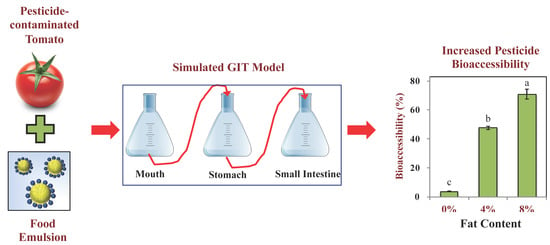
Impact of Pesticide Type and Emulsion Fat Content on the Bioaccessibility of Pesticides in Natural Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Initial Emulsion Characteristics
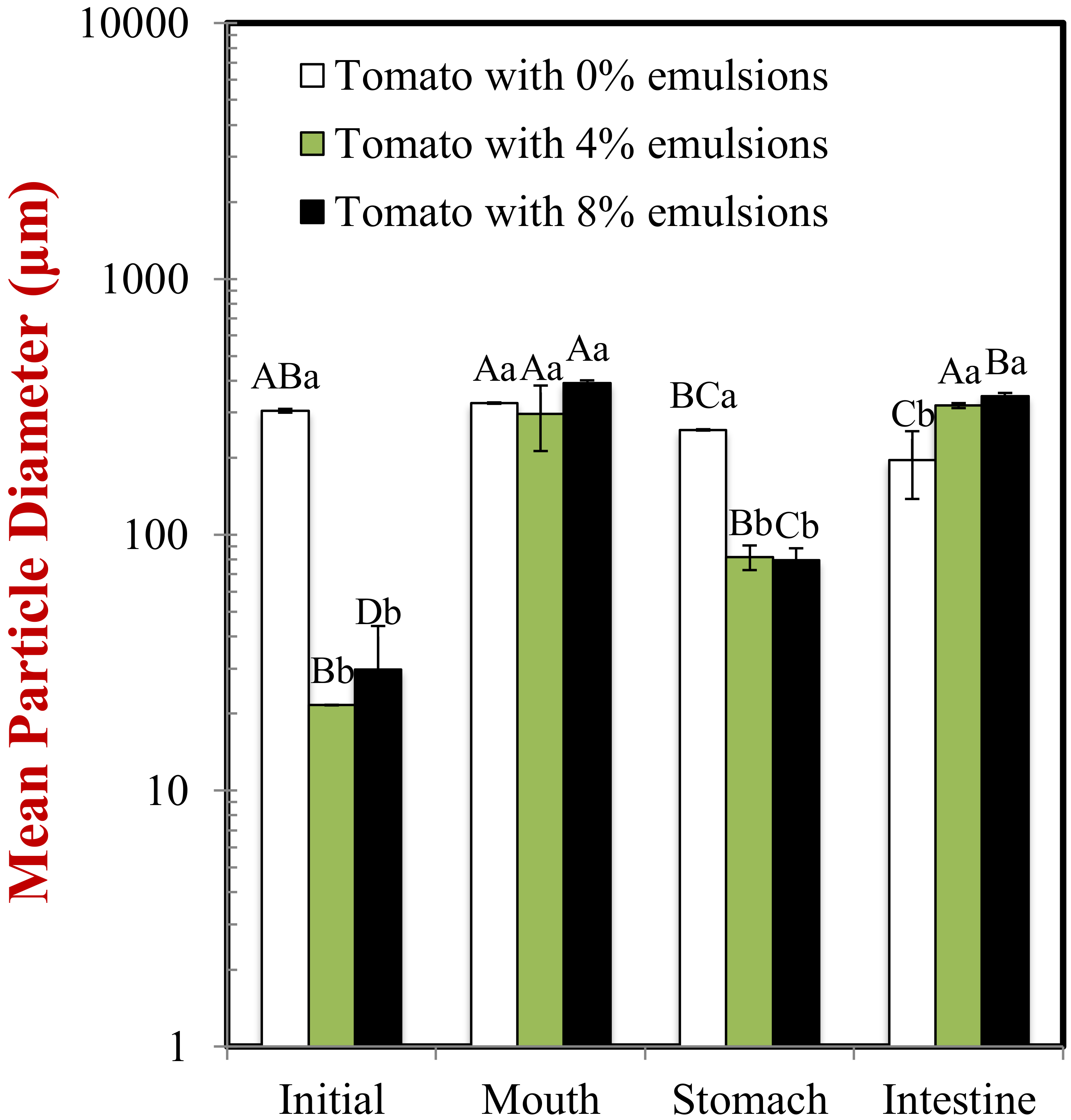
2.2. Impact of GIT Conditions on Particle Properties
2.2.1. Initial Samples
2.2.2. Mouth
2.2.3. Stomach
2.2.4. Small Intestine
2.3. Lipid Digestion Profiles
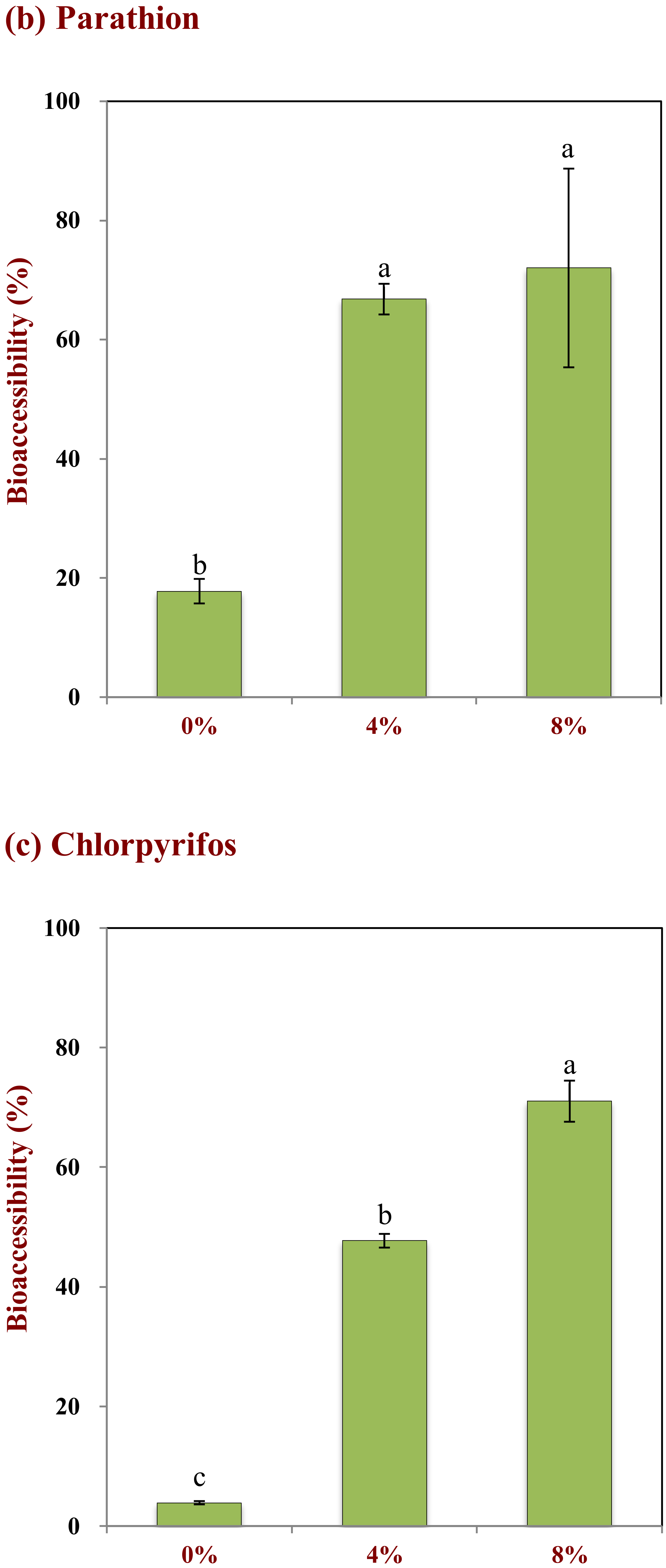
2.4. Pesticides Bioaccessibility
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Pesticide-Enriched Model Food Preparation
3.3. Emulsion Preparation
3.4. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT) Model
3.5. Particle Characterization
3.6. Pesticide Bioaccessibility
3.7. Pesticide Quantification
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vilela, A.; Cosme, F.; Pinto, T. Emulsions, Foams, and Suspensions: The Microscience of the Beverage Industry. Beverages 2018, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friberg, S.; Larsson, K.; Sjoblom, J. Food Emulsions; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J.; Xiao, H. Excipient foods: designing food matrices that improve the oral bioavailability of pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1320–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Enhancing nutraceutical bioavailability through food matrix design. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Li, F.; Xiao, H. The Nutraceutical Bioavailability Classification Scheme: Classifying Nutraceuticals According to Factors Limiting their Oral Bioavailability. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 299–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, R.; Martins, J.; Duarte, C.; Vicente, A.; Pinheiro, A.C. Advances in nutraceutical delivery systems: From formulation design for bioavailability enhancement to efficacy and safety evaluation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 270–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopec, R.E.; Failla, M.L. Recent advances in the bioaccessibility and bioavailability of carotenoids and effects of other dietary lipophiles. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 68, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, B. Nanoemulsions for food fortification with lipophilic vitamins: Production challenges, stability, and bioavailability. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1500539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikos, V.; Ranawana, V. Designing emulsion droplets of foods and beverages to enhance delivery of lipophilic bioactive components—A review of recent advances. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 52, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; McClements, D.J.; Xiao, H. Improving oral bioavailability of nutraceuticals by engineered nanoparticle-based delivery systems. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 2, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi, J.S.; Vyas, S.P.; Dixit, V. Effect of Various Lipid-Bile Salt Mixed Micelles on the Intestinal Absorption of Amphotericin-B in Rat. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1998, 24, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkhus, B.; Afseth, N.K.; Borge, G.I.A.; Grimsby, S.; Steppeler, C.; Krona, A.; Langton, M. Increased release of carotenoids and delayed in vitro lipid digestion of high pressure homogenized tomato and pepper emulsions. Food Chem. 2019, 285, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, A.A.O.; Mercadante, A. The bioaccessibility of carotenoids impacts the design of functional foods. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.Q.; Liang, R.; Williams, P.A.; Zhong, F. Factors affecting the bioaccessibility of beta-carotene in lipid-based microcapsules: Digestive conditions, the composition, structure and physical state of microcapsules. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 77, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGregor, K.J.; Embleton, J.K.; Lacy, J.E.; Perry, E.; Solomon, L.J.; Seager, H.; Pouton, C. Influence of lipolysis on drug absorption from the gastro-intestinal tract. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 25, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Velikov, K. Colloidal delivery systems in foods: A general comparison with oral drug delivery. LWT 2011, 44, 1958–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.-W.; Huang, Q. Enhancing Stability and Oral Bioavailability of Polyphenols Using Nanoemulsions; American Chemical Society (ACS): Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2009; pp. 198–212. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J.; Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, L.; Yao, M.; Xiao, H. Boosting the bioavailability of hydrophobic nutrients, vitamins, and nutraceuticals in natural products using excipient emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2016, 88, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Verkempinck, S.; Zhang, X.; Van Loey, A.; Grauwet, T.; Hendrickx, M. Comparative study on lipid digestion and carotenoid bioaccessibility of emulsions, nanoemulsions and vegetable-based in situ emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Delso, N.; Amaral-Rogers, V.; Belzunces, L.P.; Bonmatin, J.M.; Chagnon, M.; Downs, C.; Furlan, L.; Gibbons, D.W.; Giorio, C.; Girolami, V.; et al. Systemic insecticides (neonicotinoids and fipronil): trends, uses, mode of action and metabolites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 22, 5–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keikotlhaile, B.; Spanoghe, P.; Steurbaut, W. Effects of food processing on pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables: A meta-analysis approach. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantke, P.; Juraske, R. Variability of Pesticide Dissipation Half-Lives in Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3548–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Park, Y.; He, L.; Xing, B.; McClements, D.J. Effect of the Composition and Structure of Excipient Emulsion on the Bioaccessibility of Pesticide Residue in Agricultural Products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9128–9138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Enhanced delivery of lipophilic bioactives using emulsions: a review of major factors affecting vitamin, nutraceutical, and lipid bioaccessibility. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, L.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, G.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Impact of Lipid Content on the Ability of Excipient Emulsions to Increase Carotenoid Bioaccessibility from Natural Sources (Raw and Cooked Carrots). Food Biophys. 2015, 11, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikos, V.; Hayward, N.; Hayes, H.; Meroni, E.; Ranawana, V. Optimising the ratio of long- to short-chain triglycerides of the lipid phase to enhance physical stability and bioaccessibility of lycopene-loaded beverage emulsions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 54, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosiewicz, J.; McCammon, J.; Gilson, M.K. Prediction of Ph-dependent Properties of Proteins. J. Mol. Boil. 1994, 238, 415–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, L.; James, M.N.G. Carboxyl–carboxylate interactions in proteins. Nature 1982, 295, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, T.; Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, T.; McClements, D.J. Potential physicochemical basis of Mediterranean diet effect: Ability of emulsified olive oil to increase carotenoid bioaccessibility in raw and cooked tomatoes. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, T.; Liu, C.; Dai, T.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; McClemnets, D.J. Enhancement of Carotenoid Bioaccessibility from Tomatoes Using Excipient Emulsions: Influence of Particle Size. Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansil, R.; Turner, B.S. Mucin structure, aggregation, physiological functions and biomedical applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; McClements, D.J. Influence of emulsifier type on the in vitro digestion of fish oil-in-water emulsions in the presence of an anionic marine polysaccharide (fucoidan): Caseinate, whey protein, lecithin, or Tween 80. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of emulsifier type on gastrointestinal fate of oil-in-water emulsions containing anionic dietary fiber (pectin). Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.G.; Meijer, R.J.G.M.; Slangen, C.J.; Beresteijn, E.C.H. Raising the pH of the pepsin-catalysed hydrolysis of bovine whey proteins increases the antigenicity of the hydrolysates. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1995, 25, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaldi, N.; Shields, D.C. Shift in the isoelectric-point of milk proteins as a consequence of adaptive divergence between the milks of mammalian species. Boil. Direct 2011, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hu, M.; McClements, D.J. Factors affecting lipase digestibility of emulsified lipids using an in vitro digestion model: Proposal for a standardised pH-stat method. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, C.J.H.; Wasan, K.M.; Constantinides, P. Lipid-based systems for the enhanced delivery of poorly water soluble drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 615–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XLogP3 of Bendiocarb. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/2314 (accessed on 21 March 2020).
- XLogP3 of Parathion. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/991 (accessed on 21 March 2020).
- XLogP3 of Chlorpyrifos. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/2730 (accessed on 21 March 2020).
- Ghoraba, Z.; Aibaghi, B.; Soleymanpour, A. Ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by ion mobility spectrometry for the simultaneous determination of bendiocarb and azinphos-ethyl in water, soil, food and beverage samples. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 165, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Chen, L.; Tong, Q.; McClements, D.J. Designing hydrogel particles for controlled or targeted release of lipophilic bioactive agents in the gastrointestinal tract. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 72, 698–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aysal, P.; Gözek, K.; Artik, N.; Tunçbilek, A.Ş. 14 C-Chlorpyrifos Residues in Tomatoes and Tomato Products. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1999, 62, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaiko, J.; McClements, D.J. Optimization of isothermal low-energy nanoemulsion formation: Hydrocarbon oil, non-ionic surfactant, and water systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 425, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, R.; Tan, Y.; Lv, S.; McClements, D.J. Impact of Pesticide Type and Emulsion Fat Content on the Bioaccessibility of Pesticides in Natural Products. Molecules 2020, 25, 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061466
Zhang R, Zhang Z, Li R, Tan Y, Lv S, McClements DJ. Impact of Pesticide Type and Emulsion Fat Content on the Bioaccessibility of Pesticides in Natural Products. Molecules. 2020; 25(6):1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061466
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ruojie, Zipei Zhang, Ruyi Li, Yunbing Tan, Shanshan Lv, and David Julian McClements. 2020. "Impact of Pesticide Type and Emulsion Fat Content on the Bioaccessibility of Pesticides in Natural Products" Molecules 25, no. 6: 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061466
APA StyleZhang, R., Zhang, Z., Li, R., Tan, Y., Lv, S., & McClements, D. J. (2020). Impact of Pesticide Type and Emulsion Fat Content on the Bioaccessibility of Pesticides in Natural Products. Molecules, 25(6), 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061466