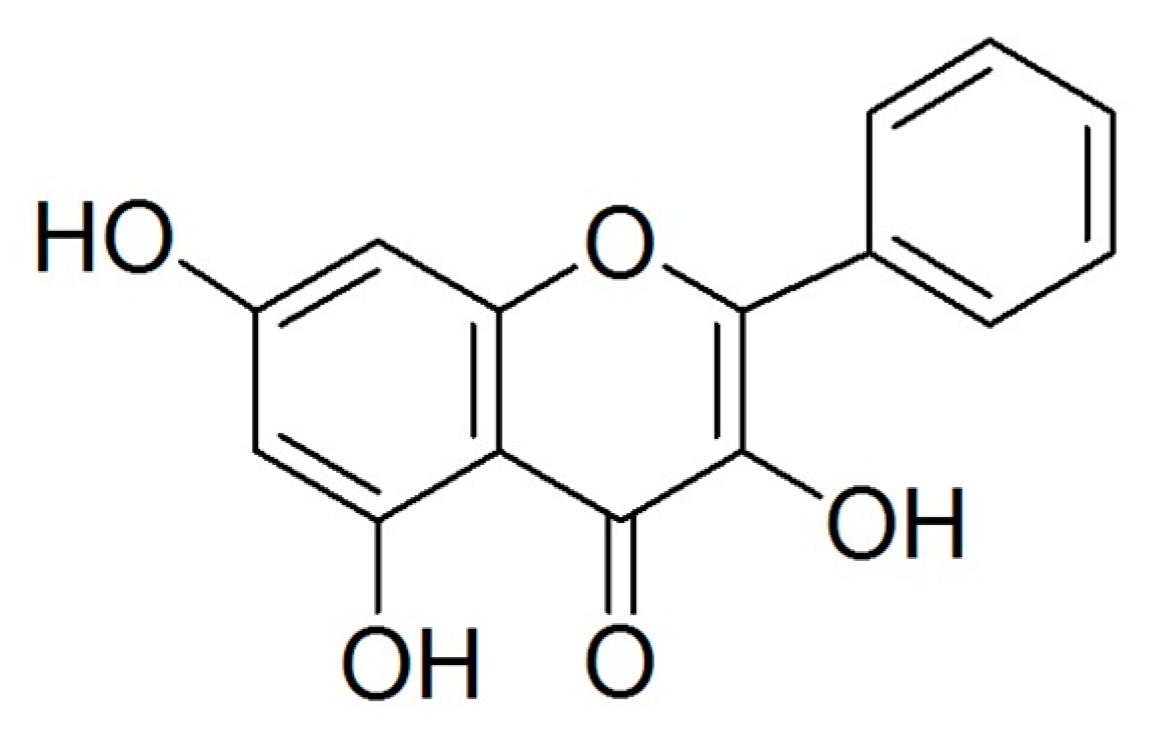
Galangin, a Flavonoid from Lesser Galangal, Induced Apoptosis via p53-Dependent Pathway in Ovarian Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
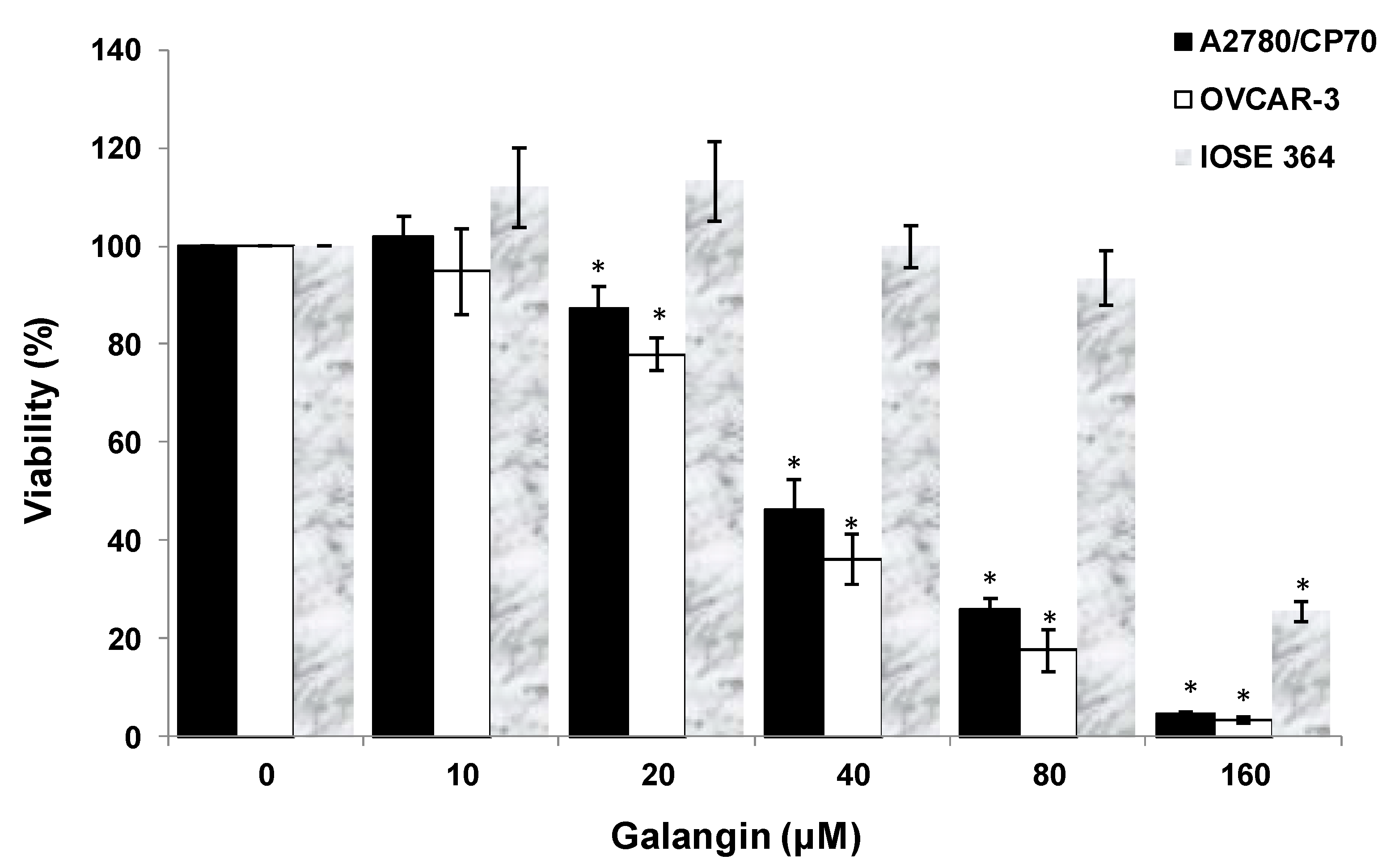
2.1. Galangin Inhibits Proliferation of Ovarian Cancer Cells
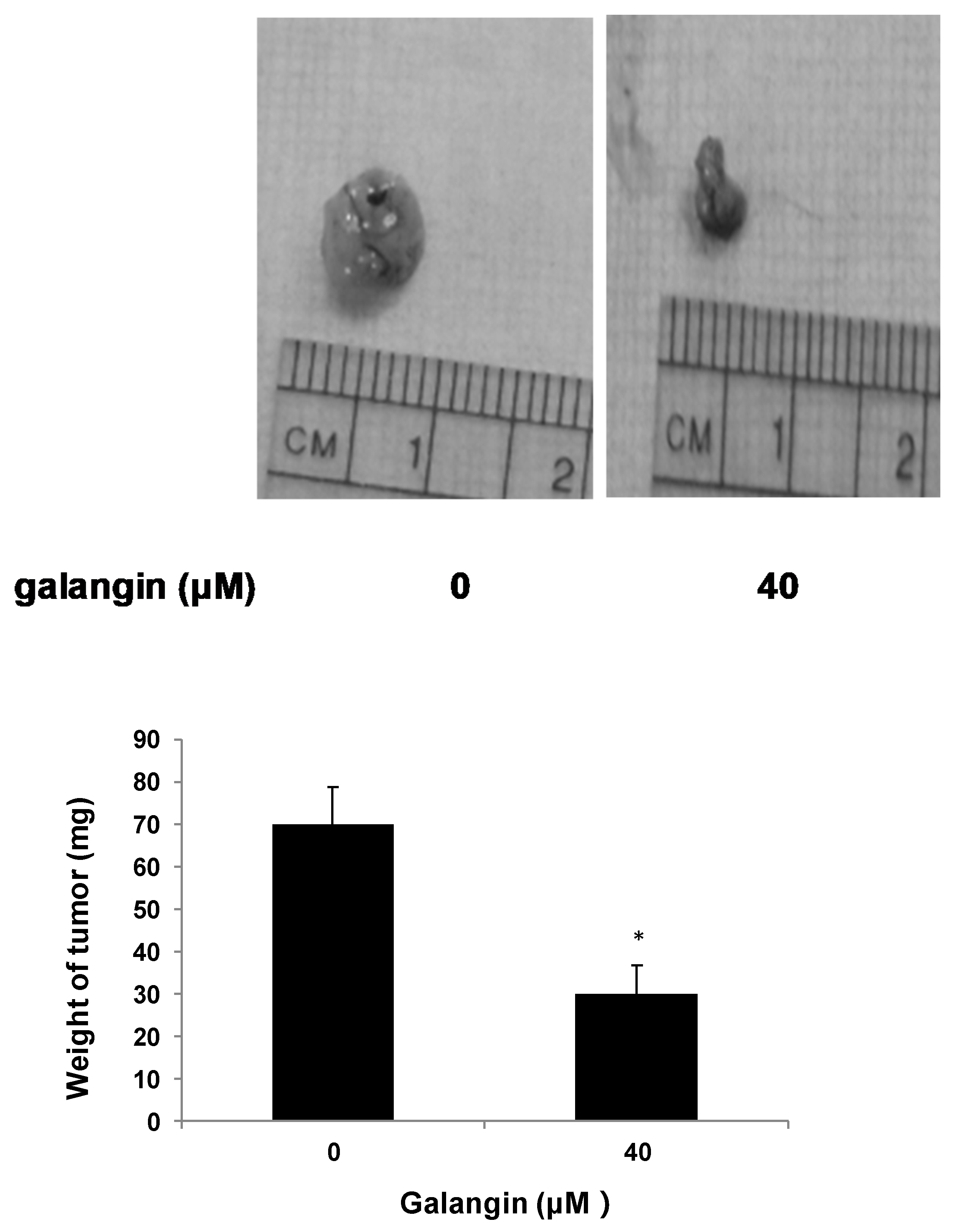
2.2. Galangin Inhibits Ovarian Cancer Cells Proliferation in Chicken Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM)
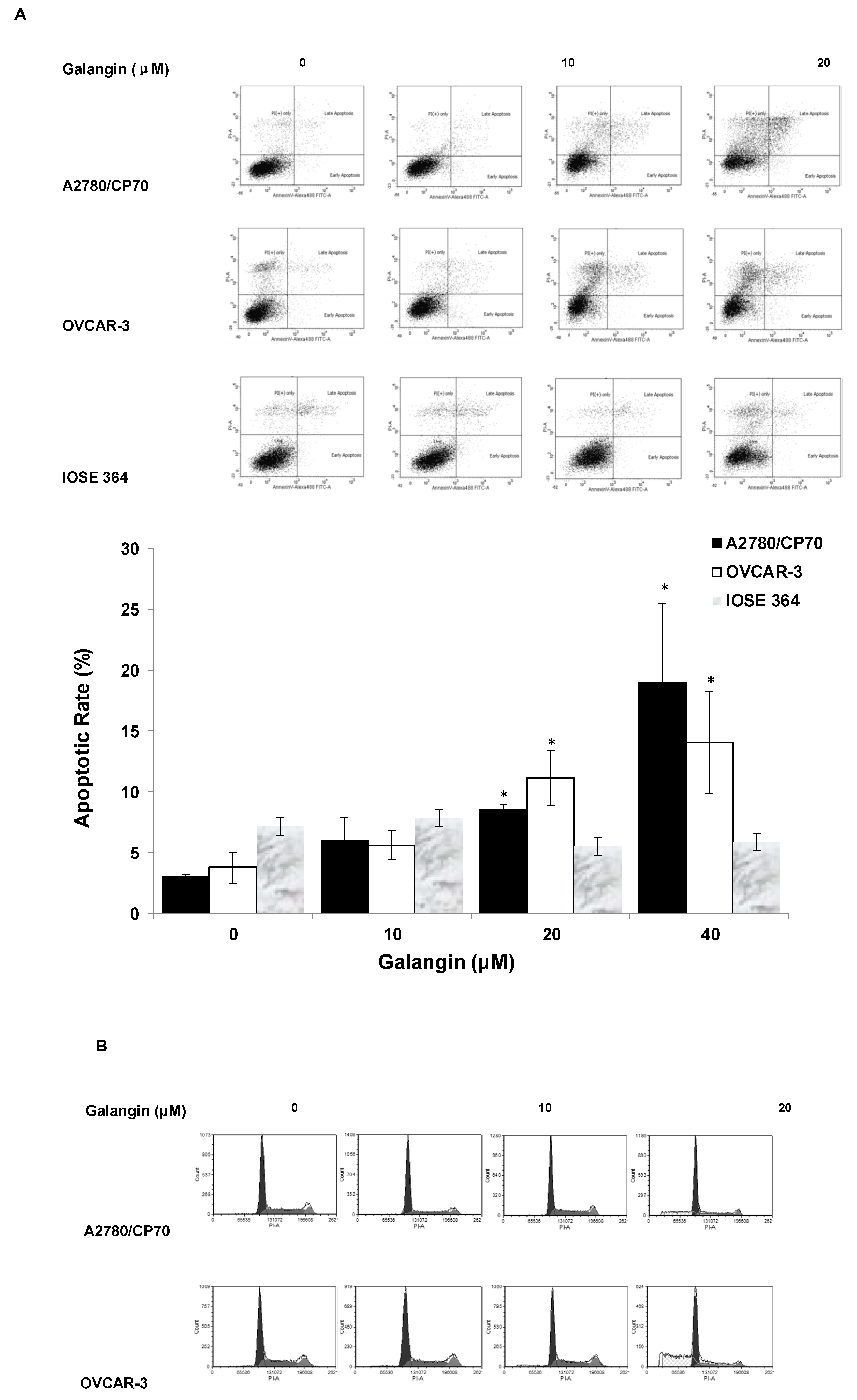
2.3. Effects of Galangin on Apoptosis and Cell Cycle in A2780/CP70 and OVCAR-3 Cells
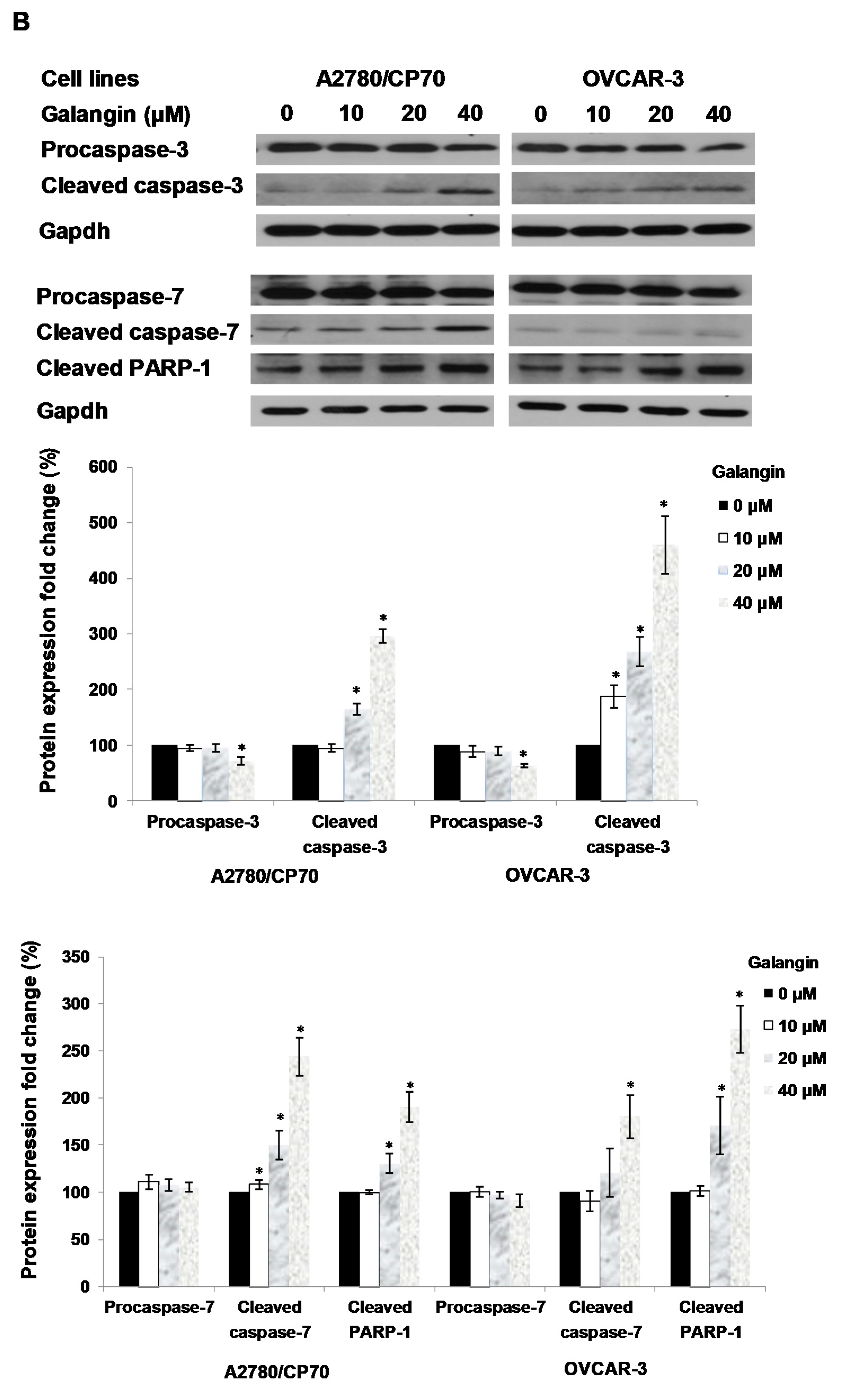
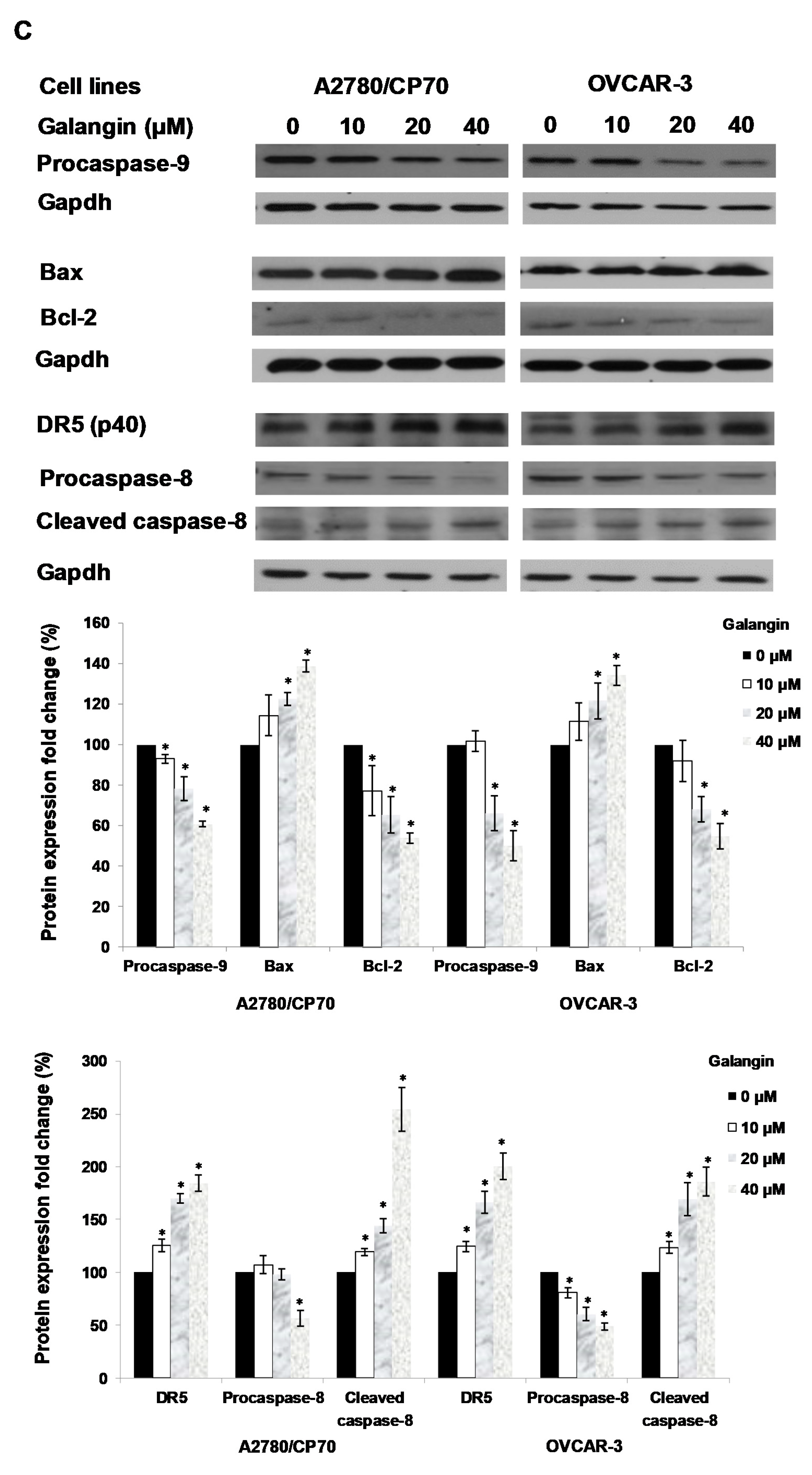
2.4. The Pathways of Galangin-Induced Apoptosis in Ovarian Cancer Cells
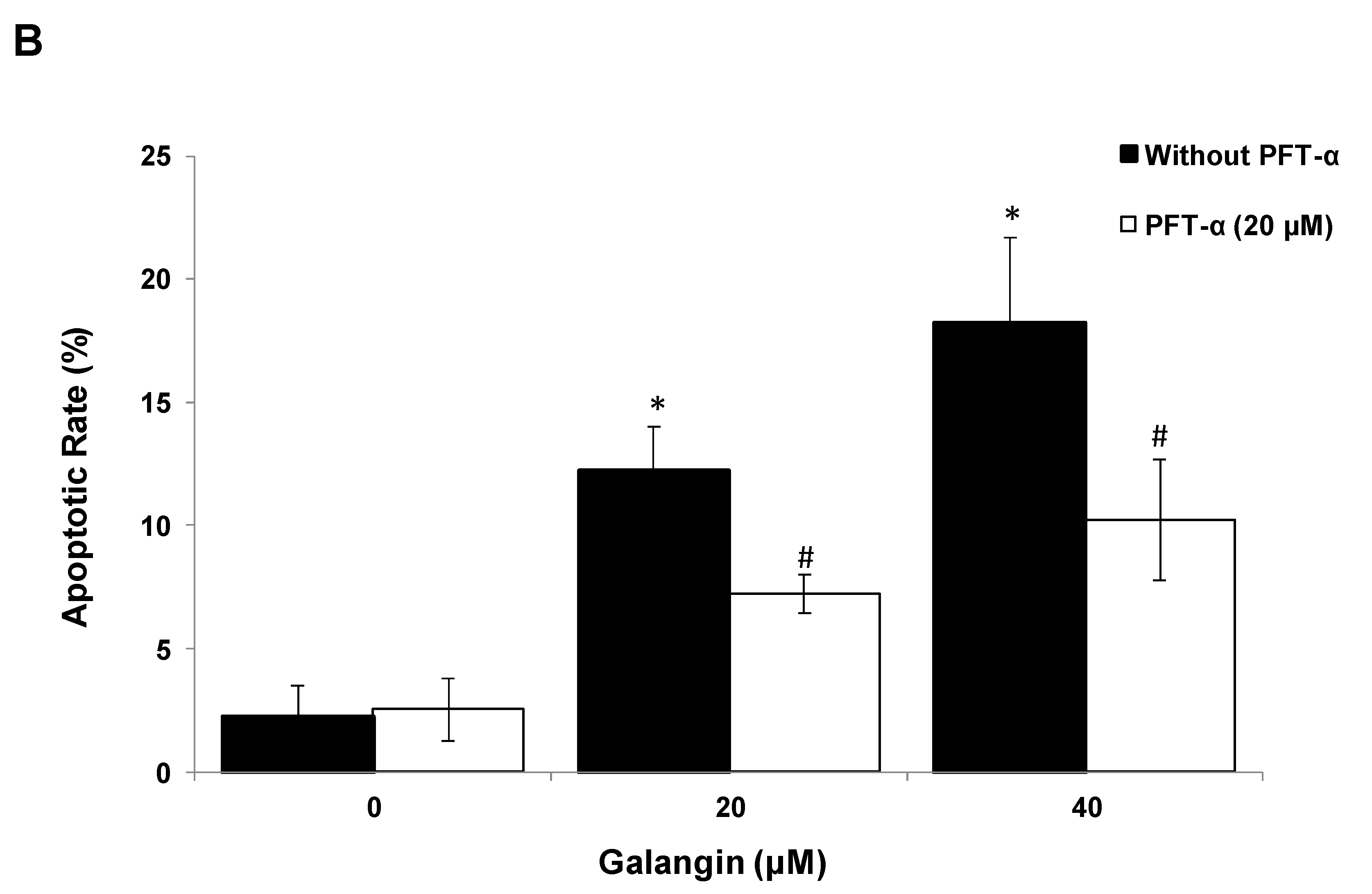
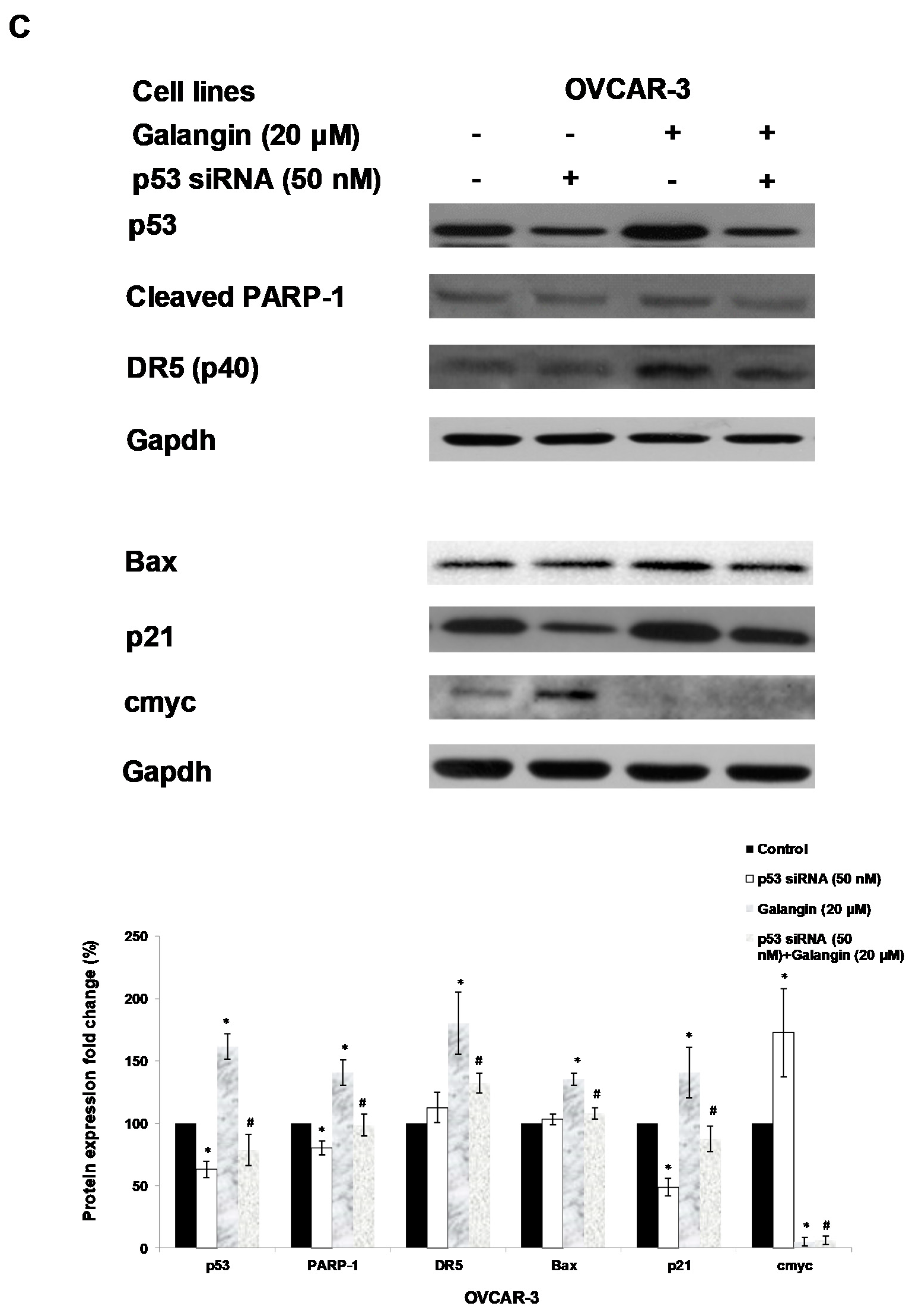
2.5. The Key Protein p53 in the Regulation of Galangin-Induced Apoptosis.
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.2. Reagents and Antibodies
4.3. Cell Viability
4.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Cell Cycle
4.5. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Cell Apoptosis
4.6. Apoptosis Assessment by Hoechst 33,342 Staining
4.7. Western Blot
4.8. Caspase-3/7 Assay
4.9. Transfection with Small Interfering RNA (siRNA)
4.10. Chicken Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM) Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.I.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.T.; Choi, J.H. Costunolide induces apoptosis in platinum-resistant human ovarian cancer cells by generating reactive oxygen species. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 123, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.M.; Compton, C.; Rankin, G.O.; Cutler, S.J.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Tu, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.C. 3-Hydroxyterphenyllin, a natural fungal metabolite, induces apoptosis and S phase arrest in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tuan, H.N.; Minh, B.H.; Tran, P.T.; Lee, J.H.; Oanh, H.V.; Ngo, Q.M.T.; Nguyen, Y.N.; Lien, P.T.K.; Tran, M.H. The Effects of 2′,4′-Dihydroxy-6′-methoxy-3′,5′- dimethylchalcone from Cleistocalyx operculatus Buds on Human Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines. Molecules 2019, 24, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Yang, J.; Hao, J.; Lv, Y.B.; Chen, L.; Lin, Q.X.; Yuan, J.Q.; Yang, X.Z. A Novel Flavonoid Kushenol Z from Sophora flavescens Mediates mTOR Pathway by Inhibiting Phosphodiesterase and Akt Activity to Induce Apoptosis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ginwala, R.; Bhavsar, R.; Chigbu, D.I.; Jain, P.; Khan, Z.K. Potential Role of Flavonoids in Treating Chronic Inflammatory Diseases with a Special Focus on the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Apigenin. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn-Jarvis, J.H.; Parihar, A.; Doseff, A.I. Dietary Flavonoids for Immunoregulation and Cancer: Food Design for Targeting Disease. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.Z.; Chen, A.Y.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Ye, X.; Rankin, G.O.; Chen, Y.C. Dietary compounds galangin and myricetin suppress ovarian cancer cell angiogenesis. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 15, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tastan, P.; Hajdu, Z.; Kusz, N.; Zupko, I.; Sinka, I.; Kivcak, B.; Hohmann, J. Sesquiterpene Lactones and Flavonoids from Psephellus pyrrhoblepharus with Antiproliferative Activity on Human Gynecological Cancer Cell Lines. Molecules 2019, 24, 3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.A.; Jeon, Y.K.; Nam, M.J. Galangin induces apoptosis in gastric cancer cells via regulation of ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1 and glutathione S-transferase P. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.T.; Luo, H.; Wu, J.; Lan, L.B.; Fan, D.H.; Zhu, K.D.; Chen, X.Y.; Wen, M.; Liu, H.M. Galangin induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the mitochondrial pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 3377–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Hua, Z. Galangin induces B16F10 melanoma cell apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway and sustained activation of p38 MAPK. Cytotechnology 2013, 65, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blagosklonny, M.V. Prospective strategies to enforce selectively cell death in cancer cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2967–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hall, M.D.; Okabe, M.; Shen, D.W.; Liang, X.J.; Gottesman, M.M. The role of cellular accumulation in determining sensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 48, 495–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.Q.; Li, Z.B.; Yang, A.N.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Liu, J.M. Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of OVCAR-3 and MCF-7 cells induced by co-immobilized TNF-alpha plus IFN-gamma on polystyrene and the role of p53 activation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6162–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.C.; Kuo, P.L.; Hsu, Y.L.; Cho, C.Y.; Lin, C.C. Ellipticine induces apoptosis through p53-dependent pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2550–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wei, C.; Rankin, G.O.; Ye, X.; Chen, Y.C. Flavonoids from Chinese bayberry leaves induced apoptosis and G1 cell cycle arrest via Erk pathway in ovarian cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 147, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Han, A.; Chen, E.; Singh, R.K.; Chichester, C.O.; Moore, R.G.; Singh, A.P.; Vorsa, N. The cranberry flavonoids PAC DP-9 and quercetin aglycone induce cytotoxicity and cell cycle arrest and increase cisplatin sensitivity in ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1924–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, T.K.; Kim, M.E.; Yoon, J.H.; Bae, S.J.; Yeom, J.; Lee, J.S. Galangin induces human colon cancer cell death via the mitochondrial dysfunction and caspase-dependent pathway. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 238, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gao, Y.; Rankin, G.O.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Cutler, S.J.; Tu, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Chaetoglobosin K induces apoptosis and G2 cell cycle arrest through p53-dependent pathway in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 418–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pervin, M.; Unno, K.; Takagaki, A.; Isemura, M.; Nakamura, Y. Function of Green Tea Catechins in the Brain: Epigallocatechin Gallate and its Metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.H.; Stephen Inbaraj, B. Nanoemulsion and Nanoliposome Based Strategies for Improving Anthocyanin Stability and Bioavailability. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, T.R.; Johnston, P.G.; Longley, D.B. Anti-Apoptotic Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in Cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Target 2009, 9, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Feng, Z.C.; Chen, A.J.; Qi, Q.C.; Han, M.Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, N.; Wang, J.W.; et al. The Natural Flavonoid Galangin Elicits Apoptosis, Pyroptosis, and Autophagy in Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulda, S.; Debatin, K.M. Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4798–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narita, M.; Shimizu, S.; Ito, T.; Chittenden, T.; Lutz, R.J.; Matsuda, H.; Tsujimoto, Y. Bax interacts with the permeability transition pore to induce permeability transition and cytochrome c release in isolated mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14681–14686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.Z.; Hannafon, B.; Gill, L.; Kelly, W.; Benbrook, D. Flex-Hets differentially normal cells by directly induce apoptosis in cancer over targeting mitochondria. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 1814–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozoren, N.; El-Deiry, W.S. Cell surface death receptor signaling in normal and cancer cells. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2003, 13, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darcy, K.M.; Brady, W.E.; McBroom, J.W.; Bell, J.G.; Young, R.C.; McGuire, W.P.; Linnolia, R.I.; Hendricks, D.; Bonome, T.; Farley, J.H. Associations between p53 overexpression and multiple measures of clinical outcome in high-risk, early stage or suboptimally-resected, advanced stage epithelial ovarian cancers: A Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2008, 111, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollstein, M.; Sidransky, D.; Vogelstein, B.; Harris, C.C. P53 Mutations in Human Cancers. Science 1991, 253, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.Y.; Delmas, D.; Vang, O.; Hsieh, T.C.; Lin, S.; Cheng, G.Y.; Chiang, H.L.; Chen, C.E.; Tang, H.Y.; Crawford, D.R.; et al. Mechanisms of ceramide-induced COX-2-dependent apoptosis in human ovarian cancer OVCAR-3 cells partially overlapped with resveratrol. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 1940–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoguchi, N.; Umeda, M.; Kato, H.; Araki, T. Proteasome Inhibitor Does Not Enhance MPTP Neurotoxicity in Mice. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 28, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Haldar, S. The relationship between Bcl2, Bax and p53: Consequences for cell cycle progression and cell death. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 4, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Lin, M.L.; Meng, M.; Chen, S.S. Galangin Induces p53-independent S-phase Arrest and Apoptosis in Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells Through Inhibiting PI3K-AKT Signaling Pathway. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, K.; Van Bockstaele, D.R.; Berneman, Z.N. The cell cycle: A review of regulation, deregulation and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell. Proliferat. 2003, 36, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartel, A.L.; Radhakrishnan, S.K. Lost in transcription: P21 repression, mechanisms, and consequences. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3980–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, J.K.; Grammer, T.C.; Lemon, K.P.; Kazlauskas, A.; Blenis, J. Pdgf-Dependent and Insulin-Dependent Pp70(S6k) Activation Mediated by Phosphatidylinositol-3-Oh Kinase. Nature 1994, 370, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, T.F.; Kaplan, D.R.; Cantley, L.C. PI3K: Downstream AKTion blocks apoptosis. Cell 1997, 88, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimura, T.; Noma, N.; Oikawa, T.; Ochiai, Y.; Kakuda, S.; Kuwahara, Y.; Takai, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Fukumoto, M. Activation of the AKT/cyclin D1/Cdk4 survival signaling pathway in radioresistant cancer stem cells. Oncogenesis 2012, 1, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds galangin are available from the authors. |


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.; Chen, A.Y.; Ye, X.; Guan, R.; Rankin, G.O.; Chen, Y.C. Galangin, a Flavonoid from Lesser Galangal, Induced Apoptosis via p53-Dependent Pathway in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071579
Huang H, Chen AY, Ye X, Guan R, Rankin GO, Chen YC. Galangin, a Flavonoid from Lesser Galangal, Induced Apoptosis via p53-Dependent Pathway in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2020; 25(7):1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071579
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Haizhi, Allen Y. Chen, Xingqian Ye, Rongfa Guan, Gary O. Rankin, and Yi Charlie Chen. 2020. "Galangin, a Flavonoid from Lesser Galangal, Induced Apoptosis via p53-Dependent Pathway in Ovarian Cancer Cells" Molecules 25, no. 7: 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071579
APA StyleHuang, H., Chen, A. Y., Ye, X., Guan, R., Rankin, G. O., & Chen, Y. C. (2020). Galangin, a Flavonoid from Lesser Galangal, Induced Apoptosis via p53-Dependent Pathway in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Molecules, 25(7), 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071579







