRG concentrates (15 brix) from six-year-old P. ginseng (Meyer) root were obtained from the Korea Ginseng Corporation (Buyeo, Republic of Korea). Carbohydrate-digesting enzymes, such as α-amylase from Aspergillus oryzae, amyloglucosidase from Aspergillus niger, and pectinesterase from orange peels, were all obtained from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). Meanwhile, polygalacturonase from Aspergillus aculeatus was purchased from Megazyme (Bray, Ireland). On the other hand, ammonium bicarbonate (NH4HCO3), dithiothreitol (DTT), formic acid (FA), iodoacetamide (IAA) trifluoroacetic acid, ammonium formate, and urea were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA). The HPLC-grade acetonitrile (ACN) and water were purchased from JT Baker (JT Baker, Phillipsburg, NJ, USA). Lyophilized trypsin was obtained from Promega (Madison, WI, USA).
4.2. Extraction of the NFP Fraction
The extraction procedure for the NFP from the KRG concentrate was carried out via ethanol precipitation, enzyme hydrolysis, and size exclusion chromatography, following the method of Lee et al. [4]. Briefly, 95% cold ethanol (EtOH) was added to the KRG concentrate. The solution was treated with α-amylase and amyloglucosidase, and then the enzyme reaction was quenched before 95% EtOH was added to precipitate the polysaccharide fraction again. The lyophilized polysaccharide was treated with pectinesterase and then hydrolyzed with polygalacturonase. The lysates were eventually prepared as dried NFP by the method described after lyophilization. The NFP was analyzed to determine its contents of ginsenosides, arginine-fructose-glucose (AFG) and acidic polysaccharide (AP). In general, acidic polysaccharides consist of acidic sugars, such as galacturonic acid, glucuronic acid, and mannuronic acid, and are known to have greater activity than neutral polysaccharides [47]. Among the acidic polysaccharides of KRG reported so far, it is the active acidic polysaccharide that contains galacturonic acid in its constituent sugars. Thus, indirect quantification, using a colorimetric method and carbazole-sulfuric acid, is generally used for polysaccharide analysis [48,49,50,51,52]. The analysis of AFG, AP, and ginsenosides was performed as previously described [53]. No ginsenosides were detected in the NSF. The AFG and AP contents of the NFP were 11.63 and 438.08 mg/g, respectively. Comparing the previous AP results of KRG, the AP content was approximately fourfold higher than that of KRG [53].
4.3. Global Proteomic Profiling Analysis
4.3.1. Animal Model
All animal experiments were conducted with the approval of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Korean Ginseng Research Institute (Daejeon, Republic of Korea) following the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
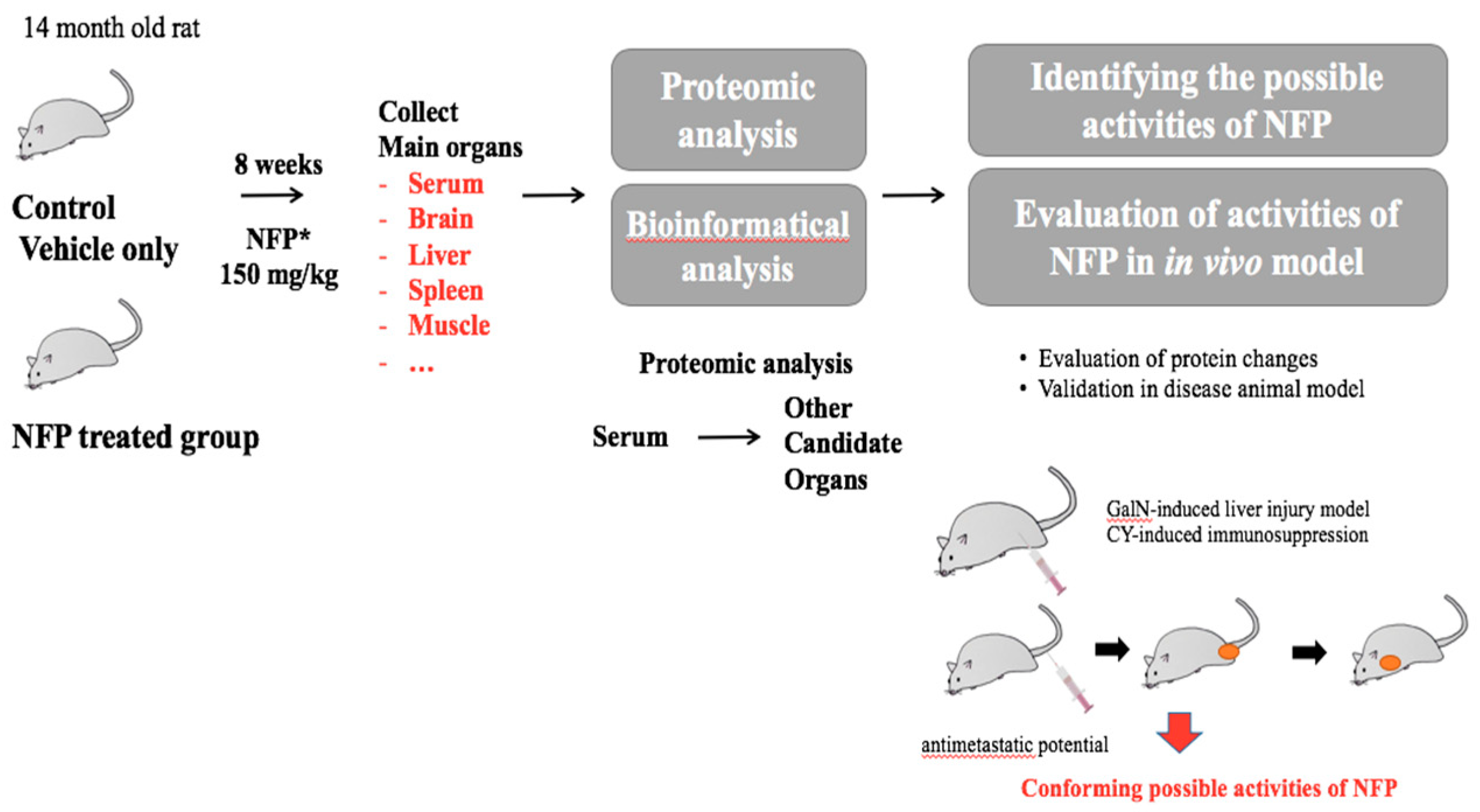
The male Sprague-Dawley rats (12 months old, Samtaco, Gyeonggi, Republic of Korea) were acclimatized at the Korean Ginseng Research Institute animal facility for 2 months before the experiment. They were housed at room temperature under humidity (36.2–56.3%) in a standard 12-h light/dark cycle. The 14-month-old male rats were randomly divided into 6 rats per group. The rats were administered 150 mg/kg NFP for 8 weeks. Only a vehicle was used for the negative control group (0 mg/kg) with a diet of animal chow and tap water. After dissection, the weights of the rat organs were measured, and the tissues were stored at −70 °C. (Figure 6).
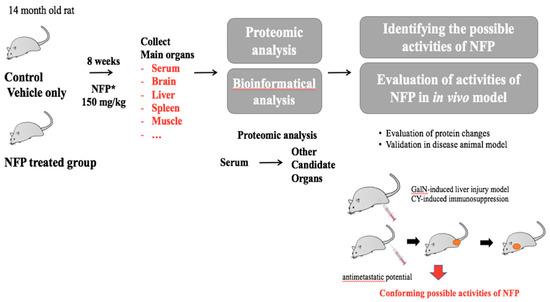
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of the experiments for the biological effects of NFP.
4.3.2. Serum Depletion
Serum samples were thawed on ice. The top three most abundant proteins were depleted using a MARS-MS3 (Agilent Technologies, Wilmington, DE) column. For this, the serum was filtered through 0.22-mm Spin-X filters and diluted (1:5) with a proprietary buffer A. The mixture was loaded onto the MARS-MS3 column on an Ultimate 3000 HPLC system (Dionex, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) with UV absorbance detector set at 214 nm. Unbound fractions containing the depleted serum were buffer-exchanged into 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) and concentrated through ultrafiltration, using the Amicon Ultra-0.5 mL 3 kDa cutoff filter (Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany), to approximately 150 mL. Protein concentration was determined by Nanodrop (ThermoFisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany) measurement at A280nm.
4.3.3. Protein Extraction
Rat spleen tissues were washed in 1X PBS and homogenized in a glass homogenizer with RIPA lysis buffer (Thermo Rockford, IL USA). The lysate was sonicated in ice for 2 min and centrifuged at 8000× g for 5 min at 4 °C twice. Rat liver and muscle tissues were homogenized using the CryoPrep™ system (Covaris, MA, USA). Approximately 1 mg of powdered, frozen tissue was transferred to 1.7-mL tubes and resuspended in radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) lysis buffer. After vortexing, each sample was sonicated in ice for 3 min and centrifuged at 3000× g for 5 min at 4 °C twice. The lysate was transferred to new 1.7-mL tubes and centrifuged at 10,000× g for 5 min. Bicinchoninic acid (BCA) quantification was performed with the Micro BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
4.3.4. 1D SDS-PAGE Fractionation and In-gel Digestion
The 1D sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) fractionation and in-gel tryptic digestion were conducted following the general protocol (Supplemental Method S1). Briefly, proteins were denatured and reduced in a lithium dodecyl sulfate (LDS) sample buffer with dithiothreitol (DTT), and then fractionated on a 4–12% gradient Bolt Bis-Tris gel (Invitrogen, MA, USA). The gel was stained with Instant Blue (Sigma-Aldrich, MO, USA). The gel lane was cut into 10 slices, then washed and destained. The proteins in the gels were reduced by DTT and alkylated with iodoacetamide (IAA). The gel particles were saturated with 12.5 ng/μL trypsin (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) for protein digestion. The digested peptides were extracted after incubation with 10% formic acid (FA). The extracted peptides were dried under a concentrator and stored at −20 °C until the liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis.
4.3.5. Protein Identification Using LC-MS/MS Analysis
The dried peptide mixture was resuspended in solvent A (0.1% formic acid). The general instrumental analysis condition followed the method previously described [6]. The serum and spleen peptide samples were separated by online reversed-phase chromatography using a Thermo Scientific EASY-nLC 1200 ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) equipped with a reversed-phase peptide trap Acclaim PepMapTM 100 autosampler (75 μm inner diameter, 2 cm length; Thermo Scientific) and a reversed-phase analytical column PepMapTM RSLC C18 (75 μm inner diameter, 15 cm length, 3 μm particle size; Thermo Scientific). After separation, this was followed by electrospray ionization at a flow rate of 300 nL/min−1. The samples were eluted using a split gradient of 3–50% solution B (80% ACN with 0.1% FA) for 60 min, and 50–80% solution B for 10 min, followed by a column wash at 100% solution B for 10 min. The chromatography system was coupled with an Orbitrap Fusion mass spectrometer operated in a data-dependent mode, with a 120,000-resolution MS1 scan (375–1500 m/z), an Automated Gain Control (AGC) target of 5e5, and a max injection time of 50 ms. Peptides above the 5e3 threshold and charges 2–7 were selected for fragmentation with dynamic exclusion after a 15-second scan at 10 ppm tolerance.
The liver peptide samples were analyzed using a Q-Exactive mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany) equipped with a nano-UHPLC Dionex system (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and an Easy-Spray Source (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Every peptide sample was separated with a linear gradient from 2% to 35% or 40% Solvent B (0.1% FA in ACN), at a flow rate of 300 nL/min over 100 min. Precursor ions were acquired in the range of 350–1400 m/z under 70 k resolution (at 200 m/z), and the top 10 precursors were subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis at 2 Th (Thomson) of precursor isolation width. A higher-energy collisional dissociation with 27% collision energy, with a target value of 1E6 ions determined by automatic gain control, 60 ms maximum injection time and 17.5 k resolution at 200 m/z, was applied for LC-MS/MS analysis.
4.3.6. Data Search, Statistical Analysis, and Bioinformatic Analysis
All searches and subsequent bioinformatics analyses were carried out based on the method previously described [6]. Briefly, collected raw files were converted into mzXML files. The peptides were assigned by the SEQUEST algorithm (Thermo Fisher Scientific) against the decoy UniProt database (UniProt, http://www.uniprot.org/). The data set was entered into the R program (version 3.5.3) with a power law global error model (PLGEM, version 1.54.1) used to determine the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) and p-value [54]. Based on PLGEM, the annotation of protein cellular localization and the evaluation of biological function were performed using the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA; Ingenuity Systems; Redwood City, CA, USA) database and the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID, https://david-d.ncifcrf.gov/).
4.4. IgM Antibody-Producing Cells in the Spleen
Six-week-old male Bagg Albino (BALB/c) mice were purchased from DBL (Chungbuk, Republic of Korea). Animal experiments were conducted with the same housing conditions described above. The BALB/C mice were divided into 5 groups of 6 mice each to quantify the IgM-producing plasma cells. The blank group (normal) and the cyclophosphamide (CY)-treated group (CY control) were administered distilled water, while the NFP-treated groups were orally administered NFP at 75, 150, and 300 mg/kg for 10 consecutive days. Four days before the autopsy, immune reactions in mice were induced by injecting them with sheep red blood cells (SRBCs) intraperitoneally. The procedure for IgM antibody-producing cells follows the method of Hyun, et al. [55]. Briefly, the SRBCs had been refrigerated and used within 2 weeks of storage. After washing the SRBCs with Earle’s Balanced Salt Solution (EBSS) via centrifugation, their concentrations were adjusted using EBSS to 5 × 108 cells/mL (5%). For the immune responses of the mice, the mice were intraperitoneally administered 50 mg/kg CY for immunosuppression, and then the mice were sacrificed to remove the spleen after three days. The spleen was placed in ice-cooled EBSS, and lightly ground using a sterile syringe, and then filtered through a mesh for subsequent centrifugation. After removing the supernatant, the procedure was repeated. The suspension was taken and mixed with EBSS to produce a five-fold diluted cell suspension. For the suspension of the SRBCs, the refrigerated cells were washed three times with EBSS by centrifugation (300× g, 10 min, 4 °C) immediately before use. A 0.5% agar solution was prepared by first dissolving the agar in EBSS containing 15 mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine-1-ethanesulfonic acid buffer solution. Once boiled, the solution was kept at 48 °C in a water bath, A 350 μL agar solution, 100 μL splenic cell solution, 25 μL SRBCs suspension, and 25 μL guinea pig complement were added and mixed thoroughly to a round-bottom tube (12 × 75 mm). Then, 200 μL of aliquot was transferred to a petri dish. After approximately 20 min, when the agar hardened, the cultivation was carried out in a 37 °C, 5% CO2 incubator for 4 h to induce plaque formation. The formed plaques were counted using an optical microscope (IX-81, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) at a 10× magnification. The cell count in the splenic cell solution was then estimated, after which the result was converted to the number of plasma cells per 1 × 106 spleen cells.
4.5. Experimental Murine Lung Metastasis
The experimental lung metastasis was performed according to Yun et al.’s method [56]. Six 6-week-old C57BL male mice (Koatech, Pyungtaek, Korea) were acclimated to laboratory conditions for 2 weeks. The mice were randomly assigned to 4 groups (n = 6/group), all of which were intravenously injected with B16F10 cells (ATCC) at a density of 2 × 106 cells/mouse through the tail. The mice in the first group, as vehicle control, were treated with saline once per day by oral gavage. The other mice groups were orally administered with NFP at doses of 75, 150, and 300 mg/kg in saline once per day for 2 weeks. On the 14th day, mice were sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation, and their lungs were dissected to count the number of metastatic colonies.
4.6. Galactosamine (GalN)-Induced Rat for Liver Injury Model
Clean male Sprague-Dawley rats were provided by Daehan Biolink Co. Ltd. (Eumsung, Korea) for the present study. The housing condition was the same as the housing condition described above. Rats were randomly assigned into six groups of equal size (6 rats/group) after a one-week adaptation period to environmental conditions. These six groups, the normal control group, the GalN group, the positive control group with milk thistle extract (100 mg/kg), and the three NFP groups, were orally gavaged with 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg once a day for 7 consecutive days. Then, GalN was injected 2 h after the final administration to induce liver injury and investigate the reduction of oxidative stress. The normal control and GalN groups received an equal amount of saline. At 24 h after the administration of the inducers and vehicles, rats were anesthetized, and blood and livers were collected. Serum samples were separated by centrifugation at 2000× g for 10 min. One part of the dissected liver was kept in 10% formalin for histopathological examination. At the same time, another part was immediately put in liquid nitrogen and kept at –90 °C to determine oxidative stress markers.
4.6.1. Evaluation of Liver Function and Oxidative Stress Markers
Serum samples were tested for aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT). Superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and malondialdehyde (MDA), a lipid peroxidation product, were analyzed using a commercial diagnostic kit (Cayman Chemical, MI, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Liver enzymes, such as serum AST and ALT, levels were measured using a Hitachi Automatic Analyzer 7600 (Haiachi, Tokyo, Japan).
4.6.2. Histologic Examination
The isolated liver tissues were fixed using 10% neutral formaldehyde. Specimens were left for an overnight wash, dehydrated in graded ethanol, cleared in xylene, and immersed in paraffin. Then, 5-micron pieces were sectioned using a rotary microtome, and slides were then dewaxed using xylene, hydrated with ethanol. The sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for histopathological evaluation. The general microscopical structure of hepatic tissues was examined under a light microscope (Olympus, Shinjuku City, Japan).
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online. Method S1: 1D SDS-PAGE Fractionation and In-gel Digestion, Table S1: Serum protein list, Table S2: Serum protein list 99.9_95_min2, Table 3: Spleen protein list, Table S4. Liver protein list.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Y.L and C.-K.H.; Methodology, S.-W.K., S.-H.Y., J.-S.K. and S.J.M.; Software, H.R.J. and S.J.M.; Validation, H.R.J., S.J.M. and M.J.K.; Formal Analysis, G.I. and E.C.Y.; Investigation, Y.Y.L, S.-W.K., S.-H.Y., and S.H.H., J.-S.K. and M.J.K.; Resources, J.-S.K.; Data Curation, Y.Y.L.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, Y.Y.L.; Writing—Review and Editing, Y.Y.L., G.I., E.C.Y. and C.H.; Visualization, Y.Y.L., S.-W.K., S.-H.Y., and S.H.H.; Supervision, C.-K.H., and C.-K.P.; Project Administration, C.-K.H.; Funding Acquisition, C.-K.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The researchers have no funding to declare.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, M.; Lee, H.S.; Hwang, M.W.; Jin, M. Effects of Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer) on bisphenol A exposure and gynecologic complaints: Single blind, randomized clinical trial of efficacy and safety. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Hyun, S.H.; Han, C.K. Red ginseng monograph. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Bae, B.S.; Park, H.W.; Ahn, N.G.; Cho, B.G.; Cho, Y.L.; Kwak, Y.S. Characterization of Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer): History, preparation method, and chemical composition. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; In, G.; Han, S.-T.; Lee, M.-H.; Lee, J.-W.; Shin, K.-S. Structural characteristics of a red ginseng acidic polysaccharide rhamnogalacturonan I with immunostimulating activity from red ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 44, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandramouli, K.; Qian, P.Y. Proteomics: Challenges, techniques, and possibilities to overcome biological sample complexity. Hum. Genom. Proteom. 2009, 239204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Seo, H.W.; Kyung, J.S.; Hyun, S.H.; Han, B.C.; Park, S.; So, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Yi, E.C. Proteomic studies of putative molecular signatures for biological effects by Korean Red Ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, A. Zheng: A systems biology approach to diagnosis and treatments. Science 2014, 346, S13–S15. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, E.L.-H.; Wong, V.K.-W.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Li, T.; Liu, L. Integrated network-based medicine: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in developing a new generation of medicine. SCIEAS 2014, 346, S16–S18. [Google Scholar]
- Palazzotto, E.; Weber, T. Omics and multi-omics approaches to study the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites in microorganisms. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merwin, N.J.; Mousa, W.K.; Dejong, C.A.; Skinnider, M.A.; Cannon, M.J.; Li, H.; Dial, K.; Gunabalasingam, M.; Johnston, C.; Magarvey, N.A. DeepRiPP integrates multiomics data to automate discovery of novel ribosomally synthesized natural products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, S.A.; Finch, C.E.; Guerin, J.C.; Nelson, J.F.; Olshansky, S.J.; Roth, G.; Smith, R.G. Handbook of Models for Human Aging; Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, K.; Simpkins, J.W.; Ji, X.; Leis, M.; Stambler, I. The Critical Need to Promote Research of Aging and Aging-related Diseases to Improve Health and Longevity of the Elderly Population. Aging Dis. 2015, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S.; Netravali, I.A.; Cariappa, A.; Mattoo, H. Siglecs and immune regulation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 357–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Virji, M.; Crocker, P.R. Recognition of sialylated meningococcal lipopolysaccharide by siglecs expressed on myeloid cells leads to enhanced bacterial uptake. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 49, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankov, R.; Yamada, K.M. Fibronectin at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 3861–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinnell, F.; Billingham, R.E.; Burgess, L. Distribution of fibronectin during wound healing in vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1981, 76, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiche, G. Role of plectin in cytoskeleton organization and dynamics. J. Cell Sci. 1998, 111, 2477–2486. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, A.H.M.; Chakrabarty, J.K.; Udden, S.M.N.; Zaki, M.H.; Chowdhury, S.M. Inflammatory Proteomic Network Analysis of Statin-treated and Lipopolysaccharide-activated Macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhrberg, C.; Hajibagheri, M.A.; Parry, D.A.; Watt, F.M. Periplakin, a novel component of cornified envelopes and desmosomes that belongs to the plakin family and forms complexes with envoplakin. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 139, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.L.; Green, K.J.; Liem, R.K. Plakins: A family of versatile cytolinker proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2002, 12, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.D.; Nam, S.W. Pathogenic diversity of RNA variants and RNA variation-associated factors in cancer development. Exp. Mol. Med 2020, 52, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagopian, J.C.; Ma, C.T.; Meade, B.R.; Albuquerque, C.P.; Ngo, J.C.; Ghosh, G.; Jennings, P.A.; Fu, X.D.; Adams, J.A. Adaptable molecular interactions guide phosphorylation of the SR protein ASF/SF2 by SRPK1. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 382, 894–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.A.; Bryant, C.E.; Doyle, S.L. Therapeutic targeting of Toll-like receptors for infectious and inflammatory diseases and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev. 2009, 61, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savinko, T.; Guenther, C.; Utila, L.M.; Llort Asens, M.; Yao, S.; Tojkander, S.; Fagerholm, S.C. Filamin A Is Required for Optimal T Cell Integrin-Mediated Force Transmission, Flow Adhesion, and T Cell Trafficking. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 3019–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Ahrens, W.A.; Phatak, S.U.; Hwang, S.; Schrum, L.W.; Bonkovsky, H.L. Association of filamin A and vimentin with hepatitis C virus proteins in infected human hepatocytes. J. Viral Hepat. 2011, 18, e568–e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, S. Filamin A inhibits the replication of H5N6 influenza virus via activating the type I interferon signaling pathway. Sci. Sin. Vitae 2018, 48, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Malathi, K.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Dayal, S.; Naji, M.; Ezelle, H.J.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, A.; Hassel, B.A. RNase L interacts with Filamin A to regulate actin dynamics and barrier function for viral entry. mBio 2014, 5, e02012–e02014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, S.H.; Park, J.Y.; Cho, E.H.; Nah, S.Y.; Kang, Y.S. Animal lectins: Potential receptors for ginseng polysaccharides. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, S.H.; Kim, S.W.; Seo, H.W.; Youn, S.H.; Kyung, J.S.; Lee, Y.Y.; Gyo, I.; Park, C.-K.; Han, C.-K. Physiological and pharmacological features of the non-saponin components in Korean Red ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kwak, Y.-S.; Song, Y.-B.; Kyung, J.-S.; Wee, J.-J.; Park, J.-D. A Further Study on the Inhibition of Tumor Growth and Metastasis by Red Ginseng Acidic Polysaccharide (RGAP). Nat. Prod. Sci. 2004, 10, 284–288. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, Y.-S.; Shin, H.-J.; Song, Y.-B.; Kyung, J.-S.; Wee, J.-J.; Park, J.-D. Effect of Oral Administration of Red ginseng acidic polysaccharide (RGAP) on the Tumor Growth Inhibition. J. Ginseng Res. 2005, 29, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.R.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Terrault, N.A.; El-Serag, H. Burden of liver disease in the United States: Summary of a workshop. Hepatology 2002, 36, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.Y.; Hong, M.; Sung, H.; Kim, S.; Suk, K.T. Effect of Korean Red Ginseng in chronic liver disease. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.Y.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, H.D.; Ahn, J.Y.; Yun, Y.S.; Song, J.Y. Protective action of the immunomodulator ginsan against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury via control of oxidative stress and the inflammatory response. Toxicol. App. Pharm. 2010, 242, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gu, L.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, A.R.; Sobol, R.W.; Chen, T.; Li, J. Administration of polysaccharide from Panax notoginseng prolonged the survival of H22 tumor-bearing mice. Onco. Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 3433–3441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J. NASH: A global health problem. Hepatology Res. 2011, 41, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, G.; Baranova, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Systematic review: The epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, P.A.; Angley, M.T.; O’Doherty, C.E.; Thomas, P.; Fenech, M. The potential role of the antioxidant and detoxification properties of glutathione in autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotruck, J.T.; Pope, A.L.; Ganther, H.E.; Swanson, A.B.; Hafeman, D.G.; Hoekstra, W.G. Selenium: Biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science 1973, 179, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manu Pereira, M.D.; Ropero, P.; Loureiro, C.; Vives Corrons, J.L. Low affinity hemoglobinopathy (Hb Vigo) due to a new mutation of beta globin gene (c200 A>T.; Lys>Ile). A cause of rare anemia misdiagnosis. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, E38–E40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Ferreira, J.C.; Gross, E.R.; Mochly-Rosen, D. Targeting aldehyde dehydrogenase 2: New therapeutic opportunities. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, J.D. Methionine metabolism in mammals. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1990, 1, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, M.; Mudd, S.H.; Mato, J.M.; Geller, A.M.; Kredich, N.M.; Chou, J.Y.; Cantoni, G.L. Consensus nomenclature for the mammalian methionine adenosyltransferase genes and gene products. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 51–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Trevijano, E.R.; Latasa, M.U.; Carretero, M.V.; Berasain, C.; Mato, J.M.; Avila, M.A. S-adenosylmethionine regulates MAT1A and MAT2A gene expression in cultured rat hepatocytes: A new role for S-adenosylmethionine in the maintenance of the differentiated status of the liver. FASEB J. 2010, 14, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, S.K.; Yang, H.; Moylan, C.A.; Pang, H.; Dellinger, A.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Garrett, M.E.; Ashley-Koch, A.; Suzuki, A.; Tillmann, H.L.; et al. Relationship between methylome and transcriptome in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Corrales, F.J.; Martinez-Cruz, L.A.; Garcia-Trevijano, E.R.; Huang, Z.Z.; Chen, L.; Kanel, G.; Avila, M.A.; Mato, J.M.; Lu, S.C. Spontaneous oxidative stress and liver tumors in mice lacking methionine adenosyltransferase 1A. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 1292–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Shin, H.-J.; Song, Y.-B.; Park, J.-D. Anticancer activities by combined treatment of red ginseng acidic polysaccharide (RGAP) and anticancer agents. J. Ginseng Res. 2003, 27, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.S.; Kim, K.H.; Sohn, E.; Park, J.D.; Kim, B.O.; Moon, E.Y.; Rhee, D.K.; Pyo, S. Red ginseng acidic polysaccharide (RGAP) in combination with IFN-gamma results in enhanced macrophage function through activation of the NF-kappaB pathway. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-S.; Pyo, S.-K.; Sohn, E.-H. Immunomodulation of NK cell activity by red ginseng acidic polysaccharide (RGAP) in ovariectomized rats. J. Ginseng Res. 2009, 33, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-W.; Do, J.-H. Extraction condition of acidic polysaccharide from Korean Red Ginseng marc. J. Ginseng Res. 2002, 26, 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Son, H.-J.; Ryu, G.-H. Chemical compositions and antioxidant activity of extract from a extruded white ginseng. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 38, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, Y.-S.; Han, M.W.; Bae, B.-S.; Ahn, N.-G.; Yu, H.Y.; Park, C.-S.; Baeg, I.-H.; Cho, B.-G. The Changes of Physicochemical Characteristics and Quality Stability of Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng CA Meyer) Stored over 20 Years. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 48, 329–338. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.J.; Jeon, S.G.; Kim, J.I.; Jeong, Y.O.; Kim, S.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, S.K.; Park, H.H.; Hong, S.B.; Oh, S.; et al. Red Ginseng Attenuates Abeta-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Abeta-mediated Pathology in an Animal Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.Y.; McKinney, K.Q.; Ghosh, S.; Iannitti, D.A.; Martinie, J.B.; Caballes, F.R.; Russo, M.W.; Ahrens, W.A.; Lundgren, D.H.; Han, D.K.; et al. Subcellular tissue proteomics of hepatocellular carcinoma for molecular signature discovery. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 5070–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, S.H.; Kim, E.S.; Lee, S.M.; Kyung, J.S.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, M.R.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, Y.S. Comparative study on immuno-enhancing effects of red ginseng fractions. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 43, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Kim, B.G.; Kang, J.S.; Park, S.K.; Lee, K.; Hyun, D.H.; Kim, H.M.; In, M.J.; Kim, D.C. Lipid-soluble ginseng extract inhibits invasion and metastasis of B16F10 melanoma cells. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: An NFP sample is available from the authors. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).