Inhibitory Potential of Polyclonal Camel Antibodies against New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase-1 (NDM-1)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Determination of Km for NDM-1, VIM-1, and L1
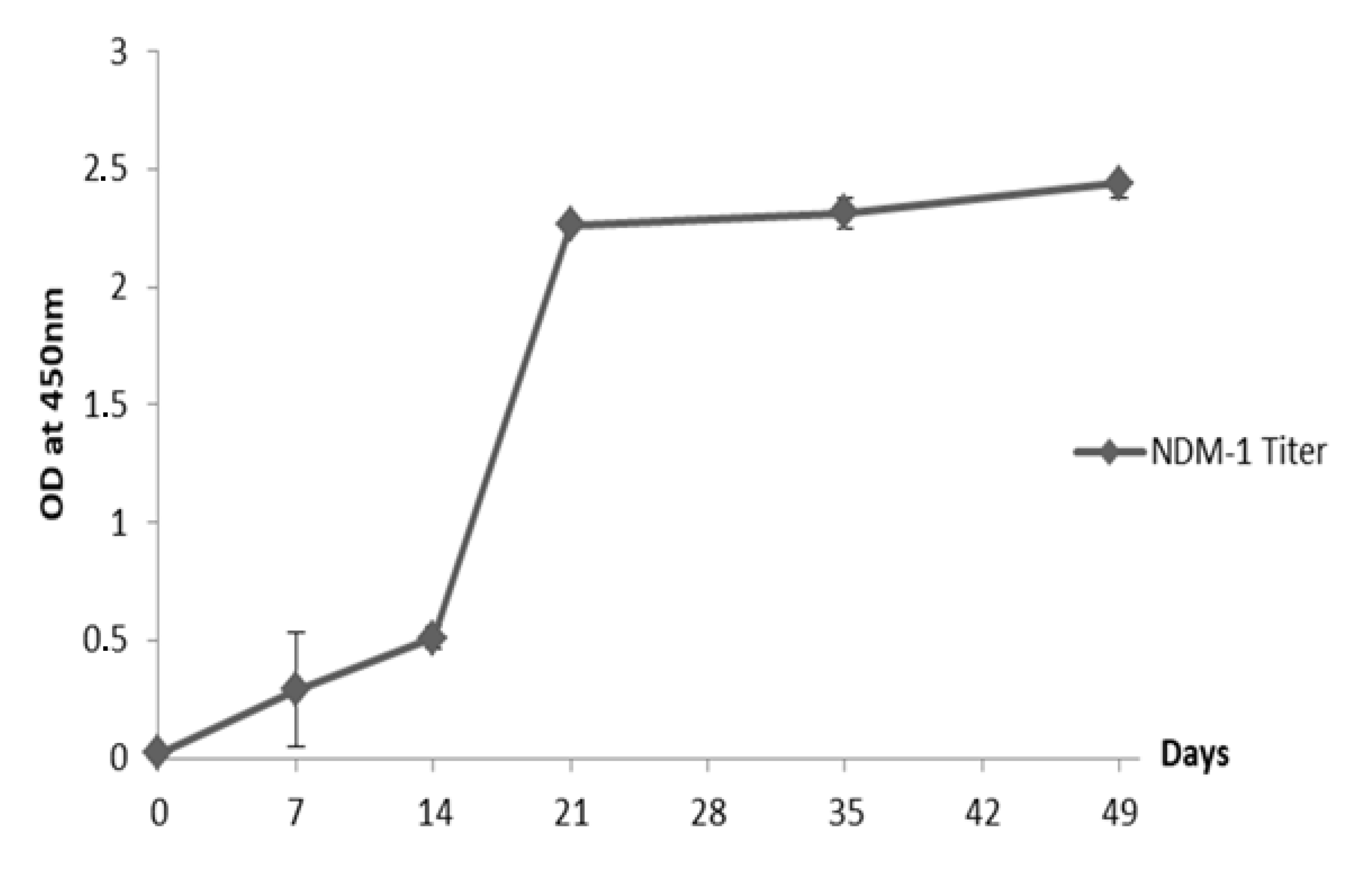
2.2. Humoral Immune Response Elicited in the Dromedary
2.3. IgG Subclass Characterization
2.4. Inhibition Kinetic Assays of NDM-1
2.5. Inhibition Kinetic Assay of VIM-1 and L1 Enzymes
2.6. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
2.7. Periplasm Extraction and Specific Activity Determination
2.8. Molecular Investigation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Enzymes, Plasmids, and Strains
4.2. Production and Purification of NDM-1 Metallo-β-lactamase
4.3. Camel Immunization Protocol
4.4. IgG Subclass Fractionation
4.5. ELISA Assessment
4.6. Determination of Km for NDM-1, VIM-1, and L1
4.7. Time-Dependent Inhibition Assays
4.8. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
4.9. Periplasm Extraction and Specific Activity Determination
4.10. Molecular Visualization
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bradford, P.A. Epidemiology of resistance. In Antimicrobial Resistance and Implications for the 21st Century, 2nd ed.; Fong, I.W., Shlaes, D., Drlica, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, D.L.; Bonomo, R.A. Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Pathogens: The Urgent Need for ‘Old’ Polymyxins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1145, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bush, K. Past and Present Perspectives on β-Lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathlouthi, N.; Al-Bayssari, C.; Bakour, S.; Rolain, J.M.; Chouchani, C. Prevalence and emergence of carbapenemases-producing Gram-negative bacteria in Mediterranean basin. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 4343–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambler, R.P. The structure of β-lactamases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1980, 289, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garau, G.; García-Sáez, I.; Bebrone, C.; Anne, C.; Mercuri, P.; Frère, J.M.; Dideberg, O. Update of the standard numbering scheme for class B beta-lactamases. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2347–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salahuddin, P.; Kumar, A.; Khan, A.U. Structure, function of serine and metallo-β-lactamases and their inhibitors. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 19, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Niu, X. Discovery of the Novel Inhibitor Against New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase Based on Virtual Screening and Molecular Modelling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, P.P.; Khan, I.A. Potential Inhibitors Against NDM-1 Type Metallo-β-Lactamases: An Overview. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Chen, J.; Xiao, B.; Kang, X.; Lao, X.; Zheng, H.; Shi, C. Discovery of NDM-1 inhibitors from natural products. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 18, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drawz, S.M.; Bonomo, R.A. Three decades of beta-lactamase inhibitors. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 160–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bush, K.; Bradford, P.A. β-Lactams and β-Lactamase Inhibitors: An Overview. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornaglia, G.; Giamarellou, H.; Rossolini, G.M. Metallo-β-lactamases: A last frontier for β-lactams? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarasamy, K.K.; Toleman, M.A.; Walsh, T.R.; Bagaria, J.; Butt, F.; Balakrishnan, R.; Chaudhary, U.; Doumith, M.; Giske, C.G.; Irfan, S.; et al. Emergence of a new antibiotic resistance mechanism in India, Pakistan, and the UK: A molecular, biological, and epidemiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.R. New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1: Detection and prevention. CMAJ 2011, 183, 1240–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Politi, L.; Gartzonika, K.; Spanakis, N.; Zarkotou, O.; Poulou, A.; Skoura, L.; Vrioni, G.; Tsakris, A. Emergenced clon of NDM-1-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Greece: Evidence of a widesprea al outbreak. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 2197–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wailan, A.M.; Paterson, D.L. The spread and acquisition of NDM-1: A multifactorial problem. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2014, 12, 91–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamers-Casterman, C.; Atarhouch, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Robinson, G.; Hamers, C.; Songa, E.B.; Bendahman, N.; Hamers, R. Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature 1993, 363, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyldermans, S.; Baral, T.N.; Retamozzo, V.C.; De Baetselier, P.; De Genst, E.; Kinne, J.; Leonhardt, H.; Magez, S.; Nguyen, V.K.; Revets, H.; et al. Camelid immunoglobulins and nanobody technology. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 128, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steeland, S.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Libert, C. Nanobodies as therapeutics: Big opportunities for small antibodies. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 1076–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolkman, J.A.; Law, D.A. Nanobodies-from llamas to therapeutic proteins. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2010, 7, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, M.M.; De Haard, H.J. Properties, production, and applications of camelid single-domain antibody fragments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 77, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conrath, K.; Pereira, A.S.; Martins, C.E.; Timóteo, C.G.; Tavares, P.; Spinelli, S.; Kinne, J.; Flaudrops, C.; Cambillau, C.; Muyldermans, S.; et al. Camelid nanobodies raised against an integral membrane enzyme, nitric oxide reductase. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauwereys, M.; Arbabi-Ghahroudi, M.; Desmyter, A.; Kinne, J.; Hölzer, W.; De Genst, E.; Wyns, L.; Muyldermans, S. Potent enzyme inhibitors derived from dromedary heavy-chain antibodies. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3512–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Transue, T.R.; De Genst, E.; Ghahroudi, M.A.; Wyns, L.; Muyldermans, S. Camel single-domain antibody inhibits enzyme by mimicking carbohydrate substrate. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 1998, 32, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrath, K.E.; Lauwereys, M.; Galleni, M.; Matagne, A.; Frère, J.M.; Kinne, J.; Wyns, L.; Muyldermans, S. Beta-lactamase inhibitors derived from single-domain antibody fragments elicited in the camelidae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 2807–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sohier, J.S.; Laurent, C.; Chevigné, A.; Pardon, E.; Srinivasan, V.; Wernery, U.; Lassaux, P.; Steyaert, J.; Galleni, M. Allosteric inhibition of VIM metallo-β-lactamases by a camelid nanobody. Biochem. J. 2013, 450, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Maryam, L.; Zarrilli, R. Structure, Genetics and Worldwide Spread of New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase (NDM): A threat to public health. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L.; Walsh, T.R.; Livermore, D.M. The emerging NDM carbapenemases. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyldermans, S. Single domain camel antibodies: Current status. Rev. Mol. Biotechnol. 2001, 74, 277–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, N.; Caravelli, B.; Docquier, J.D.; Galleni, M.; Frère, J.M.; Amicosante, G.; Rossolini, G.M. Purification and biochemical characterization of the VIM-1 metallo-β-lactamase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 3003–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wommer, S.; Rival, S.; Heinz, U.; Galleni, M.; Frère, J.M.; Franceschini, N.; Amicosante, G.; Rasmussen, B.; Bauer, R.; Adolph, H.W. Substrate-activated zinc binding of metallo-β-lactamases. Physiological importance of the mononyclear enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 24142–24147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcoccia, F.; Leiros, H.S.; Aschi, M.; Amicosante, G.; Perilli, M. Exploring the role of L209 residue in the active site of NDM-1 a metallo-β-lactamase. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccirilli, A.; Brisdelli, F.; Aschi, M.; Celenza, G.; Amicosante, G.; Perilli, M. Kinetic Profile and Molecular Dynamic Studies Show that Y229W Substitution in an NDM-1/L209F Variant Restores the Hydrolytic Activity of the Enzyme toward Penicillins, Cephalosporins, and Carbapenems. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e02270-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spyrakis, F.; Celenza, G.; Marcoccia, F.; Santucci, M.; Cross, S.; Bellio, P.; Cendron, L.; Perilli, M.; Tondi, D. Structure-based virtual screening for the discovery of novel inhibitors of New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase 1. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderrazek, R.B.; Hmila, I.; Vincke, C.; Benlasfar, Z.; Pellis, M.; Dabbek, H.; Saerens, D.; El Ayeb, M.; Muyldermans, S.; Bouhaouala-Zahar, B. Identification of potent nanobodies to neutralize the most poisonous polypeptide from scorpion venom. Biochem. J. 2009, 424, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meddeb-Mouelhi, F.; Bouhaouala-Zahar, B.; Benlasfar, Z.; Hammadi, M.; Mejri, T.; Moslah, M.; Karoui, H.; Khorchani, T.; El Ayeb, M. Immunized camel sera and derived immunoglobulin subclasses neutralizing Androctonus australis hector scorpion toxins. Toxicon 2003, 42, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmila, I.; Saerens, D.; Ben Abderrazek, R.; Vincke, C.; Abidi, N.; Benlasfar, Z.; Govaert, J.; EI Ayeb, M.; Bouhaouala-Zahar, B.; Muyldermans, S. A bispecific nanobody to provide full protection against lethal scorpion envenoming. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 3479–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meester, F.; Joris, B.; Reckinger, G.; Bellefroid-Bourguignon, C.; Frère, J.M. Automated analysis of enzyme inactivation phenomena, Application to β-lactamases and DD-peptidases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1987, 36, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, R.A. Enzymes: A Pratical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism and Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 318–449. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Performance Standard for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 28th ed.; Document M100; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018.
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeLano, W.L. Pymol: An open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4. Newsl. Protein Crystallogr. 2002, 40, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Specific IgG1, IgG2 and IgG3 against NDM-1, VIM-1 and L1 are available from the authors. |





| Fractions | V*Cc (mg) | Proportion of IgGs/Serum | Proportion of IgG Subtypes/Total IgGs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum | 4 | 100% | - |
| IgG1 | 0.7 | 17.5% | 59.82% |
| IgG2 | 0.17 | 4.25% | 14.53% |
| IgG3 | 0.3 | 7.5% | 25.64% |
| Total = 11.7% | Total = 40.17% |
| Enzymes | IgG1 | IgG2 | IgG3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μM) | IC50 (μM) | IC50 (μM) | |
| NDM-1 | 0.45 | >100 | 15 |
| NDM-1 periplasm | 0.42 | >100 | 15 |
| VIM-1 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.16 |
| VIM-1 periplasm | 0.18 | 0.036 | 0.15 |
| L1 | 0.15 | 1.0 | 0.90 |
| L1 periplasm | 0.15 | 0.95 | 0.90 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben Abderrazek, R.; Chammam, S.; Ksouri, A.; Perilli, M.; Dhaouadi, S.; Mdini, I.; Benlasfar, Z.; Amicosante, G.; Bouhaouala-Zahar, B.; Piccirilli, A. Inhibitory Potential of Polyclonal Camel Antibodies against New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase-1 (NDM-1). Molecules 2020, 25, 4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194453
Ben Abderrazek R, Chammam S, Ksouri A, Perilli M, Dhaouadi S, Mdini I, Benlasfar Z, Amicosante G, Bouhaouala-Zahar B, Piccirilli A. Inhibitory Potential of Polyclonal Camel Antibodies against New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase-1 (NDM-1). Molecules. 2020; 25(19):4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194453
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen Abderrazek, Rahma, Sarra Chammam, Ayoub Ksouri, Mariagrazia Perilli, Sayda Dhaouadi, Ines Mdini, Zakaria Benlasfar, Gianfranco Amicosante, Balkiss Bouhaouala-Zahar, and Alessandra Piccirilli. 2020. "Inhibitory Potential of Polyclonal Camel Antibodies against New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase-1 (NDM-1)" Molecules 25, no. 19: 4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194453
APA StyleBen Abderrazek, R., Chammam, S., Ksouri, A., Perilli, M., Dhaouadi, S., Mdini, I., Benlasfar, Z., Amicosante, G., Bouhaouala-Zahar, B., & Piccirilli, A. (2020). Inhibitory Potential of Polyclonal Camel Antibodies against New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase-1 (NDM-1). Molecules, 25(19), 4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194453






