Tamoxifen and the PI3K Inhibitor: LY294002 Synergistically Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LY294002 and Tamoxifen Synergistically Inhibited Breast Cancer Cells Proliferation
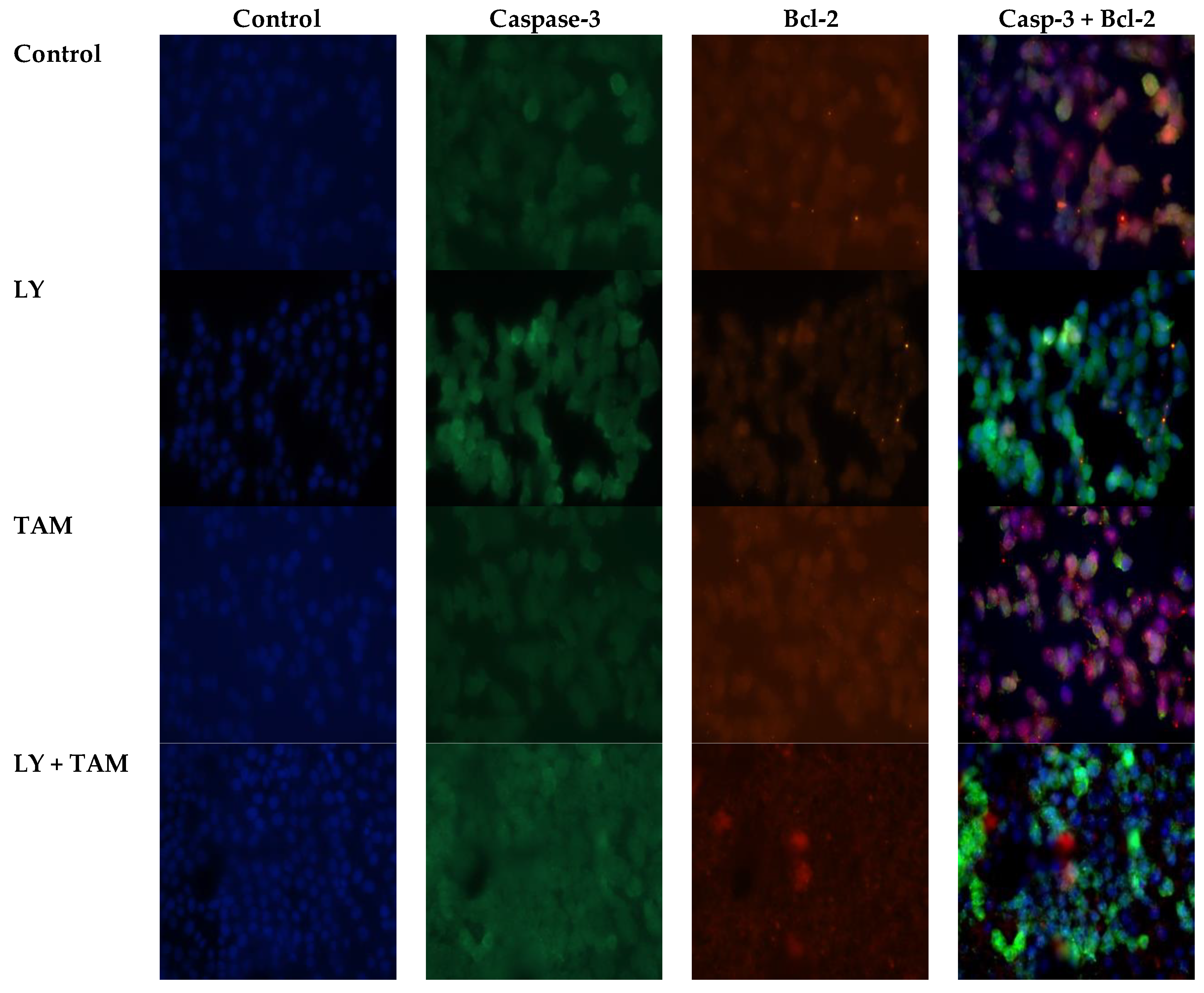
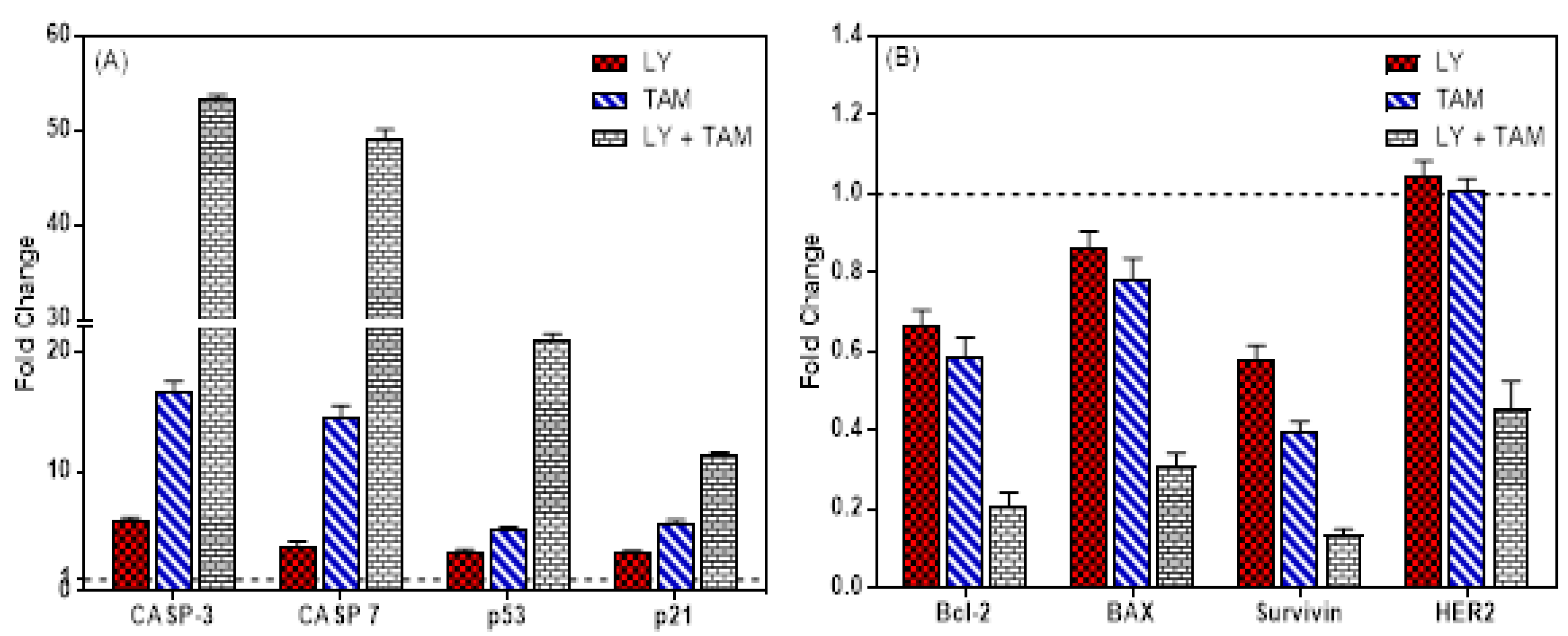
2.2. LY294002 and Tamoxifen Induced Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells
2.3. LY294002 and Tamoxifen Induced Cell Cycle Arrest in Breast Cancer Cells
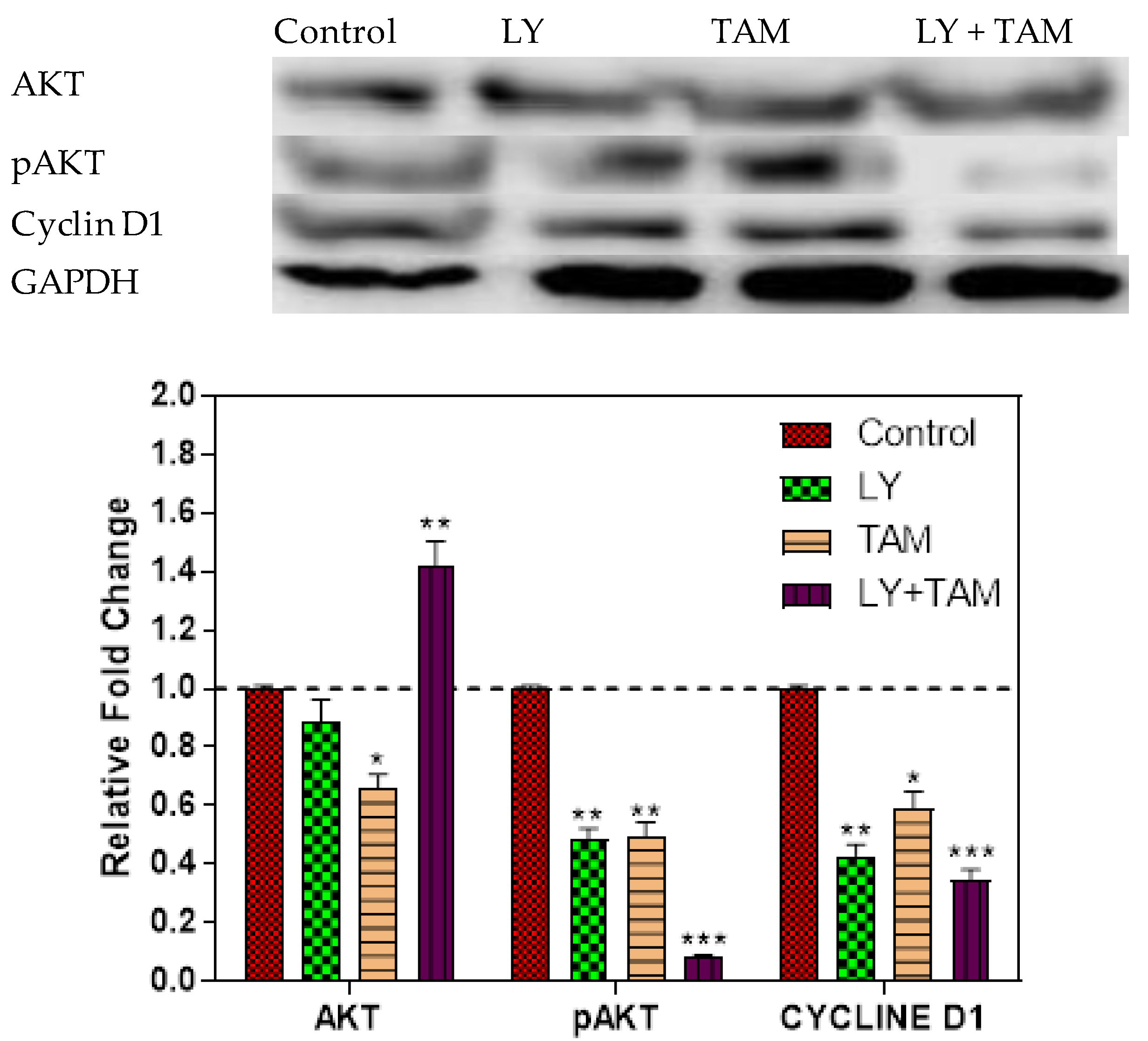
2.4. pAKT and Cyclin D1 Decreased in MCF-7 Cells Treated with LY294002 and Tamoxifen
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Compounds and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cytotoxicity and Combination Studies
4.4. Clonogenic Survival Assay
4.5. Apoptosis Assay Using Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.8. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.9. Western Immunoblotting
4.10. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shahrani, Z.; Al-Rawaji, A.I.; Al-Madouj, A.N.; Hayder, M.S. Cancer Incidence Report Saudi Arabia 2014; Saudi Cancer Registry: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2017; pp. 1–81. [Google Scholar]
- Sopik, V.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Predictors of time to death after distant recurrence in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 173, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahtani, H.M.; Alanazi, M.M.; Aleanizy, F.S.; Alqahtani, F.Y.; Alhoshani, A.; Alanazi, F.E.; Almehizia, A.A.; Abdalla, A.N.; Alanazi, M.G.; El-Azab, A.S.; et al. Synthesis, anticancer, apoptosis-inducing activities and EGFR and VEGFR2 assay mechanistic studies of 5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives: Molecular docking studies. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, M.; Sung, H.; Devi, R.; Guida, J.; Tang, T.S.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Yang, X.R. Breast cancer risk factors, survival and recurrence, and tumor molecular subtype: Analysis of 3012 women from an indigenous Asian population. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.; Hatch, L.; Price, C.R.; Palakurty, S.H.; Simoneit, E.; Radisic, A.; Pargas, A.; Shetty, I.; Lyman, M.; Couchot, P.; et al. Addressing Breast Cancer Screening Disparities Among Uninsured and Insured Patients: A Student-Run Free Clinic Initiative. J. Community Health 2019, 45, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemons, M.; Danson, S.; Howell, A. Tamoxifen (‘Nolvadex’): A review: Antitumour treatment. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2002, 28, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.M.; Hickey, S.M.; Song, Y.; Plush, S.E.; Garg, S. Novel Tamoxifen Nanoformulations for Improving Breast Cancer Treatment: Old Wine in New Bottles. Molecules 2020, 25, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvente-Poirot, S.; de Medina, P.; Record, M.; Poirot, M. From tamoxifen to dendrogenin A: The discovery of a mammalian tumor suppressor and cholesterol metabolite. Biochimie 2016, 130, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, G.M.; Barton-Burke, M. 2020–2021 Oncology Nursing Drug Handbook; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Burlington, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, K.E.; Elamin, A. Adherence to endocrine therapy and its relation to disease-free survival among breast cancer patients visiting an out-patient clinic at Khartoum Oncology Hospital, Sudan. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2020, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggins, R.B.; Schrecengost, R.S.; Guerrero, M.S.; Bouton, A.H. Pathways to tamoxifen resistance. Cancer Lett. 2007, 256, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Meng, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, W.; Miller, T.; Murph, M.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Gagea, M.; Arteaga, C.L.; et al. Targeting tyrosine-kinases and estrogen receptor abrogates resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 9049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Lee, N.V.; Hu, W.; Xu, M.; Ferre, R.A.; Lam, H.; Bergqvist, S.; Solowiej, J.; Diehl, W.; He, Y.-A.; et al. Spectrum and degree of CDK drug interactions predicts clinical performance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2273–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maira, S.-M.; Stauffer, F.; Schnell, C.; García-Echeverría, C. PI3K Inhibitors for Cancer Treatment: Where Do We Stand? Portland Press Ltd.: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, C.-G.; Zhu, B.S.; Fan, X.Q.; Liu, H.H.; Hou, X.; Zhao, K.; Qin, Z.H. Effects of LY294002 on the invasiveness of human gastric cancer in vivo in nude mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Qiu, Y.; Kong, D. Class I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, F.; Ferns, G.A.; Talebian, S.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Avan, A.; Shahidsales, S. Role of regulatory miRNAs of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of breast cancer. Gene 2020, 737, 144459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, M.A.; Fraile-Martínez, O.; Asúnsolo, Á.; Buján, J.; García-Honduvilla, N.; Coca, S. Signal Transduction Pathways in Breast Cancer: The Important Role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 9258396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, J.A. Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: Opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.A. The National Practitioner Data Bank: A primer for clinicians. J. Perinat. Neonatal Nurs. 2011, 25, 224–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falasca, M. PI3K/Akt signalling pathway specific inhibitors: A novel strategy to sensitize cancer cells to anti-cancer drugs. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.; McGarrigle, S.; Pidgeon, G.P. The next generation of PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway inhibitors in breast cancer cohorts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2018, 1870, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaizumi, H.; Higashi, C.; Tanaka, Y.; Hamada, M.; Shinzaki, W.; Azumi, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Inui, H.; Houjou, T.; Komoike, Y. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway activation in patients with ER-positive, metachronous, contralateral breast cancer treated with hormone therapy. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 1962–1968. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Ji, H.; Niu, X.; Yin, L.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q. Tumor-associated macrophages secrete CC-chemokine ligand 2 and induce tamoxifen resistance by activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR in breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, J.C.; Parveen, D.; Shah, R.D.; Desai, A.; Bhosale, D.; Chugh, A.; Ranade, D.; Karnik, S.; Khedkar, B.; Mathur, A.; et al. Secretory prostate apoptosis response (Par)-4 sensitizes multicellular spheroids (MCS) of glioblastoma multiforme cells to tamoxifen-induced cell death. FEBS Open Bio 2015, 5, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.C.; Chiu, H.C.; Syu, J.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Jian, Y.T.; Huang, Y.J.; Wo, T.Y.; Jian, Y.J.; Chang, P.Y.; Wang, T.J.; et al. Down-regulation of MSH2 expression by Hsp90 inhibition enhances cytotoxicity affected by tamoxifen in human lung cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 456, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.C.; Chiu, H.C.; Syu, J.J.; Jian, Y.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Jian, Y.T.; Huang, Y.J.; Wo, T.Y.; Lin, Y.W. Tamoxifen enhances erlotinib-induced cytotoxicity through down-regulating AKT-mediated thymidine phosphorylase expression in human non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 88, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, C.; Wang, S.; Feng, Y.; Lin, W.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, P.; Mu, Y.-G.; et al. Sensitization of glioma cells to tamoxifen-induced apoptosis by Pl3-kinase inhibitor through the GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27053. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, X.; Storr, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Rakha, E.A.; Green, A.R.; Ellis, I.O.; Martin, S.G. Caspase-3 and caspase-8 expression in breast cancer: Caspase-3 is associated with survival. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.; Lawson, D.; Cotsonis, G.; Cohen, C. Survivin and caspase-3 expression in breast cancer: Correlation with prognostic parameters, proliferation, angiogenesis, and outcome. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2008, 16, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Yu, J.H.; Wu, J.N.; Tashiro, S.I.; Onodera, S.; Minami, M.; Ikejima, T. P53-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through a caspase-3- independent, but caspase-9-dependent pathway in oridonin-treated MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2007, 28, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donovan, N.; Crown, J.; Stunell, H.; Hill, A.D.; McDermott, E.; O’Higgins, N.; Duffy, M.J. Caspase 3 in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 738–742. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, T.; Dutta, A. p21 in cancer: Intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomadaki, H.; Scorilas, A. Molecular profile of the BCL2 family of the apoptosis related genes in breast cancer cells after treatment with cytotoxic/cytostatic drugs. Connect. Tissue Res. 2008, 49, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna-Vargas, M.P.A.; Chipuk, J.E. Physiological and Pharmacological Control of BAK, BAX, and Beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Veiga, G.L.; da Silva RD, M.; Pereira, E.C.; Azzalis, L.A.; da Costa Aguiar Alves, B.; de Sousa Gehrke, F.; Gascón, T.M.; Fonseca, F.L.A. The role of Survivin as a biomarker and potential prognostic factor for breast cancer. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2019, 65, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motawi, T.M.K.; Zakhary, N.I.; Darwish, H.A.; Abdalla, H.M.; Tadros, S.A. Significance of Serum Survivin and -31G/C Gene Polymorphism in the Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer in Egypt. Clin. Breast Cancer 2019, 19, e276–e282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.F.; Zhang, D.R.; Tian, K.L.; Lou, H.Y.; Qi, X.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Duan, C.X.; Jia, L.J.; Wang, F.H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by oridonin nanosuspension. Drug Deliv. 2011, 18, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; D’Souza, S.S.; Gaonkar, S.L.; Rai, K.L.; Salimath, B.P. Growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by a new series of substituted-1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives. Investig. New Drugs 2008, 26, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänicke, R.U.; Sprengart, M.L.; Wati, M.R.; Porter, A.G. Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and morphological changes associated with apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 9357–9360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Fan, D.; Zhou, G.; Li, X.; Deng, H. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor(LY294002) induces apoptosis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, A.E.M.; Bussink, J.; Sweep, F.C.; Span, P.N. Changes in DNA Damage Repair Gene Expression and Cell Cycle Gene Expression Do Not Explain Radioresistance in Tamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer. Oncol. Res. 2020, 28, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, F.; Nahta, R.; Conforti, R.; Boulet, T.; Aziz, M.; Yuan LX, H.; Meslin, F.; Spielmann, M.; Tomasic, G.; Pusztai, L.; et al. Expression patterns and predictive value of phosphorylated AKT in early-stage breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Di, M.Y.; Yuan, J.Q.; Shen, W.X.; Zheng, D.Y.; Chen, J.Z.; Mao, C.; Tang, J.L. The prognostic value of phosphorylated Akt in breast cancer: A systematic review. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkahtani, H.M.; Abdalla, A.N.; Obaidullah, A.J.; Alanazi, M.M.; Almehizia, A.A.; Alanazi, M.G.; Ahmed, A.Y.; Alwassil, O.I.; Darwish, H.W.; Abdel-Aziz, A.A.-M.; et al. Synthesis, cytotoxic evaluation, and molecular docking studies of novel quinazoline derivatives with benzenesulfonamide and anilide tails: Dual inhibitors of EGFR/HER2. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 95, 103461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, A.M.; Abdelazeem, A.H.; Abdalla, A.N.; Ahmed, M. Pyrrolizine-5-carboxamides: Exploring the impact of various substituents on anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities. Acta Pharm. 2018, 68, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, A.D.; Bagla VP, B.; Bassene, E.; Eloff, J.N. Phytochemical Screening, Antimicrobial and Cytotoxicity Studies of Ethanol Leaf Extract of Aphaniasenegalensis (Sapindaceae). Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 14, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, A.N.; Shaheen, U.; Abdallah, Q.; Flamini, G.; Bkhaitan, M.M.; Abdelhady, M.I.; Ascrizzi, R.; Bader, A. Proapoptotic Activity of Achillea membranacea Essential Oil and Its Major Constituent 1,8-Cineole against A2780 Ovarian Cancer Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malki, W.H.; Gouda, A.M.; Ali, H.E.; Al-Rousan, R.; Samaha, D.; Abdalla, A.N.; Bustamante, J.; Elmageed, Z.Y.A.; Ali, H.I. Structural-based design, synthesis, and antitumor activity of novel alloxazine analogues with potential selective kinase inhibition. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 152, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, A.N.; Abdallah, M.E.; Aslam, A.; Bader, A.; Vassallo, A.; De Tommasi, N.; Malki, W.H.; Gouda, A.M.; Mukhtar, M.H.; El-Readi, M.Z.; et al. Synergistic Anti Leukemia Effect of a Novel Hsp90 and a Pan Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2020, 25, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, U.; Ragab, E.A.; Abdalla, A.N.; Bader, A. Triterpenoidal saponins from the fruits of Gleditsia caspica with proapoptotic properties. Phytochemistry 2018, 145, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available. |




| Gene | Sequence |
|---|---|
| Caspase-3 | F: ACATGGAAGCGAATCAATGGACTC R: AAGGACTCAAATTCTGTTGCCACC |
| Caspase-7 | F: GGACCGAGTGCCCACTTATC R: TCGCTTTGTCGAAGTTCTTGTT |
| p53 | F: CCA CCA TAA AGC TGG GGC TT R: TCT CCC CGC CTC TTT GAC TC |
| p21 | F: GAG TCC TGT TTG CTT CTG GGC A R: CTG CAT TGG GGC TGC CTA TGT A |
| BCL-2 | F: CTCTCGTCGCTACCGTCGCG R: AGGCATCCCAGCCTCCGTTATCC |
| BAX | F: GCCCTTTTGCTTCAGGGTTT R: TCCAATGTCCAGCCCATGAT |
| Survivin | F: TTGCTCCTGCACCCCAGAGC R: AGGCTCAGCGTAAGGCAGCC |
| HER2 | F: CCT CTG ACG TCC ATC GTC TC R: CGG ATC TTC TGC TGC CGT CG |
| GAPDH | F: AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG R: TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdallah, M.E.; El-Readi, M.Z.; Althubiti, M.A.; Almaimani, R.A.; Ismail, A.M.; Idris, S.; Refaat, B.; Almalki, W.H.; Babakr, A.T.; Mukhtar, M.H.; et al. Tamoxifen and the PI3K Inhibitor: LY294002 Synergistically Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25153355
Abdallah ME, El-Readi MZ, Althubiti MA, Almaimani RA, Ismail AM, Idris S, Refaat B, Almalki WH, Babakr AT, Mukhtar MH, et al. Tamoxifen and the PI3K Inhibitor: LY294002 Synergistically Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells. Molecules. 2020; 25(15):3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25153355
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdallah, Mohamed E., Mahmoud Zaki El-Readi, Mohammad Ahmad Althubiti, Riyad Adnan Almaimani, Amar Mohamed Ismail, Shakir Idris, Bassem Refaat, Waleed Hassan Almalki, Abdullatif Taha Babakr, Mohammed H. Mukhtar, and et al. 2020. "Tamoxifen and the PI3K Inhibitor: LY294002 Synergistically Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells" Molecules 25, no. 15: 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25153355
APA StyleAbdallah, M. E., El-Readi, M. Z., Althubiti, M. A., Almaimani, R. A., Ismail, A. M., Idris, S., Refaat, B., Almalki, W. H., Babakr, A. T., Mukhtar, M. H., Abdalla, A. N., & Idris, O. F. (2020). Tamoxifen and the PI3K Inhibitor: LY294002 Synergistically Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells. Molecules, 25(15), 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25153355








