Salvia officinalis L. from Italy: A Comparative Chemical and Biological Study of Its Essential Oil in the Mediterranean Context
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
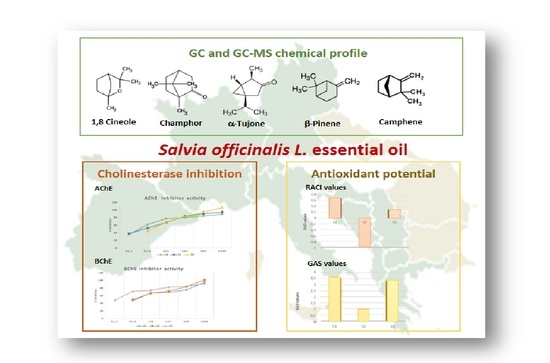
2.1. Chemical Profile
2.2. Anticholinesterase Activity
2.3. Antioxidant Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Plant Materials
3.3. Isolation of Essential Oils
3.4. Gas Chromatography (GC) and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) Analyses
3.5. In Vitro Cholinesterases Inhibitory Activity
3.6. Antioxidant Properties
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walker, J.B.; Sytsma, K.J.; Treutlein, J.; Wink, M. Salvia (Lamiaceae) is not monophyletic: Implications for the systematics, radiation, and ecological specializations of Salvia and tribe Mentheae. Am. J. Bot. 2004, 91, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.; Sun, Z.; Han, C. The pharmacological properties of Salvia essential oils. J. Appl. Pharm. 2013, 3, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Loizzo, M.R.; Abouali, M.; Salehi, P.; Sonboli, A.; Kanani, M.; Menichini, F.; Tundis, R. In vitro antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of nine Salvia species. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 2278–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tundis, R.; Iacopetta, D.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Bonesi, M.; Leporini, M.; Passalacqua, N.G.; Ceramella, J.; Menichini, F.; Loizzo, M.R. Assessment of antioxidant, antitumor and pro-apoptotic effects of Salvia fruticosa Mill. subsp. thomasii (Lacaita) Brullo, Guglielmo, Pavone & Terrasi (Lamiaceae). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 106, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kolac, U.K.; Ustuner, M.C.; Tekin, N.; Ustuner, D.; Colak, E.; Entok, E. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of Salvia officinalis on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in rats. J. Med. Food. 2017, 20, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, D.; Aleksić, J.M.; Jančić, I.; Jančić, R. A Mediterranean medicinal plant in the continental Balkans: A plastid DNA-based phylogeographic survey of Salvia officinalis (Lamiaceae) and its conservation implications. Willdenowia 2015, 45, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosavljević, I.; Jakse, J.; Javornik, B.; Satovic, Z.; Liber, Z. New microsatellite markers for Salvia officinalis (Lamiaceae) and cross-amplification in closely related species. Am. J. Bot. 2011, e316–e318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosavljević, I.; Satovic, Z.; Jakse, J.; Javornik, B.; Greguraš, D.; Jug-Dujaković, M.; Liber, Z. Development of new microsatellite markers for Salvia officinalis L. and its potential use in conservation-genetic studies of narrow endemic salvia brachyodon vandas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12082–12093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jug-Dujaković, M.; Ristić, M.; Pljevljakušić, D.; Dajić-Stevanović, Z.; Liber, Z.; Hančević, Z.; Radić, T.; Šatović, Z. High diversity of indigenous populations of Dalmatian sage (Salvia officinalis L.) in essential-oil composition. Chem. Biodiv. 2012, 9, 2309–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baricevic, D.; Bartol, T. The biological/pharmacological activity of the Salvia genus V. In Book Sage: The Genus Salvia, 1st ed.; Kintzios, S.E., Ed.; Harwood Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 143–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.; Proença, C.; Serralheiro, M.L.; Araújo, M.E. The in vitro screening for acetylcholinesterase inhibition and antioxidant activity of medicinal plants from Portugal. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 108, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Formisano, C.; Rigano, D.; Senatore, F.; Delfine, S.; Cardile, V.; Rosselli, S.; Bruno, M. Chemical composition and anticancer activity of essential oils of mediterranean sage (Salvia officinalis L.) grown in different environmental conditions. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutillas, A.B.; Carrasco, A.; Martinez-Gutierrez, R.; Tomas, V.; Tudela, J. Salvia officinalis L. essential oils from Spain: Determination of composition, antioxidant capacity, antienzymatic, and antimicrobial bioactivities. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroddi, M.; Navarra, M.; Quattropani, M.C.; Calapai, F.; Gangemi, S.; Calapai, G. Systematic review of clinical trials assessing pharmacological properties of Salvia species on memory, cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalingam, K.B.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Ping, N.S.; Haleagrahara, N. Current concepts of neurodegenerative mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, N.S.; Bollen, C.; Perry, E.K.; Ballard, C. Salvia for dementia therapy: Review of pharmacological activity and pilot tolerability clinical trial. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 75, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizzo, M.R.; Tundis, R.; Menichini, F.; Statti, G.A.; Menichini, F. Influence of ripening stage on health benefits properties of Capsicum annuum var. cuminatum L.: In vitro studies. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 184–189. [Google Scholar]
- M’hiri, N.; Ioannou, I.; Ghoul, M.; Mihoubi, M.N. Phytochemical characteristics of Citrus peels and effect of conventional and nonconventional processing on phenolic compounds: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2017, 33, 587–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiderer, C.; Torres, P.; Novak, J. Proof of geographical origin of Albanian sage by essential oil analysis. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2013, 51, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraliu, A.; Doko, A.; Hajdari, A.; Gruda, N.; Šatović, Z.; Cvetkovikj Karanfilova, I.; Stefkov, G. Essential oils chemical variability of seven populations of Salvia officinalis L. in North of Albania. Maced. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2020, 39, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetkovikj, K.I.; Stefkov, G.; Karapandzova, M.; Kulevanova, S.; Šatović, Z. Essential oils and chemical diversity of Southeast European populations of Salvia officinalis L. Chem. Biodiv. 2015, 12, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, M.B.; Jordán, M.J.; Chaouch-Hamada, R.; Landoulsi, A.; Sotomayor, J.A. Phenophase effects on sage (Salvia officinalis L.) yield and composition of essential oil. J. Appl. Res. Med. Arom. Plants 2016, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couladis, M.; Koutsauiti, A. Chemical composition of the essential oils of Salvia officinalis, S. fruticosa, Melissa officinalis, and their infusions. Ratar. Povrt. 2017, 54, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karik, U.; Ḉinar, O.; Tunçtürk, M.; Șekeroǧlu, N.; Gezici, S. Essential oil composition of some sage (Salvia spp) species cultivated in Izmir (Turkey) ecological conditions. Indian J. Pharm. Ed. Res. 2018, 52, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.S.; Padalia, R.C.; Chauhan, A. Harvesting season and plant part dependent variations in the essential oil composition of Salvia officinalis L. grown in northen India. J. Herb. Med. 2015, 5, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Gomes, P.; Fernandes-Ferreira, M. Organ- and season-dependent variation in the essential oil composition of Salvia officinalis L. cultivated at two different sites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2908–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, D.; Fallarero, A.; Brunhofer, G.; Guzik, P.; Prinz, M.; Holzgrabe, U.; Erker, T.; Vuorela, P. Identification and characterization of diarylimidazoles as hybrid inhibitors of butyrylcholinesterase and amyloid beta fibril formation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 45, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagionas, K.; Ngassapa, O.; Runyoro, D.; Graikou, K.; Gortzi, O.; Chinou, I. Chemical analysis of edible aromatic plants growing in Tanzania. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonesi, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Leporini, M.; Tenuta, M.C.; Passalacqua, N.G.; Tundis, R. Comparative evaluation of petitgrain oils from six Citrus species alone and in combination as potential functional anti-radicals and antioxidant agents. Plant Biosyst. 2017, 152, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.; Rudolph, M.J.; Burshteyn, F.; Cassidy, M.S.; Garry, E.N.; Love, J.; Franklin, M.C.; Height, J.J. Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10282–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvir, H.; Silman, I.; Harel, M.; Rosenberry, T.L.; Sussman, J.L. Acetylcholinesterase: From 3D structure to function. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 187, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Euch, S.K.; & Dorsaf, B.H.; Cazaux, S.; Bouzouita, N.; Bouajila, J. Salvia officinalis essential oil: Chemical analysis and evaluation of anti-enzymatic and antioxidant bioactivities. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2018, 120, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Morales, R.M.; Otero, A.L.C.; Mendez-Sanchez, S.C.; Da Silva, M.A.N.; Stashenko, E.E.; Duque, J.E. Mitochondrial affectation, DNA damage and AChE inhibition induced by Salvia officinalis essential oil on Aedes aegypti larvae. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C. 2019, 221, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, S.M.; Lima, A.S.; Miguel, M.G.; Pedro, L.G.; Barroso, J.G.; Figueiredo, A.C. Antioxidant anti-5-lipoxygenase and antiacetylcholinesterase activities of essential oils and decoction waters of some aromatic plants. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2012, 6, 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Orhan, I.; Kartal, M.; Kan, Y.; Sener, B. Activity of essential oils and individual components against acetyl and butyrylcholinesterase. Z. Naturforsch. 2008, 63, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Dodd, F.L.; Robertson, B.C.; Okello, E.J.; Reay, J.L.; Scholey, A.B.; Haskell, C.F. Monoterpenoid extract of sage (Salvia lavandulaefolia) with cholinesterase inhibiting properties improves cognitive performance and mood in healthy adults. J. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 25, 1088–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, H.E.; Demirci, B.; Demirci, F.; Celep, F.; Kahraman, A.; Dogan, M.; Can Bser, K.H. Chemical characterization and anticholinesterase effects of essential oils derived from Salvia species. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2016, 28, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutillas, A.B.; Carrasco, A.; Martinez-Gutierrez, R.; Tomas, V.; Tudela, J. Composition and antioxidant, antienzymatic and antimicrobial activities of volatile molecules from spanish Salvia lavandulifolia (vahl) essential oils. Molecules 2017, 22, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.S.L.; Houghton, P.J.; Jenner, P.; Keith, A.; Perry, E.K. Salvia lavandulaefolia essential oil inhibits cholinesterase in vivo. Phytomedicine 2002, 9, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, M.B.; Asghari, B.; Dinparast, L.; Zengin, G. Salvia nemorosa L.: A novel source of bioactive agents with functional connections. Food Sci. Tecnol. 2017, 75, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tundis, R.; Loizzo, M.R.; Bonesi, M.; Leporini, M.; Menichini, F.; Passalacqua, N.G. A study of Salvia fruticosa Mill subsp. thomasii (Lacaita) Brullo, Guglielmo, Pavone & Terrasi, an endemic sage of southern Italy. Plant Biosyst. 2018, 130–141. [Google Scholar]
- Senol, F.Z.; Orhan, I.E.; Erdem, S.A.; Kartal, M.; Sener, B.; Kan, Y.; Celep, F.; Kahraman, A.; Dogan, M. Evaluation of cholinesterase inhibitory and antioxidant activities of wild and cultivated samples of sage (Salvia fruticosa) by activity-guided fractionation. J. Med. Food. 2011, 14, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topcu, G.; Ozturk, M.; Kuşman, T.; Barla Demirkoz, A.A.; Kolak, U.; Ulubelen, A. Terpenoids, essential oil composition, fatty acid profile, and biological activities of Anatolian Salvia fruticosa Mill. Turk. J. Chem. 2013, 37, 619–632. [Google Scholar]
- Loizzo, M.R.; Menichini, F.; Tundis, R.; Bonesi, M.; Conforti, F.; Nadjafi, F.; Statti, G.A.; Frega, N.G.; Menichini, M. In vitro biological activity of Salvia leriifolia Benth. essential oil relevant to the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Oleo Sci. 2009, 58, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonesi, M.; Menichini, F.; Tundis, R.; Loizzo, M.; Conforti, F.; Passalacqua, N.G.; Statti, G.; Menichini, F. Acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of Pinus species essential oils and their constituents. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2010, 25, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calva, J.; Bec, N.; Gilardoni, G.; Larroque, C.; Cartuche, L.; Bicchi, C.; Montesinos, J.V. Acorenone B: AChE and BChE inhibitor as a major compound of the essential oil distilled from the Ecuadorian species Niphogeton dissecta (Benth.). Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, N.S.; Houghton, P.J.; Theobald, A.; Jenner, P.; Perry, E.K. In vitro inhibition of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase by Salvia lavandulaefolia essential oil and constituent terpenes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2000, 52, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Ezzat, S.M.; Salama, M.M.; Tadros, M.G.; Serya, R.A. Anti-acetylcholinesterase activity of essential oils and their major constituents from four Ocimum species. Z. Nat. C.J. Biosci. 2016, 71, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, M.; Yamafuji, C. Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity by bicyclic monoterpenoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1765–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, L.; Rouse, M.; Wesnes, K.A.; Moss, M. Differential effects of the aromas of Salvia species on memory and mood. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 25, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tildesley, N.T.J.; Kennedy, O.D.; Perry, E.K.; Ballard, C.G.; Wesnes, K.A.; Scholey, A.B. Positive modulation of mood and cognitive performance following administration of acute doses of Salvia lavandulaefolia essential oil to healthy young volunteers. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 83, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelina, C.; Naviglio, D.; Gallo, M.; Severina, P. FT-IR and GC-MS analyses of an antioxidant leaf essential oil from sage plants cultivated as an alternative to tobacco production. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2019, 31, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaziz, M.; Yangui, T.; Sayadi, S.; Dhouib, A. Disinfectant properties of essential oils from Salvia officinalis L. cultivated in Tunisia. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 2755–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khiya, Z.; Hayani, M.; Gamar, A.; Kharchouf, S.; Amine, S.; Berrekhis, F.; Bouzoubae, A.; Zair, T.; El Hilal, F. Valorization of the Salvia officinalis L. of the Morocco bioactive extracts: Phytochemistry, antioxidant activity and corrosion inhibition. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2019, 31, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutebouhart, H.; Didaoui, L.; Tata, S.; Sabaou, N. Effect of extraction and drying method on chemical composition, and evaluation of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of essential oils from Salvia officinalis L. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2019, 22, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.Y.; Li, R.; Jiang, Z.T.; Wang, Y.; Tan, J.; Tanga, S.H.; Zhanga, Y. Antioxidant activity screening and chemical constituents of the essential oil from rosemary by ultra-fast GC electronic nose coupled with chemical methodology. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3481–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevenger, J.F. Apparatus for the determination of volatile oils. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 1928, 17, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leporini, M.; Bonesi, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Passalacqua, N.G.; Tundis, R. The essential oil of Salvia rosmarinus Spenn. from Italy as a source of health-promoting compounds: Chemical profile and antioxidant and cholinesterase inhibitory activity. Plants 2020, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectroscopy, 4th ed.; Allured Publishing Co.: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, W.; Shibamoto, T. Qualitative Analysis of Flavour and Fragrance Volatiles by Glass Capillary Gas Chromatography; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Tenuta, M.C.; Deguin, B.; Loizzo, M.R.; Dugay, A.; Acquaviva, R.; Malfa, G.A.; Bonesi, M.; Bouzidi, C.; Tundis, R. Contribution of flavonoids and iridoids to the hypoglycaemic, antioxidant, and nitric oxide (NO) inhibitory activities of Arbutus unedo L. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Tanumihardjo, S.A. An integrated approach to evaluate food antioxidant capacity. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compound | RI a | % | I.M b | Sign. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | ||||
| Thujene | 926 | 0.46 a ± 0.05 | 0.22 b ± 0.03 | tr | 1,2 | ** |
| α-Pinene | 938 | 3.78 ± 0.43 c | 4.66 ± 0.17 a | 4.34 ± 0.36 b | 1,2,3 | ** |
| Camphene | 953 | 6.27 ± 0.74 c | 7.53 ± 0.34 b | 8.08 ± 0.55 a | 1,2,3 | ** |
| Sabinene | 973 | 0.45 ± 0.05 a | 0.18 ± 0.07 b | nd | 1,2,3 | ** |
| β-Pinene | 980 | 3.08 ± 0.42 c | 9.14 ± 1.66 a | 3.64 ± 0.21 b | 1,2,3 | ** |
| Myrcene | 993 | 1.31 ± 0.14 c | 4.86 ± 0.57 a | 2.02 ± 0.20 b | 1,2,3 | ** |
| α-Phellandrene | 1005 | 0.09 ± 0.02 c | 0.14 ± 0.04 b | 0.27 ± 0.05 a | 1,2 | ** |
| α-Terpinene | 1012 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 0.22 ± 0.06 | 1,2,3 | ns |
| p-Cymene | 1025 | 0.17 ± 0.02 b | 0.14 ± 0.03 b | 0.23 ± 0.03 a | 1,2,3 | ** |
| Limonene | 1030 | 1.78 ± 0.14 c | 1.92 ± 0.56 b | 2.42 ± 0.01 a | 1,2,3 | ** |
| 1,8-Cineole | 1034 | 9.86 ± 1.43 a | 8.80 ± 1.04c | 9.21 ± 1.32 b | 1,2,3 | ** |
| (Z)-β-Ocimene | 1038 | 0.48 ± 0.01 b | 0.63 ± 0.01 a | 0.13 ± 0.03 c | 1,2 | ** |
| (E)-β-Ocimene | 1049 | 0.18 ± 0.04 b | 0.22 ± 0.01 a | 0.10 ± 0.01 b | 1,2 | ** |
| γ-Terpinene | 1057 | 0.68 ± 0.11 a | 0.35 ± 0.01 c | 0.50 ± 0.02 b | 1,2,3 | ** |
| Terpinolene | 1086 | 1.19 ± 0.18 b | 1.14 ± 0.07 b | 1.64 ± 0.13 a | 1,2,3 | ** |
| Linalool | 1098 | tr | 0.27 ± 0.02 b | 0.99 ± 0.07 a | 1,2,3 | ** |
| α-Thujone | 1106 | 9.26 ± 1.10 a | 1.17 ± 0.04 c | 7.63 ± 0.01 b | 1,2 | ** |
| Camphor | 1145 | 16.84 ± 2.67 b | 16.16 ± 2.54 c | 18.92 ± 2.76 a | 1,2 | ** |
| Borneol | 1167 | 4.48 ± 0.18 b | 4.68 ± 0.54 a | 2.34 ± 0.11 c | 1,2 | ** |
| Terpinen-4-ol | 1176 | 0.56 ± 0.06 b | 0.44 ± 0.05 c | 0.74 ± 0.01 a | 1,2 | ** |
| α-Terpineol | 1189 | 1.06 a ± 0.08 | 0.23 ± 0.04 b | 0.99 ± 0.07 a | 1,2,3 | ** |
| (–)-Bornyl acetate | 1286 | 1.56 ± 0.14 b | 1.17 ± 0.10 c | 4.09 ± 0.01 a | 1,2 | ** |
| α-Cubebene | 1352 | 0.51 ± 0.06 c | 0.64 ± 0.06 a | 0.66 ± 0.05 a | 1,2 | ** |
| α-Ylangene | 1373 | 0.51 ± 0.04 b | 1.90 ± 0.22 a | 0.35 ± 0.01 c | 1,2 | ** |
| α-Copaene | 1377 | 0.81 ± 0.06 a | nd | 0.73 ± 0.06 a | 1,2 | ** |
| β-Cubebene | 1382 | nd | 1.09 ± 0.08 a | nd | 1,2 | ** |
| β-Bourbonene | 1385 | 1.20 ± 0.13 a | nd | 1.23 ± 0.43 a | 1,2 | ** |
| α-Bergamotene | 1403 | nd | 1.30 ± 0.06 a | nd | 1,2 | ** |
| α-Gurjunene | 1407 | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | nd | 0.34 ± 0.01 a | 1,2 | ** |
| trans-Caryophyllene | 1415 | 4.53 ± 0.15 c | 4.73 ± 0.23 b | 4.96 ± 0.14 a | 1,2,3 | ** |
| Aromadendrene | 1437 | 1.00 ± 0.06 b | 2.31 ± 0.10 a | 0.84 ± 0.06 c | 1,2 | ** |
| β-Farnesene | 1441 | nd | 0.86 ± 0.04 a | 0.67 ± 0.01 b | 1,2 | ** |
| α-Humulene | 1455 | 3.91 ± 0.32 a | 3.41 ± 0.64 b | 3.10 ± 0.01 c | 1,2 | ** |
| allo-Aromadendrene | 1463 | 0.34 ± 0.03 c | 1.15 ± 0.08 a | 0.46 ± 0.06 b | 1,2 | ** |
| β-Selinene | 1475 | 0.20 ± 0.02 a | nd | 0.24 ± 0.01 a | 1,2 | ** |
| Germacrene D | 1477 | 0.21 ± 0.04 a | nd | 0.19 ± 0.02 a | 1,2 | ** |
| γ-Muurolene | 1478 | 1.08 ± 0.15 b | 3.76 ± 0.32 a | 0.25 ± 0.01 c | 1,2 | ** |
| γ-Cadinene | 1515 | 0.85 ± 0.07 b | 0.92 ± 0.05 a | 0.87 ± 0.01 b | 1,2 | ** |
| δ-Cadinene | 1526 | 1.30 ± 0.01 b | 2.40 ± 0.23 a | 0.97 ± 0.22 c | 1,2 | ** |
| Spathulenol | 1578 | 0.64 ± 0.03 a | nd | 0.30 ± 0.01 b | 1,2 | ** |
| Caryophyllene oxide | 1580 | 0.23 ± 0.01 a | 0.17 ± 0.05 b | 0.28 ± 0.04 a | 1,2 | ** |
| Viridiflorol | 1591 | 4.13 ± 0.54 a | 3.30 ± 0.24 b | 2.90 ± 0.01 c | 1,2 | ** |
| Calarene | 1629 | 2.42 ± 0.11 a | nd | 1.77 ± 0.11 b | 1,2 | ** |
| Manoyl oxide | 1989 | 0.97 ± 0.06 a | 0.23 ± 0.01 c | 0.88 ± 0.01 b | 1,2 | ** |
| Manool | 2055 | 2.41 ± 0.43 a | 1.12 ± 0.13 c | 2.23 ± 0.13 b | 1,2 | ** |
| Sclareol | 2226 | 5.15 ± 0.54 a | 4.16 ± 0.24 b | 3.97 ± 0.01 c | 1,2 | ** |
| Total | 96.30 | 97.56 | 96.69 |
| AChE | BChE | SI (BChE/AChE) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | |||
| S1 | 47.68 ± 1.81 **** | 70.94 ± 2.80 **** | 1.48 |
| S2 | 58.35 ± 2.05 **** | 63.43 ± 2.43 **** | 1.08 |
| S3 | 77.51 ± 2.91 **** | 33.13 ± 1.33 **** | 0.42 |
| Physostigmine | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 2.0 |
| Sample | DPPH Test IC50 (µg/mL) | ABTS Test IC50 (µg/mL) | β-Carotene Bleaching Test IC50 (µg/mL) | FRAP Test μM Fe (II)/g | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t 30 min | t 60 min | ||||
| S. officinalis | |||||
| S1 | 31.58% a | 39.63 ± 3.43 **** | 54.81 ± 3.43 **** | 59.69 ± 3.66 **** | 3.11 ± 1.61 **** |
| S2 | 35.33% a | 20.64 ± 1.90 **** | 38.06 ± 2.28 **** | 46.32 ± 2.74 **** | 0.73 ± 0.09 **** |
| S3 | 32.52% a | 24.52 ± 2.67 **** | 50.07 ± 3.09 **** | 70.25 ± 3.93 **** | 1.56 ± 1.02 **** |
| Positive Control | |||||
| Ascorbic acid | 5.02 ± 0.80 | 1.71 ± 0.06 | |||
| Propyl gallate | 0.09 ± 0.004 | 0.09 ± 0.004 | |||
| BHT | 63.22 ± 4.3 | ||||
Sample Availability: Sample of sage EOs are available from the authors. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tundis, R.; Leporini, M.; Bonesi, M.; Rovito, S.; Passalacqua, N.G. Salvia officinalis L. from Italy: A Comparative Chemical and Biological Study of Its Essential Oil in the Mediterranean Context. Molecules 2020, 25, 5826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245826
Tundis R, Leporini M, Bonesi M, Rovito S, Passalacqua NG. Salvia officinalis L. from Italy: A Comparative Chemical and Biological Study of Its Essential Oil in the Mediterranean Context. Molecules. 2020; 25(24):5826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245826
Chicago/Turabian StyleTundis, Rosa, Mariarosaria Leporini, Marco Bonesi, Simone Rovito, and Nicodemo G. Passalacqua. 2020. "Salvia officinalis L. from Italy: A Comparative Chemical and Biological Study of Its Essential Oil in the Mediterranean Context" Molecules 25, no. 24: 5826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245826
APA StyleTundis, R., Leporini, M., Bonesi, M., Rovito, S., & Passalacqua, N. G. (2020). Salvia officinalis L. from Italy: A Comparative Chemical and Biological Study of Its Essential Oil in the Mediterranean Context. Molecules, 25(24), 5826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245826