DDAO Controlled Synthesis of Organo-Modified Silica Nanoparticles with Encapsulated Fluorescent Boron Dipyrrins and Study of Their Uptake by Cancerous Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
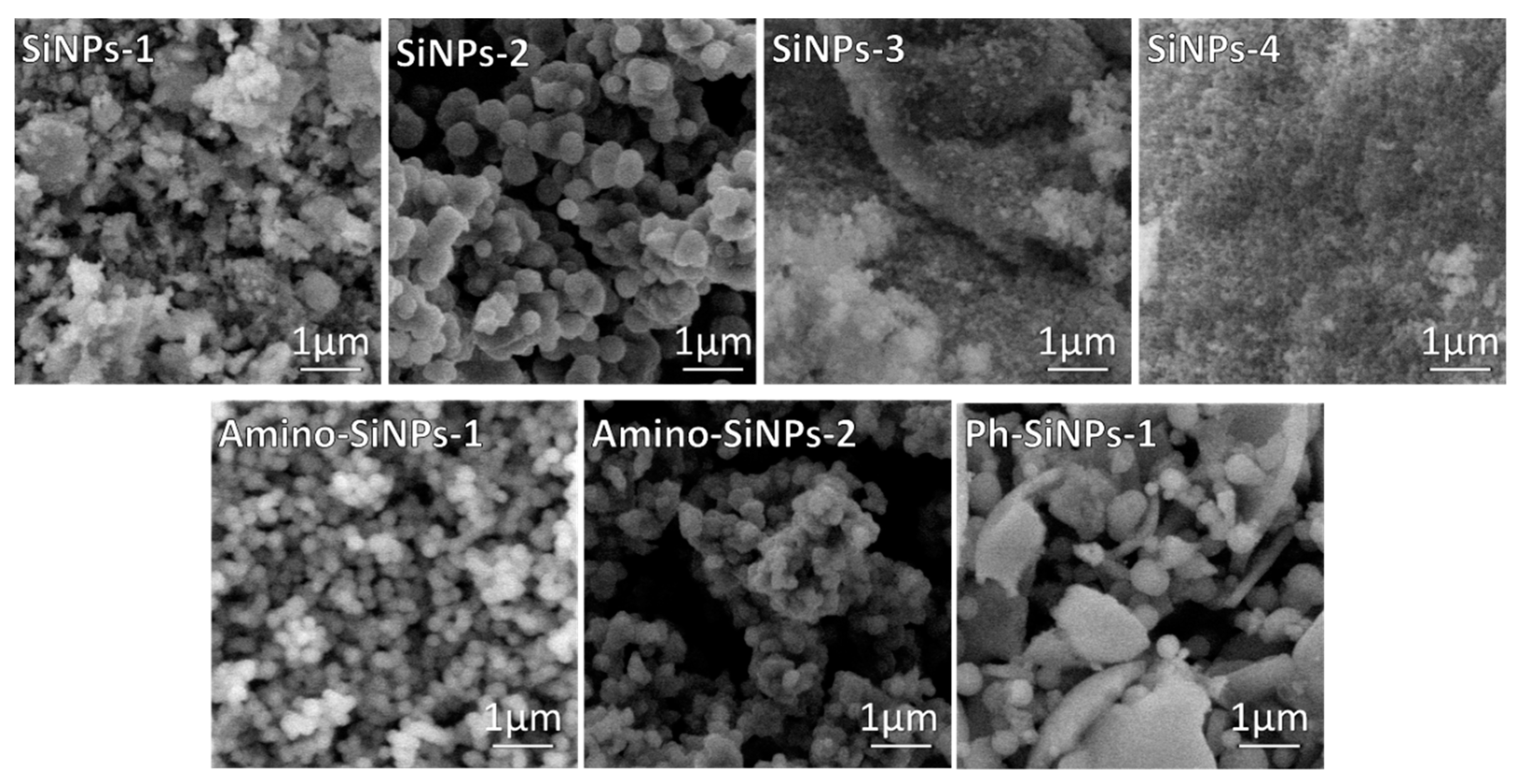
2.1. The Influence of Sol-Gel Conditions on the Morphology of Final Silica-Based Materials
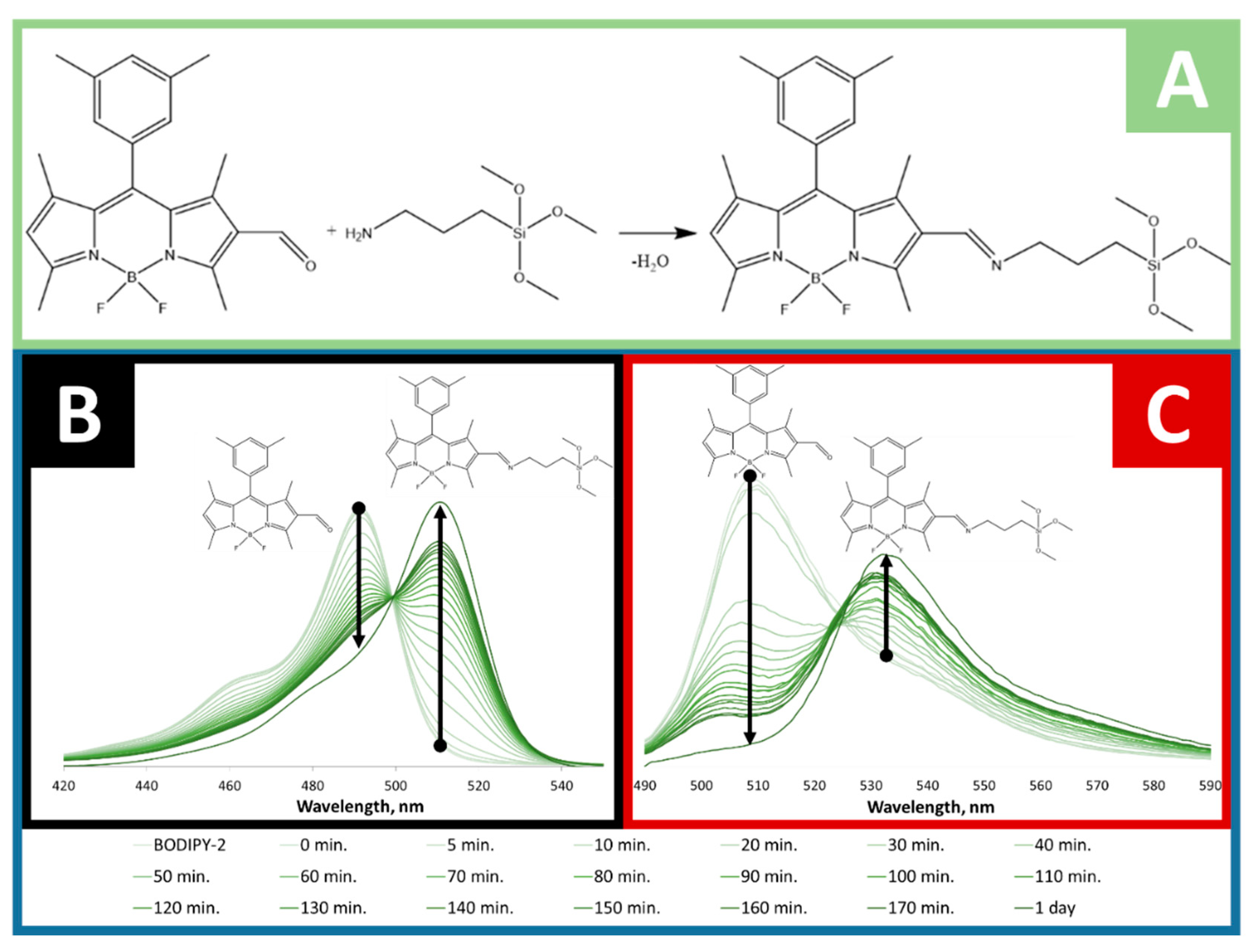
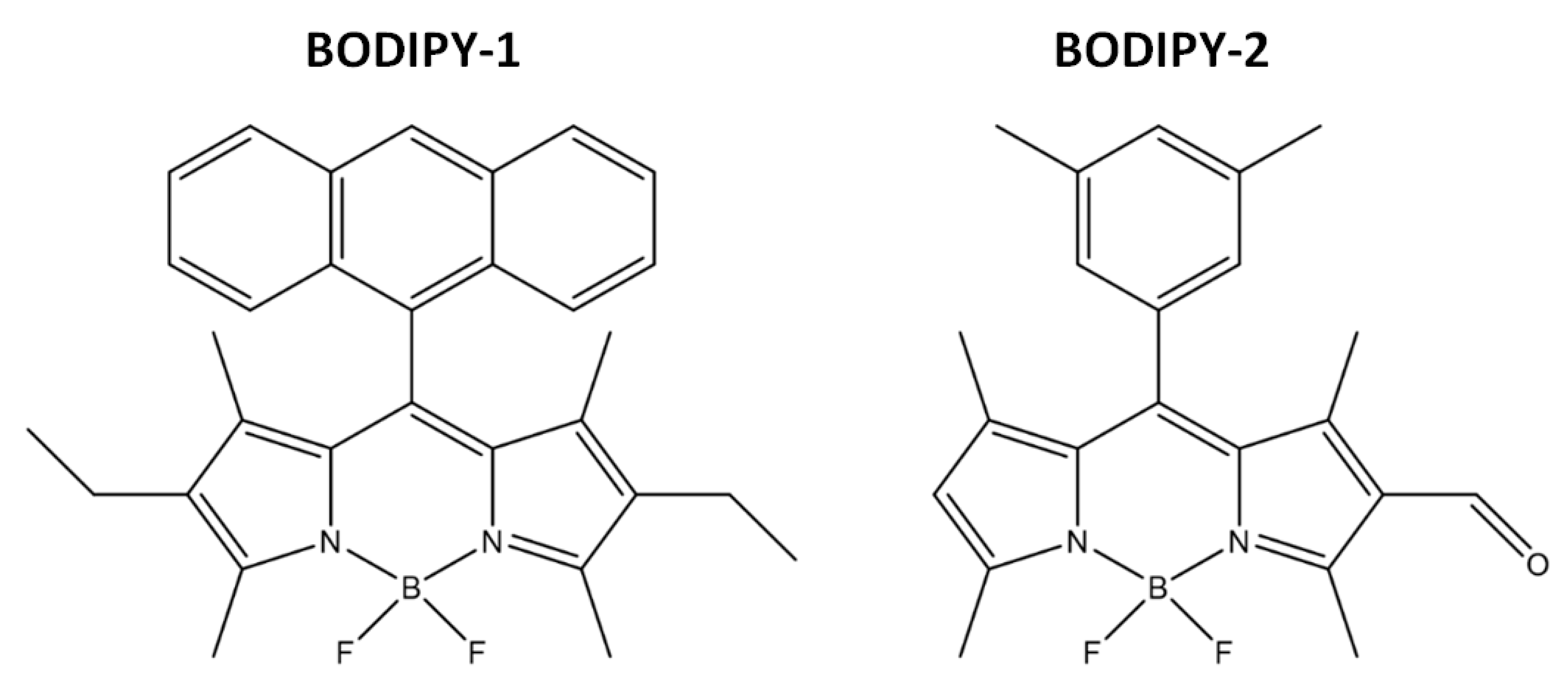
2.2. Conjugation of BODIPY-2 to APTMS and Its Spectral Properties
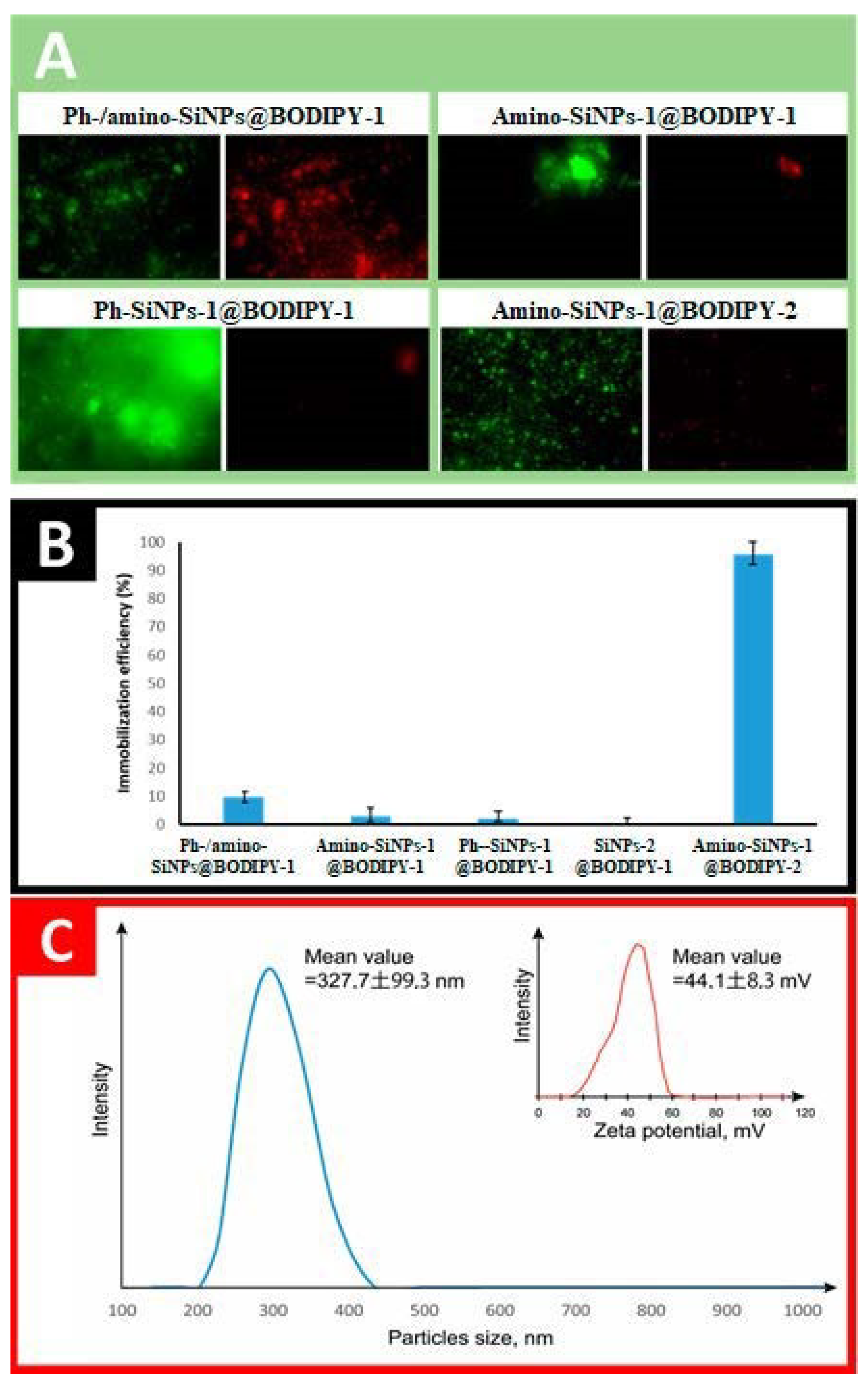
2.3. Conjugation of BODIPY-1 and BODIPY-2 with Silica-Based Materials and Its Characterization
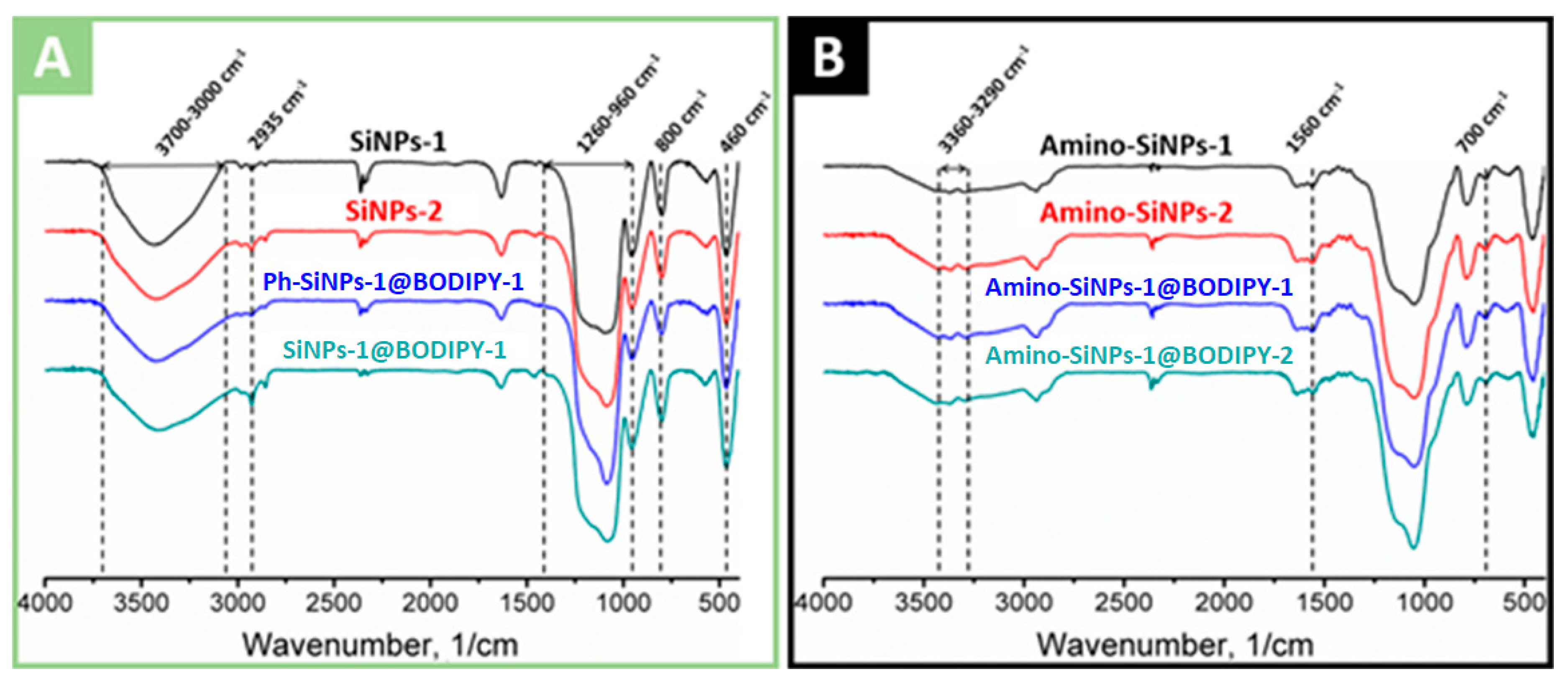
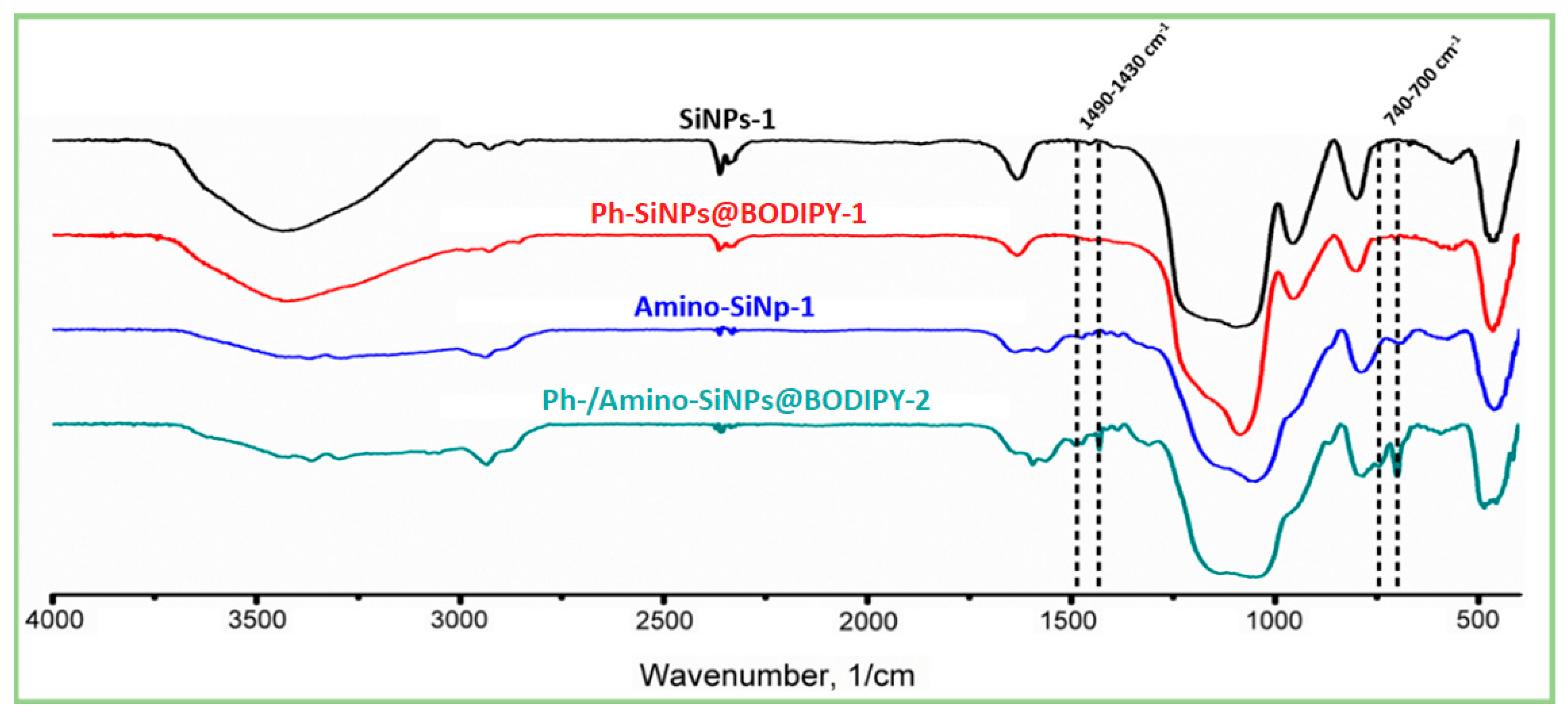
2.4. FTIR Spectra
2.5. Study of BODIPY-1 and BODIPY-2 Loading
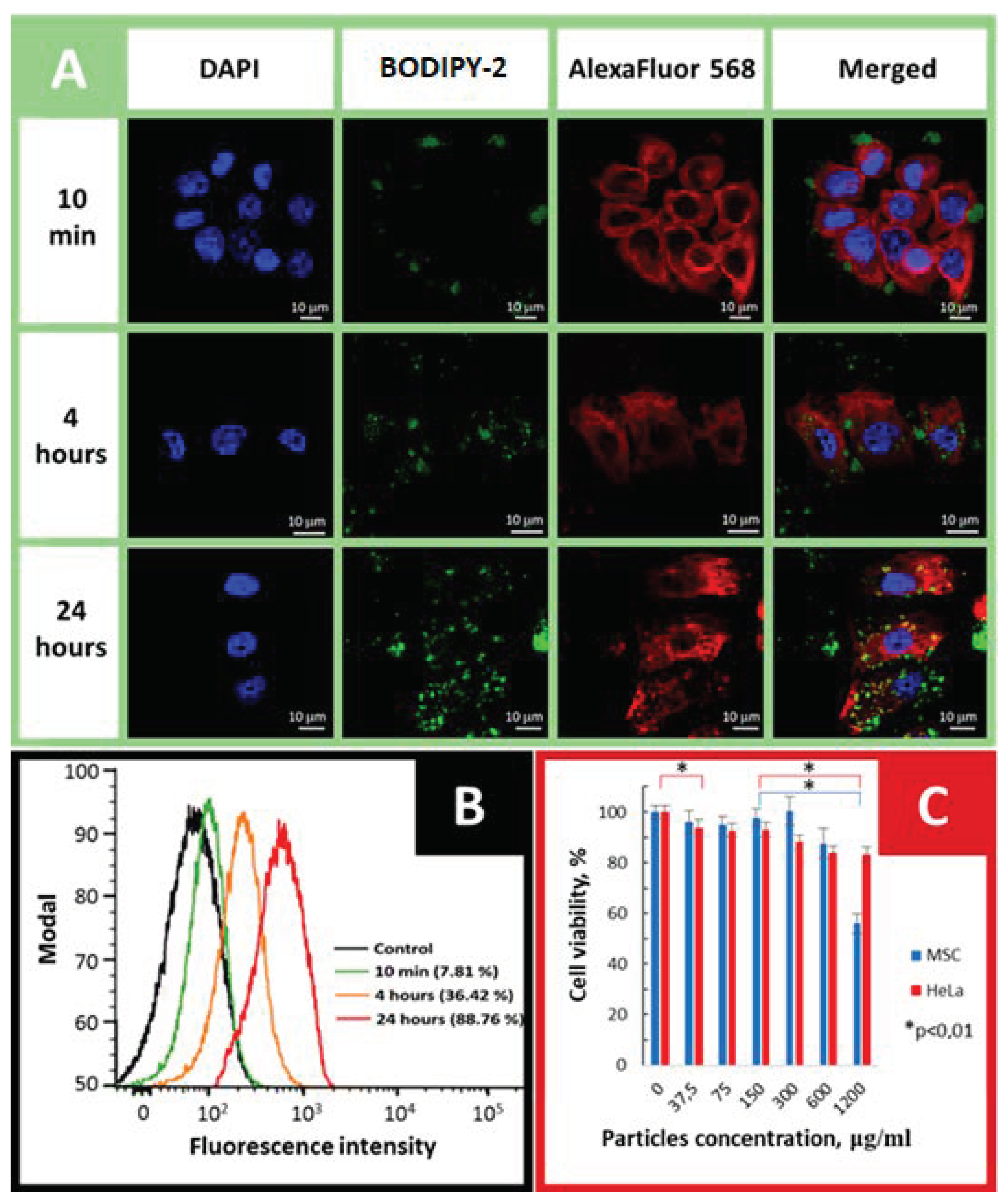
2.6. Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity Studies
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Synthesis of Silica-Based Materials Using Sol-Gel Method
4.3. Immobilization of BODIPY-1 and BODIPY-2 Into Silica-Based Materials
4.4. Samples Characterization
4.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.4.2. Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.4.3. Fluorescence Microscopy
4.4.4. UV–Vis and Fluorescence Spectra
4.5. Cell Culture
4.6. Incubation of HeLa Cells with BODIPY-Conjugated Silica Particles
4.7. Cell Viability Assay
4.8. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xing, T.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Lai, B.; Yan, L. Synthesis of polypeptide conjugated with near infrared fluorescence probe and doxorubicin for pH-responsive and image-guided drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 22290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, T.; Yang, X.; Fu, L.; Yan, L. Near infrared fluorescence probe and galactose conjugated amphiphilic copolymer for bioimaging of HepG2 cells and endocytosis. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Re Ko, N.; Kwon Oh, J. Recent advances in stimuli-responsive degradable block copolymer micelles: Synthesis and controlled drug delivery applications. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Woo, S.-K.; Kim, K.I.; Lee, T.S.; Kim, C.W.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, B.I.; Lim, S.M.; Lee, K.C.; Lee, Y.J. Simple Methods for Tracking Stem Cells with (64)Cu-Labeled DOTA-hexadecyl-benzoate. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Jeong, M.; Lee, H.; Goh, U.; Kim, H.; Kim, B.; Park, J.-H. Liposome-Based Engineering of Cells To Package Hydrophobic Compounds in Membrane Vesicles for Tumor Penetration. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 2938–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Bharatam, P.V. Pharmacoinformatic approaches to understand complexation of dendrimeric nanoparticles with drugs. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehi-Eromosele, C.O.; Ita, B.I.; Iweala, E.E.J. Silica coated LSMO magnetic nanoparticles for the pH-Responsive delivery of 5-Fluorouracil anticancer drug. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 530, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marfin, Y.S.; Solomonov, A.V.; Timin, A.S.; Rumyantsev, E.V. Recent Advances of Individual BODIPY and BODIPY-Based Functional Materials in Medical Diagnostics and Treatment. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 2745–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.; Liu, S.; Sun, T.; Guan, X.; Lin, W.; Xie, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jing, X. Near-Infrared Emitting Fluorescent BODIPY Nanovesicles for in Vivo Molecular Imaging and Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16166–16173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo, J.O.; Rusin, O.; Lim, S.; Strongin, R.M. NIR dyes for bioimaging applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Bloch, S.; Akers, W.; Achilefu, S. Near-infrared molecular probes for in vivo imaging. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umezawa, K.; Matsui, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Citterio, D.; Suzuki, K. Bright, color-tunable fluorescent dyes in the Vis/NIR region: Establishment of new “tailor-made” multicolor fluorophores based on borondipyrromethene. Chemistry 2009, 15, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J. Lipid, protein and poly(NIPAM) coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 207, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- e Oliveira, L.S.; Marçal, L.; Rocha, L.A.; de Faria, E.H.; Ciuffi, K.J.; Nassar, E.J.; Corrêa, I.C. Photoinitiator and anesthetic incorporation into mesoporous silica. Powder Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timin, A.S.; Muslimov, A.R.; Lepik, K.V.; Okilova, M.V.; Tcvetkov, N.Y.; Shakirova, A.I.; Afanasyev, B.V.; Gorin, D.A.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Intracellular Breakable and Ultrasound-Responsive Hybrid Microsized Containers for Selective Drug Release into Cancerous Cells. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2017, 34, 1600417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timin, A.S.; Solomonov, A.V.; Kumagai, A.; Miyawaki, A.; Khashirova, S.Y.; Zhansitov, A.; Rumyantsev, E.V. Magnetic polymer-silica composites as bioluminescent sensors for bilirubin detection. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 183, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhao, X.; Fang, W.; Chen, C.; Zheng, N. Self-templating synthesis of hollow mesoporous silica and their applications in catalysis and drug delivery. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-H.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-P. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timin, A.S.; Gao, H.; Voronin, D.V.; Gorin, D.A.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Inorganic/Organic Multilayer Capsule Composition for Improved Functionality and External Triggering. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1600338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.B.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.G.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, C.W.; Yu, J.S. Template synthesis of nanostructured silica with hollow core and mesoporous shell structures. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2006, 6, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Yu, S.H. Polyelectrolyte controlled large-scale synthesis of hollow silica spheres with tunable sizes and wall thicknesses. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 3641–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A. Functional Materials: From Hard to Soft Porous Frameworks. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8328–8344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, X.W.; Archer, L.A.; Yang, Z. Hollow Micro-/Nanostructures: Synthesis and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3987–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.K.; Lee, S.S.; Papaefthymiou, G.C.; Ying, J.Y. Nanoparticle Architectures Templated by SiO2/Fe2O3 Nanocomposites. Chem. Mater. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-Q.; Chen, B.-C.; Hong-Ping Lin, A.; Tang, C.-Y. Synthesis of Hollow Silica Spheres with Mesostructured Shell Using Cationic−Anionic-Neutral Block Copolymer Ternary Surfactants. Langmuir 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkhofs, S.; Willhammar, T.; Van, H.; Noortgate, D.; Kirschhock, C.E.A.; Breynaert, E.; Tendeloo, G.V.; Bals, S.; Martens, J.A. Self-Assembly of Pluronic F127-Silica Spherical Core−Shell Nanoparticles in Cubic Close-Packed Structures. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 5161–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kambara, K.; Shimura, N.; Ogawa, M. Larger Scale Syntheses of Surfactant-Templated Nanoporous Silica Spherical Particles by the Stöber Method. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 115, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Shi, J.; Chen, H.; Shen, W.; Dong, X. A facile method to synthesize novel hollow mesoporous silica spheres and advanced storage property. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 84, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lu, L.; Yang, Z.; Cool, P.; Vansant, E.F. Further investigations on the modified Stöber method for spherical MCM-41. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 97, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Chen, M.; Zhou, S.; Wu, L.; Ma, X. Fabrication of hollow silica spheres using droplet templates derived from a miniemulsion technique. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 321, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; He, B.; Gao, Z.; Li, J.; Shen, J.; Yang, W.; Yin, M. One-Pot Synthesis of Cy5-Encapsulated Photostable Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles for Bioimaging. Nano Life 2015, 05, 1540007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirashima, H.; Imai, H.; Fukui, Y. Structure of Hybrid Silica Gels Incorporated with Hydrophobic Dye Molecules. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2003, 26, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arap, W.; Pasqualini, R.; Montalti, M.; Petrizza, L.; Prodi, L.; Rampazzo, E.; Zaccheroni, N.; Marchiò, S. Luminescent silica nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2195–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, A.; Zhao, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. Bright and stable near-infrared Pluronic–silica nanoparticles as contrast agents for in vivo optical imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 5560–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Bengtsson, N.E.; Walter, G.A.; Sohn, H.-B.; Zhou, G.; Iwakuma, N.; Zeng, H.; Grobmyer, S.R.; Scott, E.W.; Moudgil, B.M. Gadolinium-Doped Silica Nanoparticles Encapsulating Indocyanine Green for Near Infrared and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Small 2012, 8, 2856–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera, E.G.; Livotto, P.R.; dos Santos, J.H.Z. Hybrid silica bearing different organosilanes produced by the modified Stöber method. Powder Technol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effati, E.; Pourabbas, B. One-pot synthesis of sub-50nm vinyl- and acrylate-modified silica nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Saltzman, W.M. Nonviral gene delivery: Thinking of silica. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 585–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambhrunkar, S.; Qu, Z.; Popat, A.; Yang, J.; Noonan, O.; Acauan, L.; Ahmad Nor, Y.; Yu, C.; Karmakar, S. Effect of surface functionality of silica nanoparticles on cellular uptake and cytotoxicity. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3642–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, S.; Treccani, L.; Dringen, R.; Rezwan, K. Modulation of Silica Nanoparticle Uptake into Human Osteoblast Cells by Variation of the Ratio of Amino and Sulfonate Surface Groups: Effects of Serum. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13821–13833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iturrioz-Rodríguez, N.; Correa-Duarte, M.A.; Fanarraga, M.L. Controlled drug delivery systems for cancer based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 3389–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Kim, B.-D.; Jo, S.; Park, S.; Son, J.; Hwang, S.; Dugasani, S.; Chang, I.; et al. Ternary and senary representations using DNA double-crossover tiles. Nanotechnology 2016, 10, 105601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doadrio, J.C.; Sousa, E.M.B.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Doadrio, A.L.; Perez-Pariente, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Functionalization of mesoporous materials with long alkyl chains as a strategy for controlling drug delivery pattern. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y. Aldehyde-functionalized dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles as potential nanocarriers for pH-responsive protein drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, T.; Lu, X. Controlled release of silyl ether camptothecin from thiol-ene click chemistry-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaharudin, N.S.; Mohamed Isa, E.D.; Ahmad, H.; Abdul Rahman, M.B.; Jumbri, K. Functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles templated by pyridinium ionic liquid for hydrophilic and hydrophobic drug release application. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugadoss, S.; Lison, D.; Godderis, L.; Van Den Brule, S.; Mast, J.; Brassinne, F.; Sebaihi, N.; Hoet, P.H. Toxicology of silica nanoparticles: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 2967–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch-Decker, S.; An, Z.; Yan, J.; Hansjosten, I.; Al-Rawi, M.; Peravali, R.; Diabaté, S.; Weiss, C. Silica Nanoparticles Provoke Cell Death Independent of p53 and BAX in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Napierska, D.; Thomassen, L.C.J.; Rabolli, V.; Lison, D.; Gonzalez, L.; Kirsch-Volders, M.; Martens, J.A.; Hoet, P.H. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of monodisperse silica nanoparticles in human endothelial cells. Small 2009, 5, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, E.; Ansari, L.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Charbgoo, F.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Silica based hybrid materials for drug delivery and bioimaging. J. Control. Release 2018, 277, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Almalik, A.; Khashab, N.M. Mesoporous Silica and Organosilica Nanoparticles: Physical Chemistry, Biosafety, Delivery Strategies, and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1700831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsiao, I.-L.; Gramatke, A.M.; Joksimovic, R.; Sokolowski, M.; Gradzielski, M.; Haase, A. Size and Cell Type Dependent Uptake of Silica Nanoparticles. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liao, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, P.; Guo, K.; Kong, J.; Ji, C.; Liu, B. Size-dependent cellular uptake efficiency, mechanism, and cytotoxicity of silica nanoparticles toward HeLa cells. Talanta 2013, 107, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timin, A.S.; Rumyantsev, E.V.; Solomonov, A.V.; Musabirov, I.I.; Sergeev, S.N.; Ivanov, S.P.; Berlier, G.; Balantseva, E. Preparation and characterization of organo-functionalized silicas for bilirubin removal. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 464, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfin, Y.S.; Merkushev, D.A.; Usoltsev, S.D.; Shipalova, M.V.; Rumyantsev, E.V. Fluorescent Properties of 8-Substituted BODIPY Dyes: Influence of Solvent Effects. J. Fluoresc. 2015, 25, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolemen, S.; Cakmak, Y.; Erten-Ela, S.; Altay, Y.; Brendel, J.; Thelakkat, M.; Akkaya, E.U. Solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells using red and near-IR absorbing bodipy sensitizers. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 3812–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goncharenko, A.A.; Tarasyuk, I.A.; Marfin, Y.S.; Grzhegorzhevskii, K.V.; Muslimov, A.R.; Bondarenko, A.B.; Lebedev, M.D.; Kuz’min, I.A.; Vashurin, A.S.; Lepik, K.V.; et al. DDAO Controlled Synthesis of Organo-Modified Silica Nanoparticles with Encapsulated Fluorescent Boron Dipyrrins and Study of Their Uptake by Cancerous Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 3802. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173802
Goncharenko AA, Tarasyuk IA, Marfin YS, Grzhegorzhevskii KV, Muslimov AR, Bondarenko AB, Lebedev MD, Kuz’min IA, Vashurin AS, Lepik KV, et al. DDAO Controlled Synthesis of Organo-Modified Silica Nanoparticles with Encapsulated Fluorescent Boron Dipyrrins and Study of Their Uptake by Cancerous Cells. Molecules. 2020; 25(17):3802. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173802
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoncharenko, Aleksandr A., Ilya A. Tarasyuk, Yuriy S. Marfin, Kirill V. Grzhegorzhevskii, Albert R. Muslimov, Andrey B. Bondarenko, Maxim D. Lebedev, Ilya A. Kuz’min, Artur S. Vashurin, Kirill V. Lepik, and et al. 2020. "DDAO Controlled Synthesis of Organo-Modified Silica Nanoparticles with Encapsulated Fluorescent Boron Dipyrrins and Study of Their Uptake by Cancerous Cells" Molecules 25, no. 17: 3802. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173802
APA StyleGoncharenko, A. A., Tarasyuk, I. A., Marfin, Y. S., Grzhegorzhevskii, K. V., Muslimov, A. R., Bondarenko, A. B., Lebedev, M. D., Kuz’min, I. A., Vashurin, A. S., Lepik, K. V., Timin, A. S., & Rumyantsev, E. V. (2020). DDAO Controlled Synthesis of Organo-Modified Silica Nanoparticles with Encapsulated Fluorescent Boron Dipyrrins and Study of Their Uptake by Cancerous Cells. Molecules, 25(17), 3802. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173802







