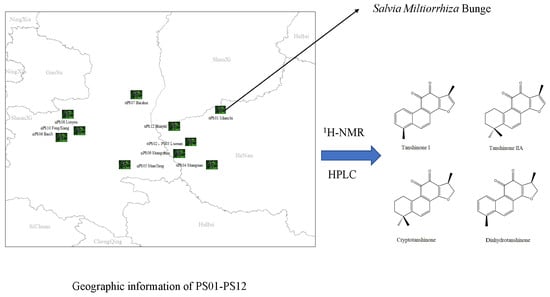
Quantitative Determination and Validation of Four Ketones in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge Using Quantitative Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Quantitative Analysis of SMB Using 1H-qNMR
2.2. Validation of qNMR Analytical Method
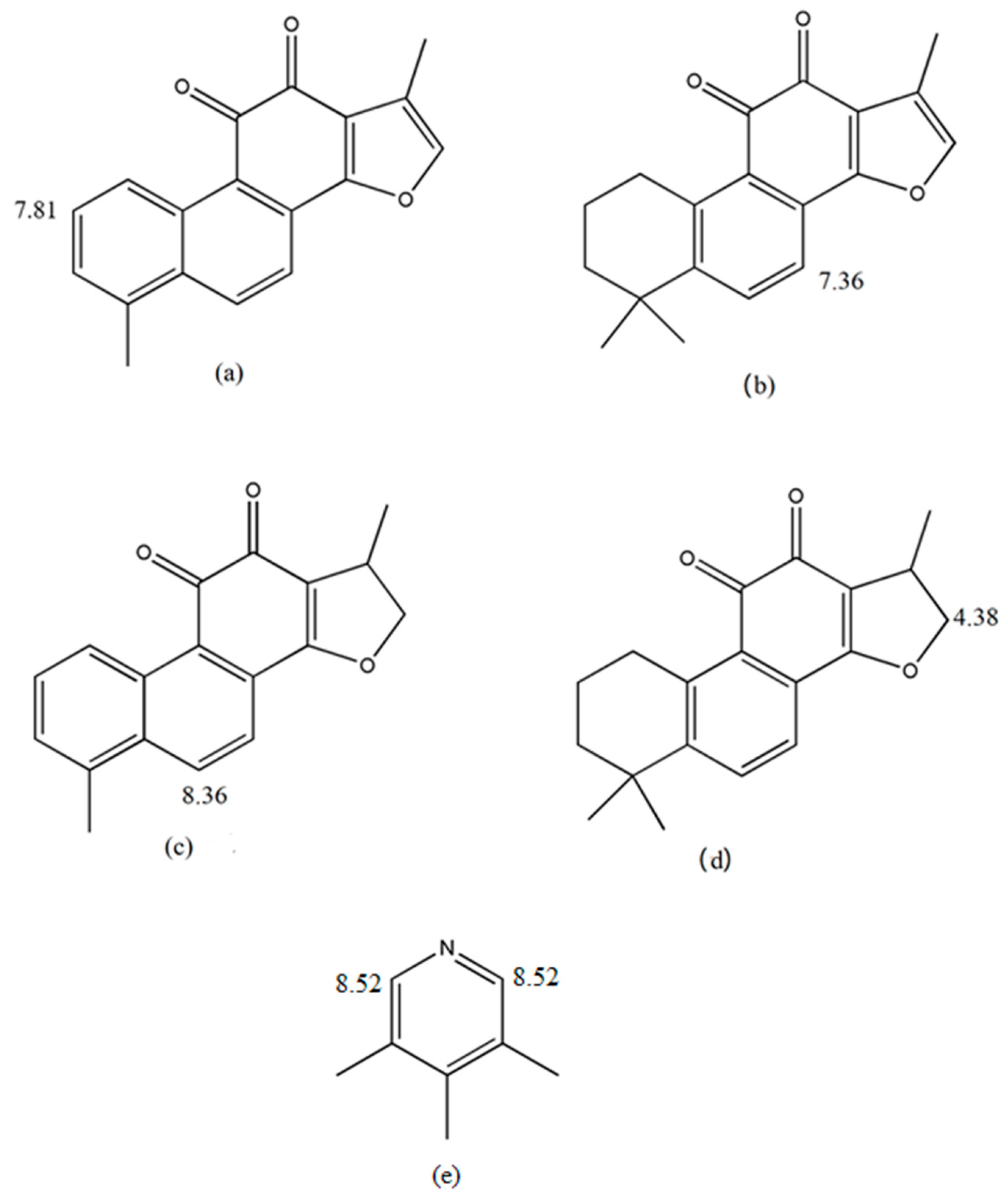
2.2.1. Specificity and Selectivity
2.2.2. Linearity, LOD and LOQ
2.2.3. Stability
2.2.4. Accuracy
2.2.5. Precision and Intermediate Precision
2.2.6. Robustness
2.3. Quantitative Analysis of SMB by HPLC
2.4. Real Sample Determination
2.4.1. Quantitative NMR Analysis of Real Samples
2.4.2. Sample Representation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Material and Reagents
3.2. Instruments and Parameters
3.3. Preparation of Sample Solution
3.4. Internal Standards
3.5. Quantitative NMR Analysis
3.6. HPLC Analysis
3.7. Chemometrics Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kai, G.Y.; Xu, G.H.; Zhou, C.C.; Liao, P.; Xiao, J.B.; Luo, X.Q.; You, L.J.; Zhang, L. Metabolic engineering tanshinone biosynthetic pathway in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root cultures. Metab. Eng. 2011, 13, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Luo, X.Q.; Ju, G.H.; Yu, X.H.; Hao, X.L.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, J.B.; Cui, L.J.; Kai, G.Y. Increased accumulation of the cardio-cerebrovascular disease treatment drug tanshinone in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots by the enzymes 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase and 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase. Funct. Integr. Genomics 2014, 14, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Huang, F.F.; Deng, C.P.; Wang, Y.; Kai, G.Y. Bioactivities, biosynthesis and biotechnological production of phenolic acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2018, 59, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.W.; Wu, J.Y. Tanshinone biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza and production in plant tissue cultures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 88, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Huang, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhou, Z.W.; Ding, M.Q.; Shi, M.; Huang, F.F.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Kai, G.Y. Comprehensive transcriptome profiling of Salvia miltiorrhiza for discovery of genes associated with the biosynthesis of tanshinone and salvianolic acids. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, e10554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Ding, Y.Y.; He, L.L.; Liu, S.Z. Clinical research investigating salvianolate injection for treating coronary angina pectoris of Qi blood stagnation. Curr. Res. Integr. Med. 2015, 1, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Zhou, C.; Li, D.; Liu, P.; Huang, M.; Shen, X. Cryptotanshinone inhibits human glioma cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo through SHP-2-dependent inhibition of STAT3 activation. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.D.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, K.M.; Choi, S.M.; Park, J.H. Synergistic Effect between cryptotanshinone and antibiotics against clinic methicillin and vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Evid-Based Compl. Alt. 2014, e450572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X. Advances in pharmacological research and clinical application of tanshinone. Bright Chin. Med. 2011, 26, 1514. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.L.; Ou, H.X.; Zhang, M.; Gong, D.; Zhao, Z.W.; Chen, L.Y.; Xia, X.D.; Mo, Z.C.; Tang, C.K. Tanshinone IIA Promotes Macrophage Cholesterol Efflux and Attenuates Atherosclerosis of apoE-/- Mice by Omentin-1/ABCA1 Pathway. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Qiao, Y.J.; Hou, L.F.; He, X.L. Researches on tanshinone of Salvia miltiorrhiza’s fat-soluble active ingredient. J. Hebei Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2015, 35, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.G.; Li, J.S.; Ding, Z.Y.; Li, Y.Z.; Wang, J.L.; Chen, S.J.; Miao, J.L. Tanshinone I inhibits the growth and metastasis of osteosarcoma via suppressing JAK/STAT3 signalling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 6454–6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.Q.; Cheng, R.B.; Chen, Z. Research progress on molecular mechanism of tumor cell apoptosis induced by cryptotanshinone. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2013, 31, 2631–2632. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.Z.; Huang, F.C.; Chen, J.T. Inhibitory effect of dihydrotanshinone on proliferation of colorectal cancer cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. Chin. J. Clin. Pharm. 2019, 35, 1633–1635. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Liao, R.X. Protective effect and mechanism of tanshinone IIA on neuronal apoptosis after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats. Chin. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 31, 443–444. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.L.; Qin, X.W.; Ma, N.; Jiang, X.P.; Yang, L.L. The content of four tanshinones in danshen tablets was determined by HPLC. Northwestern J. Pharm. 2019, 34, 487–491. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, J.; Dai, X.; Qin, F.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y. Rapid Identification of Tanshinone IIA Metabolites in an Amyloid-β1-42 Induced Alzherimer’s Disease Rat Model using UHPLC-Q-Exactive Qrbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2019, 24, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.N.; Duan, L.G. Determination of cryptotanshinone and tanshinone Ⅱ A in human plasma by LC-MS/MS. Chin. J. Clin. Pharm. 2019, 35, 690–693. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, T.F. Studies on the Tanshinone Components and Determination Method of Salvia miltiorrhiza. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. NMR-based metabolomic analysis of plants. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.C.; Ge, C.R.; Zhou, G.H.; Zhang, W.G.; Liao, G.Z. 1H NMR-based metabolic characterization of Chinese Wuding chicken meat. Food. Chem. 2019, 274, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarek, A.; Klys, A.; Olszewska, M.A. A validated 1H qNMR method for direct and simultaneous quantification of esculin, fraxin and (−)-epicatechin in Hippocastani cortex. Talanta 2019, 192, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.M.; Zhao, T.; Yang, T.; Wang, C.H.; Bligh, S.W.A.; Wang, Z.T. HPLC fingerprints combined with principal component analysis, hierarchical cluster analysis and linear discriminant analysis for the classification and differentiation of Peganum sp. indigenous to China. Phytochem. Anal. 2010, 3, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardila, J.A.; Funari, C.S.; Andrade, Z.M.; Cavalheiro, A.J.; Carneiro, R.L. Cluster analysis of commercial samples of Bauhinia spp. using HPLC-UV/PDA and MCR-ALS/PCA without peak alignment procedure. Phytochem. Anal. 2015, 5, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.H.; Liu, N.; Yang, Z.; Song, W.J.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.L.; Lucio, M.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Chen, G.N.; Cai, Z.W. GC/MS-based metabolomics reveals fatty acid biosynthesis and cholesterol metabolism in cell lines infected with influenza A virus. Talanta 2010, 1, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E.A.S.; Saboia, G.; Jorge, N.C.; Hoffmann, C.; Isaias, R.M.D.S.; Soares, G.L.G.; Zini, C.A. Development of a HS-SPME-GC/MS protocol assisted by chemometric tools to study herbivore-induced volatiles in Mycia splendens. Talanta 2017, 175, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malz, F.; Jancke, H. Validation of quantitative NMR. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2005, 38, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadape, H.; Parikh, K. Quantitative determination and validation of Carvedilol in pharmaceuticals using quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 2341–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |





| Reference | Calibration Curves | Range (mg/mL) | r2 | LOD (mg/mL) | LOQ (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryptotanshinone | Y = 0.926X − 0.006 | 0.02–0.18 | 0.999 | 0.02 | 0.05 |
| Tanshinone I | Y = 1.231X − 0.003 | 0.02–0.24 | 0.997 | 0.04 | 0.11 |
| Tanshinone IIA | Y = 0.715X − 0.018 | 0.03–0.33 | 0.992 | 0.09 | 0.28 |
| Dihydrotanshinone | Y = 0.740X − 0.001 | 0.02–0.24 | 0.985 | 0.04 | 0.11 |
| Tanshinone I | Tanshinone IIA | Dihydrotanshinone | Cryptotanshinone | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Times (h) | Content (mg/g) | Difference (mg/g) | Content (mg/g) | Difference (mg/g) | Content (mg/g) | Difference (mg/g) | Content (mg/g) | Difference (mg/g) |
| 0 | 0.65 | NA | 1.75 | NA | 0.37 | NA | 0.98 | NA |
| 6 | 0.69 | 0.04 | 1.79 | 0.04 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.97 | 0.01 |
| 12 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 1.76 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.02 | 1.02 | 0.04 |
| 18 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 1.70 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.02 | 1.02 | 0.04 |
| 24 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 1.77 | 0.02 | 0.39 | 0.02 | 1.02 | 0.04 |
| RSD% | 2.11 | 1.92 | 2.82 | 2.49 | ||||
| Compounds | Tanshinone I | Tanshinone IIA | Dihydrotanshinone | Cryptotanshinone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 (mean/%, n = 3) | 65.16 | 74.09 | 121.08 | 71.13 |
| RSD/%, n = 3 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.52 | 0.80 |
| Level 2 (mean/%, n = 3) | 96.30 | 85.37 | 102.27 | 123.21 |
| RSD/%, n = 3 | 0.89 | 1.08 | 1.29 | 0.59 |
| Level 3 (mean/%, n = 3) | 85.85 | 114.01 | 145.81 | 93.50 |
| RSD/%, n = 3 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.72 |
| Study | Precision | Intermediate precision | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tanshinone I (mg/g) | Tanshinone IIA (mg/g) | Dihydrotanshinone (mg/g) | Cryptotanshinone (mg/g) | Tanshinone I (mg/g) | Tanshinone IIA (mg/g) | Dihydrotanshinone (mg/g) | Cryptotanshinone (mg/g) | |
| 1 | 0.63 | 1.72 | 0.36 | 0.95 | 0.68 | 1.76 | 0.38 | 1.00 |
| 2 | 0.66 | 1.73 | 0.38 | 1.00 | 0.65 | 1.75 | 0.38 | 0.98 |
| 3 | 0.65 | 1.71 | 0.38 | 1.02 | 0.69 | 1.72 | 0.40 | 0.98 |
| 4 | 0.63 | 1.72 | 0.36 | 0.95 | 0.69 | 1.76 | 0.40 | 0.99 |
| 5 | 0.67 | 1.76 | 0.38 | 0.98 | 0.66 | 1.73 | 0.38 | 1.00 |
| 6 | 0.65 | 1.75 | 0.37 | 0.98 | 0.67 | 1.77 | 0.39 | 1.02 |
| RSD% | 2.47 | 1.12 | 2.65 | 2.81 | 2.81 | 2.43 | 1.11 | 1.52 |
| Parameters | Tanshinone I (mg/g) | Tanshinone IIA (mg/g) | Dihydrotanshinone (mg/g) | Cryptotanshinone (mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of scans | 6 | 0.65 | 1.75 | 0.37 | 1.08 |
| 32 | 0.67 | 1.70 | 0.39 | 1.11 | |
| 48 | 0.65 | 1.74 | 0.38 | 1.06 | |
| 64 | 0.67 | 1.77 | 0.39 | 1.06 | |
| RSD% | 1.75 | 1.69 | 2.50 | 2.19 | |
| Relaxing delay | 15 | 0.67 | 1.70 | 0.39 | 1.02 |
| 20 | 0.65 | 1.68 | 0.38 | 0.99 | |
| 25 | 0.67 | 1.70 | 0.39 | 1.02 | |
| 30 | 0.67 | 1.70 | 0.39 | 1.02 | |
| RSD% | 1.50 | 0.59 | 1.29 | 1.48 | |
| Acquisition time | 2s | 0.65 | 1.67 | 0.37 | 0.98 |
| 4s | 0.67 | 1.64 | 0.39 | 0.93 | |
| 6s | 0.64 | 1.65 | 0.36 | 0.95 | |
| RSD% | 2.24 | 0.92 | 2.63 | 2.64 | |
| Samples | Methods | Cryptotanshinone | Tanshinone I | Tanshinone IIA | Dihydrotanshinone | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (mg/g) ± SD | RSD% | Content (mg/g) ± SD | RSD% | Content (mg/g) ± SD | RSD% | Content (mg/g) ± SD | RSD% | ||
| PS01 | HPLC | 0.29 ± 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.33 ± 0.00 | 0.01 | 1.21 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 0.01 |
| NMR | 0.29 ± 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.30 ± 0.05 | 0.17 | 1.19 ± 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.18 | |
| PS02 | HPLC | 0.68 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.39 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.42 ± 0.00 | 0.00 |
| NMR | 0.66 ± 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.40 ± 0.00 | 0.03 | 1.36 ± 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| PS03 | HPLC | 0.61 ± 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.46 ± 0.00 | 0.01 | 1.51 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.40 ± 0.00 | 0.01 |
| NMR | 0.69 ± 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.49 ± 0.03 | 0.06 | 1.51 ± 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 0.04 | |
| PS04 | HPLC | 0.68 ± 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.54 ± 0.00 | 0.01 | 1.62 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.47 ± 0.00 | 0.00 |
| NMR | 0.67 ± 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.54 ± 0.02 | 0.04 | 1.60 ± 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.45 ± 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| PS05 | HPLC | 0.31 ± 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.87 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.23 ± 0.00 | 0.00 |
| NMR | 0.37 ± 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.88 ± 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.29 ± 0.03 | 0.11 | |
| PS06 | HPLC | 0.31 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.95 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.14 ± 0.00 | 0.01 |
| NMR | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 0.05 | 1.01 ± 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 0.18 | |
| PS07 | HPLC | 1.06 ± 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.67 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.84 ± 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.49 ± 0.00 | 0.00 |
| NMR | 1.03 ± 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.66 ± 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.83 ± 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.42 ± 0.06 | 0.15 | |
| PS08 | HPLC | 0.37 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.38 ± 0.00 | 0.01 | 1.34 ± 0.24 | 0.00 | 0.20 ± 0.00 | 0.00 |
| NMR | 0.38 ± 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.38 ± 0.02 | 0.04 | 1.25 ± 0.00 | 0.18 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 0.06 | |
| PS09 | HPLC | 0.82 ± 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.59 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.99 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.34 ± 0.00 | 0.00 |
| NMR | 0.76 ± 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.57 ± 0.04 | 0.06 | 1.91 ± 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 0.06 | |
| PS10 | HPLC | 0.38 ± 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.45 ± 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.38 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.21 ± 0.00 | 0.01 |
| NMR | 0.39 ± 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.42 ± 0.02 | 0.04 | 1.24 ± 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 0.05 | |
| PS11 | HPLC | 0.63 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.38 ± 0.00 | 0.01 | 1.36 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.34 ± 0.03 | 0.00 |
| NMR | 0.68 ± 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.38 ± 0.03 | 0.08 | 1.19 ± 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | 0.09 | |
| PS12 | HPLC | 1.08 ± 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.50 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.02 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.49 ± 0.01 | 0.00 |
| NMR | 1.18 ± 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 0.05 | 1.97 ± 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.47 ± 0.01 | 0.01 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Hou, Z.; Su, F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Yang, D.; Liang, Z. Quantitative Determination and Validation of Four Ketones in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge Using Quantitative Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Molecules 2020, 25, 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092043
Li Y, Hou Z, Su F, Chen J, Zhang X, Xu L, Yang D, Liang Z. Quantitative Determination and Validation of Four Ketones in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge Using Quantitative Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Molecules. 2020; 25(9):2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092043
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuanyuan, Zhuoni Hou, Feng Su, Jipeng Chen, Xiaodan Zhang, Ling Xu, Dongfeng Yang, and Zongsuo Liang. 2020. "Quantitative Determination and Validation of Four Ketones in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge Using Quantitative Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy" Molecules 25, no. 9: 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092043
APA StyleLi, Y., Hou, Z., Su, F., Chen, J., Zhang, X., Xu, L., Yang, D., & Liang, Z. (2020). Quantitative Determination and Validation of Four Ketones in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge Using Quantitative Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Molecules, 25(9), 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092043