Roll-to-Roll Production of Spider Silk Nanofiber Nonwoven Meshes Using Centrifugal Electrospinning for Filtration Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
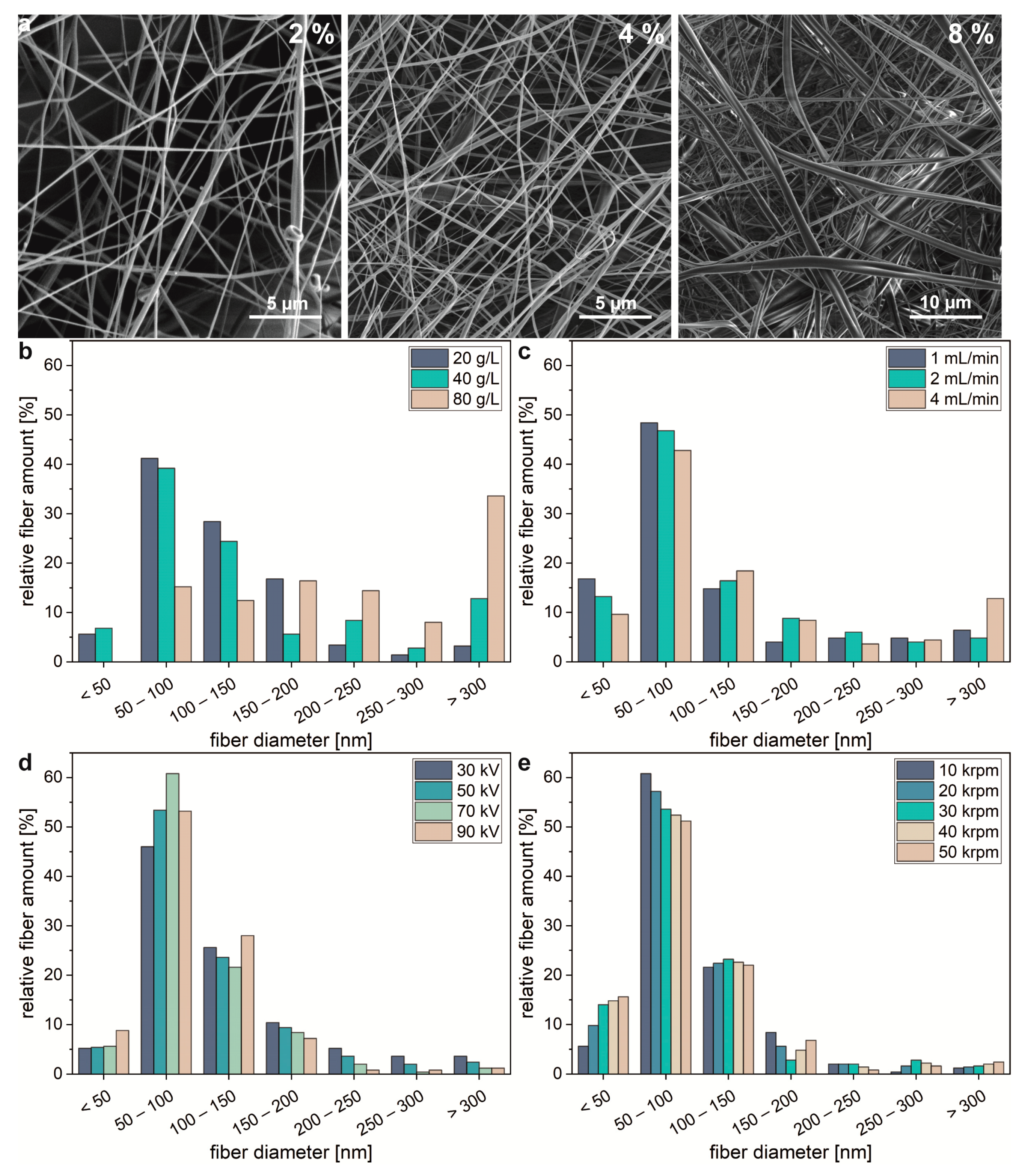
2.1. Centrifugal Electrospinning of Spider Silk Proteins
2.2. Effect of CES on β-Sheet Content in as Spun Spider Silk Fibers
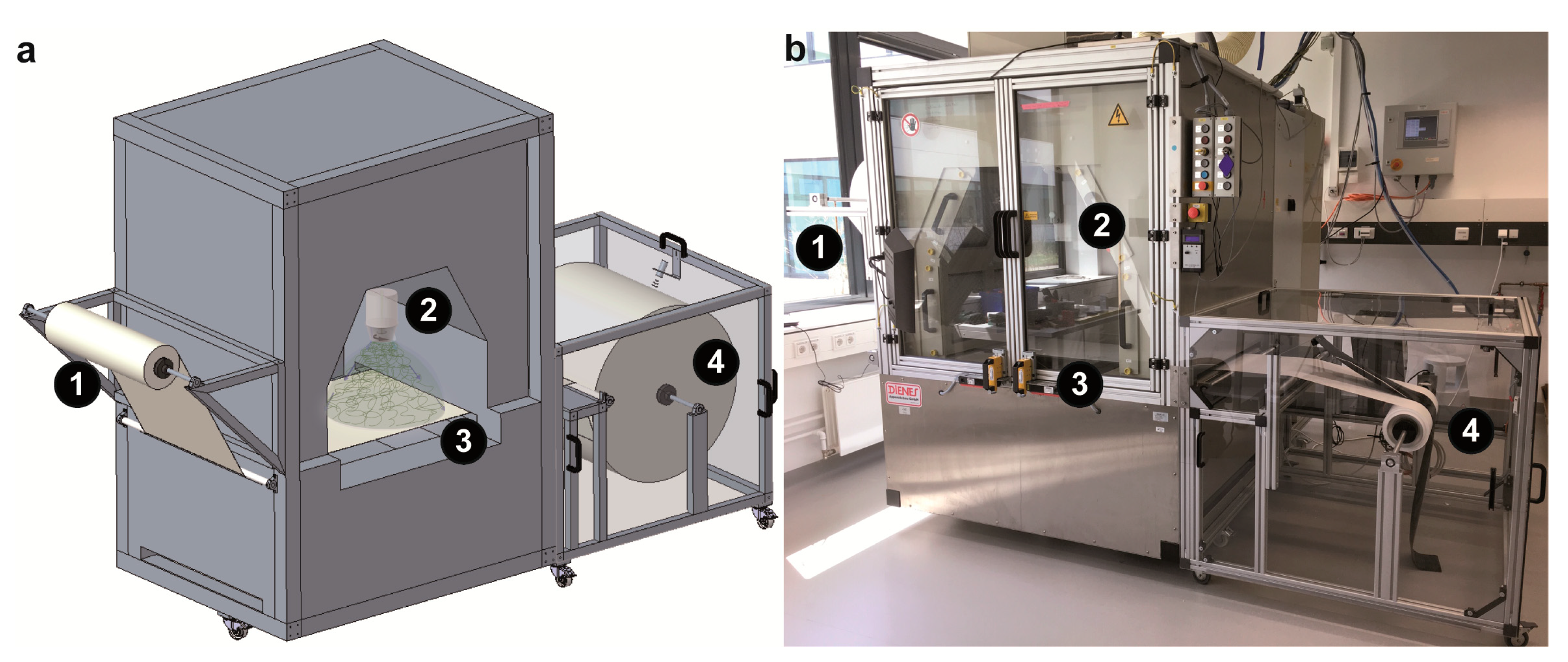
2.3. Roll-to-Roll Nonwoven Mesh Production
2.4. Application of CES-Produced Spider Silk Meshes as Fine Dust Filters
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Centrifugal Electrospinning of Recombinant Spider Silk Proteins
3.2. Post-Treatment of Spider Silk Nonwoven Meshes
3.3. Secondary Structure Characterization Using FTIR
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy of Spider Silk Meshes
3.5. Birefringence Analysis
3.6. Quantification of Filter Efficiency and Quality Factor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, J.O.; Thundiyil, J.G.; Stolbach, A. Clearing the Air: A Review of the Effects of Particulate Matter Air Pollution on Human Health. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.H.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, D.H.; Ko, S.W.; Hwang, T.I.; Kim, J.W.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Development of Nanofiber Reinforced Double Layered Cabin Air Filter Using Novel Upward Mass Production Electrospinning Set Up. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 2132–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundarrajan, S.; Tan, K.; Lim, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun Nanofibers for Air Filtration Applications. Procedia Eng. 2014, 75, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, X.-H.; Wang, S.-Y. Filtration properties of electrospinning nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genaidy, A.; Tolaymat, T.; Sequeira, R.; Rinder, M.; Dionysiou, D. Health effects of exposure to carbon nanofibers: Systematic review, critical appraisal, meta analysis and research to practice perspectives. Sci. Total. Environ. 2009, 407, 3686–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denny, M. Physical-Properties of Spiders Silk and Their Role in Design of Orb-Webs. J. Exp. Biol. 1976, 65, 483–506. [Google Scholar]
- Gosline, J.M.; Demont, M.E.; Denny, M.W. The Structure and Properties of Spider Silk. Endeavour 1986, 10, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackledge, T.A.; Hayashi, C.Y. Silken toolkits: Biomechanics of silk fibers spun by the orb web spider Argiope argentata (Fabricius 1775). J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 2452–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allmeling, C.; Jokuszies, A.; Reimers, K.; Kall, S.; Choi, C.Y.; Brandes, G.; Kasper, C.; Scheper, T.; Guggenheim, M.; Vogt, P.M. Spider silk fibres in artificial nerve constructs promote peripheral nerve regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2008, 41, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollrath, F.; Barth, P.; Basedow, A.; Engstrom, W.; List, H. Local tolerance to spider silks and protein polymers in vivo. In Vivo 2002, 16, 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Jokisch, S.; Neuenfeldt, M.; Scheibel, T. Silk-Based Fine Dust Filters for Air Filtration. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2017, 1, 1700079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, G.; Jokisch, S.; Scheibel, T. Air Filter Devices Including Nonwoven Meshes of Electrospun Recombinant Spider Silk Proteins. JOVE J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 75, e50492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthews, J.A.; Wnek, G.E.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning of Collagen Nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.-W.; Kim, D.-S.; Kang, S.-Y.; Marquez, M.; Joo, Y. Structural studies of electrospun cellulose nanofibers. Polymer 2006, 47, 5097–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, P.; Zhu, K.; Chen, W. A facile technique to prepare biodegradable coaxial electrospun nanofibers for controlled release of bioactive agents. J. Control Release 2005, 108, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mit-uppatham, C.; Nithitanakul, M.; Supaphol, P. Ultrafine Electrospun Polyamide-6 Fibers: Effect of Solution Conditions on Morphology and Average Fiber Diameter. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2004, 205, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Koeck, K.; Scheibel, T. Spider Silk for Tissue Engineering Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Newehy, M.H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Kenawy, E.; Abdel-Megeed, A. Nanospider Technology for the Production of Nylon-6 Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 626589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forward, K.M.; Rutledge, G.C. Free surface electrospinning from a wire electrode. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Fu, K.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhu, J.D.; Yanilmaz, M.; Dirican, M.; Zhang, X.W. Centrifugal spinning: A novel approach to fabricate porous carbon fibers as binder-free electrodes for electric double-layer capacitors. J. Power Source 2015, 273, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Lu, Y. Centrifugal Spinning: An Alternative Approach to Fabricate Nanofibers at High Speed and Low Cost. Polym. Rev. 2014, 54, 677–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.A.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Duan, H.G.; Zhou, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, X.D.; Wang, W.; Lan, W.; et al. Superhigh-Throughput Needleless Electrospinning Using a Rotary Cone as Spinneret. Small 2010, 6, 1612–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, F.; Jokisch, S.; Bargel, H.; Scheibel, T. Centrifugal Electrospinning Enables the Production of Meshes of Ultrathin Polymer Fibers. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 4360–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Choi, K.H.; Ghim, H.D.; Kim, S.S.; Chun, D.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Lyoo, W.S. Role of molecular weight of atactic poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) in the structure and properties of PVA nanofabric prepared by electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: A review. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larrondo, L.; John Manley, R.S. Electrostatic fiber spinning from polymer melts. I. Experimental observations on fiber formation and properties. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 1981, 19, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, G.; Neugirg, B.R.; Kluge, D.; Fery, A.; Scheibel, T. Mechanical Testing of Engineered Spider Silk Filaments Provides Insights into Molecular Features on a Mesoscale. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazawa, K.; Malay, A.D.; Masunaga, H.; Norma-Rashid, Y.; Numata, K. Simultaneous effect of strain rate and humidity on the structure and mechanical behavior of spider silk. Commun. Mater. 2020, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Work, R.W. Dimensions, Birefringences, and Force-Elongation Behavior of Major and Minor Ampullate Silk Fibers from Orb-Web-Spinning Spiders—The Effects of Wetting on these Properties. Text. Res. J. 1977, 47, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, K.; Sato, R.; Yazawa, K.; Hikima, T.; Masunaga, H. Crystal structure and physical properties of Antheraea yamamai silk fibers: Long poly(alanine) sequences are partially in the crystalline region. Polymer 2015, 77, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F. Development of an Artificial Silk Protein on the Basis of a Lacewing Egg Stalk Protein. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Bayreuth, Bayreuth, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Echalier, A.; Glazer, R.; Fülöp, V.; Geday, M.A. Assessing crystallization droplets using birefringence. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. Dbiological Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katoh, K.; Hammar, K.; Smith, P.J.; Oldenbourg, R. Birefringence imaging directly reveals architectural dynamics of filamentous actin in living growth cones. Mol. Biol. Cell 1999, 10, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldenbourg, R.; Salmon, E.D.; Tran, P.T. Birefringence of Single and Bundled Microtubules. Biophys. J. 1998, 74, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Kaplan, D.; Cebe, P. Determining Beta-Sheet Crystallinity in Fibrous Proteins by Thermal Analysis and Infrared Spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6161–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Müller, F.; Zainuddin, S.; Scheibel, T. Roll-to-Roll Production of Spider Silk Nanofiber Nonwoven Meshes Using Centrifugal Electrospinning for Filtration Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 5540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235540
Müller F, Zainuddin S, Scheibel T. Roll-to-Roll Production of Spider Silk Nanofiber Nonwoven Meshes Using Centrifugal Electrospinning for Filtration Applications. Molecules. 2020; 25(23):5540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235540
Chicago/Turabian StyleMüller, Fabian, Shakir Zainuddin, and Thomas Scheibel. 2020. "Roll-to-Roll Production of Spider Silk Nanofiber Nonwoven Meshes Using Centrifugal Electrospinning for Filtration Applications" Molecules 25, no. 23: 5540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235540
APA StyleMüller, F., Zainuddin, S., & Scheibel, T. (2020). Roll-to-Roll Production of Spider Silk Nanofiber Nonwoven Meshes Using Centrifugal Electrospinning for Filtration Applications. Molecules, 25(23), 5540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235540







