Morolic Acid 3-O-Caffeate Inhibits Adipogenesis by Regulating Epigenetic Gene Expression
Abstract
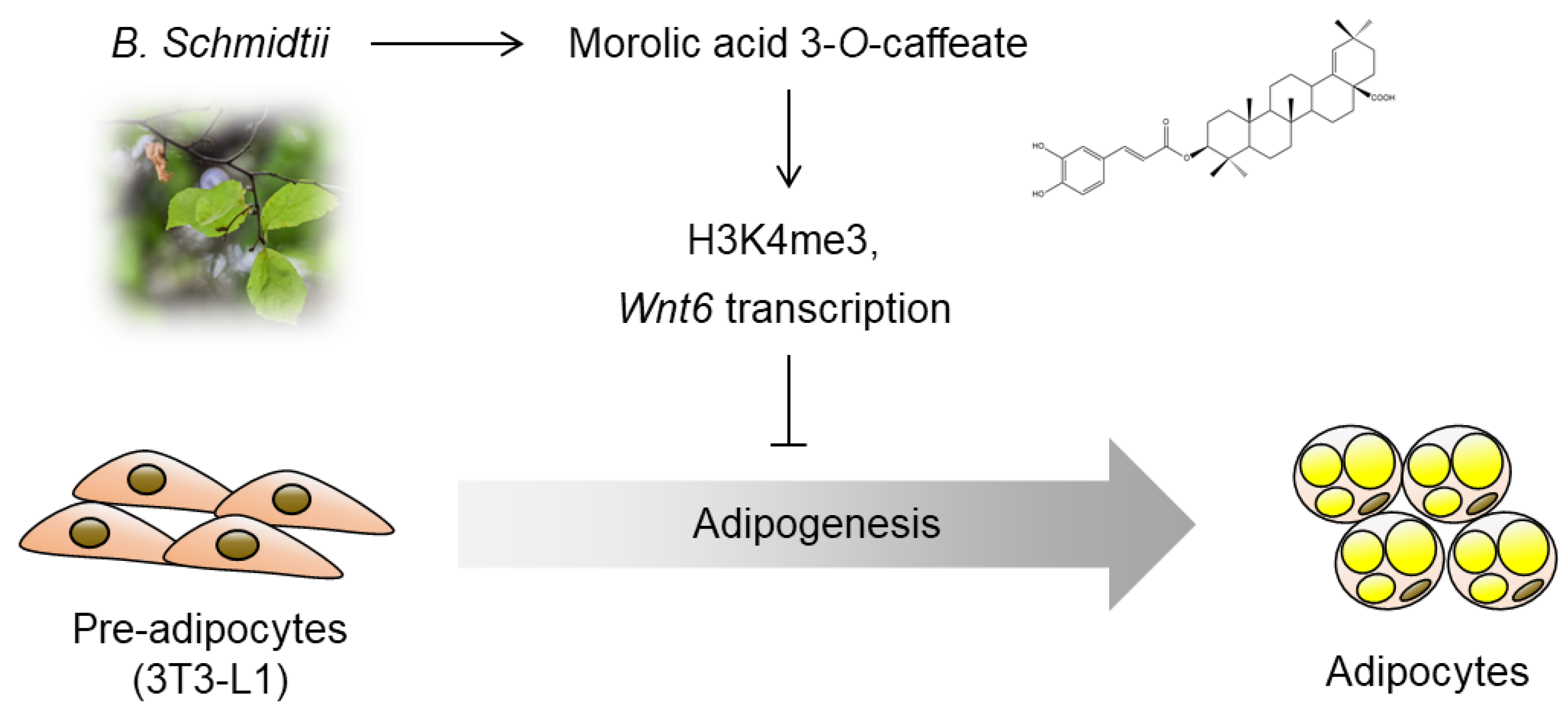
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
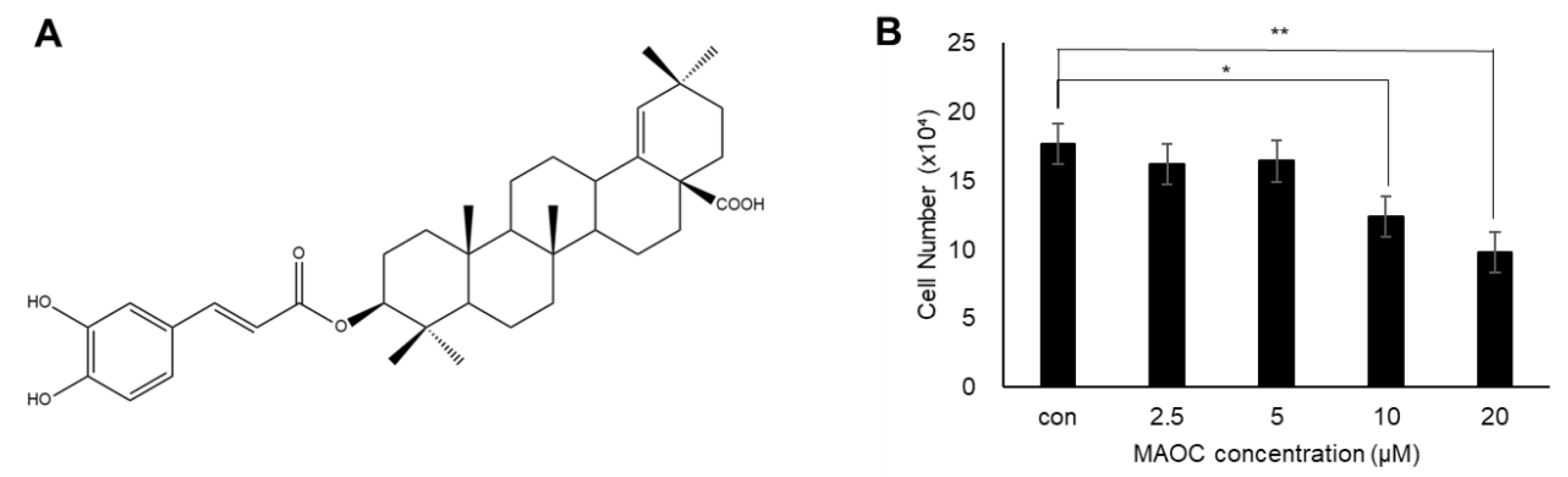
2.1. Viability of 3T3-L1 Cells Treated with Morolic Acid 3-O-Caffeate
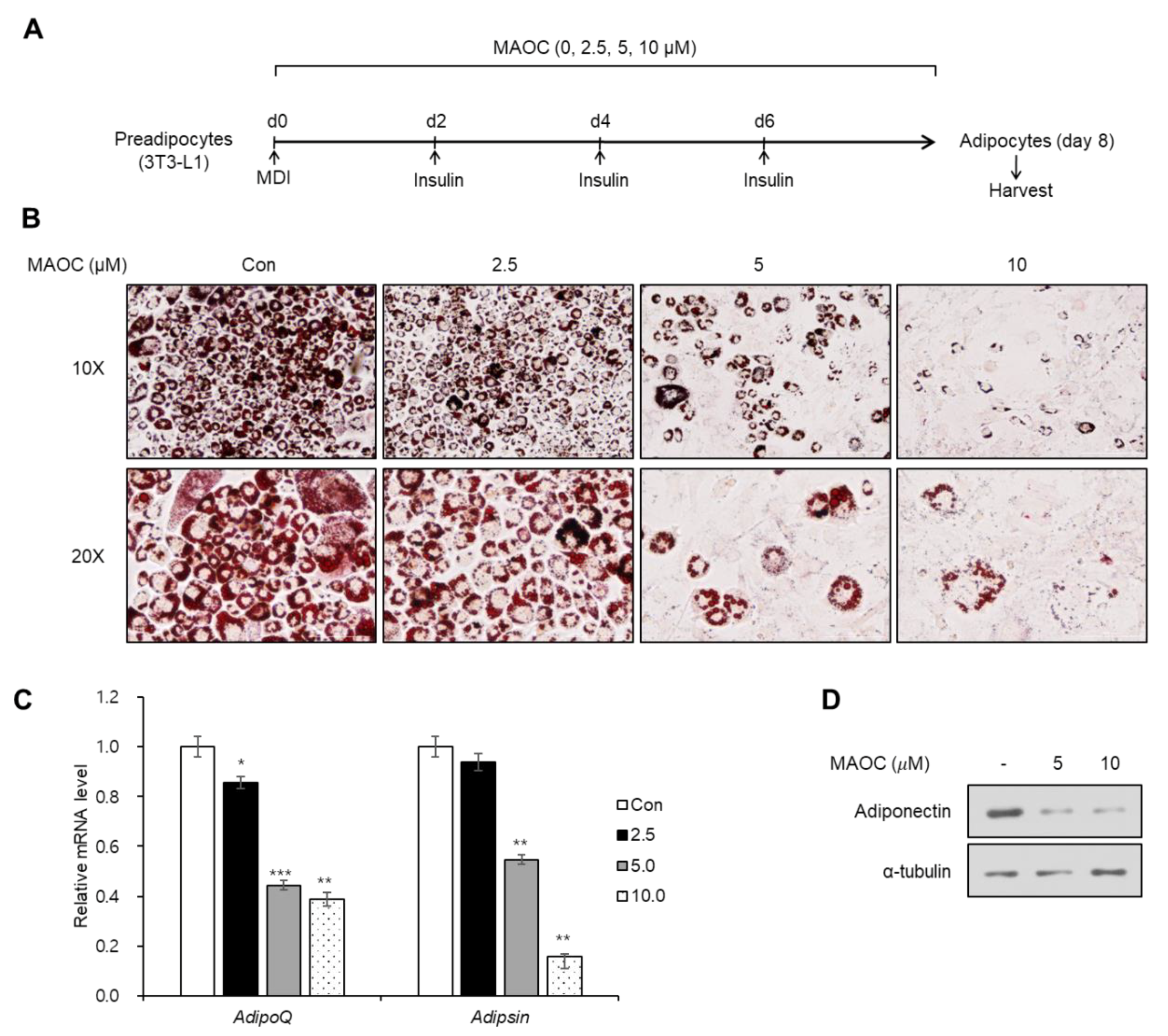
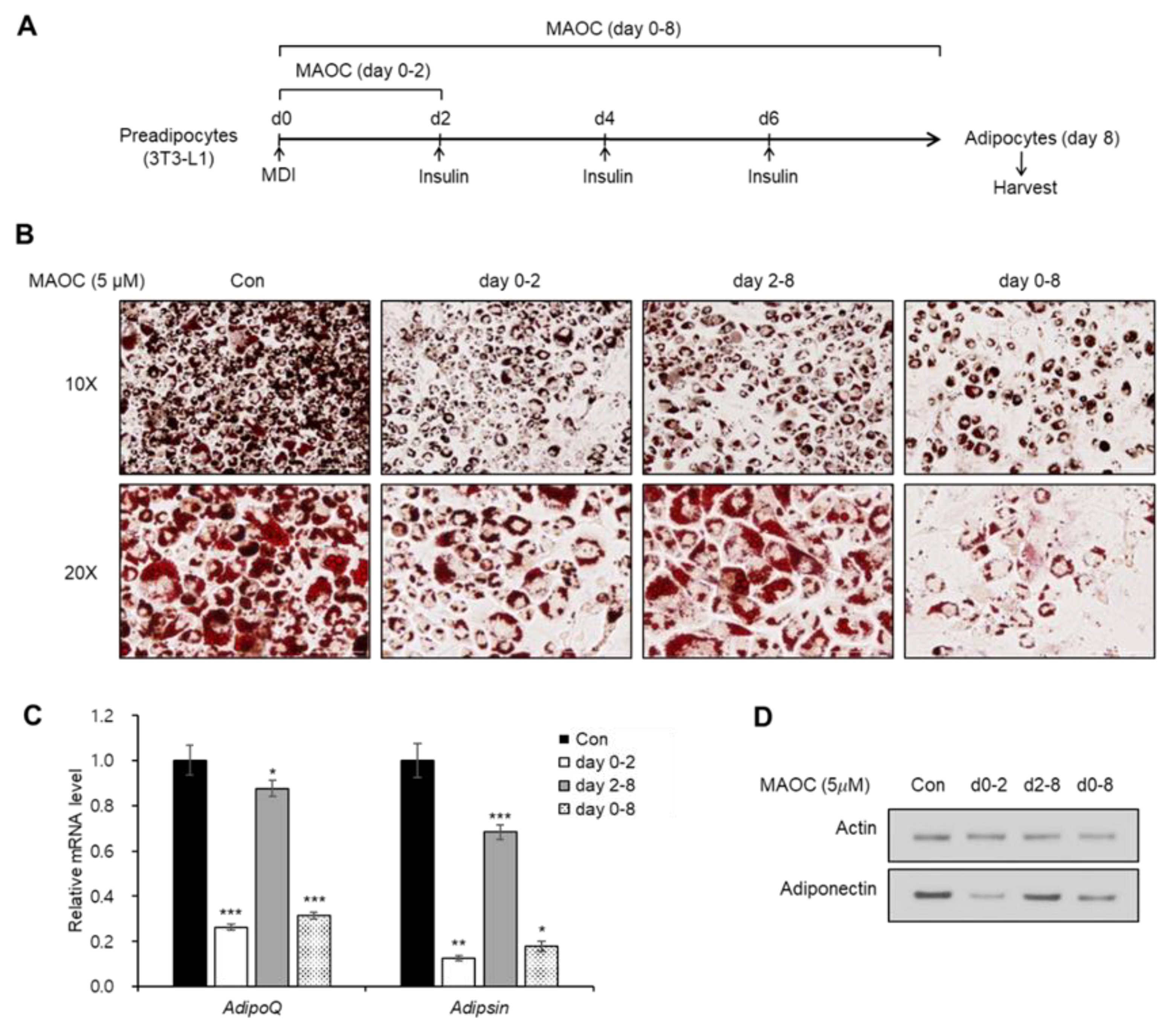
2.2. Inhibitory Effects of Morolic Acid 3-O-Caffeate on Adipogenesis
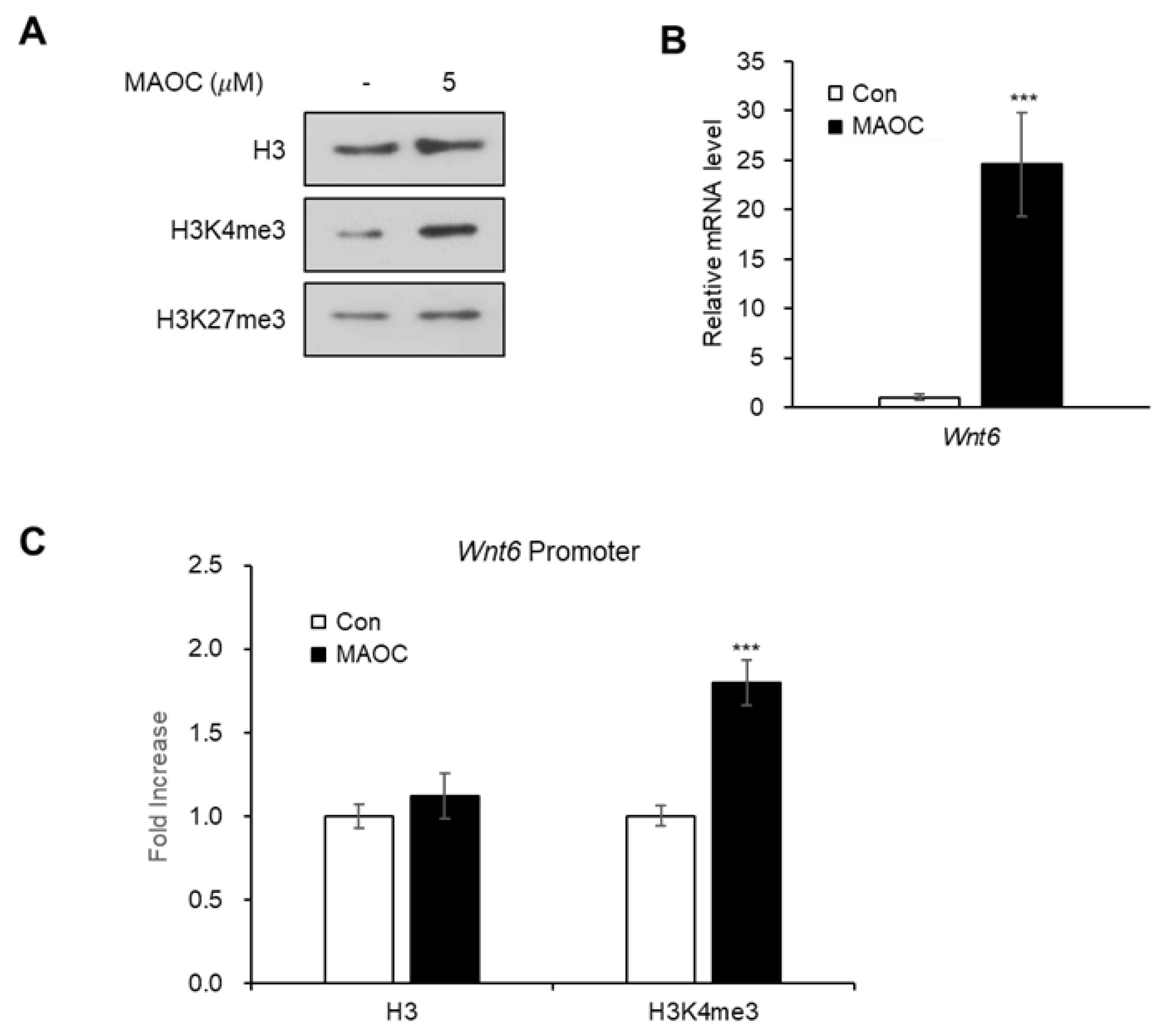
2.3. Epigenetic Activation of Wnt6 Expression by Morolic Acid 3-O-Caffeate
3. Materials and Methodsα
3.1. Isolation of Morolic Acid 3-O-Caffeate (MAOC)
3.2. Cell Culture and Differentiation
3.3. Cell Counting
3.4. Oil Red O Staining
3.5. Reverse Transcription (RT) and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
3.6. Western Blot
3.7. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-qPCR
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spiegelman, B.M.; Flier, J.S. Obesity and the Regulation of Energy Balance. Cell 2001, 104, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaben, A.L.; Scherer, P.E. Adipogenesis and metabolic health. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.J.; Cha, J.M.; Subedi, L.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, K.R. Phenolic constituents from the twigs of Betula schmidtii collected in Goesan, Korea. Phytochemistry 2019, 167, 112085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.J.; Subedi, L.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, S.U.; Lee, K.R. Bioactive triterpenoids from twigs of Betula schmidtii. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 77, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.-Y.; Kang, S.-W.; Kim, J.-L.; Li, J.; Lee, E.-S.; Gong, J.-H.; Han, S.J.; Kang, Y.-H. Oleanolic acid reduces markers of differentiation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Nutr. Res. 2010, 30, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C. Ursolic acid inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through LKB1/AMPK pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Garibay, A.S.; López-Vázquez, A.; García-Bañuelos, J.; Sánchez-Enríquez, S.; Sandoval-Rodríguez, A.S.; Arreola, S.D.T.; Bueno-Topete, M.R.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Hita, M.E.G.; Domínguez-Rosales, J.A.; et al. Effect of Ursolic Acid on Insulin Resistance and Hyperinsulinemia in Rats with Diet-Induced Obesity: Role of Adipokines Expression. J. Med. Food 2020, 23, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulda, S.; Scaffidi, C.; Susin, S.A.; Krammer, P.H.; Kroemer, G.; Peter, M.E.; Debatin, K.M. Activation of mitochondria and release of mitochondrial apoptogenic factors by betulinic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 33942–33948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.I.; Savinova, O.V.; Nikolaeva, S.N.; Boreko, E.I.; Flekhter, O.B. Antiviral activity of betulin, betulinic and betulonic acids against some enveloped and non-enveloped viruses. Fitoterapia 2003, 74, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-D.; Jung, H.-Y.; Ryu, H.G.; Kim, B.; Jeon, J.; Yoo, H.Y.; Park, C.H.; Choi, B.-H.; Hyun, C.-K.; Kim, K.-T.; et al. Betulinic acid inhibits high-fat diet-induced obesity and improves energy balance by activating AMPK. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, G.A.-M.; Abu-Taweel, G.M.; Rajagopal, R.; Sun-Ju, K.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, Y.O.; Mothana, R.A.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Siddiqui, N.A.; et al. Betulinic acid lowers lipid accumulation in adipocytes through enhanced NCoA1-PPARγ interaction. J. Infect. Public Health 2019, 12, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.T.; Hochfeld, W.E.; Myburgh, R.; Pepper, M.S. Adipocyte and adipogenesis. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 92, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.-Q.; Otto, T.C.; Lane, M.D. Mitotic clonal expansion: A synchronous process required for adipogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawthorn, W.P.; Bree, A.J.; Yao, Y.; Du, B.; Hemati, N.; Martinez-Santibañez, G.; MacDougald, O.A. Wnt6, Wnt10a and Wnt10b inhibit adipogenesis and stimulate osteoblastogenesis through a β-catenin-dependent mechanism. Bone 2012, 50, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.D.; MacDougald, O.A. Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, K. Epigenetic regulation of adipogenesis by histone methylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 2012, 1819, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-W.; Hong, S.; Jin, Q.; Wang, L.; Lee, J.-E.; Gavrilova, O.; Ge, K. Histone methylation regulator PTIP is required for PPARgamma and C/EBPalpha expression and adipogenesis. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jin, Q.; Lee, J.E.; Su, I.H.; Ge, K. Histone H3K27 methyltransferase Ezh2 represses Wnt genes to facilitate adipogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7317–7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.A.; Um, S.H.; Lee, J.; Yoo, J.H.; Bang, S.Y.; Park, E.K.; Lee, M.G.; Nam, K.H.; Jeon, Y.J.; Park, J.W.; et al. S6K1 Phosphorylation of H2B Mediates EZH2 Trimethylation of H3: A Determinant of Early Adipogenesis. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Guo, Y.Y.; Li, B.Y.; Peng, W.Q.; Tang, Q.Q. Histone demethylase KDM5A is transactivated by the transcription factor C/EBPβ and promotes preadipocyte differentiation by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 9642–9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamburger, M.; Riese, U.; Graf, H.; Melzig, M.F.; Ciesielski, S.; Baumann, D.; Dittmann, K.; Wegner, C. Constituents in evening primrose oil with radical scavenging, cyclooxygenase, and neutrophil elastase inhibitory activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5533–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knorr, R.; Hamburger, M. Quantitative analysis of anti-inflammatory and radical scavenging triterpenoid esters in evening primrose oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3319–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, W.; Hong, S.S.; Kim, N.; Yang, Y.T.; Shin, Y.S.; Lee, C.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, D. Bioactive triterpenoids from Callistemon lanceolatus. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2009, 32, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.H.; Yi, S.A.; Lee, J.; Lee, M.G.; Park, J.H.; Oh, H.; Lee, J.; Park, J.W.; Han, J.W. Eudesmin impairs adipogenic differentiation via inhibition of S6K1 signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Lee, J.C.; Ha, S.W.; Bang, S.Y.; Park, E.K.; Yi, S.A.; Lee, M.G.; Kim, D.S.; Nam, K.H.; Yoo, J.H.; et al. Requirement of protein l-isoaspartyl O-methyltransferase for transcriptional activation of trefoil factor 1 (TFF1) gene by estrogen receptor alpha. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 420, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.A.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, G.W.; Ryu, H.W.; Park, J.W.; Lee, J.; Han, J.; Park, J.H.; Oh, H.; Lee, J.; et al. HPV-mediated nuclear export of HP1γ drives cervical tumorigenesis by downregulation of p53. Cell Death. Differ. 2020, 27, 2537–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compound (morolic acid 3-O-caffeate) are available from the authors. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chae, S.I.; Yi, S.A.; Nam, K.H.; Park, K.J.; Yun, J.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, J.; Han, J.-W. Morolic Acid 3-O-Caffeate Inhibits Adipogenesis by Regulating Epigenetic Gene Expression. Molecules 2020, 25, 5910. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245910
Chae SI, Yi SA, Nam KH, Park KJ, Yun J, Kim KH, Lee J, Han J-W. Morolic Acid 3-O-Caffeate Inhibits Adipogenesis by Regulating Epigenetic Gene Expression. Molecules. 2020; 25(24):5910. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245910
Chicago/Turabian StyleChae, Sook In, Sang Ah Yi, Ki Hong Nam, Kyoung Jin Park, Jihye Yun, Ki Hyun Kim, Jaecheol Lee, and Jeung-Whan Han. 2020. "Morolic Acid 3-O-Caffeate Inhibits Adipogenesis by Regulating Epigenetic Gene Expression" Molecules 25, no. 24: 5910. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245910
APA StyleChae, S. I., Yi, S. A., Nam, K. H., Park, K. J., Yun, J., Kim, K. H., Lee, J., & Han, J.-W. (2020). Morolic Acid 3-O-Caffeate Inhibits Adipogenesis by Regulating Epigenetic Gene Expression. Molecules, 25(24), 5910. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245910






