PET Radiotracers for CNS-Adrenergic Receptors: Developments and Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Receptor | Distribution | Distinct Functions and Associated Disorders | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α1 | α1A | High levels in olfactory system, hypothalamic nuclei, and brainstem. Moderate levels in amygdala, cerebral cortex, and cerebellum | Involved in neurotransmission of NE as well as γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and NMDA. May mediate effects of anti-depressants in treating depression and obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) | [18,20,21,22,23,24] |
| α1B | Thalamic nuclei, lateral nucleus of amygdala, cerebral cortex, some septal regions, brain stem regions | May play a role in behavioral activation. Associated with addiction, and neurodegenerative disorders (Multiple System Atrophy) | [18,20,21,24,25,26,27] | |
| α1D | Olfactory bulb, cerebral cortex, hippocampus, reticular thalamic nuclei, and amygdala | Mediates changes in locomotor behaviors. Associated with stress. | [18,20,23,28,29] | |
| α2 | α2A | Locus coeruleus, midbrain, hypothalamus, amygdala, cerebral cortex, and brain stem | Mediate functions of most of the α2-agonists used in sedation, antinociception, and behavioral actions. Associated with ADHD, anxiety | [18,23,30,31,32,33,34,35] |
| α2B | Thalamus, hypothalamus, cerebellar Purkinje layer | Mediate antinociceptive action of nitrous oxide | [18,30,31] | |
| α2C | Hippocampus, striatum, olfactory tubercle, medulla, and basal ganglia | Involved in the neuronal release of NE as well as dopamine and serotonin. Potential therapeutic targets in depression & schizophrenia | [18,30,31,36,37,38,39] | |
| β | β1 | Homologous distribution. Expression was found (mostly β1 and β2) in frontal cortex, striatum, thalamus, putamen, amygdala, cerebellum, cerebral cortex and hippocampus. | Essential to motor learning, emotional memory storage and regulation of neuronal regeneration. Associated with mood disorders, aging, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease. | [16,18,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48] |
| β2 | ||||
| β3 | ||||
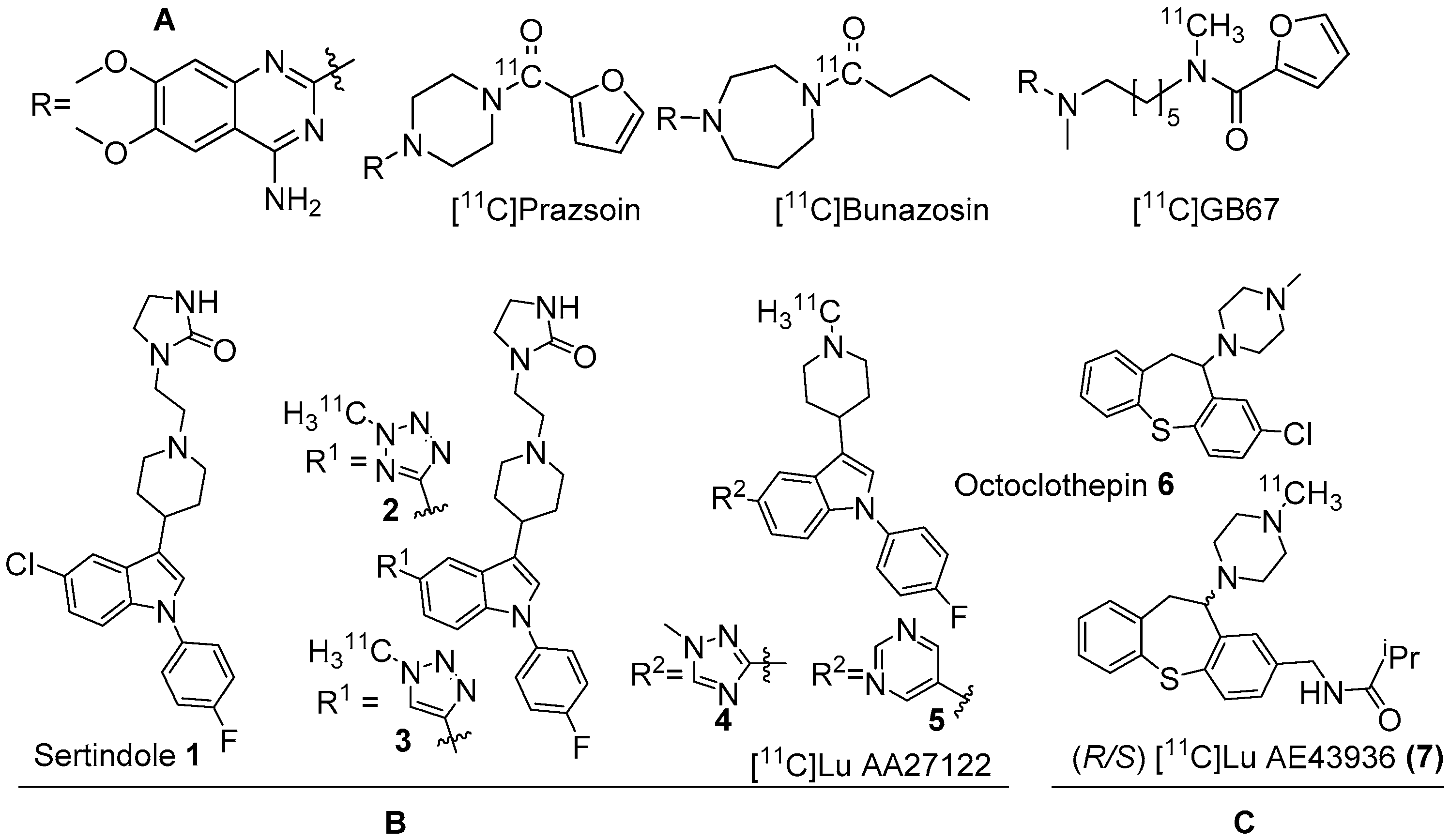
2. α1-AR PET Radiotracers
3. α2-AR Subtype and Nonspecific PET Radiotracers
3.1. α2A-Specific PET Radiotracers
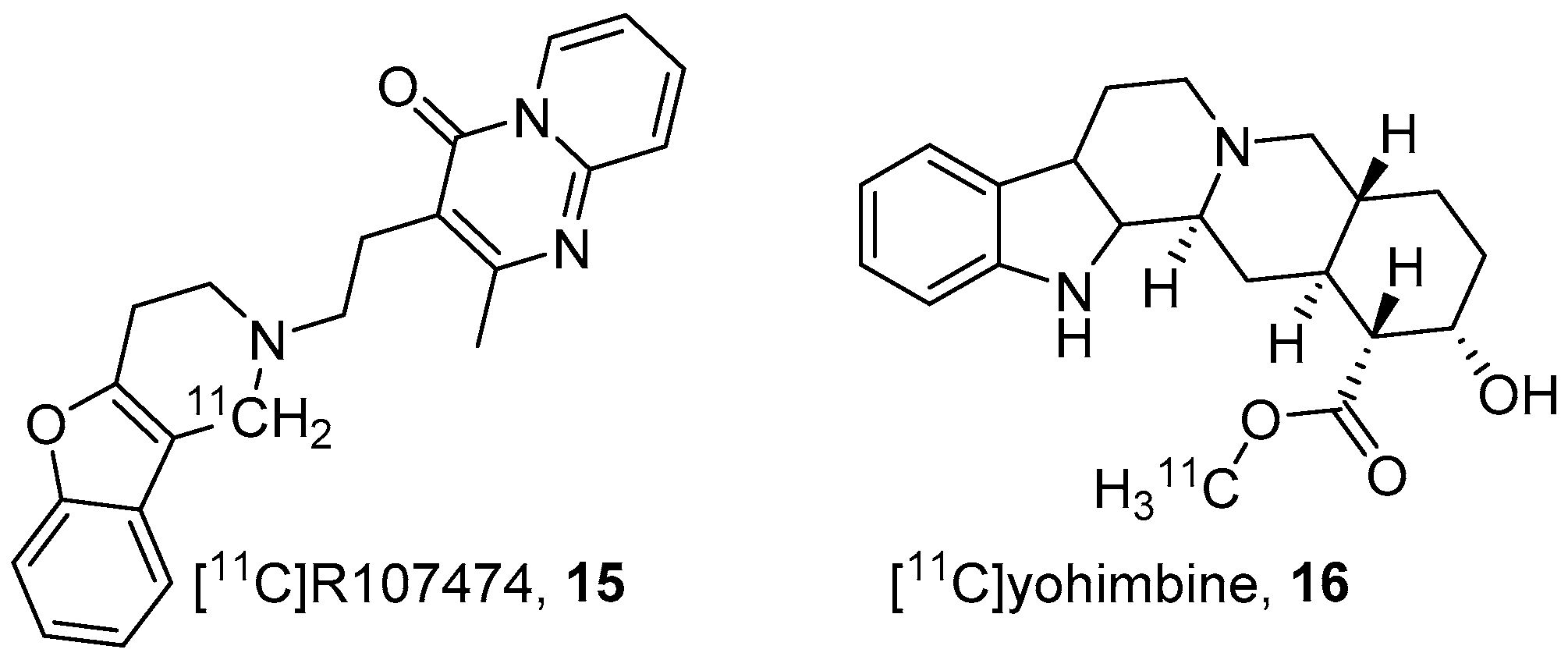
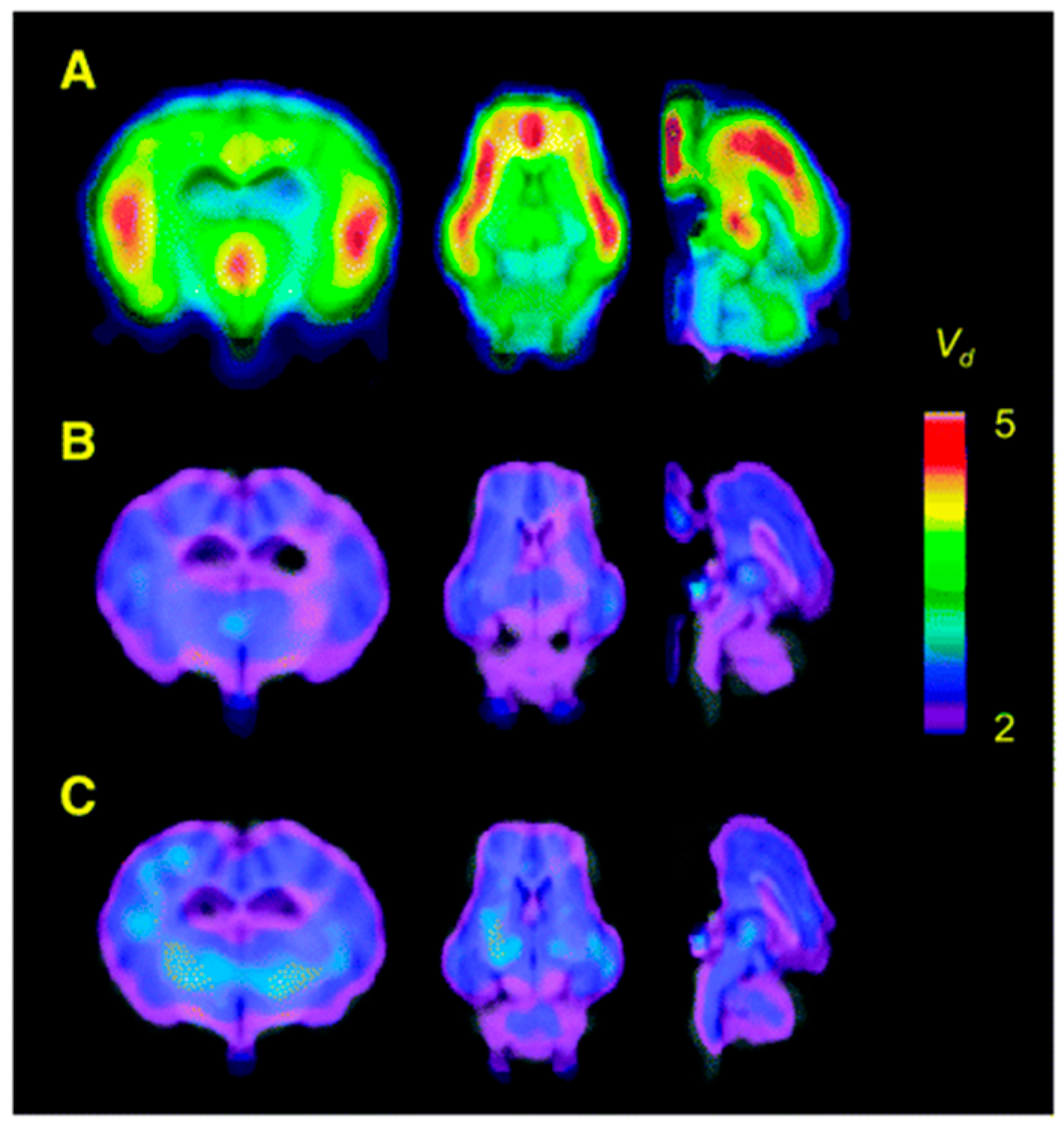
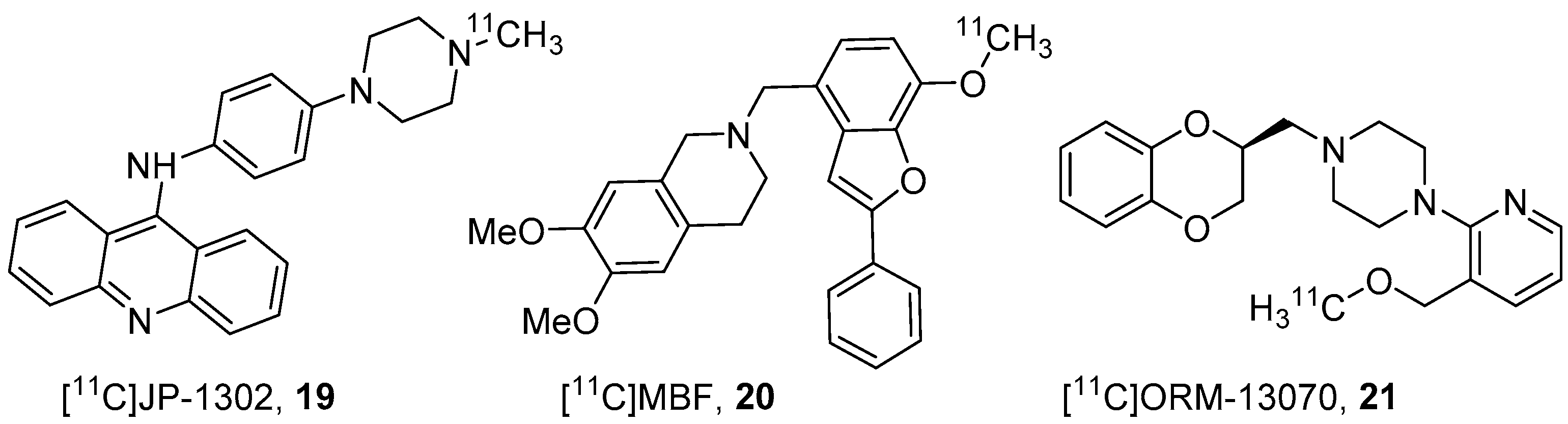
3.2. α2C-Specific PET Radiotracers
4. β-ARs and Nonselective PET Radiotracers
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scott, J.A. Positron Emission Tomography: Basic Science and Clinical Practice. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2004, 182, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Kumar, U. Positron emission tomography: An overview. J. Med. Phys. 2006, 31, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCluskey, S.P.; Plisson, C.; Rabiner, E.A.; Howes, O. Advances in CNS PET: The state-of-the-art for new imaging targets for pathophysiology and drug development. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 451–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankovic, Z. CNS Drug Design: Balancing Physicochemical Properties for Optimal Brain Exposure. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 2584–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adenot, M.; Lahana, R. Blood-Brain Barrier Permeation Models: Discriminating between Potential CNS and Non-CNS Drugs Including P-Glycoprotein Substrates. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2004, 44, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agdeppa, E.D.; Spilker, M.E. A review of imaging agent development. AAPS J. 2009, 11, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.S.; Mann, J. PET Tracers for Serotonin Receptors and Their Applications. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunphy, M.P.S.; Lewis, J.S. Radiopharmaceuticals in preclinical and clinical development for monitoring of therapy with PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneader, W. The discovery and synthesis of epinephrine. Drug News Perspect. 2001, 14, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, G. Epinephrine: A short history. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 350–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.T.; Weinshenker, D. Adrenaline rush: The role of adrenergic receptors in stimulant-induced behaviors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhofer, G.; Kopin, I.J.; Goldstein, D.S. Catecholamine metabolism: A contemporary view with implications for physiology and medicine. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirshner, N. Biosynthesis of adrenaline and noradrenaline. Pharmacol. Rev. 1959, 11, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flatmark, T. Catecholamine biosynthesis and physiological regulation in neuroendocrine cells. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2000, 168, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar-Slamloo, Y.; Fazlali, Z. Dopamine and Noradrenaline in the Brain; Overlapping or Dissociate Functions? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strosberg, A.D. Structure, function, and regulation of adrenergic receptors. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlquist, R.P. A study of the adrenotropic receptors. Am. J. Physiol. 1948, 153, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, M.; Hein, L. Adrenergic receptor knockout mice: Distinct functions of 9 receptor subtypes. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 101, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Bylund, B.; Lefkowitz, J.; Eikenburg, C.; Ruffolo, R.; Langer, Z.; Minneman, P. International Union of Pharmacology X. Recommendation for Nomenclature of adrenoreceptors: Consensus update. Am. Soc. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 47, 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Day, H.E.W.; Campeau, S.; Watson, S.J.; Akil, H. Distribution of α(1a)-, α(1b)- and α(1d)-adrenergic receptor mRNA in the rat brain and spinal cord. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1997, 13, 115–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doze, V.A.; Handel, E.M.; Jensen, K.A.; Darsie, B.; Luger, E.J.; Haselton, J.R.; Talbot, J.N.; Rorabaugh, B.R. α1A- and α1B-adrenergic receptors differentially modulate antidepressant-like behavior in the mouse. Brain Res. 2009, 1285, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, A. Characterization of a1-Adrenergic Receptor Subtypes in Rat Brain: A Reevaluation of [3H] WB41 04 and [3H] Prazosin Binding. Pharmacol. Exet. Am. Chem. Sciety Pharmacol. Experiemntal Ther. 1986, 29, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Reader, T.A.; Brière, R.; Grondin, L. Alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenoceptor binding in cerebral cortex: Competition studies with [3H]prazosin and [3H]idazoxan. J. Neural Transm. 1987, 68, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouin, C.; Darracq, L.; Trovero, F.; Blanc, G.; Glowinski, J.; Cotecchia, S.; Tassin, J.P. α1b-Adrenergic Receptors Control Locomotor and Rewarding Effects of Psychostimulants and Opiates. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 2873–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuscik, M.J.; Sands, S.; Ross, S.A.; Waugh, D.J.J.; Gaivin, R.J.; Morilak, D.; Perez, D.M. Overexpression of the α(1B)-adrenergic receptor causes apoptotic neurodegeneration: Multiple system atrophy. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, R.; Ohmori, E.; Isogaya, M.; Moriwaki, M.; Kumagai, H. Design and synthesis of selective α1B adrenoceptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 4045–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreng, M.; Cotecchia, S.; Schenk, F. A behavioral study of alpha-1b adrenergic receptor knockout mice: Increased reaction to novelty and selectively reduced learning capacities. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2001, 75, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadalge, A.; Coughlin, L.; Fu, H.; Wang, B.; Valladares, O.; Valentino, R.; Blendy, J.A. A1D Adrenoceptor Signaling Is Required for Stimulus Induced Locomotor Activity. Mol. Psychiatry 2003, 8, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckner, S.A.; Milicic, I.; Daza, A.; Lynch, J.J.; Kolasa, T.; Nakane, M.; Sullivan, J.P.; Brioni, J.D. A-315456: A selective α1D-adrenoceptor antagonist with minimal dopamine D2 and 5-HT1A receptor affinity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 433, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, C.; Limbird, L.E. Localization and trafficking of α2-adrenergic receptor subtypes in cells and tissues. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 84, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, M.; García-Sevilla, J.A. α 2-Adrenoceptor Subtypes Identified by [3H]RX821002 Binding in the Human Brain: The Agonist Guanoxabenz Does Not Discriminate Different Forms of the Predominant α2A Subtype. J. Neurochem. 1994, 63, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilsbach, R.; Hein, L. Are the pharmacology and physiology of α 2adrenoceptors determined by α 2-heteroreceptors and autoreceptors respectively? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasilewska, A.; Sączewski, F.; Hudson, A.L.; Ferdousi, M.; Scheinin, M.; Laurila, J.M.; Rybczyńska, A.; Boblewski, K.; Lehmann, A. Fluorinated analogues of marsanidine, a highly α2-AR/imidazoline I1 binding site-selective hypotensive agent. Synthesis and biological activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 87, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyczmonik, A.; Keller, T.; López-Picón, F.R.; Forsback, S.; Kirjavainen, A.K.; Takkinen, J.S.; Wasilewska, A.; Scheinin, M.; Haaparanta-Solin, M.; Sączewski, F.; et al. Radiosynthesis and Preclinical Evaluation of an α2A-Adrenoceptor Tracer Candidate, 6-[18F]Fluoro-marsanidine. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 21, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakaran, J.; Majo, V.J.; Milak, M.S.; Mali, P.; Savenkova, L.; Mann, J.J.; Parsey, R.V.; Kumar, J.S.D. Synthesis and in vivo evaluation of [11C]MPTQ: A potential PET tracer for alpha2A-adrenergic receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3654–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arponen, E.; Helin, S.; Marjamäki, P.; Grönroos, T.; Holm, P.; Löyttyniemi, E.; Någren, K.; Scheinin, M.; Haaparanta-Solin, M.; Sallinen, J.; et al. A PET tracer for brain α2C adrenoceptors, 11C-ORM-13070: Radiosynthesis and preclinical evaluation in rats and knockout mice. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Akiyama, M.; Yui, J.; Yamasaki, T.; Hatori, A.; Kumata, K.; Wakizaka, H.; Takei, M.; Nengaki, N.; Yanamoto, K.; et al. In vivo evaluation of limiting brain penetration of probes for α2C-adrenoceptor using small-animal positron emission tomography. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2010, 1, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallinen, J.; Höglund, I.; Engström, M.; Lehtimäki, J.; Virtanen, R.; Sirviö, J.; Wurster, S.; Savola, J.M.; Haapalinna, A. Pharmacological characterization and CNS effects of a novel highly selective α2C-adrenoceptor antagonist JP-1302. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 150, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoto, P.; Suilamo, S.; Oikonen, V.; Arponen, E.; Helin, S.; Herttuainen, J.; Hietamäki, J.; Holopainen, A.; Kailajärvi, M.; Peltonen, J.M.; et al. 11C-ORM-13070, a novel PET ligand for brain α2C-adrenoceptors: Radiometabolism, plasma pharmacokinetics, whole-body distribution and radiation dosimetry in healthy men. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sscarpace, P.J.; Abrass, I.B. Alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptor function in the brain during senescence. Neurobiol. Aging 1988, 9, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.C.; Ren, X.; Sagen, J.; Pandey, G.N. β-Adrenergic receptor subtypes in stress-induced behavioral depression. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1995, 51, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallukat, G. The β-adrenergic receptors. Herz 2002, 27, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu’O’Ng, K.V.Q.; Nguyen, L.T.H. The role of beta-adrenergic receptor blockers in Alzheimer’s disease: Potential genetic and cellular signaling mechanisms. Am. J. Alzheimers. Dis. Demen. 2013, 28, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dell, T.J.; Connor, S.A.; Guglietta, R.; Nguyen, P.V. β-Adrenergic receptor signaling and modulation of long-term potentiation in the mammalian hippocampus. Learn. Mem. 2015, 22, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelinas, J.; Nguyen, P. Neuromodulation of Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity, Learning, and Memory by Noradrenaline. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2008, 7, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachter, S.B.; Gilbert, E.M. Beta-adrenergic receptors, from their discovery and characterization through their manipulation to beneficial clinical application. Cardiology 2012, 122, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, J.N.; Lexow, N.; Kim, S.J.; Artymyshyn, R.; Senzon, S.; Lawerence, D.; Cassanova, M.F.; Kleinman, J.E.; Bird, E.D.; Winokur, A. Distribution of beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes in human post-mortem brain: Alterations in limbic regions of schizophrenics. Synapse 1992, 10, 228–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waarde, A.; Vaalburg, W.; Doze, P.; Bosker, F.; Elsinga, P. PET Imaging of Beta-Adrenoceptors in Human Brain: A Realistic Goal or a Mirage? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 10, 1519–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pike, V.W.; Law, M.P.; Osman, S.; Davenport, R.J.; Rimoldi, O.; Giardinà, D.; Camici, P.G. Selection, design and evaluation of new radioligands for PET studies of cardiac adrenoceptors. Pharm. Acta Helv. 2000, 74, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Werner, R.A.; Javadi, M.S.; Maya, Y.; Decker, M.; Lapa, C.; Herrmann, K.; Higuchi, T. Radionuclide imaging of neurohormonal system of the heart. Theranostics 2015, 5, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, J.; Wang, G.J.; Telang, F.; Fowler, J.S.; Alexoff, D.; Zabroski, J.; Jayne, M.; Hubbard, B.; King, P.; Carter, P.; et al. Imaging the norepinephrine transporter in humans with (S,S)-[11C]O-methyl reboxetine and PET: Problems and progress. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2007, 34, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Kudo, T.; Lapa, C.; Buck, A.; Higuchi, T. Recent advances in radiotracers targeting norepinephrine transporter: Structural development and radiolabeling improvements. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 851–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.; Mun, J.; Jarkas, N.; Stehouwer, J.S.; Voll, R.J.; Tamagnan, G.D.; Howell, L.; Votaw, J.R.; Kilts, C.D.; Nemeroff, C.B.; et al. Synthesis, Radiosynthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Carbon-11 and Fluorine-18 Labeled Reboxetine Analogs: Potential Positron Emission Tomography Radioligands for in Vivo Imaging of the Norepinephrine Transporter. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriguchi, S.; Kimura, Y.; Ichise, M.; Arakawa, R.; Takano, H.; Seki, C.; Ikoma, Y.; Takahata, K.; Nagashima, T.; Yamada, M.; et al. PET quantification of the norepinephrine transporter in human brain with (S,S)-18F-FMeNER-D2. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Narayanaswami, V.; Drake, L.R.; Brooks, A.F.; Meyer, J.H.; Houle, S.; Kilbourn, M.R.; Scott, P.J.H.; Vasdev, N. Classics in Neuroimaging: Development of PET Tracers for Imaging Monoamine Oxidases. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1867–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.S.; Logan, J.; Shumay, E.; Alia-Klein, N.; Wang, G.J.; Volkow, N.D. Monoamine oxidase: Radiotracer chemistry and human studies. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2015, 58, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswami, V.; Dahl, K.; Bernard-Gauthier, V.; Josephson, L.; Cumming, P.; Vasdev, N. Emerging PET Radiotracers and Targets for Imaging of Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Outlook Beyond TSPO. Mol. Imaging 2018, 17, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piascik, M.T.; Perez, D.M. α1-Adrenergic receptors: New insights and directions. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 298, 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, R.M.; Perez, D.M.; Hwa, J.; Piascik, M.T. α1 -Adrenergic Receptor Subtypes. Circ. Res. 1996, 78, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.J.; Minneman, K.P. Recent progress in α1-adrenergic receptor research. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, T.D.; Jensen, B.C.; Baker, A.J.; Simpson, P.C. Cardiac alpha1-adrenergic receptors: Novel aspects of expression, signaling mechanisms, physiologic function, and clinical importance. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 308–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, B.C.; O’Connell, T.D.; Simpson, P.C. Alpha-1-adrenergic receptors in heart failure: The adaptive arm of the cardiac response to chronic catecholamine stimulation. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 63, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, A.L.; Creese, I. Characterization of Alpha-1-Adrenergic Receptor Subtypes in Rat-Brain—A Reevaluation of [H-3] Wb4104 and [H-3] Prazosin Binding. Mol. Pharmacol. 1986, 29, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romero-grimaldi, C.; Moreno-lo, B. Age-Dependent Effect of Nitric Oxide on Subventricular Zone and Olfactory Bulb. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 346, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campeau, S.; Nyhuis, T.J.; Kryskow, E.M.; Masini, C.V.; Babb, J.A.; Sasse, S.K.; Greenwood, B.N.; Fleshner, M.; Day, H.E.W. Stress rapidly increases alpha 1d adrenergic receptor mRNA in the rat dentate gyrus. Brain Res. 2010, 1323, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szot, P.; White, S.S.; Greenup, J.L.; Leverenz, J.B.; Peskind, E.R.; Raskind, M.A. Changes in Adrenoreceptors in The Prefrontal Cortex Of Subjects With Dementia: Evidence Of Compensatory Changes. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, D.M.; Doze, V.A. Cardiac and neuroprotection regulated by alpha1-AR subtypes. J. Recept Signal. Transduct Res. 2011, 31, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, D. Alpha-1 adrenergic Blockers: Current Usage Considerations. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2005, 7, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miriam, H.; Hein, L. α1-Adrenozeptor-Antagonisten. Bei BPS und Hypertonie. Pharm. unserer Zeit 2008, 37, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.P.; Osman, S.; Pike, V.W.; Davenport, R.J.; Cunningham, V.J.; Rimoldi, O.; Rhodes, C.G.; Giardinà, D.; Camici, P.G. Evaluation of [11C]GB67, a novel radioligand for imaging myocardial (α1-adrenoceptors with positron emission tomography. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2000, 27, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, S.; Eriksson, B.; Oxenstierna, G.; Halldin, C.; Farde, L. Suggested minimal effective dose of risperidone based on PET-measured D2 and 5-HT(2A) receptor occupancy in schizophrenic patients. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyberg, S.; Olsson, H.; Nilsson, U.; Maehlum, E.; Halldin, C.; Farde, L. Low striatal and extra-striatal D2 receptor occupancy during treatment with the atypical antipsychotic sertindole. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2002, 162, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balle, T.; Perregaard, J.; Ramirez, M.T.; Larsen, A.K.; Søby, K.K.; Liljefors, T.; Andersen, K. Synthesis and structure-affinity relationship investigations of 5-heteroaryl-substituted analogues of the antipsychotic sertindole. A new class of highly selective α1 adrenoceptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balle, T.; Halldin, C.; Andersen, L.; Alifrangis, L.H.; Badolo, L.; Jensen, K.G.; Chou, Y.W.; Andersen, K.; Perregaard, J.; Farde, L. New α1-adrenoceptor antagonists derived from the antipsychotic sertindole—Carbon-11 labelling and pet examination of brain uptake in the cynomolgus monkey. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2004, 31, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airaksinen, A.J.; Finnema, S.J.; Balle, T.; Varnäs, K.; Bang-Andersen, B.; Gulyás, B.; Farde, L.; Halldin, C. Radiosynthesis and evaluation of new α1-adrenoceptor antagonists as PET radioligands for brain imaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2013, 40, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risgaard, R.; Ettrup, A.; Balle, T.; Dyssegaard, A.; Hansen, H.D.; Lehel, S.; Madsen, J.; Pedersen, H.; Püschl, A.; Badolo, L.; et al. Radiolabelling and PET brain imaging of the α1-adrenoceptor antagonist Lu AE43936. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2013, 40, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, M.; Jorgensen, P.N.; Christoffersen, C.T.; Jensen, K.G.; Balle, T.; Bang-Andersen, B. Discovery of novel α1-adrenoceptor ligands based on the antipsychotic sertindole suitable for labeling as PET ligands. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bøgesø, K.P.; Arnt, J.; Hyttel, J.; Pedersen, H.; Liljefors, T. Octoclothepin Enantiomers. A Reinvestigation of Their Biochemical and Pharmacological Activity in Relation to a New Receptor-Interaction Model for Dopamine D-2 Receptor Antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 1991, 34, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liow, J.S.; Lu, S.; McCarron, J.A.; Hong, J.; Musachio, J.L.; Pike, V.W.; Innis, R.B.; Zoghbi, S.S. Effect of a P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor, Cyclosporin A, on the Disposition in Rodent Brain and Blood of the 5-HT1A Receptor Radioligand, [11C](R)-(––)-RWAY. Synapse 2007, 61, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.R.; Bryans, J.; Conlon, K.; McMurray, G.; Stobie, A.; Whitlock, G.A. Novel 2-imidazoles as potent, selective and CNS penetrant α1A adrenoceptor partial agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 6437–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, G.A.; Brennan, P.E.; Roberts, L.R.; Stobie, A. Potent and selective α1A adrenoceptor partial agonists-Novel imidazole frameworks. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 3118–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bücheler, M.M.; Hadamek, K.; Hein, L. Two α2-adrenergic receptor subtypes, α2A and α2C, inhibit transmitter release in the brain of gene-targeted mice. Neuroscience 2002, 109, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Tiemann, D.; Park, E.; Salehi, A. Alpha-2 Agonists. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2017, 35, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.P.; Ferguson, C.N.; Jones, R.M. Alpha-2 and imidazoline receptor agonists. Their pharmacology and therapeutic role. Anaesthesia 1999, 54, 146–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciorek, P.M.; Pierce, V.; Shepperson, N.B.; Waterfall, J.F. An investigation into the selectivity of a novel series of benzoquinolizines for α2-adrenoceptors in vivo. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1984, 82, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettibone, D.J.; Flagg, S.D.; Totarol, J.A.; Clineschmidt, B.V.; Huff, J.R.; Young, S.D.; Chen, R. [3H]L-657, 743 (MK-912): A new, high affinity, selective radioligand for brain α-2 adrenoceptors. Life Sci. 1989, 44, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleus, R.C.; Shiue, C.Y.; Shiue, G.G.; Rysavy, J.A.; Huang, H.; Cornish, K.G.; Sunderland, J.J.; Bylund, D.B. Synthesis and biodistribution of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor antagonist (11C)WY26703. Use as a radioligand for positron emission tomography. Receptor 1992, 2, 241–252. [Google Scholar]
- Shiue, C.Y.; Pleus, R.C.; Shiue, G.G.; Rysavy, J.A.; Sunderland, J.J.; Cornish, K.G.; Young, S.D.; Bylund, D.B. Synthesis and biological evaluation of [11C]MK-912 as an α2- adrenergic receptor radioligand for PET studies. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1998, 25, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BK, F.D.; Terrazzino, S.; Tavitian, B.; Hinnen, F.; Vaufrey, F.; Crouzel, C. XIIth international symposium on radiopharmaceutical chemistry: Abstracts and programme. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1997, 40, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, S.P.; Hirani, E.; Opacka-Juffry, J.; Osman, S.; Myers, R.; Gunn, R.N.; McCarron, J.A.; Clark, R.D.; Melichar, J.; Nutt, D.J.; et al. Evaluation of [O-methyl-11C]RS.15385-197 as a positron emission tomography radioligand for central α2-adrenoceptors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2000, 27, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeda, D.; Sipil, H.T.; Bramoull, Y.; Enas, J.D.; Vaufrey, F.; Doll, F.; Crouzel, C. Synthesis of [11C]atipamezole, a potential PET ligand for the α2-adrenergic receptor in the brain. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2002, 45, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marthi, K.; Bender, D.; Watanabe, H.; Smith, D.F. PET evaluation of a tetracyclic, atypical antidepressant, [N-methyl-11C]mianserin, in the living porcine brain. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2002, 29, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marthi, K.; Bender, D.; Gjedde, A.; Smith, D.F. [11C]Mirtazapine for PET neuroimaging: Radiosynthesis and initial evaluation in the living porcine brain. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2002, 12, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marthi, K.; Jakobsen, S.; Bender, D.; Hansen, S.B.; Smith, S.B.; Hermansen, F.; Rosenberg, R.; Smith, D.F. [N-methyl-11C]Mirtazapine for positron emission tomography neuroimaging of antidepressant actions in humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2004, 174, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.F.; Stork, B.S.; Wegener, G.; Ashkanian, M.; Jakobsen, S.; Bender, D.; Audrain, H.; Vase, K.H.; Hansen, S.B.; Videbech, P.; et al. [11C]mirtazapine binding in depressed antidepressant nonresponders studied by PET neuroimaging. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2009, 206, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Mey, M.; Windhorst, A.D.; Klok, R.P.; Herscheid, J.D.M.; Kennis, L.E.; Bischoff, F.; Bakker, M.; Langlois, X.; Heylen, L.; Jurzak, M.; et al. Synthesis and biodistribution of [11C]R107474, a new radiolabeled α2-adrenoceptor antagonist. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 4526–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, S.; Pedersen, K.; Smith, D.F.; Jensen, S.B.; Munk, O.L.; Cumming, P. Detection of a 2 -Adrenergic Receptors in Brain of Living Pig with 11 C-Yohimbine. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 2008–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nahimi, A.; Jakobsen, S.; Munk, O.L.; Vang, K.; Phan, J.A.; Rodell, A.; Gjedde, A. Mapping α2 adrenoceptors of the human brain with11C-yohimbine. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, J.I.; Alcázar, J.; Alonso, J.M.; Alvarez, R.M.; Bakker, M.H.; Biesmans, I.; Cid, J.M.; De Lucas, A.I.; Fernández, J.; Font, L.M.; et al. Discovery of a new series of centrally active tricyclic isoxazoles combining serotonin (5-HT) reuptake inhibition with α2- adrenoceptor blocking activity. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 2054–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa̧czewski, F.; Kornicka, A.; Rybczyńska, A.; Hudson, A.L.; Shu, S.M.; Gdaniec, M.; Boblewski, K.; Lehmann, A. 1-[(imidazolidin-2-yl)imino]indazole. Highly α2/I 1 selective agonist: Synthesis, X-ray structure, and biological activity. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 3599–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, K.; Kashima, H.; Iida, K.; Enokizono, J.; Uchida, S.I.; Nonaka, H.; Kurokawa, M.; Shimada, J. Novel 4-(6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl)methylbenzofuran derivatives as selective α2C-adrenergic receptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnema, S.J.; Hughes, Z.A.; Haaparanta-Solin, M.; Stepanov, V.; Nakao, R.; Varnäs, K.; Varrone, A.; Arponen, E.; Marjamäki, P.; Pohjanoksa, K.; et al. Amphetamine decreases α2C-adrenoceptor binding of [11C]ORM-13070: A PET study in the primate brain. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, J.M.; Kuhar, M.J. Beta adrenergic receptor localization in rat brain by light microscopic autoradiography. Neurochem. Int. 1982, 4, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, R.; Ruberg, M.; Raisman, R.; Agid, Y. Adrenergic receptors in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 1984, 322, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfner, F.; Höglinger, G.U.; Kuhlenbäumer, G.; Pottegård, A.; Wod, M.; Christensen, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Deuschl, G. β-adrenoreceptors and the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, V.; Rajkowska, G.; Luker, S.N.; Dilley, G.; Meltzer, H.Y.; Overholser, J.C.; Stockmeier, C.A.; Ordway, G.A. Brain noradrenergic receptors in major depression and schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 1999, 21, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, J.; Rhodes, C.G.; Hughes, J.M.; De Silva, R.; Lefroy, D.C.; Ind, P.W.; Qing, F.; Brady, F.; Luthra, S.K.; Steel, C.J. In vivo quantification of pulmonary B-adrenoceptor density in humans with (S)-[11C]CGP-12177 and PET. Am. Physiol. Soc. 1993, 75, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsinga, P.H.; Doze, P.; Van Waarde, A.; Pieterman, R.M.; Blanksma, P.K.; Willemsen, A.T.M.; Vaalburg, W. Imaging of β-adrenoceptors in the human thorax using (S)-[11C]CGP12388 and positron emission tomography. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 433, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
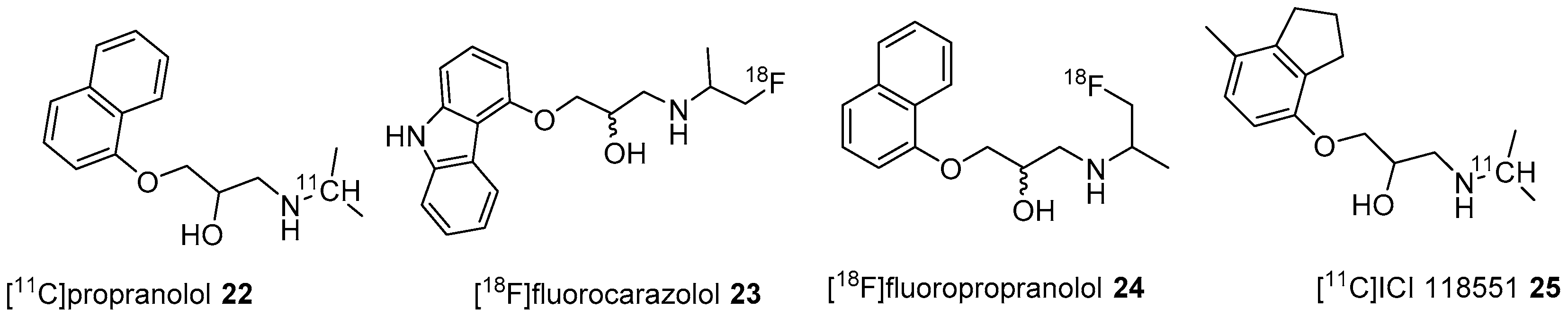
- Berger, G.; Maziere, M.; Prenant, C.; Sastre, J.; Syrota, A.; Comar, D. Synthesis of 11 C propranolol. J. Radioanal. Chem. 1982, 74, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, G.; Ulin, J.; Långström, B. Synthesis of the 11C-labelled β-adrenergic receptor ligands atenolol, metoprolol and propranolol. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A 1989, 40, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
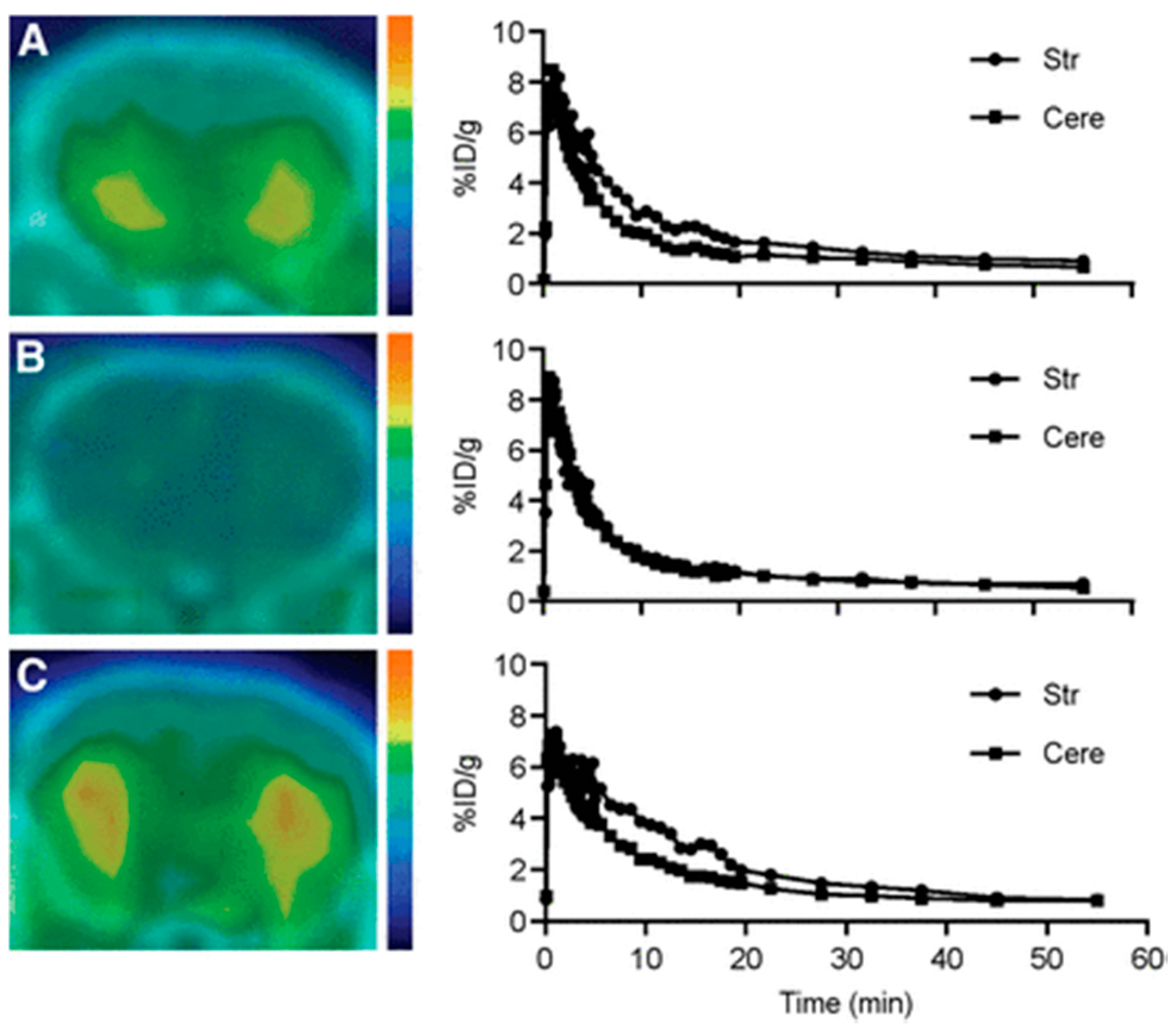
- Berridge, M.S.; Nelson, A.D.; Zheng, L.; Leisure, G.P.; Miraldi, F. Specific beta-adrenergic receptor binding of carazolol measured with PET. J. Nucl. Med. 1994, 35, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Berridge, M.S.; Ernsberger, P. Synthesis, Binding Properties, and 18F Labeling of Fluorocarazolol, a High-Affinity β-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonist. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 3219–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doze, P.; Van Waarde, A.; Elsinga, P.H.; Van-Loenen Weemaes, A.M.A.; Willemsen, A.T.M.; Vaalburg, W. Validation of S-1′-[18F]fluorocarazolol for in vivo imaging and quantification of cerebral β-adrenoceptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 353, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doze, P.; Elsinga, P.H.; De Vries, E.F.J.; Van Waarde, A.; Vaalburg, W. Mutagenic activity of a fluorinated analog of the beta-adrenoceptor ligand carazolol in the Ames test. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2000, 27, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewson, T.J.; Stekhova, S.; Kinsey, B.; Chen, L.; Wiens, L.; Barber, R. Synthesis and biodistribution of R- and S-isomers of [18F]- fluoropropranolol, a lipophilic ligand for the β-adrenergic receptor. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1999, 26, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, R.M.; Matarrese, M.; Soloviev, D.; Simonelli, P.; Rigamonti, M.; Gobbo, C.; Todde, S.; Carpinelli, A.; Galli Kienle, M.; Fazio, F. Synthesis and in vivo evaluation of [11C]ICI 118551 as a putative subtype selective β2-adrenergic radioligand. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 204, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloviev, D.V.; Matarrese, M.; Moresco, R.M.; Todde, S.; Bonasera, T.A.; Sudati, F.; Simonelli, P.; Magni, F.; Colombo, D.; Carpinelli, A.; et al. Asymmetric synthesis and preliminary evaluation of (R)- and (S)-[11C]bisoprolol, a putative β1-selective adrenoceptor radioligand. Neurochem. Int. 2001, 38, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doze, P.; Elsinga, P.H.; Maas, B.; Van Waarde, A.; Wegman, T.; Vaalburg, W. Synthesis and evaluation of radiolabeled antagonists for imaging of β-adrenoceptors in the brain with PET. Neurochem. Int. 2002, 40, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doze, P.; Van Waarde, A.; Tewson, T.J.; Vaalburg, W.; Elsinga, P.H. Synthesis and evaluation of (S)-[18F]-fluoroethylcarazolol for in vivo β-adrenoceptor imaging in the brain. Neurochem. Int. 2002, 41, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Waarde, A.; Doorduin, J.; de Jong, J.R.; Dierckx, R.A.; Elsinga, P.H. Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of (S)-[11C]-exaprolol, a novel β-adrenoceptor ligand for PET. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, K.A.; van Oosten, E.M.; Wilson, A.A.; Meyer, J.H.; Houle, S.; Vasdev, N. Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of [18F]-fluoro-(2S)-Exaprolol for imaging cerebral β-adrenergic receptors with PET. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 53, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirfeizi, L.; Rybczynska, A.A.; van Waarde, A.; Campbell-Verduyn, L.; Feringa, B.L.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Elsinga, P.H. [18F]-(fluoromethoxy)ethoxy)methyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol ([18F FPTC) a novel PET-ligand for cerebral beta-adrenoceptors. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2014, 41, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alluri, S.R.; Kim, S.W.; Volkow, N.D.; Kil, K.-E. PET Radiotracers for CNS-Adrenergic Receptors: Developments and Perspectives. Molecules 2020, 25, 4017. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25174017
Alluri SR, Kim SW, Volkow ND, Kil K-E. PET Radiotracers for CNS-Adrenergic Receptors: Developments and Perspectives. Molecules. 2020; 25(17):4017. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25174017
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlluri, Santosh Reddy, Sung Won Kim, Nora D. Volkow, and Kun-Eek Kil. 2020. "PET Radiotracers for CNS-Adrenergic Receptors: Developments and Perspectives" Molecules 25, no. 17: 4017. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25174017
APA StyleAlluri, S. R., Kim, S. W., Volkow, N. D., & Kil, K.-E. (2020). PET Radiotracers for CNS-Adrenergic Receptors: Developments and Perspectives. Molecules, 25(17), 4017. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25174017






