Imaging Sequences for Hyperpolarized Solids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Image Equation
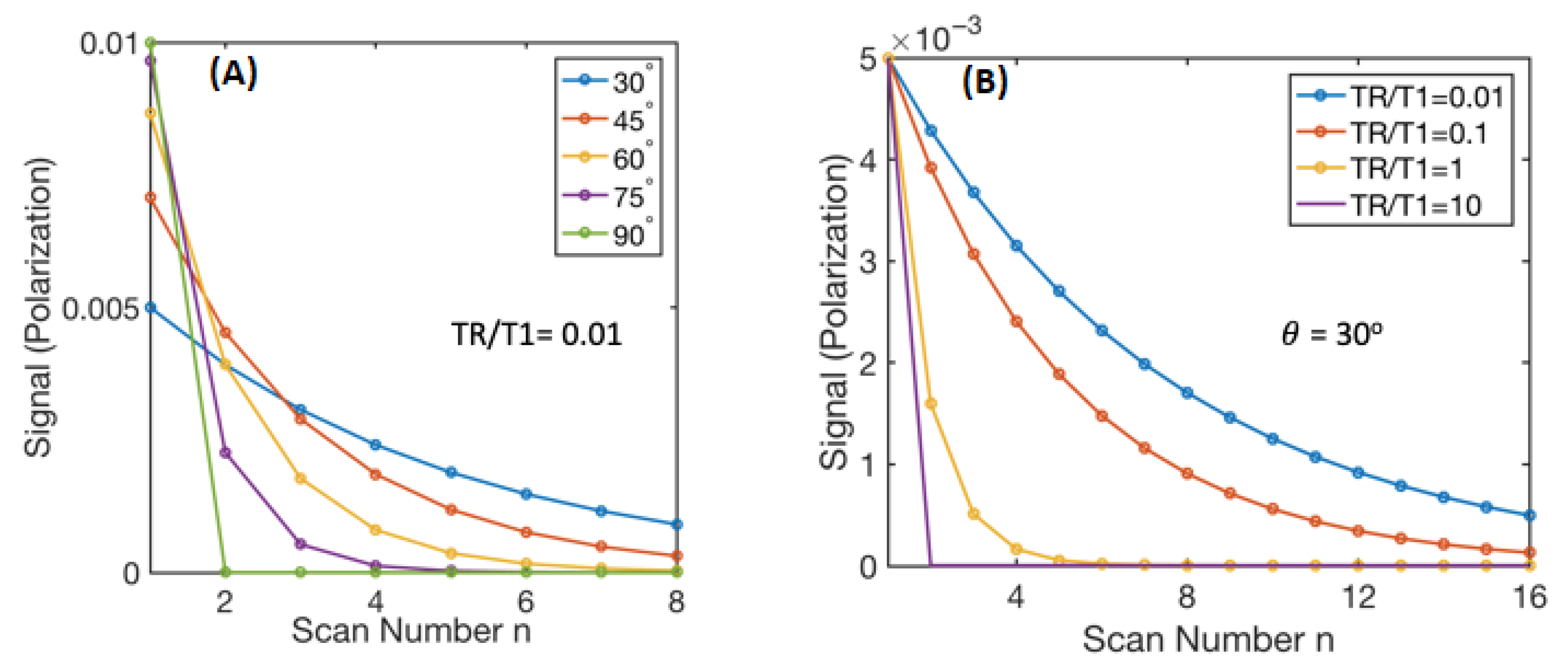
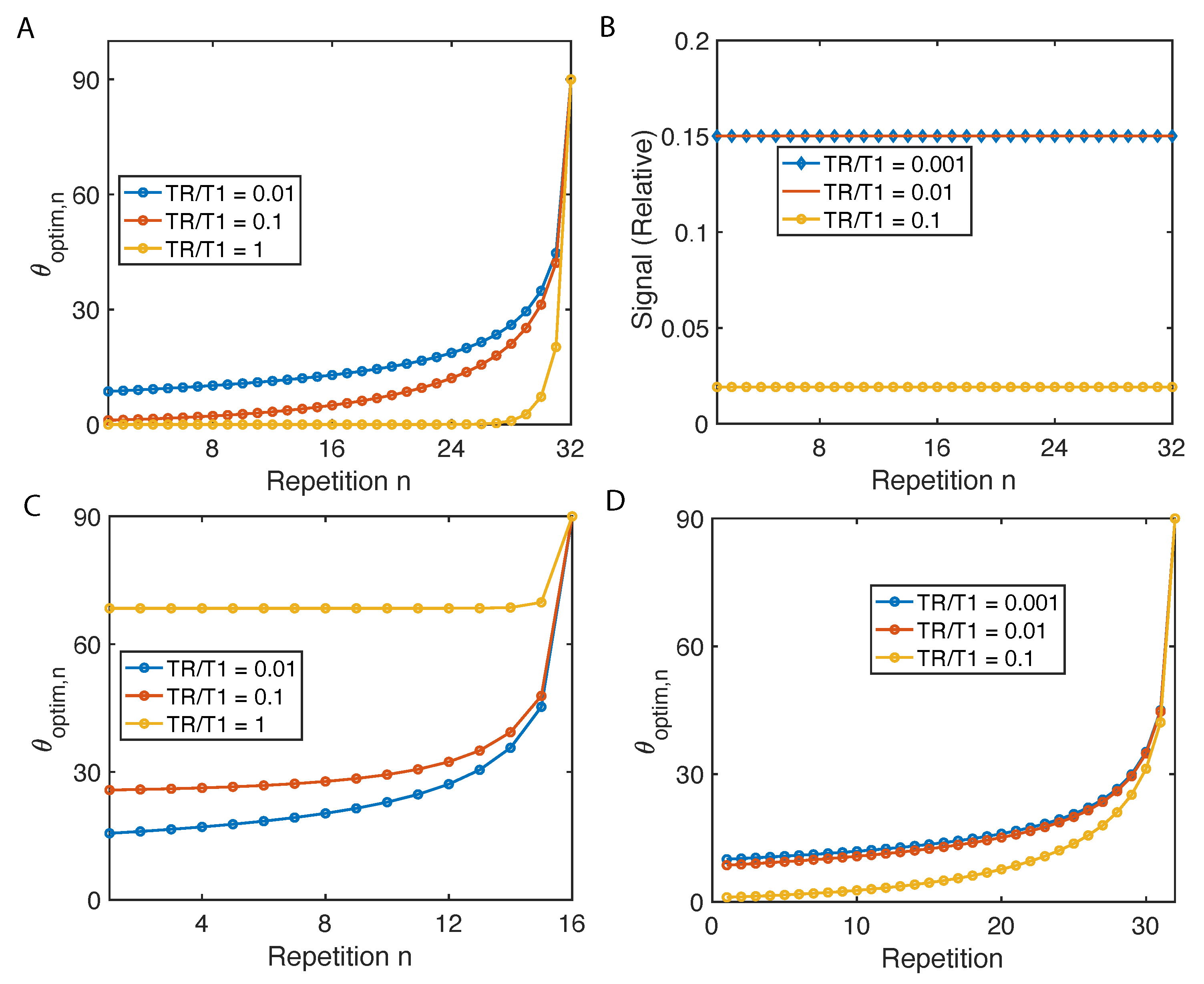
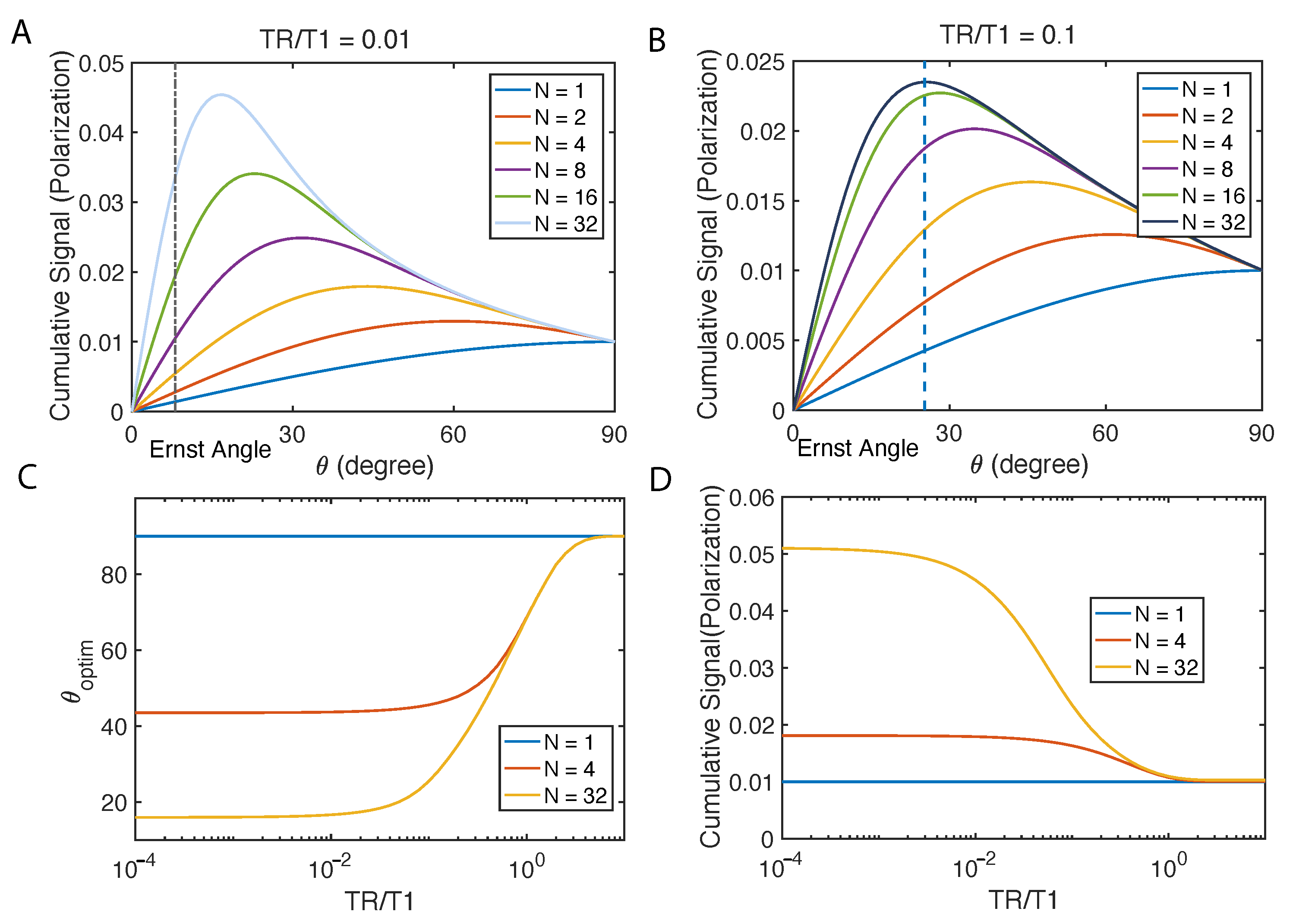
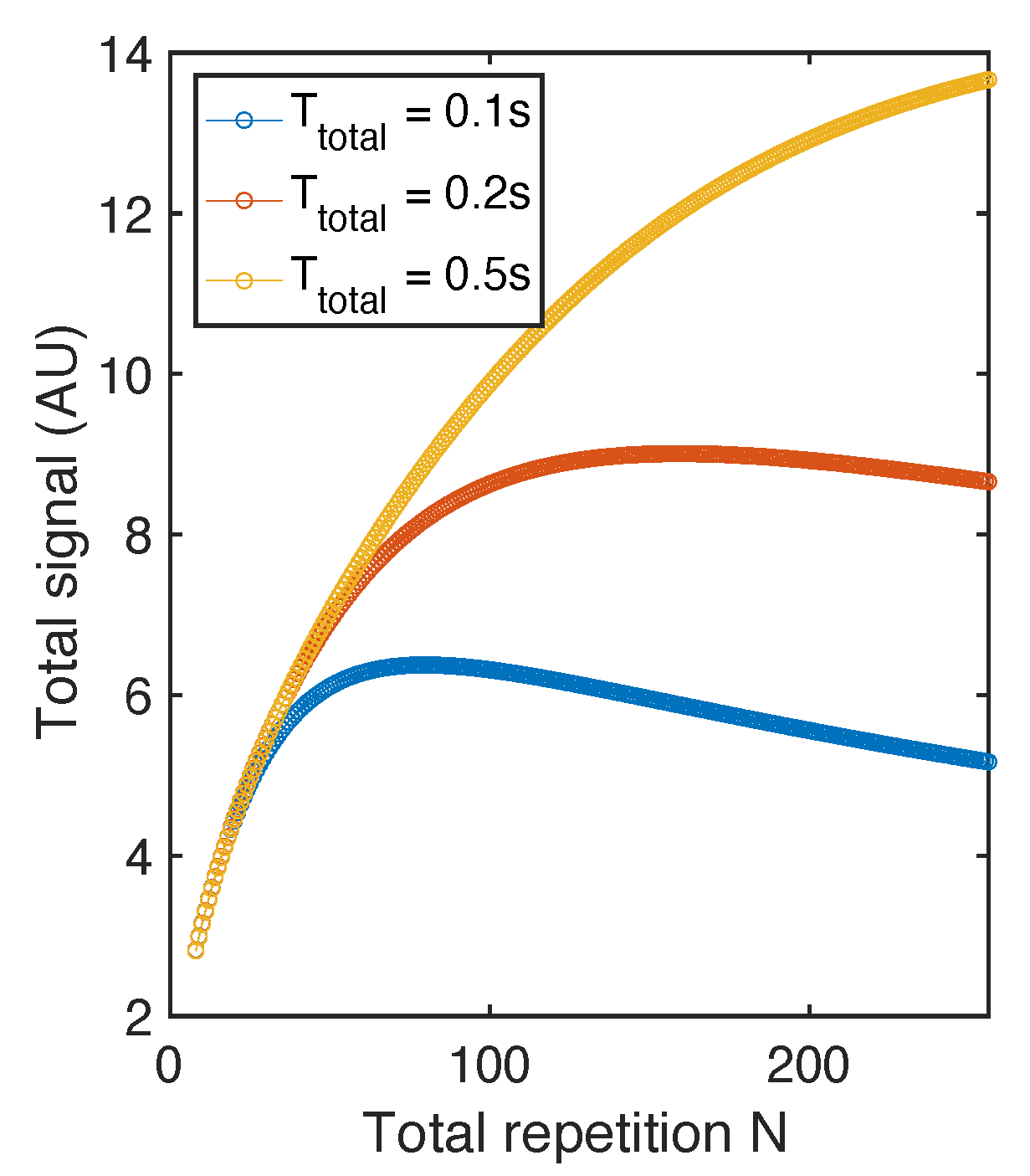
2.2. Flip Angle Consideration
2.3. Gradient Consideration
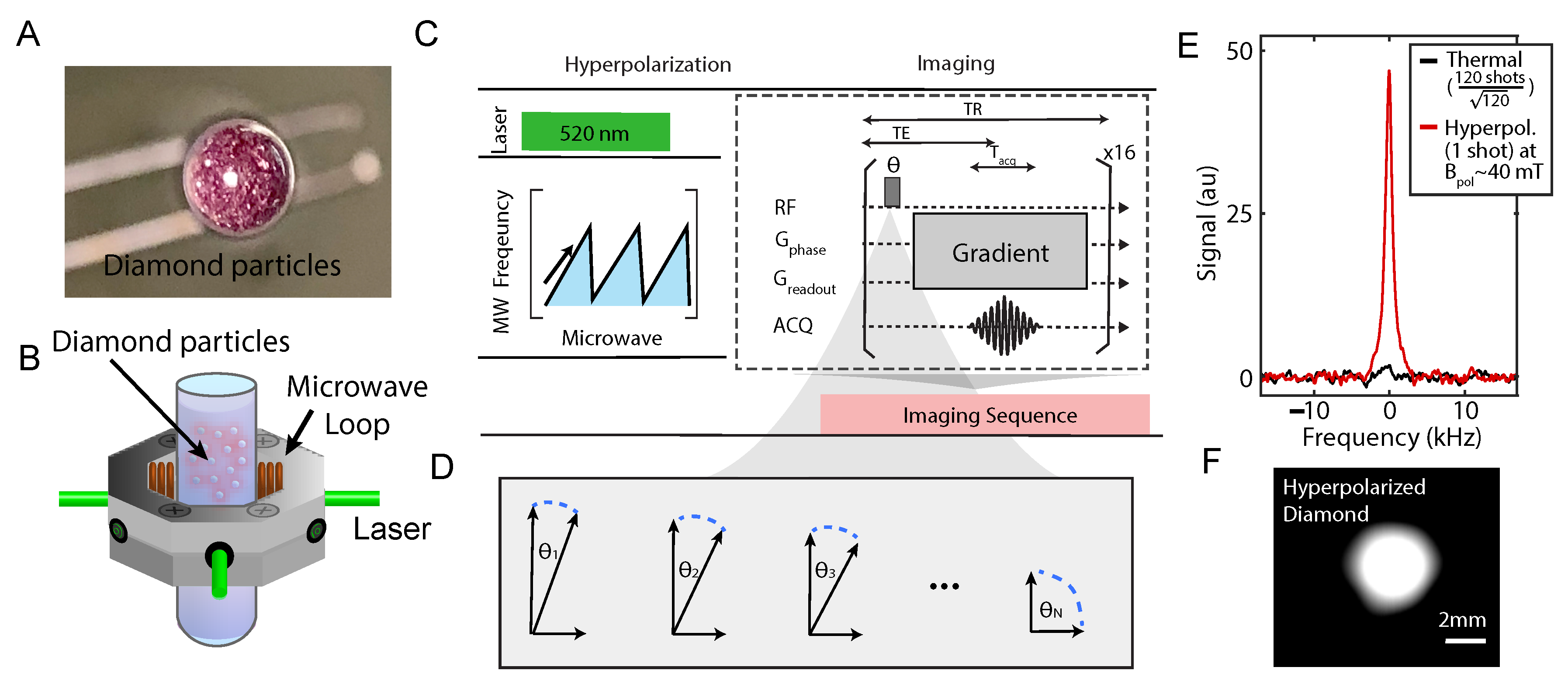
2.4. Hyperpolarized Diamond Imaging Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Simulation and Optimization
4.2. Hyperpolarization and Imaging
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Derivation
Appendix A.1. Variable Flip Angle for Constant Magnetization
Appendix A.2. Variable Flip Angle for Maximum Cumulative Magnetization
Appendix B. Magnetization Simulation
References
- Ernst, R.; Bodenhausen, G.; Wokaun, A. Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in One and Two Dimensions; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich, K. NMR studies of structure and function of biological macromolecules (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3340–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, P.G. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Medicine and Biology; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Huettel, S.A.; Song, A.W.; McCarthy, G. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Abragam, A.; Goldman, M. Principles of Dynamic Nuclear Polarization. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1978, 41, 395–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theis, T.; Ganssle, P.; Kervern, G.; Knappe, S.; Kitching, J.; Ledbetter, M.; Budker, D.; Pines, A. Parahydrogen-enhanced zero-field nuclear magnetic resonance. Nat. Phys. 2011, 7, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikhov, K.M.; Molin, Y.N.; Sagdeev, R.; Buchachenko, A. Spin Polarization and Magnetic Effects in Radical Reactions; Elsevier Science Ltd: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Guthi, J.S.; Yang, S.G.; Huang, G.; Li, S.; Khemtong, C.; Kessinger, C.W.; Peyton, M.; Minna, J.D.; Brown, K.C.; Gao, J. MRI-visible micellar nanomedicine for targeted drug delivery to lung cancer cells. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajoy, A.; Liu, K.; Nazaryan, R.; Lv, X.; Zangara, P.R.; Safvati, B.; Wang, G.; Arnold, D.; Li, G.; Lin, A.; et al. Orientation-independent room temperature optical 13C hyperpolarization in powdered diamond. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelezko, F.; Wrachtrup, J. Single defect centres in diamond: A review. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 2006, 203, 3207–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Walton, J.; Druga, E.; Wang, F.; Aguilar, A.; McKnelly, T.; Nazaryan, R.; Wu, L.; Shenderova, O.; Vigneron, D.; et al. High contrast dual-mode optical and 13C magnetic resonance imaging in diamond particles. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.08064. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, J.I.; Perevedentseva, E.; Chung, P.H.; Liu, K.K.; Cheng, C.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Cheng, C.L. Nanometer-sized diamond particle as a probe for biolabeling. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 2199–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.S.; Bezinge, L.; Gliddon, H.D.; Huang, D.; Dold, G.; Gray, E.R.; Heaney, J.; Dobson, P.J.; Nastouli, E.; Morton, J.J.; et al. Spin-enhanced nanodiamond biosensing for ultrasensitive diagnostics. Nature 2020, 587, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Zhou, H.; Landig, R.; Wu, H.Y.; Yu, X.; Von Stetina, S.E.; Kucsko, G.; Mango, S.E.; Needleman, D.J.; Samuel, A.D.T.; et al. Probing and manipulating embryogenesis via nanoscale thermometry and temperature control. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14636–14641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shagieva, F.; Zaiser, S.; Neumann, P.; Dasari, D.; Stohr, R.; Denisenko, A.; Reuter, R.; Meriles, C.; Wrachtrup, J. Microwave-assisted cross-polarization of nuclear spin ensembles from optically pumped nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 3731–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, D.G. Principles of Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Standford Univ.: Stanford, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Abragam, A. Principles of Nuclear Magnetism; Oxford Univ. Press: Oxford, UK, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Takegoshi, K.; McDowell, C. A “magic echo” pulse sequence for the high-resolution NMR spectra of abundant spins in solids. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1985, 116, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, M.A.; Michaud, M.; VanHouten, J.N.; Insogna, K.L.; Madri, J.A.; Barrett, S.E. Phosphorus-31 MRI of hard and soft solids using quadratic echo line-narrowing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5190–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.Y.; Du, J.; Chung, C.B. UTE imaging in the musculoskeletal system. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 41, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, K.T. Advanced Methods for Radial Data Sampling in Magnetic Resonance Imaging; SUB University of Goettingen: Göttingen, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ajoy, A.; Nazaryan, R.; Druga, E.; Liu, K.; Aguilar, A.; Han, B.; Gierth, M.; Oon, J.T.; Safvati, B.; Tsang, R.; et al. Room temperature “optical nanodiamond hyperpolarizer”: Physics, design, and operation. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 023106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dementyev, A.; Cory, D.; Ramanathan, C. Dynamic nuclear polarization in silicon microparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 127601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, A.L.; Klimov, P.V.; Ivády, V.; Szász, K.; Christle, D.J.; Koehl, W.F.; Gali, Á.; Awschalom, D.D. Optical polarization of nuclear spins in silicon carbide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 247603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, X.; Walton, J.; Druga, E.; Nazaryan, R.; Mao, H.; Pines, A.; Ajoy, A.; Reimer, J. Imaging Sequences for Hyperpolarized Solids. Molecules 2021, 26, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010133
Lv X, Walton J, Druga E, Nazaryan R, Mao H, Pines A, Ajoy A, Reimer J. Imaging Sequences for Hyperpolarized Solids. Molecules. 2021; 26(1):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010133
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Xudong, Jeffrey Walton, Emanuel Druga, Raffi Nazaryan, Haiyan Mao, Alexander Pines, Ashok Ajoy, and Jeffrey Reimer. 2021. "Imaging Sequences for Hyperpolarized Solids" Molecules 26, no. 1: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010133
APA StyleLv, X., Walton, J., Druga, E., Nazaryan, R., Mao, H., Pines, A., Ajoy, A., & Reimer, J. (2021). Imaging Sequences for Hyperpolarized Solids. Molecules, 26(1), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010133




