Synthesis of Benzimidazole–Based Analogs as Anti Alzheimer’s Disease Compounds and Their Molecular Docking Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Benzimidazole-Based Thiosemicarbazide
2.2. Synthesis of Benzimidazole Schiff Base
2.3. Structure Activity Relationship
2.3.1. Acetylcholinesterase Activity of Benzimidazole-Based Thiosemicarbazide
2.3.2. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition Activity of Benzimidazole Schiff Bases
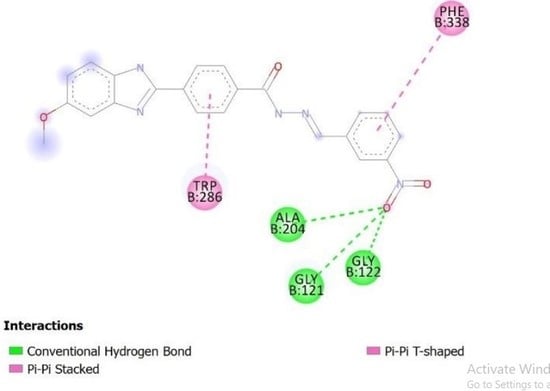
2.4. Molecular Docking Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Benzimidazole-Based Thiosemicarbazide 1(a–j)
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Benzimidazole-Based Schiff Bases 2(a–m)
3.3. Docking Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, S.; Iftikhar, F.; Ullah, F.; Sadiq, A.; Rashid, U. Rational design and synthesis of dihydropyrimidine based dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2016, 69, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auld, D.S.; Kornecook, T.J.; Bastianetto, S.; Quirion, R. Alzheimer’s disease and the basal forebrain cholinergic system: Relations to β-amyloid peptides, cognition, and treatment strategies. Prog. Neurobiol. 2002, 68, 209–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.L.; Craig, P.L.; Parsons, O.A. Neuropsychology of dementia. Neurol. Clin. 1986, 4, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisen, P.S.; Davis, K.L. The search for disease-modifying treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 1997, 48, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jann, M.W. Preclinical pharmacology of metrifonate. Pharmacotherapy 1998, 18, 55–67. [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié, J.; Pezzementi, L.; Bon, S.; Krejci, E.; Vallette, F.M. Molecular and cellular biology of cholinesterases. Prog. Neurobiol. 1993, 41, 31–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, G.; Greig, H.N.; Khan, A.J.; Kamal, A.M. Status of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecobichon, D.J.; Comeau, A.M. Pseudocholinesterases of mammalian plasma: Physicochemical properties and organophosphate inhibition in eleven species. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1973, 24, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, F.; Ullah, H.; Taha, M.; Wadood, A.; Javed, M.T.; Rehman, W.; Nawaz, M.; Ashraf, M.; Ali, M.; Sajid, M.; et al. Synthesis and in vitro acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory potential of hydrazide-based Schiff bases. Bioorg. Chem. 2016, 68, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, A.; Bolognesi, M.L.; Minarini, A.; Rosini, M.; Tumiatti, V.; Recanatini, M.; Melchiorre, C. Multi-target-directed ligands to combat neurodegenerative diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 347–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, K.; Mintzer, J.; Truyen, L.; Wessel, T.; Wilkinson, D. Effects of a flexible galantamine dose in Alzheimer’s disease: A randomised, controlled trial. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 71, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mesulam, M.; Guillozet, A.; Shaw, P.; Quinn, B. Widely spread butyrylcholinesterase can hydrolyze acetylcholine in the normal and Alzheimer brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2002, 9, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greig, N.H.; Utsuki, T.; Yu, Q.S.; Zhu, X.; Holloway, H.W.; Perry, T.; Lee, B.; Ingram, D.K.; Lahiri, D.K. A new therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease treatment: Attention to butyrylcholinesterase. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2001, 17, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabr, M.T.; Abdel-Raziq, M.S. Design and synthesis of donepezil analogues as dual AChE and BACE-1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 80, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, G.W.; Rabins, P.V.; Barry, P.P.; Buckholtz, N.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Ferris, S.H.; Finkel, S.I.; Gwyther, L.P.; Khachaturian, Z.S.; Lebowitz, B.D.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer disease and related disorders: Consensus statement of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry, the Alzheimer’s Association, and the American Geriatrics Society. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1997, 278, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, D. New drug treatment for Alzheimer’s disease: Lessons for healthcare policy. Brit. Med. J. 1998, 316, 762–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelev, S.; Okello, E.; Perry, N.S.; Wilkins, R.M.; Perry, E.K. Synergistic and antagonistic interactions of anticholinesterase terpenoids in Salvia lavandulaefolia essential oil. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 75, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Sung, S.H.; Park, M.J.; Kim, Y.C. Coumarins isolated from Angelica gigas inhibit acetylcholinesterase: Structure−Activity relationships. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 683–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.; Nawaz, S.A.; Malik, A.; Choudhary, M.I. Isolation and cholinesterase-inhibition studies of sterols from Haloxylon recurvum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.; Rahim, F.; Zaman, K.; Selvaraj, M.; Uddin, N.; Farooq, R.K.; Nawaz, M.; Sajid, M.; Nawaz, F.; Ibrahim, M.; et al. Synthesis, α-glycosidase inhibitory potential and molecular docking study of benzimidazole derivatives. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 95, 103555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, F.; Zaman, K.; Taha, M.; Ullah, H.; Ghufran, M.; Wadood, A.; Rehman, W.; Uddin, N.; Shah, S.A.; Sajid, M.; et al. Synthesis, in vitro alpha-glucosidase inhibitory potential of benzimidazole bearing bis-Schiff bases and their molecular docking study. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 94, 103394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawawi, N.K.; Taha, M.; Ahmat, N.; Ismail, N.H.; Wadood, A.; Rahim, F. Synthesis, molecular docking studies of hybrid benzimidazole as α-glucosidase inhibitor. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 70, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawawi, N.K.; Taha, M.; Ahmat, N.; Wadood, A.; Ismail, N.H.; Rahim, F.; Azam, S.S.; Abdullah, N. Benzimidazole derivatives as new α-glucosidase inhibitors and in silico studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2016, 64, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.; Rahim, F.; Hayat, S.; Selvaraj, M.; Farooq, R.K.; Shah, S.A.; Zakaria, Z.A. Synthesis of diabetic II inhibitors based on 2-mercaptobenzimidazole and their molecular docking study. Preprints 2019, 2019110375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaman, K.; Rahim, F.; Taha, M.; Ullah, H.; Wadood, A.; Nawaz, M.; Khan, F.; Wahab, Z.; Shah, S.A.; Rehman, A.U.; et al. Synthesis, in vitro urease inhibitory potential and molecular docking study of Benzimidazole analogues. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 89, 103024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, J.; Rudolph, M.J.; Burshteyn, F.; Cassidy, M.S.; Gary, E.N.; Love, J.; Franklin, M.C.; Height, J.J. Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10282–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| S. No | R | AChEIC50 (µM) | BuChE IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1a |  | 11.30 ± 0.30 | 22.60 ± 0.50 |
| 1b |  | 1.30 ± 0.10 | 2.40 ± 0.10 |
| 1c |  | 0.60 ± 0.05 | 1.50 ± 0.10 |
| 1d |  | 5.90 ± 0.10 | 29.10 ± 0.30 |
| 1e |  | 6.20 ± 0.10 | 10.30 ± 0.20 |
| 1f |  | 8.50 ± 0.20 | 12.90 ± 0.20 |
| 1g |  | 0.80 ± 0.05 | 2.40 ± 0.10 |
| 1h |  | 5.50 ± 0.10 | 12.80 ± 0.20 |
| 1i |  | 7.30 ± 0.10 | 13.40 ± 0.20 |
| 1j |  | 12.90 ± 0.20 | 24.40 ± 0.30 |
| Standard drug | donepezil | 0.016 ± 0.12 | 4.5 ± 0.11 |
| S. No | R | AChEIC50 (µM) | BuChE IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2a |  | 3.40 ± 0.10 | 7.50 ± 0.30 |
| 2b |  | 8.50 ± 0.20 | 12.10 ± 4.0 |
| 2c |  | 1.50 ± 0.10 | 4.10 ± 0.10 |
| 2d |  | 3.10 ± 0.10 | 6.20 ± 0.10 |
| 2e |  | 0.60 ± 0.05 | 2.20 ± 0.10 |
| 2f |  | 4.20 ± 0.10 | 7.60 ± 0.10 |
| 2g |  | 10.70 ± 0.20 | 22.60 ± 0.10 |
| 2h |  | 0.90 ± 0.05 | 2.20 ± 0.30 |
| 2i |  | 12.70 ± 0.20 | 24.40 ± 0.30 |
| 2j |  | 16.60 ± 0.30 | 26.36 ± 0.50 |
| 2k |  | 18.90 ± 0.40 | 29.6 ± 0.50 |
| 2l |  | 2.30 ± 0.10 | 5.15 ± 0.10 |
| 2m |  | 21.10 ± 0.30 | 32.50 ± 0.50 |
| Standard drug | donepezil | 0.016 ± 0.12 | 4.5 ± 0.11 |
| No. of Compound | Free Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | H–Bonds (HBs) | Number of Closest Residues to the Docked Ligand in the Active Site | IC50 ± SEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzimidazole Thiosemicarbazide Derivatives | ||||
| 1a | −12.01 | 4 | 7 | 11.30 ± 0.30 |
| 1b | −11.97 | 5 | 9 | 1.30 ± 0.10 |
| 1c | −12.94 | 4 | 9 | 0.60 ± 0.05 |
| 1d | −12.26 | 5 | 6 | 5.90 ± 0.10 |
| 1e | −11.38 | 8 | 9 | 6.20 ± 0.10 |
| 1f | −11.39 | 5 | 8 | 8.50 ± 0.20 |
| 1g | −12.58 | 8 | 7 | 0.80 ± 0.05 |
| 1h | −12.24 | 4 | 9 | 5.50 ± 0.10 |
| 1i | −12.38 | 5 | 10 | 7.30 ± 0.10 |
| 1j | −12.23 | 4 | 8 | 12.90 ± 0.20 |
| Benzimidazole Schiff Bases | ||||
| 2a | −6.11 | 5 | 10 | 3.40 ± 0.10 |
| 2b | −7.46 | 3 | 5 | 8.50 ± 0.20 |
| 2c | −6.10 | 1 | 8 | 1.50 ± 0.10 |
| 2d | −6.54 | 2 | 7 | 3.10 ± 0.10 |
| 2e | −6.80 | 1 | 8 | 0.60 ± 0.05 |
| 2f | −5.84 | 2 | 7 | 4.20 ± 0.10 |
| 2g | −8.10 | 2 | 5 | 10.70 ± 0.20 |
| 2h | −4.49 | 1 | 8 | 0.90 ± 0.05 |
| 2i | −0.73 | 1 | 7 | 12.70 ± 0.20 |
| 2j | −9.07 | 0 | 4 | 16.60 ± 0.30 |
| 2k | −5.96 | 1 | 8 | 18.90 ± 0.40 |
| 2l | −6.02 | 1 | 8 | 2.30 ± 0.10 |
| 2m | −5.92 | 1 | 10 | 21.10 ± 0.30 |
| donepezil (Std) | −11.11 | 1 | 8 | 0.016 ± 0.12 |
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adalat, B.; Rahim, F.; Taha, M.; Alshamrani, F.J.; Anouar, E.H.; Uddin, N.; Shah, S.A.A.; Ali, Z.; Zakaria, Z.A. Synthesis of Benzimidazole–Based Analogs as Anti Alzheimer’s Disease Compounds and Their Molecular Docking Studies. Molecules 2020, 25, 4828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204828
Adalat B, Rahim F, Taha M, Alshamrani FJ, Anouar EH, Uddin N, Shah SAA, Ali Z, Zakaria ZA. Synthesis of Benzimidazole–Based Analogs as Anti Alzheimer’s Disease Compounds and Their Molecular Docking Studies. Molecules. 2020; 25(20):4828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204828
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdalat, Bushra, Fazal Rahim, Muhammad Taha, Foziah J. Alshamrani, El Hassane Anouar, Nizam Uddin, Syed Adnan Ali Shah, Zarshad Ali, and Zainul Amiruddin Zakaria. 2020. "Synthesis of Benzimidazole–Based Analogs as Anti Alzheimer’s Disease Compounds and Their Molecular Docking Studies" Molecules 25, no. 20: 4828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204828
APA StyleAdalat, B., Rahim, F., Taha, M., Alshamrani, F. J., Anouar, E. H., Uddin, N., Shah, S. A. A., Ali, Z., & Zakaria, Z. A. (2020). Synthesis of Benzimidazole–Based Analogs as Anti Alzheimer’s Disease Compounds and Their Molecular Docking Studies. Molecules, 25(20), 4828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204828