Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Arylketones Catalyzed by Enantiopure Ruthenium(II)/Pybox Complexes Containing Achiral Phosphonite and Phosphinite Ligands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Ruthenium(II)/R-pybox Catalysts 1a–1c and 2a–2c
2.2. Catalytic Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Comments
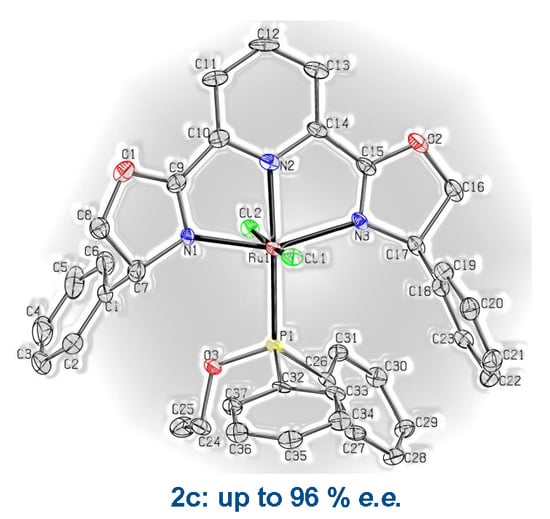
3.2. X-Ray Crystal Structure Determination of Complexes 1a·2CHCl3 and 2c·2.5CH2Cl2
3.3. General Procedure for Hydrogen Transfer Reactions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Demmans, K.Z.; Olson, M.E.; Morris, R.H. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones with Well-Defined Manganese(I) PNN and PNNP Complexes. Organometallics 2018, 37, 4608–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelucci, G.; Baldino, S.; Baratta, W. Recent Advances in Osmium-Catalyzed Hydrogenation and Dehydrogenation Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Astruc, D. The Golden Age of Transfer Hydrogenation. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 6621–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foubelo, F.; Nájera, C.; Yus, M. Catalytic asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones: Recent advances. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2015, 26, 769–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, J.; Nishiyama, H. Recent Topics of Transfer Hydrogenation. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 3133–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoszewicz, A.; Ahlsten, N.; Martín-Matute, B. Enantioselective Synthesis of Alcohols and Amines by Iridium-Catalyzed Hydrogenation, Transfer Hydrogenation, and Related Processes. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 7274–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malacea, R.; Poli, R.; Manoury, E. Asymmetric hydrosilylation, transfer hydrogenation, and hydrogenation of ketones catalyzed by iridium complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 729–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.H. Asymmetric hydrogenation, transfer hydrogenation and hydrosilylation of ketones catalyzed by iron complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2282–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Xiao, J. Broader, Greener, and More Efficient: Recent Advances in Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation. Chem. Asian J. 2008, 3, 1750–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikariya, T.; Blacker, A.J. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones with Bifunctional Transition Metal-Based Molecular Catalysts. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.F.; Xiao, J.L. Aqueous-phase asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones—A greener approach to chiral alcohols. Chem. Commun. 2007, 2449–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladiali, S.; Alberico, E. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation: Chiral ligands and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noyori, R.; Hashiguchi, S. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation Catalyzed by Chiral Ruthenium Complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 1997, 30, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X. A New Chiral Bis(oxazolinylmethyl)amine Ligand for Ru-Catalyzed Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 3817–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enthaler, S.; Hagemann, B.; Bohr, S.; Anilkumar, G.; Tse, M.K.; Bitterlich, B.; Junge, K.; Erre, G.; Beller, M. New Ruthenium Catalysts for Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Prochiral Ketones. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Z. Ru(II) pyridyl-based NNN complex catalysts for (asymmetric) transfer hydrogenation of ketones at room temperature. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Zhao, M.; Yu, Z. Ruthenium(II) Pyrazolyl–Pyridyl–Oxazolinyl Complex Catalysts for the Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 10843–10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Zhao, M.; Du, W.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, K.; Wu, P.; Yu, Z. Highly Active Ruthenium(II) Complex Catalysts Bearing an Unsymmetrical NNN Ligand in the (Asymmetric) Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 4737–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuervo, D.; Gamasa, M.P.; Gimeno, J. New Chiral Ruthenium(II) Catalysts Containing 2,6-Bis(4′-(R)-phenyloxazolin-2′-yl)pyridine (Ph-pybox) Ligands for Highly Enantioselective Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, E.; Lastra, E.; Gamasa, M.P. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones Catalyzed by Enantiopure Osmium(II) Pybox Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 6193–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Julián, E.; Menéndez-Pedregal, E.; Claros, M.; Vaquero, M.; Díez, J.; Lastra, E.; Gamasa, P.; Pizzano, A. Practical synthesis of enantiopure benzylamines by catalytic hydrogenation or transfer hydrogenation reactions in isopropanol using a Ru-pybox catalyst. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menéndez-Pedregal, E.; Díez, J.; Manteca, A.; Sánchez, J.; Bento, A.C.; García-Navas, R.; Mollinedo, F.; Lastra, E. Antitumor activity of new enantiopure pybox-ruthenium complexes. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 13955–13967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuervo, D.; Menéndez-Pedregal, E.; Díez, J.; Gamasa, M.P. Mononuclear ruthenium(II) complexes bearing the (S,S)-iPr-pybox ligand. J. Organometal. Chem. 2011, 696, 1861–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolman, C.A. Steric effects of phosphorus ligands in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1977, 77, 313–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolman, C.A. Electron donor-acceptor properties of phosphorus ligands. Substituent additivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1970, 92, 2953–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In order to get access to the corresponding (R)-alcohols, the optimization of the ATH reaction of ketones using the iPr-pybox catalyst 1c was attempted. Unfortunately, following the optimization pattern described for complex 2c (entry 13, Table 2) only moderate results (up to 96% conversion and 61% e.e.) could be achieved in the reduction of acetophenone (unpublished results).
- The reduction of aryl ketones with electron-withdrawing susbstituents (2-,3- and 4-bromoacetophenone) using the catalyst [RuCl2{PPh2(OEt)}{(R,R)-Ph-pybox}] (2c) led to poorer results (<23% conversion and < 45% ee) (unpublished results).
- Samec, J.S.M.; Bäckvall, J.-E.; Andersson, P.G.; Brandt, P. Mechanistic aspects of transition metal-catalyzed hydrogen transfer reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, S.E.; Hadzovic, A.; Morris, R.H. Mechanisms of the H2-hydrogenation and transfer hydrogenation of polar bonds catalyzed by ruthenium hydride complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 2201–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckvall, J.E. Transition metal hydrides as active intermediates in hydrogen transfer reactions. J. Organomet. Chem. 2002, 652, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pàmies, O.; Bäckvall, J.-E. Studies on the Mechanism of Metal-Catalyzed Hydrogen Transfer from Alcohols to Ketones. Chem. Eur. J. 2001, 7, 5052–5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unfortunately, all attempts to synthesize the cis-dichloro (R,R)-Ph-pybox complexes containing phosphonite and phosphinite ligands have failed, leading to either trans-dichloro isomers (2a-2c) or an uncharacterized mixture of products, thus precluding a comparative study of the trans-complexes 2 and the corresponding cis-complexes (unpublished results). cis.
- Nishiyama, H.; Itoh, Y.; Sugawara, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Aoki, K.; Itoh, K. Chiral Ruthenium(II)–Bis(2-oxazolin-2-yl)pyridine Complexes. Asymmetric Catalytic Cyclopropanation of Olefins and Diazoacetates. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1995, 68, 1247–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, H.; Itoh, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Park, S.-B.; Itoh, K. New Chiral Ruthenium Bis(oxazolinyl)pyridine Catalyst. Efficient Asymmetric Cyclopropanation of Olefins with Diazoacetates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 2223–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CrysAlisPro CCD and CrysAlisPro RED; Oxford Diffraction Ltd.: Abingdon, UK, 2008.
- Farrugia, L.J. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: An update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beurskens, P.T.; Beurskens, G.; de Gelder, R.; Smits, J.M.M.; García-Granda, S.; Gould, R.O.; Smykalla, C. The DIRDIF Program System, Technical Report of the Crystallographic Laboratory; University of Nijmegen: Nijmegen, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Spek, A.L. PLATON: A Multipurpose Crystallographic Tool; University of Utrecht: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXL2013: Program for the Refinement of Crystal Structures; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- International Tables for X-Ray Crystallography; Kynoch Press: Birminghan, UK, 1974; Volume 4.
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |


 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalyst | Time (min) | Conv. (%) a | e.e. (%) a | |
| 1 | [RuCl2{PPh(OMe)2}(iPr-pybox)] (1a) | 15 | 63 | 16 (R) |
| 2 | 90 | 97 | 20 (R) | |
| 3 | [RuCl2{PPh2(OMe)}(iPr-pybox)] (1b) | 15 | 96 | 43 (R) |
| 4 | [RuCl2{PPh2(OEt)}(iPr-pybox)] (1c) | 15 | 95 | 62 (R) |
| 5 | [RuCl2{PPh(OMe)2}(Ph-pybox)] (2a) | 15 | 67 | 5 (S) |
| 6 | 90 | 98 | 11 (S) | |
| 7 | [RuCl2{PPh2(OMe)}(Ph-pybox)] (2b) | 15 | 48 | 46 (S) |
| 8 | 90 | 92 | 46 (S) | |
| 9 | [RuCl2{PPh2(OEt)}(Ph-pybox)] (2c) | 15 | 95 | 63 (S) |
| Catalyst Loading (mol %) | iPrOH (mL) | Base | Ketone/BaseRatio | Time (min) | Conversion (%) b | e.e. (%) (S) b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2 | 50 | KOtBu | 500/24 | 15 | 95 | 63 |
| 2 | 0.1 | 50 | KOtBu | 500/24 | 30 | 79 | 67 |
| 3 | 0.3 | 50 | KOtBu | 500/24 | 15 | 91 | 70 |
| 4 | 0.4 | 50 | KOtBu | 500/24 | 15 | 93 | 66 |
| 5 | 0.3 | 75 | KOtBu | 500/24 | 5 | 91 | 87 |
| 6 | 0.3 | 75 | KOtBu | 500/24 | 15 | 97 | 83 |
| 7 | 0.3 | 75 | NaOH | 500/24 | 10 | 95 | 83 |
| 8 | 0.3 | 75 | NaOtBu | 500/24 | 5 | 97 | 89 |
| 9 | 0.3 | 75 | NaOtBu | 500/24 | 10 | 97 | 86 |
| 10 | 0.3 | 75 | KOH | 500/24 | 30 | 95 | 67 |
| 11 | 0.3 | 75 | Cs2CO3 | 500/24 | 30 | 95 | 78 |
| 12 | 0.3 | 75 | NaOtBu | 500/12 | 5 | 96 | 92 |
| 13 | 0.3 | 75 | NaOtBu | 500/6 | 5 | 97 | 90 |
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ketone | Time (min) | TOF (h−1) b | Conversion (%) c | e.e. (%) (S) c | |
| 1 |  | 5 | 3840 | 96 | 92 |
| 2 |  | 10 | 3040 | 97 | 96 |
| 3 |  | 5 | 3840 | 96 | 87 |
| 4 |  | 5 | 3920 | 98 | 90 |
| 5 |  | 5 | 3440 | 86 | 89 |
| 6 |  | 45 | 500 | 54 | 72 |
| 7 | 90 | 500 | 75 | 68 | |
| 8 |  | 10 | 720 | 51 | 91 |
| 9 | 60 | 720 | 90 | 87 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Claros, M.; de Julián, E.; Díez, J.; Lastra, E.; Gamasa, M.P. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Arylketones Catalyzed by Enantiopure Ruthenium(II)/Pybox Complexes Containing Achiral Phosphonite and Phosphinite Ligands. Molecules 2020, 25, 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25040990
Claros M, de Julián E, Díez J, Lastra E, Gamasa MP. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Arylketones Catalyzed by Enantiopure Ruthenium(II)/Pybox Complexes Containing Achiral Phosphonite and Phosphinite Ligands. Molecules. 2020; 25(4):990. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25040990
Chicago/Turabian StyleClaros, Miguel, Eire de Julián, Josefina Díez, Elena Lastra, and M. Pilar Gamasa. 2020. "Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Arylketones Catalyzed by Enantiopure Ruthenium(II)/Pybox Complexes Containing Achiral Phosphonite and Phosphinite Ligands" Molecules 25, no. 4: 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25040990
APA StyleClaros, M., de Julián, E., Díez, J., Lastra, E., & Gamasa, M. P. (2020). Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Arylketones Catalyzed by Enantiopure Ruthenium(II)/Pybox Complexes Containing Achiral Phosphonite and Phosphinite Ligands. Molecules, 25(4), 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25040990