Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Assessment of Their Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity and Study of Capping Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
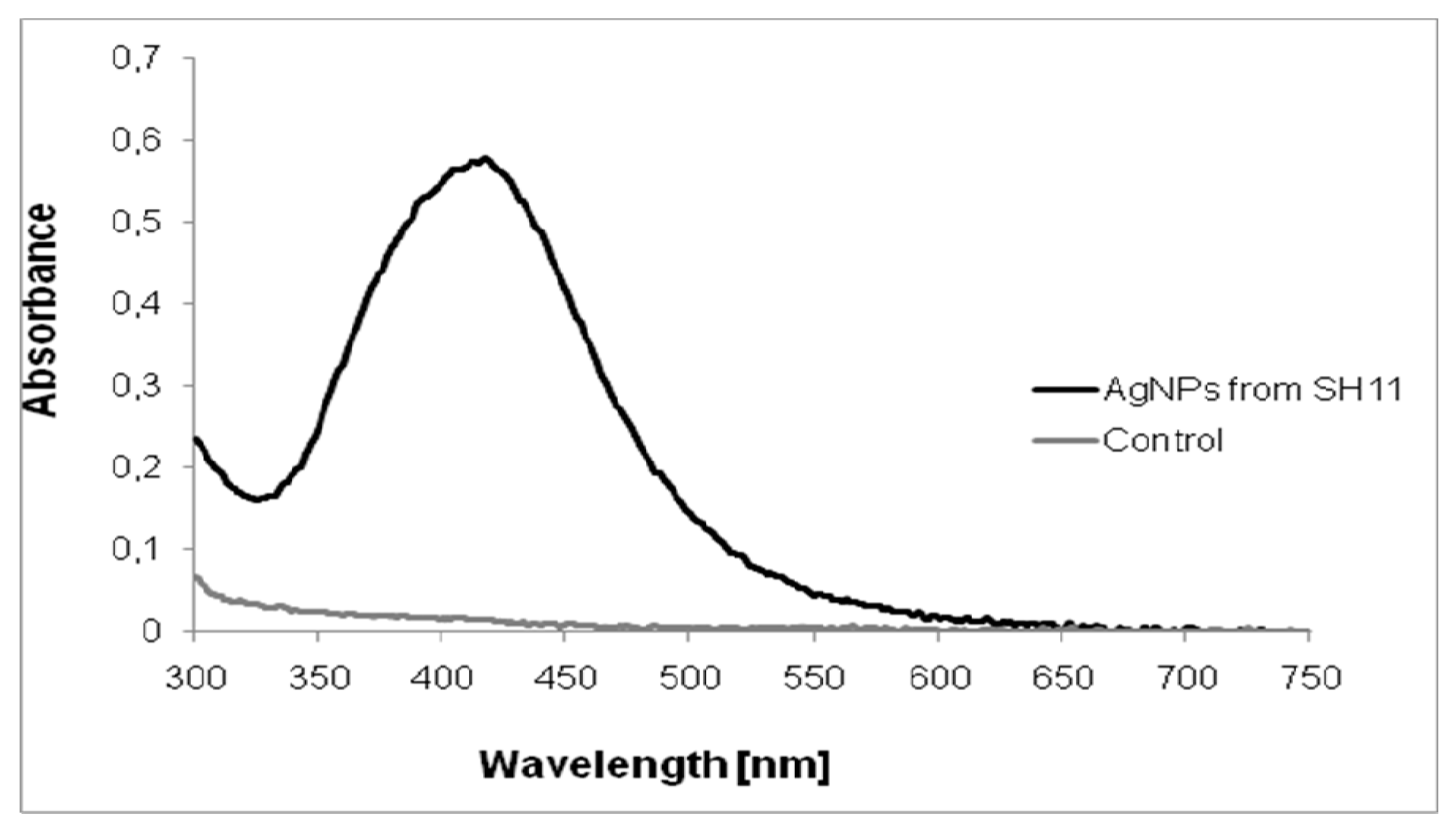
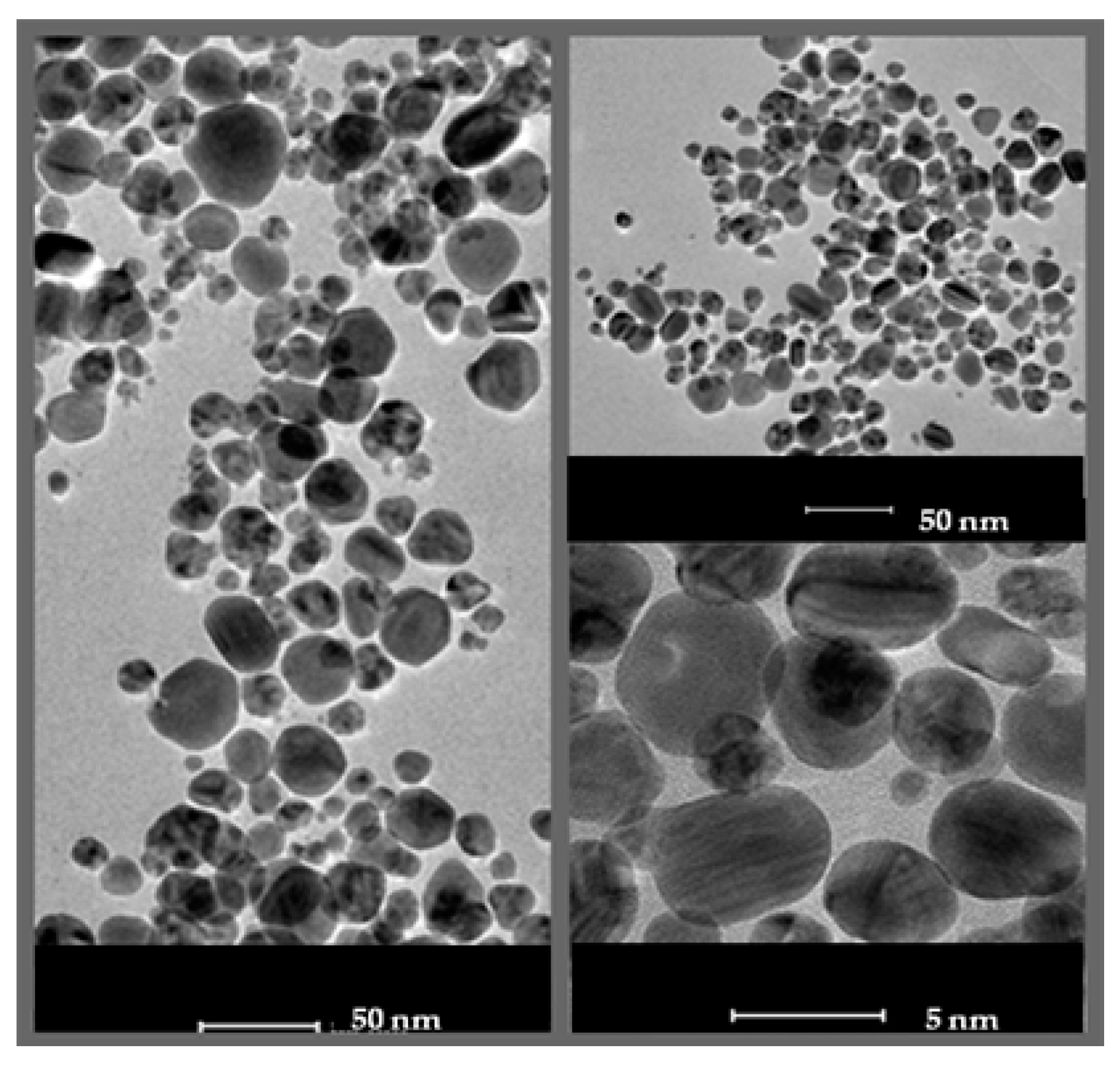
2.1. Characterization of AgNPs
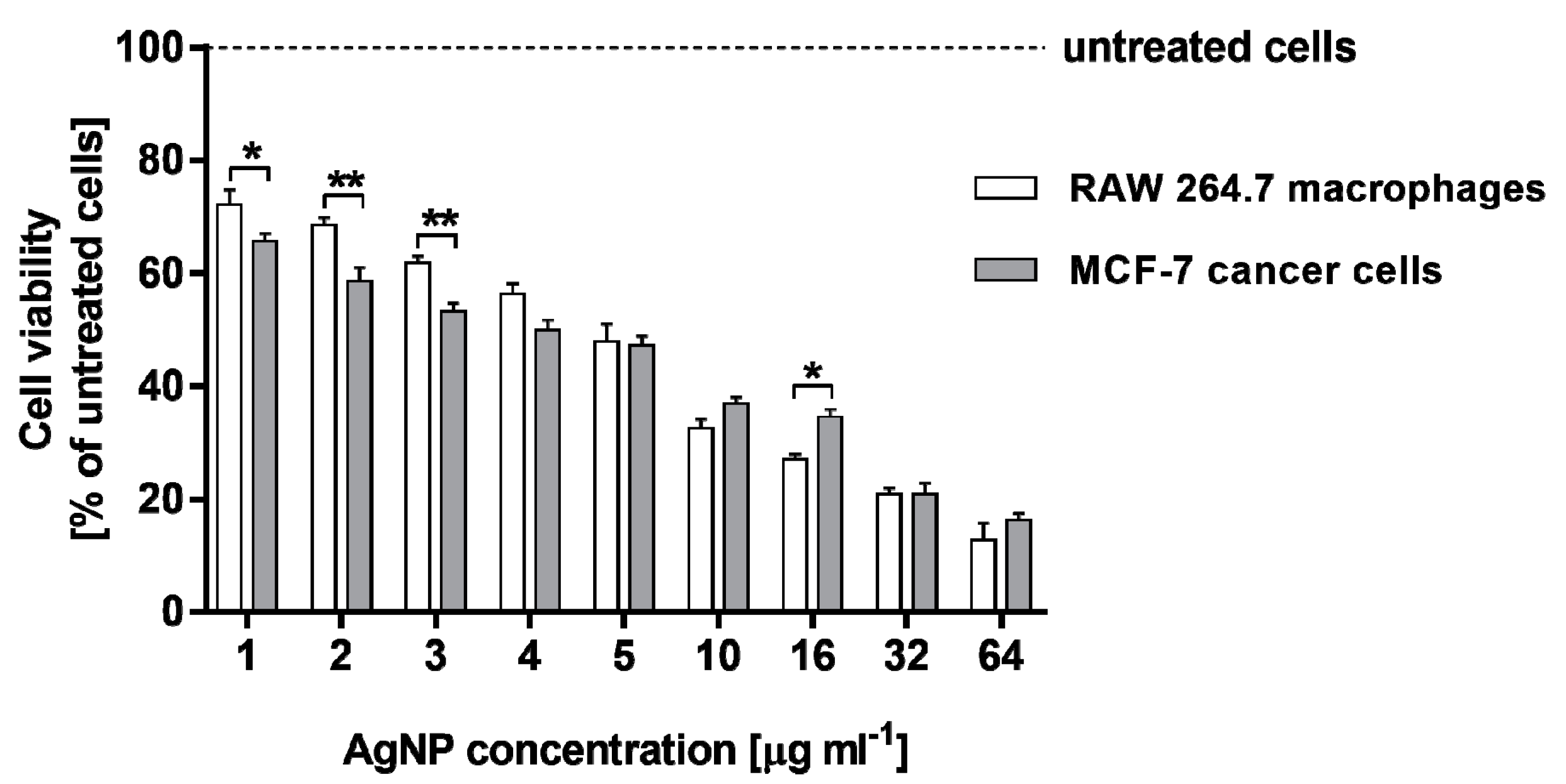
2.2. Cytotoxicity of AgNPs against RAW 264.7 Macrophages and MCF-7 Cancer Cells
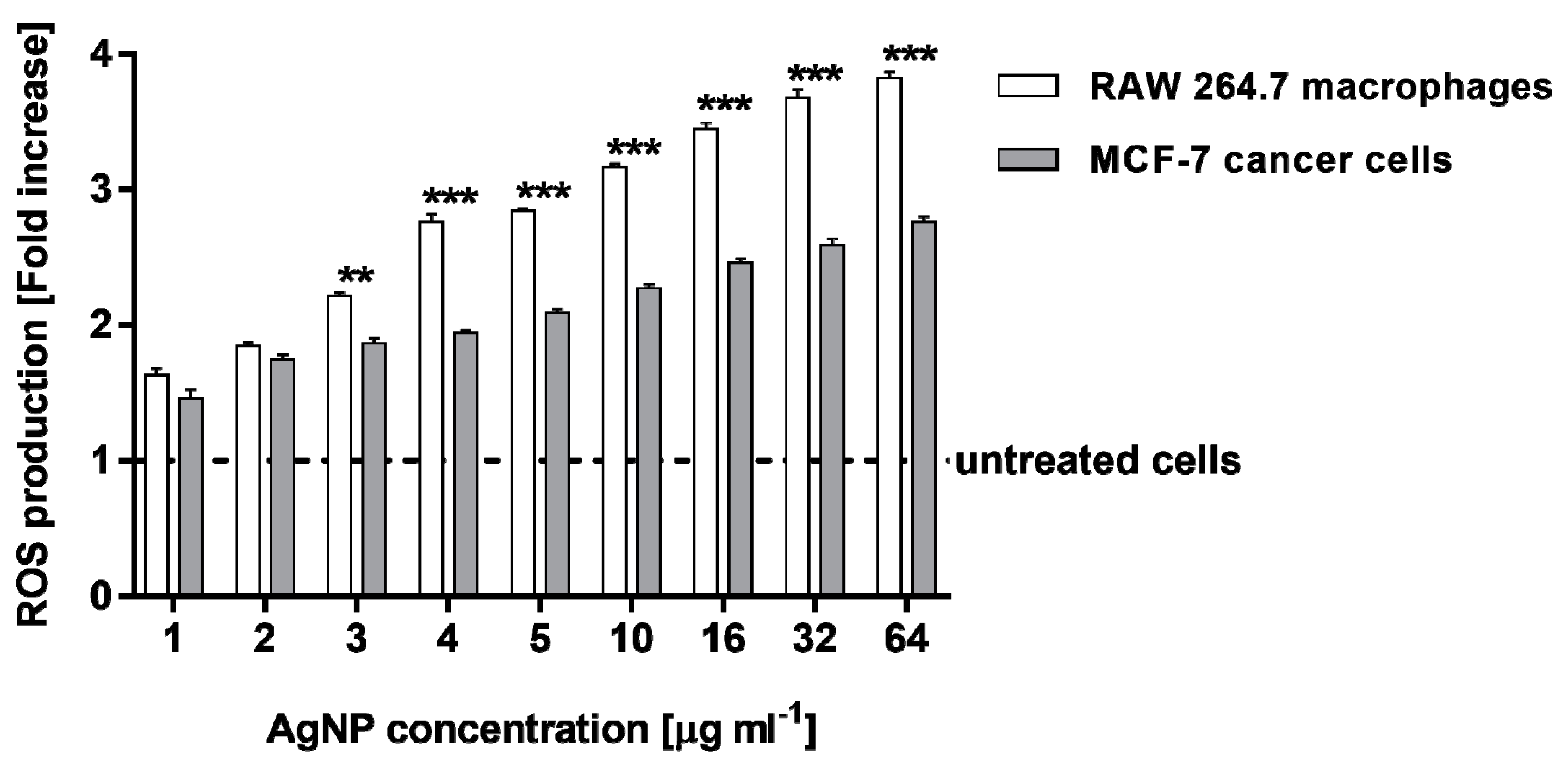
2.3. Estimation of Reactive Oxygen Species Levels in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and MCF-7 Cancer Cells
2.4. Ames Test
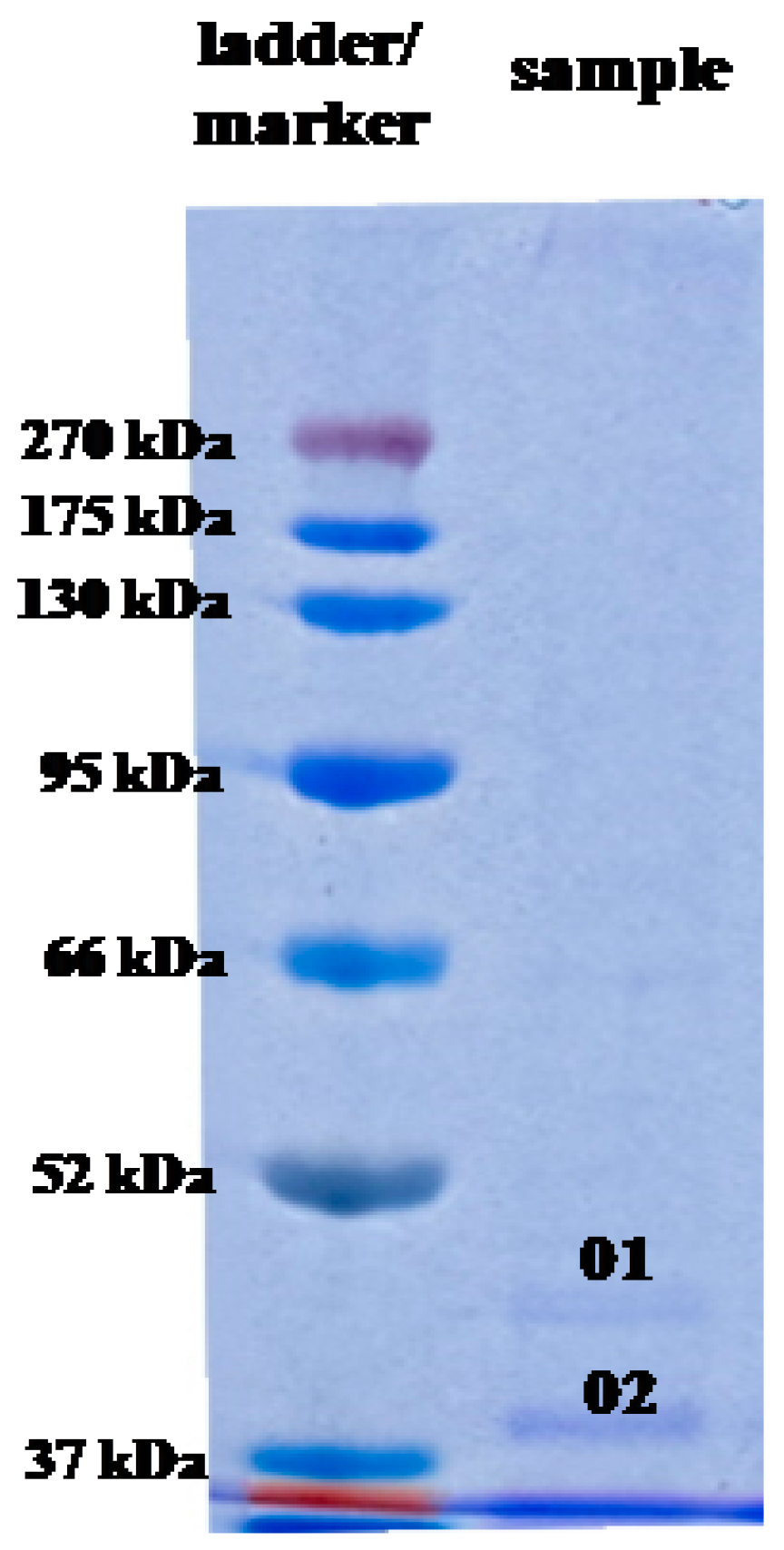
2.5. Analysis of AgNP Capping Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bionanoparticle Synthesis
4.2. Characterization of Biosynthesized AgNPs
4.2.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy Analysis
4.2.2. Zeta Potential Analysis
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cell Viability
4.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.6. Measurement of Cellular Reactive Oxygen Species Levels
4.7. Statistical Analysis
4.8. Ames Test
4.9. Analyses of Capping Proteins
4.9.1. Preparation of Samples for Identification of Proteins
4.9.2. SDS-PAGE
4.9.3. Identification of Proteins by LC-MS/MS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, C.; Tang, J.; Liu, X.; Ren, X.; Zhen, M.; Wang, L. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) leaf extract for reductive catalysis. Materials 2019, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boulaiz, H.; Alvarez, P.J.; Ramirez, A.; Marchal, J.A.; Prados, J.; Rodríguez-Serrano, F.; Perán, M.; Melguizo, C.; Aranega, A. Nanomedicine: Application areas and development prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3303–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.; Kim, K.-J.; Lee, D.G. A novel mechanism for the antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Biometals 2014, 27, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behravan, M.; Panahi, A.H.; Naghizadeh, A.; Ziaee, M.; Mahdavi, R.; Mirzapour, A. Facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Berberis vulgaris leaf and root aqueous extract and its antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masum, M.I.; Siddiq, A.M.; Al, K.A.; Zhang, Y.; Abdallah, Y.; Ibrahim, E.; Qiu, W.; Yan, C.; Li, B. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Phyllanthus emblica fruit extract and its inhibitory action against the pathogen Acidovorax oryzae strain RS-2 of rice bacterial brown strip. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, properties, applications, and therapeutic approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.; Panwar, J.; Yun, Y. Biogenic synthesis of metallic nanoparticles by plant extracts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatoprak, G.; Aydin, G.; Altinsoy, B.; Altinkaynak, C.; Koşar, M.; Ocsoy, I. The effect of Pelargonium endlicherianum Fenzl. root extracts on formation of nanoparticles and their antimicrobial activities. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2017, 97, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, C.H.N.; Faria, G.C.; Mayrink, C.W.; Tasic, L. Bio-based synthesis of silver nanoparticles from orange waste: Effects of distinct biomolecule coatings on size, morphology, and antimicrobial activity. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2018, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, M.; Alveroglu, E. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles having different cover layer and investigation of cover layer effect on the adsorption of lysozyme and bovine serum albumin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 81, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Basu, A.; Kundu, S. Green synthesis of protein capped silver nanoparticles from phytopathogenic fungus Macrophomina phaseolina (Tassi) Goid with antimicrobial properties against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poblete, H.; Agarwal, A.; Thomas, S.S.; Bohne, C.; Ravichandran, R.; Phopase, J.B.; Alarcon, E.I.; Comer, J. Understanding the interaction between biomolecules and silver nanoparticles. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 341a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saallah, S.; Lenggoro, I.W. Nanoparticles carrying biological molecules: Recent advances and applications. KONA Powder Part. J. 2018, 35, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wypij, M.; Golińska, P.; Rai, M.; Dahm, H. Actinobacterial-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their activity against pathogenic bacteria. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Gupta, I.; Ingle, A.P.; Biswas, J.K.; Sinitsyna, O.V. Nanomaterials, what are they, why they cause ecotoxicity, and how this can be dealt with? In Nanomaterials, Ecotoxicity, Safety, and Public Perception, 1st ed.; Rai, M., Biswas, J.K., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jeevanandam, J.; Barhoum, A.; Chan, J.S.; Dufresne, A.; Danquah, M.K. Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials, history, sources, toxicity and regulations. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1050–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oberdörster, G.; Sharp, Z.; Atudorei, V.; Elder, A.; Gelein, R.; Kreyling, W.; Cox, C. Translocation of inhaled ultrafine particles to the brain. Inhal. Toxicol. 2004, 16, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, H.; Kanevsky, A.S.; Wu, H.; Brimacombe, K.R.; Fung, S.H.; Sousa, A.A.; Auh, S.; Wilson, C.M.; Sharma, K.; Aronova, M.A.; et al. Effective transvascular delivery of nanoparticles across the blood-brain tumor barrier into malignant glioma cells. J. Transl. Med. 2008, 6, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonavane, G.; Tomoda, K.; Makino, K. Biodistribution of colloidal gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration, effect of particle size. Colloids Surf. B 2008, 66, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, K.; Stone, V. Current hypotheses on the mechanism of toxicity of ultrafine particles. Ann. Dell’Istituto Super. Sanitã 2003, 39, 405–410. [Google Scholar]
- Rathod, D.; Golinska, P.; Wypij, M.; Dahm, H.; Rai, M. A new report of Nocardiopsis valliformis strain OT1 from alkaline Lonar crater of India and its use in synthesis of silver nanoparticles with special reference to evaluation of antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 205, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Składanowski, M.; Golinska, P.; Rudnicka, K.; Dahm, H.; Rai, M. Evaluation of cytotoxicity, immune-compatibility and antibacterial activity of biogenic silver nanoparticles. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 205, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wypij, M.; Czarnecka, J.; Świecimska, M.; Dahm, H.; Rai, M.; Golińska, P. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of biogenic silver nanoparticles synthesized from Streptomyces xinghaiensis OF1 strain. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wypij, M.; Świecimska, M.; Czarnecka, J.; Dahm, H.; Rai, M.; Golinska, P. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized from two haloalkaliphilic actinobacterial strains alone and in combination with antibiotics. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1411–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, A.; Ingle, A.; Whiteley, C.; Rai, M. Mycogenic metal nanoparticles: Progress and applications. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A.; Gaikwad, S.; Gupta, I.; Gade, A.; Silvério da Silva, S. Nanotechnology based anti-infectives to fight microbial intrusions. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupryashina, M.A.; Vetchinkina, E.P.; Burov, A.M.; Ponomareva, E.G.; Nikitina, V.E. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by Azospirillum brasilense. Microbiology 2013, 82, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, Y.K.; Behera, S.K. Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles by Streptomyces sp. SS2. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 2263–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, R.; Feitosa, L.O.; Ballottin, D.; Marcato, P.D.; Tasic, L.; Durán, N. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of biogenic silver nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 429, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinski, N.; Colvin, V.; Drezek, R. Cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Small 2008, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Qasim, M.; Park, P.; Yoo, H.; Choi, D.Y.; Song, H.; Park, C.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, K. Cytotoxic potential and molecular pathway analysis of silver nanoparticles in human colon cancer cells HCT116. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Dayem, A.A.; Eppakayala, V.; Park, J.H.; Cho, S.G.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, J.H. Green synthesis of anisotropic silver nanoparticles and its potential cytotoxicity in human breast cancer cells (MCF-7). J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; Bao, G. Physical process of nanoparticle cellular endocytosis. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 8655–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rani, P.V.A.; Mun, G.L.K.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar]
- Kittler, S.; Greulich, C.; Diendorf, J.; Koller, M.; Epple, M. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles increases during storage because of slow dissolution under release of silver ions. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4548–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Yi, J.; Kim, Y.; Choi, K.; Park, K. Silver nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity by a Trojan-horse type mechanism. Toxicol. Vitr. 2010, 24, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensberg, M.C.; Wei, Q.; McLamore, E.S.; Porterfield, D.M.; Wei, A.; Sepúlveda, M.S. Toxicological studies on silver nanoparticles: Challenges and opportunities in assessment, monitoring and imaging. Nanomedicine (Lond.) 2011, 6, 879–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, S.G.; O’Claonadh, N.; Casey, A.; Chambers, G. Comparative in vitro cytotoxicity study of silver nanoparticle on two mammalian cell lines. Toxicol. Vitr. 2012, 26, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pratsinis, A.; Hervella, P.; Leroux, J.C.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Sotiriou, G.A. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in macrophages. Small 2013, 9, 2576–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, I.L.; Hsieh, Y.K.; Wang, C.F.; Chen, I.C.; Huang, Y.J. Trojan-horse mechanism in the cellular uptake of silver nanoparticles verified by direct intra- and extracellular silver speciation analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3813–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz Ahmed, K.B.; Nagy, A.M.; Brown, R.P.; Zhang, Q.; Malghan, S.G.; Goering, P.L. Silver nanoparticles: Significance of physicochemical properties and assay interference on the interpretation of in vitro cytotoxicity studies. Toxicol. Vitr. 2017, 38, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkiel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martindale, J.L.; Holbrook, N.J. Cellular response to oxidative stress: Signaling for suicide and survival. J. Cell. Physiol. 2002, 192, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Song, K.S.; Ryu, H.R.; Sung, J.H.; Park, J.D.; Park, H.M.; Song, N.W.; Shin, B.S.; Marshak, D. Biopersistence of silver nanoparticles in tissues from Sprague-Dawley rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akter, M.; Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.; Ullah, A.K.; Hossain, K.F.; Banik, S.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. A systematic review on silver nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity: Physicochemical properties and perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Yoo, Y.H.; Choi, Y.H. Sanguinarine induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer HCT-116 cells through ROS-mediated Egr-1 activation and mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 220, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Jeong, J.K.; Han, J.W.; Zhang, X.F.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Multidimensional effects of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles in Helicobacter pylori, Helicobacter felis, and human lung (L132) and lung carcinoma A549 cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, C.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Bactericidal and cytotoxic properties of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grzelak, A.; Wojewodzka, M.; Meczynska-Wielgosz, S.; Zuberek, M.; Wojciechowska, D.; Kruszewski, M. Crucial role of chelatable iron in silver nanoparticles induced DNA damage and cytotoxicity. Redox Biol. 2018, 15, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AshaRani, P.V.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Anti-proliferative activity of silver nanoparticles. BMC Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabella, S.; Carney, R.P.; Brunetti, V.; Malvindi, M.A.; Al-Juffali, N.; Vecchio, G.; Janes, S.M.; Bakr, O.M.; Cingolani, R.; Stellacci, F.; et al. A general mechanism for intracellular toxicity of metal-containing nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7052–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.P.; Ramarao, P. Cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking and cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 213, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalzon, B.; Aude-Garcia, C.; Collin-Faure, V.; Diemer, H.; Béal, D.; Dussert, F.; Fenel, D.; Schoehn, G.; Cianférani, S.; Carrière, M.; et al. Differential proteomics highlights macrophage-specific responses to amorphous silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 9641–9658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Chen, D.H.; Yan, J.; Chen, Y.; Mittelstaedt, R.A.; Zhang, Y. Genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles evaluated using the Ames test and in vitro micronucleus assay. Mutat. Res. 2012, 745, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, T. Progress in genotoxicity evaluation of engineered nanomaterials. In Nanomaterials—Toxicity and Risk Assessment, 1st ed.; Larramendy, M.L., Soloneski, S., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2015; pp. 141–160. [Google Scholar]
- Beedanagari, S.; Vulimiri, S.V.; Bhatia, S.; Mahadevan, B. Genotoxicity biomarkers: Molecular basis of genetic variability and susceptibility. In Biomarkers in Toxicology, 1st ed.; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 729–742. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.R.; Park, Y.J.; Shin, D.Y.; Oh, S.M.; Chung, K.H. Appropriate in vitro methods for genotoxicity testing of silver nanoparticles. Environ. Health Toxicol. 2013, 28, e2013003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisin, E.R.; Murray, A.R.; Keane, M.J.; Shi, X.C.; Schwegler-Berry, D.; Gorelik, O. Single-walled carbon nanotubes: Geno- and cytotoxic effects in lung fibroblast V79 cells. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2007, 70, 2071–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landsiedel, R.; Kapp, M.D.; Schulz, M.; Wiench, K.; Oesch, F. Genotoxicity investigations on nanomaterials: Methods, preparation and characterization of test material, potential artifacts and limitations- many questions, some answers. Mutat. Res. 2009, 681, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Husen, A.; Rao, R.A.K. A review on biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biocidal properties. Nanobiotechnology 2018, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Nakazato, G.; Seabra, A.B. Antimicrobial activity of biogenic silver nanoparticles, and silver chloride nanoparticles: An overview and comments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6555–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.L.; Harada, T.; Christian, D.A.; Patano, D.A.; Tsai, R.K.; Discher, D.E. Minimal ‘self’ peptides that inhibit phagocytic clearance and enhance delivery of nanoparticles. Science 2013, 339, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballottin, D.; Fulaz, S.; Souza, M.L.; Corio, P.; Rodrigues, A.G.; Souza, A.O.; Gaspari, P.M.; Gomes, A.F.; Gozzo, F.; Tasic, L. Elucidating protein involvement in the stabilization of the biogenic silver nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbalinardo, M.; Caicci, F.; Cavallini, M.; Gentili, D. Protein corona mediated uptake and cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in mouse embryonic fibroblast. Small 2018, 4, e1801219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, S.; Schöttler, S.; Kotman, N.; Baier, G.; Musyanovych, A.; Kuharev, J.; Landfester, K.; Schild, H.; Jahn, O.; Tenzer, S.; et al. Protein corona of nanoparticles: Distinct proteins regulate the cellular uptake. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Lee, B.J. Protein corona: A new approach for nanomedicine design. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3137–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, V.; Das, K.P. Interaction of silver nanoparticles with proteins: A characteristic protein concentration dependent profile of SPR signal. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Krishna Prasad, G.V.R.; Mukhopadhaya, A. Vibrio cholerae Porin OmpU induces caspase-independent programmed cell death upon translocation to the host cell mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 31051–31068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Müller, A.; Günther, D.; Düx, F.; Naumann, M.; Meyer, T.F.; Rudel, T. Neisserial porin (PorB) causes rapid calcium influx in target cells and induces apoptosis by the activation of cysteine proteases. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shirling, E.B.; Gottlieb, D. Methods for characterization of Streptomyces sp. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1966, 16, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogita, Z.I.; Markert, C.L. A miniaturized system for electrophoresis on polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 99, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlow, E.; Lane, D. Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |


| MTT Assay | LDH Assay |
| IC50 (µg·mL−1) | IC50 (µg·mL−1) |
| RAW 264.7 cells | |
| 3.78 ± 0.02 | 43.5 ± 0.08 |
| MCF-7 cells | |
| 4.78 ± 0.03 | 112.9 ± 0.08 |
| Dose (µg/plate) | Number of Bacterial Colonies/Plate (Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|
| negative control | 20.0 ± 4 |
| 0.15 | 24.0 ± 1 |
| 0.25 | 18.0 ± 3 |
| 0.5 | 10.0 ± 1 |
| 1.0 | 4.0 ± 2 |
| 1.5 | 2.0 ± 2 |
| 3.0 | 4.0 ± 1 |
| 6.0 | T |
| 12.5 | T |
| 25.0 | T |
| 37.5 | T |
| 50.0 | T |
| 100.0 | T |
| positive control | 1084 ± 35 |
| Band Number | Accession | Description | Taxonomy | Coverage (%) | MW (kDa) | Calculated pI | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | WP_108997678.1 | Hypothetical protein, partial | Escherichia coli | 43.0 | 44.0 | 8.47 | 4614 |
| WP_040269305.1 | OprD family porin | Pseudomonas rhodesiae | 43.0 | unknown | 5.73 | 1759 | |
| WP_094066152.1 | MULTISPECIES: OprD family porin | Pseudomonas fluorescens group | 49.0 | unknown | 5.73 | 1650 | |
| WP_016712004.1 | MULTISPECIES: OprD family porin | Pseudomonas | 43.0 | unknown | 4.91 | 1445 | |
| 02 | WP_108997678.1 | Hypothetical protein, partial | Escherichia coli | 42.0 | 38.0 | 8.47 | 4376 |
| WP_008643071.1 | MULTISPECIES: porin | Cupriavidus | 44.0 | unknown | 8.81 | 2241 | |
| WP_008645123.1 | Porin | Cupriavidus sp. HMR-1 | 54.0 | unknown | 9.08 | 1951 | |
| WP_103519360.1 | Porin | Ralstonia pickettii | 52.0 | unknown | 9.44 | 1477 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wypij, M.; Jędrzejewski, T.; Ostrowski, M.; Trzcińska, J.; Rai, M.; Golińska, P. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Assessment of Their Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity and Study of Capping Proteins. Molecules 2020, 25, 3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133022
Wypij M, Jędrzejewski T, Ostrowski M, Trzcińska J, Rai M, Golińska P. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Assessment of Their Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity and Study of Capping Proteins. Molecules. 2020; 25(13):3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133022
Chicago/Turabian StyleWypij, Magdalena, Tomasz Jędrzejewski, Maciej Ostrowski, Joanna Trzcińska, Mahendra Rai, and Patrycja Golińska. 2020. "Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Assessment of Their Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity and Study of Capping Proteins" Molecules 25, no. 13: 3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133022
APA StyleWypij, M., Jędrzejewski, T., Ostrowski, M., Trzcińska, J., Rai, M., & Golińska, P. (2020). Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Assessment of Their Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity and Study of Capping Proteins. Molecules, 25(13), 3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133022






