Mechanistic Understanding of Peptide Analogues, DALDA, [Dmt1]DALDA, and KGOP01, Binding to the Mu Opioid Receptor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Comparison of In Vitro Binding and Activation Profiles of DALDA, [Dmt1]DALDA, and KGOP01 to the MOR
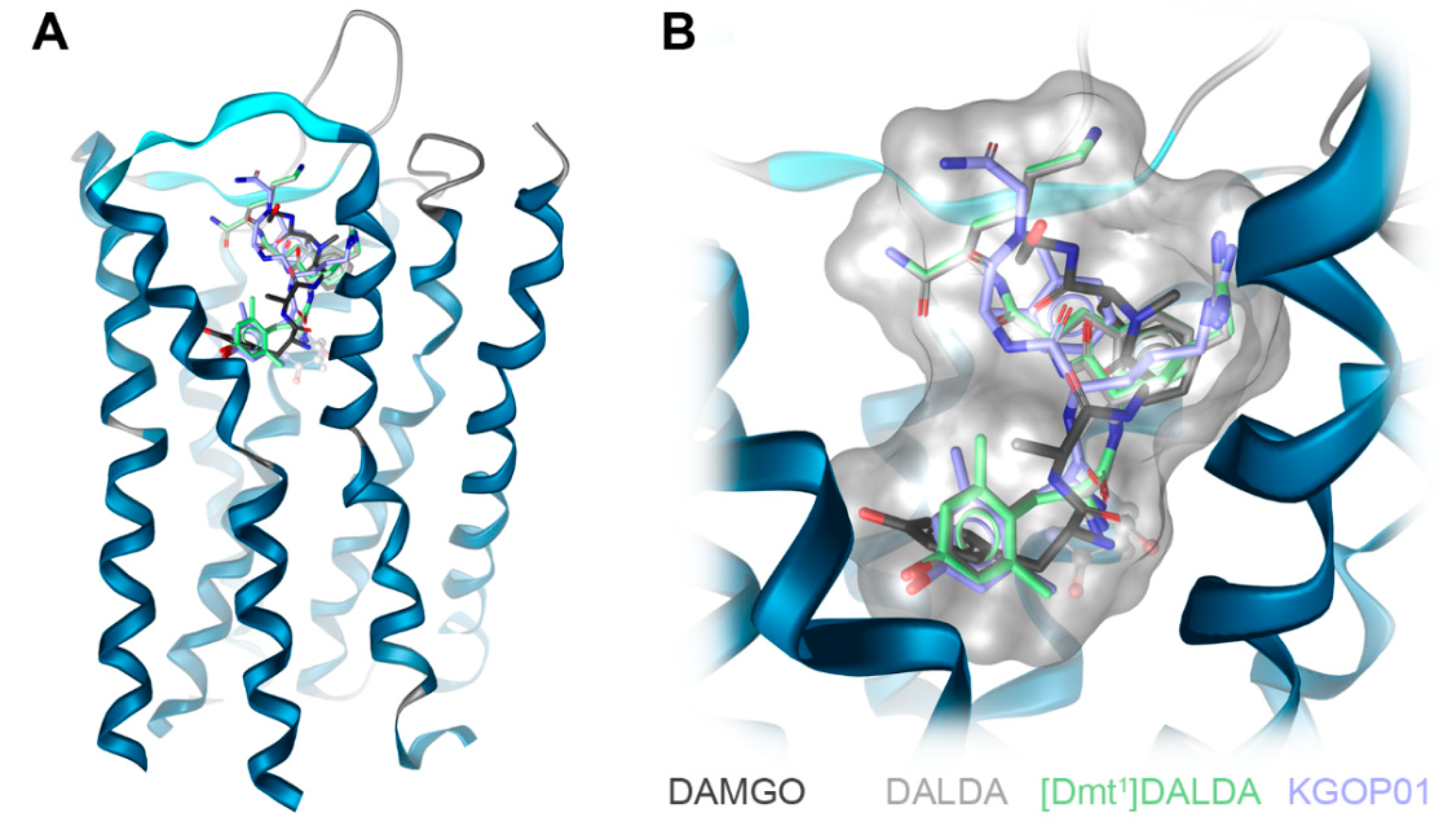
2.2. In Silico Investigation of DALDA, [Dmt1]DALDA, and KGOP01 Binding to the MOR
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Peptide and Peptidomimetic Ligands
3.3. Cell Culture
3.4. Competitive Radioligand Binding Assays
3.5. [35S]GTPγS Binding Assays
3.6. Data Analysis
3.7. Molecular Modeling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pasternak, G.W. Mu opioid pharmacology: 40 years to the promised land. Adv. Pharmacol. 2018, 82, 261–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stein, C. Opioid receptors. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corder, G.; Castro, D.C.; Bruchas, M.R.; Scherrer, G. Endogenous and exogenous opioids in pain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 41, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darcq, E.; Kieffer, B.L. Opioid receptors: Drivers to addiction. Nature 2018, 19, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spetea, M.; Asim, M.F.; Wolber, G.; Schmidhammer, H. The μ opioid receptor and ligands acting at the μ opioid receptor, as therapeutics and potential therapeutics. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 7415–7434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Jones, E.B.; Einstein, E.B.; Wargo, E.M. Prevention and treatment of opioid misuse and addiction: A review. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, D.H.; Heilig, M.; Shaham, Y. Science-based actions can help address the opioid crisis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezniuk, I.; Fricker, L.D. Endogenous opioids. In The Opiate Receptors, 2nd ed.; Pasternak, G.W., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 93–120. [Google Scholar]
- Fichna, J.; Janecka, A.; Constentin, J.; Do Rego, J.C. The endomorphin system and its evolving neurophysiological role. Pharmacol. Rev. 2007, 59, 88–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, L.; Melchiorri, P.; Lattanzi, R. Pharmacology of amphibian opiate peptides. Peptides 2000, 21, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, J.V.; McLaughlin, J.P. Opioid peptides: Potential for drug development. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2012, 9, e23–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, S.D.; Jinsmaa, Y.; Salvadori, S.; Okada, Y.; Lazarus, L.H. Dmt and opioid peptides: A potent alliance. Pept. Sci. 2003, 71, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiller, P.W. Opioid peptide-derived analgesics. In Drug Addiction: From Basic Research to Therapy; Rapaka, R.S., Sadee, W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Janecka, A.; Perlikowska, R.; Gach, K.; Wyrebska, A.; Fichna, J. Development of opioid peptide analogs for pain relief. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janecka, A.; Gentilucci, L. Cyclic endomorphin analogs in targeting opioid receptors to achieve pain relief. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, R.; Janecka, A. Strategies to improve bioavailability and in vivo efficacy of the endogenous opioid peptides endomorphin-1 and endomorphin-2. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 16, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, A.K.; Hruby, V.J. Investigational peptide and peptidomimetic μ and δ opioid receptor agonists in the relief of pain. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2014, 23, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shonberg, J.; Kling, R.C.; Gmeiner, P.; Löber, S. GPCR crystal structures: Medicinal chemistry in the pocket. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3880–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K. The molecular basis of G protein-coupled receptor activation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 897–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilger, D.; Masureel, M.; Kobilka, B.K. Structure and dynamics of GPCR signaling complexes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, M.; Nguyen, T.N.; Omieczynski, C.; Wolber, G. Strategies for the discovery of biased GPCR ligands. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.M.L.; Filizola, M. Insights from molecular dynamics simulations of a number of G-protein coupled receptor targets for the treatment of pain and opioid use disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manglik, A.; Kruse, A.C.; Kobilka, T.S.; Thian, F.S.; Mathiesen, J.M.; Sunahara, R.K.; Pardo, L.; Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K.; Granier, S. Crystal structure of the mu-opioid receptor bound to a morphinan antagonist. Nature 2012, 485, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Manglik, A.; Venkatakrishnan, A.J.; Laeremans, T.; Feinberg, E.N.; Sanborn, A.L.; Kato, H.E.; Livingston, K.E.; Thorsen, T.S.; Kling, R.C.; et al. Structural insights into μ-opioid receptor activation. Nature 2015, 524, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehl, A.; Hu, H.; Maeda, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Q.; Paggi, J.M.; Latorraca, N.R.; Hilger, D.; Dawson, R.; Matile, H.; et al. Structure of the µ-opioid receptor–Gi protein complex. Nature 2018, 558, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manglik, A.; Lin, H.; Aryal, D.K.; McCorvy, J.D.; Dengler, D.; Corder, G.; Levit, A.; Kling, R.C.; Bernat, V.; Hübner, H.; et al. Structure-based discovery of opioid analgesics with reduced side effects. Nature 2016, 537, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaserer, T.; Lantero, A.; Schmidhammer, H.; Spetea, M.; Schuster, D. μ Opioid receptor: Novel antagonists and structural modeling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Yeliseev, A.; Liu, R. Ligand interaction, binding site and G protein activation of the mu opioid receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 702, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartuzi, D.; Kaczor, A.A.; Matosiuk, D. Activation and allosteric modulation of human μ opioid receptor in molecular dynamics. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 2421–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wtorek, K.; Artali, R.; Piekielna-Ciesielska, J.; Koszuk, J.; Kluczyk, A.; Gentilucci, L.; Janecka, A. Endomorphin-2 analogs containing modified tyrosines: Biological and theoretical investigation of the influence on conformation and pharmacological profile. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 179, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strack, M.; Bedini, A.; Yip, K.T.; Lombardi, S.; Siegmund, D.; Stoll, R.; Spampinato, S.M.; Metzler-Nolte, N. A blocking group scan using a spherical organometallic complex identifies an unprecedented binding mode with potent activity in vitro and in vivo for the opioid peptide dermorphin. Chemistry 2016, 22, 14605–14610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, P.W.; Nguyen, T.M.; Chung, N.N.; Lemieux, C. Dermorphin analogues carrying an increased positive net charge in their “message” domain display extremely high mu opioid receptor selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, P.W.; Nguyen, T.M.; Berezowska, I.; Dupuis, S.; Weltrowska, G.; Chung, N.N.; Lemieux, C. Synthesis and in vitro opioid activity profiles of DALDA analogues. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 35, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemyn, K.; Kleczkowska, P.; Lesniak, A.; Dyniewicz, J.; Van der Poorten, O.; Van den Eynde, I.; Keresztes, A.; Varga, E.; Lai, J.; Porreca, F.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of compact, conformationally constrained bifunctional opioid agonist—Neurokinin-1 antagonist peptidomimetics. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 92, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoyama, M.; Shimoyama, N.; Zhao, G.M.; Schiller, P.W.; Szeto, H.H. Antinociceptive and respiratory effects of intrathecal H-Tyr-D-Arg-Phe-Lys-NH2 (DALDA) and [Dmt1] DALDA. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 364–371. [Google Scholar]
- Neilan, C.L.; Nguyen, T.M.; Schiller, P.W.; Pasternak, G.W. Pharmacological characterization of the dermorphin analog [Dmt1]DALDA, a highly potent and selective mu-opioid peptide. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 419, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riba, P.; Ben, Y.; Nguyen, T.M.; Furst, S.; Schiller, P.W.; Lee, N.M. [Dmt1)]DALDA is highly selective and potent at mu opioid receptors, but is not cross-tolerant with systemic morphine. Curr. Med. Chem. 2002, 9, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, P.W. Bi- or multifunctional opioid peptide drugs. Life Sci. 2010, 86, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoyama, M.; Schiller, P.W.; Shimoyama, N.; Toyama, S.; Szeto, H.H. Superior analgesic effect of H-Dmt-D-Arg-Phe-Lys-NH2 ([Dmt1]DALDA), a multifunctional opioid peptide, compared to morphine in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2012, 80, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Lu, D.; Chen, Z.; Ding, Y.; Chung, N.N.; Li, T.; Schiller, P.W. [Dmt1]DALDA analogues modified with tyrosine analogues at position 1. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3629–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubu, S.; Eddinger, K.A.; Yamaguchi, S.; Huerta-Esquivel, L.L.; Schiller, P.W.; Yaksh, T.L. Characterization of analgesic actions of the chronic intrathecal infusion of H-Dmt-D-Arg-Phe-Lys-NH2 in rat. Neuromodulation 2019, 22, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drieu la Rochelle, A.; Guillemyn, K.; Dumitrascuta, M.; Martin, C.; Utard, V.; Quillet, R.; Schneider, S.; Daubeuf, F.; Willemse, T.; Mampuys, P.; et al. A bifunctional-biased mu-opioid agonist-neuropeptide FF receptor antagonist as analgesic with improved acute and chronic side effects. Pain 2018, 159, 1705–1718. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.; Dumitrascuta, M.; Mannes, M.; Lantero, A.; Bucher, D.; Walker, K.; Van Wanseele, Y.; Oyen, E.; Hernot, S.; Van Eeckhaut, A.; et al. Biodegradable amphipathic peptide hydrogels as extended-release system for opioid peptides. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 9784–9789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handa, B.K.; Lane, A.C.; Lord, J.A.H.; Morgan, B.A.; Rance, M.J.; Smith, C.F.C. Analogues of β-LPH61–64 possessing selective agonist activity at μ-opiate receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1981, 70, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, K.A.; Shang, Y.; Filizola, M. Insights into the function of opioid receptors from molecular dynamics simulations of available crystal structures. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 2834–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Willet, P.; Glen, R.C.; Leach, A.R.; Taylor, R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 267, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolber, G.; Langer, T. LigandScout: 3-D Pharmacophores derived from protein-bound ligands and their use as virtual screening filters. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2005, 45, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrascuta, M.; Ben Haddou, T.; Guerrieri, E.; Noha, S.M.; Schläfer, L.; Schmidhammer, H.; Spetea, M. Synthesis, pharmacology, and molecular docking studies on 6-desoxo-N-methylmorphinans as potent μ-opioid receptor agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 9407–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (k1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (i50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar]
- Labute, P. Protonate3D: Assignment of ionization states and hydrogen coordinates to macromolecular structures. Proteins 2009, 75, 87–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, D.; Šribarn, D.; Noonan, T.; Deng, L.; Nguyen, T.N.; Pach, S.; Machalz, D.; Bermudez, M.; Wolber, G. Next generation 3D pharmacophore modeling. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2020, e1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

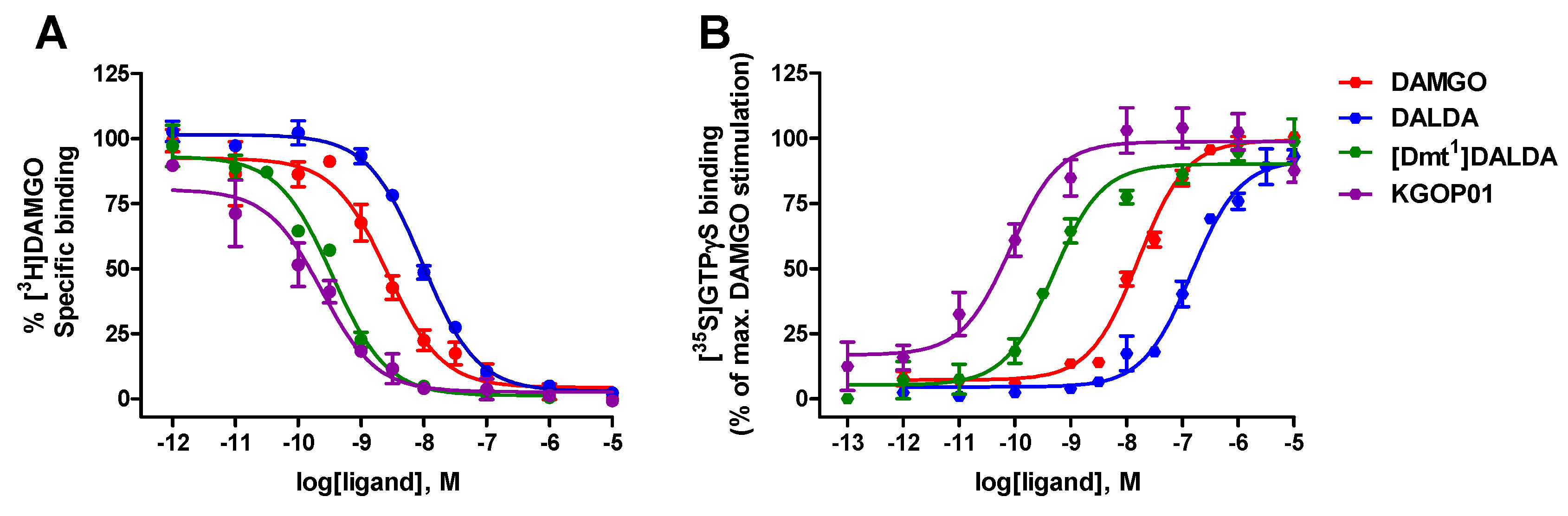





| Opioid Peptide | Binding Affinity a | Agonist Activity b | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ki (nM) | EC50 (nM) | % stim. | |
| DAMGO | 1.46 ± 0.37 | 18.1 ± 2.0 | 100 |
| DALDA | 6.36 ± 0.24 | 149 ± 28 | 92 ± 2 |
| [Dmt1]DALDA | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.51 ± 0.06 | 90 ± 4 |
| KGOP01 | 0.11 ± 0.05 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 99 ± 6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dumitrascuta, M.; Bermudez, M.; Ballet, S.; Wolber, G.; Spetea, M. Mechanistic Understanding of Peptide Analogues, DALDA, [Dmt1]DALDA, and KGOP01, Binding to the Mu Opioid Receptor. Molecules 2020, 25, 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092087
Dumitrascuta M, Bermudez M, Ballet S, Wolber G, Spetea M. Mechanistic Understanding of Peptide Analogues, DALDA, [Dmt1]DALDA, and KGOP01, Binding to the Mu Opioid Receptor. Molecules. 2020; 25(9):2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092087
Chicago/Turabian StyleDumitrascuta, Maria, Marcel Bermudez, Steven Ballet, Gerhard Wolber, and Mariana Spetea. 2020. "Mechanistic Understanding of Peptide Analogues, DALDA, [Dmt1]DALDA, and KGOP01, Binding to the Mu Opioid Receptor" Molecules 25, no. 9: 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092087
APA StyleDumitrascuta, M., Bermudez, M., Ballet, S., Wolber, G., & Spetea, M. (2020). Mechanistic Understanding of Peptide Analogues, DALDA, [Dmt1]DALDA, and KGOP01, Binding to the Mu Opioid Receptor. Molecules, 25(9), 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092087








