Quinoline-Based Molecules Targeting c-Met, EGF, and VEGF Receptors and the Proteins Involved in Related Carcinogenic Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
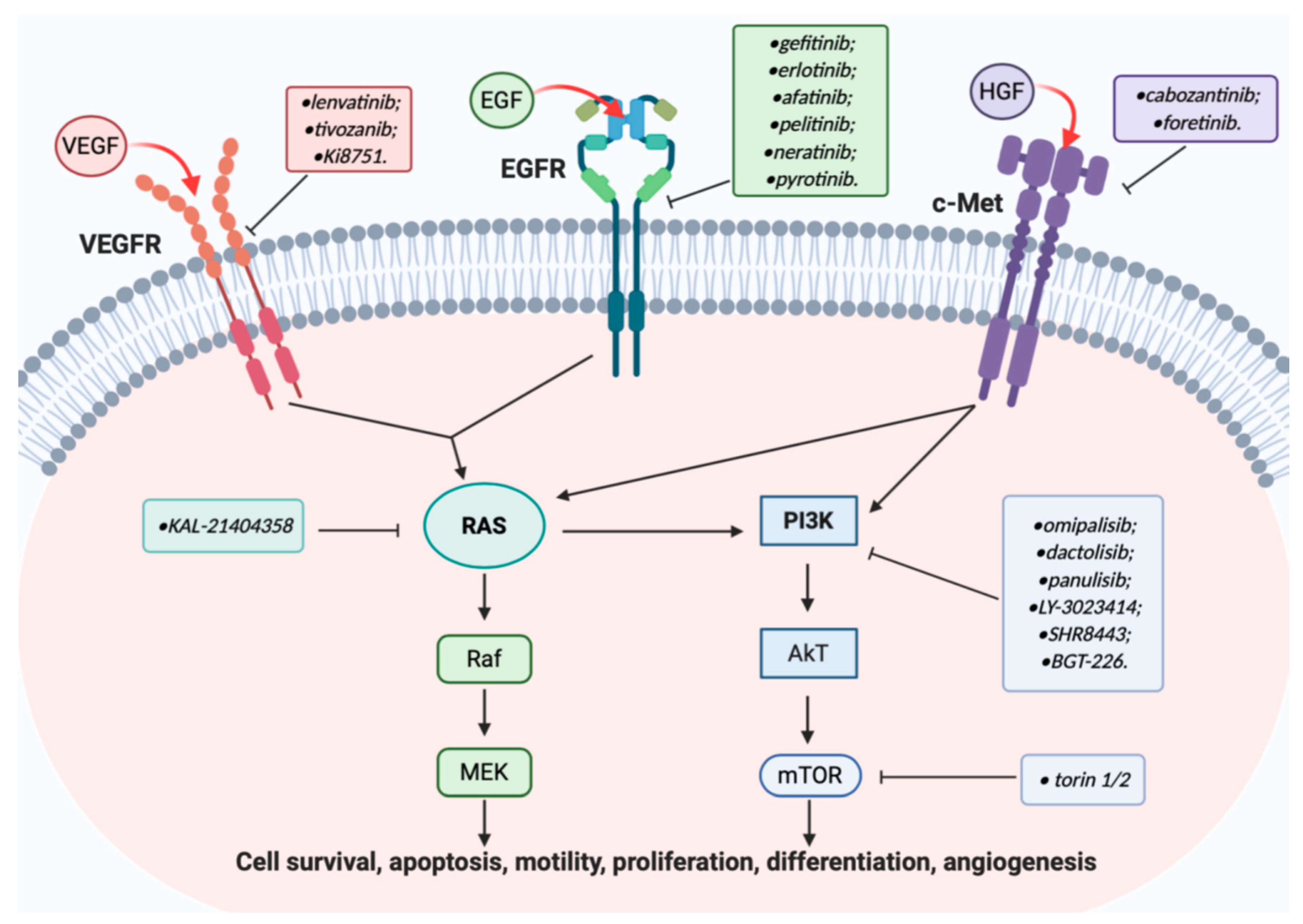
EGFR, c-MET, and VEGFR Signal Pathways in Cancer Cell
2. Quinolines as Inhibitors of Carcinogenic Pathways
2.1. Quinoline Based Inhibitors of c-Met Receptor
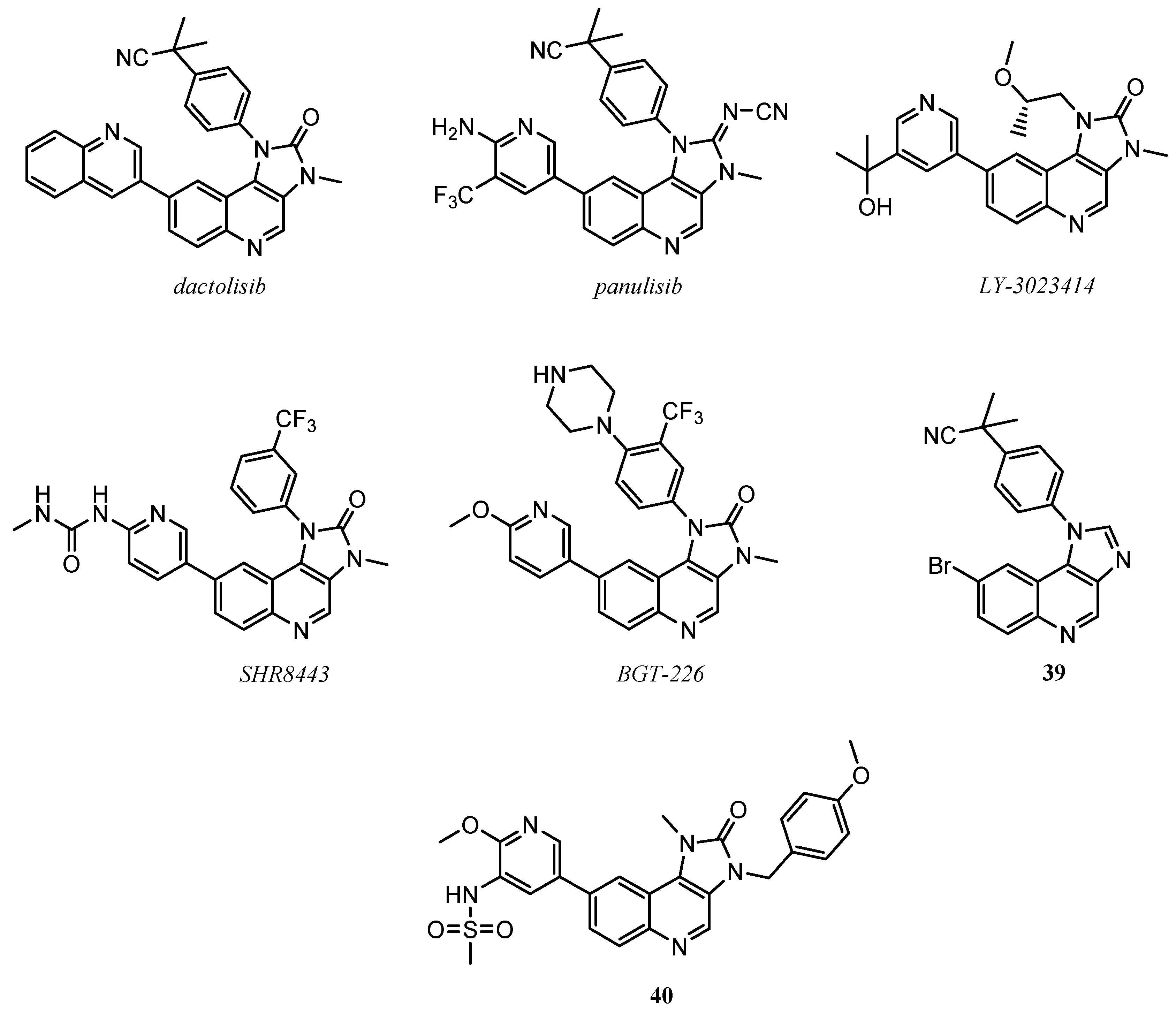
2.2. Quinoline as Inhibitor of PI3k/AkT/mTOR Pathway
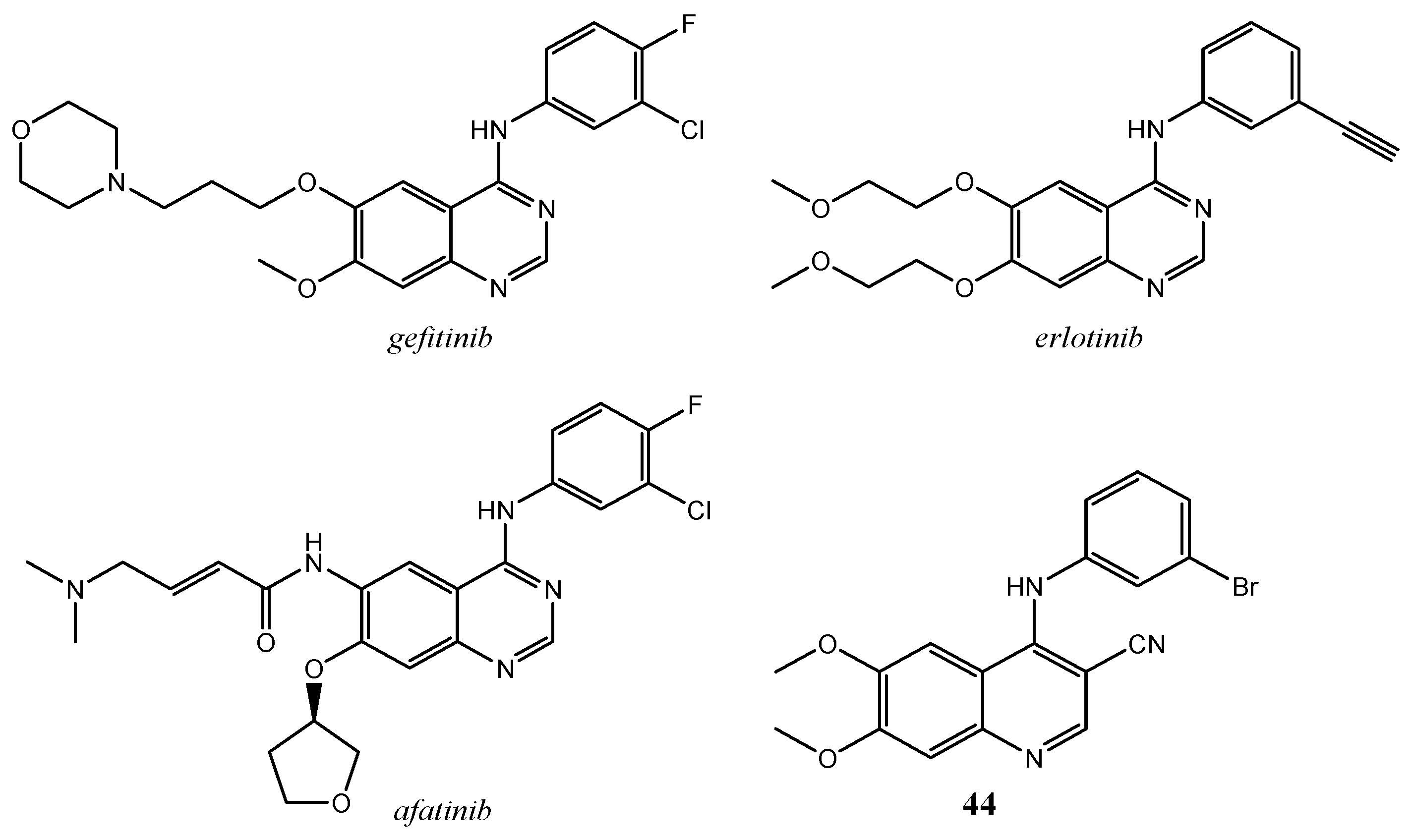
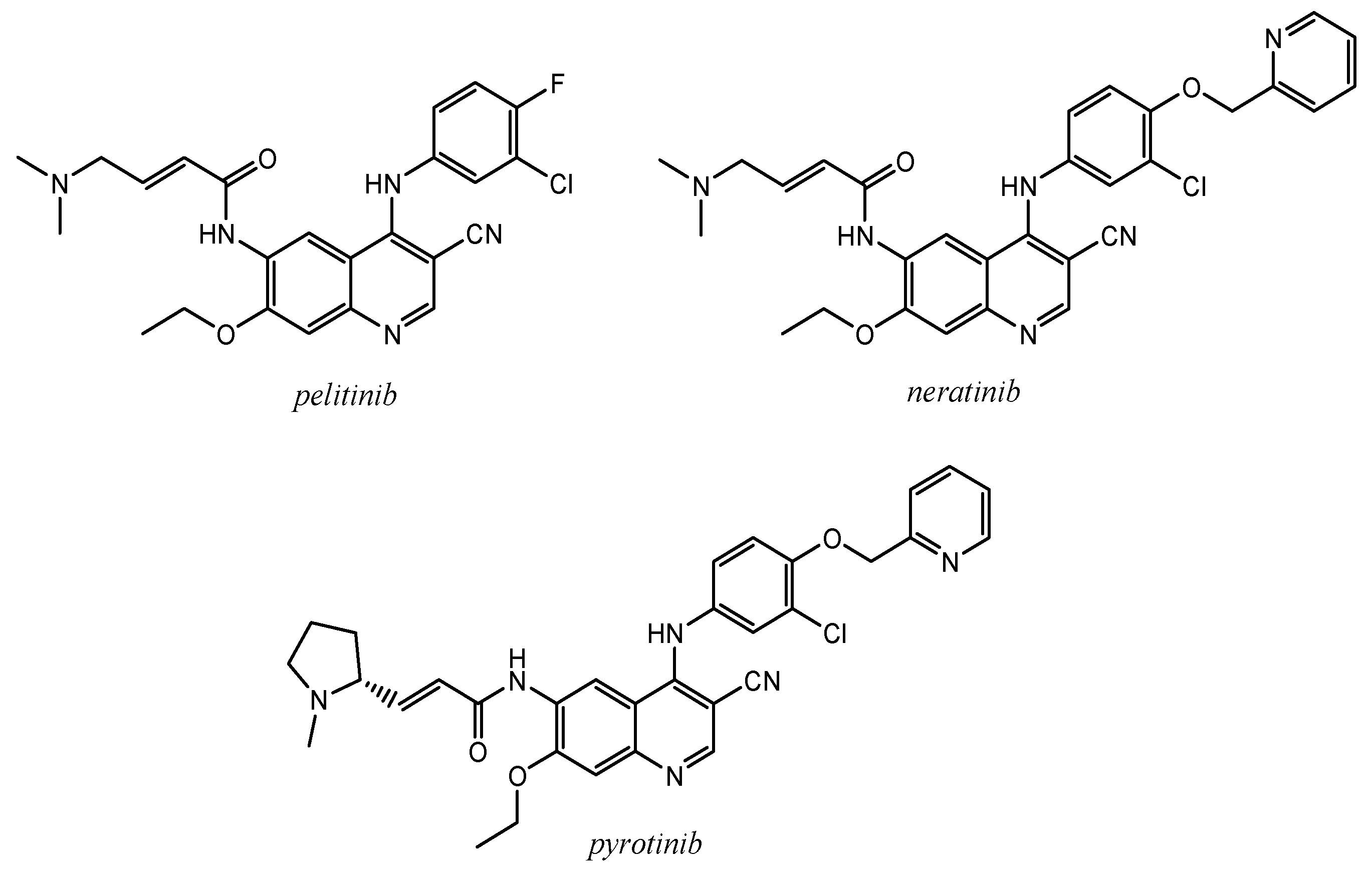
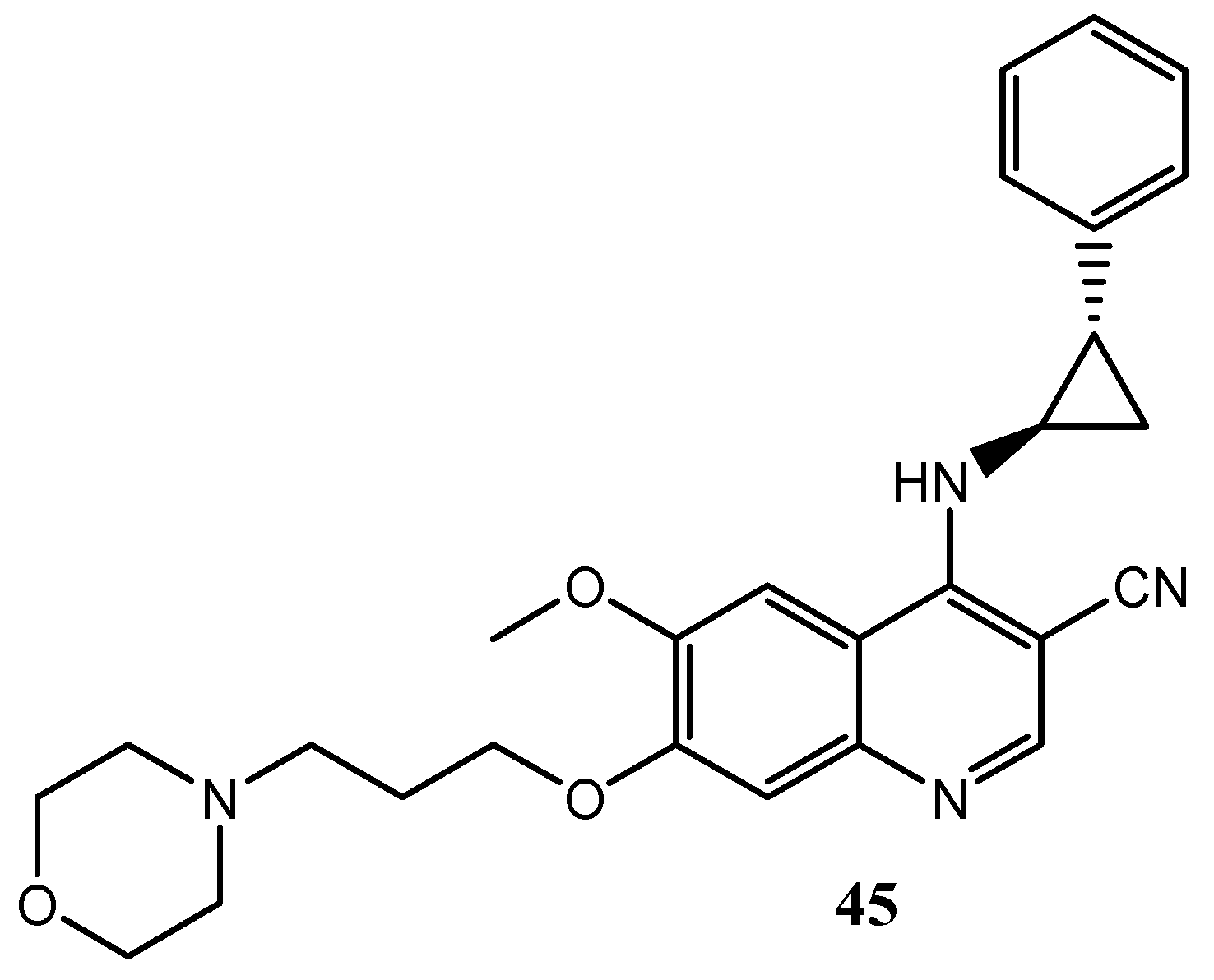
2.3. Quinoline Derivatives as Inhibitors of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors
2.4. Quinoline Derivatives as Inhibitors of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor
2.5. Quinoline Derivatives as Inhibitors of Ras/Raf/MEK Pathway
3. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marella, A.; Tanwar, O.P.; Saha, R.; Ali, M.R.; Srivastava, S.; Akhter, M.; Shaquiquzzaman, M.; Alam, M.M. Quinoline: A versatile heterocyclic. Saudi. Pharm. J. 2013, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Afzal, O.; Kumar, S.; Haider, M.R.; Ali, M.R.; Kumar, R.; Jaggi, M.; Bawa, S. A review on anticancer potential of bioactive heterocycle quinoline. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 871–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musiol, R. An overview of quinoline as a privileged scaffold in cancer drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R. Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 19–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R. Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors: A 2020 update. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 152, 104609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.E.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Deininger, M.W.; Mauro, M.J.; Chuah, C.; Kim, D.W.; Dyagil, I.; Glushko, N.; Milojkovic, D.; le Coutre, P.; et al. Bosutinib Versus Imatinib for Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Results From the Randomized BFORE Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zschäbitz, S.; Grüllich, C. Lenvantinib: A Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor of VEGFR 1-3, FGFR 1-4, PDGFRα, KIT and RET. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018, 211, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
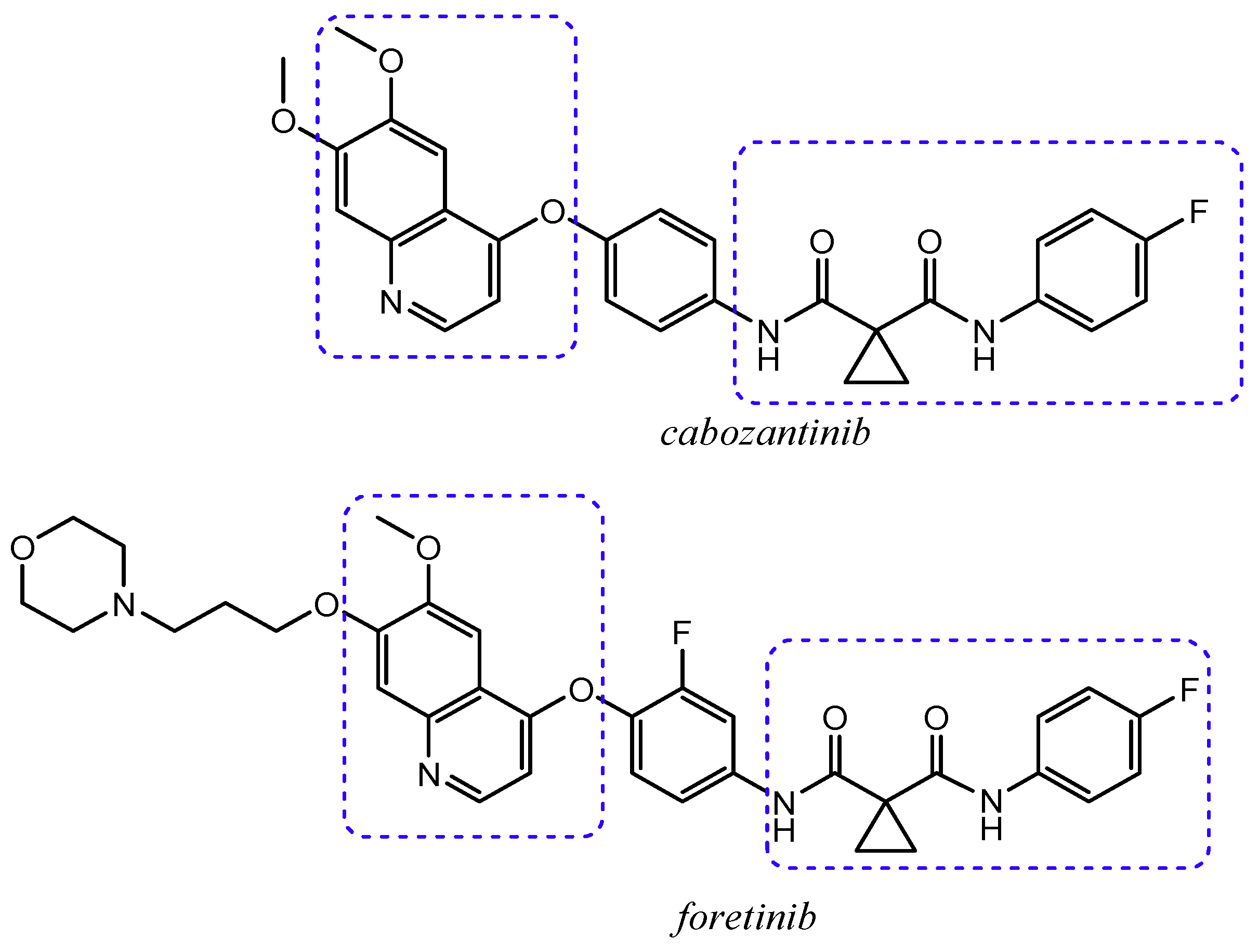
- Markowitz, J.N.; Fancher, K.M. Cabozantinib: A Multitargeted Oral Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor. Pharmacotherapy 2018, 38, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, E.D. Neratinib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Ando, K.; Ohba, M.; Ohmori, T. Receptor Tyrosine Kinase-Targeted Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, M.; Jin, K.; Wang, S.; Wei, H.; Fan, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Function of the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase in carcinogenesis and associated therapeutic opportunities. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birchmeier, C.; Birchmeier, W.; Gherardi, E.; Vande Woude, G.F. Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organ, S.L.; Tsao, M.S. An overview of the c-MET signaling pathway. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2011, 3, S7–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, M.; Kochhar, K.; Nakamura, T.; Iyer, A. Hepatocyte growth factor-induced signal transduction in two normal mouse epithelial cell lines. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1995, 36, 465–474. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, L.; Muzumdar, M.D.; Zhu, A.X. Targeting the HGF/c-MET pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2310–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maroun, C.R.; Rowlands, T. The Met receptor tyrosine kinase: A key player in oncogenesis and drug resistance. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 142, 316–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerling, B.M.; Akcakanat, A. Targeting PI3K/mTOR signaling in cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7351–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Cheng, H.; Roberts, T.M.; Zhao, J.J. Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, K.K.; Toker, A. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway and therapy resistance in cancer. F1000Prime Rep. 2015, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; He, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, L. Recent advances in the development of dual VEGFR and c-Met small molecule inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 108, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola, S.; Varese, M.; Sanchez-Navarro, M.; Giralt, E. A Third Shot at EGFR: New Opportunities in Cancer Therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 941–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J.; Ferguson, K.M. The EGFR family: Not so prototypical receptor tyrosine kinases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2014, 6, a020768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citri, A.; Yarden, Y. EGF-ERBB signalling: Towards the systems level. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, M. VEGF-VEGFR Signals in Health and Disease. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2014, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.P.; LeCouter, J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.; Maiello, M.R.; D’Alessio, A.; Pergameno, M.; Normanno, N. The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and the PI3K/AKT signalling pathways: Role in cancer pathogenesis and implications for therapeutic approaches. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16 (Suppl. 2), S17–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asati, V.; Mahapatra, D.K.; Bharti, S.K. PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways inhibitors as anticancer agents: Structural and pharmacological perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 109, 314–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarden, Y. The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer: Signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37 (Suppl. 4), S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakes, F.M.; Chen, J.; Tan, J.; Yamaguchi, K.; Shi, Y.; Yu, P.; Qian, F.; Chu, F.; Bentzien, F.; Cancilla, B.; et al. Cabozantinib (XL184), a novel MET and VEGFR2 inhibitor, simultaneously suppresses metastasis, angiogenesis, and tumor growth. Mol. Cancer Ther 2011, 10, 2298–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Underiner, T.L.; Herbertz, T.; Miknyoczki, S.J. Discovery of small molecule c-Met inhibitors: Evolution and profiles of clinical candidates. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Engst, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yu, P.; Won, K.A.; Mock, L.; Lou, T.; Tan, J.; Li, C.; Tam, D.; et al. Inhibition of tumor cell growth, invasion, and metastasis by EXEL-2880 (XL880, GSK1363089), a novel inhibitor of HGF and VEGF receptor tyrosine kinases. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8009–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Ye, Z.D.; Shen, C.; Tie, H.X.; Wang, L.; Shi, L. Synthesis of novel 6,7-dimethoxy-4-anilinoquinolines as potent c-Met inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; He, C.; Gong, P. Design, synthesis and antitumour activity of bisquinoline derivatives connected by 4-oxy-3-fluoroaniline moiety. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 64, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, P.K.; Ghate, M.D. Recent advances in the discovery of small molecule c-Met Kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 1103–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Kou, J.; Xiao, Z.; Tian, F.; Hu, J.; Zheng, P.; Zhu, W. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 6,7-Disubstituted-4-phenoxyquinoline Derivatives Bearing Pyridazinone Moiety as c-Met Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Yang, D.; Yang, X.; Nie, M.; Wu, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Gong, P. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 4-phenoxyquinoline derivatives containing 3-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinoxaline moiety as c-Met kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 4475–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, N.; Zhao, S.; Xi, S.; Wang, J.; Jing, T.; Zhang, W.; Guo, M.; Gong, P.; Zhai, X. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 4-(2-fluorophenoxy)quinoline derivatives as selective c-Met inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Hou, Y.; Yin, W.; Zhou, S.; Qian, P.; Guo, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Y. Discovery of a novel 6,7-disubstituted-4-(2-fluorophenoxy)quinolines bearing 1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxamide moiety as potent c-Met kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 119, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liao, H.; Liu, M.; Feng, G.; Fu, B.; Li, R.; Cheng, M.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, P. Discovery andw biological evaluation of novel 6,7-disubstituted-4-(2-fluorophenoxy)quinoline derivatives possessing 1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxamide moiety as c-Met kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 6438–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Hu, G.; Guo, Z.; Sun, D.; Zhang, L.; Bu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gong, P. Design and biological evaluation of novel 4-(2-fluorophenoxy)quinoline derivatives bearing an imidazolone moiety as c-Met kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 4410–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Xu, C.; Ji, X.; Hu, G.; Ren, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Gong, P.; Sun, T. Design and optimization of novel 4-(2-fluorophenoxy)quinoline derivatives bearing a hydrazone moiety as c-Met kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 87, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Du, X.; Chong, L.; Gong, P.; Guo, C. Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships of novel 6,7-disubstituted-4-phenoxyquinoline derivatives as potential antitumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 69, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Gao, Y.; Han, J.; Cui, B.; Gong, P. Discovery of novel 4-(2-fluorophenoxy)quinoline derivatives bearing 4-oxo-1,4-dihydrocinnoline-3-carboxamide moiety as c-Met kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 2843–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Tao, H.; Wu, D.; Bai, J.; Shi, Y.; Gong, P. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 4-phenoxy-6,7-disubstituted quinolines possessing semicarbazone scaffolds as selective c-Met inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 2013, 346, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhai, X. Novel quinoline derivatives and their applications. U.S. Patent 9783499 B2, 10 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, P.P.; Funk, L.; Meng, J.; Alton, G.; Padrique, E.; Mroczkowski, B. Structure activity relationships of quinoline-containing c-Met inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H. Preparation of Quinoline Compounds Containing 1,2,4-Triazine-Dione and Use as c-Met Kinase Inhibitors for Treating Proliferative Diseases. U.S. Patent 20130252958 A1, 26 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Duan, Y.; Xiong, H.; Chen, T.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, W.; et al. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of 6,7-disubstituted-4-phenoxyquinoline derivatives bearing the 1,8-naphthyridin-2-one moiety. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ai, J.; Shi, D.; Peng, X.; Ji, Y.; Liu, J.; Geng, M.; Li, Y. Discovery of novel type II c-Met inhibitors based on BMS-777607. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 80, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiang, R.; Qin, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Gong, P. Synthesis and antitumor activity of novel 4-(2-fluorophenoxy)quinoline derivatives bearing the 4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide moiety. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 2013, 346, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Du, X.; Zhu, W.; Li, R.; Lin, H.; Li, P.; Cheng, M.; Gong, P.; Zhao, Y. Discovery of novel 6,7-disubstituted-4-phenoxyquinoline derivatives bearing 5-(aminomethylene)pyrimidine-2,4,6-trione moiety as c-Met kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 1236–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Guo, R.; Hu, J.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, P. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 6,7-disubstituted-4-phenoxyquinoline derivatives bearing 4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazine-1-carboxamide moieties as c-Met kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 3642–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Ren, J.; Liu, M.; Ren, L.; Liu, Y.; Gong, P. Design, synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of 6,7-disubstituted-4-phenoxyquinoline derivatives as potential antitumor agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2014, 57, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Bao, G.; Wang, L.; Cheng, M.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, H.; Gong, P. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 4-phenoxy-6,7-disubstituted quinolines possessing (thio)semicarbazones as c-Met kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 1331–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ai, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Geng, M.; Zhang, A. Synthesis and c-Met kinase inhibition of 3,5-disubstituted and 3,5,7-trisubstituted quinolines: Identification of 3-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)-5-(3-nitrobenzylamino)-7- (trifluoromethyl)quinoline as a novel anticancer agent. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 2127–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Ai, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, T.; Zhao, A.; Peng, X.; Wang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Yao, Q.; Xu, Y.; et al. Multisubstituted quinoxalines and pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidines: Synthesis and SAR study as tyrosine kinase c-Met inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 6368–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ai, J.; Yue, J.; Peng, X.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, A.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; et al. Further SAR studies on 3,5-diamino-7-trifluoromethylquinolines as highly potent tyrosine kinase c-Met inhibitors: Efforts to correct hERG inhibition. MedChemComm 2012, 3, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishii, H.; Chiba, T.; Morikami, K.; Fukami, T.A.; Sakamoto, H.; Ko, K.; Koyano, H. Discovery of 6-benzyloxyquinolines as c-Met selective kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, V.T.; Pettersen, S.; Haugen, M.H.; Olberg, D.E.; Maelandsmo, G.M.; Klaveness, J. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 6-substituted quinolines derived from cabozantinib as c-Met inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 2019, 352, e1900101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.J.; McTigue, M.; Nambu, M.; Tran-Dube, M.; Pairish, M.; Shen, H.; Jia, L.; Cheng, H.; Hoffman, J.; Le, P.; et al. Discovery of a novel class of exquisitely selective mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-MET) protein kinase inhibitors and identification of the clinical candidate 2-(4-(1-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-6-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1 -yl)ethanol (PF-04217903) for the treatment of cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 8091–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, S.; Boer, J.; Maduskuie, T.P.; Falahatpisheh, N.; Li, Y.; Yeleswaram, S. Species-specific metabolism of SGX523 by aldehyde oxidase and the toxicological implications. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Infante, J.R.; Rugg, T.; Gordon, M.; Rooney, I.; Rosen, L.; Zeh, K.; Liu, R.; Burris, H.A.; Ramanathan, R.K. Unexpected renal toxicity associated with SGX523, a small molecule inhibitor of MET. Invest. New Drugs 2013, 31, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolkema, M.P.; Bohets, H.H.; Arkenau, H.T.; Lampo, A.; Barale, E.; de Jonge, M.J.A.; van Doorn, L.; Hellemans, P.; de Bono, J.S.; Eskens, F.A.L.M. The c-Met Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor JNJ-38877605 Causes Renal Toxicity through Species-Specific Insoluble Metabolite Formation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2297–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.W.; Xiao, W.; Gao, Z.T.; Yu, Z.T.; Zhang, J.Y.J. Metabolism of c-Met Kinase Inhibitors Containing Quinoline by Aldehyde Oxidase, Electron Donating, and Steric Hindrance Effect. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Hao, Y.; Shi, C.; Xia, G.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y. Discovery and optimization of a series of imidazo[4,5-b]pyrazine derivatives as highly potent and exquisitely selective inhibitors of the mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-Met) protein kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4281–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, L.D.; Hao, Y.; Chen, N.; Bai, R.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, C.C.; Li, G.S.; Hao, L.J.; Shi, C.; et al. Identification of 3-substituted-6-(1-(1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)ethyl)quinoline derivatives as highly potent and selective mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-Met) inhibitors via metabolite profiling-based structural optimization. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 134, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, S.D.; Adams, N.D.; Burgess, J.L.; Chaudhari, A.M.; Darcy, M.G.; Donatelli, C.A.; Luengo, J.I.; Newlander, K.A.; Parrish, C.A.; Ridgers, L.H.; et al. Discovery of GSK2126458, a Highly Potent Inhibitor of PI3K and the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munster, P.; Aggarwal, R.; Hong, D.; Schellens, J.H.; van der Noll, R.; Specht, J.; Witteveen, P.O.; Werner, T.L.; Dees, E.C.; Bergsland, E.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Study of GSK2126458, an Oral Pan-Class I Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumor Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, N.; Siegmund, A.; Liu, L.; Yang, K.; Bryan, M.C.; Andrews, K.L.; Bo, Y.; Booker, S.K.; Caenepeel, S.; Freeman, D.; et al. Phospshoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) dual inhibitors: Discovery and structure-activity relationships of a series of quinoline and quinoxaline derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 4735–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Ying, H.; Ma, X.; Qiu, N.; Wu, P.; Yang, B.; Hu, Y. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 4-alkynyl-quinoline derivatives as PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 99, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lv, X.; Ma, X.; Hu, Y. Discovery of a series of N-(5-(quinolin-6-yl)pyridin-3-yl)benzenesulfonamides as PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Shen, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhan, S.; Ding, B.; Lv, X. Novel 4-Acrylamido-Quinoline Derivatives as Potent PI3K/mTOR Dual Inhibitors: The Design, Synthesis, and. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wan, W.Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, G.L.; Liu, X.G. Recent development of ATP-competitive small molecule phosphatidylinostitol-3-kinase inhibitors as anticancer agents. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 7181–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Lv, X.; Qiu, N.; Yang, B.; He, Q.; Hu, Y. Discovery of novel quinoline-based mTOR inhibitors via introducing intra-molecular hydrogen bonding scaffold (iMHBS): The design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 7585–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Qiu, N.; Yang, B.; He, Q.; Hu, Y. Novel quinoline-derived mTOR inhibitors with remarkable enzymatic and cellular activities: The design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Med. Chem. Commun. 2016, 7, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Lei, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B.; Yang, Z.; Li, W.; Zhu, W.; Xu, S. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Phenylsulfonylurea Derivatives as PI3K/mTOR Dual Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Echeverria, C.; Stauffer, F.; Furet, P. 1,3-Dihydro-Imidazo[4,5-c]Quinolin-2-Ones as Lipid Kinase Inhibitors. U.S. Patent PCT/EP2006/004725, 23 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Maira, S.M.; Stauffer, F.; Brueggen, J.; Furet, P.; Schnell, C.; Fritsch, C.; Brachmann, S.; Chène, P.; De Pover, A.; Schoemaker, K.; et al. Identification and characterization of NVP-BEZ235, a new orally available dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor with potent in vivo antitumor activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serra, V.; Markman, B.; Scaltriti, M.; Eichhorn, P.J.; Valero, V.; Guzman, M.; Botero, M.L.; Llonch, E.; Atzori, F.; Di Cosimo, S.; et al. NVP-BEZ235, a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, prevents PI3K signaling and inhibits the growth of cancer cells with activating PI3K mutations. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8022–8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiarini, F.; Grimaldi, C.; Ricci, F.; Tazzari, P.L.; Evangelisti, C.; Ognibene, A.; Battistelli, M.; Falcieri, E.; Melchionda, F.; Pession, A.; et al. Activity of the novel dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8097–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bendell, J.C.; Kurkjian, C.; Infante, J.R.; Bauer, T.M.; Burris, H.A.; Greco, F.A.; Shih, K.C.; Thompson, D.S.; Lane, C.M.; Finney, L.H.; et al. A phase 1 study of the sachet formulation of the oral dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 given twice daily (BID) in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Qian, X.J.; Qin, W.; Deng, R.; Wu, X.Q.; Qin, J.; Feng, G.K.; Zhu, X.F. Dual phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 has a therapeutic potential and sensitizes cisplatin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fazio, N.; Buzzoni, R.; Baudin, E.; Antonuzzo, L.; Hubner, R.A.; Lahner, H.; WW, D.E.H.; Raderer, M.; Teule, A.; Capdevila, J.; et al. A Phase II Study of BEZ235 in Patients with Everolimus-resistant, Advanced Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 713–719. [Google Scholar]
- Seixas, J.D.; Luengo-Arratta, S.A.; Diaz, R.; Saldivia, M.; Rojas-Barros, D.I.; Manzano, P.; Gonzalez, S.; Berlanga, M.; Smith, T.K.; Navarro, M.; et al. Establishment of a structure-activity relationship of 1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinoline-based kinase inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 as a lead for African sleeping sickness. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4834–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, R.; Zahler, R.; Sahu, B.; Agarwal, V.R.; Naik, N. Substituted Imidazoquinoline Derivatives as Kinase Inhibitors. U.S. Patent PCT/IB2011/053161, 19 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesha, V.A.; Joshi, A.; Venkataraman, M.; Sonawane, V.; Bhatia, D.; Tannu, P.; Bose, J.; Choudhari, S.; Srivastava, A.; Pandey, P.K.; et al. P7170, a novel inhibitor of mTORC1/mTORC2 and Activin receptor-like Kinase 1 (ALK1) inhibits the growth of non small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jalota-Badhwar, A.; Bhatia, D.R.; Boreddy, S.; Joshi, A.; Venkatraman, M.; Desai, N.; Chaudhari, S.; Bose, J.; Kolla, L.S.; Deore, V.; et al. P7170: A Novel Molecule with Unique Profile of mTORC1/C2 and Activin Receptor-like Kinase 1 Inhibition Leading to Antitumor and Antiangiogenic Activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bean, J.R.; Hosford, S.R.; Symonds, L.K.; Owens, P.; Dillon, L.M.; Yang, W.; Shee, K.; Schwartz, G.N.; Marotti, J.D.; Muller, K.E.; et al. The PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor P7170 demonstrates potent activity against endocrine-sensitive and endocrine-resistant ER+ breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 149, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vicier, C.; Dieci, M.V.; Arnedos, M.; Delaloge, S.; Viens, P.; Andre, F. Clinical development of mTOR inhibitors in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barda, D.A.; Mader, M.M. Imidazo[4,5-c]Quinolin-2-one Compound and its Use as PI3 Kinase/mTor Dual Inhibitor. U.S. Patent PCT/US2012/020897, 19 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.C.; Mader, M.M.; Cook, J.A.; Iversen, P.; Ajamie, R.; Perkins, E.; Bloem, L.; Yip, Y.Y.; Barda, D.A.; Waid, P.P.; et al. Characterization of LY3023414, a Novel PI3K/mTOR Dual Inhibitor Eliciting Transient Target Modulation to Impede Tumor Growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2344–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bendell, J.C.; Varghese, A.M.; Hyman, D.M.; Bauer, T.M.; Pant, S.; Callies, S.; Lin, J.; Martinez, R.; Wickremsinhe, E.; Fink, A.; et al. A First-in-Human Phase 1 Study of LY3023414, an Oral PI3K/mTOR Dual Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3253–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Dong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Bai, D. Imidazo Quinoline Derivative and Medicinal Salt Thereof, Preparation Method Thereof and Use in Medicine Thereof. U.S. Patent PCT/CN2012/081330, 18 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.; Chen, X.; Zheng, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Lou, L. Pharmacologic characterization of SHR8443, a novel dual inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 107977–107990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, K.Y.; Tsai, S.Y.; Wu, C.M.; Yen, C.J.; Chuang, B.F.; Chang, J.Y. Novel phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mTOR dual inhibitor, NVP-BGT226, displays potent growth-inhibitory activity against human head and neck cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7116–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glienke, W.; Maute, L.; Wicht, J.; Bergmann, L. The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BGT226 induces cell cycle arrest and regulates Survivin gene expression in human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Tumour Biol. 2012, 33, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampa-Schittenhelm, K.M.; Heinrich, M.C.; Akmut, F.; Rasp, K.H.; Illing, B.; Dohner, H.; Dohner, K.; Schittenhelm, M.M. Cell cycle-dependent activity of the novel dual PI3K-MTORC1/2 inhibitor NVP-BGT226 in acute leukemia. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumann, P.; Schneider, L.; Mandl-Weber, S.; Oduncu, F.; Schmidmaier, R. Simultaneous targeting of PI3K and mTOR with NVP-BGT226 is highly effective in multiple myeloma. Anticancer Drugs 2012, 23, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katanasaka, Y.; Kodera, Y.; Yunokawa, M.; Kitamura, Y.; Tamura, T.; Koizumi, F. Synergistic anti-tumor effects of a novel phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin dual inhibitor BGT226 and gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett. 2014, 347, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simioni, C.; Cani, A.; Martelli, A.M.; Zauli, G.; Alameen, A.A.; Ultimo, S.; Tabellini, G.; McCubrey, J.A.; Capitani, S.; Neri, L.M. The novel dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BGT226 displays cytotoxic activity in both normoxic and hypoxic hepatocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17147–17160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Muro, K.; Sato, M.; Moriya, A. Phase I study of BGT226, a pan-PI3K and mTOR inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced solid cancers. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019, 84, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Lei, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Cao, L.; Ye, K.; Zhu, W.; Xu, S. Design, synthesis, and antitumor evaluation of quinoline-imidazole derivatives. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 2018, 351, e1700407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahekar, R.; Dave, B.; Soman, S.; Patel, D.; Chopade, R.; Funde, R.; Kumar, J.; Sachchidanand, S.; Giri, P.; Chatterjee, A.; et al. Discovery of 1,3-dihydro-2H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-2-ones based novel, potent and PI3Kdelta selective inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, E.; Reddy, M.V. 3-Aminothieno[3,2-c]Quinoline Derivatives, Methods of Preparation and Uses. U.S. Patent PCT/US2013/027778, 26 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Yu, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W.; Qin, Z.; Wang, C.; et al. Highly Selective, Potent, and Oral mTOR Inhibitor for Treatment of Cancer as Autophagy Inducer. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 881–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chang, J.W.; Wang, J.; Kang, S.A.; Thoreen, C.C.; Markhard, A.; Hur, W.; Zhang, J.; Sim, T.; Sabatini, D.M.; et al. Discovery of 1-(4-(4-propionylpiperazin-1-yl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-(quinolin-3-yl)benzo[h][1,6]naphthyridin-2(1H)-one as a highly potent, selective mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 7146–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Kang, S.A.; Thoreen, C.C.; Hur, W.; Ahmed, T.; Sabatini, D.M.; Gray, N.S. Discovery of 9-(6-aminopyridin-3-yl)-1-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)benzo[h][1,6]naphthyridin-2(1H)-one (Torin2) as a potent, selective, and orally available mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor for treatment of cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wissner, A.; Berger, D.M.; Boschelli, D.H.; Floyd, M.B., Jr.; Greenberger, L.M.; Gruber, B.C.; Johnson, B.D.; Mamuya, N.; Nilakantan, R.; Reich, M.F.; et al. 4-Anilino-6,7-dialkoxyquinoline-3-carbonitrile inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor kinase and their bioisosteric relationship to the 4-anilino-6,7-dialkoxyquinazoline inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3244–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wissner, A.; Mansour, T.S. The development of HKI-272 and related compounds for the treatment of cancer. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 2008, 341, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wissner, A.; Overbeek, E.; Reich, M.F.; Floyd, M.B.; Johnson, B.D.; Mamuya, N.; Rosfjord, E.C.; Discafani, C.; Davis, R.; Shi, X.; et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 6,7-disubstituted 4-anilinoquinoline-3-carbonitriles. The design of an orally active, irreversible inhibitor of the tyrosine kinase activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER-2). J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsou, H.R.; Overbeek-Klumpers, E.G.; Hallett, W.A.; Reich, M.F.; Floyd, M.B.; Johnson, B.D.; Michalak, R.S.; Nilakantan, R.; Discafani, C.; Golas, J.; et al. Optimization of 6,7-disubstituted-4-(arylamino)quinoline-3-carbonitriles as orally active, irreversible inhibitors of human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 kinase activity. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 1107–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabindran, S.K.; Discafani, C.M.; Rosfjord, E.C.; Baxter, M.; Floyd, M.B.; Golas, J.; Hallett, W.A.; Johnson, B.D.; Nilakantan, R.; Overbeek, E.; et al. Antitumor activity of HKI-272, an orally active, irreversible inhibitor of the HER-2 tyrosine kinase. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3958–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, C.H.; Mengwasser, K.E.; Toms, A.V.; Woo, M.S.; Greulich, H.; Wong, K.K.; Meyerson, M.; Eck, M.J. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Yang, C.; Wan, H.; Zhang, G.; Feng, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhong, D.; Lou, L.; Tao, W. Discovery and development of pyrotinib: A novel irreversible EGFR/HER2 dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor with favorable safety profiles for the treatment of breast cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 110, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhu, W.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Xing, P.; Lan, B.; Li, M.; et al. Phase I Study and Biomarker Analysis of Pyrotinib, a Novel Irreversible Pan-ErbB Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients With Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3105–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, W.; Jiang, Z.; Tong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Yu, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, S.; et al. Pyrotinib or Lapatinib Combined With Capecitabine in HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer With Prior Taxanes, Anthracyclines, and/or Trastuzumab: A Randomized, Phase II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2610–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, H.A. Pyrotinib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 1751–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannala, M.; Kher, S.; Wilson, N.; Gaudette, J.; Sircar, I.; Zhang, S.H.; Bakhirev, A.; Yang, G.; Yuen, P.; Gorcsan, F.; et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of 4-(2-aryl-cyclopropylamino)-quinoline-3-carbonitriles as EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 5978–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, D.A.; Abou El Ella, D.A.; El-Motwally, A.M.; Aly, R.M. Molecular design and synthesis of certain new quinoline derivatives having potential anticancer activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 102, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, R.M.; Serya, R.A.T.; El-Motwally, A.M.; Esmat, A.; Abbas, S.; Abou El Ella, D.A. Novel quinoline-3-carboxamides (Part 2): Design, optimization and synthesis of quinoline based scaffold as EGFR inhibitors with potent anticancer activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 75, 368–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, M.A.; El-Husseiny, W.M.; Abdel-Aziz, N.I.; El-Azab, A.S.; Abuelizz, H.A.; Abdel-Aziz, A.A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-styrylquinolines as antitumour agents and EGFR kinase inhibitors: Molecular docking study. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makawana, J.A.; Sangani, C.B.; Lin, L.; Zhu, H.L. Schiff’s base derivatives bearing nitroimidazole and quinoline nuclei: New class of anticancer agents and potential EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1734–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, R.F.; Samir, E.M.; Abdelhamed, M.N.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Abbas, S.E. Synthesis and anti-proliferative activity of some new quinoline based 4,5-dihydropyrazoles and their thiazole hybrids as EGFR inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 83, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelbaset, M.S.; Abdel-Aziz, M.; Ramadan, M.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; Abbas Bukhari, S.N.; Ali, T.F.S.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.A. Discovery of novel thienoquinoline-2-carboxamide chalcone derivatives as antiproliferative EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, E.A.; Zaghary, W.A.; Amin, K.M.; Abou Taleb, N.A.; Mekawey, A.A.I.; Eldehna, W.M.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Hammad, S.F. Synthesis and in vitro anticancer evaluation of some fused indazoles, quinazolines and quinolines as potential EGFR inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 89, 102985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, K.; Shimizu, T.; Ohyama, S.; Murooka, H.; Iwai, A.; Nakamura, K.; Hasegawa, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Takahashi, K.; et al. Novel potent orally active selective VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Synthesis, structure-activity relationships, and antitumor activities of N-phenyl-N’-{4-(4-quinolyloxy)phenyl}ureas. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Taguchi, E.; Miura, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Takahashi, K.; Bichat, F.; Guilbaud, N.; Hasegawa, K.; Kubo, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; et al. KRN951, a highly potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, has antitumor activities and affects functional vascular properties. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9134–9142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taguchi, E.; Nakamura, K.; Miura, T.; Shibuya, M.; Isoe, T. Anti-tumor activity and tumor vessel normalization by the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor KRN951 in a rat peritoneal disseminated tumor model. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.; Normanno, N. Tivozanib, a pan-VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the potential treatment of solid tumors. IDrugs 2010, 13, 636–645. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, K.; Ikemori-Kawada, M.; Jestel, A.; von König, K.; Funahashi, Y.; Matsushima, T.; Tsuruoka, A.; Inoue, A.; Matsui, J. Distinct binding mode of multikinase inhibitor lenvatinib revealed by biochemical characterization. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McTigue, M.; Murray, B.W.; Chen, J.H.; Deng, Y.L.; Solowiej, J.; Kania, R.S. Molecular conformations, interactions, and properties associated with drug efficiency and clinical performance among VEGFR TK inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18281–18289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kajal, K.; Panda, A.K.; Bhat, J.; Chakraborty, D.; Bose, S.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Sarkar, T.; Chatterjee, S.; Kar, S.K.; Sa, G. Andrographolide binds to ATP-binding pocket of VEGFR2 to impede VEGFA-mediated tumor-angiogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.Q.; Zhu, Z.W.; Zhu, H.L. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of quinoline amide derivatives as novel VEGFR-2 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6653–6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboul-Enein, M.N.; El-Azzouny, A.M.; Ragab, F.A.; Hamissa, M.F. Design, Synthesis, and Cytotoxic Evaluation of Certain 7-Chloro-4-(piperazin-1-yl)quinoline Derivatives as VEGFR-II Inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 2017, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westman, J.; Wannberg, J.; Nekhotiaeva, N.; Backman, U. Quinoline-S-Carboxylic Acid Derivatives as Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. U.S. Patent PCT/EP2008/053763, 9 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wu, C.; Lin, X.; Cai, X.; Liu, L.; Luo, G.; You, Q.; Xiang, H. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 3-aryl-quinolin derivatives as anti-breast cancer agents targeting ERalpha and VEGFR-2. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Bos, P.H.; Chambers, J.M.; Dupont, M.M.; Stockwell, B.R. K-Ras(G12D) Has a Potential Allosteric Small Molecule Binding Site. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 2542–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Feng, J.; Long, Y.O.; Liu, Y.; Wu, T.; Ren, P.; Liu, Y. Fused-Tricyclic Inhibitors of KRAS and Methods of Use Thereof. U.S. Patent PCT/US2016/027673, 20 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- El-Gamal, M.I.; Khan, M.A.; Abdel-Maksoud, M.S.; Gamal El-Din, M.M.; Oh, C.H. A new series of diarylamides possessing quinoline nucleus: Synthesis, in vitro anticancer activities, and kinase inhibitory effect. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 87, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gamal, M.I.; Khan, M.A.; Tarazi, H.; Abdel-Maksoud, M.S.; Gamal El-Din, M.M.; Yoo, K.H.; Oh, C.H. Design and synthesis of new RAF kinase-inhibiting antiproliferative quinoline derivatives. Part 2: Diarylurea derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Damasy, A.K.; Seo, S.H.; Cho, N.C.; Kang, S.B.; Pae, A.N.; Kim, K.S.; Keum, G. Design, synthesis, in-vitro antiproliferative activity and kinase profile of new picolinamide based 2-amido and ureido quinoline derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 101, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Damasy, A.K.; Seo, S.H.; Cho, N.C.; Pae, A.N.; Kim, E.E.; Keum, G. Design and synthesis of new 2-anilinoquinolines bearing N-methylpicolinamide moiety as potential antiproliferative agents. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 89, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Xie, N.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S. 3,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-g]quinolin-2(3H)-one derivatives as novel Raf kinase inhibitors. MedChemComm 2013, 4, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wu, B.; Powell, D.; Wissner, A.; Floyd, M.B.; Kovacs, E.D.; Toral-Barza, L.; Kohler, C. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 3-cyano-4-(phenoxyanilino)quinolines as MEK (MAPKK) inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 2825–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wu, B.; Eudy, N.; Wang, Y.; Ye, F.; Powell, D.; Wissner, A.; Feldberg, L.R.; Kim, S.C.; Mallon, R.; et al. MEK (MAPKK) inhibitors. Part 2: Structure-activity relationships of 4-anilino-3-cyano-6,7-dialkoxyquinolines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 1407–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, D.; Dutia, M.; Powell, D.; Wu, B.; Wissner, A.; Boschelli, D.H.; Floyd, M.B.; Zhang, N.; Torres, N.; Levin, J.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of 4-anilino-6,7-dialkoxy-3-quinolinecarbonitriles as inhibitors of kinases of the Ras-MAPK signaling cascade. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 3031–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, D.M.; Dutia, M.; Powell, D.; Floyd, M.B.; Torres, N.; Mallon, R.; Wojciechowicz, D.; Kim, S.; Feldberg, L.; Collins, K.; et al. 4-Anilino-7-alkenylquinoline-3-carbonitriles as potent MEK1 kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 9202–9211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, M.G.; Moebitz, H.; Panigrahi, S.K.; Poddutoori, R.; Samajdar, S. Compounds and Compositions as Inhibitors of Mek. U.S. Patent PCT/IB2014/063918, 9 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.Y.; Chen, H.; Li, D.D.; Li, A.L.; Wang, W.Y.; Gu, W. Design, synthesis, and anticancer evaluation of novel quinoline derivatives of ursolic acid with hydrazide, oxadiazole, and thiadiazole moieties as potent MEK inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 955–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

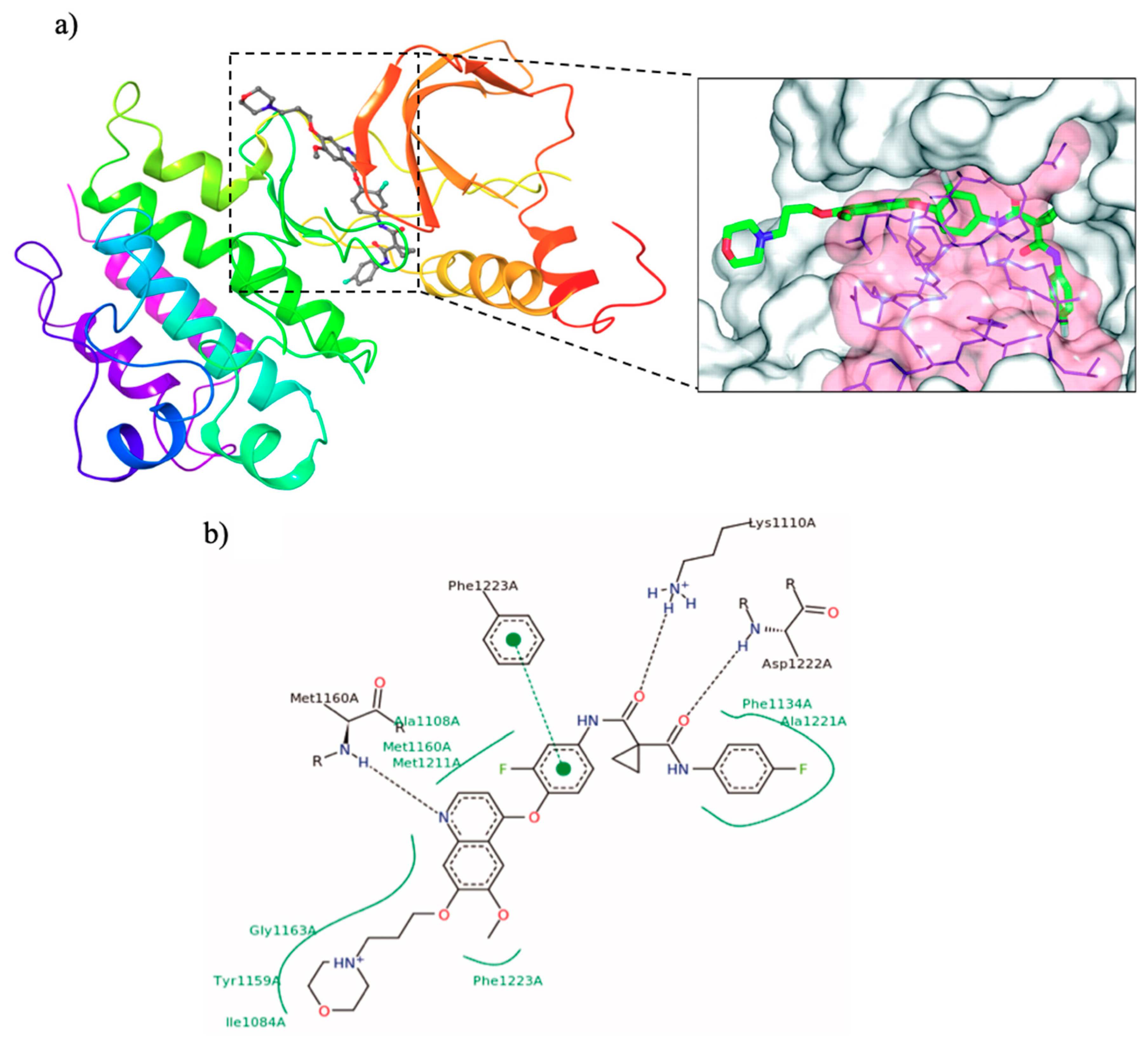

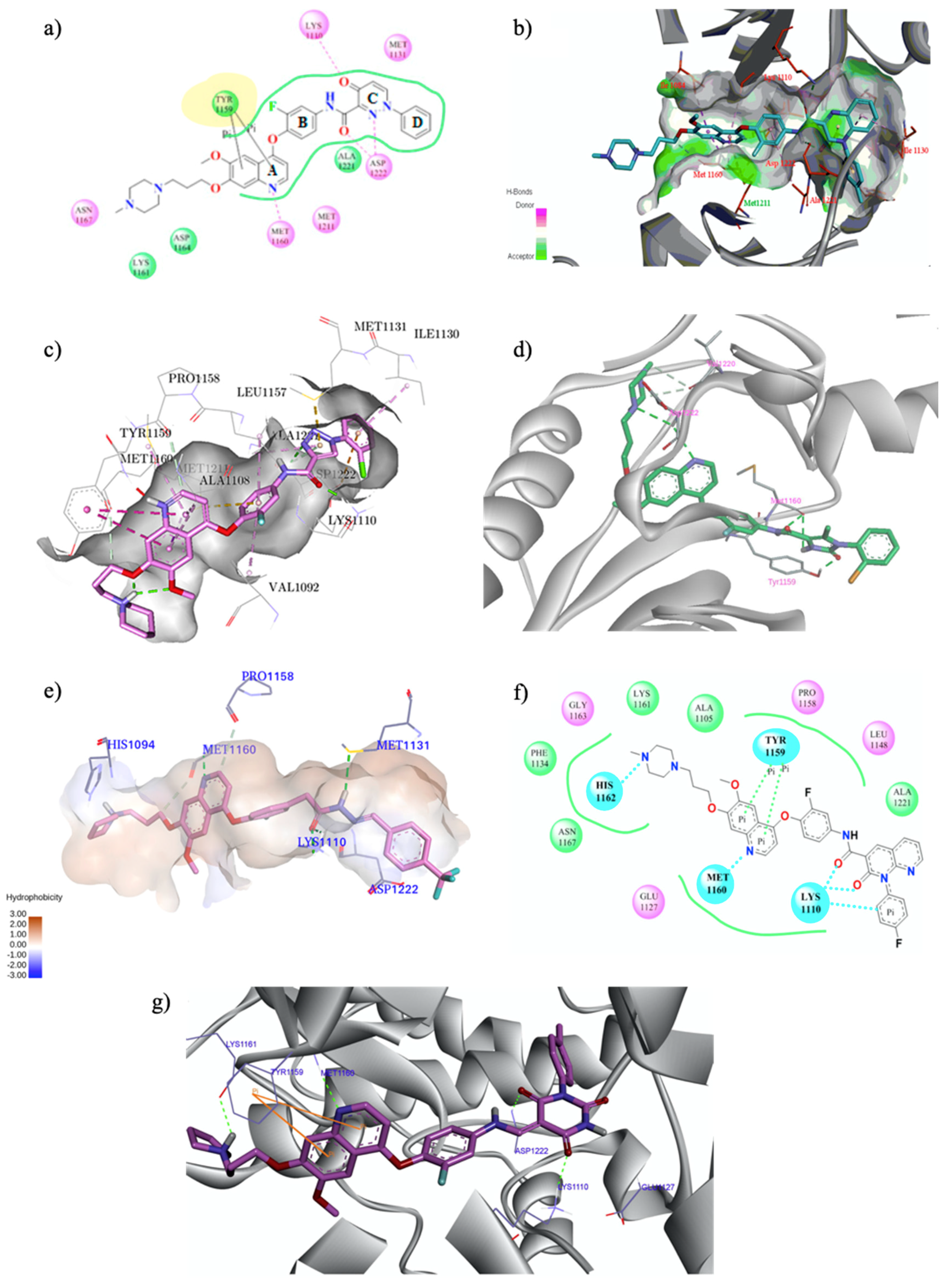



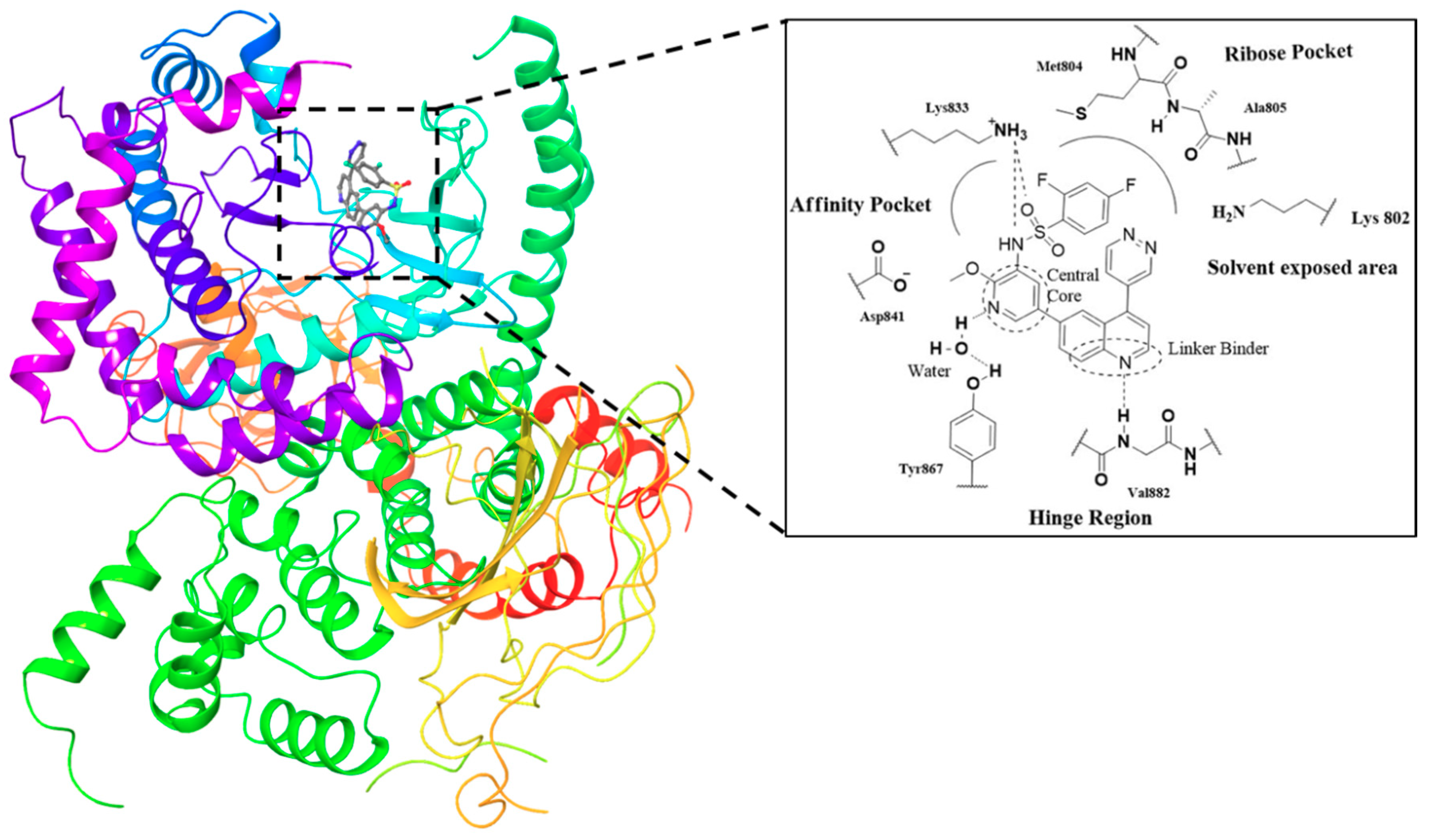
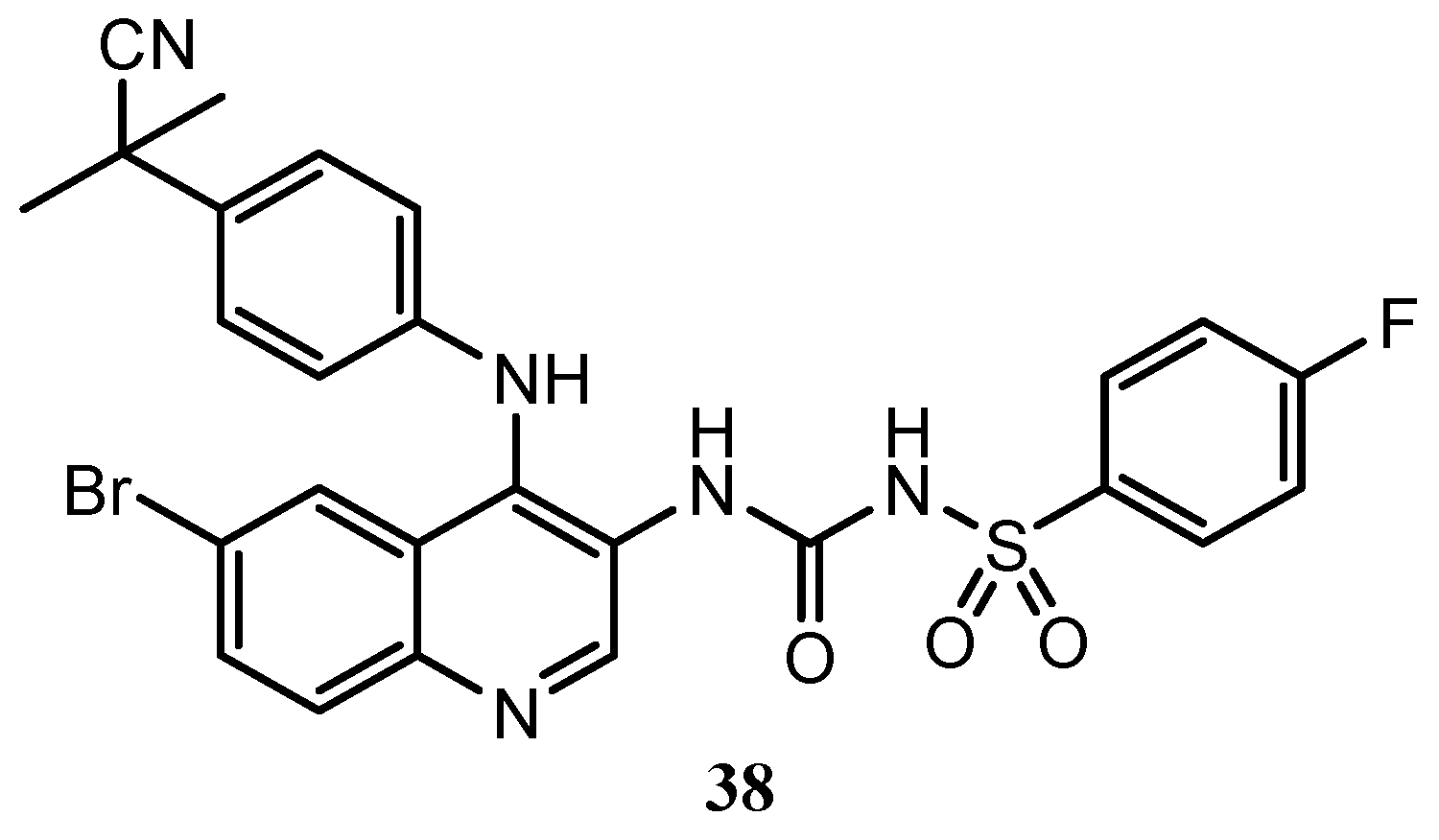




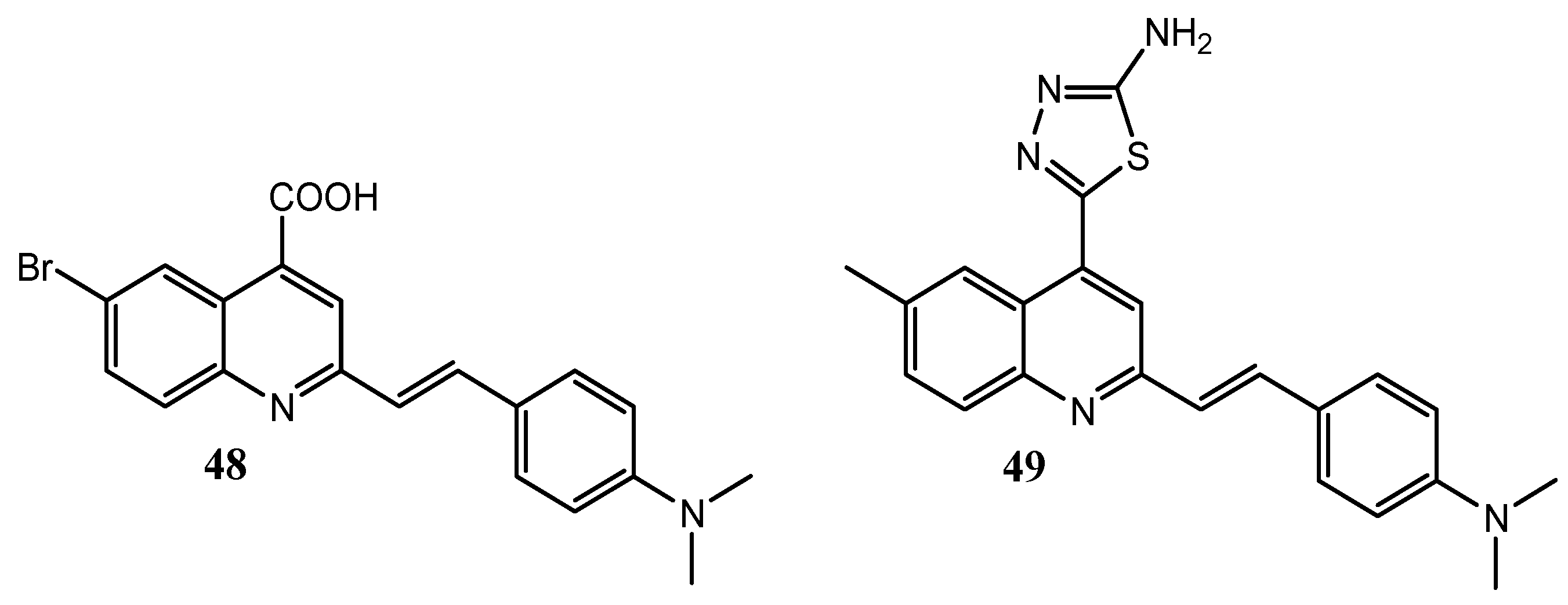
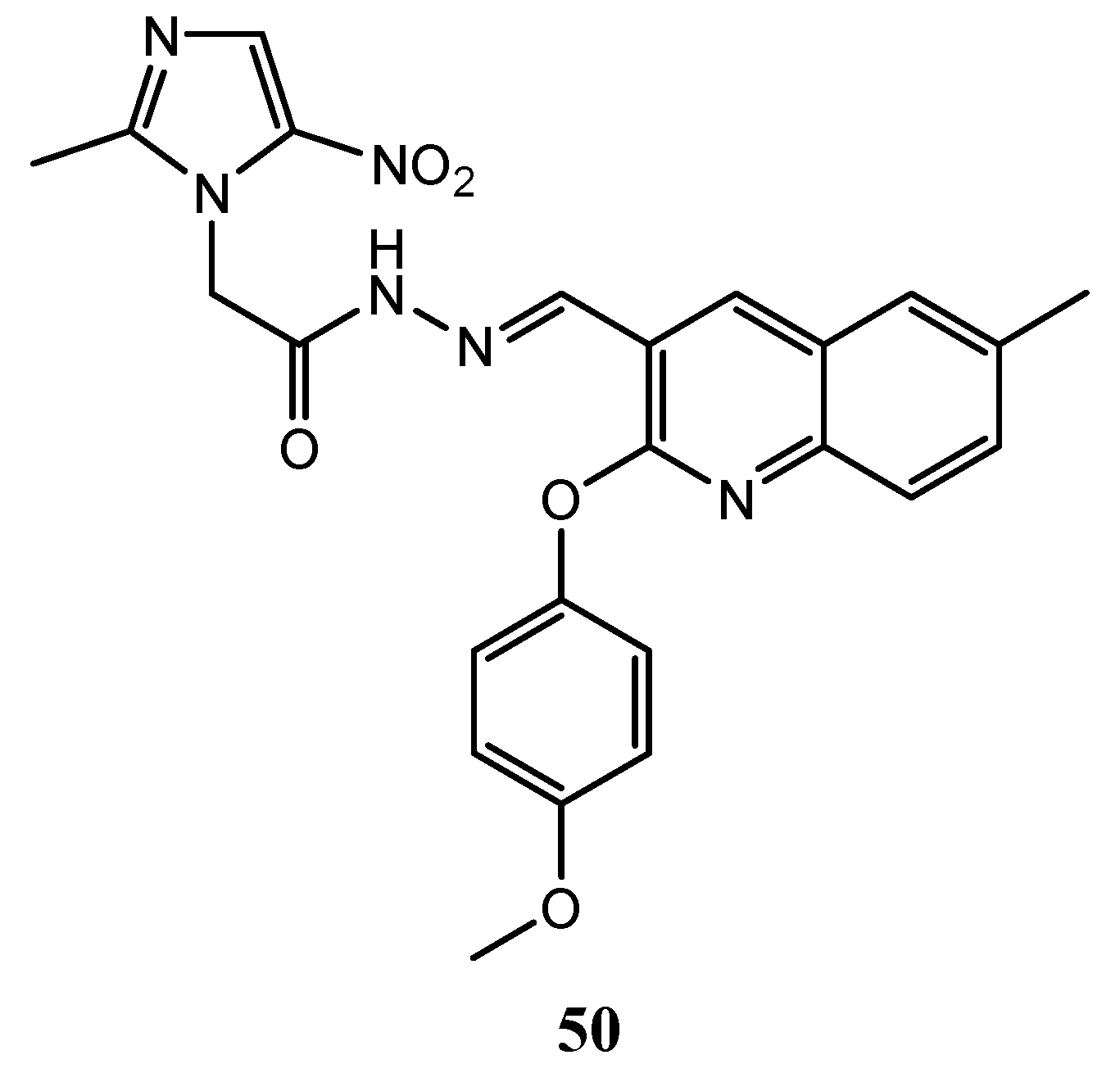
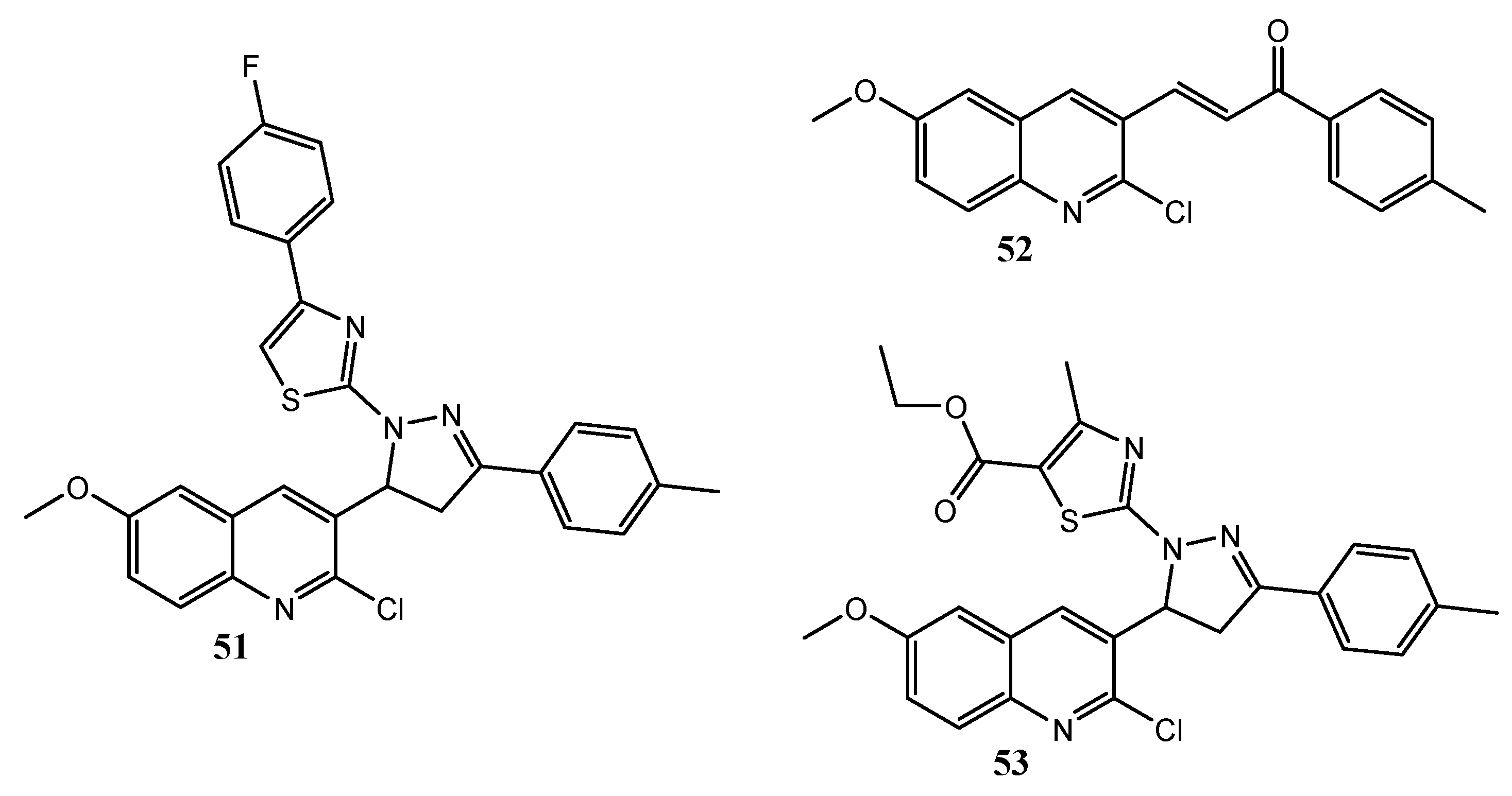
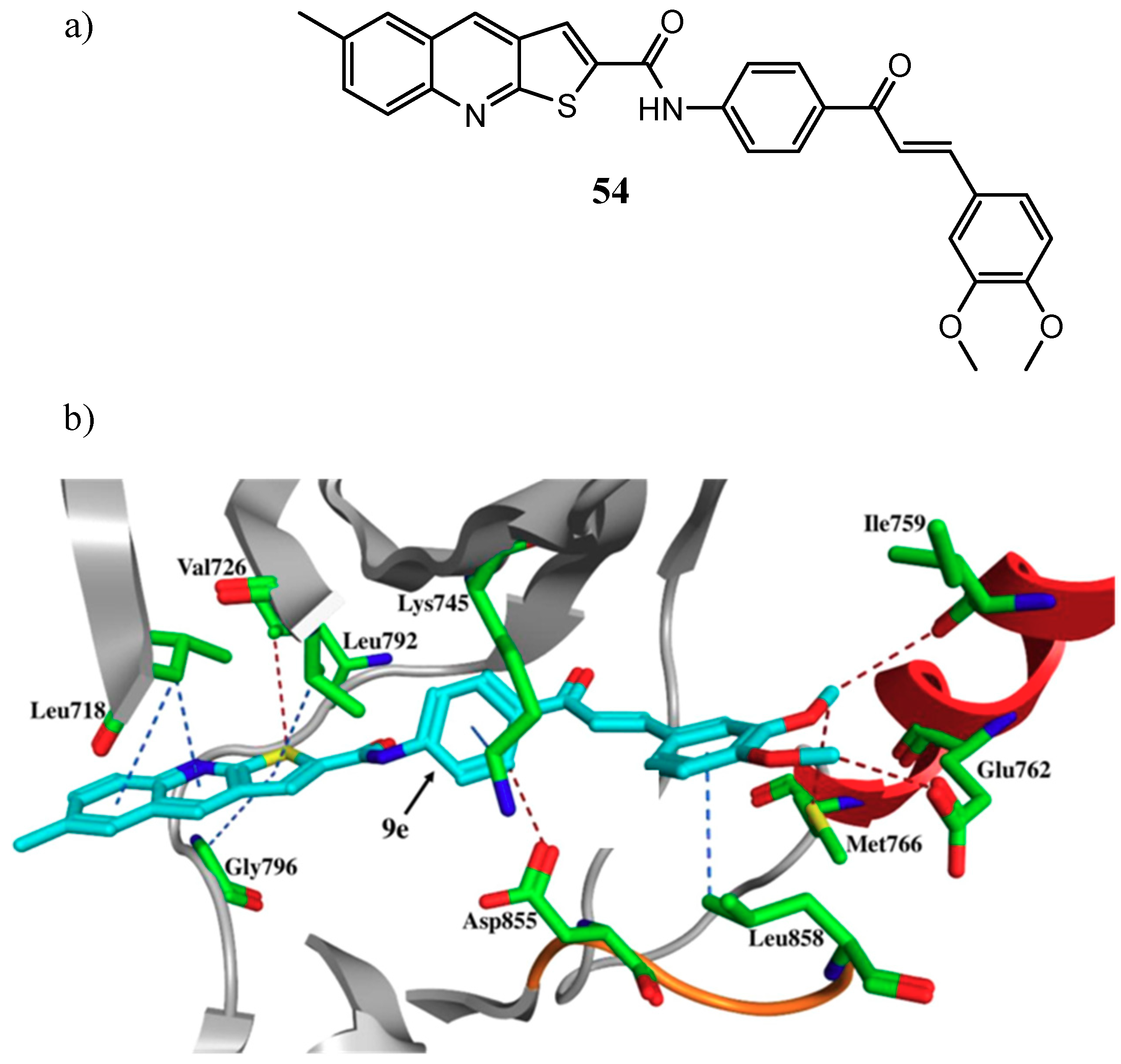
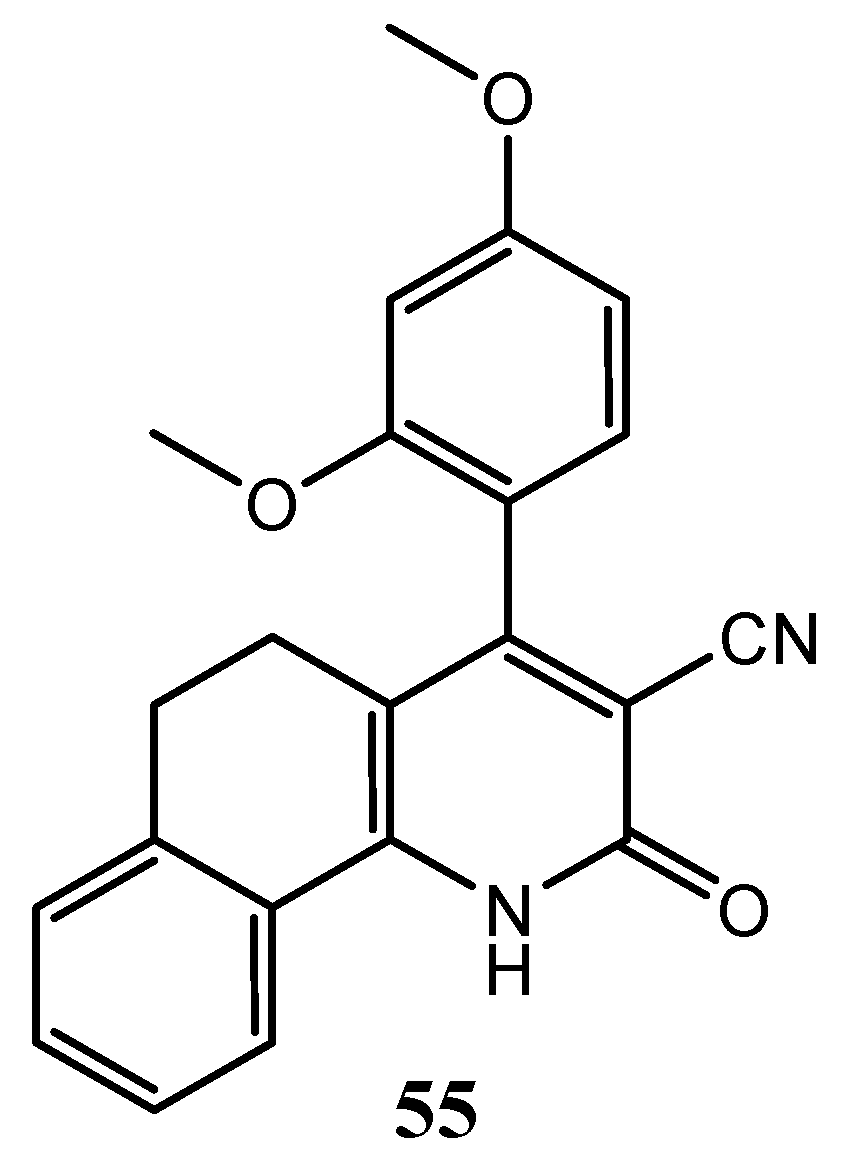

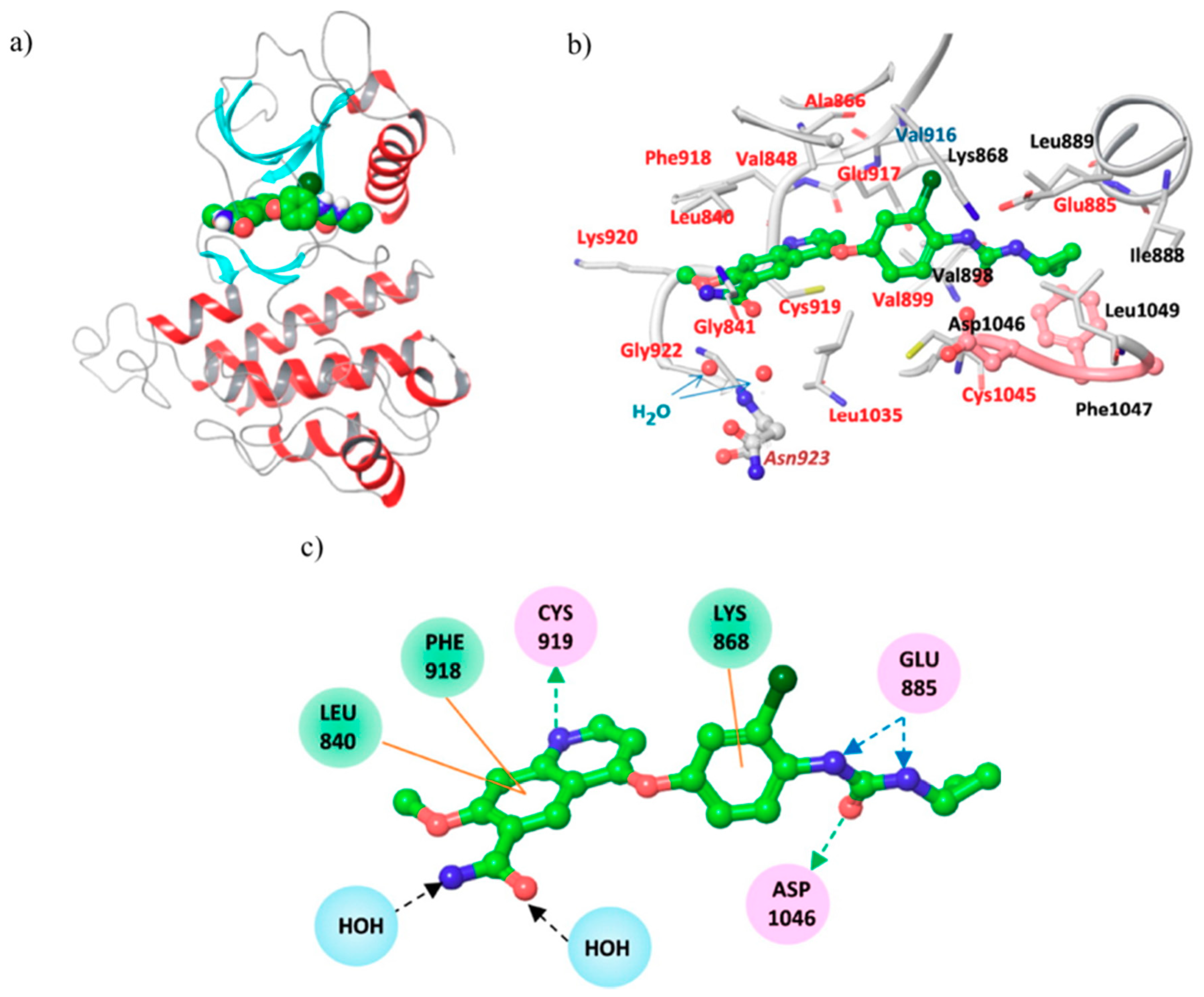
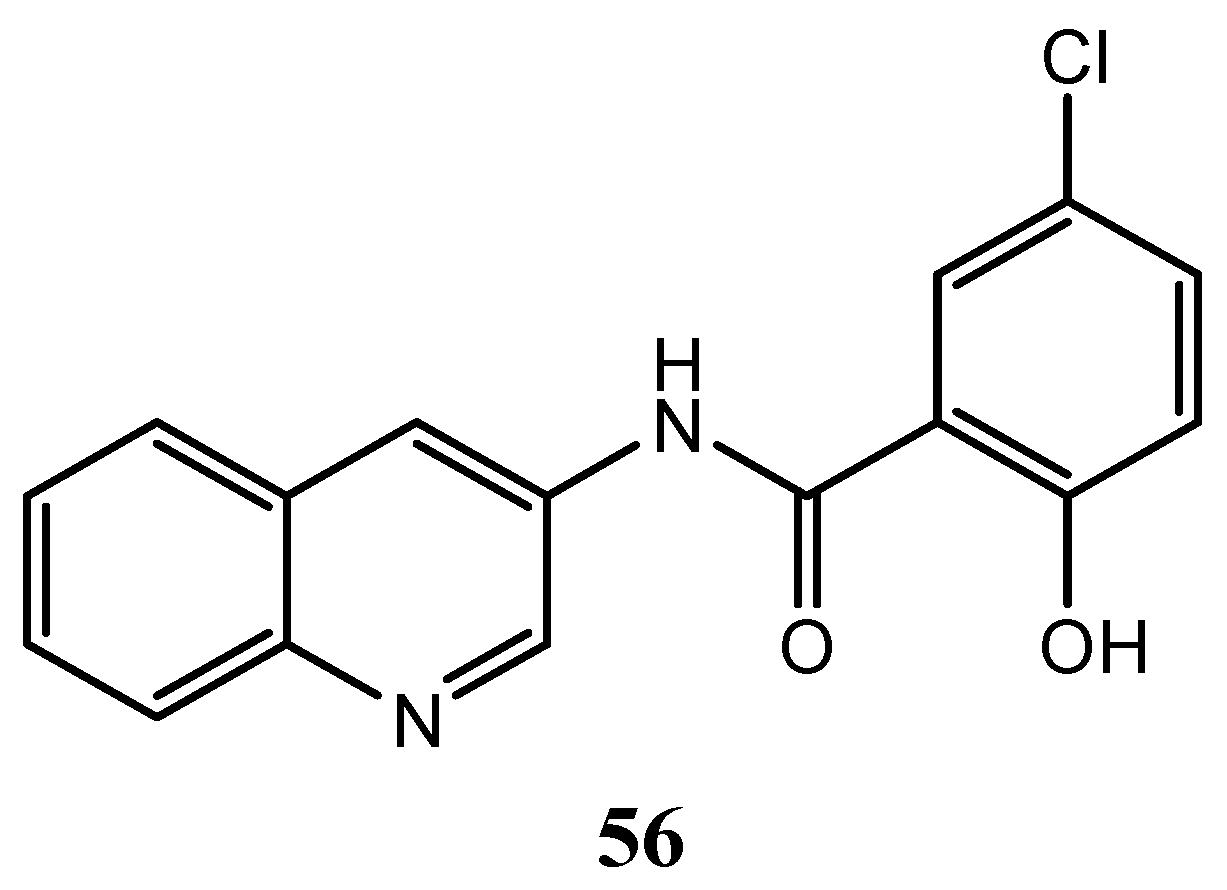

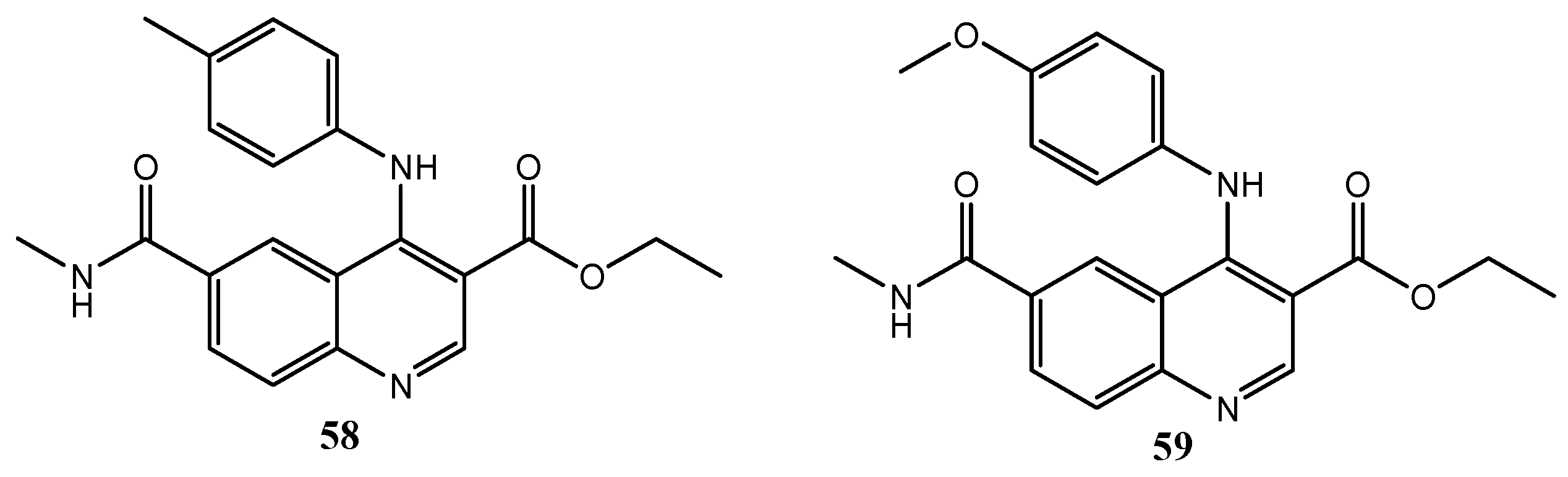
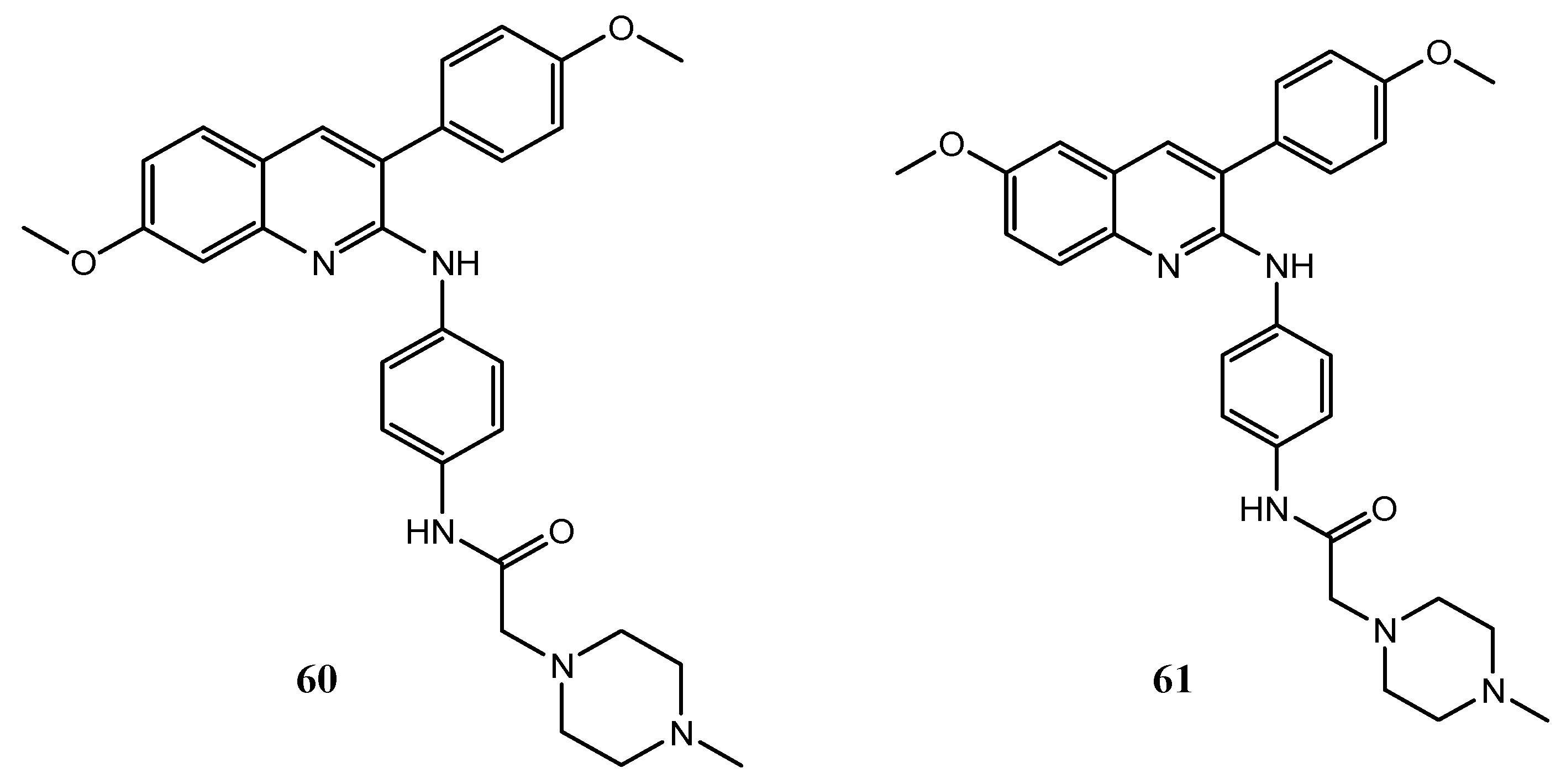
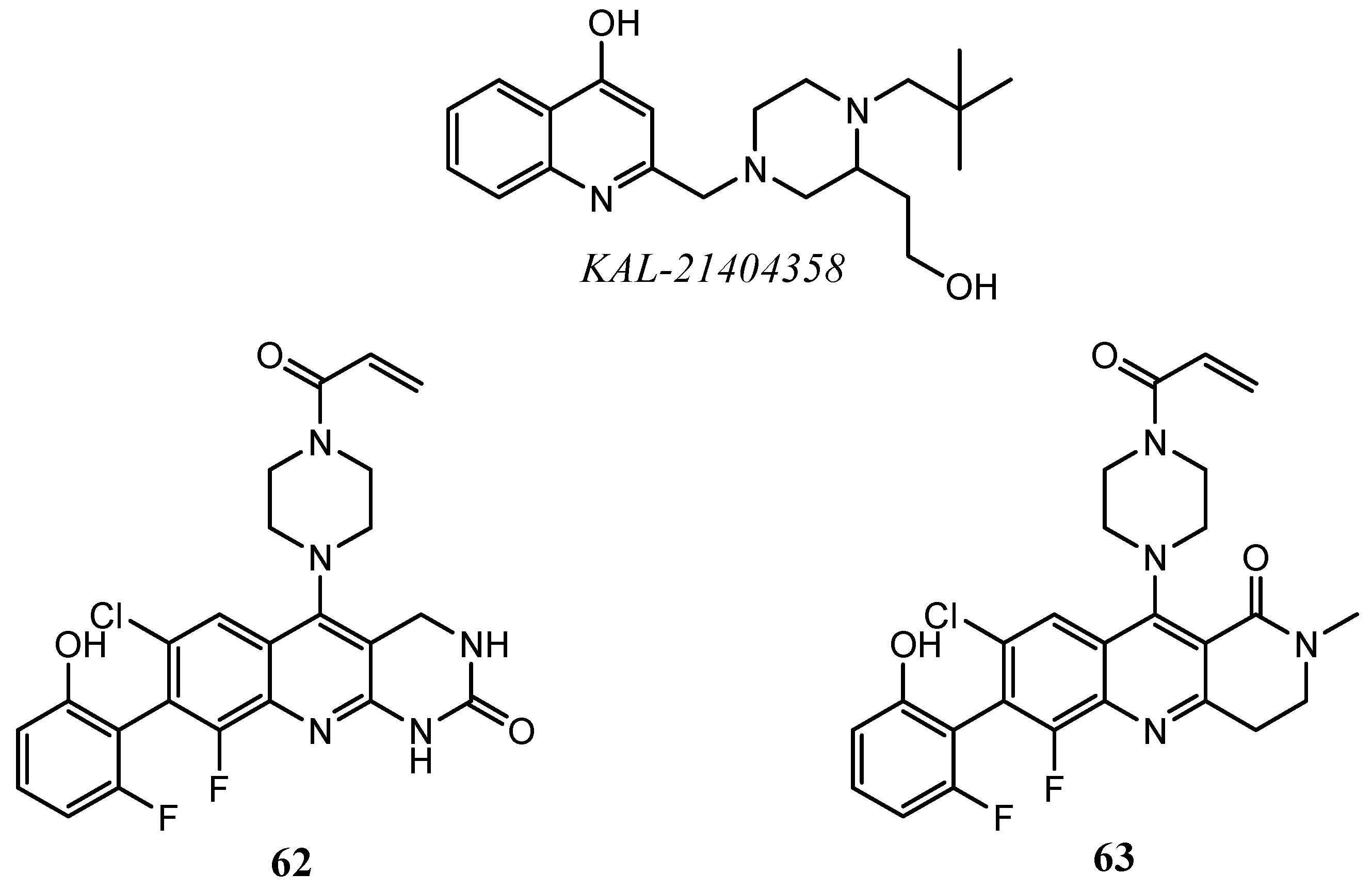
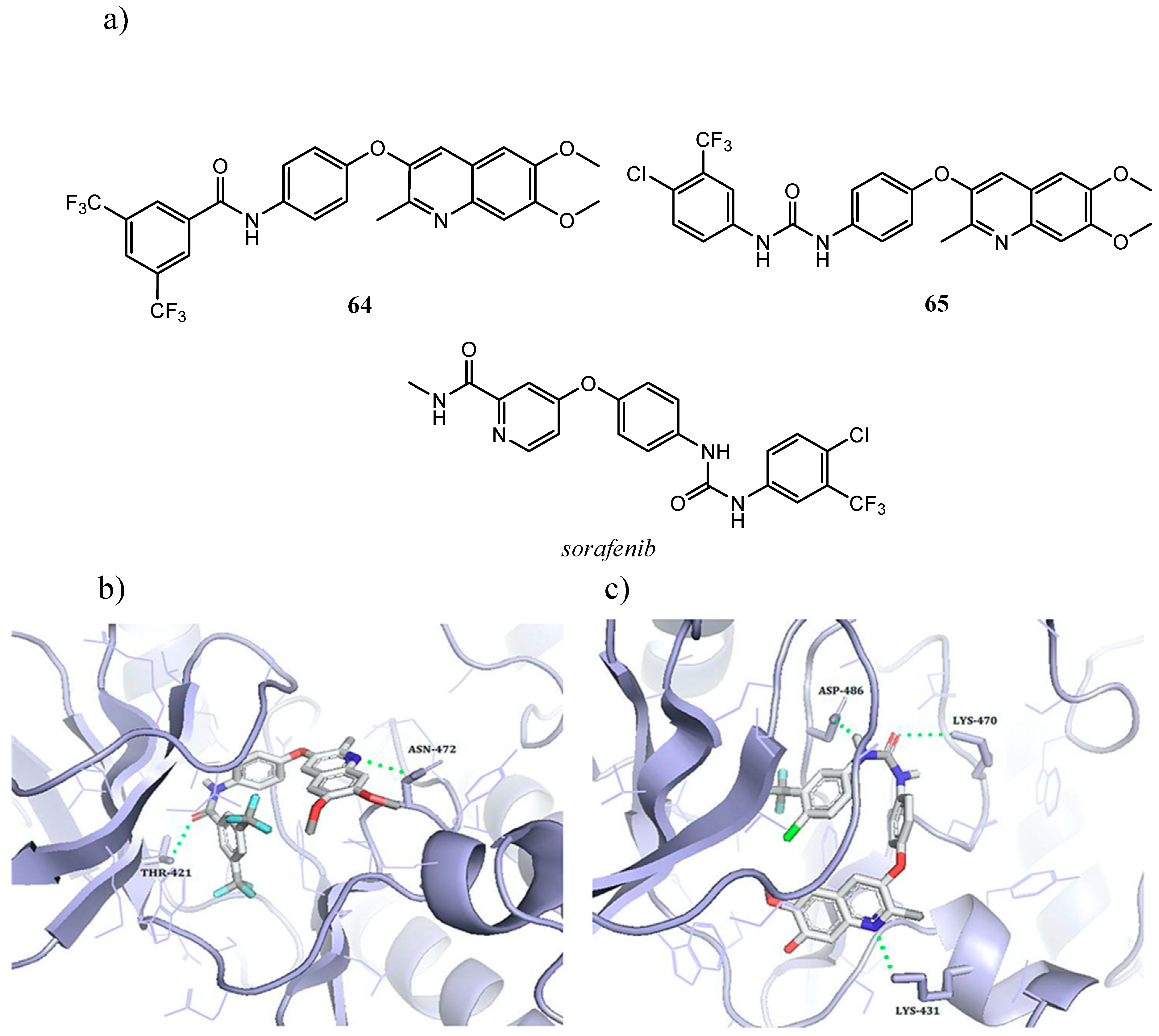
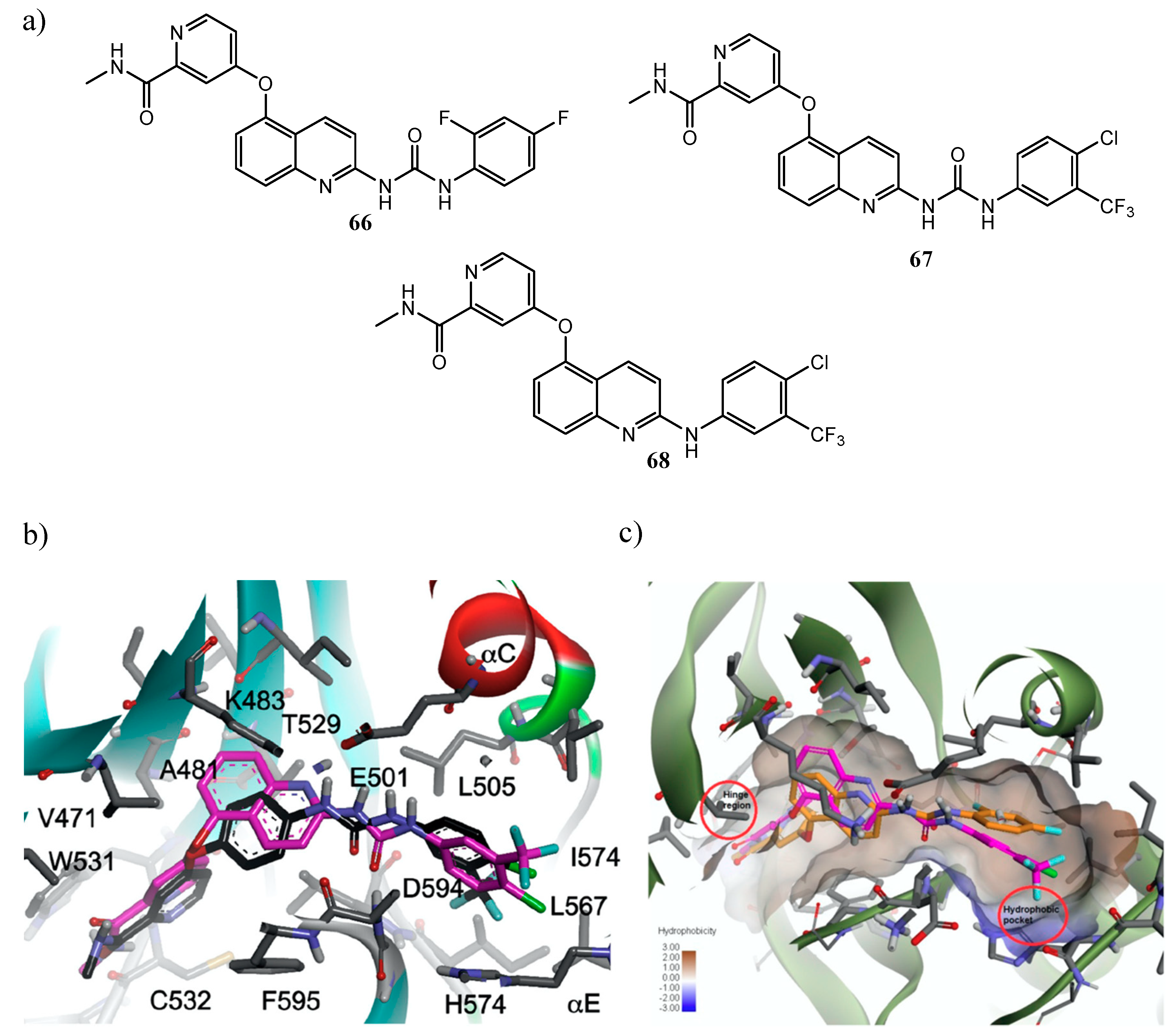
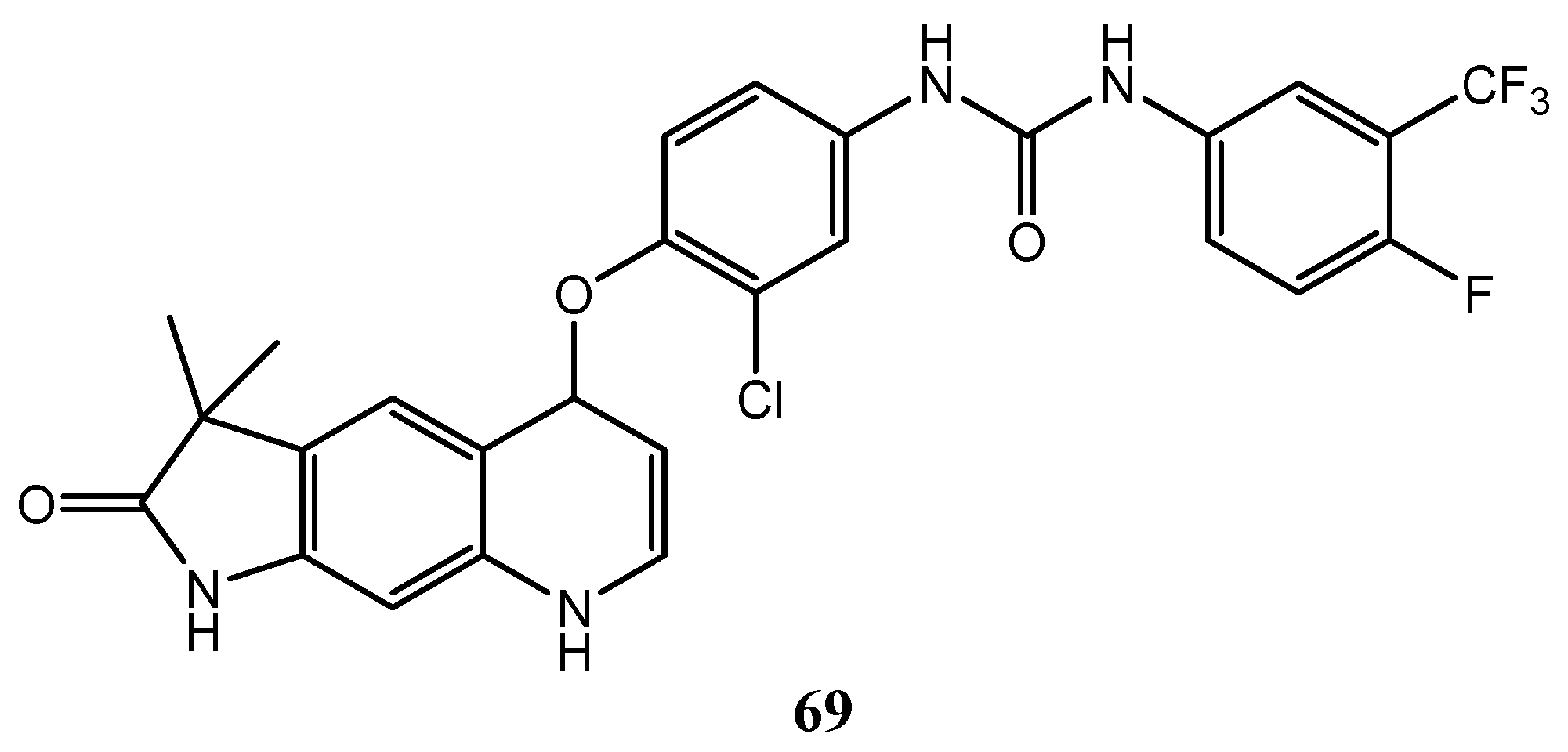
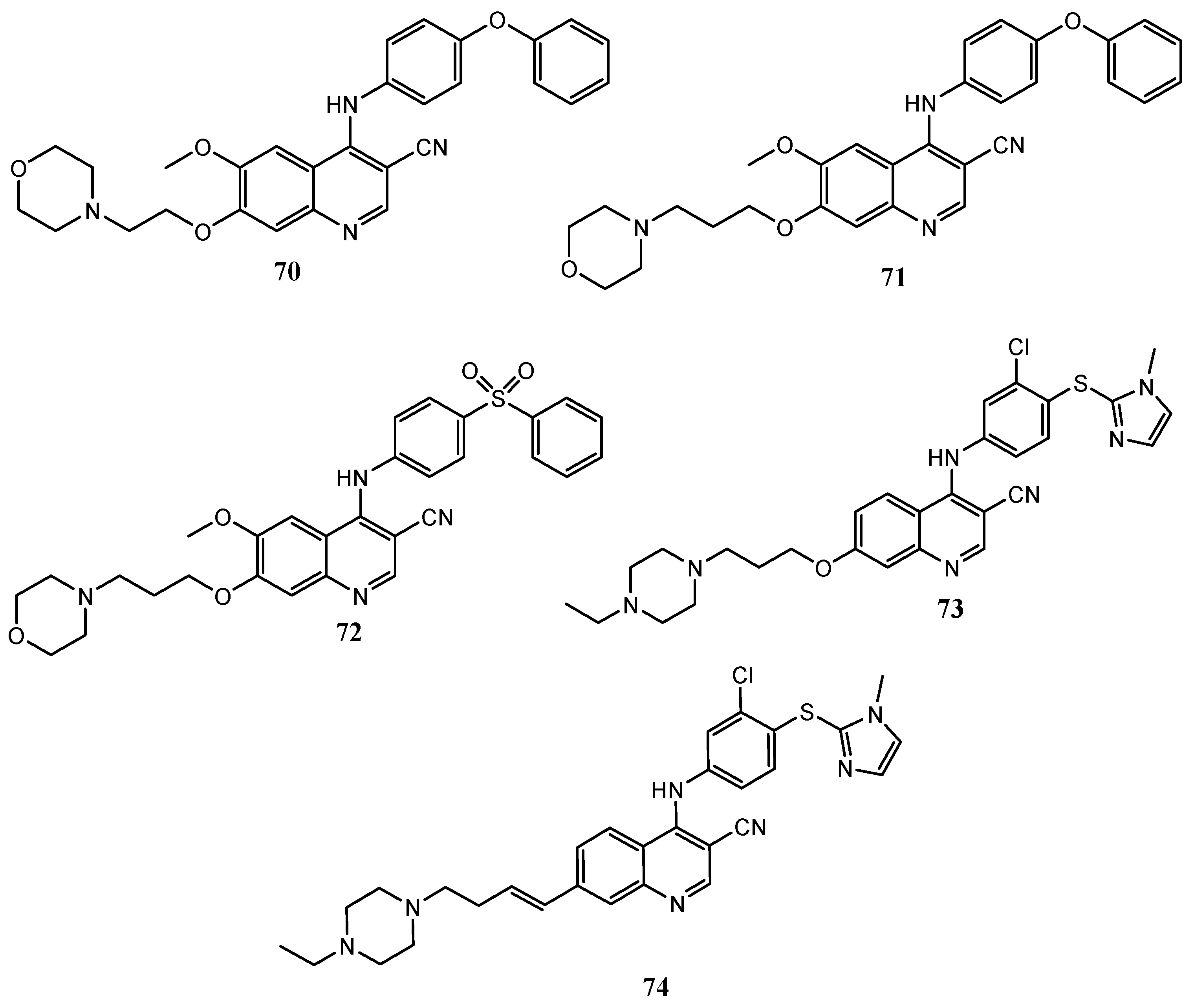
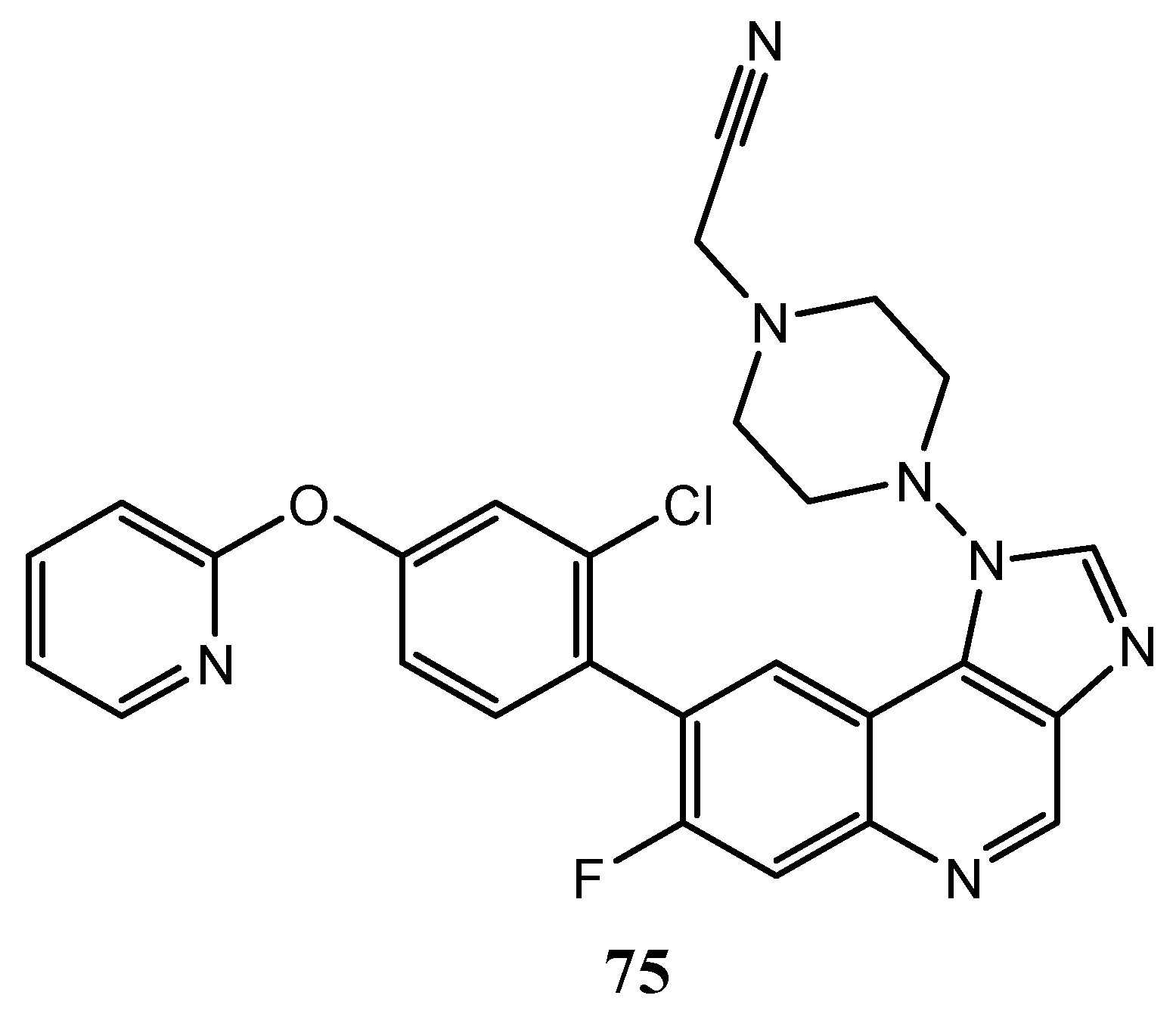
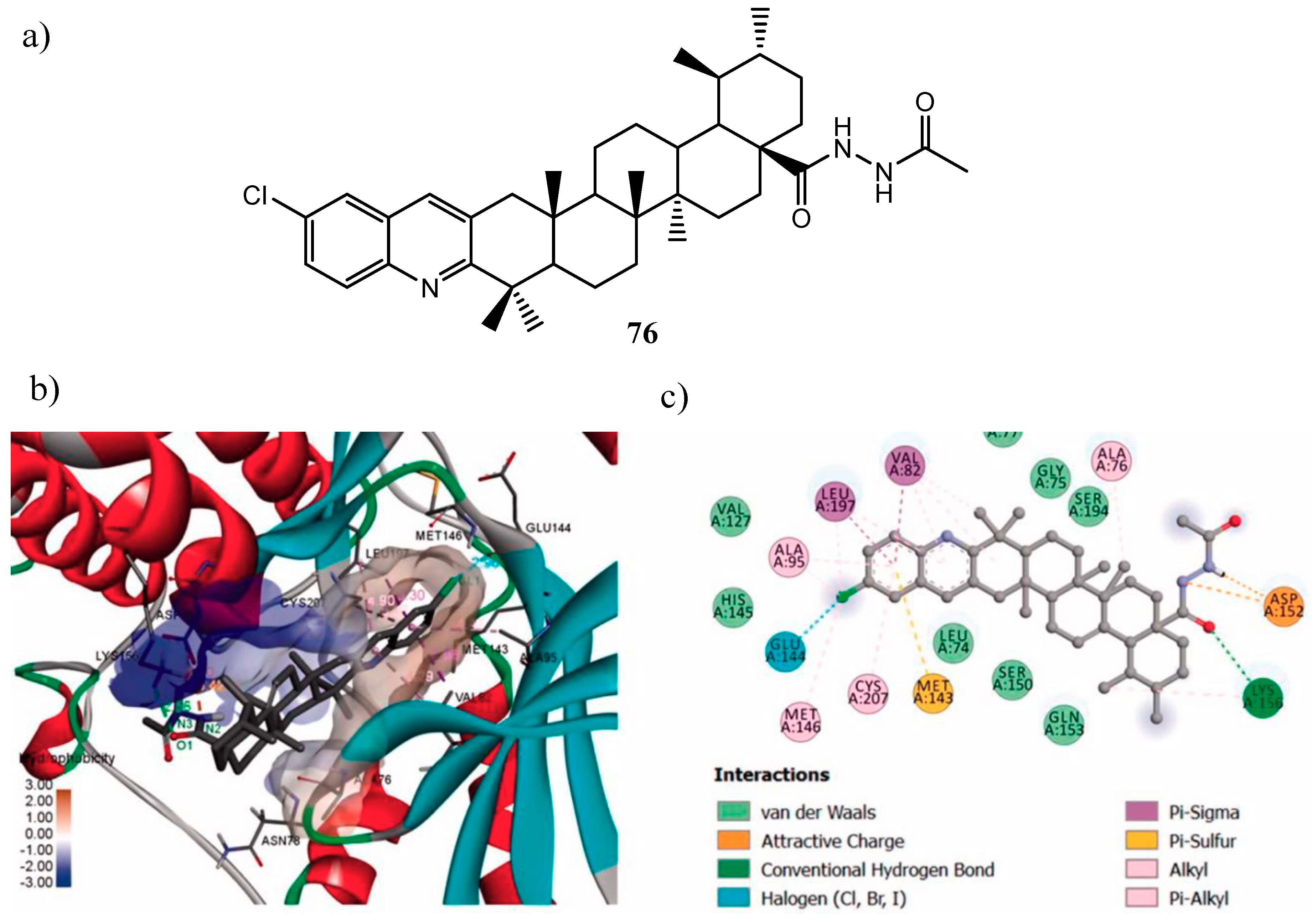
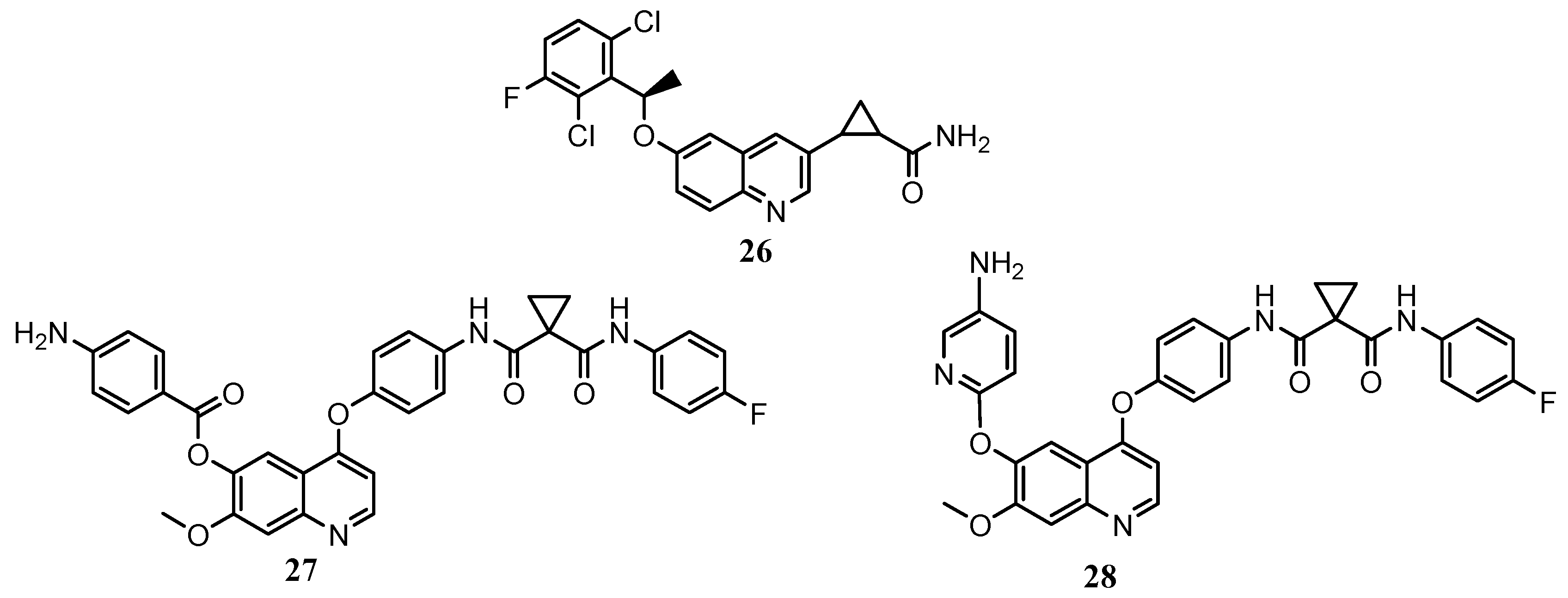
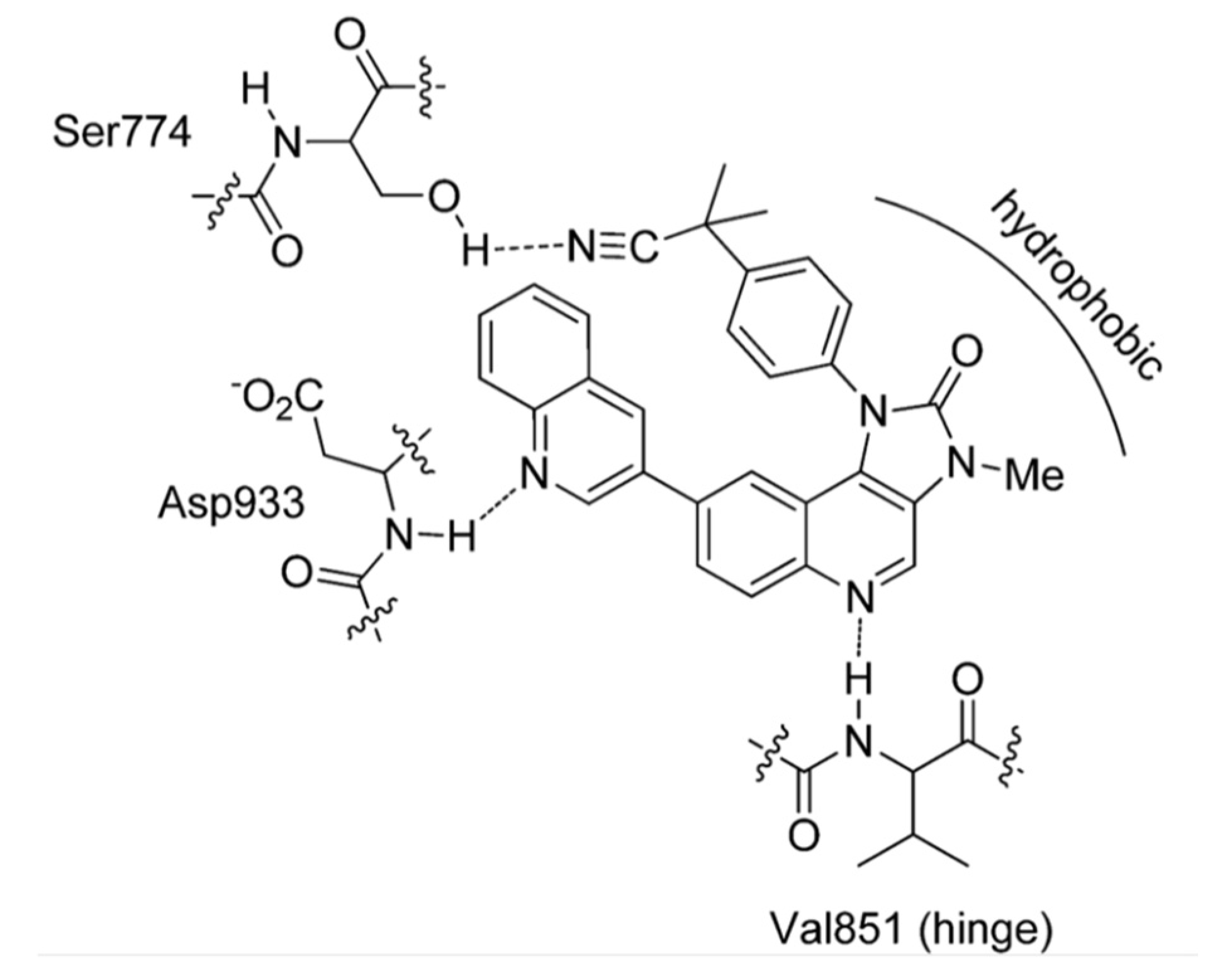
| Quinoline Compound | Linker | IC50 (μM) Sensitive Cell Lines | IC50 on c-Met (nM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | pyridazinone-3- carboxamide | A549 (IC50 = 0.003 ± 0.001) HepG2 (IC50 = 0.49 ± 0.003) MCF-7 (IC50 = 0.006 ± 0.001) | 0.6 | [35] |
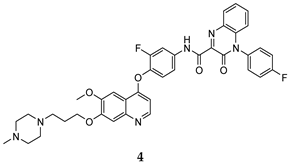 | 3-oxo-3,4- dihydroquinoxaline | HT-29 (IC50 = 0.06 ± 0.001) A549 (IC50 = 0.050 ± 0.006) H460 (IC50 = 0.18 ± 0.01) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.023 ± 0.005) U87 MG (IC50 = 0.66 ± 0.09) | 0.9 | [36] |
 | 1H-imidazole-4- carboxamide | HT-29 (IC50 = 0.08 ± 0.02) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.22 ± 0.03) A549 (IC50 = 0.07 ± 0.01) | 1.1 ± 0.21 | [37] |
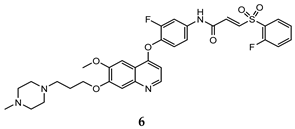 | (E)-3-hydrosulfonyl acrylamide | HT-29 (IC50 = 0.15 ± 0.003) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.28 ± 0.003) A549 (IC50 = 0.15 ± 0.05) | 17 ± 0.20 | [37] |
 | 1,2,3-triazole-4- carboxamide | HT-29 (IC50 = 0.10 ± 0.003) H460 (IC50 = 0.18 ± 0.03) A549 (IC50 = 0.07 ± 0.01) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.03 ± 0.01) | 2.27 | [38] |
 | 1,2,3-triazole-4- carboxamide | A549 (IC50 = 0.08 ± 0.004) H460 (IC50 = 0.15 ± 0.03) HT-29 (IC50 = 0.12 ± 0.02) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.021 ± 0.003) U87MG (IC50 = 0.85 ± 0.12) | 1.04 ± 0.09 | [39] |
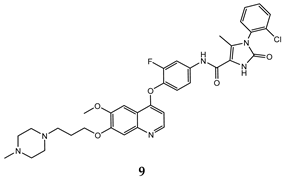 | 2-imidazolone-4- carboxamide | A549 (IC50 = 0.25 ± 0.02) H460 (IC50 = 0.10 ± 0.008) HT-29 (IC50 = 0.086 ± 0.005) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.014 ± 0.004) | 1.42 ± 0.14 | [40] |
 | acylhydrazone | HT-29 (IC50 = 0.15 ± 0.03) H460 (IC50 = 0.031 ± 0.008) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.37 ± 0.08) A549 (IC50 = 0.080 ± 0.01) U87MG (IC50 = 0.29 ± 0.08) | 1.86 | [41] |
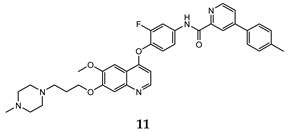 | pyridine -2-carboxyamide | HT-29 (IC50 = 0.026 ± 0.003) H460 (IC50 = 0.037 ± 0.01) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.073 ± 0.01) A549 (IC50 = 0.10 ± 0.02) U87MG (IC50 = 0.81 ± 0.19) | 1.39 | [42] |
 | 2-phenylquinoline-4- carboxamide | H460 (IC50 = 0.011 ± 0.002) HT-29 (IC50 = 0.062 ± 0.01) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.011 ± 0.003) U87MG (IC50 = 0.15 ± 0.03) SMMC-7721 (IC50 = 0.03 ± 0.004) | 1.32 | [33] |
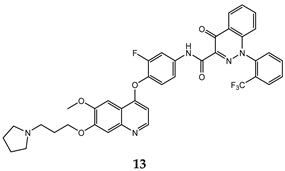 | 4-oxo-1,4-dihydrocinnoline-3-carboxamide | A549 (IC50 = 0.035 ± 0.0042) H460(IC50 = 0.055 ± 0.010) HT29 (IC50 = 0.11 ± 0.016) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.022 ± 0.0035) U87MG (IC50 = 0.35 ± 0.060) SMMC-7721 (IC50 = 0.25 ± 0.072) | 0.59 ± 0.07 | [43] |
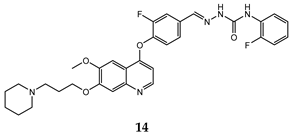 | acyclic semicarbazone | HT-29 (IC50 = 0.059 ± 0.0039) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.016 ± 0.0012) A549 (IC50 = 0.0090 ± 0.0012) MDA-MB-231 (IC50 = 0.77 ± 0.064) | 4.3 | [44] |
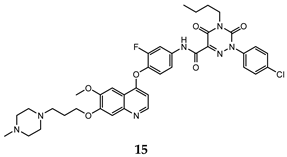 | l,2,4-triazine-3,5-dione | H460 (IC50 = 0.14) HT-29 (IC50 = 0.21) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.066) SMMC-7721 (IC50 = 0.73) | 6.3 | [47] |
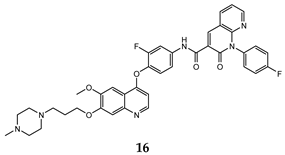 | 1,8-naphthyridin-2-one | HepG2 (IC50 = 0.23 ± 0.01) MCF-7 (IC50 = 0.42 ± 0.06) A549 (IC50 = 0.21 ± 0.02) | 2.36 | [48] |
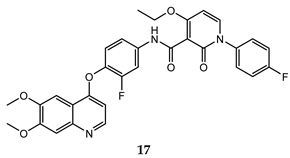 | 2-oxo-1,2-dihydropiridine-3-carboxamide | MKN45 (IC50 = 0.039 ± 0.009) BaF3/TRP-Met ((IC50 = 0.019 ± 0.0088) | 0.9 ± 0.1 | [49] |
 | 4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide | H460 (IC50 = 0.075) HT-29 (IC50 = 0.051) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.010) U87MG (IC50 = 0.53) SMMC-7721 (IC50 = 0.20) | 1.35 | [50] |
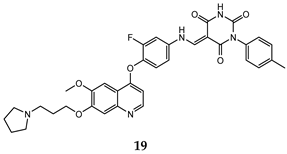 | 5-(aminomethylene) pyrimidine-2,4,6-trione moiety | HT-29 (IC50 = 0.13 ± 0.060) H460 (IC50 = 0.051 ± 0.0080) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.057 ± 0.0040) A549 (IC50 = 0.072 ± 0.0060) U87MG (IC50 = 0.64 ± 0.045) | 1.15 | [51] |
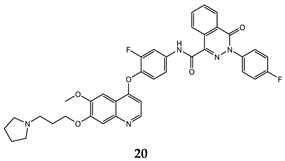 | 4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazine-1-carboxamide | H460 (IC50 = 0.055 ± 0.010) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.071 ± 0.011) HT-29 (IC50 = 0.13 ± 0.016) MDA-MB-231 (IC50 = 0.43 ± 0.050) | 1.63 | [52] |
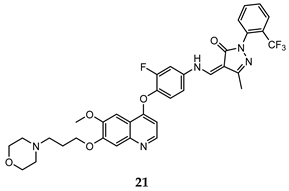 | pyrazolone | HT-29 (IC50 = 0.14 ± 0.02) H460 (IC50 = 0.18 ± 0.03) A549 (IC50 = 0.09 ± 0.02) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.03 ± 0.001) U87MG (IC50 = 1.06 ± 0.05) | 2.20 | [53] |
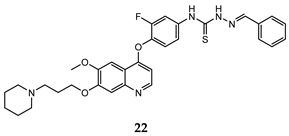 | (thio)semicarbazones | A549 (IC50 = 0.33 ± 0.02) HT-29 (IC50 = 0.21 ± 0.02) MKN-45 (IC50 = 0.71 ± 0.08) MDA-MB-231 (IC50 = 1.2 ± 0.17) | 8.92 | [54] |
| Quinoline Compound | Inhibition Data (IC50 or GI50) In Antiproliferative Assays | Enzymatic Inhibition Data (IC50 or Ki) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
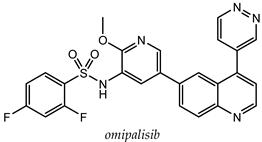 | T47D (IC50 = 3 nM) BT474 (IC50 = 2.4 nM) | PI3Kα IC50 = 0.04 nM; mTORC1 Ki = 0.18 nM; mTORC2 Ki = 0.3 nM | [67] |
 | U-87 MG (IC50 = 16 ± 5.8 nM) | PI3Kα (IC50 = 4.6 ± 3 nM; Ki = 0.6 ± 0.5 nM); mTOR IC50 = 3.9 ± 1 nM | [69] |
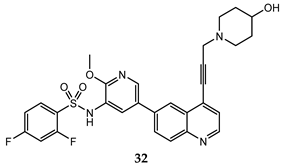 | PC-3 (IC50 = 0.37 μM); HCT-116 (IC50 = 2.47 μM) | PI3Kα IC50 = 1.63 nM mTOR IC50 = 3.6 nM | [70] |
 | PC-3 (IC50 = 0.08 μM)); HCT-116 (IC50 = 0.47 μM) | PI3Kα IC50 = 1.7 nM mTOR IC50 = 10.0 nM | [71] |
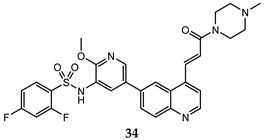 | PC-3 (GI50 = 0.40 μM); HCT-116 (GI50 = 0.47 μM) | PI3Kα IC50 = 0.50 nM mTOR IC50 = 1.3 nM | [72] |
| Compound | Antiproliferative Assays (IC50, μM) | mTOR Inhibition Data (IC50, nM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
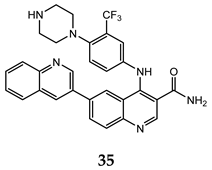 | HCT-116 (IC50 = 0.46 μM) PC-3 (IC50 = 0.61 μM) MCF-7 (IC50 = 0.24 μM) | 14 | [74] |
 | HCT-116 (IC50 = 0.36 μM) PC-3 (IC50 = 0.50 μM) MCF-7 (IC50 = 0.11 μM) | 22 | [75] |
 | HCT-116 (IC50 = 0.11 μM) PC-3 (IC50 = 0.17 μM) MCF-7 (IC50 = 0.05 μM) | 30 | [75] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martorana, A.; La Monica, G.; Lauria, A. Quinoline-Based Molecules Targeting c-Met, EGF, and VEGF Receptors and the Proteins Involved in Related Carcinogenic Pathways. Molecules 2020, 25, 4279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184279
Martorana A, La Monica G, Lauria A. Quinoline-Based Molecules Targeting c-Met, EGF, and VEGF Receptors and the Proteins Involved in Related Carcinogenic Pathways. Molecules. 2020; 25(18):4279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184279
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartorana, Annamaria, Gabriele La Monica, and Antonino Lauria. 2020. "Quinoline-Based Molecules Targeting c-Met, EGF, and VEGF Receptors and the Proteins Involved in Related Carcinogenic Pathways" Molecules 25, no. 18: 4279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184279
APA StyleMartorana, A., La Monica, G., & Lauria, A. (2020). Quinoline-Based Molecules Targeting c-Met, EGF, and VEGF Receptors and the Proteins Involved in Related Carcinogenic Pathways. Molecules, 25(18), 4279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184279