Longitudinal Bone Growth Stimulating Effect of Allium macrostemon in Adolescent Female Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect on Body Weight and Food Intake
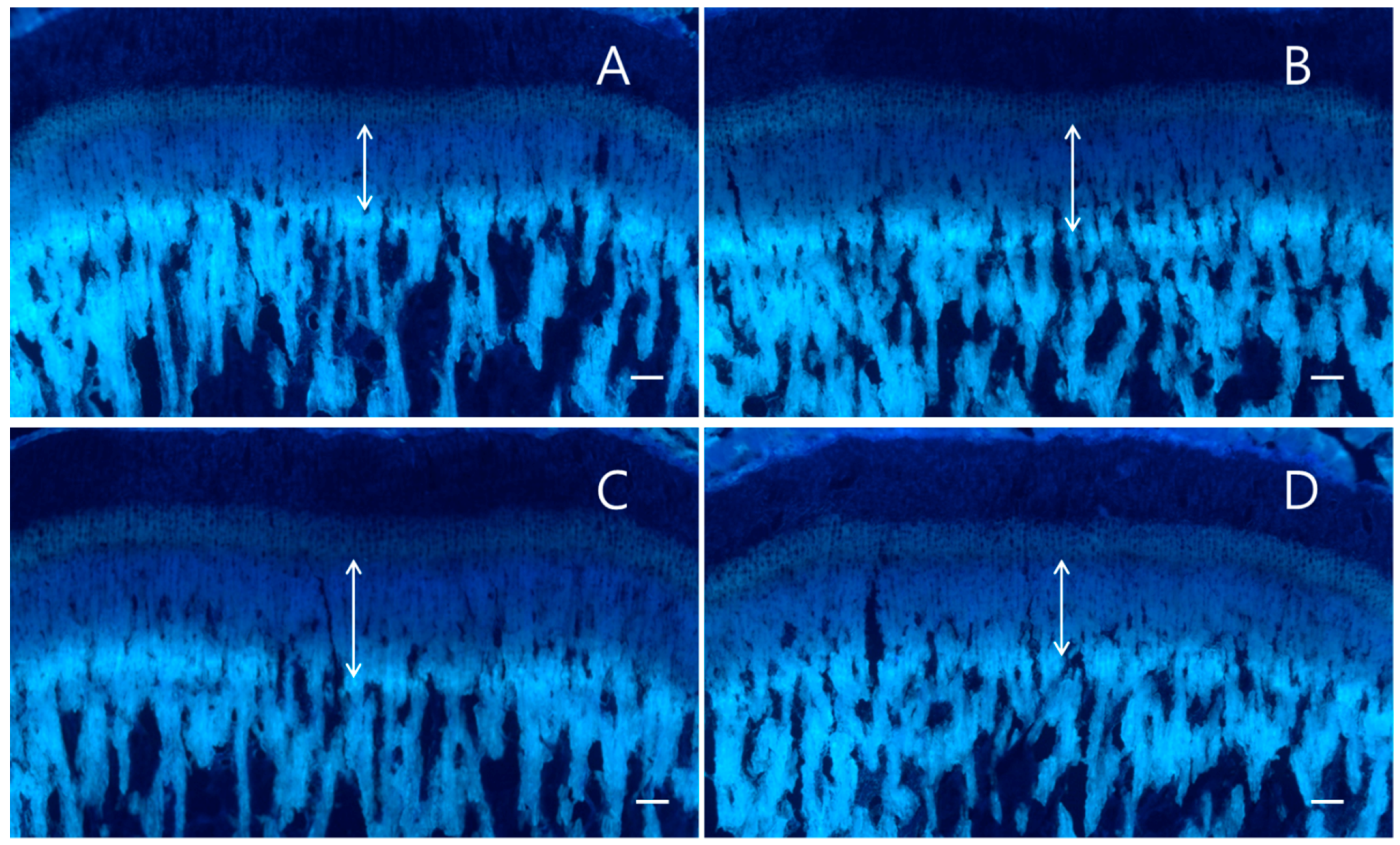
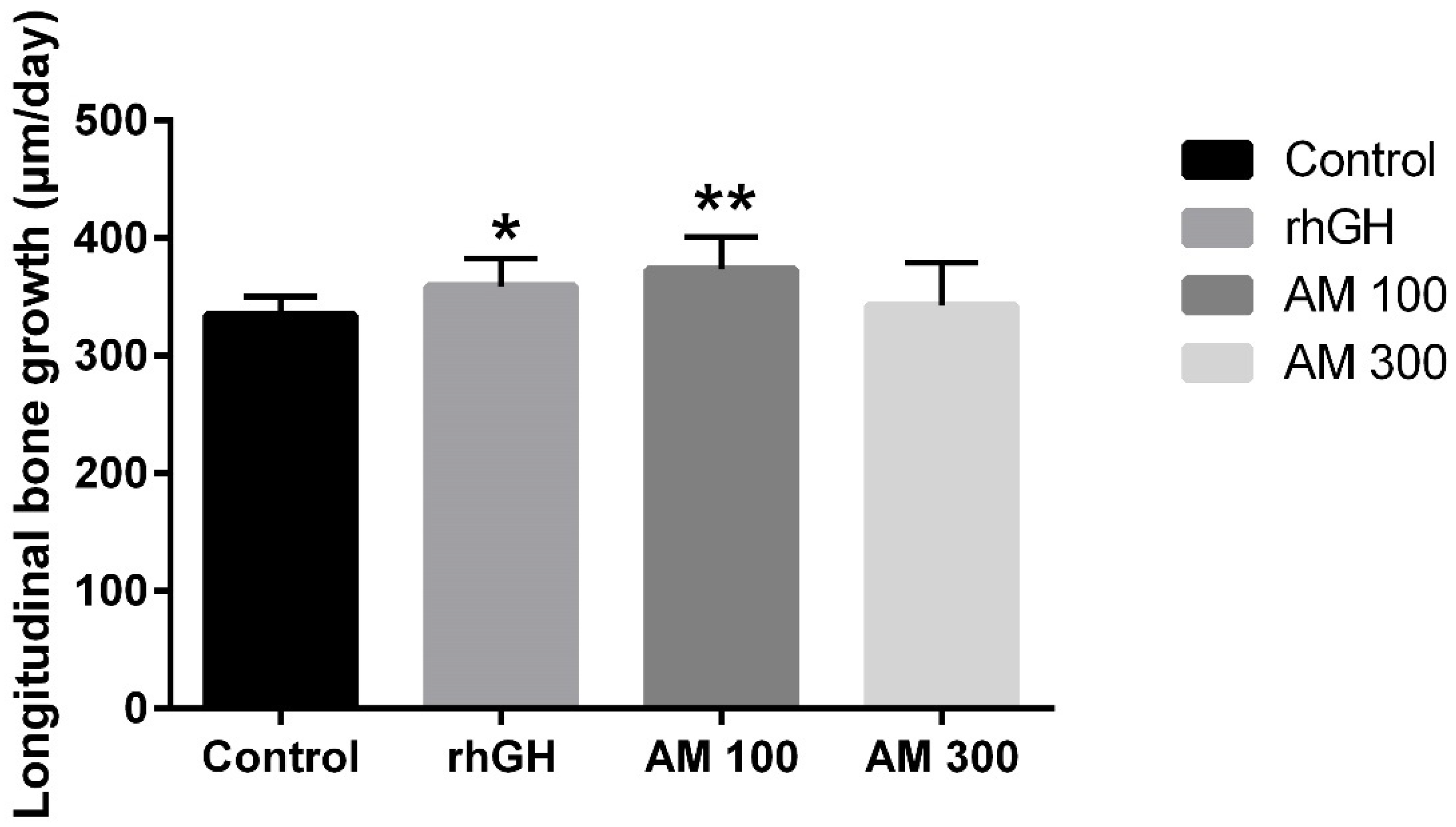
2.2. Effect on Longitudinal Bone Growth
2.3. Effect on IGF-1 and BMP-2 Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Preparation of the Extract
4.2. Animals
4.3. Weight and Feed Intake Check, A. macrostemon Administration, and Tetracycline Hydrochloride Injection
4.4. Tissue Preparation and Detection of Longitudinal Bone Growth
4.5. Measurement of IGF-1 and BMP-2 in the Growth Plates
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jee, Y.H.; Andrade, A.C.; Baron, J.; Nilsson, O. Genetics of Short Stature. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North. Am. 2017, 46, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, H.M.; Schönau, E. On longitudinal bone growth, short stature, and related matters: Insights about cartilage physiology from the Utah paradigm. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 14, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, T.R.; Chen, C.H. Bone biomarker for the clinical assessment of osteoporosis: Recent developments and future perspectives. Biomark. Res. 2017, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, S.Y.; Leem, K.H.; Kim, H. Effects of Acanthopanacis Senticosi Radix and its subfractions on longitudinal bone growth of adolescent rats. Korea J. Herbol. 2003, 18, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Park, S.K.; Kim, C.Y.; Chung, S.Y.; Chang, G.T. Amomum villosum induces longitudinal bone growth in adolescent female rats. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2012, 32, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leem, K.H.; Kim, H. Effect of Cibotium barometz on the Growth of Longitudinal Bone in Adolescent Male Rats. Korea J. Herbol. 2001, 16, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.I.; Song, M.; Lee, D.; Song, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.; Choi, H.Y.; Kim, H. Effects of Eucommia ulmoides extract on longitudinal bone growth rate in adolescent female rats. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, Y.S.; Song, J.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, H.J.; Guo, H.; Kim, H. Effects of Phlomis umbrosa Root on Longitudinal Bone Growth Rate in Adolescent Female Rats. Molecules 2016, 21, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, Y.H.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Hong, S.A.; Park, E.S.; Nam, Y.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, S.J.; Sohn, U.D.; Kim, H.; et al. Effects of Aqueous Extract of Phyllostachyos Caulis in Taeniam on Longitudinal Bone Growth in Adolescent Rats. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Compendium of Materia Medica. China. 1596. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Dou, C.; Li, N.; Kang, F.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Yang, X.; Dong, S. Alliin Attenuated RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by Scavenging Reactive Oxygen Species through Inhibiting Nox1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; You, M.; Shen, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y. Allicin Reversed the Process of Frailty in Aging Male Fischer 344 Rats With Osteoporosis. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Mehla, R.K.; Sirohi, S.K.; Roy, B. The effect of dietary garlic supplementation on body weight gain, feed intake, feed conversion efficiency, faecal score, faecal coliform count and feeding cost in crossbred dairy calves. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2010, 42, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoola, S.O.; Uzoamaka, O.O. Effect of Allium sativum on growth, feed utilization and haematological parameters of Clarias gariepinus juvenile. Afr. J. Livest. Ext. 2013, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Goodarzi, M.; Nanekarani, S.; Landy, N. Effect of dietary supplementation with onion (Allium cepa L.) on performance, carcass traits and intestinal microflora composition in broiler chickens. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2014, 4, S297–S301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovecki, V.; Mayer, D.; Slaus, M.; Strinovic, D.; Skavic, J. Prediction of stature based on radiographic measurements of cadaver long bones: A study of the Croatian population. J. Forensic. Sci. 2007, 52, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duyar, I.; Pelin, C. Body height estimation based on tibia length in different stature groups. Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 2003, 122, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhondi-Meybodi, M.; Aghaei, M.A.; Hashemian, Z. The role of diet in the management of non-ulcer dyspepsia. Middle East J. Dig. Dis. 2015, 7, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, S.; Masamoto, K.; Sumiyoshi, H.; Kunihiro, K.; Fuwa, T. [Effect of raw and extracted-aged garlic juice on growth of young rats and their organs after peroral administration (author’s transl)]. J. Toxicol. Sci. 1980, 5, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Eerden, B.C.; Karperien, M.; Wit, J.M. Systemic and local regulation of the growth plate. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 782–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomaszewski, R.; Bohosiewicz, J.; Gap, A.; Bursig, H.; Wysocka, A. Autogenous cultured growth plate chondrocyte transplantation in the treatment of physeal injury in rabbits. Bone Jt. Res. 2014, 3, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, H. Bone growth mechanisms and the effects of cytotoxic drugs. Arch. Dis. Child. 1999, 81, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isaksson, O.G.; Lindahl, A.; Nilsson, A.; Isgaard, J. Mechanism of the stimulatory effect of growth hormone on longitudinal bone growth. Endocr. Rev. 1987, 8, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roith, D.; Bondy, C.; Yakar, S.; Liu, J.L.; Butler, A. The somatomedin hypothesis: 2001. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeChiara, T.M.; Robertson, E.J.; Efstratiadis, A. Parental imprinting of the mouse insulin-like growth factor II gene. Cell 1991, 64, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.P.; Baker, J.; Perkins, A.S.; Robertson, E.J.; Efstratiadis, A. Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell 1993, 75, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, E.J.; Tatarczuch, L.; Mirams, M. The skeleton: A multi-functional complex organ: The growth plate chondrocyte and endochondral ossification. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 211, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakou, T. Bone morphogenetic proteins: From basic studies to clinical approaches. Bone 1998, 22, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozney, J.M.; Rosen, V. Bone morphogenetic protein and bone morphogenetic protein gene family in bone formation and repair. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1998, 346, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.A.; Rosen, V.; D’Alessandro, J.S.; Bauduy, M.; Cordes, P.; Harada, T.; Israel, D.I.; Hewick, R.M.; Kerns, K.M.; LaPan, P.; et al. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein induces bone formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 2220–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, K.R.; Xu, X.L.; Tang, T.T.; Zhu, Z.A.; Yu, C.F.; Lou, J.R.; Zhang, X.L. Repairing of goat tibial bone defects with BMP-2 gene-modified tissue-engineered bone. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2005, 77, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Park, Y.; Pandit, N.R.; Kim, J.; Song, M.; Park, J.; Choi, H.Y.; Kim, H. The herbal formula HT042 induces longitudinal bone growth in adolescent female rats. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, N.; Kim, Y.S.; Song, J.; Kim, H. Effects of Eleutherococcus Extract Mixture on Endochondral Bone Formation in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.S. Effect of Bojungikki-tang on the Bone Growth in Adolescent Rats. Master’s Thesis, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, C.H.; Jung, J.W.; Seo, Y.T.; Jang, Y.P.; Ryu, J.H. Antidepressant-like activity of the aqueous extract of Allium macrostemon in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rol De Lama, M.A.; Perez-Romero, A.; Tresguerres, J.A.; Hermanussen, M.; Ariznavarreta, C. Recombinant human growth hormone enhances tibial growth in peripubertal female rats but not in males. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2000, 142, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Day | Control | rhGH | AM 100 | AM 300 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 106.8 ± 6.2 | 106.5 ± 4.4 | 107.9 ± 5.4 | 106.5 ± 3.4 | 0.892 |
| 2 | 110.6 ± 7.2 | 109.7 ± 5.2 | 112.4 ± 5.0 | 109.2 ± 3.4 | 0.482 |
| 3 | 117.1 ± 7.3 | 117.3 ± 5.8 | 119.7 ± 5.4 | 115.8 ± 3.2 | 0.414 |
| 4 | 121.9 ± 7.8 | 122.0 ± 5.9 | 124.8 ± 5.2 | 120.3 ± 3.9 | 0.314 |
| 5 | 126.5 ± 7.9 | 126.9 ± 6.0 | 130.6 ± 6.0 | 124.6 ± 3.0 | 0.111 |
| 6 | 131.5 ± 8.2 | 131.2 ± 6.2 | 134.8 ± 6.0 | 128.5 ± 3.0 | 0.111 |
| 7 | 137.0 ± 7.9 | 137.2 ± 7.4 | 140.7 ± 6.4 | 133.8 ± 3.8 | 0.101 |
| 8 | 139.8 ± 8.4 | 140.4 ± 7.2 | 144.3 ± 6.1 # | 135.9 ± 4.0 # | 0.031 * |
| 9 | 143.3 ± 8.0 | 144.0 ± 7.1 | 149.2 ± 7.6 # | 140.6 ± 4.6 # | 0.033 * |
| 10 | 145.3 ± 7.4 | 145.7 ± 8.9 | 150.9 ± 8.9 # | 140.1 ± 6.7 # | 0.019 * |
| 11 | 147.6 ± 8.1 | 146.8 ± 9.3 | 152.1 ± 9.3 # | 142.8 ± 6.3 # | 0.068 |
| Control | rhGH | AM 100 | AM 300 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight gain (%/rat) | 38.26 ± 3.99 | 37.88 ± 6.86 | 41.13 ± 7.69 | 34.20 ± 8.07 | 0.118 |
| Daily food intake gain (g/cage) | 597.3 ± 7.7 # | 613.5 ± 19.6 # | 650.0 ± 22.1 # | 565.3 ± 12.6 # | 0.002 ** |
| Control | rhGH | AM 100 | AM 300 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall expressions (n) | 30.7 ± 2.9 # | 92.7 ± 13.8 # | 64.7 ± 8.4 | 66.0 ± 4.4 | < 0.001 *** |
| Resting zone | 4.3 ± 0.6 # | 17.7 ± 4.5 # | 11.3 ± 0.6 # | 6.3 ± 1.5 | 0.001 ** |
| Proliferative zone | 12.0 ± 1.7 # | 50.0 ± 5.2 # | 32.3 ± 4.5 | 34.3 ± 5.1 | < 0.001 *** |
| Hypertrophic zone | 14.3 ± 2.1 # | 25.0 ± 4.4 # | 21.3 ± 4.5 | 25.3 ± 0.6 # | 0.012 * |
| Control | rhGH | AM 100 | AM 300 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall expressions (n) | 24.0 ± 3.6 # | 52.3 ± 5.5 | 42.0 ± 6.6 | 44.7 ± 4.9 | 0.001 ** |
| Resting zone | 2.7 ± 3.1 | 5.7 ± 5.5 | 3.7 ± 4.0 | 3.7 ± 3.5 | 0.840 |
| Proliferative zone | 12.3 ± 3.1 # | 27.7 ± 3.5 | 22.0 ± 3.6 | 24.3 ± 3.5 | 0.003 ** |
| Hypertrophic zone | 9.0 ± 1.0 # | 19.0 ± 2.0 | 16.3 ± 2.1 | 16.7 ± 3.1 | 0.002 ** |
Sample Availability: Samples of the A. macrostemon are available from the authors. | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Chang, G.T.; Lee, D. Longitudinal Bone Growth Stimulating Effect of Allium macrostemon in Adolescent Female Rats. Molecules 2020, 25, 5449. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225449
Kim H-J, Lee SH, Lee SH, Lee J, Kim H, Chang GT, Lee D. Longitudinal Bone Growth Stimulating Effect of Allium macrostemon in Adolescent Female Rats. Molecules. 2020; 25(22):5449. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225449
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyung-Joong, Sun Haeng Lee, Sung Hyun Lee, Jihong Lee, Hocheol Kim, Gyu Tae Chang, and Donghun Lee. 2020. "Longitudinal Bone Growth Stimulating Effect of Allium macrostemon in Adolescent Female Rats" Molecules 25, no. 22: 5449. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225449
APA StyleKim, H.-J., Lee, S. H., Lee, S. H., Lee, J., Kim, H., Chang, G. T., & Lee, D. (2020). Longitudinal Bone Growth Stimulating Effect of Allium macrostemon in Adolescent Female Rats. Molecules, 25(22), 5449. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225449







