Past, Present and Future Perspectives on Halloysite Clay Minerals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Supramolecular Functionalization
2.1. Functionalized Halloysite as Filler
2.2. Functionalized Halloysite for Environmental Purposes
2.3. Functionalized Halloysite in Catalysis
2.4. Functionalized Halloysite as Drug Carrier
3. Covalent Modification of the External Halloysite Surface
3.1. Amino Modified Halloysite (3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) Grafting)
3.2. Thiol Modified HNTs (3-Mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane Grafting)
3.3. Vinyl Modified HNTs (KH570 Silane Grafting)
3.4. Azido Modified HNTs (Grafting of 3-azidopropyltrimethoxysilaneAzidopropyltrimethoxysilane)
3.5. Miscellaneous
4. Modification of the Inner Lumen
5. Intercalation
6. Chemical Manipulation
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pasbakhsh, P.; Ismail, H.; Fauzi, M.N.A.; Bakar, A.A. Influence of maleic anhydride grafted ethylene propylene diene monomer (MAH-g-EPDM) on the properties of EPDM nanocomposites reinforced by halloysite nanotubes. Polym. Test. 2009, 28, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Tan, D.; Annabi-Bergaya, F. Properties and applications of halloysite nanotubes: Recent research advances and future prospects. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 112–113, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretti, C.; Cataldo, S.; Gianguzza, A.; Lando, G.; Lazzara, G.; Pettignano, A.; Sammartano, S. Thermodynamics of Proton Binding of Halloysite Nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 7849–7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerabadran, N.G.; Price, R.R.; Lvov, Y.M. Clay nanotubes for encapsulation and sustained release of drugs. Nano 2007, 2, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konnova, S.A.; Sharipova, I.R.; Demina, T.A.; Osin, Y.N.; Yarullina, D.R.; Ilinskaya, O.N.; Lvov, Y.M.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Biomimetic cell-mediated three-dimensional assembly of halloysite nanotubes. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4208–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullayev, E.; Abbasov, V.; Tursunbayeva, A.; Portnov, V.; Ibrahimov, H.; Mukhtarova, G.; Lvov, Y. Self-healing coatings based on halloysite clay polymer composites for protection of copper alloys. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4464–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullayev, E.; Lvov, Y. Halloysite clay nanotubes as a ceramic “skeleton” for functional biopolymer composites with sustained drug release. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2894–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasbakhsh, P.; Churchman, G.J.; Keeling, J.L. Characterisation of properties of various halloysites relevant to their use as nanotubes and microfibre fillers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 74, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wu, H.; Higaki, Y.; Takahara, A. Halloysite Nanotubes: Green Nanomaterial for Functional Organic-Inorganic Nanohybrids. Chem. Rec. 2018, 18, 986–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Stetsyshyn, Y. Stability of Halloysite, Imogolite, and Boron Nitride Nanotubes in Solvent Media. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vergaro, V.; Abdullayev, E.; Lvov, Y.M.; Zeitoun, A.; Cingolani, R.; Rinaldi, R.; Leporatti, S. Cytocompatibility and Uptake of Halloysite Clay Nanotubes. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yah, W.O.; Xu, H.; Soejima, H.; Ma, W.; Lvov, Y.; Takahara, A. Biomimetic Dopamine Derivative for Selective Polymer Modification of Halloysite Nanotube Lumen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 12134–12137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Barone, G.; Biddeci, G.; Cavallaro, G.; Di Blasi, F.; Lazzara, G.; Nicotra, G.; Spinella, C.; Spinelli, G.; Riela, S. Halloysite nanotubes-carbon dots hybrids multifunctional nanocarrier with positive cell target ability as a potential non-viral vector for oral gene therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 552, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrullina, G.I.; Akhatova, F.S.; Lvov, Y.M.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Toxicity of halloysite clay nanotubes in vivo: A Caenorhabditis elegans study. Environ. Sci. Nano 2015, 2, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Viseras Iborra, C.; Cavallaro, G.; Colletti, C.G.; García-Villén, F.; Lazzarad, G.; Riela, S. Advanced material based on halloysite and hectorite clay minerals covalently linked with complementary properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Price, R.; Gaber, B.P.; Lvov, Y. In-vitro release characteristics of tetracycline HCl, khellin and nicotinamide adenine dineculeotide from halloysite; a cylindrical mineral. J. Microencapsul. 2001, 18, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, A.S.; Stilwell, G.; Cliff, R.O.; Kahn, B.; Spargo, B.J.; Rollwagen, F.; Monroy, R.L. Biocompatibility of lipid microcylinders: Effect on cell growth and antigen presentation in culture. Biomaterials 1992, 13, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levis, S.R.; Deasy, P.B. Characterisation of halloysite for use as a microtubular drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 243, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.; Price, R.; Gaber, B.; Ichinose, I. Thin film nanofabrication via layer-by-layer adsorption of tubule halloysite, spherical silica, proteins and polycations. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 198–200, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levis, S.R.; Deasy, P.B. Use of coated microtubular halloysite for the sustained release of diltiazem hydrochloride and propranolol hydrochloride. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 253, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, H.M.; Deasy, P.B.; Ziaka, E.; Claffey, N. Formulation and preliminary in vivo dog studies of a novel drug delivery system for the treatment of periodontitis. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 274, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchukin, D.G.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Price, R.R.; Lvov, Y.M. Halloysite Nanotubes as Biomimetic Nanoreactors. Small 2005, 1, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Guo, B.; Jia, D. Thermal stability and flame retardant effects of halloysite nanotubes on poly(propylene). Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Ye, L. High impact strength epoxy nanocomposites with natural nanotubes. Polymer 2007, 48, 6426–6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, B.; Du, M.; Lei, Y.; Jia, D. Natural inorganic nanotubes reinforced epoxy resin nanocomposites. J. Polym. Res. 2008, 15, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, B.; Du, M.; Jia, D. Drying induced aggregation of halloysite nanotubes in polyvinyl alcohol/halloysite nanotubes solution and its effect on properties of composite film. Appl. Phys. A 2007, 88, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, P. Halloysite nanotubes/polystyrene (HNTs/PS) nanocomposites via in situ bulk polymerization. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2008, 94, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marney, D.C.O.; Russell, L.J.; Wu, D.Y.; Nguyen, T.; Cramm, D.; Rigopoulos, N.; Wright, N.; Greaves, M. The suitability of halloysite nanotubes as a fire retardant for nylon 6. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Fauzi, M.N.A.; Abu Bakar, A. Morphological, thermal and tensile properties of halloysite nanotubes filled ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, B.; Du, M.; Cai, X.; Jia, D. Properties of halloysite nanotube-epoxy resin hybrids and the interfacial reactions in the systems. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 455703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, P. Polyaniline-coated halloysite nanotubes via in-situ chemical polymerization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 2091–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, B.; Zou, Q.; Du, M.; Jia, D. Interactions between halloysite nanotubes and 2,5-bis(2-benzoxazolyl) thiophene and their effects on reinforcement of polypropylene/halloysite nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 205709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Chen, F.; Lei, Y.; Liu, X.; Wan, J.; Jia, D. Styrene-butadiene rubber/halloysite nanotubes nanocomposites modified by sorbic acid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 7329–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Guo, B.; Jia, D. Newly emerging applications of halloysite nanotubes: A review. Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Guo, B.; Jia, D. Functional thiol ionic liquids as novel interfacial modifiers in SBR/HNTs composites. Polymer 2011, 52, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ng, K.M.; Chan, C.-M.; Sun, G.; Wu, J. High-impact polystyrene/halloysite nanocomposites prepared by emulsion polymerization using sodium dodecyl sulfate as surfactant. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 358, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Qiu, M.; Guo, B.; Zhang, L.; Lvov, Y. Nanodot-Loaded Clay Nanotubes as Green and Sustained Radical Scavengers for Elastomer. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
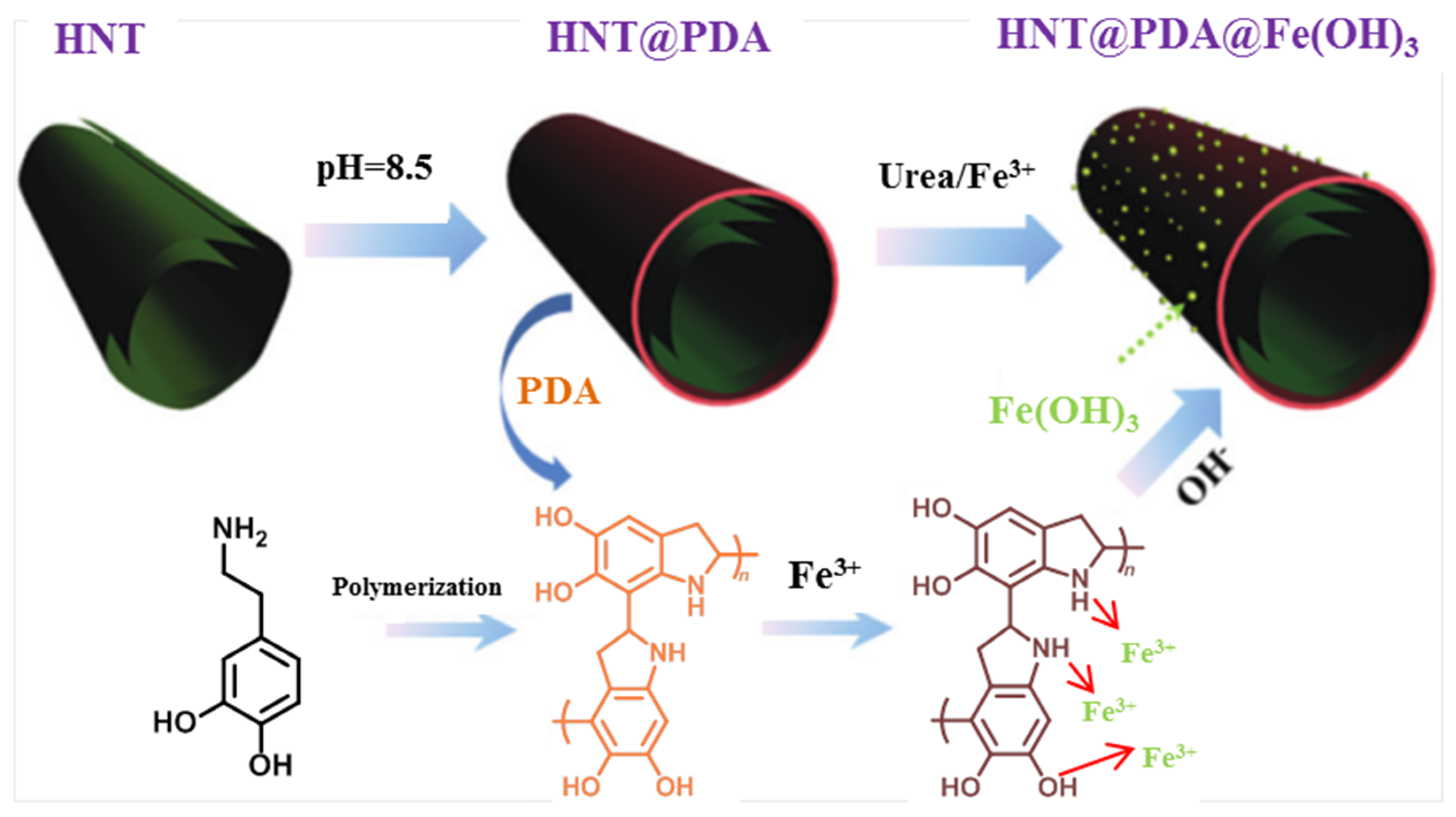
- Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Jiménez González, A.; Wang, D.-Y. Bioinspired polydopamine-induced assembly of ultrafine Fe(OH)3 nanoparticles on halloysite toward highly efficient fire retardancy of epoxy resin via an action of interfacial catalysis. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 3926–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.F.R.; Soares, S.F.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Figueiredo, J.L. Adsorption of dyes on activated carbons: Influence of surface chemical groups. Carbon 2003, 41, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, S.K.; Dash, S.; Patel, S.; Mishra, B.K. Adsorption of organic molecules on silica surface. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 121, 77–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gong, K.; Su, L.; Guo, Z.; Mao, L. Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye onto Carbon Nanotubes: A Route to an Electrochemically Functional Nanostructure and Its Layer-by-Layer Assembled Nanocomposite. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3457–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, P. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue on halloysite nanotubes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 112, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinhua, W.; Xiang, Z.; Bing, Z.; Yafei, Z.; Rui, Z.; Jindun, L.; Rongfeng, C. Rapid adsorption of Cr (VI) on modified halloysite nanotubes. Desalination 2010, 259, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Qian, D.; Wu, D.; Ma, X. Magnetic halloysite nanotubes/iron oxide composites for the adsorption of dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Liu, R.; Chen, T.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J. Halloysite nanotube-Fe3O4 composite for removal of methyl violet from aqueous solutions. Desalination 2012, 293, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Jiang, G.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, W. Photocatalytic Activity of Heterostructures Based on TiO2 and Halloysite Nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 4154–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballav, N.; Choi, H.J.; Mishra, S.B.; Maity, A. Polypyrrole-coated halloysite nanotube clay nanocomposite: Synthesis, characterization and Cr(VI) adsorption behaviour. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 102, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Palmisano, G.; Parisi, F. Halloysite nanotube with fluorinated lumen: Non-foaming nanocontainer for storage and controlled release of oxygen in aqueous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 417, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Owoseni, O.; Nyankson, E.; Zhang, Y.; Adams, S.J.; He, J.; McPherson, G.L.; Bose, A.; Gupta, R.B.; John, V.T. Release of Surfactant Cargo from Interfacially-Active Halloysite Clay Nanotubes for Oil Spill Remediation. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13533–13541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, A. Amine-Impregnated Mesoporous Silica Nanotube as an Emerging Nanocomposite for CO2 Capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17312–17320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, T. Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance of electrospun carbon-doped TiO2/halloysite nanotube hybrid nanofibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 439, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaro, M.; Riela, S.; Cavallaro, G.; Colletti, C.G.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Lazzara, G. Ecocompatible Halloysite/Cucurbit[8]uril Hybrid as Efficient Nanosponge for Pollutants Removal. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Armetta, F.; Cavallaro, G.; Chillura Martino, D.F.; Gruttadauria, M.; Lazzara, G.; Riela, S.; d’Ischia, M. Effect of halloysite nanotubes filler on polydopamine properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 555, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Wu, D.; Wan, H.; Jia, L.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, R. Facile synthesis and characterization of halloysite@W18O49 nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 183, 105319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Casiello, M.; D’Accolti, L.; Lazzara, G.; Nacci, A.; Nicotra, G.; Noto, R.; Pettignano, A.; Spinella, C.; Riela, S. One-pot synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles supported on halloysite nanotubes for catalytic applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 189, 105527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguzzi, C.; Donnadio, A.; Quaglia, G.; Latterini, L.; Viseras, C.; Ambrogi, V. Halloysite-Doped Zinc Oxide for Enhanced Sunscreening Performance. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 6575–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, G.S.; de Freitas Castro, K.A.D.; Wypych, F.; Nakagaki, S. Immobilization of metalloporphyrins into nanotubes of natural halloysite toward selective catalysts for oxidation reactions. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2008, 283, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, M. Silver nanoparticle supported on halloysite nanotubes catalyzed reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 3989–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Zhang, B.; Wan, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. Chitosan–halloysite hybrid-nanotubes: Horseradish peroxidase immobilization and applications in phenol removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 214, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhai, R.; Xiang, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, R. Natural Nanotube-Based Biomimetic Porous Microspheres for Significantly Enhanced Biomolecule Immobilization. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Zhang, B.; Liu, L.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. Immobilization of enzyme biocatalyst on natural halloysite nanotubes. Catal. Commun. 2010, 12, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, J.; Yendluri, R.; Lvov, Y. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes for Enzyme Immobilization. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Rudolph, V.; Zhu, Z. Nanotubules-supported Ru nanoparticles for preferential CO oxidation in H2-rich stream. Adv. Powder Technol. 2012, 23, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Ge, L.; Rudolph, V.; Zhu, Z. Halloysite nanotube supported Ru nanocatalysts synthesized by the inclusion of preformed Ru nanoparticles for preferential oxidation of CO in H2-rich atmosphere. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 4141–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, J. Effect of preparation method on halloysite supported cobalt catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2012, 21, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, G.S.; Lima, O.J.d.; Ciuffi, K.J.; Wypych, F.; Nakagaki, S. Iron(III) porphyrin supported on metahalloysite: An efficient and reusable catalyst for oxidation reactions. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.C.; Ahn, H.; Choi, M.C.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Rhee, H. Pd nanoparticles immobilized on PNIPAM–halloysite: Highly active and reusable catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions in water. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2014, 28, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, G.; Lv, D.; Dong, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, D. Effective activation of halloysite nanotubes by piranha solution for amine modification via silane coupling chemistry. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 52916–52925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viseras, M.T.; Aguzzi, C.; Cerezo, P.; Viseras, C.; Valenzuela, C. Equilibrium and kinetics of 5-aminosalicylic acid adsorption by halloysite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 108, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viseras, M.-T.; Aguzzi, C.; Cerezo, P.; Cultrone, G.; Viseras, C. Supramolecular structure of 5-aminosalycilic acid/halloysite composites. J. Microencapsul. 2009, 26, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.R.; Shoaib, M.H.; Azhar, M.; Um, S.H.; Yousuf, R.I.; Hashmi, S.; Dar, A. In-vitro assessment of cytotoxicity of halloysite nanotubes against HepG2, HCT116 and human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gong, J.; Gui, Z.; Hu, T.; Xu, X. Halloysite nanotubes-induced Al accumulation and oxidative damage in liver of mice after 30-day repeated oral administration. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozhina, E.; Batasheva, S.; Gomzikova, M.; Naumenko, E.; Fakhrullin, R. Multicellular spheroids formation: The synergistic effects of halloysite nanoclay and cationic magnetic nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 565, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergaro, V.; Lvov, Y.M.; Leporatti, S. Halloysite clay nanotubes for resveratrol delivery to cancer cells. Macromol. Biosci. 2012, 12, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Abdullayev, E.; Hollister, A.; Mills, D.; Lvov, Y.M. Clay nanotube/poly(methyl methacrylate) bone cement composites with sustained antibiotic release. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2012, 297, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Cavallaro, G.; Colletti, C.G.; D’Azzo, G.; Guernelli, S.; Lazzara, G.; Pieraccini, S.; Riela, S. Halloysite nanotubes for efficient loading, stabilization and controlled release of insulin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 524, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurczewska, J.; Pecyna, P.; Ratajczak, M.; Gajęcka, M.; Schroeder, G. Halloysite nanotubes as carriers of vancomycin in alginate-based wound dressing. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carazo, E.; Borrego-Sánchez, A.; García-Villén, F.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; Aguzzi, C.; Viseras, C.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I.; Cerezo, P. Assessment of halloysite nanotubes as vehicles of isoniazid. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 160, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenci, M.; Rossi, S.; Aguzzi, C.; Carazo, E.; Sandri, G.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Grisoli, P.; Viseras, C.; Caramella, C.M.; Ferrari, F. Carvacrol/clay hybrids loaded into in situ gelling films. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, L.; Spepi, A.; Agnolucci, M.; Cristani, C.; Giovannetti, M.; Tiné, M.R.; Duce, C. Kinetics of release and antibacterial activity of salicylic acid loaded into halloysite nanotubes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Lazzara, G.; Noto, R.; Riela, S. Halloysite nanotubes: A green resource for materials and life sciences. Rend. Lincei 2020, 31, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Colletti, C.G.; Lazzara, G.; Riela, S. The Use of Some Clay Minerals as Natural Resources for Drug Carrier Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veerabadran, N.G.; Mongayt, D.; Torchilin, V.; Price, R.R.; Lvov, Y.M. Organized Shells on Clay Nanotubes for Controlled Release of Macromolecules. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebaur, A.; Garea, S.A.; Iovu, H. New polymer–halloysite hybrid materials—potential controlled drug release system. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shi, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Shen, H.; Jia, N. Multifunctional nanocarrier based on clay nanotubes for efficient intracellular siRNA delivery and gene silencing. J. Biomater. Appl. 2014, 28, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Li, B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, A.; Zhang, J. Superhydrophobic Gated Polyorganosilanes/Halloysite Nanocontainers for Sustained Drug Release. Adv. Mater. Interface 2014, 1, 1300136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Minullina, R.; Abdullayev, E.; Fakhrullin, R.; Mills, D.; Lvov, Y. Enhanced efficiency of antiseptics with sustained release from clay nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzamukova, M.R.; Naumenko, E.A.; Lvov, Y.M.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Enzyme-activated intracellular drug delivery with tubule clay nanoformulation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcudi, F.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Massaro, M.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Riela, S. Selective Functionalization of Halloysite Cavity by Click Reaction: Structured Filler for Enhancing Mechanical Properties of Bionanocomposite Films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 15095–15101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biddeci, G.; Cavallaro, G.; Di Blasi, F.; Lazzara, G.; Massaro, M.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Riela, S.; Spinelli, G. Halloysite nanotubes loaded with peppermint essential oil as filler for functional biopolymer film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaremi, M.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Aw, Y.K.; Lee, S.M.; Milioto, S. Effect of Morphology and Size of Halloysite Nanotubes on Functional Pectin Bionanocomposites for Food Packaging Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 17476–17488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krepker, M.; Shemesh, R.; Danin Poleg, Y.; Kashi, Y.; Vaxman, A.; Segal, E. Active food packaging films with synergistic antimicrobial activity. Food Control 2017, 76, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, R.T.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Lee, S.M.; Kit, A.Y. ZnO deposited/encapsulated halloysite–poly (lactic acid) (PLA) nanocomposites for high performance packaging films with improved mechanical and antimicrobial properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 111, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yendluri, R.; Otto, D.P.; De Villiers, M.M.; Vinokurov, V.; Lvov, Y.M. Application of halloysite clay nanotubes as a pharmaceutical excipient. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 521, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, G.; Aguzzi, C.; Rossi, S.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Bruni, G.; Boselli, C.; Cornaglia, A.I.; Riva, F.; Viseras, C.; Caramella, C.; et al. Halloysite and chitosan oligosaccharide nanocomposite for wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2017, 57, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dramou, P.; Fizir, M.; Taleb, A.; Itatahine, A.; Dahiru, N.S.; Mehdi, Y.A.; Wei, L.; Zhang, J.; He, H. Folic acid-conjugated chitosan oligosaccharide-magnetic halloysite nanotubes as a delivery system for camptothecin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-Y.; Zhou, Y.-M.; Gao, R.-Y.; Liu, X.-C.; Du, H.-H.; Zhang, J.-L.; Ai, X.-C.; Zhang, J.-P.; Fu, L.-M.; Skibsted, L.H. Naturally occurring nanotube with surface modification as biocompatible, target-specific nanocarrier for cancer phototherapy. Biomaterials 2019, 190–191, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Gao, Y.; Song, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H. Halloysite nanotube-based H2O2-responsive drug delivery system with a turn on effect on fluorescence for real-time monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrami-Hasan-Kohal, M.; Ghorbani, M.; Mahmoodzadeh, F.; Nikzad, B. Development of reinforced aldehyde-modified kappa-carrageenan/gelatin film by incorporation of halloysite nanotubes for biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhina, E.; Ishmukhametov, I.; Batasheva, S.; Akhatova, F.; Fakhrullin, R. Nanoarchitectonics meets cell surface engineering: Shape recognition of human cells by halloysite-doped silica cell imprints. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, P.; Southon, P.D.; Liu, Z.; Green, M.E.R.; Hook, J.M.; Antill, S.J.; Kepert, C.J. Functionalization of Halloysite Clay Nanotubes by Grafting with γ-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 15742–15751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidecka, K.; Giacoboni, J.; Picconi, P.; Vago, R.; Licandro, E. Quantification of amino groups on halloysite surfaces using the Fmoc-method. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 13944–13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Yuan, P.; Annabi-Bergaya, F.; Yu, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, H.; He, H. Natural halloysite nanotubes as mesoporous carriers for the loading of ibuprofen. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 179, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Yuan, P.; Annabi-Bergaya, F.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; He, H. Loading and in vitro release of ibuprofen in tubular halloysite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 96, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, H.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, H. Natural halloysite nanotubes modified as an aspirin carrier. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 44197–44202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-F.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, H.-B.; Jia, N.-Q. Functionalized halloysite nanotube-based carrier for intracellular delivery of antisense oligonucleotides. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, T.; Yan, X.; Ding, J.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, J. Halloysite nanotubes@reduced graphene oxide composite for removal of dyes from water and as supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 4264–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Buffa, S.; Bonini, M.; Ridi, F.; Severi, M.; Losi, P.; Volpi, S.; Al Kayal, T.; Soldani, G.; Baglioni, P. Design and characterization of a composite material based on Sr(II)-loaded clay nanotubes included within a biopolymer matrix. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 448, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, G.; He, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Z. Novel polyvinylidene fluoride nanofiltration membrane blended with functionalized halloysite nanotubes for dye and heavy metal ions removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar-Krishnan, S.; Hernandez-Rangel, A.; Pal, U.; Ceballos-Sanchez, O.; Flores-Ruiz, F.J.; Prokhorov, E.; Arias de Fuentes, O.; Esparza, R.; Meyyappan, M. Surface functionalized halloysite nanotubes decorated with silver nanoparticles for enzyme immobilization and biosensing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2553–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, S.; Lazzara, G.; Massaro, M.; Muratore, N.; Pettignano, A.; Riela, S. Functionalized halloysite nanotubes for enhanced removal of lead(II) ions from aqueous solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 156, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Massaro, M.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Parisi, F.; Riela, S. Biocompatible poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-halloysite nanotubes for thermoresponsive curcumin release. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 8944–8951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Schembri, V.; Campisciano, V.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Parisi, F.; Riela, S. Design of PNIPAAM covalently grafted on halloysite nanotubes as a support for metal-based catalysts. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 55312–55318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurczewska, J.; Cegłowski, M.; Messyasz, B.; Schroeder, G. Dendrimer-functionalized halloysite nanotubes for effective drug delivery. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 153, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmatpour, H.; Haddadi-Asl, V.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H. Synthesis of pH-sensitive poly (N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate)-grafted halloysite nanotubes for adsorption and controlled release of DPH and DS drugs. Polymer 2015, 65, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandarloo, H.; Arshadi, M.; Abbaspourrad, A. Magnetic Dendritic Halloysite Nanotube for Highly Selective Recovery of Heparin Digested from Porcine Intestinal Mucosa. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14561–14573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandarloo, H.; Arshadi, M.; Enayati, M.; Abbaspourrad, A. Highly Efficient Recovery of Heparin Using a Green and Low-Cost Quaternary Ammonium Functionalized Halloysite Nanotube. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15349–15360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Liu, M. Polyethyleneimine grafted short halloysite nanotubes for gene delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 81, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Wu, Y.-P.; Gao, H.-Y.; Li, Y.-F.; He, R.-R.; Liu, M. Functionalization of Halloysite Nanotubes via Grafting of Dendrimer for Efficient Intracellular Delivery of siRNA. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 2606–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, A.A.; Jang, J.; Lee, D.S. Supermagnetically Tuned Halloysite Nanotubes Functionalized with Aminosilane for Covalent Laccase Immobilization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15492–15501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillu, D.; Agnihotri, S. Cellulase Immobilization onto Magnetic Halloysite Nanotubes: Enhanced Enzyme Activity and Stability with High Cellulose Saccharification. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 900–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Riela, S.; Guernelli, S.; Parisi, F.; Lazzara, G.; Baschieri, A.; Valgimigli, L.; Amorati, R. A synergic nanoantioxidant based on covalently modified halloysite-trolox nanotubes with intra-lumen loaded quercetin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2229–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, C.; Arrigo, R.; D’Anna, F.; Di Blasi, F.; Dintcheva, N.T.; Lazzara, G.; Parisi, F.; Riela, S.; Spinelli, G.; Massaro, M. Hybrid supramolecular gels of Fmoc-F/halloysite nanotubes: Systems for sustained release of camptothecin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3217–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Deng, Z.; Li, J.; Ren, T.; Huang, L.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, S. β-Cyclodextrin coated and folic acid conjugated magnetic halloysite nanotubes for targeting and isolating of cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Swientoniewski, L.T.; Omarova, M.; Li, M.-C.; Negulescu, I.I.; Jiang, N.; Darvish, O.A.; Panchal, A.; Blake, D.A.; Wu, Q.; et al. Investigation of Amphiphilic Polypeptoid-Functionalized Halloysite Nanotubes as Emulsion Stabilizer for Oil Spill Remediation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2019, 11, 27944–27953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Huo, L.; Wu, Y.; Ba, X. Coumarin-anchored halloysite nanotubes for highly selective detection and removal of Zn(II). Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taroni, T.; Cauteruccio, S.; Vago, R.; Franchi, S.; Barbero, N.; Licandro, E.; Ardizzone, S.; Meroni, D. Thiahelicene-grafted halloysite nanotubes: Characterization, biological studies and pH triggered release. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 520, 146351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.; Jeon, Y.; Lee, S.U.; Sim, J.H.; Ryu, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Sohn, D. Aggregation and Stabilization of Carboxylic Acid Functionalized Halloysite Nanotubes (HNT-COOH). J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 18230–18235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yao, H.; Xu, L.; Ou, H.; Huo, P.; Li, X.; Yan, Y. Selective Recognition of 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Magnetic Halloysite Nanotubes Composites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 5440–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chang, Y.; Yang, J.; You, Y.; He, R.; Chen, T.; Zhou, C. Functionalized halloysite nanotube by chitosan grafting for drug delivery of curcumin to achieve enhanced anticancer efficacy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2253–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y.-F.; He, R.-R.; Liu, M. Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy of Doxorubicin for Breast Cancer Using Chitosan Oligosaccharide-Modified Halloysite Nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26578–26590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamina, A.M.; Fizir, M.; Itatahine, A.; He, H.; Dramou, P. Preparation of multifunctional PEG-graft-Halloysite Nanotubes for Controlled Drug Release, Tumor Cell Targeting, and Bio-imaging. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaro, M.; Colletti, C.G.; Guernelli, S.; Lazzara, G.; Liu, M.; Nicotra, G.; Noto, R.; Parisi, F.; Pibiri, I.; Spinella, C.; et al. Photoluminescent hybrid nanomaterials from modified halloysite nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 7377–7384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, J.; Gan, M.; Ou, H.; Yan, Y.; Shi, W.; Yu, L. Acid–chromic chloride functionalized natural clay-particles for enhanced conversion of one-pot cellulose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 11664–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Riela, S.; Cavallaro, G.; Gruttadauria, M.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Lazzara, G. Eco-friendly functionalization of natural halloysite clay nanotube with ionic liquids by microwave irradiation for Suzuki coupling reaction. J. Organomet. Chem. 2014, 749, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massaro, M.; Riela, S.; Lazzara, G.; Gruttadauria, M.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R. Green conditions for the Suzuki reaction using microwave irradiation and a new HNT-supported ionic liquid-like phase (HNT-SILLP) catalyst. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2014, 28, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellani, L.; Giorgetti, L.; Riela, S.; Lazzara, G.; Scialabba, A.; Massaro, M. Ecotoxicity of halloysite nanotube–supported palladium nanoparticles in Raphanus sativus L. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 2503–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Colletti, C.G.; Buscemi, G.; Cataldo, S.; Guernelli, S.; Lazzara, G.; Liotta, L.F.; Parisi, F.; Pettignano, A.; Riela, S. Palladium nanoparticles immobilized on halloysite nanotubes covered by a multilayer network for catalytic applications. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 13938–13947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Riela, S.; Lo Meo, P.; Noto, R.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Functionalized halloysite multivalent glycocluster as a new drug delivery system. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 7732–7738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Riela, S.; Baiamonte, C.; Blanco, J.L.J.; Giordano, C.; Lo Meo, P.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Parisi, F.; Pizzolanti, G.; et al. Dual drug-loaded halloysite hybrid-based glycocluster for sustained release of hydrophobic molecules. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 87935–87944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Piana, S.; Colletti, C.G.; Noto, R.; Riela, S.; Baiamonte, C.; Giordano, C.; Pizzolanti, G.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; et al. Multicavity halloysite-amphiphilic cyclodextrin hybrids for co-delivery of natural drugs into thyroid cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 4074–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Massaro, M.; Amorati, R.; Cavallaro, G.; Guernelli, S.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Poma, P.; Riela, S. Direct chemical grafted curcumin on halloysite nanotubes as dual-responsive prodrug for pharmacological applications. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2016, 140, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaro, M.; Colletti, C.G.; Lazzara, G.; Guernelli, S.; Noto, R.; Riela, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Halloysite-Cyclodextrin Nanosponges for Enhanced Dyes Adsorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3346–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massaro, M.; Campofelice, A.; Colletti, C.G.; Lazzara, G.; Noto, R.; Riela, S. Functionalized halloysite nanotubes: Efficient carrier systems for antifungine drugs. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Riela, S. Organo-clay nanomaterials based on halloysite and cyclodextrin as carriers for polyphenolic compounds. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massaro, M.; Colletti, C.G.; Fiore, B.; La Parola, V.; Lazzara, G.; Guernelli, S.; Zaccheroni, N.; Riela, S. Gold nanoparticles stabilized by modified halloysite nanotubes for catalytic applications. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Dai, X.; Chen, L.; Cui, Y.; Qiang, C.; Sun, Q.; Dai, J. Thiol–Yne Click Synthesis of Polyamide–Amine Dendritic Magnetic Halloysite Nanotubes for the Efficient Removal of Pb(II). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasbakhsh, P.; Ismail, H.; Fauzi, M.N.A.; Bakar, A.A. EPDM/modified halloysite nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murariu, M.; Dechief, A.L.; Paint, Y.; Peeterbroeck, S.; Bonnaud, L.; Dubois, P. Polylactide (PLA)-Halloysite Nanocomposites: Production, Morphology and Key-Properties. J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 20, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y. A novel molecularly imprinted material based on magnetic halloysite nanotubes for rapid enrichment of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wei, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, P.; Pan, J.; Zou, T.; Li, C.; Yan, Y. Highly-controllable imprinted polymer nanoshell at the surface of magnetic halloysite nanotubes for selective recognition and rapid adsorption of tetracycline. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 7967–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Yao, P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Lvov, Y. Highly Aging-Resistant Elastomers Doped with Antioxidant-Loaded Clay Nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8156–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riela, S.; Massaro, M.; Colletti, C.G.; Bommarito, A.; Giordano, C.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Poma, P.; Lazzara, G. Development and characterization of co-loaded curcumin/triazole-halloysite systems and evaluation of their potential anticancer activity. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Massaro, M.; Colletti, C.G.; Noto, R.; Riela, S.; Poma, P.; Guernelli, S.; Parisi, F.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Pharmaceutical properties of supramolecular assembly of co-loaded cardanol/triazole-halloysite systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 478, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Riela, S.; Cavallaro, G.; Colletti, C.G.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Parisi, F.; Lazzara, G. Palladium supported on Halloysite-triazolium salts as catalyst for ligand free Suzuki cross-coupling in water under microwave irradiation. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 408, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Poma, P.; Colletti, C.G.; Barattucci, A.; Bonaccorsi, P.M.; Lazzara, G.; Nicotra, G.; Parisi, F.; Salerno, T.M.G.; Spinella, C.; et al. Chemical and biological evaluation of cross-linked halloysite-curcumin derivatives. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 184, 105400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos-Ramírez, S.; Oca-Ramírez, G.M.d.; Ramos-Fernández, E.V.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A.; Pastor-Blas, M.M.; González-Montiel, A. Surface modification of natural halloysite clay nanotubes with aminosilanes. Application as catalyst supports in the atom transfer radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate. Appl. Catal. A 2011, 406, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Zhang, J.-S.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.-H.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Liu, J.-D. Preparation and Characterization of Silane Coupling Agent Modified Halloysite for Cr(VI) Removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 10246–10252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Du, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, K. Preparation and Characterization of Novel Polyethersulfone Hybrid Ultrafiltration Membranes Bending with Modified Halloysite Nanotubes Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 3081–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, L.; Jiang, P. Epoxidation of soybean oil catalyzed by peroxo phosphotungstic acid supported on modified halloysite nanotubes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 6637–6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahri-Laleh, N.; Sadjadi, S.; Poater, A. Pd immobilized on dendrimer decorated halloysite clay: Computational and experimental study on the effect of dendrimer generation, Pd valance and incorporation of terminal functionality on the catalytic activity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 531, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and antibacterial activity of copper nanoparticle/halloysite nanotube nanocomposites via reverse atom transfer radical polymerization. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 41993–41996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Jiang, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Grafting Amphiphilic Brushes onto Halloysite Nanotubes via a Living RAFT Polymerization and Their Pickering Emulsification Behavior. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataee-Kachouei, T.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.; Mohammadpoor-Baltork, I.; Mirkhani, V.; Moghadam, M.; Tangestaninejad, S.; Notash, B. Ce(IV) immobilized on halloysite nanotube–functionalized dendrimer (Ce(IV)–G2): A novel and efficient dendritic catalyst for the synthesis of pyrido[3,2-c]coumarin derivatives. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, e5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhong, S. Functionalization of halloysite nanotubes by enlargement and hydrophobicity for sustained release of analgesic. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 487, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Hung, G.-Y.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Zhou, C.; Liu, M. Fabrication of high performance superhydrophobic coatings by spray-coating of polysiloxane modified halloysite nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Pickett, K.; Panchal, A.; Liu, M.; Lvov, Y. Superhydrophobic Polyurethane Foam Coated with Polysiloxane-Modified Clay Nanotubes for Efficient and Recyclable Oil Absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25445–25456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Duan, Y.; Wang, F.; Gao, P.; Jia, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, C. Silane-modified halloysite/Fe3O4 nanocomposites: Simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and Sb(V) and positive effects of Cr(VI) on Sb(V) adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 311, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, Q.; Niu, B.; Liao, J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, N. A Dual-Surface Amidoximated Halloysite Nanotube for High-Efficiency Economical Uranium Extraction from Seawater. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14979–14985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yah, W.O.; Takahara, A.; Lvov, Y.M. Selective Modification of Halloysite Lumen with Octadecylphosphonic Acid: New Inorganic Tubular Micelle. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Higaki, Y.; Ma, W.; Wu, H.; Yah, W.O.; Otsuka, H.; Lvov, Y.M.; Takahara, A. Internally Modified Halloysite Nanotubes as Inorganic Nanocontainers for a Flame Retardant. Chem. Lett. 2013, 42, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Ren, T.; Ji, Y.; Han, L.; Wu, Y.; Song, H.; Bai, L.; Ba, X. Selective Modification of Halloysite Nanotubes with 1-Pyrenylboronic Acid: A Novel Fluorescence Probe with Highly Selective and Sensitive Response to Hyperoxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 23805–23811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Bai, L.; Zhang, H.; Song, H.; Hu, L.; Wu, Y.; Ba, X. Smart H2O2-Responsive Drug Delivery System Made by Halloysite Nanotubes and Carbohydrate Polymers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 31626–31633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedzo, K.G.; Ngnie, G.; Detellier, C. PdNP Decoration of Halloysite Lumen via Selective Grafting of Ionic Liquid onto the Aluminol Surfaces and Catalytic Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4862–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joussein, E.; Petit, S.; Delvaux, B. Behavior of halloysite clay under formamide treatment. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 35, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, K.P.; Fukamachi, C.R.B.; Wypych, F.; Mangrich, A.S. Dehydrated halloysite intercalated mechanochemically with urea: Thermal behavior and structural aspects. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 338, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellouk, S.; Belhakem, A.; Marouf-Khelifa, K.; Schott, J.; Khelifa, A. Cu(II) adsorption by halloysites intercalated with sodium acetate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 360, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Deng, S.; Ye, L.; Yang, C.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C. Effects of unfolded and intercalated halloysites on mechanical properties of halloysite–epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Part A 2011, 42, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.D.; Bavykin, D.V.; Walsh, F.C. The stability of halloysite nanotubes in acidic and alkaline aqueous suspensions. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 065705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.-B.; Pan, L.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Liu, S.-T.; Ye, Y.; Xia, M.-S.; Chen, X.-G. Effects of acid treatment on the physico-chemical and pore characteristics of halloysite. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 396, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullayev, E.; Joshi, A.; Wei, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lvov, Y. Enlargement of Halloysite Clay Nanotube Lumen by Selective Etching of Aluminum Oxide. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7216–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepanik, B.; Słomkiewicz, P.; Garnuszek, M.; Czech, K. Adsorption of chloroanilines from aqueous solutions on the modified halloysite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 101, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, A. Adsorption and release of ofloxacin from acid- and heat-treated halloysite. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, D.; Ferri, J.M.; Ripoll, L.; Hidalgo, M.; Lopez-Martinez, J.; Balart, R. Characterization of selectively etched halloysite nanotubes by acid treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Wicklein, B.; Lo Dico, G.; Lazzara, G.; del Real, G.; Aranda, P.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Functional biohybrid materials based on halloysite, sepiolite and cellulose nanofibers for health applications. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 3830–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massaro, M.; Buscemi, G.; Arista, L.; Biddeci, G.; Cavallaro, G.; D’Anna, F.; Di Blasi, F.; Ferrante, A.; Lazzara, G.; Rizzo, C.; et al. Multifunctional Carrier Based on Halloysite/Laponite Hybrid Hydrogel for Kartogenin Delivery. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colletti, C.G.; Massaro, M.; Lazzara, G.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Pibiri, I.; Noto, R.; Riela, S. Synthesis, characterization and study of covalently modified triazole laponite® edges. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 187, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
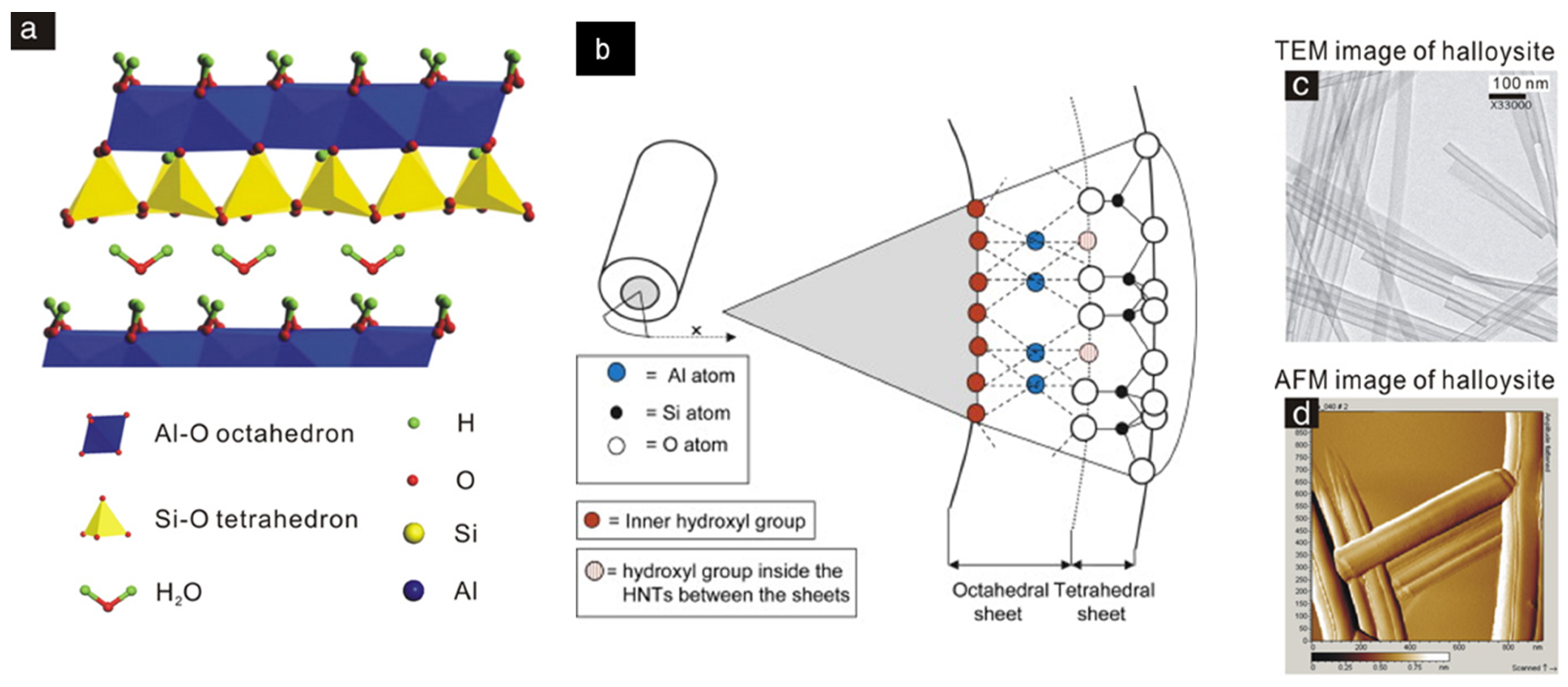
























| Chemical Formula | Al2Si2O5(OH)4·nH2O |
|---|---|
| Length | 0.2–2 μm |
| Outer diameter | 40–70 nm |
| Inner diameter | 10–40 nm |
| Aspect ratio (L/D) | 10–50 |
| Elastic modulus (theoretical value) | 140 GPa (130–340 GPa) |
| Mean particle size in aqueous solution | 143 nm |
| Particle size range in aqueous solution | 22.1–81.6 m2/g [8] |
| BET surface area | 50–400 nm |
| Pore space | 22.1–46.8% |
| Lumen space | 11–395 |
| Density | 2.14–2.59 g/cm3 |
| Average pore size | 79.7–100.2 Å |
| Structural water release temperature | 400–600 °C |
| Polymer Matrix | Properties of Nanocomposites in Comparison with Neat Polymers | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Epoxy resin | Increase in thermal stability and impact strength | [24,25] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol | Increase in thermal stability | [26] |
| Polystyrene | Increase in thermal stability | [27] |
| Nylon 6 | Increase flame retardancy | [28] |
| Ethylene propylene diene monomer | Increase in tensile strength, stiffness, ductility, thermal stability and flame retardancy | [29] |
| Epoxy/cyanate ester resin | Decrease of coefficient of thermal expansion, increase in the moduli and rubbery state | [30] |
| Polyaniline | Increase in the conductivity | [31] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Massaro, M.; Noto, R.; Riela, S. Past, Present and Future Perspectives on Halloysite Clay Minerals. Molecules 2020, 25, 4863. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204863
Massaro M, Noto R, Riela S. Past, Present and Future Perspectives on Halloysite Clay Minerals. Molecules. 2020; 25(20):4863. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204863
Chicago/Turabian StyleMassaro, Marina, Renato Noto, and Serena Riela. 2020. "Past, Present and Future Perspectives on Halloysite Clay Minerals" Molecules 25, no. 20: 4863. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204863
APA StyleMassaro, M., Noto, R., & Riela, S. (2020). Past, Present and Future Perspectives on Halloysite Clay Minerals. Molecules, 25(20), 4863. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204863








