Role of Photoactive Phytocompounds in Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer
Abstract
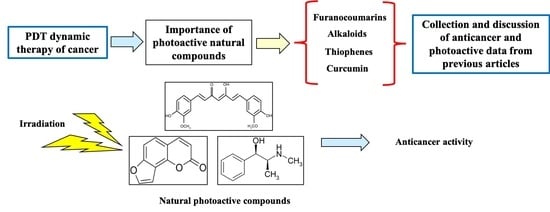
1. Introduction
2. Basic Principles of Photodynamic Therapy
| Photosensitiser | Commercial Name | λ max (nm) | Structure | Type of Cancer | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-Generation Photosensitiser | |||||
| Hematoporphyrin derivatives | Photofrin Photoheme | 630 |  | Lung, bladder, skin, cervical, breast cancer. | [17,42] |
| Second-Generation Photosensitisers | |||||
| 5-Aminolevulinic acid | Levulan Alasens | 635 |  | Bladder, skin, lung, ovary and gastrointestinal cancer. | [43,44,45] |
| Meta-tetra(hydroxyphenyl) chlorin | Foscan | 652 |  | Approved drug for the treatment of bronchial and oesophageal cancers. | [46,47,48] |
| Chlorin e6 | MACEDACEPhotoditazine | 664 |  | Gynaecological diseases, prostate cancer, fibrosarcoma, Liver, brain, lung, and oral cancers. | [49,50,51] |
| Benzoporphyrin | Visudyne | 690 |  | Prostate and skin cancer. | [52,53] |
| Texaphyrins | Lutrin, Antrin, Optrin, Xcytrin | 720–760 |  | Hepatocellular cancer, leukaemia, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, colon, prostate, bronchial and oesophageal cancers. | [54,55,56,57,58] |
| Phthalocyanines | Photosense | 640–690 |  | Breast, cervical, skin, lung, liver, colon and gastrointestinal cancers. | [17,59,60,61] |
| Purpurins | Purlytin | 660 |  | Breast cancer, prostate cancer and Kaposi’s sarcoma. | [62,63,64] |
3. PDT’s Cancer Cell Death Mechanism
4. PS from Natural Resources
5. Natural Photoactive Compounds from Plants
5.1. Furanocoumarins
5.2. Polyacetylene and Thiophenes
5.3. Curcumins
5.4. Alkaloids
5.5. Anthraquinones (AQ)
6. Theorical Studies for Assessing the Photoactivity of Natural Compounds
7. Advantages and Scope of Natural PSs
8. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Hussein, A.; Harith, M.; Abrahamse, H. Assessment of DNA Damage after Photodynamic Therapy Using a Metallophthalocyanine Photosensitizer. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, W.S.; Cummings, M.R.; Spencer, C.A. Concepts of Genetics, 8th ed.; Pearson Education International: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Matés, J.M.; Segura, J.A.; Alonso, F.J.; Márquez, J.D. Intracellular redox status and oxidative stress: Implications for cell proliferation, apoptosis, and carcinogenesis. Arch. Toxicol. 2008, 82, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Montero, R.; Sossa-Azuela, H.; Gutiérrez-Hernández, D.; Zamudio, V.; Hernández-Bautista, I.; Valadez-Godínez, S. Novel Mathematical Model of Breast Cancer Diagnostics Using an Associative Pattern Classification. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Song, J.; Nie, L.; Chen, X.S. Reactive oxygen species generating systems meeting challenges of photodynamic cancer therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6597–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskaran, R.; Lee, J.; Yang, S.-G. Clinical development of photodynamic agents and therapeutic applications. Biomater. Res. 2018, 22, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida, D.R.Q.; Terra, L.F.; Labriola, L.; Dos Santos, A.F.; Baptista, M.S. Photodynamic therapy in cancer treatment—An update review. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2019, 2019, 10–20517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Khachemoune, A. An update on topical photodynamic therapy for clinical dermatologists. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2019, 30, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, M.A.; Pagliara, M.M.; Lanza, A.; Sammarco, M.G.; Caputo, C.G.; Grimaldi, G.; Scupola, A. Photodynamic Therapy in Ocular Oncology. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.M.; Adelzadeh, L.; Wu, J.J. Photodynamic therapy for psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2014, 26, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.; Siopa, J.R.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Teixeira, M.D.C.; Santos, D.J.; Pires, M.D.A.; Andreani, T. New strategies for the treatment of autoimmune diseases using nanotechnologies. Emerg. Nanotechnol. Immunol. 2018, 135–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatz, K.; Schneider, U.; Henrich, P.B.; Braun, B.; Sacu, S. Ranibizumab plus Verteporfin Photodynamic Therapy in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration: 12 Months of Retreatment and Vision Outcomes from a Randomized Study. Ophthalmologia 2014, 233, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oniszczuk, A.; Wojtunik-Kulesza, K.A.; Oniszczuk, T.; Kasprzak, K. The potential of photodynamic therapy (PDT)—Experimental investigations and clinical use. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 912–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, C.; Longo, J.P.F.; Azevedo, R.B.; Zhang, H.; Muehlmann, L.A. An updated overview on the development of new photosensitizers for anticancer photodynamic therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 8, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granelli, S.G.; Diamond, I.; McDonagh, A.F.; Wilson, C.B.; Nielsen, S.L. Photochemotherapy of glioma cells by visible light and hematoporphyrin. Cancer Res. 1975, 35, 2567–2570. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamse, H.; Hamblin, M.R. Photomedicine and Stem Cells: The Janus Face of Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) to Kill Cancer Stem Cells, and Photobiomodulation (PBM) to Stimulate Normal Stem Cells; Morgan & Claypool Publishers: Bristol, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, L.M.; Dos Santos, F.V.; Lyon, J.P.; Maftoum-Costa, M.; Soares, C.P.; Da Silva, N.S. Photodynamic Therapy: Porphyrins and Phthalocyanines as Photosensitizers. Aust. J. Chem. 2008, 61, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Mansoori, B.; Baradaran, B. Regulation of miRNAs by herbal medicine: An emerging field in cancer therapies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 86, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Mansoori, B.; Aghapour, M.; Baradaran, B. Urtica dioica dichloromethane extract induce apoptosis from intrinsic pathway on human prostate cancer cells (PC3). Cell. Mol. Boil. 2016, 62, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, A.; Mansoori, B.; Goldar, S.; Shanehbandi, D.; Khaze, V.; Mohammadnejad, L.; Baghbani, E.; Baradaran, B. Effects of Urtica dioica dichloromethane extract on cell apoptosis and related gene expression in human breast cancer cell line (MDA-MB-468). Cell. Mol. Boil. 2016, 62, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Alali, F.Q.; Tawaha, K. Dereplication of bioactive constituents of the genus hypericum using LC-(+,−)-ESI-MS and LC-PDA techniques: Hypericum triquterifolium as a case study. Saudi Pharm. J. 2009, 17, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, C. Ready for a comeback of natural products in oncology. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.B.; Tiwari, V.K. Natural products: An evolving role in future drug discovery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4769–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.C. Photodynamic Therapy Based on Arrabidaea chica (Crajiru) Extract Nanoemulsion: In vitro Activity against Monolayers and Spheroids of Human Mammary Adenocarcinoma MCF-7 Cells. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.J.; Appleton, D.R.; Mustafa, M.R.; Lee, H.B. Rapid Identification of Cyclic Tetrapyrrolic Photosensitisers for Photodynamic Therapy Using On-line Hyphenated LC-PDA-MS Coupled with Photo-cytotoxicity Assay. Phytochem. Anal. 2011, 23, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalkos, D.; Gioti, E.; Stalikas, C.; Meyer, H.; Papazoglou, T.; Filippidis, G.; Papazoglou, T.G. Photophysical properties of Hypericum perforatum L. extracts—Novel photosensitizers for PDT. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2006, 82, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisser-Labouèbe, M.; Lange, N.; Gurny, R.; Delie, F. Hypericin-loaded nanoparticles for the photodynamic treatment of ovarian cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 326, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirmalek, S.A.; Azizi, M.A.; Jangholi, E.; Yadollah-Damavandi, S.; Javidi, M.A.; Parsa, Y.; Parsa, T.; Salimi-Tabatabaee, S.A.; Kolagar, H.G.; Alizadeh-Navaei, R. Cytotoxic and apoptogenic effect of hypericin, the bioactive component of Hypericum perforatum on the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. Cancer Cell Int. 2016, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonar, D.; Süloğlu, A.K.; Selmanoğlu, G.; Sünnetçioğlu, M.M. An Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spin labeling study in HT-29 Colon adenocarcinoma cells after Hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy. BMC Mol. Cell Boil. 2019, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Ichikawa, H.; Garodia, P.; Weerasinghe, P.; Sethi, G.; Bhatt, I.D.; Pandey, M.K.; Shishodia, S.; Nair, M.G. From traditional Ayurvedic medicine to modern medicine: Identification of therapeutic targets for suppression of inflammation and cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2006, 10, 87–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, D.; Singh, K.; Singh, V.K. Therapeutic and pharmacological aspects of photodynamic product chlorophyllin. Eur. J. Biol. Res. 2019, 9, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Juzeniene, A.; Nielsen, K.P.; Moan, J. Biophysical Aspects of Photodynamic Therapy. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2006, 25, 7–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, B.P.; Abrahamse, H. A Review on Novel Breast Cancer Therapies: Photodynamic Therapy and Plant Derived Agent Induced Cell Death Mechanisms. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniogo, E.C.; George, B.P.; Abrahamse, H. The role of photodynamic therapy on multidrug resistant breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, R.R.; Sibata, C.H. Oncologic photodynamic therapy photosensitizers: A clinical review. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2010, 7, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Roskams, T.; De Witte, P.A.M. Antivascular tumor eradication by hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 76, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascencio, M.; Collinet, P.; Farine, M.; Mordon, S. Protoporphyrin IX fluorescence photobleaching is a useful tool to predict the response of rat ovarian cancer following hexaminolevulinate photodynamic therapy. Lasers Surg. Med. 2008, 40, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.D.; Nowis, D.; Golab, J.; Vandenabeele, P.; Krysko, D.V.; Agostinis, P. Immunogenic cell death, DAMPs and anticancer therapeutics: An emerging amalgamation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2010, 1805, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano, A.P.; Demidova, T.N.; Hamblin, M.R. Mechanisms in photodynamic therapy: Part three-Photosensitizer pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, tumor localization and modes of tumor destruction. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2005, 2, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilby, P.R. Singlet oxygen: There is indeed something new under the sun. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oseroff, A.R.; Blumenson, L.R.; Wilson, B.D.; Mang, T.S.; Bellnier, D.A.; Parsons, J.C.; Frawley, N.; Cooper, M.; Zeitouni, N.; Dougherty, T.J. A dose ranging study of photodynamic therapy with porfimer sodium (Photofrin®) for treatment of basal cell carcinoma. Lasers Surg. Med. 2006, 38, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juzeniene, A.; Juzenas, P.; Ma, L.-W.; Iani, V.; Moan, J. Effectiveness of different light sources for 5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy. Lasers Med. Sci. 2004, 19, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, P. Methyl aminolaevulinate–photodynamic therapy: A review of clinical trials in the treatment of actinic keratoses and nonmelanoma skin cancer. Yearb. Dermatol. Dermatol. Surg. 2008, 2008, 322–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffes, E.W.; McCullough, J.L.; Weinstein, G.D.; Kaplan, R.; Glazer, S.D.; Taylor, J. Photodynamic therapy of actinic keratoses with topical aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride and fluorescent blue light. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; He, C.; Lin, W. A Chlorin-Based Nanoscale Metal–Organic Framework for Photodynamic Therapy of Colon Cancers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7600–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.M.; Nathan, T.; Lees, W.; Mosse, C.; Freeman, A.; Emberton, M.; Bown, S. Photodynamic therapy using meso tetra hydroxy phenyl chlorin (mTHPC) in early prostate cancer. Lasers Surg. Med. 2006, 38, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosjean, P.; Savary, J.-F.; Wagnières, G.; Mizeret, J.; Woodtli, A.; Theumann, J.-F.; Fontolliet, C.; Bergh, H.V.D.; Monnier, P. Tetra(m-hydroxyphenyl)chlorin clinical photodynamic therapy of early bronchial and oesophageal cancers. Lasers Med. Sci. 1996, 11, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessel, D. Pharmacokinetics of N-aspartyl chlorin e6 in cancer patients. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 1997, 39, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taber, S.W.; Fingar, V.H.; Coots, C.T.; Wieman, T.J. Photodynamic therapy using mono-L-aspartyl chlorin e6 (Npe6) for the treatment of cutaneous disease: A Phase I clinical study. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 2741–2746. [Google Scholar]
- Lagudaev, D.M. Sorokatyĭ Photodynamic therapy of prostatic adenoma. Urologiia 2007, 4, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Momma, T.; Hamblin, M.R.; Wu, H.C.; Hasan, T. Photodynamic therapy of orthotopic prostate cancer with benzoporphyrin derivative: Local control and distant metastasis. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 5425–5431. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, J.G.; Waterfield, E.; Richter, A.M.; Smits, C.; Lui, H.; Hruza, L.; Anderson, R.R.; Salvatori, V. Photodynamic therapy of malignancies with benzoporphyrin derivative monoacid ring A. Europto Biomedical Optics ’93 1994, 2078, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.W.; Woodburn, K.W.; Wright, M.; Mody, T.D.; Fan, Q.; Sessler, J.L.; Dow, W.C.; Miller, R.A. Lutetium Texaphyrin (PCI-0123): A Near-Infrared, Water-Soluble Photosensitizer. Photochem. Photobiol. 1996, 63, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessler, J.L.; Miller, R.A. Texaphyrins: New drugs with diverse clinical applications in radiation and photodynamic therapy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 59, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Mick, R.; Busch, T.; Zhu, T.C.; Finlay, J.; Yu, G.; Yodh, A.; Malkowicz, S.; Smith, D.; Whittington, R.; et al. Preliminary results of interstitial motexafin lutetium-mediated PDT for prostate cancer. Lasers Surg. Med. 2006, 38, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockson, S.G.; Lorenz, D.P.; Cheong, W.-F.; Woodburn, K.W. Photoangioplasty: An emerging clinical cardiovascular role for photodynamic therapy. Circulation 2000, 102, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogias, E.; Vougioukas, V.; Hubbe, U.; Halatsch, M.-E. Minimally Invasive Approach for the Treatment of Lateral Lumbar Disc Herniations. Technique and Results. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2007, 50, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wood, S.R.; Holroyd, J.A.; Brown, S.B. The Subcellular Localization of Zn(ll) Phthalocyanines and Their Redistribution on Exposure to Light. Photochem. Photobiol. 1997, 65, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuchinskaya, T.; Moreno, M.; Cook, M.J.; Edwards, D.R.; Russell, D.A. Targeted photodynamic therapy of breast cancer cells using antibody–phthalocyanine–gold nanoparticle conjugates. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2011, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhejane, P.R.; Houreld, N.N.; Abrahamse, H. Multiorganelle Localization of Metallated Phthalocyanine Photosensitizer in Colorectal Cancer Cells (DLD-1 and CaCo-2) Enhances Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, D.W.C. Rostaporfin (Miravant Medical Technologies). IDrugs 2002, 5, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, M.; Somers, R.H.; Greenburg, R.; Ackler, J. Photodynamic therapy in the management of metastatic cutaneous adenocarcinomas: Case reports from phase 1/2 studies using tin ethyl etiopurpurin (SnET2). J. Surg. Oncol. 1998, 67, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, S.H.; Keck, R.W.; Hampton, J.A. Transperineal Photodynamic Ablation of the Canine Prostate. J. Urol. 1996, 156, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinis, P.; Berg, K.; Cengel, K.A.; Foster, T.H.; Girotti, A.W.; Gollnick, S.O.; Hahn, S.M.; Hamblin, M.R.; Juzeniene, A.; Kessel, D.; et al. Photodynamic therapy of cancer: An update. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 250–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiners, J.J.; Agostinis, P.; Berg, K.; Oleinick, N.L.; Kessel, D. Assessing autophagy in the context of photodynamic therapy. Autophagy 2010, 6, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, C.; Abrahamse, H. Utilisation of Targeted Nanoparticle Photosensitiser Drug Delivery Systems for the Enhancement of Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules 2018, 23, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, R.W.; Gamlin, J.N. A compilation of singlet oxygen yields from biologically relevant molecules. Photochem. Photobiol. 1999, 70, 391–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, N.; Kohtani, S.; Nakagaki, R. Molecular aspects of furocoumarin reactions: Photophysics, photochemistry, photobiology, and structural analysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2005, 6, 168–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracarolli, L.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Pereira, A.C.; Júnior, N.S.M.; Silva-Junior, G.J.; Bachmann, L.; Wainwright, M.; Bastos, J.K.; Braga, G.U. Inactivation of plant-pathogenic fungus Colletotrichum acutatum with natural plant-produced photosensitizers under solar radiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2016, 162, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chobot, V.; Vytlačilová, J.; Kubicová, L.; Opletal, L.; Jahodář, L.; Laakso, I.; Vuorela, P. Phototoxic activity of a thiophene polyacetylene from Leuzea carthamoides. Fitoterapia 2006, 77, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, B.; Agüero, M.B.; Zygadlo, J.; Tapia, A.; Solís, C.; De Arias, A.R.; Yaluff, G.; Zacchino, S.; Feresin, G.E.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G. Antimicrobial activity of extracts, essential oil and metabolites obtained from tagetes mendocina. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2009, 54, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Lee, J.W.; Jang, H.; Choi, J.E.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, N.; Hong, J.T.; Lee, M.K.; Hwang, B.Y. Dimeric sesquiterpene and thiophenes from the roots of Echinops latifolius. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5995–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postigo, A.; Funes, M.; Petenatti, E.; Bottai, H.; Pacciaroni, A.; Sortino, M. Antifungal photosensitive activity of Porophyllum obscurum (Spreng.) DC.: Correlation of the chemical composition of the hexane extract with the bioactivity. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2017, 20, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Abdallah, H.M.; El Halawany, A.M.; Mohamed, G.A. Naturally occurring thiophenes: Isolation, purification, structural elucidation, and evaluation of bioactivities. Phytochem. Rev. 2015, 15, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Lee, J.-H. Photosensitizer effect of curcumin on UVB-irradiated HaCaT cells through activation of caspase pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Lin, J.-N.; Ma, J.-W.; Yang, N.-S.; Ho, C.-T.; Kuo, S.-C.; Way, T.-D. Demethoxycurcumin induces autophagic and apoptotic responses on breast cancer cells in photodynamic therapy. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 12, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, W.; Aznar, R.; Sánchez, G. Curcumin-Mediated Photodynamic Inactivation of Norovirus Surrogates. Food Environ. Virol. 2016, 8, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kang, S.-M.; Jeong, S.-H.; Chung, K.-H.; Kim, B.-I. Antibacterial photodynamic therapy with curcumin and Curcuma xanthorrhiza extract against Streptococcus mutans. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2017, 20, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavya, M.; Hebbar, H.U. Efficacy of blue LED in microbial inactivation: Effect of photosensitization and process parameters. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 290, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morten, A.G.; Martinez, L.J.; Holt, N.; Sik, R.H.; Reszka, K.; Chignell, C.F.; Tonnesen, H.H.; Roberts, J.E. Photophysical Studies on Antimalariai Drugs. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 69, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbaraj, J.J.; Kukielczak, B.M.; Bilski, P.; Sandvik, S.L.; Chignell, C.F. Photochemistry and Photocytotoxicity of Alkaloids from Goldenseal (Hydrastis canadensis L.) 1. Berberine. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 1529–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flors, C.; Prat, C.; Suau, R.; Najera, F.; Nonell, S. Photochemistry of Phytoalexins Containing Phenalenone-like Chromophores: Photophysics and Singlet Oxygen Photosensitizing Properties of the Plant Oxoaporphine Alkaloid Oxoglaucine. Photochem. Photobiol. 2005, 81, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, C.; Thomas, A.H. Photophysics and photochemistry of pterins in aqueous solution. Acc. Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillipson, J.D.; Roberts, M.F.; Zenk, M.H. The Chemistry and Biology of Isoquinoline Alkaloids; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vignoni, M.; Erra-Balsells, R.; Epe, B.; Cabrerizo, F.M. Intra- and extra-cellular DNA damage by harmine and 9-methyl-harmine. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2014, 132, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, L.O.; Roman, E.A.; Thomas, A.H.; Dántola, M.L. Photooxidation of Tryptophan and Tyrosine Residues in Human Serum Albumin Sensitized by Pterin: A Model for Globular Protein Photodamage in Skin. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 4777–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yañuk, J.G.; Denofrio, M.P.; Rasse-Suriani, F.A.O.; Villarruel, F.D.; Fassetta, F.; Einschlag, F.S.G.; Erra-Balsells, R.; Epe, B.; Cabrerizo, F.M. DNA damage photo-induced by chloroharmine isomers: Hydrolysis versus oxidation of nucleobases. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 2170–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daub, M.E.; Herrero, S.; Chung, K.-R. Photoactivated perylenequinone toxins in fungal pathogenesis of plants. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 252, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, S.C.N.; Comini, L.R.; Sarmiento, M.; Becerra, C.; Albesa, I.; Argüello, G.A.; Cabrera, J.L. Natural anthraquinones probed as Type I and Type II photosensitizers: Singlet oxygen and superoxide anion production. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2005, 78, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comini, L.R.; Montoya, S.C.N.; Sarmiento, M.; Cabrera, J.L.; Argüello, G.A. Characterizing some photophysical, photochemical and photobiological properties of photosensitizing anthraquinones. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2007, 188, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelopoulou, M.; Grigalavicius, M.; Berg, K.; Ménard, M.; Theodossiou, T.A. Cytotoxic and Photocytotoxic Effects of Cercosporin on Human Tumor Cell Lines. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 95, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panno, M.L.; Giordano, F.; Palma, M.G.; Bartella, V.; Rago, V.; Maggiolini, M.; Sisci, D.; Lanzino, M.; De Amicis, F.; Ando, S. Evidence that bergapten, independently of its photoactivation, enhances p53 gene expression and induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panno, M.L.; Giordano, F.; Rizza, P.; Pellegrino, M.; Zito, D.; Giordano, C.; Mauro, L.; Catalano, S.; Aquila, S.; Sisci, D.; et al. Bergapten induces ER depletion in breast cancer cells through SMAD4-mediated ubiquitination. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-M.; Lee, J.H.; Sethi, G.; Kim, C.; Baek, S.H.; Nam, D.; Chung, W.-S.; Shim, B.S.; Ahn, K.S.; Kim, S.-H. Bergamottin, a natural furanocoumarin obtained from grapefruit juice induces chemosensitization and apoptosis through the inhibition of STAT3 signaling pathway in tumor cells. Cancer Lett. 2014, 354, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-M.; Lee, E.-J.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, W.M.; Nam, D.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.-G.; Um, J.-Y.; Shim, B.S.; Ahn, K.S. Simvastatin in combination with bergamottin potentiates TNF-induced apoptosis through modulation of NF-κB signalling pathway in human chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Pharm. Boil. 2016, 54, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.-C.; Qu, X.; Yu, H.-F.; Zhang, H.-M.; Wang, Z.-H.; Zhang, Z.-T. Antitumor and apoptotic effects of bergaptol are mediated via mitochondrial death pathway and cell cycle arrest in human breast carcinoma cells. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatani, T.; Matsuzaki, T.; Kim, S.; Baba, N.; Ichiyama, S.; Miyamoto, H.; Nakajima, H. Treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) by extracorporeal photochemotherapy. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1990, 1, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethea, D.; Fullmer, B.; Syed, S.; Seltzer, G.; Tiano, J.; Rischko, C.; Gillespie, L.; Brown, D.; Gasparro, F.P. Psoralen photobiology and photochemotherapy: 50 years of science and medicine. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1999, 19, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, K.E. PUVA, Psoralens and Skin Cancer. Skin Cancer UV Radiat. 1997, 416–424. [Google Scholar]
- El-Domyati, M.; Moftah, N.H.; Nasif, G.A.; Abdel-Wahab, H.M.; Barakat, M.T.; Abdel-Aziz, R.T. Evaluation of apoptosis regulatory proteins in response to PUVA therapy for psoriasis. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2013, 29, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtick, U.; Wang, X.N.; Marshall, S.R.; Von Bergwelt-Baildon, M.; Scheid, C.; Dickinson, A.M. In Vitro PUVA Treatment Preferentially Induces Apoptosis in Alloactivated T Cells. Transplantation 2012, 94, e31–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, I.M.; Chimenti, S.; Gasparro, F.P. Psoralen-protein photochemistry—A forgotten field. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 1995, 27, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aelst, B.; Devloo, R.; Zachee, P.; T’Kindt, R.; Sandra, K.; Vandekerckhove, P.; Compernolle, V.; Feys, H.B. Psoralen and Ultraviolet A Light Treatment Directly Affects Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Signal Transduction by Altering Plasma Membrane Packing. J. Boil. Chem. 2016, 291, 24364–24376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Gooden, D.; Liu, L.; Zhao, S.; Soderblom, E.J.; Toone, E.J.; Beyer, W.F.; Walder, H.; Spector, N. Photo-Activated Psoralen Binds the ErbB2 Catalytic Kinase Domain, Blocking ErbB2 Signaling and Triggering Tumor Cell Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, G.; Colón, K.L.; Fuller, A.; Sainuddin, T.; Bradner, E.; McCain, J.; Monro, S.M.A.; Yin, H.; Hetu, M.W.; Cameron, C.G.; et al. Cyclometalated Ruthenium(II) Complexes Derived from α-Oligothiophenes as Highly Selective Cytotoxic or Photocytotoxic Agents. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 7694–7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Jin, W.-R.; Shi, Q.; He, H.; Ma, Z.; Qu, H.-B. Two novel thiophenes from Echinops grijissi Hance. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 10, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galushko, S.; Shishkina, I.; Alekseeva, I. Relationship between retention parameters in reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography and antitumour activity of some pyrimidine bases and nucleosides. J. Chromatogr. A 1991, 547, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Johnson, S.; Powell, D.; McGinnis, J.P.; Miranda, M.; Rabindran, S.K. Inhibition of tumor cell proliferation by thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(1H)-one-based analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 3763–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagarsamy, V.; Meena, S.; Ramseshu, K.; Solomon, V.; Thirumurugan, K.; Dhanabal, K.; Murugan, M. Synthesis, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, ulcerogenic index and antibacterial activities of novel 2-methylthio-3-substituted-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo (b) thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-ones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 41, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starcevic, K.; Kralj, M.; Piantanida, I.; Šuman, L.; Pavelic, K.; Karminski-Zamola, G. Synthesis, photochemical synthesis, DNA binding and antitumor evaluation of novel cyano- and amidino-substituted derivatives of naphtho-furans, naphtho-thiophenes, thieno-benzofurans, benzo-dithiophenes and their acyclic precursors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 41, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, M.A.; Romero, M.A.; Navarro, J.A. Cyclic assemblies formed by metal ions, pyrimidines and isogeometrical heterocycles: DNA binding properties and antitumour activity. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2009, 362, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prachayasittikul, S.; Worachartcheewan, A.; Nantasenamat, C.; Chinworrungsee, M.; Sornsongkhram, N.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of 2-thiopyrimidine-4-one analogs as antimicrobial and anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Shi, Q.; Hong, C.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, Z.; Qu, H. Cytotoxic properties of thiophenes from Echinops grijissi Hance. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunagaran, D.; Rashmi, R.; Kumar, T.R.S. Induction of Apoptosis by Curcumin and Its Implications for Cancer Therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2005, 5, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tønnesen, H.H.; De Vries, H.; Karlsen, J.; Van Henegouwen, G.B. Studies on Curcumin and Curcuminoids IX: Investigation of the Photobiological Activity of Curcumin Using Bacterial Indicator Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1987, 76, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, T.A.; McGowan, W.M.; Shand, M.A.; Srinivasan, V.S. Photokilling of bacteria by the natural dye curcumin. Arch. Microbiol. 1989, 151, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haukvik, T.; Bruzell, E.; Kristensen, S.; Tønnesen, H.H. Photokilling of bacteria by curcumin in selected polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG 400) preparations. Studies on curcumin and curcuminoids, XLI. Die Pharm. 2010, 65, 600–606. [Google Scholar]
- Nardo, L.; Andreoni, A.; Másson, M.; Haukvik, T.; Tønnesen, H.H. Studies on Curcumin and Curcuminoids. XXXIX. Photophysical Properties of Bisdemethoxycurcumin. J. Fluoresc. 2010, 21, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzell, E.M.; Morisbak, E.; Tønnesen, H.H. Studies on curcumin and curcuminoids. XXIX. Photoinduced cytotoxicity of curcumin in selected aqueous preparations. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2005, 4, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardo, L.; Andreoni, A.; Bondani, M.; Másson, M.; Haukvik, T.; Tønnesen, H.H. Studies on Curcumin and Curcuminoids. XLVI. Photophysical Properties of Dimethoxycurcumin and Bis-dehydroxycurcumin. J. Fluoresc. 2011, 22, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardo, L.; Andreoni, A.; Bondani, M.; Másson, M.; Tønnesen, H.H. Studies on curcumin and curcuminoids. XXXIV. Photophysical properties of a symmetrical, non-substituted curcumin analogue. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2009, 97, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, N.C.; Fontana, C.R.; Gerbi, M.E.M.; Bagnato, V.S. Overall-Mouth Disinfection by Photodynamic Therapy Using Curcumin. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2012, 30, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego-Filho, F.D.A.; De Araujo, M.T.; De Oliveira, K.T.; Bagnato, V.S. Validation of Photodynamic Action via Photobleaching of a New Curcumin-Based Composite with Enhanced Water Solubility. J. Fluoresc. 2014, 24, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedhar, A.; Sarkar, I.; Rajan, P.; Pai, J.; Malagi, S.; Kamath, V.; Barmappa, R. Comparative evaluation of the efficacy of curcumin gel with and without photo activation as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in the treatment of chronic periodontitis: A split mouth clinical and microbiological study. J. Nat. Sci. Boil. Med. 2015, 6, 102–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacRobert, A.J.; Komerik, N. Photodynamic Therapy as an Alternative Antimicrobial Modality for Oral Infections. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2006, 25, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadarsini, K.I. Photophysics, photochemistry and photobiology of curcumin: Studies from organic solutions, bio-mimetics and living cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2009, 10, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, R.K.; Singh, A.K.; Gaddipati, J.; Srimal, R.C. Multiple biological activities of curcumin: A short review. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yance, D.R.; Sagar, S.M. Targeting Angiogenesis with Integrative Cancer Therapies. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvioli, S.; Sikora, E.; Cooper, E.L.; Franceschi, C. Curcumin in Cell Death Processes: A Challenge for CAM of Age-Related Pathologies. Evidence-Based Complement Altern. Med. 2007, 4, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.; Evangelopoulos, A.; Schizas, N.; Kazazis, C. Potential anticancer properties and mechanisms of action of curcumin. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 645–651. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.-Y.; Zhong, X.; Yum, H.-W.; Lee, H.-J.; Kundu, J.K.; Na, H.-K.; Surh, Y.-J. Curcumin Inhibits STAT3 Signaling in the Colon of Dextran Sulfate Sodium-treated Mice. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 18, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovigo, L.N.; Pavarina, A.C.; Carmello, J.C.; Machado, A.L.; Brunetti, I.L.; Bagnato, V.S. Susceptibility of clinical isolates of Candida to photodynamic effects of curcumin. Lasers Surg. Med. 2011, 43, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernd, A. Visible light and/or UVA offer a strong amplification of the anti-tumor effect of curcumin. Phytochem. Rev. 2013, 13, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.-H.; Wu, H.-J. Anti-apoptotic effects of curcumin on photosensitized human epidermal carcinoma A431 cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 92, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, N.C.; Fontana, C.R.; Bagnato, V.S.; Gerbi, M.E.M. Photodynamic Effects of Curcumin Against Cariogenic Pathogens. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2012, 30, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyhe, S. Morphine: New aspects in the study of an ancient compound. Life Sci. 1994, 55, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shao, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Tong, L.; Li, C.; Shen, X.; Ding, J. BM6, a new semi-synthetic vinca alkaloid, exhibits its potent in vivo anti-tumor activities via its high binding affinity for tubulin and improved pharmacokinetic profiles. Cancer Boil. Ther. 2007, 6, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Gao, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, H.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Miao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Shen, H.; et al. Chimmitecan, a Novel 9-Substituted Camptothecin, with Improved Anticancer Pharmacologic Profiles In vitro and In vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xun, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. A systematic review of the anticancer properties of berberine, a natural product from Chinese herbs. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2009, 20, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, K.S.; Kim, H.-J.; So, H.-S.; Park, R.; Kim, T.Y. Berberine-induced apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G cells is mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress accompanying reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial dysfunction. Boil. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 1644–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogo, C.V.; Machado, N.G.; Barbosa, I.A.; Serafim, T.L.; Burgeiro, A.; Oliveira, P.J. Berberine as a Promising Safe Anti-Cancer Agent- Is there a Role for Mitochondria? Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Lu, J.-J.; Huang, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, G.; Gong, J.; Zhong, Z.; Xu, Z.; Dang, Y.; et al. Anti-cancer natural products isolated from chinese medicinal herbs. Chin. Med. 2011, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgeiro, A.A.C.; Gajate, C.; Dakir, E.H.; Villa-Pulgarin, J.A.; Oliveira, P.J.; Mollinedo, F. Involvement of mitochondrial and B-RAF/ERK signaling pathways in berberine-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2011, 22, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, M.-J.; So, H.-S.; Cho, H.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Sohn, J.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Chung, S.-Y.; Park, R. Berberine, a Natural Product, Combined with Cisplatin Enhanced Apoptosis through a Mitochondria/Caspase-Mediated Pathway in HeLa Cells. Boil. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, J.-M.; Hyun, M.-S.; Lim, S.; Lee, W.-Y.; Kim, N. The combination of berberine and irradiation enhances anti-cancer effects via activation of p38 MAPK pathway and ROS generation in human hepatoma cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 107, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreazza, N.L.; Vevert-Bizet, C.; Bourg-Heckly, G.; Sureau, F.; Salvador, M.J.; Bonneau, S. Berberine as a Photosensitizing Agent for Antitumoral Photodynamic Therapy: Insights into its Association to Low Density Lipoproteins. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 510, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Gupta, P.; Bandyopadhyay, S.K.; Patro, B.S.; Chattopadhyay, S. Coralyne, a protoberberine alkaloid, causes robust photosenstization of cancer cells through ATR-p38 MAPK-BAX and JAK2-STAT1-BAX pathways. Chem. Interact. 2018, 285, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, J.P.; Labrador, V.; Freire, P.F.; Molero, M.L.; Hazen, M. Ultrastructural changes induced in HeLa cells after phototoxic treatment with harmine. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2004, 24, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnason, J.T.; Towers, G.H.N.; Abramowski, Z.; Campos, F.; Champagne, D.; McLachlan, D.; Philogène, B.J.R. Berberine: A naturally occurring phototoxic alkaloid. J. Chem. Ecol. 1984, 10, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.-L.; Wang, M.; Zhu, H.; Li, K.; Zhu, R.-R.; Sun, X.-Y.; Yao, S.-D.; Wu, Q.-S.; Wang, S.-L. Characterization of the transient species generated by the photoionization of Berberine: A laser flash photolysis study. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 73, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantova, S.; Letašiová, S.; Brezová, V.; Cipak, L.; Lábaj, J. Photochemical and phototoxic activity of berberine on murine fibroblast NIH-3T3 and Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2006, 85, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, H.; Ledwani, L. A review on anthraquinones isolated from Cassia species and their applications. Indian J. Nat. Prod. Resour. 2012, 3, 291–319. [Google Scholar]
- Seigler, D.S. Plant Secondary Metabolism; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, I.; Bertolotti, S.G.; Biasutti, M.; Soltermann, A.T.; García, N.A. Quinones and hydroxyquinones as generators and quenchers of singlet molecular oxygen. Can. J. Chem. 1997, 75, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłowska, J.; Tarasiuk, J.; Wolf, C.R.; Paine, M.J.I.; Borowski, E. Differential Ability of Cytostatics From Anthraquinone Group to Generate Free Radicals in Three Enzymatic Systems: NADH Dehydrogenase, NADPH Cytochrome P450 Reductase, and Xanthine Oxidase. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2003, 13, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A. Herbal Drugs as Therapeutic Agents; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Montoya, S.C.N.; Comini, L.; Vittar, B.R.; Fernández, I.M.; Rivarola, V.A.; Cabrera, J.L. Phototoxic effects of Heterophyllaea pustulata (Rubiaceae). Toxicon 2008, 51, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comini, L.; Fernandez, I.; Vittar, N.R.; Montoya, S.N.; Cabrera, J.L.; Rivarola, V.A. Photodynamic activity of anthraquinones isolated from Heterophyllaea pustulata Hook f. (Rubiaceae) on MCF-7c3 breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vittar, N.B.R.; Awruch, J.; Azizuddin, K.; Rivarola, V.A. Caspase-independent apoptosis, in human MCF-7c3 breast cancer cells, following photodynamic therapy, with a novel water-soluble phthalocyanine. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Boil. 2010, 42, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirillo, J.; De Simone, B.C.; Russo, N. Photophysical properties prediction of selenium- and tellurium-substituted thymidine as potential UVA chemotherapeutic agents. Theor. Chem. Accounts 2015, 135, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, G.; Alberto, M.E.; De Simone, B.C.; Marino, T.; Russo, N. Can Expanded Bacteriochlorins Act as Photosensitizers in Photodynamic Therapy? Good News from Density Functional Theory Computations. Molecules 2016, 21, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Doustvandi, M.A.; Mohammadnejad, F.; Kamari, F.; Gjerstorff, M.F.; Baradaran, B.; Hamblin, M.R. Photodynamic therapy for cancer: Role of natural products. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 26, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.K.; Goswami, L.N.; Chen, Y.; Gryshuk, A.; Missert, J.R.; Oseroff, A.; Dougherty, T.J. Nature: A rich source for developing multifunctional agents. tumor-imaging and photodynamic therapy. Lasers Surg. Med. 2006, 38, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Name | Absorption Maxima | Chemical Property and Groups | Natural Sources | Possible Mode of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Furanocoumarins | 333 nm | Aromatic compounds possessing a furan ring. | Angelicae dahuricae, Tetradium daniellii, Glehnia littoralis, Heracleum persicum, Syzygium Sps, Ruta graveolens, Ficus sps. | DNA intercalation under dark type 2 PDT reaction. Crosslinking and adduct formation with DNA and RNA. Cell membrane damage. | [68,69,70] |
| Polyacetylenes and Thiophenes | 488 nm | Furanoacetylenes thiarubrines, thiophenes, polyacetylene (aliphatic compounds with more than three conjugated triple bonds), thiophenes (aromatic acetylenes; e.g., phenylheptatriyne). | Asteraceae spp, Heliopsisa, Rudbeckia spp, Arnica, Centaurea scabiosa, Tagetes erecta, Porophyllum obscurum, Echinops, Bidens, Ambrosia chamissonis, T. minuta, E. latifolius, E. sgrijissi, Rhaponticum uniflorum. | Membrane damage or erythrocyte leakage; type 1 and type 2 PDT reaction, as well as type 1 and 2 PDT mixed reaction. | [71,72,73,74,75] |
| Curcumins | 420–480 nm | Dicinnamoylmethane, curcumin, curcuminoids, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin. | Curcuma longa. | Cell membrane is the primary target of curcuminoids. Induction of caspase-mediated cell death. | [76,77,78] |
| Alkaloids | 360 nm | Chinolin alkaloids, pterins, benzylisoquinolines, beta-carbolines, harmine. | Guatteria blepharophylla, Berberis vulgaris, Sanguinaria Canadensis, Mahonia aquifolium Peganum harmala, Indigofera tinctoria. | Photo-oxidises histidine and tryptophan, resulting in DNA crosslinking. Photooxidation, type 1 PDT mechanism and targets mitochondria. | [79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87] |
| Anthraquinones | 437 nm | Hydroxyanthraquinones, rhein, physcion, emodin, rubiadin, damnacanthol, soranjidiol, alizarin, purpurin, rubiadin, aloe-emodin, 1,5-dihydroxy przewalsquinone B, ziganein, uredinorubellins, caeruleoramularin, hypericin, cercosporin, elsinochromes A-C pleichrome, hypocrellin. | Polygonum cuspidatum, Heterophyllaea pustulata, H. lycioides Aloe vera, Rheum palmatum, Rumex crispus Polyathia suberosa, Dactylopius coccus, Xanthoria parietina, Drechslera avenae, Ramularia collo-cygni. H. perforatum, Fagopyrum esculentum. | Type 1 and 2 PDT action. | [88,89,90,91] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muniyandi, K.; George, B.; Parimelazhagan, T.; Abrahamse, H. Role of Photoactive Phytocompounds in Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer. Molecules 2020, 25, 4102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184102
Muniyandi K, George B, Parimelazhagan T, Abrahamse H. Role of Photoactive Phytocompounds in Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer. Molecules. 2020; 25(18):4102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184102
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuniyandi, Kasipandi, Blassan George, Thangaraj Parimelazhagan, and Heidi Abrahamse. 2020. "Role of Photoactive Phytocompounds in Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer" Molecules 25, no. 18: 4102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184102
APA StyleMuniyandi, K., George, B., Parimelazhagan, T., & Abrahamse, H. (2020). Role of Photoactive Phytocompounds in Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer. Molecules, 25(18), 4102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184102