Screening of an Endophyte Transforming Polydatin to Resveratrol from Reynoutria Japonica Houtt and the Optimization of Its Transformation Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Contents Determination of Polydatin, Resveratrol and Emodin in Different Tissues of R. japonica
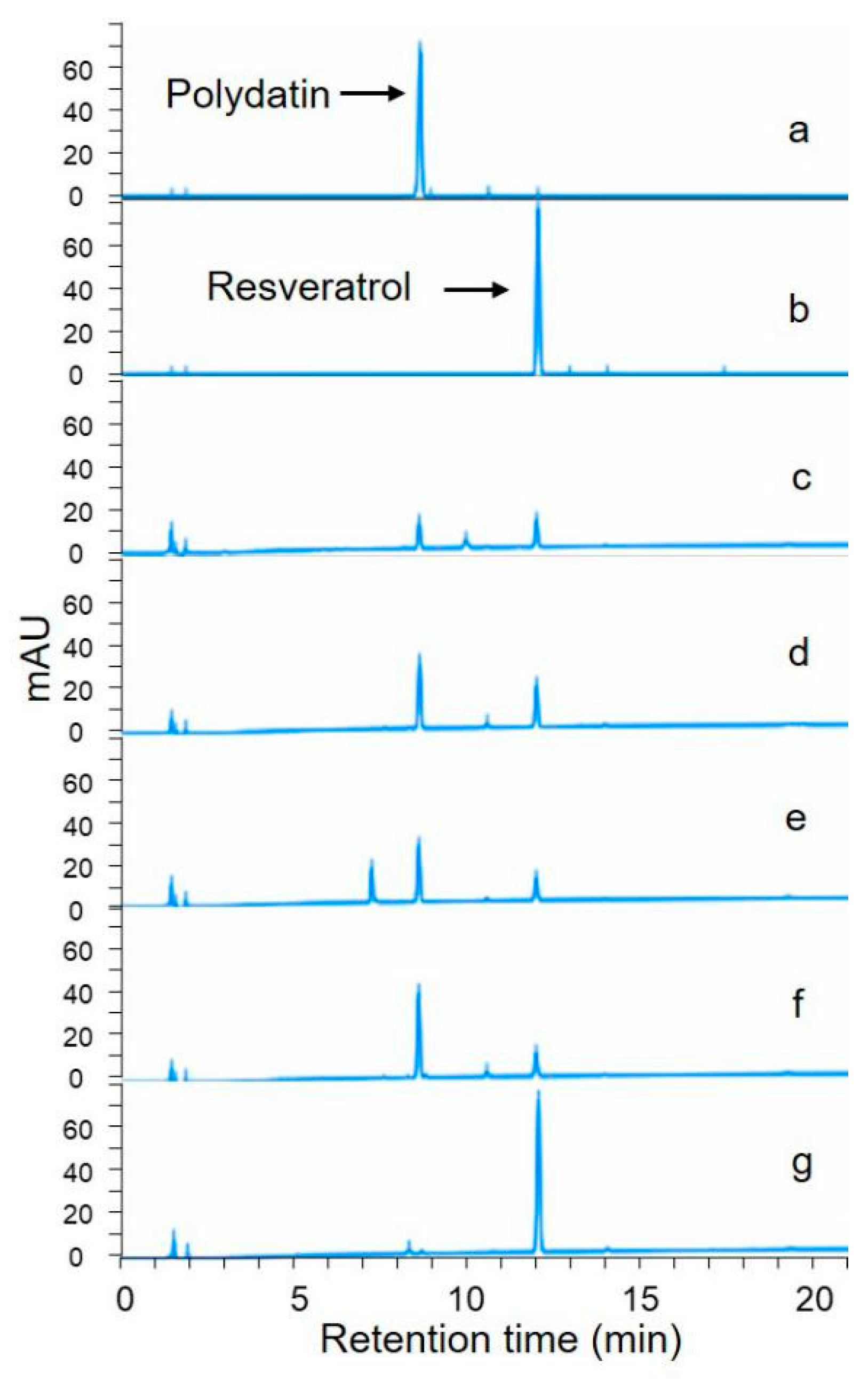
2.2. Screening of Resveratrol Producing Endophytes
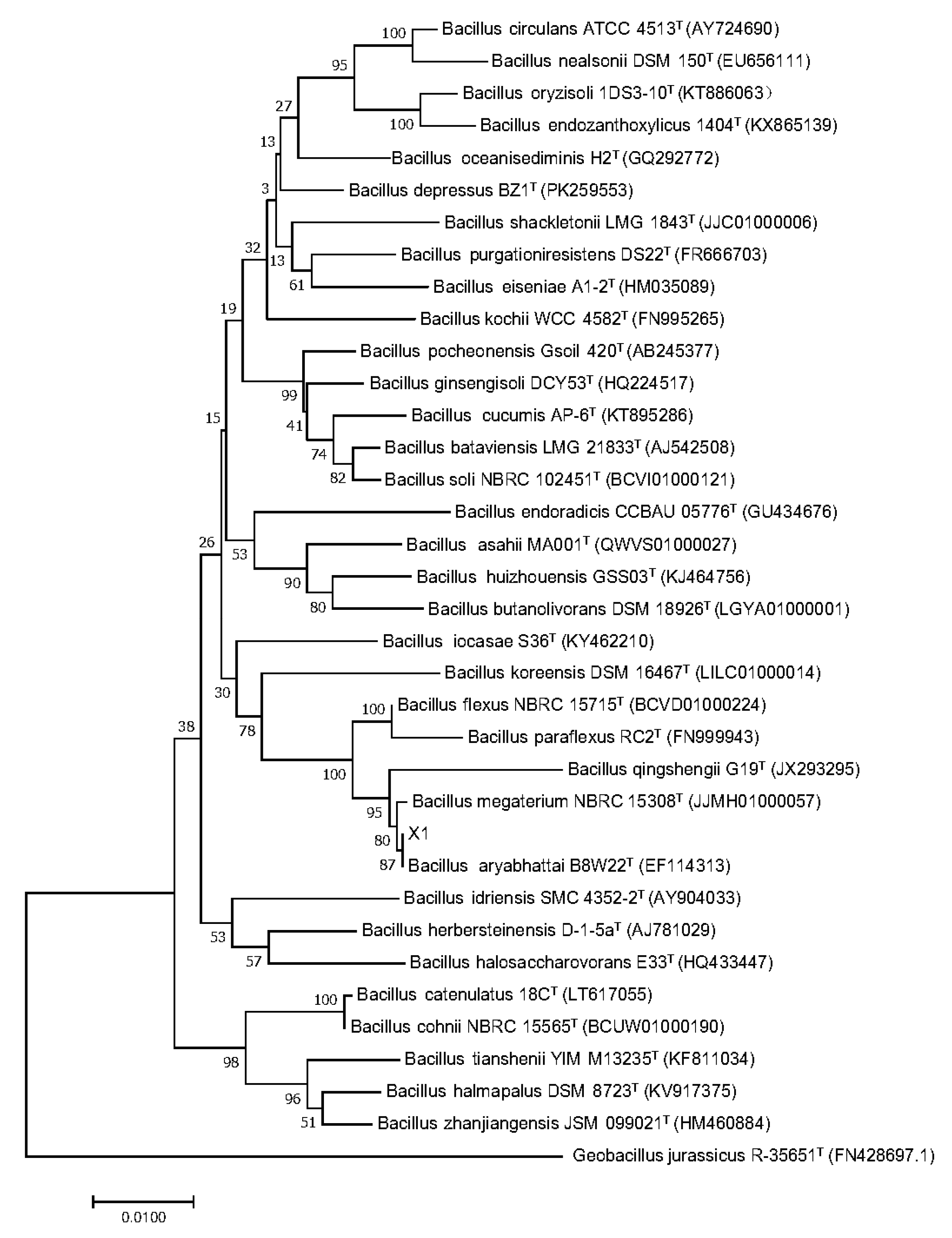
2.3. Strain Identification of X1
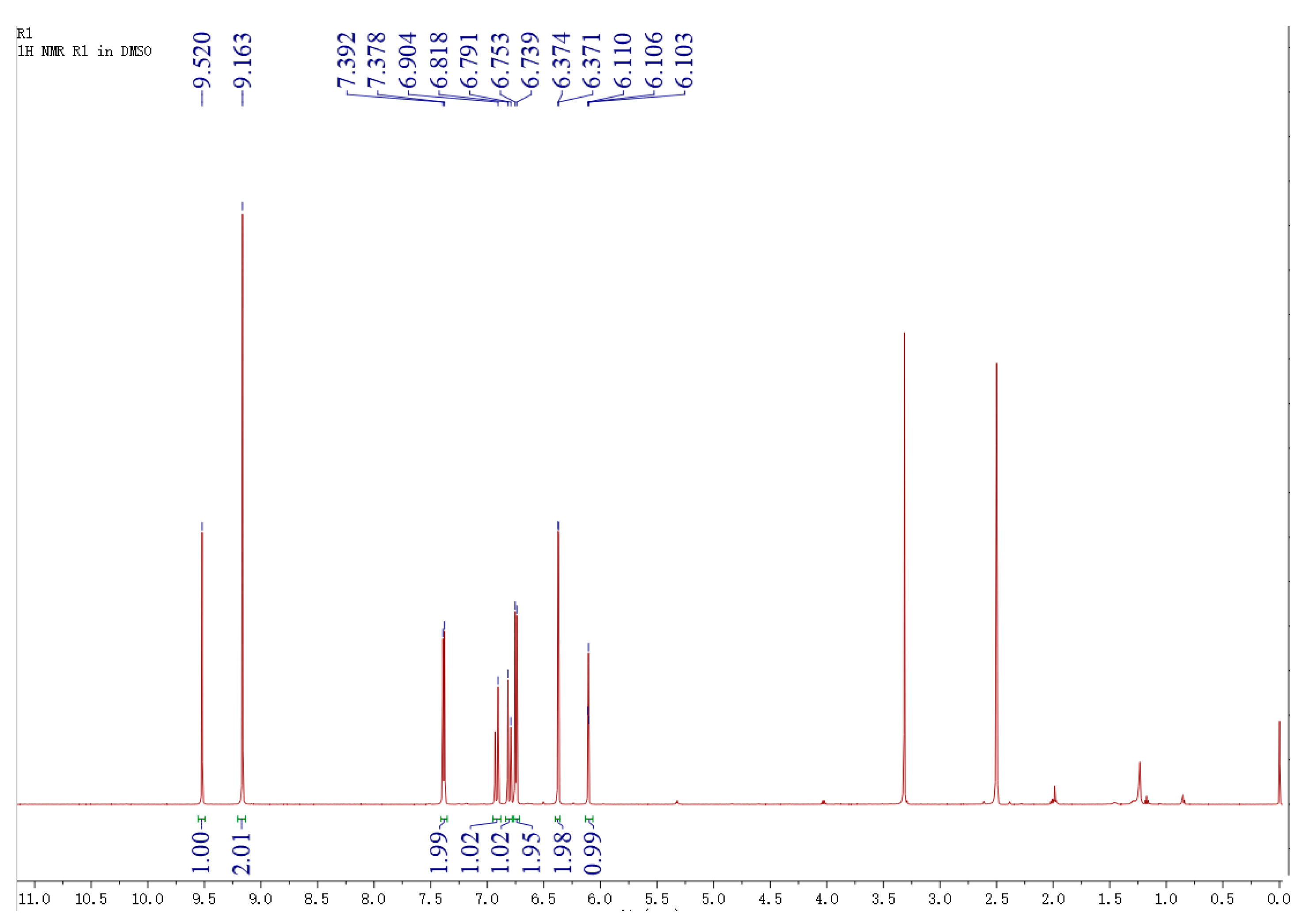
2.4. Identification of Biotransformation Product Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H-NMR)
2.5. Optimization of Biotransformation Conditions of X1 Strain
2.5.1. Plackett–Burman (PB) Test Result
2.5.2. Central Composite Design Test
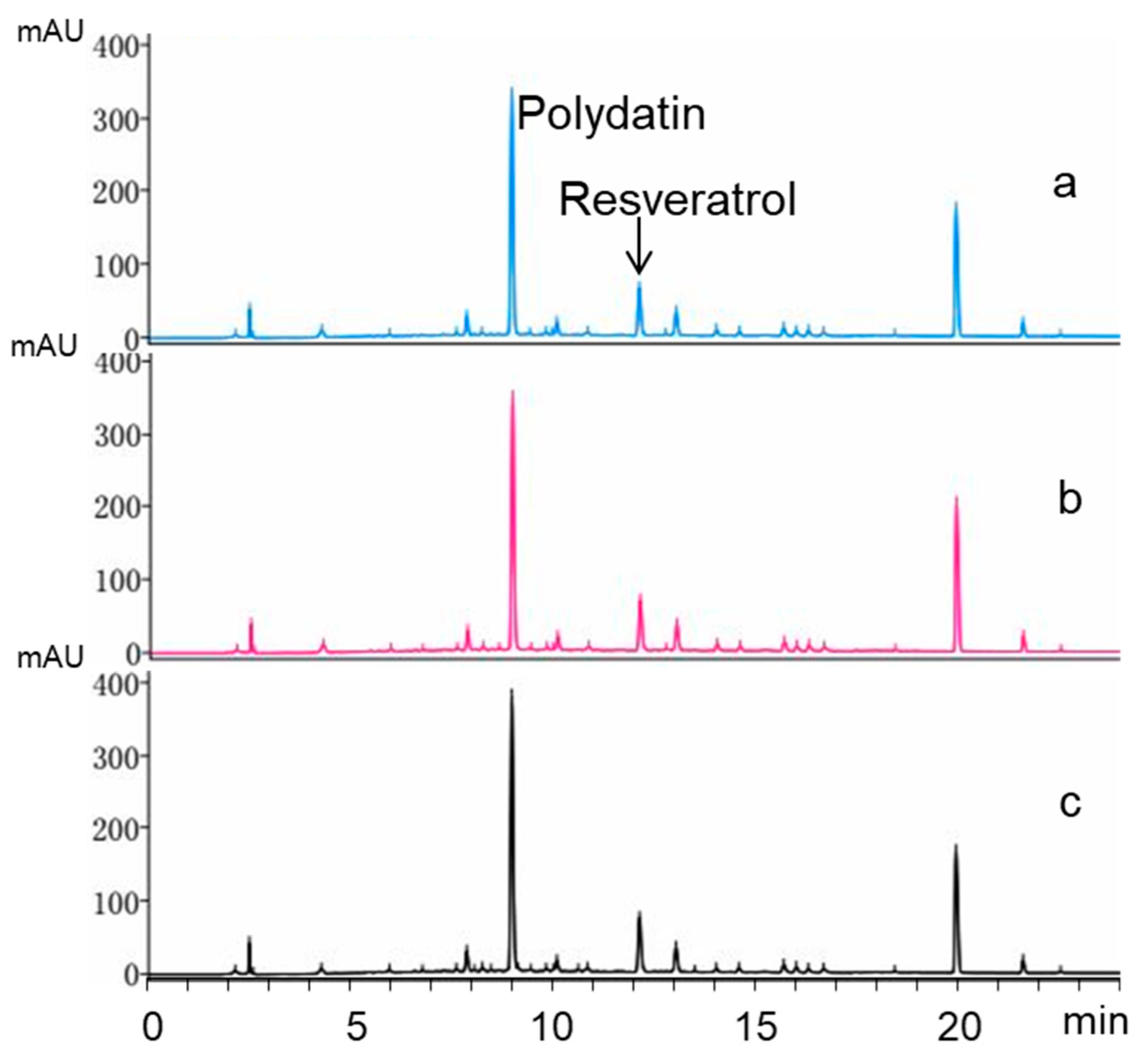
2.6. Biotransformation Using Crude Extract as Substrate
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Sample
4.2. Chemical Reagents
4.3. Isolation of Endophytes from Root Tissue of R. japonica
4.4. Screening of Transforming Polydatin to Resveratrol
4.5. Content Determination of Polydatin, Resveratrol and Emodin in Different Plant Tissues and in X1 Culture
4.6. 16S rRNA Amplification, Sequencing and Phylogenetic Tree Construction of Screened Microbe
4.7. Identification of Biotransformation Product
4.8. Optimization of Biotransformation Condition
4.9. Biotransformation Using Crude Extract as Substrate
4.10. Inhibition Effects of Glucose on the Biotransformation from Polydatin to Resveratrol
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burns, J.; Yokota, T.; Ashihara, H.; Michael, E.J.L.; Alan, C. Plant foods and herbal sources of resveratrol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3337–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.W.; Jiang, C.X.; Piao, S.J.; Chen, W.S. Determination of four active ingredients in Polygonum cuspidatum from different regions by HPLC method. Pharm. Care Res. 2017, 17, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, A.Y.; Motechin, R.A.; Wiesenfeld, M.Y.; Holz, M.K. The therapeutic potential of resveratrol: A review of clinical trials. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ismael, L.G.; Jose, D.C.; Enrique, G.V.; Laura, U.F.; Alfredo, H.M.; Luis, A.H.; Elizabeth, A.R.; Resveratrol Patricio, G. Resveratrol induces downregulation of DNA repair genes in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 22, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Rajasekaran, D.; Elavarasan, J.; Sivalingam, M.; Ganapathy, E.; Kumar, A.; Kalpana, K.; Sakthisekaran, D. Resveratrol interferes with N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma at early and advanced stages in male Wistar rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2011, 4, 1211. [Google Scholar]
- Kalra, N.; Roy, P.; Prasad, S.; Shukla, Y. Resveratrol induces apoptosis involving mitochondrial pathways in mouse skin tumorigenesis. Life Sci. 2008, 82, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oi, N.; Jeong, C.H.; Nadas, J.; Cho, Y.Y.; Pugliese, A. Resveratrol, a red wine polyphenol, suppresses pancreatic cancer by inhibiting leukotriene A4 hydrolase. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9755–9764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harikumar, K.B.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Sethi, G.; Diagaradjane, P.; Anand, P.; Pandey, M.K.; Gelovani, J.; Krishnan, S.; Guha, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Resveratrol, a multitargeted agent, can enhance antitumor activity of gemcitabine in vitro and in orthotopic mouse model of human pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 2010, 127, 257–268. [Google Scholar]
- Baur, J.A.; Sinclair D, A. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Pan, X.L.; Li, C.; Zhou, C.; Deng, F.Y.; Li, T.H. Density Functional Theory Calculations for Resveratrol. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 1869–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Hu, W.; Zhang, D.D. Resveratrol, a Polyphenol Phytoalexin, Protects against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 2324–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.V.W.; Armstrong, G.O.; Van der Merwe, M.J.; Lambrechts, M.G.; Vivier, M.A.; Pretorius, I.S. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the synthesis of the wine-related antioxidant resveratrol. FEMS Yeast Res. 2003, 4, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balkhi, M.H.; Mohammad, M.A.; Tisserant, L.P.; Boitel-Conti, M. Development of a liquid-liquid extraction method of resveratrol from cell culture media using solubility parameters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 170, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tantong, S.; Incharoensakdi, A.; Sirikantaramas, S.; Lindblad, P. Potential of Synechocystis PCC 6803 as a novel cyanobacterial chassis for heterologous expression of enzymes in the trans-resveratrol biosynthetic pathway. Protein Expr. Purif. 2016, 121, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Ye, L.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Shieh, C.J. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of the botanical dietary supplement resveratrol and other constituents of Polygonum cuspidatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1810–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.V.; García, J.I.; Mayoral, J.A. An expedient synthesis of resveratrol through a highly recoverable palladium catalyst. Tetrahedron 2016, 73, 5581–5584. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, K.T.; Lee, P.C.; Dannert, C.S. Biosynthesis of plant specific stilbene polyketides in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. BMC Biotechnol. 2006, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeandet, P.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Clément, C.; Nabavi, S.F.; Habtemariam, S.; Nabavi, S.M.; Cordelier, S. Engineering stilbene metabolic pathways in microbial cells. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 2264–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.L.; Sun, Q.L.; Shen, J.; Zhang, T.; Gao, P.; Sunet, Q. Microbial transformation of polydatin and emodin-8-b-D-glucoside of Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. Et Zucc into resveratrol and emodin respectively by Rhizopus microsporus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.F.; Li, S.H.; Zhang, T.; Mu, W.M.; Jiang, B. Properties of a novel polydatin-β-D-glucosidase from Aspergillus niger SK34.002 and its application in enzymatic preparation of resveratrol. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2588–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Yan, A.X.; Yang, X.Y.; Cai, Y.L.; Chen, J.C. An optimum fermentation model established by genetic algorithm for biotransformation from crude polydatin to resveratrol. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.X.; Dong, Y.S.; Zhang, D.J.; Xiu, Z.L. Biotransformation of peceid in Polygonum cuspidatum to resveratrol by Aspergillus oryzae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, D.K.; Feng, W.; Ni, H.M.; Cao, S.; Lu, F.P.; Li, Y. An innovative biotransformation to produce resveratrol by Bacillus safensis. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15448–15456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beekwilder, J.; Wolswinkel, R.; Jonker, H.; Hall, R.; RicdeVos, C.H.; Bovyet, A. Production of resveratrol in recombinant microorganisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5670–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Li, S.Z.; Li, J.; Pan, X.Q.; Cahoon, R.E.; Jaworski, J.G.; Wang, X.M.; Jez, J.M.; Chen, F.; Yu, O. Using unnatural protein fusions to engineer resveratrol biosynthesis in yeast and mammalian cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 13030–13031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeandet, P.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Silva, A.S.; Clément, C.; Nabavi, S.F.; Battino, M.; Rasekhian, M.; Belwal, T.; Habtemariam, S.; Koffas, M.; et al. Whole-cell biocatalytic, enzymatic and green chemistry methods for the production of resveratrol and its derivatives. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 38, 107461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, S.; Gupta, S.; Ahmed, M.; Dhar, M.K. Endophytic fungi from medicinal plants: A treasure hunt for bioactive metabolites. Phytochem. Rev. 2012, 11, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Xu, J.; Liang, Z.T.; Dong, X.P.; Chen, H.B.; Zhao, Z.Z. Tissue-Specific Analysis of Secondary Metabolites Creates a Reliable Morphological Criterion for Quality Grading of Polygoni multiflori Radix. Molecules 2018, 23, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.C.; Peters, R.J.; Weirather, J.; Weirather, J.; Luo, H.M.; Liao, B.S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.J.; Ji, A.J.; Zhang, B.; et al. Full-length transcriptome sequences and splice variants obtained by a combination of sequencing platforms applied to different root tissues of Salvia miltiorrhiza and tanshinone biosynthesis. Plant J. 2015, 82, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Tian, W.J.; Pan, Z.R.; Lin, T.; Wang, G.H.; Zhou, Q.; Xue, Y.H.; Chen, H.F. Polyphenols from Polygonum cuspidatum Reactivate Latent HIV. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2020, 56, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodda, S.R.; Aich, A.; Sarkar, N.; Jain, P.; Jain, S.; Mondal, S.; Aikat, K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.S. Structural and functional insights of β-glucosidases identified from the genome of Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1156, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, Y.; Kumagai, H.; Kurihara, H.; Yamazaki, K.; Sawano, R.; Inoue, N. β-Glucosidase inhibitory activities of phenylpropanoid glycosides, vanicoside A and B from Polygonum sachalinense rhizome. Fitoterapia 2006, 77, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, E.F.J.; Fritsch, T.M. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.W.; Chen, Y.Y.; Shi, Q. Identification of bacteria associated with periapical abscesses of primary teeth by sequence analysis of 16S rDNA clone libraries. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 141, 103954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Kwon, S.J.; Lim, J.M.; Kim, Y.S.; Seo, H.S.; Chun, J.S. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N. The neighbour-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol Evol. 1987, 4, 406–452. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.H.; Zhang, L.N.; Sui, A.L.; Qu, B.Q. Optimization of Fermentation Process Parameters for Ginsenoside Re Bioconversion by Plackett-Burman and Box-Benhnken Design. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 76, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.X.; Eskridge, K.; Liu, E.; Wilkins, M. Enhancement of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) production by 10-fold from alkaline pretreatment liquor with an oxidative enzyme-mediator-surfactant system under Plackett-Burman and central composite designs. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |



| Tissues Tested | Polydatin (mg/g) | Resveratrol (mg/g) | Emodin (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf | N.D. | <0.2 | N.D. |
| Stem | <0.2 | <0.02 | N.D. |
| Rhizome-phloem | 47.57 ± 2.21 | 3.81 ± 0.95 | 0.80 ± 0.16 |
| Rhizome-xylem | 14.77 ± 1.04 | 0.64 ± 0.36 | 0.21 ± 0.11 |
| Root-phloem | 33.20 ± 2.95 | 2.13 ± 0.25 | 0.85 ± 0.31 |
| Root-xylem | 11.47 ± 1.36 | 0.57 ± 0.15 | 0.32 ± 0.17 |
| No. | Biotransformation Rate (%) | Organism | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | 37.13 ± 2.16 | Penicillium oxalicum | MT795727 |
| Z3 | 47.77 ± 1.68 | Penicillium steckii | MT795729 |
| Z4 | 25.88 ± 3.24 | Cladosporium cladosporioides | MT795730 |
| Z5 | 26.74 ± 1.95 | Penicillium brasilianum | MT795731 |
| X1 | 97.44 ± 2.57 | Bacillus aryabhattai | MT792074 |
| Factors | F Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Models | 6.02 | 0.034 |
| Culture time (h) | 17.89 | 0.008 |
| Initial medium pH | 3.87 | 0.106 |
| Inoculation rate (%) | 2.70 | 0.161 |
| Culture temperature (°C) | 4.53 | 0.087 |
| Shaking speed (rpm) | 0.02 | 0.889 |
| Substrate concentration (mg/mL) | 7.10 | 0.045 |
| Quadratic Sum | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F Value | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 7866.48 | 5 | 1753.30 | 106.40 | <0.0001 |
| A | 728.43 | 1 | 728.43 | 49.26 | 0.0002 |
| B | 714.90 | 1 | 714.90 | 48.35 | 0.0002 |
| AB | 1368.11 | 1 | 1368.11 | 92.53 | <0.0001 |
| A2 | 1625.33 | 1 | 1625.33 | 109.92 | <0.0001 |
| 4009.66 | 1 | 4009.66 | 271.17 | <0.0001 | |
| Residual error | 103.50 | 7 | 14.79 | ||
| Mismatch error | 61.10 | 3 | 20.37 | 1.92 | 0.2677 |
| Pure error | 42.40 | B24 | 10.60 | ||
| Sum | 7969.99 | 12 | |||
| R2 = 0.9870, R2Adj = 0.9777 | |||||
| No. | Biotransformation Rate Y (%) | Average (%) | Relative Standard Deviasion (RSD) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 93.33 | 92.61 | 0.73 |
| 2 | 92.53 | ||
| 3 | 91.98 |
| Components Tested | X1 Culture and Polydatin Addition | Polydatin Transformation Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| RJE 1.0 mg/mL | Initial stage 5% | 92.15 ± 2.51 |
| RJE 5.0 mg/mL | Initial stage 5% | 20.58 ± 4.23 |
| RJE 10.0 mg/mL | Initial stage 5% | <5% |
| Glucose 2.0 mg/mL | Initial stage 5% + 0.47 mg/mL polydatin | <5% |
| ethanol soluble fraction equivalents to RJE 10.0 mg/mL | Initial stage 5% | <5% |
| emodin equivalents to RJE 10.0 mg/mL | Initial stage 5% + 0.47 mg/mL polydatin | 94.43 ± 3.06 |
| petroleum fraction equivalents to RJE 10.0 mg/mL | Initial stage 5% + 0.47 mg/mL polydatin | 95.86 ± 4.25 |
| dichloroform fraction equivalents to RJE 10.0 mg/mL | Initial stage 5% + 0.47 mg/mL polydatin | 86.43 ± 1.56 |
| ethyl acetate fraction equivalent to RJE 10.0 mg/mL | Initial stage 5% + 0.47 mg/mL polydatin | <5% |
| n-butanol fraction equivalents to RJE 10.0 mg/mL | Initial stage 5% + 0.47 mg/mL polydatin | 91.75 ± 5.91 |
| water fraction equivalents to RJE 10.0 mg/mL | Initial stage 5% + 0.47 mg/mL polydatin | 98.25 ± 4.77 |
| t/min | A/% | B/% |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 95 |
| 3 | 15 | 85 |
| 10 | 30 | 70 |
| 20 | 50 | 50 |
| 25 | 100 | 0 |
| Factor | Level | |
|---|---|---|
| −1 | 1 | |
| Culture time (h) | 6 | 10 |
| Initial medium pH | 6.5 | 7.0 |
| Inoculation rate (%) | 3 | 7 |
| Culture temperature (℃) | 33 | 37 |
| Shaking speed (rpm) | 120 | 180 |
| Substrate concentration (mg/mL) | 0.35 | 0.7 |
| Factors | Levels | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −α | −1 | 0 | 1 | α | |
| A-culture time/h | 5.17 | 6.00 | 8.00 | 10.00 | 10.83 |
| B-substrate concentration/(mg/mL) | 0.24 | 0.30 | 0.45 | 0.60 | 0.66 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yan, T.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Jia, L.; Jia, J.; Hu, G. Screening of an Endophyte Transforming Polydatin to Resveratrol from Reynoutria Japonica Houtt and the Optimization of Its Transformation Parameters. Molecules 2020, 25, 4830. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204830
Liu J, Zhang X, Yan T, Wang F, Li J, Jia L, Jia J, Hu G. Screening of an Endophyte Transforming Polydatin to Resveratrol from Reynoutria Japonica Houtt and the Optimization of Its Transformation Parameters. Molecules. 2020; 25(20):4830. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204830
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jin, Xueqing Zhang, Ting Yan, Faling Wang, Jing Li, Lingyun Jia, Jingming Jia, and Gaosheng Hu. 2020. "Screening of an Endophyte Transforming Polydatin to Resveratrol from Reynoutria Japonica Houtt and the Optimization of Its Transformation Parameters" Molecules 25, no. 20: 4830. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204830
APA StyleLiu, J., Zhang, X., Yan, T., Wang, F., Li, J., Jia, L., Jia, J., & Hu, G. (2020). Screening of an Endophyte Transforming Polydatin to Resveratrol from Reynoutria Japonica Houtt and the Optimization of Its Transformation Parameters. Molecules, 25(20), 4830. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204830




