Effect of Ethanol on the Textural Properties of Whey Protein and Egg White Protein Hydrogels during Water-Ethanol Solvent Exchange
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
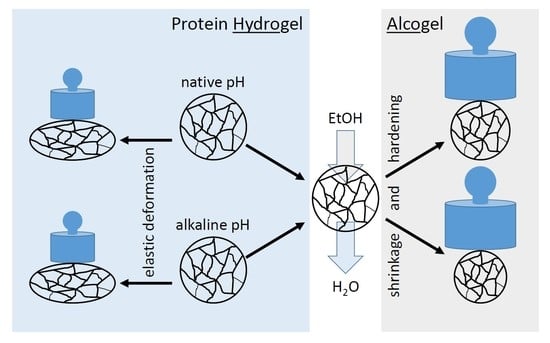
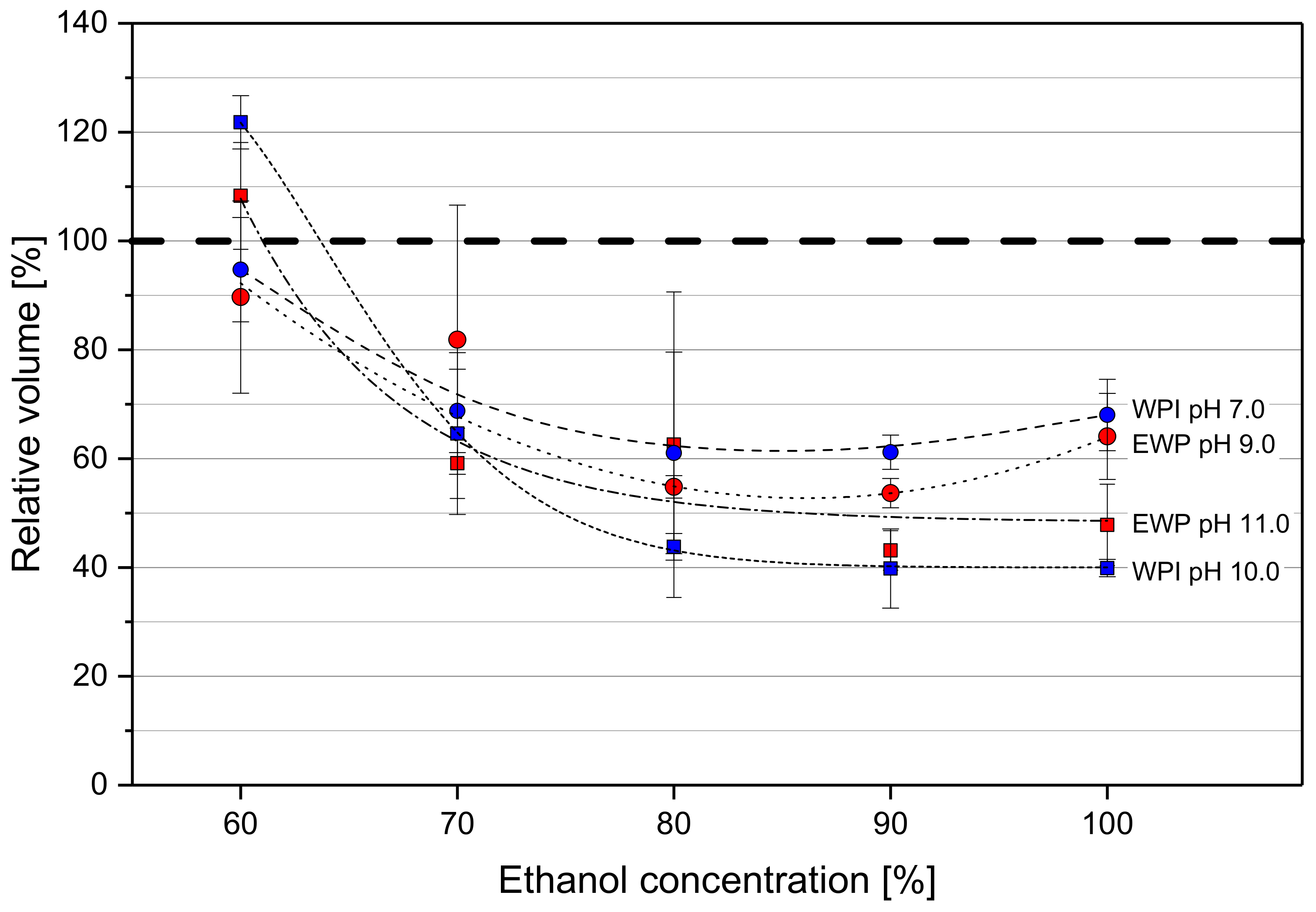
2.1. Shrinkage of Protein Hydrogel Spheres as A Function of Ethanol Concentration and pH during Thermal Gel Formation
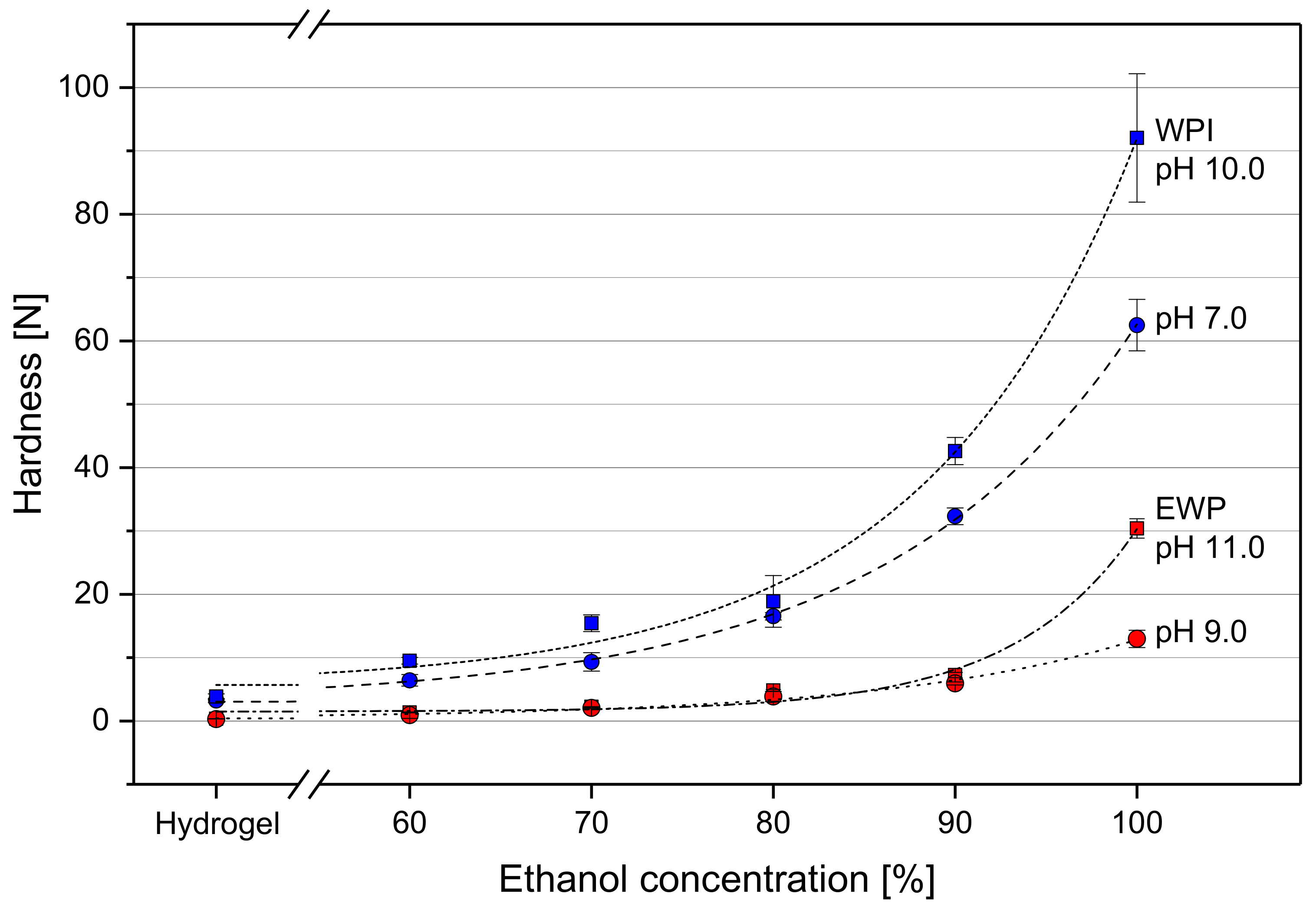
2.2. Hardening of Gel Spheres Induced by EtOH
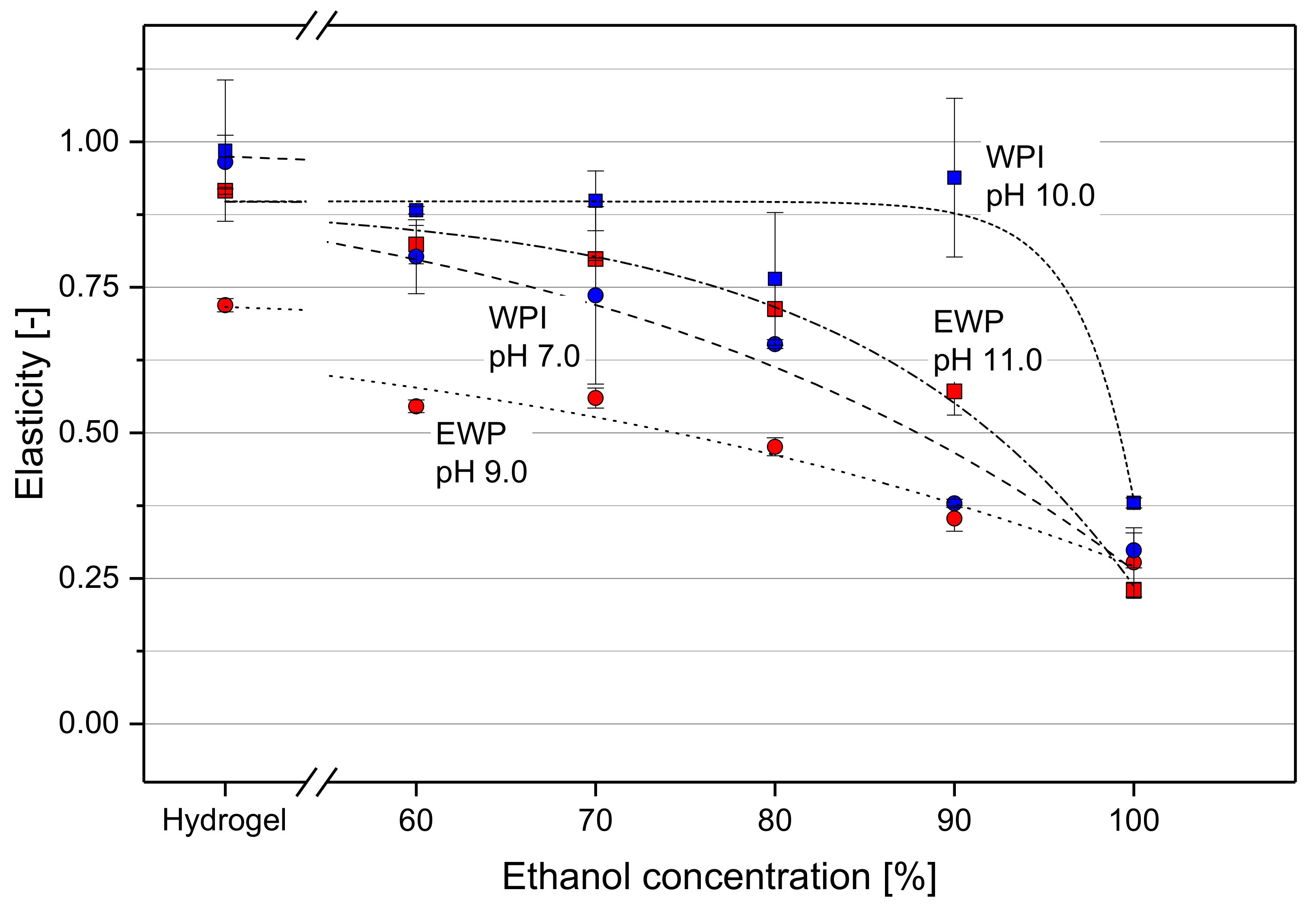
2.3. Effect of EtOH on Elasticity of Gel Spheres
2.4. Interaction of Ions Contained in the Protein Gel with the Exchange Solution
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
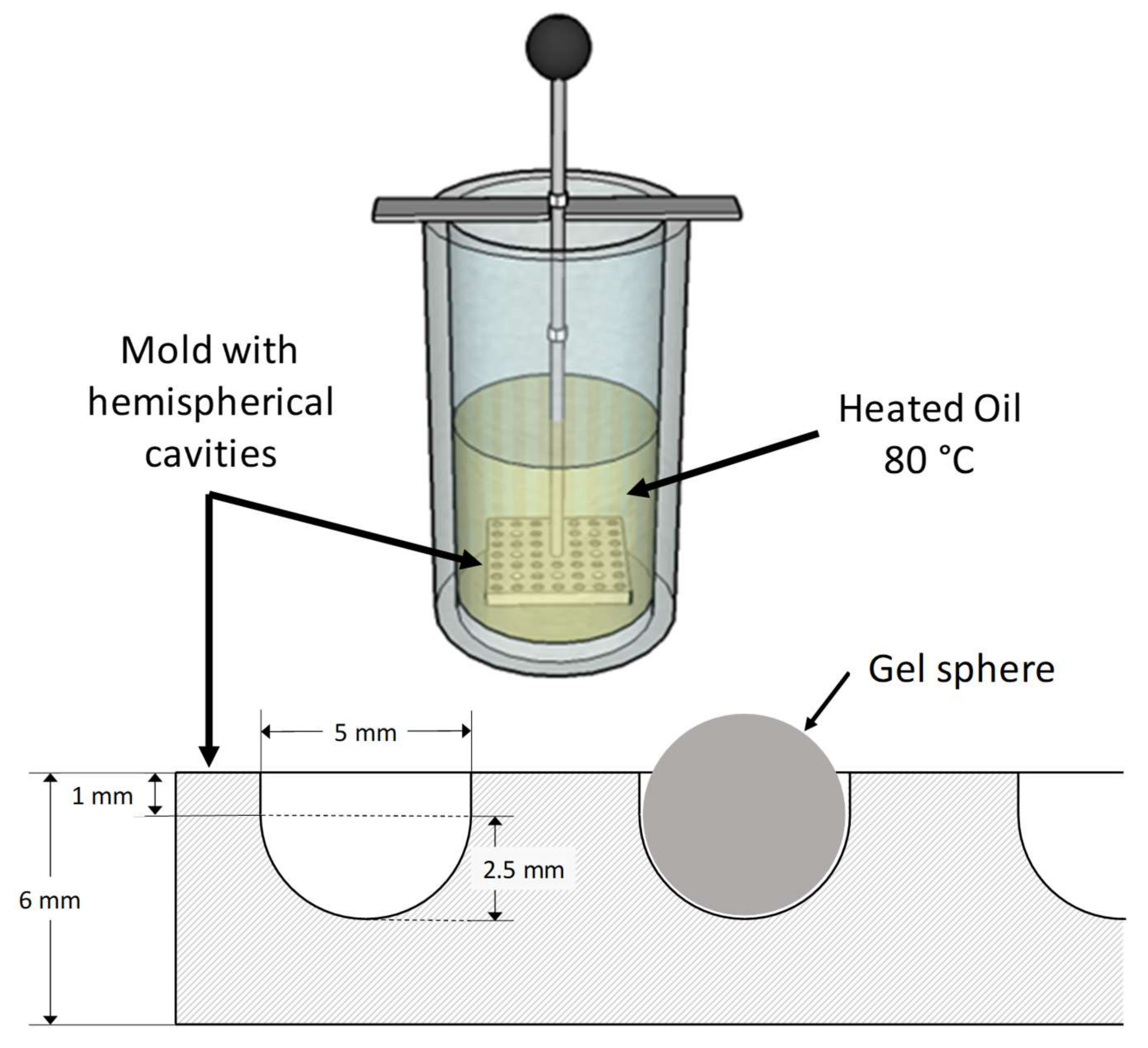
4.2.1. Preparation of Spherical Protein Hydrogel Samples
4.2.2. Solvent Exchange of Water by EtOH
4.2.3. Physical Characterization of Spherical Samples
4.2.4. Measurement of Dissolved Ions from Protein Gel Structure during Solvent Exchange
4.2.5. Determination of Extracted Ions from Protein Gel during Solvent Exchange
4.2.6. Statistical Evaluation and Data Presentation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoshizawa, S.; Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. Dependence of ethanol effects on protein charges. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 68, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, S.T.; Skjaak-Braek, G.; Elgsaeter, A.; Smidsroed, O. Swelling of covalently crosslinked alginate gels: Influence of ionic solutes and nonpolar solvents. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 3589–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sason, G.; Nussinovitch, A. Characterization of κ-carrageenan gels immersed in ethanol solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, M.; García-González, C.A.; Subrahmanyam, R.; Smirnova, I.; Kulozik, U. Preparation of novel whey protein-based aerogels as drug carriers for life science applications. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 72, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, C.A.; Alnaief, M.; Smirnova, I. Polysaccharide-based aerogels—Promising biodegradable carriers for drug delivery systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1425–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmer, I.; Kleemann, C.; Kulozik, U.; Heinrich, S.; Smirnova, I. Development of egg white protein aerogels as new matrix material for microencapsulation in food. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2015, 106, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergar, J.; Maver, U. Review of aerogel-based materials in biomedical applications. J. Sol.-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 77, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmer, I.; Karnetzke, J.; Kleemann, C.; Lehtonen, M.; Mikkonen, K.S.; Kulozik, U.; Smirnova, I. Encapsulation of fish oil in protein aerogel micro-particles. J. Food Eng. 2019, 260, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, S.; Sadeghpour, A.; Malfait, W.J.; Konishi, A.; Otake, K.; Yoda, S. Formation of Nanofibrous Structure in Biopolymer Aerogel during Supercritical CO2 Processing: The Case of Chitosan Aerogel. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 2051–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanyam, R.; Gurikov, P.; Dieringer, P.; Sun, M.; Smirnova, I. On the Road to Biopolymer Aerogels—Dealing with the Solvent. Gels 2015, 1, 291–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurikov, P.; Subrahmanyam, R.; Griffin, J.S.; Steiner, S.A.; Smirnova, I. 110th Anniversary: Solvent Exchange in the Processing of Biopolymer Aerogels: Current Status and Open Questions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 18590–18600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havea, P.; Watkinson, P.; Kuhn-Sherlock, B. Heat-induced whey protein gels: Protein-protein interactions and functional properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1506–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen-Nia, M.; Amiri, H. Measurement and modelling of static dielectric constants of aqueous solutions of methanol, ethanol and acetic acid at T = 293.15 K and 91.3 kPa. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2013, 57, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løkra, S.; Helland, M.H.; Claussen, I.C.; Strætkvern, K.O.; Egelandsdal, B. Chemical characterization and functional properties of a potato protein concentrate prepared by large-scale expanded bed adsorption chromatography. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N.; Narizhneva, N.V.; Kirschstein, S.O.; Winter, S.; Löber, G. Conformational transitions provoked by organic solvents in β-lactoglobulin: Can a molten globule like intermediate be induced by the decrease in dielectric constant? Fold. Des. 1997, 2, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cassanelli, M.; Norton, I.; Mills, T. Effect of alcohols on gellan gum gel structure: Bridging the molecular level and the three-dimensional network. Food Struct. 2017, 14, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boral, S.; Gupta, A.N.; Bohidar, H.B. Swelling and de-swelling kinetics of gelatin hydrogels in ethanol-water marginal solvent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2006, 39, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, E.; Robert, P.; Renard, D.; Llamas, G. Investigation of β-Lactoglobulin Gelation in Water/Ethanol Solutions. Int. Dairy J. 1998, 8, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirbel, F.; Kinsella, J.E. Effects of thiol reagents and ethanol on strength of whey protein gels. Food Hydrocoll. 1988, 2, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Jiang, A.; Chen, L. Characterization of ethanol-induced egg white gel and transportation of active nutraceuticals. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 130, 109530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota-Nakaoka, N.; Goto, Y. Alcohol-induced denaturation of β-lactoglobulin: A close correlation to the alcohol-induced α-helix formation of melittin. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 1999, 7, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, H.; Hirano, A.; Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. Effects of alcohol on the solubility and structure of native and disulfide-modified bovine serum albumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufour, E.; Haertl’, T. Alcohol-induced changes of β-lactoglobulin-retinol-binding stoichiometry. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1990, 4, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mine, Y. Recent advances in the understanding of egg white protein functionality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 6, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, H.M.; Jimenez-Flores, R.; Bleck, G.T.; Brown, E.M.; Butler, J.E.; Creamer, L.K.; Hicks, C.L.; Hollar, C.M.; Ng-Kwai-Hang, K.F.; Swaisgood, H.E. Nomenclature of the Proteins of Cows’ Milk—Sixth Revision. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 1641–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhlov, A.R.; Philippova, O.E.; Sitnikova, N.L.; Starodubtsev, S.G. Supramolecular structures in polyelectrolyte gels. Faraday Disc. 1995, 101, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, M.; Hörmansperger, J.; Fuchs, T.; Kulozik, U. Swelling behaviour, charge and mesh size of thermal protein hydrogels as influenced by pH during gelation. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, S.; Ko, S.; Xiao, L. Use of whey proteins for encapsulation and controlled delivery applications. J. Food Eng. 2007, 83, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.P.; Macedo, E.A. Solubility of NaCl, NaBr, and KCl in Water, Methanol, Ethanol, and Their Mixed Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2005, 50, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseki, T.; Kitabatake, N.; Doi, E. Irreversible thermal denaturation and formation of linear aggregates of ovalbumin. Food Hydrocoll. 1989, 3, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Cheftel, J.C. Texture characteristics, protein solubility, and sulfhydryl group/disulfide bond contents of heat-induced gels of whey protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1988, 36, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.; Herbig, A.-L.; Moreau, A.; Delaplace, G. Influence of calcium on β-lactoglobulin denaturation kinetics: Implications in unfolding and aggregation mechanisms. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 5794–5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, E.; Kitabatake, N. Structure of glycinin and ovalbumin gels. Food Hydrocoll. 1989, 3, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, A.; Takahashi, K.; Kuroda, N.; Froning, G.W. Heat-induced Egg White Gels as Affected by pH. J. Food Sci. 1998, 63, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukes, T.H.; Schmidt, C.L.A. The apparent dissociation constants of certain amino acids and related substances in water-ethanol mixtures. J. Biol. Chem. 1934, 105, 359–371. [Google Scholar]
- Gelsema, W.J.; De Ligny, C.L.; Van der Veen, N.G. Isoelectric points of proteins, determined by isoelectric focusing in the presence of urea and ethanol. J. Chromatogr. A 1979, 171, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Plancken, I.; Van Loey, A.; Hendrickx, M.E.G. Changes in sulfhydryl content of egg white proteins due to heat and pressure treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5726–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, C.; Selmer, I.; Smirnova, I.; Kulozik, U. Tailor made protein based aerogel particles from egg white protein, whey protein isolate and sodium caseinate: Influence of the preceding hydrogel characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H.; Durães, L.; Portugal, A. An overview on silica aerogels synthesis and different mechanical reinforcing strategies. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2014, 385, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, M.; Kulozik, U. Whey protein gels for the entrapment of bioactive anthocyanins from bilberry extract. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnia, J.C.; Birgersson, E.; Mujumdar, A.S. Finite deformation of fast-response thermo-sensitive hydrogels—A computational study. Polymer 2012, 53, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, M.C. Food Texture and Viscosity. Concept and Measurement; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; ISBN 0121190625. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
| Exchange Solvent | WPI pH 7.0 Na+ (%) | WPI pH 7.0 Ca2+ (%) | EWP pH 9.0 Na+ (%) | EWP pH 9.0 K+ (%) | EWP pH 9.0 Ca2+ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | 81.9 ± 4.6 | 32.5 ± 2.1 | 98.3 ± 2.8 | 83.5 ± 2.0 | 91.0 ± 21.7 |
| EtOH 60% | 35.1 ± 2.1 | 9.6 ± 1.0 | 88.3 ± 1.1 | 77.0 ± 1.0 | 14.2 ± 0.2 |
| EtOH 100% | 4.4 ± 1.1 | 1.2 ± 0.8 | 65.0 ± 1.0 | 57.3 ± 1.3 | 31.4 ± 2.8 |
| EWP | WPI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gel State | pH 9.0 (N/mm) | pH 11.0 (N/mm) | pH 7.0 (N/mm) | pH 10.0 (N/mm) |
| Hydrogel | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.00 | 1.11 ± 0.12 | 1.33 ± 0.13 |
| Alcogel | 5.6 ± 0.8 | 15.0 ± 0.9 | 25.2 ± 2.3 | 41.0 ± 5.7 |
| Aerogel | 12.5 ± 2.9 1 | 21.6 ± 1.6 1 | 148.9 ± 16.9 2 | 180.5 ± 13.5 2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kleemann, C.; Zink, J.; Selmer, I.; Smirnova, I.; Kulozik, U. Effect of Ethanol on the Textural Properties of Whey Protein and Egg White Protein Hydrogels during Water-Ethanol Solvent Exchange. Molecules 2020, 25, 4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194417
Kleemann C, Zink J, Selmer I, Smirnova I, Kulozik U. Effect of Ethanol on the Textural Properties of Whey Protein and Egg White Protein Hydrogels during Water-Ethanol Solvent Exchange. Molecules. 2020; 25(19):4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194417
Chicago/Turabian StyleKleemann, Christian, Joël Zink, Ilka Selmer, Irina Smirnova, and Ulrich Kulozik. 2020. "Effect of Ethanol on the Textural Properties of Whey Protein and Egg White Protein Hydrogels during Water-Ethanol Solvent Exchange" Molecules 25, no. 19: 4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194417
APA StyleKleemann, C., Zink, J., Selmer, I., Smirnova, I., & Kulozik, U. (2020). Effect of Ethanol on the Textural Properties of Whey Protein and Egg White Protein Hydrogels during Water-Ethanol Solvent Exchange. Molecules, 25(19), 4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194417