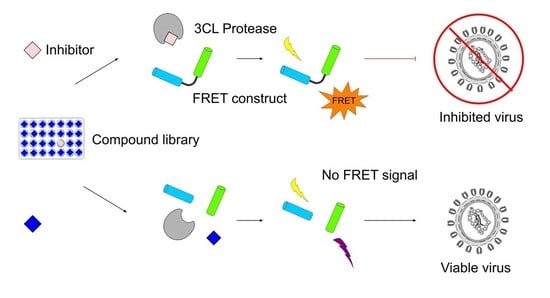
High-Throughput Screening for Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 Protease Using a FRET-Biosensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Proteolysis of an eCFP-Venus Biosensor by SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro
2.2. Characterisation and Application of the eCFP-Venus Biosensor for High Throughput Screening
3. Discussion
Evaluation of Inhibitors Detected in This Screen
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Protein Expression
4.2. Enzymatic Activity and Inhibition Assays
4.3. Chemicals
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Menni, C.; Valdes, A.M.; Freidin, M.B.; Sudre, C.H.; Nguyen, L.H.; Drew, D.A.; Ganesh, S.; Varsavsky, T.; Cardoso, M.J.; Visconti, A.; et al. Real-time tracking of self-reported symptoms to predict potential COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2020. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Le, T.T.; Andreadakis, Z.; Kumar, A.; Roman, R.G.; Tollefsen, S.; Saville, M.; Mayhew, S. The COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, D.; Sun, X.; Curth, U.; Drosten, C.; Sauerhering, L.; Becker, S.; Rox, K.; Hilgenfeld, R. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved alpha-ketoamide inhibitors. Science 2020, 368, 409–412. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.W.; Tian, J.H.; Pei, Y.Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, J.A.; Olson, A.N.; Neupane, K.; Munshi, S.; San Emeterio, J.; Pollack, L.; Woodside, M.T.; Dinman, J.D. Structural and functional conservation of the programmed-1 ribosomal frameshift signal of SARS coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 10741–10748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, A.A.; Fatima, K.; Mohammad, T.; Fatima, U.; Singh, I.K.; Singh, A.; Atif, S.M.; Hariprasad, G.; Hasan, G.M.; Hassan, M.I. Insights into SARS-CoV-2 genome, structure, evolution, pathogenesis and therapies: Structural genomics approach. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Du, X.; Xu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.; et al. Structure of M-pro from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors. Nature 2020, 582, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hilgenfeld, R. From SARS to MERS: Crystallographic studies on coronaviral proteases enable antiviral drug design. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 4085–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, A.; Wang, Y.I.; Zeng, C.; Huang, X.; Xu, S.; Su, C.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Guo, D. Prediction and biochemical analysis of putative cleavage sites of the 3C-like protease of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Virus Res. 2015, 208, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuck, C.P.; Chong, L.T.; Chen, C.; Chow, H.F.; Wan, D.C.; Wong, K.B. Profiling of Substrate Specificity of SARS-CoV 3CL(pro). PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilianski, A.; Mielech, A.M.; Deng, X.; Baker, S.C. Assessing Activity and Inhibition of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Papain-Like and 3C-Like Proteases Using Luciferase-Based Biosensors. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 11955–11962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagai, T.; Miyawaki, A. A high-throughput method for development of FRET-based indicators for proteolysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 319, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H.; Chung, T.D.; Oldenburg, K.R. A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.Y.; Shoichet, B.K. A detergent-based assay for the detection of promiscuous inhibitors. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, C.; Baty, F.; Streibig, J.C.; Gerhard, D. Dose-Response Analysis Using R. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0146021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sies, H.; Parnham, M.J. Potential therapeutic use of ebselen for COVID-19 and other respiratory viral infections. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 156, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, C.A.; Bylehn, F.; Perez-Lemus, G.R.; Alvarado, W.; de Pablo, J.J. Molecular characterization of Ebselen binding activity to SARS-CoV-2 main protease. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.09805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birck, M.R.; Holler, T.P.; Woodard, R.W. Identification of a slow tight-binding inhibitor of 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid 8-phosphate synthase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 9334–9335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoun, A.M.; Chockalingam, K.; Bobardt, M.; Simeon, R.; Chang, J.; Gallay, P.; Chen, Z. PD 404,182 Is a Virocidal Small Molecule That Disrupts Hepatitis C Virus and Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chockalingam, K.; Simeon, R.L.; Rice, C.M.; Chen, Z. A Cell Protection Screen Reveals Potent Inhibitors of Multiple Stages of the Hepatitis C Virus Life Cycle. Antivir. Res. 2010, 86, A32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoun-Emanuelli, A.M.; Bobardt, M.; Moncla, B.; Mankowski, M.K.; Ptak, R.G.; Gallay, P.; Chen, Z. Evaluation of PD 404,182 as an Anti-HIV and Anti-Herpes Simplex Virus Microbicide. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghebremariam, Y.T.; Erlanson, D.A.; Cooke, J.P. A Novel and Potent Inhibitor of Dimethylarginine Dimethylaminohydrolase: A Modulator of Cardiovascular Nitric Oxide. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 348, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muth, M.; Jänsch, N.; Kopranovic, A.; Krämer, A.; Wössner, N.; Jung, M.; Kirschhöfer, F.; Brenner-Weiß, G.; Meyer-Almes, F.J. Covalent inhibition of histone deacetylase 8 by 3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrimido[1,2-c][1,3]benzothiazin-6-imine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, J.C.; Asgian, J.L.; Ekici, Ö.D.; James, K.E. Irreversible inhibitors of serine, cysteine, and threonine proteases. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4639–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlotsky, J.M. Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C: Current and Future. Hepatitis C Virus: From Mol. Virol. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 369, 321–342. [Google Scholar]
- Groen, K.; Van De Donk, N.W.; Stege, C.A.; Zweegman, S.; Nijhof, I.S. Carfilzomib for relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 2663–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auffret, M.; Drapier, S.; Verin, M. New tricks for an old dog: A repurposing approach of apomorphine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 843, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosset, K.A.; Malek, N.; Morgan, F.; Grosset, D.G. Phase IIa randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study of inhaled apomorphine as acute challenge for rescuing ‘off’ periods in patients with established Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2013, 20, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.B.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.; Naguyen, T.T.; Park, S.J.; Chang, J.S.; Park, K.H.; et al. Biflavonoids from Torreya nucifera displaying SARS-CoV 3CL(pro) inhibition. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 7940–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Luo, C.; Liu, H.; Xu, W.; Chen, G.; Liew, O.W.; Zhu, W.; Puah, C.M.; Shen, X.; et al. Binding interaction of quercetin-3-beta-galactoside and its synthetic derivatives with SARS-CoV 3CL(pro): Structure-activity relationship studies reveal salient pharmacophore features. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 8295–8306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds and plasmids used in this study are available from the authors. |





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brown, A.S.; Ackerley, D.F.; Calcott, M.J. High-Throughput Screening for Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 Protease Using a FRET-Biosensor. Molecules 2020, 25, 4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204666
Brown AS, Ackerley DF, Calcott MJ. High-Throughput Screening for Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 Protease Using a FRET-Biosensor. Molecules. 2020; 25(20):4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204666
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrown, Alistair S., David F. Ackerley, and Mark J. Calcott. 2020. "High-Throughput Screening for Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 Protease Using a FRET-Biosensor" Molecules 25, no. 20: 4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204666
APA StyleBrown, A. S., Ackerley, D. F., & Calcott, M. J. (2020). High-Throughput Screening for Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 Protease Using a FRET-Biosensor. Molecules, 25(20), 4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204666