Memantine Derivatives as Multitarget Agents in Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Memantine and Cholinesterase Inhibitor Hybrids
2.1. Tacrine-Adamantanes Hybrids
2.2. Galantamine-Memantine Hybrids
2.3. Aminoadamantane-Carbazole/Tetrahydrocarbazole Hybrids
3. Memantine-Antioxidant Hybrids to Explore Neuroinflammation
3.1. Memantine-Ferulic Acid Hybrids
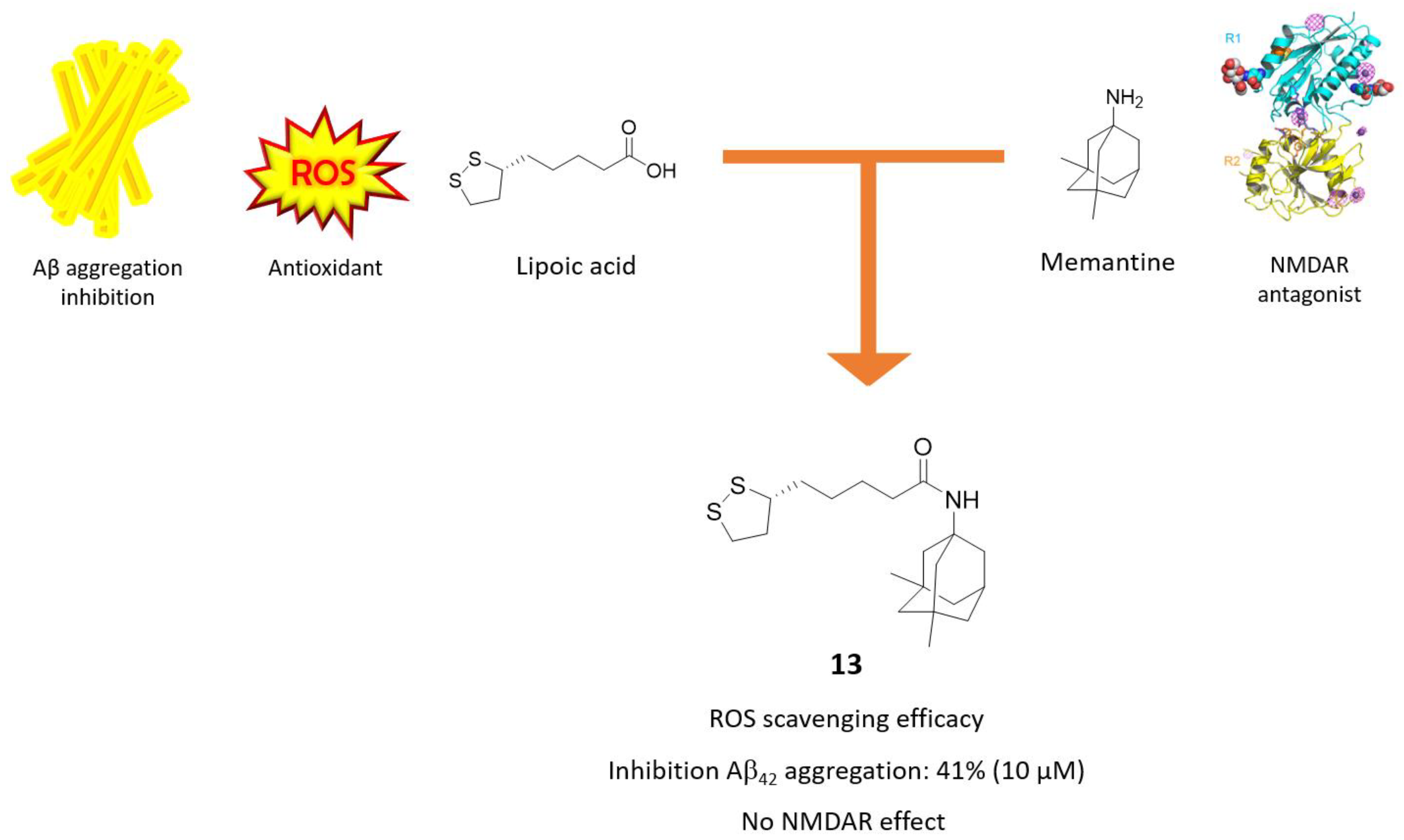
3.2. Memantine-Glutathione/Lipoic Acid Hybrids
3.3. Amantadine-Propargylamine Hybrids
4. Miscellaneous Memantine Derivatives
4.1. Memantine-Polyamine Conjugates
4.2. H2S-Releasing Memantine Prodrug
4.3. Dual P2X7-NMDA Receptor Antagonists
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parsons, M.P.; Raymond, L.A. Extrasynaptic NMDA receptor involvement in central nervous system disorders. Neuron 2014, 82, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Léveillé, F.; El Gaamouch, F.; Gouix, E.; Lecocq, M.; Lobner, D.; Nicole, O.; Buisson, A. Neuronal viability is controlled by a functional relation between synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 4258–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folch, J.; Busquets, O.; Ettcheto, M.; Sánchez-López, E.; Castro-Torres, R.D.; Verdaguer, E.; Garcia, M.L.; Olloquequi, J.; Casadesús, G.; Beas-Zarate, C.; et al. Memantine for the Treatment of Dementia: A Review on its Current and Future Applications. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 62, 1223–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, P.; Chen, H.S.; Zhang, D.; Lipton, S.A. Memantine preferentially blocks extrasynaptic over synaptic NMDA receptor currents in hippocampal autapses. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 11246–11250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lipton, S.A. Pathologically activated therapeutics for neuroprotection. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Xia, P.; Cui, J.; Talantova, M.; Bodhinathan, K.; Li, W.; Saleem, S.; Holland, E.A.; Tong, G.; Piña-Crespo, J.; et al. Pharmacologically targeted NMDA receptor antagonism by NitroMemantine for cerebrovascular disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipton, S.A. Paradigm shift in neuroprotection by NMDA receptor blockade: Memantine and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.G.; Danysz, W.; Dekundy, A.; Pulte, I. Memantine and cholinesterase inhibitors: Complementary mechanisms in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotox. Res. 2013, 24, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnham, K.J.; Bush, A.I. Biological metals and metal-targeting compounds in major neurodegenerative diseases. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6727–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, M.A.; Chand, K.; Chaves, S. Recent progress in multifunctional metal chelators as potential drugs for Alzheimer’s disease. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 327–328, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, S. NMDA receptor activity regulates transcription of antioxidant pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 381–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Lipton, S.A. Preventing Ca2+-mediated nitrosative stress in neurodegenerative diseases: Possible pharmacological strategies. Cell Calcium 2010, 47, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kodis, E.J.; Choi, S.; Swanson, E.; Ferreira, G.; Bloom, G.S. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated calcium influx connects amyloid-β oligomers to ectopic neuronal cell cycle reentry in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Okamoto, S.; Lipton, S.A.; Xu, H. Oligomeric Aβ-induced synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2014, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banks, W.A. A Spectrum of Topics for 2019: Advances in Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress, Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Cardiovascular Disease, Autism, Exosomes, and Central Nervous System Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosini, M.; Simoni, E.; Minarini, A.; Melchiorre, C. Multi-target design strategies in the context of Alzheimer’s disease: Acetylcholinesterase inhibition and NMDA receptor antagonism as the driving forces. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 1914–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosini, M.; Simoni, E.; Caporaso, R.; Minarini, A. Multitarget strategies in Alzheimer’s disease: Benefits and challenges on the road to therapeutics. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosini, M. Polypharmacology: The rise of multitarget drugs over combination therapies. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colović, M.B.; Krstić, D.Z.; Lazarević-Pašti, T.D.; Bondžić, A.M.; Vasić, V.M. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Pharmacology and toxicology. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Sun, H. Recent progress in the identification of selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 132, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korabecny, J.; Spilovska, K.; Mezeiova, E.; Benek, O.; Juza, R.; Kaping, D.; Soukup, O. A Systematic Review on Donepezil-based Derivatives as Potential Cholinesterase Inhibitors for Alzheimers Disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 5625–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; He, S.; Chen, Y.; Feng, F.; Qu, W.; Sun, H. Donepezil-based multi-functional cholinesterase inhibitors for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchekina, S.V.; Kots, E.D.; Novichkova, D.A.; Petrov, K.A.; Masson, P. Role of Acetylcholinesterase in beta-amyloid Aggregation Studied by Accelerated Molecular Dynamics. BioNanoScience 2017, 7, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Stiller, C.; Endres, E.; Scheiner, M.; Gunesch, S.; Sotriffer, C.; Maurice, T.; Decker, M. Highly Selective Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors with Tunable Duration of Action by Chemical Modification of Transferable Carbamate Units Exhibit Pronounced Neuroprotective Effect in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 9116–9140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horak, M.; Holubova, K.; Nepovimova, E.; Krusek, J.; Kaniakova, M.; Korabecny, J.; Vyklicky, L.; Kuca, K.; Stuchlik, A.; Ricny, J.; et al. The pharmacology of tacrine at N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 75, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, A.; Cacabelos, R.; Oset-Gasque, M.J.; Samadi, A.; Marco-Contelles, J. Novel tacrine-related drugs as potential candidates for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancar, M.; Ho, K.; Mohid, S.A.; Thai, N.Q.; Bednarikova, Z.; Nguyen, H.L.; Bhunia, A.; Nepovimova, E.; Li, M.S.; Gazova, Z. 7-Methoxytacrine and 2-Aminobenzothiazole Heterodimers: Structure-Mechanism Relationship of Amyloid Inhibitors Based on Rational Design. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misik, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Pejchal, J.; Kassa, J.; Korabecny, J.; Soukup, O. Cholinesterase Inhibitor 6-Chlorotacrine—In Vivo Toxicological Profile and Behavioural Effects. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilovska, K.; Korabecny, J.; Kral, J.; Horova, A.; Musilek, K.; Soukup, O.; Drtinova, L.; Gazova, Z.; Siposova, K.; Kuca, K. 7-Methoxytacrine-adamantylamine heterodimers as cholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer’s disease treatment--synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modeling studies. Molecules 2013, 18, 2397–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilovska, K.; Korabecny, J.; Horova, A.; Musilek, K.; Nepovimova, E.; Drtinova, L.; Gazova, Z.; Siposova, K.; Dolezal, R.; Jun, D.; et al. Design, synthesis and in vitro testing of 7-methoxytacrine-amantadine analogues: A novel cholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Chem. Res. 2015, 24, 2645–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazova, Z.; Soukup, O.; Sepsova, V.; Siposova, K.; Drtinova, L.; Jost, P.; Spilovska, K.; Korabecny, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Fedunova, D.; et al. Multi-target-directed therapeutic potential of 7-methoxytacrine-adamantylamine heterodimers in the Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyklicky, V.; Smejkalova, T.; Krausova, B.; Balik, A.; Korinek, M.; Borovska, J.; Horak, M.; Chvojkova, M.; Kleteckova, L.; Vales, K.; et al. Preferential Inhibition of Tonically over Phasically Activated NMDA Receptors by Pregnane Derivatives. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 2161–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniakova, M.; Nepovimova, E.; Kleteckova, L.; Skrenkova, K.; Holubova, K.; Chrienova, Z.; Hepnarova, V.; Kucera, T.; Kobrlova, T.; Vales, K.; et al. Combination of Memantine and 6-Chlorotacrine as Novel Multi-Target Compound against Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2019, 16, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde, E.; Sureda, F.X.; Vázquez, S. Novel benzopolycyclic amines with NMDA receptor antagonist activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 2678–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Areales, F.J.; Turcu, A.L.; Barniol-Xicota, M.; Pont, C.; Pivetta, D.; Espargaró, A.; Bartolini, M.; De Simone, A.; Andrisano, V.; Pérez, B.; et al. A novel class of multitarget anti-Alzheimer benzohomoadamantane‒chlorotacrine hybrids modulating cholinesterases and glutamate NMDA receptors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 180, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, M.D.; Alkondon, M.; Pereira, E.F.; Aracava, Y.; Eisenberg, H.M.; Maelicke, A.; Albuquerque, E.X. The nicotinic allosteric potentiating ligand galantamine facilitates synaptic transmission in the mammalian central nervous system. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi, S.; Marszalec, W.; Zhao, X.; Yeh, J.Z.; Narahashi, T. Mechanism of action of galantamine on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat cortical neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 310, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGehee, D.S.; Heath, M.J.; Gelber, S.; Devay, P.; Role, L.W. Nicotine enhancement of fast excitatory synaptic transmission in CNS by presynaptic receptors. Science 1995, 269, 1692–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.P.; Tarozzo, G.; Reggiani, A.; Piomelli, D.; Cavalli, A. Galantamine potentiates the neuroprotective effect of memantine against NMDA-induced excitotoxicity. Brain Behav. 2013, 3, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, E.; Daniele, S.; Bottegoni, G.; Pizzirani, D.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Goldoni, L.; Tarozzo, G.; Reggiani, A.; Martini, C.; Piomelli, D.; et al. Combining galantamine and memantine in multitargeted, new chemical entities potentially useful in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 9708–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reggiani, A.M.; Simoni, E.; Caporaso, R.; Meunier, J.; Keller, E.; Maurice, T.; Minarini, A.; Rosini, M.; Cavalli, A. In Vivo Characterization of ARN14140, a Memantine/Galantamine-Based Multi-Target Compound for Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, M.; Merino, V.; Rosini, M.; Cavalli, A.; Kalia, Y.N. Controlled Iontophoretic Delivery in vitro and in vivo of ARN14140—A Multitarget Compound for Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 3460–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saturnino, C.; Iacopetta, D.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Rosano, C.; Caruso, A.; Caporale, A.; Marra, N.; Marengo, B.; Pronzato, M.A.; Parisi, O.I.; et al. N-alkyl carbazole derivatives as new tools for Alzheimer’s disease: Preliminary studies. Molecules 2014, 19, 9307–9317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieper, A.A.; McKnight, S.L.; Ready, J.M. P7C3 and an unbiased approach to drug discovery for neurodegenerative diseases. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6716–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubdar, N.; Golshani, M.; Jalili-Baleh, L.; Nadri, H.; Küçükkilinç, T.T.; Ayazgök, B.; Moradi, A.; Moghadam, F.H.; Abdolahi, Z.; Ameri, A.; et al. New classes of carbazoles as potential multi-functional anti-Alzheimer’s agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 91, 103164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadian, R.; Nadri, H.; Moradi, A.; Bukhari, S.N.A.; Mahdavi, M.; Asadi, M.; Akbarzadeh, T.; Khaleghzadeh-Ahangar, H.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Amini, M. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of selective and potent Carbazole-based butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4952–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachurin, S.O.; Shevtsova, E.F.; Makhaeva, G.F.; Grigoriev, V.V.; Boltneva, N.P.; Kovaleva, N.V.; Lushchekina, S.V.; Shevtsov, P.N.; Neganova, M.E.; Redkozubova, O.M.; et al. Novel conjugates of aminoadamantanes with carbazole derivatives as potential multitarget agents for AD treatment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballatore, C.; Brunden, K.R.; Huryn, D.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.; Smith, A.B. Microtubule stabilizing agents as potential treatment for Alzheimer’s disease and related neurodegenerative tauopathies. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 8979–8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Feng, J.; Wu, M. Dysfunction of NMDA receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokolov, V.B.; Aksinenko, A.Y.; Goreva, T.V.; Epishina, T.A.; Grigor’ev, V.V.; Gabrel’yan, A.V.; Vinogradova, D.V.; Neganova, M.E.; Shevtsova, E.F.; Bachurin, S.O. Molecular design of multitarget neuroprotectors 3. Synthesis and bioactivity of tetrahydrocarbazole-aminoadamantane conjugates. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2016, 65, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bernhardi, R.; Eugenín-von Bernhardi, L.; Eugenín, J. Microglial cell dysregulation in brain aging and neurodegeneration. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benchekroun, M.; Romero, A.; Egea, J.; León, R.; Michalska, P.; Buendía, I.; Jimeno, M.L.; Jun, D.; Janockova, J.; Sepsova, V.; et al. The Antioxidant Additive Approach for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy: New Ferulic (Lipoic) Acid Plus Melatonin Modified Tacrines as Cholinesterases Inhibitors, Direct Antioxidants, and Nuclear Factor (Erythroid-Derived 2)-Like 2 Activators. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 9967–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosini, M.; Simoni, E.; Caporaso, R.; Basagni, F.; Catanzaro, M.; Abu, I.F.; Fagiani, F.; Fusco, F.; Masuzzo, S.; Albani, D.; et al. Merging memantine and ferulic acid to probe connections between NMDA receptors, oxidative stress and amyloid-β peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 180, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalili-Baleh, L.; Forootanfar, H.; Küçükkılınç, T.T.; Nadri, H.; Abdolahi, Z.; Ameri, A.; Jafari, M.; Ayazgok, B.; Baeeri, M.; Rahimifard, M.; et al. Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel multi-target-directed ligands for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease based on coumarin and lipoic acid scaffolds. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 152, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A.; Simon, M.C. Glutathione metabolism in cancer progression and treatment resistance. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 2291–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tibullo, D.; Li Volti, G.; Giallongo, C.; Grasso, S.; Tomassoni, D.; Anfuso, C.D.; Lupo, G.; Amenta, F.; Avola, R.; Bramanti, V. Biochemical and clinical relevance of alpha lipoic acid: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity, molecular pathways and therapeutic potential. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 66, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Hirohata, M.; Yamada, M. Alpha-lipoic acid exhibits anti-amyloidogenicity for beta-amyloid fibrils in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 341, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozio, P.; Cerasa, L.S.; Laserra, S.; Cacciatore, I.; Cornacchia, C.; Di Filippo, E.S.; Fulle, S.; Fontana, A.; Di Crescenzo, A.; Grilli, M.; et al. Memantine-sulfur containing antioxidant conjugates as potential prodrugs to improve the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonson, D.E.; Binda, C. Monoamine Oxidases. In Membrane Protein Complexes: Structure and Function; Harris, J.R., Boekema, E.J., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2018; pp. 117–140. [Google Scholar]
- Schedin-Weiss, S.; Inoue, M.; Hromadkova, L.; Teranishi, Y.; Yamamoto, N.G.; Wiehager, B.; Bogdanovic, N.; Winblad, B.; Sandebring-Matton, A.; Frykman, S.; et al. Monoamine oxidase B is elevated in Alzheimer disease neurons, is associated with γ-secretase and regulates neuronal amyloid β-peptide levels. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, J.; Geldenhuys, W.J.; Van der Schyf, C.J.; Oliver, D.W.; Kruger, H.G.; Govender, T.; Malan, S.F. Polycyclic cage structures as lipophilic scaffolds for neuroactive drugs. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zindo, F.T.; Barber, Q.R.; Joubert, J.; Bergh, J.J.; Petzer, J.P.; Malan, S.F. Polycyclic propargylamine and acetylene derivatives as multifunctional neuroprotective agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 80, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sestito, S.; Daniele, S.; Pietrobono, D.; Citi, V.; Bellusci, L.; Chiellini, G.; Calderone, V.; Martini, C.; Rapposelli, S. Memantine prodrug as a new agent for Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumamoto, T.; Nakajima, M.; Uga, R.; Ihayazaka, N.; Kashihara, H.; Katakawa, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Saiki, R.; Nishimura, K.; Igarashi, K. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of polyamine-memantine hybrids as NMDA channel blockers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karoutzou, O.; Kwak, S.H.; Lee, S.D.; Martínez-Falguera, D.; Sureda, F.X.; Vázquez, S.; Kim, Y.C.; Barniol-Xicota, M. Towards a Novel Class of Multitarget-Directed Ligands: Dual P2X7-NMDA Receptor Antagonists. Molecules 2018, 23, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, L.; Sugiyama, H.; Takigawa, M.; Katagiri, D.; Tomitori, H.; Nishimura, K.; Kaur, N.; Phanstiel, O.; Kitajima, M.; Takayama, H.; et al. Comparative studies of anthraquinone- and anthracene-tetraamines as blockers of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 320, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takayama, H.; Yaegashi, Y.; Kitajima, M.; Han, X.; Nishimura, K.; Okuyama, S.; Igarashi, K. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of tricyclic heterocycle-tetraamine conjugates as potent NMDA channel blockers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 4729–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saiki, R.; Yoshizawa, Y.; Minarini, A.; Milelli, A.; Marchetti, C.; Tumiatti, V.; Toida, T.; Kashiwagi, K.; Igarashi, K. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of polymethylene tetraamine derivatives as NMDA receptor channel blockers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3901–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestito, S.; Nesi, G.; Pi, R.; Macchia, M.; Rapposelli, S. Hydrogen Sulfide: A Worthwhile Tool in the Design of New Multitarget Drugs. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basagni, F.; Lanni, C.; Minarini, A.; Rosini, M. Lights and shadows of electrophile signaling: Focus on the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shefa, U.; Yeo, S.G.; Kim, M.S.; Song, I.O.; Jung, J.; Jeong, N.Y.; Huh, Y. Role of Gasotransmitters in Oxidative Stresses, Neuroinflammation, and Neuronal Repair. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1689341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Physiological role of hydrogen sulfide and polysulfide in the central nervous system. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 63, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, Y.; Tsugane, M.; Oka, J.; Kimura, H. Hydrogen sulfide induces calcium waves in astrocytes. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieślak, M.; Wojtczak, A. Role of purinergic receptors in the Alzheimer’s disease. Purinergic Signal. 2018, 14, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deussing, J.M.; Arzt, E. P2X7 Receptor: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Depression? Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, R.; Krautloher, A.; Ramírez-Fernández, A.; Nicke, A. P2X7 Interactions and Signaling—Making Head or Tail of It. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, L.; Woods, L.T.; Khalafalla, M.G.; Weisman, G.A. Purinergic signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 151, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.; Amar, M.; Dalle, C.; Youssef, I.; Boucher, C.; Le Duigou, C.; Brückner, M.; Prigent, A.; Sazdovitch, V.; Halle, A.; et al. New role of P2X7 receptor in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Illes, P.; Rubini, P.; Ulrich, H.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, Y. Regulation of Microglial Functions by Purinergic Mechanisms in the Healthy and Diseased CNS. Cells 2020, 9, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic signalling and disorders of the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Ding, X.; Khan, T.M.; Rong, W.; Franke, H.; Illes, P. P2X7 receptor-sensitivity of astrocytes and neurons in the substantia gelatinosa of organotypic spinal cord slices of the mouse depends on the length of the culture period. Neuroscience 2017, 349, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marotta, G.; Basagni, F.; Rosini, M.; Minarini, A. Memantine Derivatives as Multitarget Agents in Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2020, 25, 4005. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25174005
Marotta G, Basagni F, Rosini M, Minarini A. Memantine Derivatives as Multitarget Agents in Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules. 2020; 25(17):4005. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25174005
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarotta, Giambattista, Filippo Basagni, Michela Rosini, and Anna Minarini. 2020. "Memantine Derivatives as Multitarget Agents in Alzheimer’s Disease" Molecules 25, no. 17: 4005. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25174005
APA StyleMarotta, G., Basagni, F., Rosini, M., & Minarini, A. (2020). Memantine Derivatives as Multitarget Agents in Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules, 25(17), 4005. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25174005