Duplex Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering-Based Lateral Flow Immunosensor for the Low-Level Detection of Antibiotic Residues in Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
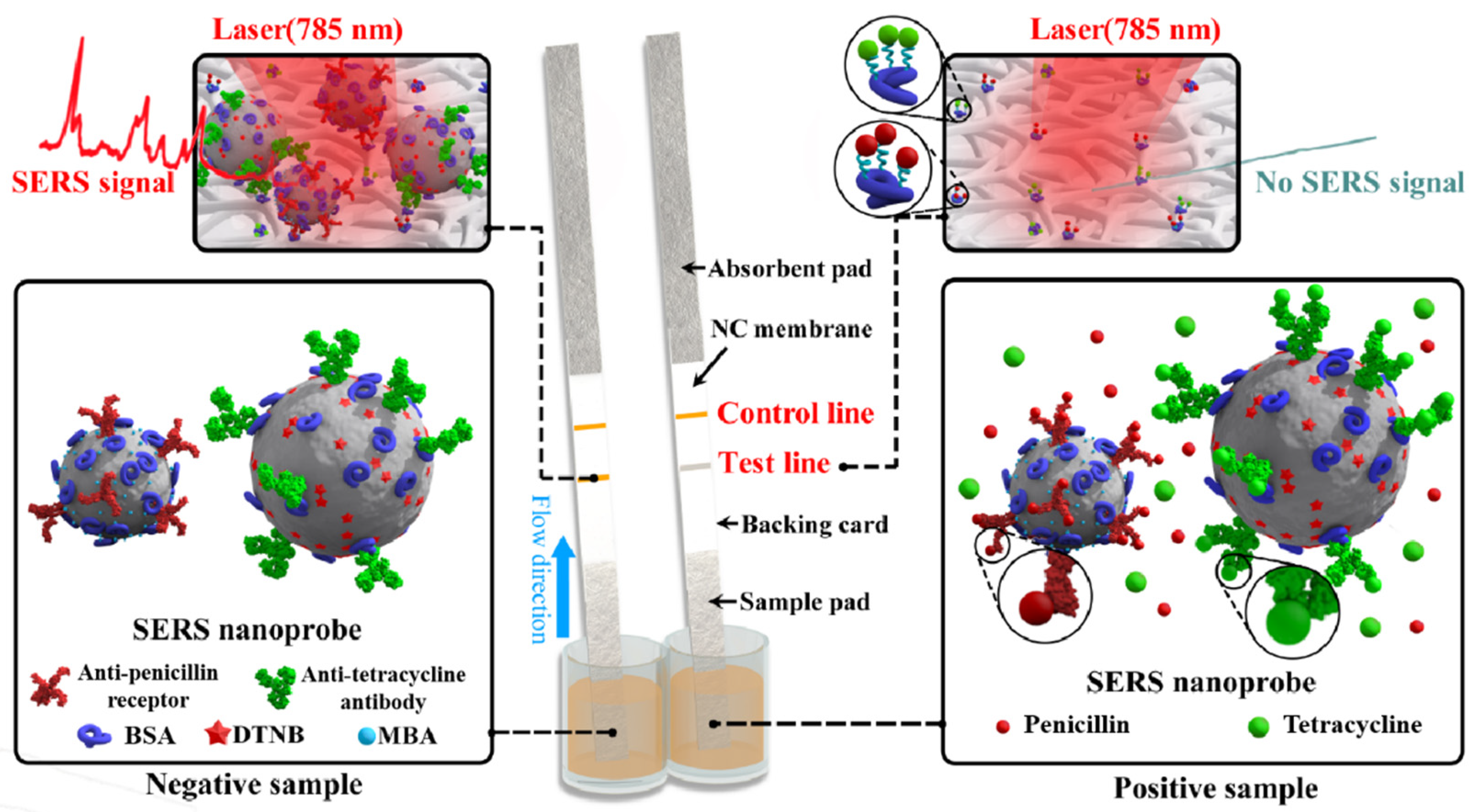
2.1. Scheme of Duplex SERS-Based Lateral Flow Immunosensor
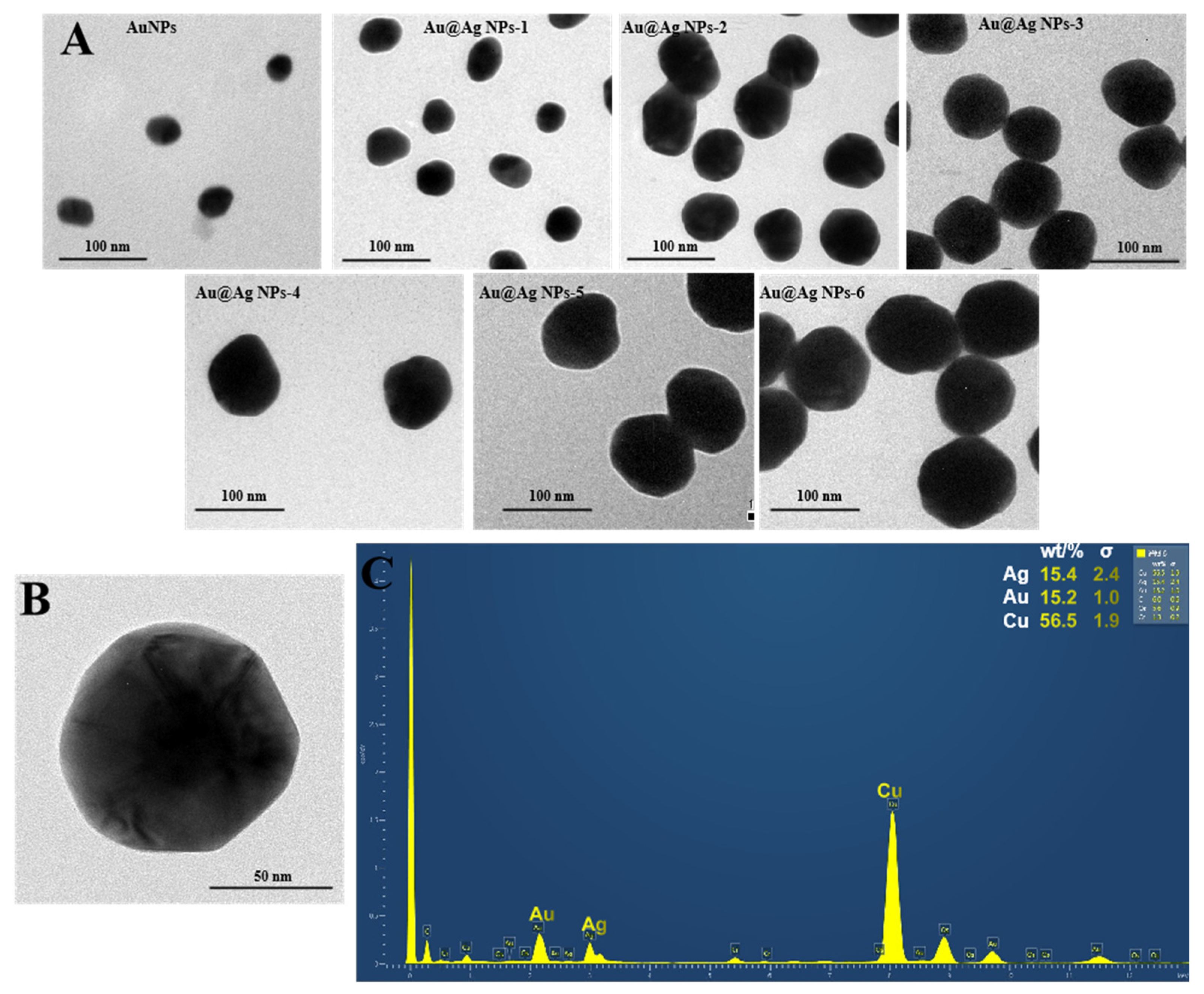
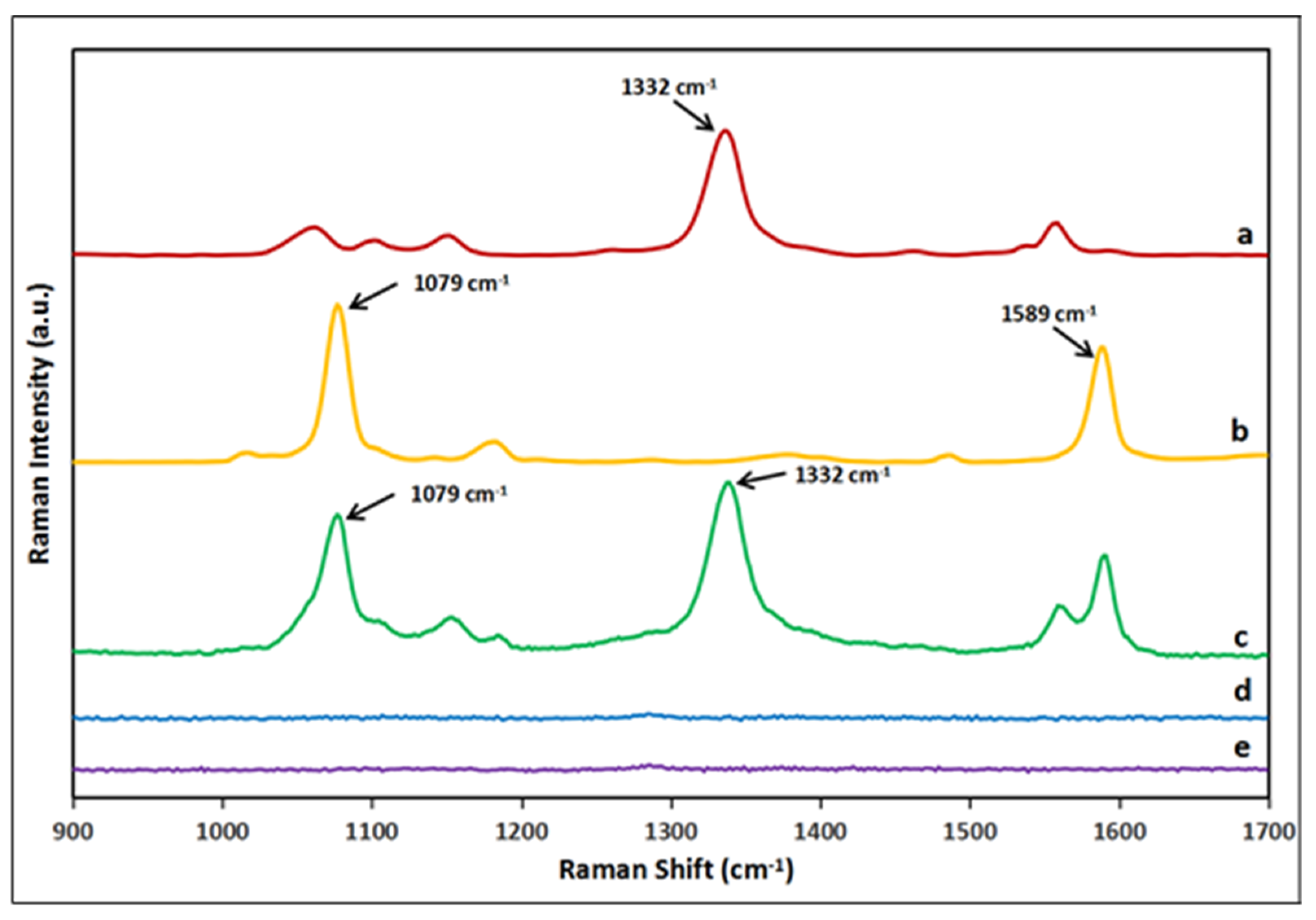
2.2. SERS Nanoprobe Preparation
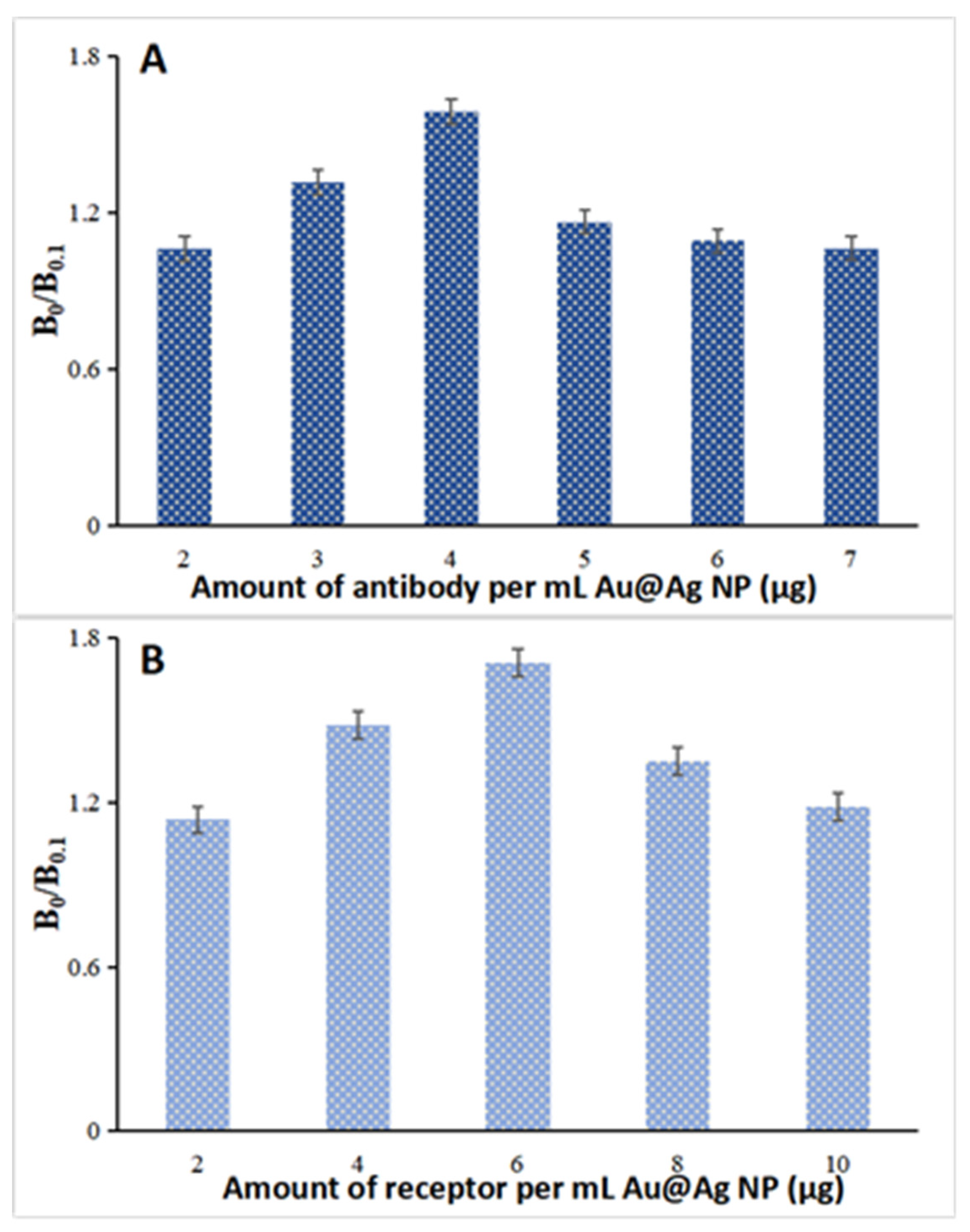
2.3. SERS-Based Lateral Flow Immunosensor
2.4. Method Validation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Au@Ag NPs’ Synthesis
3.3. SERS Nanoprobe Preparation
3.4. Lateral Flow Strip Assembly
3.5. SERS-Based Immunosensing Assay
3.6. Spiked Recovery Experiment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudin, V. Advances in biosensor development for the screening of antibiotic residues in food products of animal origin—A comprehensive review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, B.M.; Levy, S.B. Food Animals and Antimicrobials: Impacts on Human Health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission, E. COMMISSION DECISION (EU) No 37/2010 of December 2009 on pharmacologically active substances and their classification regarding maximum residue limits in foodstuffs of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Comm. 2010, 15, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Larsson, D.G.J. Concentrations of antibiotics predicted to select for resistant bacteria: Proposed limits for environmental regulation. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cháfer-Pericás, C.; Maquieira, Á.; Puchades, R. Fast screening methods to detect antibiotic residues in food samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 1038–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.W.; Zheng, N.; Yu, Z.N.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.M.; Qu, X.Y.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, Y.D.; Wang, J.Q. Simultaneous determination of 38 veterinary antibiotic residues in raw milk by UPLC–MS/MS. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Yao, Y.; Ping, J.; Ying, Y. Recent advances in nanomaterial-based biosensors for antibiotics detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisossadati, M.J.; Danesh, N.M.; Borna, F.; Gholamzad, M.; Ramezani, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M. Lateral flow based immunobiosensors for detection of food contaminants. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, V.; Walkenfort, B.; König, M.; Salehi, M.; Schlücker, S. Rapid, Quantitative, and Ultrasensitive Point-of-Care Testing: A Portable SERS Reader for Lateral Flow Assays in Clinical Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zong, S.; Wu, L.; Zhu, D.; Cui, Y. SERS-Activated Platforms for Immunoassay: Probes, Encoding Methods, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7910–7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, M.D.; Lipert, R.J.; Siperko, L.M.; Wang, G.; Narayanan, R. SERS as a bioassay platform: Fundamentals, design, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granger, J.H.; Schlotter, N.E.; Crawford, A.C.; Porter, M.D. Prospects for point-of-care pathogen diagnostics using surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3865–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, T.; Song, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, D.; Li, W. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)-based immunochromatographic assay (ICA) for the simultaneous detection of two pyrethroid pesticides. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2019, 283, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Yang, H.; Liu, C.; Zhao, K.; Li, J.; Deng, A. Ultrasensitive detection of diclofenac in water samples by a novel surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-based immunochromatographic assay using AgMBA@SiO2-Ab as immunoprobe. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2019, 283, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-K.; Stanciu, L.A. Bisphenol A detection using gold nanostars in a SERS improved lateral flow immunochromatographic assay. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 276, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Xie, K.; Huang, L.; Wang, L.; Ye, J.; Xiao, M.; Ma, L.; Jia, A.; Tang, Y. A novel SERS-based lateral flow assay for differential diagnosis of wild-type pseudorabies virus and gE-deleted vaccine. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2019, 282, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Kim, K.; Choi, N.; Wang, X.; Lee, J.; Jeon, J.H.; Rhie, G.-e.; Choo, J. Highly sensitive detection of high-risk bacterial pathogens using SERS-based lateral flow assay strips. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 270, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Huang, L.; Liu, B.; Ni, H.; Sun, L.; Su, E.; Chen, H.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, X. Quantitative and ultrasensitive detection of multiplex cardiac biomarkers in lateral flow assay with core-shell SERS nanotags. Biosens. Bioelectron 2018, 106, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Huang, J.; Sun, Y.; Deng, R.; Teng, M.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G. A SERS-based multiple immuno-nanoprobe for ultrasensitive detection of neomycin and quinolone antibiotics via a lateral flow assay. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Choi, N.; Cheng, Z.; Ko, J.; Chen, L.; Choo, J. Simultaneous Detection of Dual Nucleic Acids Using a SERS-Based Lateral Flow Assay Biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-b.; Du, X.-j.; Zang, Y.-X.; Li, P.; Wang, S. SERS-Based Lateral Flow Strip Biosensor for Simultaneous Detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enterica Serotype Enteritidis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10290–10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Covián, L.; Montes-García, V.; Girard, A.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Faulds, K.; Graham, D.; Blanco-López, M.C. Au@Ag SERRS tags coupled to a lateral flow immunoassay for the sensitive detection of pneumolysin. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobita, T.; Oda, M.; Azuma, T. Segmental flexibility and avidity of IgM in the interaction of polyvalent antigens. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 40, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration. Analytical Procedures and Methods Validation for Drugs and Biologics, Guidance for Industry; Food and Drug Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2015. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/87801/download (accessed on 1 July 2015).
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, M.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Y. Rapid and Automated Detection of Six Contaminants in Milk Using a Centrifugal Microfluidic Platform with Two Rotation Axes. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7958–7964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Kong, D.; Liu, L.; Song, S.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. Development of an ELISA and Immunochromatographic Assay for Tetracycline, Oxytetracycline, and Chlortetracycline Residues in Milk and Honey Based on the Class-Specific Monoclonal Antibody. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Kuang, H.; Li, A.; Xu, C. A gold immunochromatographic assay for the rapid and simultaneous detection of fifteen β-lactams. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16381–16388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Han, M.; Liu, J.; Zhao, P.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L. Near-infrared fluorescence-based multiplex lateral flow immunoassay for the simultaneous detection of four antibiotic residue families in milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Zheng, W.; Chen, Y.; Ran, B.; Qian, Z.; Jiang, X. Cu-T1 Sensor for Versatile Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2833–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Chang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Duan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Visual and fluorometric lateral flow immunoassay combined with a dual-functional test mode for rapid determination of tetracycline antibiotics. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Yu, M.; Wang, Y.; Hu, W.; Cheng, D.; Swihart, M.T.; Song, Y. Multi-color quantum dot-based fluorescence immunoassay array for simultaneous visual detection of multiple antibiotic residues in milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 72, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.; Yoo, H.; Lee, H.; Jeon, S. Colorimetric detection of penicillin G in milk using antibody-functionalized dendritic platinum nanoparticles. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 255, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frens, G. Controlled Nucleation for the Regulation of the Particle Size in Monodisperse Gold Suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Analyte | LOD | Assay Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme immunoassay | Penicillin G | 0.1 ng/mL | >60 min | [26] |
| Fluorometric lateral flow immunoassay | Tetracycline | 20 ng/mL | >10 min | [27] |
| Multiplex lateral flow immunoassay | Penicillin G | 0.05 ng/mL | ~20 min | [28] |
| Tetracycline | 0.04 ng/mL | |||
| Immunochromatographic assay | Penicillin G | 0.5 ng/mL | ~20 min | [29] |
| Microfluidic immunoassay | Tetracycline | 1.01 μg/kg | ~17 min | [30] |
| Quantum dot-based fluorescence immunoassay | Penicillin G | 0.005 ng/mL | ~90 min | [31] |
| Tetracycline | 0.005 ng/mL | |||
| Colorimetric immunosensor | Penicillin G | 1 ng/mL | 5 min | [32] |
| Potassium thiocyanate (KSCN)-mediated Fe-T1 sensor | Tetracycline | 2.31 ng/mL | >2 h | [33] |
| SERS-based immunosensor | Tetracycline Penicillin G | 0.015 ng/mL 0.010 ng/mL | ~20 min | This study |
| Analytes | Spiked Level (ng/mL) | Detected Level (Mean Value ± SD, ng/mL) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetracycline | 2.0 | 2.14 ± 0.32 | 106.9 | 15.8 |
| 4.0 | 3.55 ± 0.54 | 88.8 | 13.6 | |
| 10.0 | 9.63 ± 1.18 | 96.3 | 11.8 | |
| Penicillin | 2.0 | 2.15 ± 0.20 | 107.5 | 10.2 |
| 4.0 | 4.45 ± 0.44 | 111.3 | 10.9 | |
| 10.0 | 9.07 ± 0.96 | 90.7 | 9.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, R.; Tang, S.; Luo, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Yang, C.; He, L.; Chen, Y. Duplex Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering-Based Lateral Flow Immunosensor for the Low-Level Detection of Antibiotic Residues in Milk. Molecules 2020, 25, 5249. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225249
Fan R, Tang S, Luo S, Liu H, Zhang W, Yang C, He L, Chen Y. Duplex Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering-Based Lateral Flow Immunosensor for the Low-Level Detection of Antibiotic Residues in Milk. Molecules. 2020; 25(22):5249. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225249
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Ruiqi, Shusheng Tang, Sunlin Luo, Hu Liu, Wanjun Zhang, Chunjiang Yang, Lidong He, and Yiqiang Chen. 2020. "Duplex Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering-Based Lateral Flow Immunosensor for the Low-Level Detection of Antibiotic Residues in Milk" Molecules 25, no. 22: 5249. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225249
APA StyleFan, R., Tang, S., Luo, S., Liu, H., Zhang, W., Yang, C., He, L., & Chen, Y. (2020). Duplex Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering-Based Lateral Flow Immunosensor for the Low-Level Detection of Antibiotic Residues in Milk. Molecules, 25(22), 5249. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225249






