Modeling of Cu(II) Adsorption from an Aqueous Solution Using an Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of RHC4
2.2. Algorithms
2.3. Aqueous pH Influence on Cu(II) Adsorption
2.4. Influence of Cu(II) Concentration and Contact Time
2.5. Influence of RHC4 Dose
2.6. Kinetics
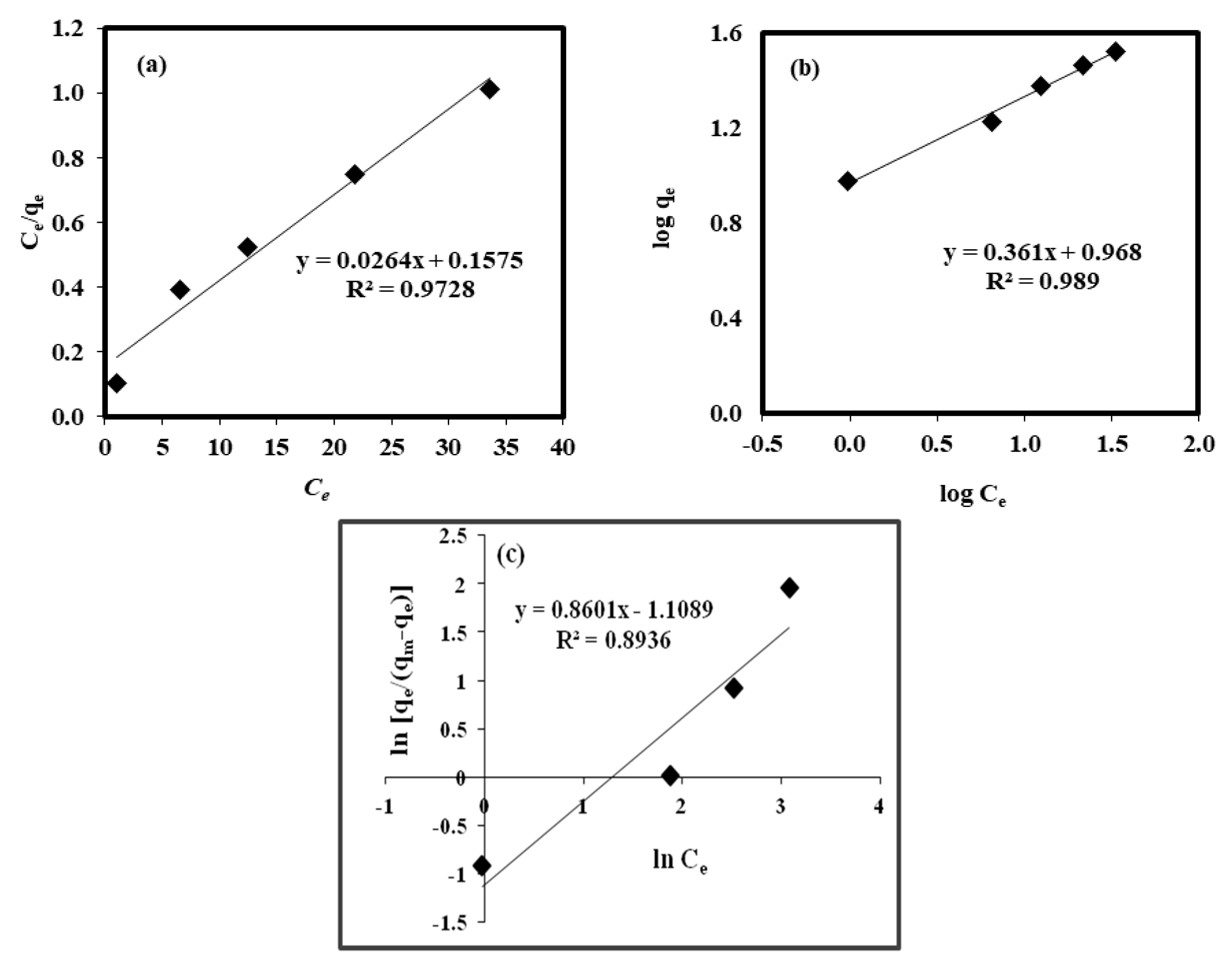
2.7. Isotherms
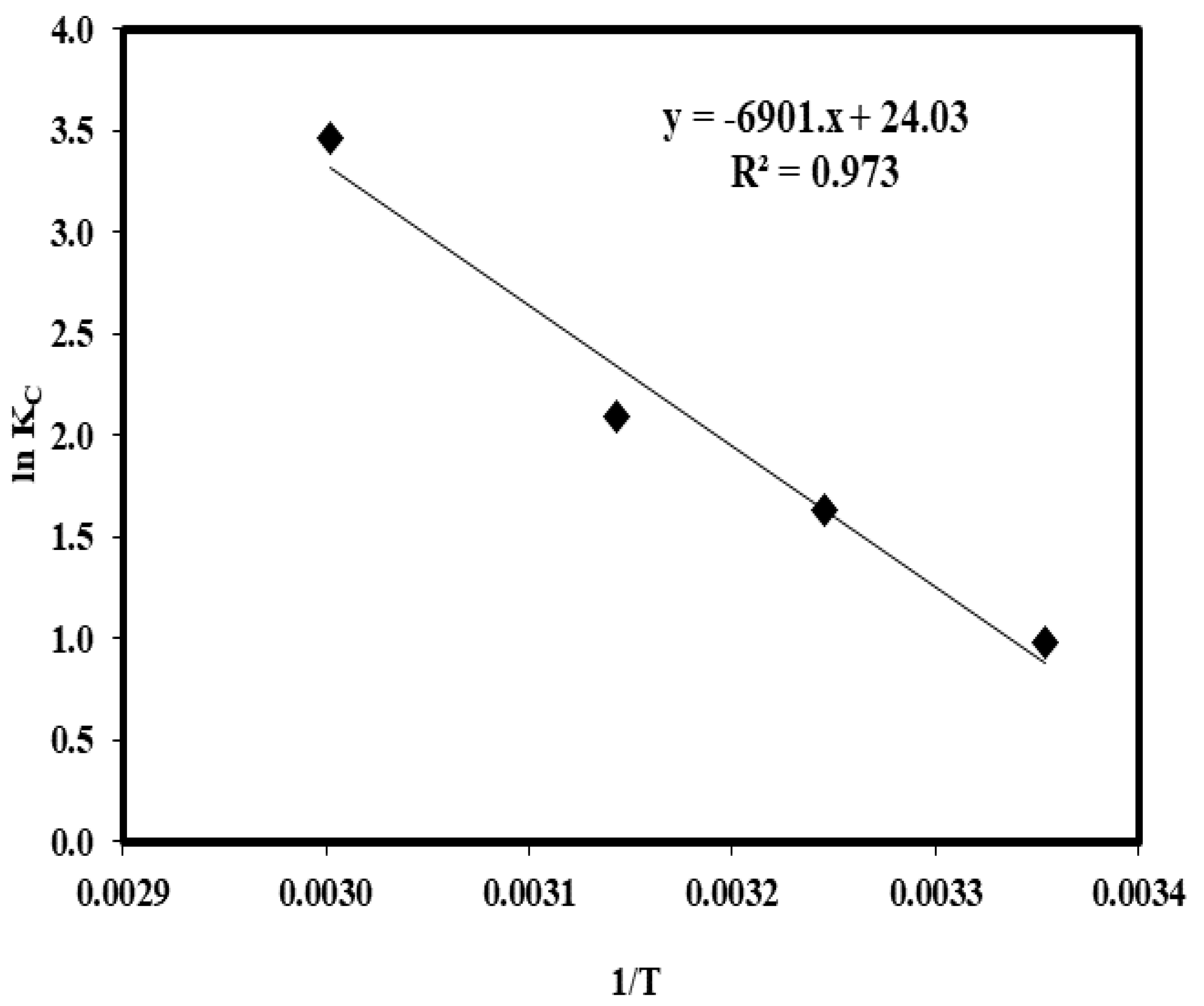
2.8. Influence of Temperature and Thermodynamic Parameters
2.9. Cu(II) Adsorption Efficiency of Different Types of Adsorbents
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Development and Physicochemical Properties of RHC4
3.2. Adsorption Experiment
3.3. Modeling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ben-Ali, S.; Jaouali, I.; Souissi-Najar, S.; Ouederni, A. Characterization and adsorption capacity of raw pomegranate peel biosorbent for copper removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3809–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Liu, X.; Han, M.; Ma, W. Adsorption kinetic character of copper ions onto a modified chitosan transparent thin membrane from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xianfang, Z.; Ruckenstein, E. Supported chitosan-dye affinity membranes and their protein adsorption. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 117, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beppu, M.; Arruda, E.; Vieira, R.; Santos, N. Adsorption of Cu (II) on porous chitosan membranes functionalized with histidine. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 240, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Gupta, S.S. Kaolinite, montmorillonite, and their modified derivatives as adsorbents for removal of Cu (II) from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 50, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Isa, M.H.; Chaudhuri, M.; Mustafa, M.R.U.; Saeed, M.O. Determination of adsorption capacity of agricultural-based carbon for Ni (II) adsorption from aqueous solution. In Proceedings of Applied Mechanics and Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Bach, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Isa, M.H.; Ibrahim, N.; Aziz, H.A.; Adlan, M.N.; Sabiani, N.H.M.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.L.; Kutty, S.R.M. Removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution using treated oil palm fibre. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.; Ab Wahap, S.A.B.; Chaudhuri, M. Adsorption of arsenite from water by rice husk silica. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2012, 11, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, T.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Chaudhuri, M. Adsorptive removal of reactive yellow 15 from aqueous solution by coconut coir activated carbon. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2010, 28, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Isa, M.H.; Mustafa, M.R.U.; Yeek-Chia, H.; Baloo, L.; Manan, T.S.B.A.; Saeed, M.O. Cr (VI) adsorption from aqueous solution by an agricultural waste based carbon. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56365–56374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudakavi, J.; Puttanna, K. Decontamination of chromium containing ground water by adsorption using chemically modified activated carbon fabric. Int. J. Chem. Mol. Eng. 2016, 9, 884–890. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C. Advances in pretreatment and clarification technologies. In Comprehensive Water Quality and Purification; CH2M Hill, Inc.: Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 60–74. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelfattah, I.; Ismail, A.A.; Sayed, F.A.; Almedolab, A.; Aboelghait, K.M. Biosorption of heavy metals ions in real industrial wastewater using peanut husk as efficient and cost effective adsorbent. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2016, 6, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Pan, Y.; Cai, P.; Guo, T.; Xiao, H. Single and binary adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using sugarcane cellulose-based adsorbent. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johari, K.; Saman, N.; Song, S.T.; Chin, C.S.; Kong, H.; Mat, H. Adsorption enhancement of elemental mercury by various surface modified coconut husk as eco-friendly low-cost adsorbents. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 109, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingamdinne, L.P.; Yang, J.-K.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Koduru, J.R. Low-cost magnetized Lonicera japonica flower biomass for the sorption removal of heavy metals. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 165 Pt 1, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiyili, H.; Çetintaş, S.; Bingöl, D. Removal of some heavy metals onto mechanically activated fly ash: Modeling approach for optimization, isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2017, 109, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnane, M.; Tounsadi, H.; Elmoubarki, R.; Mahjoubi, F.Z.; Elhalil, A.; Saqrane, S.; Abdennouri, M.; Qourzal, S.; Barka, N. Alkaline treated carob shells as sustainable biosorbent for clean recovery of heavy metals: Kinetics, equilibrium, ions interference and process optimisation. Ecolog. Eng. 2017, 101, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.H.; Sanaei, D.; Ali, I.; Bhatnagar, A. Removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution using treated waste newspaper as a low-cost adsorbent: Kinetic modeling and isotherm studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Saeed, K.; Mabood, F. Removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous medium using chemically modified banana peels as efficient low-cost adsorbent. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.S.; Cunha, J.M.; Dortzbacher, G.F.; Dotto, G.L. Adsorption of Co (II) from aqueous solutions onto rice husk modified by ultrasound assisted and supercritical technologies. Process Safety Environ. Protect. 2017, 109, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandanlou, R.; Masoumi, H.R.F.; Ahmad, M.B.; Shameli, K.; Basri, M.; Kalantari, K. Enhancement of heavy metals sorption via nanocomposites of rice straw and Fe3O4 nanoparticles using artificial neural network (ANN). Ecolog. Eng. 2016, 91, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, Y.; Zakaria, A.; Sairi, N.A.; Amin Matori, K.; Fard Masoumi, H.R.; Sadrolhosseini, A.R.; Jahangirian, H. Artificial neural network modelling of photodegradation in suspension of manganese doped zinc oxide nanoparticles under visible-light irradiation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Puebla, R.; Aroca, R.; Valenzuela-Calahorro, C.; Garrido, J. Retention of cobalt on a humin derived from brown coal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, P.; Qiu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, W. Metal loaded zeolite adsorbents for hydrogen cyanide removal. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakbanpote, W.; Goodman, B.A.; Thiravetyan, P. Copper adsorption on rice husk derived materials studied by EPR and FTIR. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 304, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladoja, N.A.; Ololade, I.A.; Alimi, O.A.; Akinnifesi, T.A.; Olaremu, G.A. Iron incorporated rice husk silica as a sorbent for hexavalent chromium attenuation in aqueous system. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 2691–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.H.K.; Ramana, D.; Seshaiah, K.; Reddy, A. Biosorption of Ni (II) from aqueous phase by Moringa oleifera bark, a low cost biosorbent. Desalination 2011, 268, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedna, M.; Johns, M.; Clarke, S.; Marshall, W.; Rao, R. Potential of agricultural by-product-based activated carbons for use in raw sugar decolourisation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1997, 75, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusz, A.; Oleszczuk, P.; Dobrowolski, R. Application of laboratory prepared and commercially available biochars to adsorption of cadmium, copper and zinc ions from water. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 196, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, I.; Srivastava, V.; Kumar, G.; Mishra, I. Characterization and utilization of mesoporous fertilizer plant waste carbon for adsorptive removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 278, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamari, A.; Yusoff, S.N.M.; Abdullah, F.; Putra, W.P. Biosorptive removal of Cu(II), Ni(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions using coconut dregs residue: Adsorption and characterisation studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1912–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Ngo, H.; Guo, W.; Setiadi, T. Adsorption and desorption of copper (II) ions onto garden grass. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 121, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, L.; Huang, H.; Chen, Z.; Wei, X.; Jiang, J. Activated carbon/CoFe2O4 composites: Facile synthesis, magnetic performance and their potential application for the removal of malachite green from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, T.; Pehlivan, E. Removal of Copper (II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Walnut-, Hazelnut-and Almond-Shells. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2007, 35, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güzel, F.; Aksoy, Ö.; Akkaya, G. Evaluation of Pomegranate (Punica Granatum L.) Pulps for the Removal of Copper (II) Ions: Kinetic, Equilibrium, and Desorption Studies. J. Dispersion Sci. Technol. 2014, 35, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, H.; Tiadi, N.; Mohanty, M.; Mohanty, C. Studies on adsorption behavior of an industrial waste for removal of chromium from aqueous solution. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 23, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe. Kungliga Sven. Vetensk. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.; McKay, G.; Wase, D.; Forster, C. Study of the sorption of divalent metal ions on to peat. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2000, 18, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, M. Kinetics of chemisorption of gases on solids. Chem. Rev. 1960, 60, 267–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L.; Juang, R.-S. Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çoruh, S.; Geyikci, F. Adsorption of copper (II) ions on montmorillonite and sepiolite clays: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2012, 45, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nemr, A. Potential of pomegranate husk carbon for Cr (VI) removal from wastewater: Kinetic and isotherm studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, L.; Franus, M.; Madej, J.; Kołodyńska, D.; Hubicki, Z. Zeolites in Phenol Removal in the Presence of Cu (II) Ions—Comparison of Sorption Properties after Chitosan Modification. Materials 2020, 13, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Wu, J.; Fan, J.; Qian, W.; Zhou, X.; Qian, C.; Jin, X.; Wang, L.; Bai, J.; Ying, H. Adsorption of butanol from aqueous solution onto a new type of macroporous adsorption resin: Studies of adsorption isotherms and kinetics simulation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Mustafa, M.R.U.; Isa, M.H.; Manan, T.S.B.A.; Ho, Y.-C.; Lim, J.-W.; Yusof, N.Z. Artificial neural network (ANN) for modelling adsorption of lead (Pb (II)) from aqueous solution. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, L.T. Characterization and adsorptive behaviour of snail shell-rice husk (SS-RH) calcined particles (CPs) towards cationic dye. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, E.; Lu, S.; Gibb, S.; Villaescusa, I. A comparison of low-cost biosorbents and commercial sorbents for the removal of copper from aqueous media. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, C.; Radhika, R.; Suba, S. Uptake of dyes by a promising locally available agricultural solid waste: Coir pith. Waste Manag. 2001, 21, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isa, M.H.; Lang, L.S.; Asaari, F.A.; Aziz, H.A.; Ramli, N.A.; Dhas, J.P.A. Low cost removal of disperse dyes from aqueous solution using palm ash. Dyes Pigments 2007, 74, 446–453. [Google Scholar]
- Şengil, İ.A.; Özacar, M. Biosorption of Cu (II) from aqueous solutions by mimosa tannin gel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiral, H.; Güngör, C. Adsorption of copper (II) from aqueous solutions on activated carbon prepared from grape bagasse. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 124, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Ngo, H.; Guo, W.; Nguyen, T. Palm oil fruit shells as biosorbent for copper removal from water and wastewater: Experiments and sorption models. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 113, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.S.; Caetano, L.; Ferreira, G.; Padilha, P.M.; Saeki, M.J.; Zara, L.F.; Martines, M.A.U.; Castro, G.R. Banana peel applied to the solid phase extraction of copper and lead from river water: Preconcentration of metal ions with a fruit waste. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3446–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhao, M.; Song, G.; Huang, H. Modification of pineapple peel fibre with succinic anhydride for Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ removal from aqueous solutions. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofomaja, A.; Naidoo, E.; Modise, S. Biosorption of copper (II) and lead (II) onto potassium hydroxide treated pine cone powder. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, B.S.; Curran, M.; Hasan, S.; Ghosh, T. Adsorption characteristics of Cu and Ni on Irish peat moss. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamoglu, M.; Tekir, O. Removal of copper (II) and lead (II) ions from aqueous solutions by adsorption on activated carbon from a new precursor hazelnut husks. Desalination 2008, 228, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.M.; Ramesh, A.; Rao, G.P.C.; Seshaiah, K. Removal of copper and cadmium from the aqueous solutions by activated carbon derived from Ceiba pentandra hulls. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 129, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Ulmanu, M.; Marañón, E.; Fernández, Y.; Castrillón, L.; Anger, I.; Dumitriu, D. Removal of copper and cadmium ions from diluted aqueous solutions by low cost and waste material adsorbents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 142, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.; Huang, C.; Huang, H. Equilibrium sorption isotherm for metal ions on tree fern. Process. Biochem. 2002, 37, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elías, A.; Ibarra-Berastegi, G.; Arias, R.; Barona, A. Neural networks as a tool for control and management of a biological reactor for treating hydrogen sulphide. Bioprocess. Biosystems Eng. 2006, 29, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairez, I.; García-Peña, I.; Cabrera, A. Dynamic numerical reconstruction of a fungal biofiltration system using differential neural network. J. Process Control 2009, 19, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rene, E.R.; Veiga, M.C.; Kennes, C. Experimental and neural model analysis of styrene removal from polluted air in a biofilter. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Int. Res. Process Environ. Clean Technol. 2009, 84, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the rice husk char (RHC4) are available from the authors. |



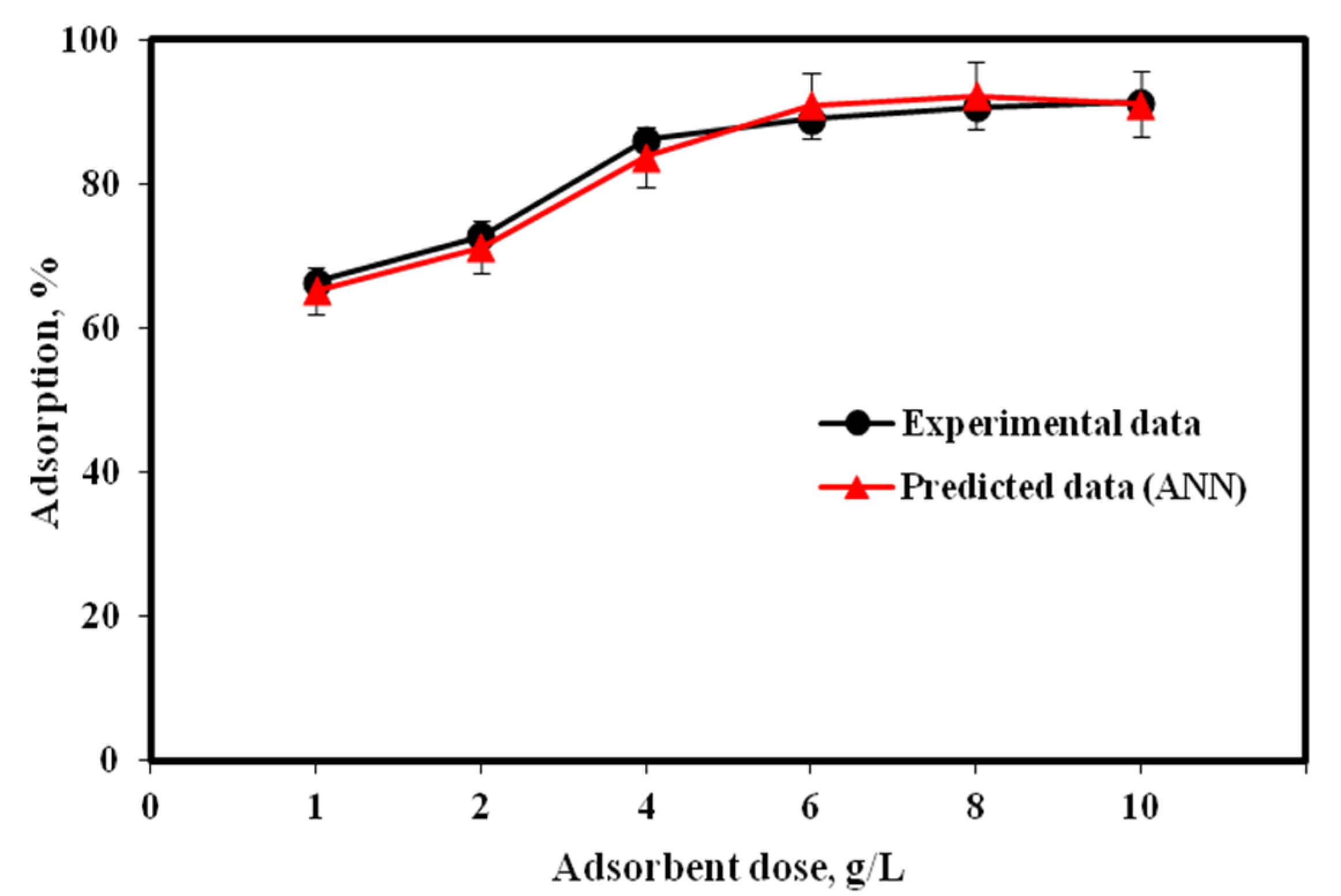

| Algorithm | Function | Optimal Neuron Number | MSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resilient | trainrp | 16 | 57.48 | 0.908 |
| Fletcher–Reeves conjugate gradient | traincgf | 10 | 3.84 | 0.989 |
| Polak–Ribière–Polyak conjugate gradient | traincgp | 10 | 4.78 | 0.986 |
| Powell–Beale conjugate gradient | traincgb | 10 | 3.88 | 0.988 |
| Levenberg–Marquardt | trainlm | 6 | 4.50 | 0.987 |
| Scaled conjugate gradient | trainscg | 10 | 6.79 | 0.981 |
| BFGS quasi-Newton | trainbfg | 18 | 7.83 | 0.980 |
| One-step secant | trainoss | 8 | 7.07 | 0.979 |
| Model | Parameters | Cu(II) Concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 mg/L | 40 mg/L | 60 mg/L | 80 mg/L | ||
| qe,exp (mg g−1) | 9.51 | 16.73 | 23.76 | 29.11 | |
| Pseudo-first-order | qe,cal (mg g−1) | 1.1 | 2.1 | 3.73 | 4.98 |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.02 | 0.023 | 0.016 | ||
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.97 | |
| SSE | 8.41 | 14.63 | 20.03 | 24.13 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | qe,cal (mg g−1) | 9.61 | 16.94 | 24.39 | 29.41 |
| k2 (g mg−1 min−1) | 0.071 | 0.038 | 0.016 | 0.012 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| SSE | 0.1 | 0.21 | 0.63 | 0.3 | |
| Elovich | α (mg/g min) | 233,279 | 82,015 | 58,965 | 29,128 |
| β (g/mg) | 2.89 | 1.54 | 0.97 | 0.67 | |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.92 | 0.96 | |
| SSE | 1.09 | 0.64 | 0.77 | 0.78 | |
| Intraparticle diffusion | kp (mg g−1 min−1/2) | 0.12 | 0.22 | 0.38 | 0.53 |
| C (mg g−1 ) | 8.23 | 14.35 | 19.47 | 23.12 | |
| R2 | 0.969 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.98 | |
| SSE | 1.28 | 2.38 | 4.29 | 5.99 | |
| Isotherm | Constants | R2 | SSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | Qo (mg/g) | b (L/g) | 0.97 | 0.50 |
| 38.46 | 0.16 | |||
| Freundlich | Kf (mg/g) | 1/n | 0.98 | 0.02 |
| 9.28 | 0.36 | |||
| Sips | bs | 1/n | 0.89 | 0.69 |
| 0.27 | 0.86 | |||
| T (°C) | qe (mg/g) | KC | ∆Go | ∆Ho (kJ/mol) | ∆So (J/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 °C | 29.11 | 2.64 | −2.44 | 57.37 | 199.78 |
| 35 °C | 33.48 | 5.14 | −4.19 | ||
| 45 °C | 35.62 | 8.14 | −5.55 | ||
| 60 °C | 38.78 | 31.92 | −9.59 |
| Adsorbent | Surface Area (m2/g) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw pomegranate peel | 598.78 | 30.12 | [1] |
| Grape bagasse activated carbon | 1455 | 37.17 | [52] |
| Palm oil fruit shell | 39.76 | 20–60 | [53] |
| Banana peel | 2.0 | 20.97 | [54] |
| Pineapple peel fiber | - | 27.68 | [55] |
| Pine cone powder | - | 26.23 | [56] |
| Irish peat moss | 203.41 | 17.6 | [57] |
| Hazelnut husk | 4.31 | 6.645 | [58] |
| Ceiba pentandra hulls | 521 | 20.8 | [59] |
| Cellulose pulp waste | 2.64 | 4.98 | [60] |
| Compost | 1.36 | 12.77 | [60] |
| Tree fern | 2.39 | 11.7 | [61] |
| Rice husk char | 76.47 | 38.46 | This study |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, T.; Binti Abd Manan, T.S.; Isa, M.H.; Ghanim, A.A.J.; Beddu, S.; Jusoh, H.; Iqbal, M.S.; Ayele, G.T.; Jami, M.S. Modeling of Cu(II) Adsorption from an Aqueous Solution Using an Artificial Neural Network (ANN). Molecules 2020, 25, 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143263
Khan T, Binti Abd Manan TS, Isa MH, Ghanim AAJ, Beddu S, Jusoh H, Iqbal MS, Ayele GT, Jami MS. Modeling of Cu(II) Adsorption from an Aqueous Solution Using an Artificial Neural Network (ANN). Molecules. 2020; 25(14):3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143263
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Taimur, Teh Sabariah Binti Abd Manan, Mohamed Hasnain Isa, Abdulnoor A.J. Ghanim, Salmia Beddu, Hisyam Jusoh, Muhammad Shahid Iqbal, Gebiaw T Ayele, and Mohammed Saedi Jami. 2020. "Modeling of Cu(II) Adsorption from an Aqueous Solution Using an Artificial Neural Network (ANN)" Molecules 25, no. 14: 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143263
APA StyleKhan, T., Binti Abd Manan, T. S., Isa, M. H., Ghanim, A. A. J., Beddu, S., Jusoh, H., Iqbal, M. S., Ayele, G. T., & Jami, M. S. (2020). Modeling of Cu(II) Adsorption from an Aqueous Solution Using an Artificial Neural Network (ANN). Molecules, 25(14), 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143263






