PDI-Regulated Disulfide Bond Formation in Protein Folding and Biomolecular Assembly
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Conservative Primary and Dynamic Tertiary Structures of hPDI
3. Biochemical Activities of hPDI
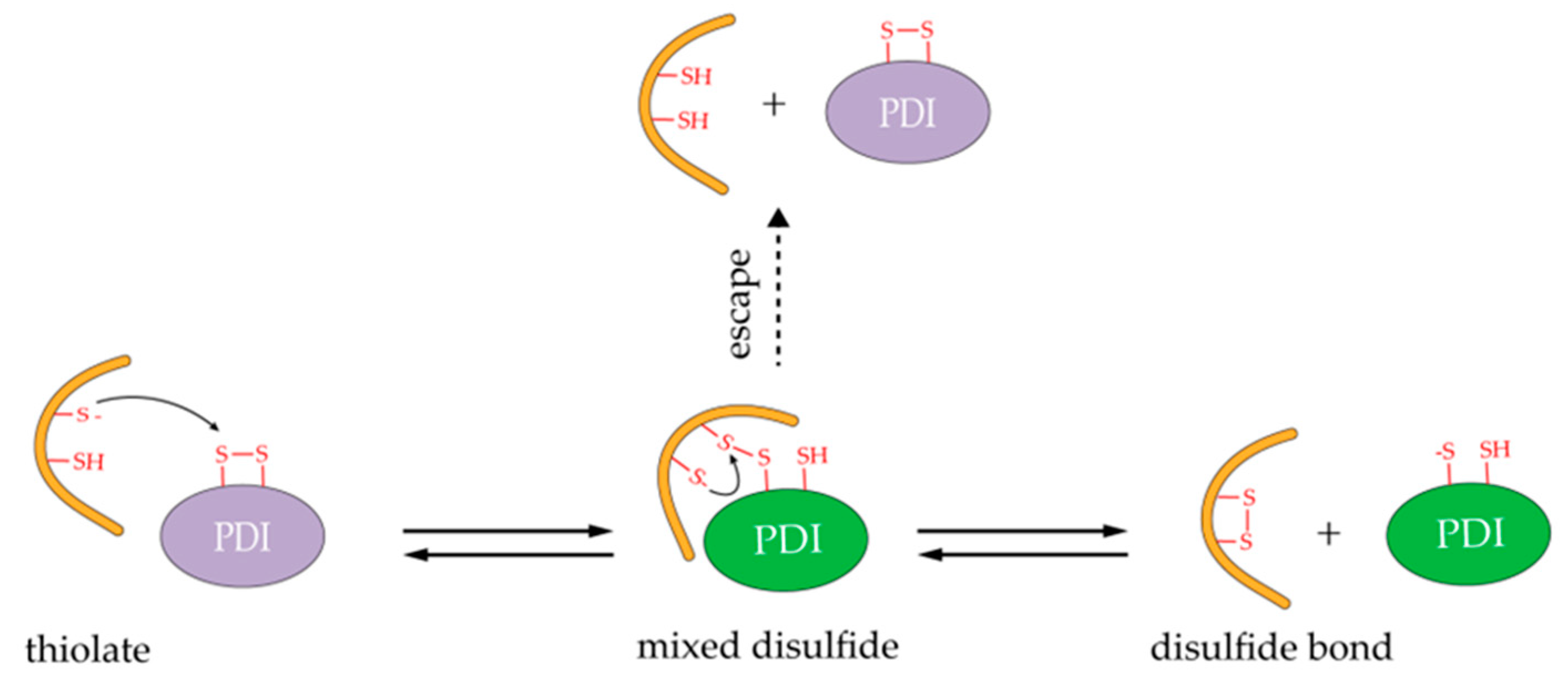
3.1. Oxidoreductase Activity
3.2. Isomerase Activity
3.3. Chaperone Activity
4. Substrate Binding and Domain Coordination in hPDI
5. Catalysis Mechanism and Redox Regeneration of hPDI
6. Formation of Gluten Network Catalyzed by wPDI
6.1. GMP and wPDI in Wheat Flour
6.2. Proposed Catalytic Mechanism of wPDI
7. Other Functions of PDI
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anfinsen, C.B. Principles that govern the folding of protein chains. Science 1973, 181, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellis, R.J. Proteins as molecular chaperones. Nature 1987, 328, 378–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, R.J. Molecular chaperones: Assisting assembly in addition to folding. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, C.R.; Lake, D.F. Oxidative Protein Folding: Nature’s Knotty Challenge. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 2014, 21, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, S.; Matsusaki, M.; Arai, K.; Hidaka, Y.; Inaba, K.; Okumura, M.; Muraoka, T. Coupling effects of thiol and urea-type groups for promotion of oxidative protein folding. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arolas, J.L.; Aviles, F.X.; Chang, J.-Y.; Ventura, S. Folding of small disulfide-rich proteins: Clarifying the puzzle. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, B.P.; Weissman, J.S. Oxidative protein folding in eukaryotes: Mechanisms and consequences. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 164, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.S.; Kwon, O.Y.; Arvan, P. An endoplasmic reticulum storage disease causing congenital goiter with hypothyroidism. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 133, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.D.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. Models of amyloid seeding in Alzheimer’s disease and scrapie: Mechanistic truths and physiological consequences of the time-dependent solubility of amyloid proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997, 66, 385–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.J.; Qu, B.H.; Pedersen, P.L. Defective protein folding as a basis of human disease. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995, 20, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, C.M.; Liu, Y.; Sifers, R.N. Dissecting glycoprotein quality control in the secretory pathway. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, J.L.; Werner, E.D.; Dubas, M.E.; Goeckeler, J.L.; Kruse, K.B.; McCracken, A.A. The requirement for molecular chaperones during endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation demonstrates that protein export and import are mechanistically distinct. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 3453–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldberger, R.F.; Epstein, C.J.; Anfinsen, C.B. Acceleration of Reactivation of Reduced Bovine Pancreatic Ribonuclease by a Microsomal System from Rat Liver. J. Biol. Chem. 1963, 238, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Venetianer, P.; Straub, F.B. The enzymic reactivation of reduced ribonuclease. BBA-Spec. Enzymol. Subj. 1963, 67, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatahet, F.; Ruddock, L.W. Protein disulfide isomerase: A critical evaluation of its function in disulfide bond formation. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 2009, 11, 2807–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Berg, B.; Chung, E.W.; Robinson, C.V.; Mateo, P.L.; Dobson, C.M. The oxidative refolding of hen lysozyme and its catalysis by protein disulfide isomerase. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 4794–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Creighton, T.E.; Hillson, D.A.; Freedman, R.B. Catalysis by protein-disulphide isomerase of the unfolding and refolding of proteins with disulphide bonds. J. Mol. Biol. 1980, 142, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creighton, T.E.; Bagley, C.J.; Cooper, L.; Darby, N.J.; Freedman, R.B.; Kemmink, J.; Sheikh, A. On the biosynthesis of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI): Structure, processing, folding and disulphide bond formation of the precursor in vitro and in microsomes. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 232, 1176–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, J.S.; Kimt, P.S. Efficient catalysis of disulphide bond rearrangements by protein disulphide isomerase. Nature 1993, 365, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, M.; Noi, K.; Kanemura, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Saio, T.; Inoue, Y.; Hikima, T.; Akiyama, S.; Ogura, T.; Inaba, K. Dynamic assembly of protein disulfide isomerase in catalysis of oxidative folding. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Wang, C.C. Protein disulfide isomerase is regulated in multiple ways: Consequences for conformation, activities, and pathophysiological functions. Bioessays 2020, e2000147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denisov, A.Y.; Määttänen, P.; Dabrowski, C.; Kozlov, G.; Thomas, D.Y.; Gehring, K. Solution structure of the bb′ domains of human protein disulfide isomerase. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Huo, L.; Wang, L.; Feng, W.; Wang, C.C. Human protein-disulfide isomerase is a redox-regulated chaperone activated by oxidation of domain a′. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Li, W.; Ren, J.Q.; Fang, J.Q.; Ke, H.M.; Gong, W.M.; Feng, W.; Wang, C.C. Structural insights into the redox-regulated dynamic conformations of human protein disulfide isomerase. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 2013, 19, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.Q.; Huang, Z.; Liu, G.; Huang, Y.B.; Hou, Y. Effects of Domains of Wheat Protein Disulfide Isomerase on its Properties. J. South China Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2017, 45, 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Paolacci, A.R.; Ciaffi, M.; Dhanapal, A.P.; Tanzarella, O.A.; Porceddu, E.; d’Aloisio, E. Protein disulphide isomerase family in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): Protein structure and expression analysis. Plant Genet. Resour.-C 2011, 9, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccarthy, A.A.; Haebel, P.W.; Trrnen, A.; Rybin, V.; Metcalf, P. Crystal structure of the protein disulfide bond isomerase, DsbC, from Escherichia coli. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, S.; Higashino, Y.; Kitao, Y.; Masuda, T.; Urade, R. Expression and characterization of protein disulfide isomerase family proteins in bread wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, D.M.; SÖLING, H.-D. The protein disulphide-isomerase family: Unravelling a string of folds. Biochem. J. 1999, 339, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiri, E.; Levitan, A.; Guo, F.; Christopher, D.; Schaefer, D.; Zrÿd, J.P.; Danon, A. Characterization of three PDI-like genes in Physcomitrella patens and construction of knock-out mutants. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2002, 267, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galligan, J.J.; Petersen, D.R. The human protein disulfide isomerase gene family. Hum. Genom. 2012, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Kojima, R.; Okumura, M.; Hagiwara, M.; Masui, S.; Maegawa, K.; Saiki, M.; Horibe, T.; Suzuki, M.; Inaba, K. Synergistic cooperation of PDI family members in peroxiredoxin 4-driven oxidative protein folding. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsusaki, M.; Kanemura, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Lee, Y.H.; Inaba, K.; Okumura, M. The protein disulfide isomerase family: From proteostasis to pathogenesis. BBA-Gen. Subj. 2020, 1864, 129338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Aloisio, E.; Paolacci, A.R.; Dhanapal, A.P.; Tanzarella, O.A.; Porceddu, E.; Ciaffi, M. The Protein Disulfide Isomerase gene family in bread wheat (T. aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houston, N.L.; Fan, C.; Xiang, J.Q.-Y.; Schulze, J.M.; Jung, R.; Boston, R.S. Phylogenetic Analyses Identify 10 Classes of the Protein Disulfide Isomerase Family in Plants, Including Single-Domain Protein Disulfide Isomerase-Related Proteins. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 762–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freedman, R.B.; Klappa, P.; Ruddock, L.W. Protein disulfide isomerases exploit synergy between catalytic and specific binding domains. EMBO Rep. 2002, 3, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Hu, S.Q.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.J.; Lin, L.I.; Hou, Y. Gene Cloning, Expression and Characterization of Protein Disulfide Isomerase from Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Food Sci. 2017, 38, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Darby, N.J.; van Straaten, M.; Penka, E.; Vincentelli, R.; Kemmink, J. Identifying and characterizing a second structural domain of protein disulfide isomerase. FEBS Lett. 1999, 448, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freedman, R.B.; Ganea, P.J.; Hawkins, H.C.; Hlodan, R.; McLaughlin, S.H.; Parry, J.W.L. Experimental and theoretical analyses of the domain architecture of mammalian protein disulphide-isomerase. Biol. Chem. 1998, 379, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanna, L.; Arne, H. Determination of the reduction-oxidation potential of the thioredoxin-like domains of protein. Biochem. 1993, 32, 6649–6656. [Google Scholar]
- Fass, D.; Thorpe, C. Chemistry and Enzymology of Disulfide Cross-Linking in Proteins. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1169–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chivers, P.T.; Prehoda, K.E.; Raines, R.T. The CXXC motif: A rheostat in the active site. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 4061–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemmink, J.; Darby, N.J.; Dijkstra, K.; Nilges, M.; Creighton, T.E. The folding catalyst protein disulfide isomerase is constructed of active and inactive thioredoxin modules. Curr. Biol. 1997, 7, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klappa, P.; Ruddock, L.W.; Darby, N.J.; Freedman, R.B. The b′ domain provides the principal peptide-binding site of protein disulfide isomerase but all domains contribute to binding of misfolded proteins. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, P.Y.; Churchich, J.E. Recognition of Protein Substrates by Protein-disulfide Isomerase A SEQUENCE OF THE b′ DOMAIN RESPONDS TO SUBSTRATE BINDING. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 32757–32761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okumura, M.; Kadokura, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Yutani, K.; Kanemura, S.; Hikima, T.; Hidaka, Y.; Ito, L.; Shiba, K.; Masui, S. Inhibition of the Functional Interplay between Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Oxidoreduclin-1α (Ero1α) and Protein-disulfide Isomerase (PDI) by the Endocrine Disruptor Bisphenol A. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27004–27018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munro, S.; Pelham, H.R.B. A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell 1987, 48, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, B.; Gilbert, H.F. Protein disulfide isomerase. BBA-Proteins Proteom. 2004, 1699, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulp, M.S.; Frickel, E.M.; Ellgaard, L.; Weissman, J.S. Domain architecture of protein-disulfide isomerase facilitates its dual role as an oxidase and an isomerase in Ero1p-mediated disulfide formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Li, S.J.; Sidhu, A.; Zhu, L.; Liang, Y.; Freedman, R.B.; Wang, C.C. Reconstitution of human Ero1-Lα/protein-disulfide isomerase oxidative folding pathway in vitro position-dependent differences in role between the a and a′ domains of protein-disulfide isomerase. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.C. Protein disulfide-isomerase, a folding catalyst and a redox-regulated chaperone. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2015, 83, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Yu, P.; Liang, H.; Fu, J.; Luo, Z.; Yang, D. The wPDI Redox Cycle Coupled Conformational Change of the Repetitive Domain of the HMW-GS 1Dx5-A Computational Study. Molecules 2020, 25, 4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyette, J.; Evangelista, B.; Tatulian, S.A.; Teter, K. Stability and conformational resilience of protein disulfide isomerase. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 3572–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagiutsumi, M.; Satoh, T.; Kato, K. Structural basis of redox-dependent substrate binding of protein disulfide isomerase. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serve, O.; Kamiya, Y.; Maeno, A.; Nakano, M.; Murakami, C.; Sasakawa, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Harada, T.; Kurimoto, E.; Yagi-Utsumi, M.; et al. Redox-dependent domain rearrangement of protein disulfide isomerase coupled with exposure of its substrate-binding hydrophobic surface. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 396, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasako, M.; Maeno, A.; Kurimoto, E.; Harada, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Oka, T.; Takayama, Y.; Iwata, A.; Kato, K. Redox-dependent domain rearrangement of protein disulfide isomerase from a thermophilic fungus. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6953–6962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Cui, L.; Ding, X.; Niu, L.L.; Yang, F.Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.C.; Lou, J. Compact conformations of human protein disulfide isomerase. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, V.D.; Wallis, K.; Howard, M.J.; Haapalainen, A.M.; Salo, K.E.H.; Saaranen, M.J.; Sidhu, A.; Wierenga, R.K.; Freedman, R.B.; Ruddock, L.W. Alternative conformations of the x region of human protein disulphide-isomerase modulate exposure of the substrate binding b’ domain. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 383, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, L.; Rasmussen, M.I.; Chailyan, A.; Houen, G.; Højrup, P. Probing the structure of human protein disulphide isomerase by chemical cross-linking combined with mass spectrometry. J. Proteome 2014, 108, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koivunen, P.; Salo, K.E.H.; Myllyharju, J.; Ruddock, L.W. Three Binding Sites in Protein-disulfide Isomerase Cooperate in Collagen Prolyl 4-Hydroxylase Tetramer Assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 5227–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byrne, L.J.; Sidhu, A.; Wallis, A.K.; Ruddock, L.W.; Freedman, R.B.; Howard, M.J.; Williamson, R.A. Mapping of the ligand-binding site on the b′ domain of human PDI: Interaction with peptide ligands and the x-linker region. Biochem. J. 2009, 423, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, G.; Xiang, S.; Noiva, R.; Lennarz, W.J.; Schindelin, H. The Crystal Structure of Yeast Protein Disulfide Isomerase Suggests Cooperativity between Its Active Sites. Cell 2006, 124, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, G.; Kober, F.X.; Lewandrowski, U.; Sickmann, A.; Lennarz, W.J.; Schindelin, H. The catalytic activity of protein-disulfide isomerase requires a conformationally flexible molecule. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 33630–33640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serve, O.; Kamiya, Y.; Kato, K. Redox-dependent chaperoning, following PDI footsteps. Proteom. Res. J. 2012, 3, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, K.W.; Gilbert, H.F. Oxidation of kinetically trapped thiols by protein disulfide isomerase. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 13642–13650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, N.J.; Creighton, T.E. Functional properties of the individual thioredoxin-like domains of protein disulfide isomerase. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 11725–11735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanen, H.I.; Salo, K.E.H.; Pirneskoski, A.; Ruddock, L.W. pH dependence of the peptide thiol-disulfide oxidase activity of six members of the human protein disulfide isomerase family. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 2006, 8, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappi, A.K.; Ruddock, L.W. Reexamination of the role of interplay between glutathione and protein disulfide isomerase. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 409, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benham, A.M.; van Lith, M.; Sitia, R.; Braakman, I. Ero1–PDI interactions, the response to redox flux and the implications for disulfide bond formation in the mammalian endoplasmic reticulum. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2013, 368, 20110403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Wang, J.J.; Hou, Y.; Huang, Y.B.; Zhang, Y.P.; Li, C.Z.; Li, L.; Hu, S.Q. Recombinant Wheat Endoplasmic Reticulum Oxidoreductin 1 Improved Wheat Dough Properties and Bread Quality. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2162–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, J.J.; Hou, Y.; Huang, Y.B.; Wang, J.J.; Li, C.Z.; Guo, S.J.; Li, L.; Hu, S.Q. Characterization of wheat endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductin 1 and its application in Chinese steamed bread. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Gilbert, H.F. Discrimination between native and non-native disulfides by protein-disulfide isomerase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 15747–15752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wedemeyer, W.J.; Welker, E.; Narayan, M.; Scheraga, H.A. Disulfide bonds and protein folding. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 4207–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, K.W.; Lyles, M.M.; Gilbert, H.F. Catalysis of oxidative protein folding by mutants of protein disulfide isomerase with a single active-site cysteine. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 1972–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, H.F. Protein disulfide isomerase and assisted protein folding. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 29399–29402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, R.; Pace, N.J.; Brown, D.R.; Weerapana, E. 1, 3, 5-Triazine as a modular scaffold for covalent inhibitors with streamlined target identification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2497–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Manevich, Y.; Tew, K.D.; Townsend, D.M. S-glutathionylation of protein disulfide isomerase regulates estrogen receptor stability and function. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 2012, 273549. [Google Scholar]
- Puig, A.; Gilbert, H.F. Protein disulfide isomerase exhibits chaperone and anti-chaperone activity in the oxidative refolding of lysozyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 7764–7771. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, J.; Klappa, P.; Freedman, R.B.; Lilie, H.; Rudolph, R. Catalytic Activity and Chaperone Function of Human Protein-disulfide Isomerase Are Required for the Efficient Refolding of Proinsulin. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.C.; Tsou, C.L. Protein disulfide isomerase is both an enzyme and a chaperone. FASEB J. 1993, 7, 1515–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wang, C.C.; Tsou, C.L. Chaperone-like activity of protein disulfide isomerase in the refolding of a protein with no disulfide bonds. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 24550–24552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, J.L.; Wang, C.C. Chaperone-like activity of protein disulfide-isomerase in the refolding of rhodanese. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 231, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakob, U.; Buchner, J. Assisting spontaneity: The role of Hsp90 and small Hsps as molecular chaperones. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1994, 19, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wang, C.C. A mutant truncated protein disulfide isomerase with no chaperone activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 27572–27576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quan, H.; Fan, G.; Wang, C.C. Independence of the chaperone activity of protein disulfide isomerase from its thioredoxin-like active site. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 17078–17080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayano, T.; Hirose, M.; Kikuchi, M. Protein disulfide isomerase mutant lacking its isomerase activity accelerates protein folding in the cell. FEBS Lett. 1995, 377, 505–511. [Google Scholar]
- LaMantia, M.; Lennarz, W.J. The essential function of yeast protein disulfide isomerase does not reside in its isomerase activity. Cell 1993, 74, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, N.; Mor-Cohen, R.; Sheptovitsky, V.H.; Romanenco, O.; Hess, O.; Lahav, J. Integrin-mediated cell adhesion requires extracellular disulfide exchange regulated by protein disulfide isomerase. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 381, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Tsou, C.L. Enzymes as chaperones and chaperones as enzymes. FEBS Lett. 1998, 425, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, X.M.; Zhu, B.T. Human pancreas-specific protein disulfide-isomerase (PDIp) can function as a chaperone independently of its enzymatic activity by forming stable complexes with denatured substrate proteins. Biochem. J. 2010, 429, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Solovyov, A.; Gilbert, H.F.; Holmgren, A.; Lundström-Ljung, J. Combinations of protein-disulfide isomerase domains show that there is little correlation between isomerase activity and wild-type growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 27975–27980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darby, N.J.; Penka, E.; Vincentelli, R. The multi-domain structure of protein disulfide isomerase is essential for high catalytic efficiency. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 276, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klappa, P.; Hawkins, H.C.; Freedman, R.B. Interactions between protein disulphide isomerase and peptides. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 248, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klappa, P.; Koivunen, P.; Pirneskoski, A.; Karvonen, P.; Ruddock, L.W.; Kivirikko, K.I.; Freedman, R.B. Mutations that destabilize the a′ domain of human protein-disulfide isomerase indirectly affect peptide binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 13213–13218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bulaj, G. Formation of disulfide bonds in proteins and peptides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2005, 23, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.W.; Gilbert, H.F. Scanning and escape during protein-disulfide isomerase-assisted protein folding. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 8845–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darby, N.J.; Freedman, R.B.; Creighton, T.E. Dissecting the mechanism of protein disulfide isomerase: Catalysis of disulfide bond formation in a model peptide. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 7937–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frand, A.R.; Kaiser, C.A. The Ero1 gene of yeast is required for oxidation of protein dithiols in the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, M.G.; Travers, K.J.; Weissman, J.S. Ero1p: A novel and ubiquitous protein with an essential role in oxidative protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabibbo, A.; Pagani, M.; Fabbri, M.; Rocchi, M.; Farmery, M.R.; Bulleid, N.J.; Sitia, R. ERo1-L, a human protein that favors disulfide bond formation in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 4827–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavender, T.J.; Bulleid, N.J. Molecular mechanisms regulating oxidative activity of the Ero1 family in the endoplasmic reticulum. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 2010, 13, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Araki, K.; Inaba, K. Structure, Mechanism, and Evolution of Ero1 Family Enzymes. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 2012, 16, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, E.; Sevier, C.S.; Heldman, N.; Vitu, E.; Bentzur, M.; Kaiser, C.A.; Thorpe, C.; Fass, D. Generating disulfides enzymatically: Reaction products and electron acceptors of the endoplasmic reticulum thiol oxidase Ero1p. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masui, S.; Vavassori, S.; Fagioli, C.; Sitia, R.; Inaba, K. Molecular Bases of Cyclic and Specific Disulfide Interchange between Human ERO1α Protein and Protein-disulfide Isomerase (PDI). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 16261–16271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baker, K.M.; Chakravarthi, S.; Langton, K.P.; Sheppard, A.M.; Lu, H.; Bulleid, N.J. Low reduction potential of Ero1α regulatory disulphides ensures tight control of substrate oxidation. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 2988–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Appenzeller-Herzog, C.; Riemer, J.; Christensen, B.; Sørensen, E.S.; Ellgaard, L. A novel disulphide switch mechanism in Ero1α balances ER oxidation in human cells. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 2977–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoli, G.; Simmen, T.; Anelli, T.; Molteni, S.N.; Fesce, R.; Sitia, R. Two conserved cysteine triads in human Ero1alpha cooperate for efficient disulfide bond formation in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30047–30052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sevier, C.S.; Kaiser, C.A. Ero1 and redox homeostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum. BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2008, 1783, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moilanen, A.; Ruddock, L.W. Non-native proteins inhibit the ER oxidoreductin 1 (Ero1)–protein disulfide-isomerase relay when protein folding capacity is exceeded. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, jbc.RA119.011766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwasaki, K.; Kamauchi, S.; Wadahama, H.; Ishimoto, M.; Kawada, T.; Urade, R. Molecular cloning and characterization of soybean protein disulfide isomerase family proteins with nonclassic active center motifs. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 4130–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamauchi, S.; Wadahama, H.; Iwasaki, K.; Nakamoto, Y.; Nishizawa, K.; Ishimoto, M.; Kawada, T.; Urade, R. Molecular cloning and characterization of two soybean protein disulfide isomerases as molecular chaperones for seed storage proteins. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 2644–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, C.W.; Čemažar, M.; Clark, R.J.; Horibe, T.; Renda, R.F.; Anderson, M.A.; Craik, D.J. A novel plant protein-disulfide isomerase involved in the oxidative folding of cystine knot defense proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20435–20446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, L.J.; Jiang, C.C.; Wang, F.M.; Yang, P.; Feng, Z.Y. Genome-wide characterization and transcriptional analysis of the protein disulfide isomerase-like genes in barley (Hordeum vulgare). Acta Agron. Sin. 2019, 45, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Luo, Z.; Li, M.; Gao, J.; Liang, Z.; Sun, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, D. Wheat protein disulfide isomerase improves bread properties via different mechanisms. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.L.; Yu, Z.T.; Cao, M.; Shen, X.X.; Li, N.; Li, X.H.; Ma, W.J.; Weißgerber, H.; Zeller, F.; Hsam, S.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of HMW glutenin subunits from 1Sl genome of Aegilops longissima positively affecting wheat breadmaking quality. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shewry, P.R. The synthesis, processing, and deposition of gluten proteins in the developing wheat grain. Cereal Foods World 1999, 44, 587–589. [Google Scholar]
- Feeney, K.A.; Wellner, N.; Gilbert, S.; Halford, N.G.; Tatham, A.S.; Shewry, P.R.; Belton, P.S. Molecular structures and interactions of repetitive peptides based on wheat glutenin subunits depend on chain length. Biopolymers 2003, 72, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R.; Tatham, A.S. Disulphide Bonds in Wheat Gluten Proteins. J. Cereal Sci. 1997, 25, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, A.; Sparvoli, F.; Ceriotti, A. Role of individual disulfide bonds in the structural maturation of a low molecular weight glutenin subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 32322–32329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weegels, P.L.; vandePijpekamp, A.M.; Graveland, A.; Hamer, R.J.; Schofield, J.D. Depolymerisation and Re-polymerisation of Wheat Glutenin during Dough Processing. I. Relationships between Glutenin Macropolymer Content and Quality Parameters. J. Cereal Sci. 1996, 23, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneel, C.; Lagrain, B.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Redox agents and N-ethylmaleimide affect the extractability of gluten proteins during fresh pasta processing. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagrain, B.; Thewissen, B.G.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Mechanism of gliadin–glutenin cross-linking during hydrothermal treatment. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoni, Y.; Segal, G.; Zhu, X.; Galili, G. Nucleotide sequence of a wheat cDNA encoding protein disulfide isomerase. Plant Physiol. 1995, 107, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ciaffi, M.; Paolacci, A.R.; Dominici, L.; Tanzarella, O.A.; Porceddu, E. Molecular characterization of gene sequences coding for protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum). Gene 2001, 265, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaffi, M.; Paolacci, A.R.; D”Aloisio, E.; Tanzarella, O.A.; Porceddu, E. Cloning and characterization of wheat PDI (protein disulfide isomerase) homoeologous genes and promoter sequences. Gene 2006, 366, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.W.; Li, N.; Lu, X.B.; Prodanovic, S.; Xu, Y.H.; Zhang, W.Y.; Yan, Y.M. Quality properties and expression profiling of protein disulfide isomerase genes during grain development of three spring wheat near isogenic lines. Genetika 2016, 48, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimwade, B.; Tatham, A.S.; Freedman, R.B.; Shewry, P.R.; Napier, J.A. Comparison of the expression patterns of genes coding for wheat gluten proteins and proteins involved in the secretory pathway in developing caryopses of wheat. Plant Mol. Biol. 1996, 30, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuPont, F.M.; Hurkman, W.J.; Tanaka, C.K.; Chan, R. BiP, HSP70, NDK and PDI in wheat endosperm. I. Accumulation of mRNA and protein during grain development. Physiol. Plant. 1998, 103, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, E.; Bell, A.E.; Brockway, B.E. The effect of protein disulphide isomerase on dough rheology assessed by fundamental and empirical testing. Food Chem. 1998, 61, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; Nishimura, K.; Urade, R. Relationship between endogenous protein disulfide isomerase family proteins and glutenin macropolymer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12970–12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, J.J.; Hou, Y.; Huang, Y.B.; Li, C.Z.; Li, L.; Hu, S.Q. Improvements of Modified Wheat Protein Disulfide Isomerases with Chaperone Activity Only on the Processing Quality of Flour. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2016, 10, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, M.; Fabbri, M.; Benedetti, C.; Fassio, A.; Pilati, S.; Bulleid, N.J.; Cabibbo, A.; Sitia, R. Endoplasmic Reticulum Oxidoreductin 1-L beta (ERO1-L beta), a Human Gene Induced in the Course of the Unfolded Protein Response. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23685–23692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onda, Y.; Kumamaru, T.; Kawagoe, Y. ER membrane-localized oxidoreductase Ero1 is required for disulfide bond formation in the rice endosperm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14156–14161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsusak, M.; Okuda, A.; Masuda, T.; Koishihara, K.; Mita, R.; Iwasaki, K.; Hara, K.; Naruo, Y.; Hirose, A.; Tsuchi, Y. Cooperative Protein Folding by Two Protein Thiol Disulfide Oxidoreductases and ERO1 in Soybean. Plant Physiol. 2015, 170, 774–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Otsu, M.; Bertoli, G.; Fagioli, C.; Guerini-Rocco, E.; Nerini-Molteni, S.; Ruffato, E.; Sitia, R. Dynamic retention of Ero1alpha and Ero1beta in the endoplasmic reticulum by interactions with PDI and ERp44. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 2006, 8, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hüttner, S.; Wieser, H. Studies on distribution and binding of endogenous glutathione in wheat dough and gluten. I. Distribution of glutathione in Osborne fractions. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2001, 213, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttner, S.; Wieser, H. Studies on the distribution and binding of endogenous glutathione in wheat dough and gluten. II. Binding sites of endogenous glutathione in glutenins. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2001, 213, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet, A.; Rosell, C.M.; Caballero, P.A.; Gomez, M.; Perez-Munuera, I.; Lluch, M.A. Glucose oxidase effect on dough rheology and bread quality: A study from macroscopic to molecular level. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joye, I.J.; Lagrain, B.; Delcour, J.A. Use of chemical redox agents and exogenous enzymes to modify the protein network during breadmaking—A review. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 50, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, A.I.S.; Laurindo, F.R.M. Protein disulfide isomerases: Redox connections in and out of the endoplasmic reticulum. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 617, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turano, C.; Coppari, S.; Altieri, F.; Ferraro, A. Proteins of the PDI family: Unpredicted non-ER locations and functions. J. Cell Physiol. 2002, 193, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlajaniemi, T.; Helaakoski, T.; Tasanen, K.; Myllylä, R.; Huhtala, M.L.; Koivu, J.; Kivirikko, K.I. Molecular cloning of the beta-subunit of human prolyl 4-hydroxylase. This subunit and protein disulphide isomerase are products of the same gene. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetterau, J.R.; Combs, K.A.; Spinner, S.N.; Joiner, B.J. Protein disulfide isomerase is a component of the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 9801–9807. [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley, M.J.; Batten, M.R.; Lumb, R.A.; Bulleid, N.J. Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum: PDI mediates the ER retention of unassembled procollagen C-propeptides. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 1114–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de A. Paes, A.M.; Veríssimo-Filho, S.; Guimaraes, L.L.; Silva, A.C.B.; Takiuti, J.T.; Santos, C.X.C.; Janiszewski, M.; Laurindo, F.R.M.; Lopes, L.R. Protein disulfide isomerase redox-dependent association with p47phox: Evidence for an organizer role in leukocyte NADPH oxidase activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 799–810. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Sankar, S.; Neamati, N. Protein disulfide isomerase: A promising target for cancer therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 222–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Shergalis, A.; Lu, D.; Kyani, A.; Liu, Z.W.; Ljungman, M.; Neamati, N. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel allosteric protein disulfide isomerase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 3447–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.S.; Uehara, T.; Nomura, Y. Role of ubiquilin associated with protein-disulfide isomerase in the endoplasmic reticulum in stress-induced apoptotic cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35386–35392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willems, S.H.; Tape, C.J.; Stanley, P.L.; Taylor, N.A.; Mills, I.G.; Neal, D.E.; McCafferty, J.; Murphy, G. Thiol isomerases negatively regulate the cellular shedding activity of ADAM17. Biochem. J. 2010, 428, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, S. Up-regulation of Protein-disulfide Isomerase in Response to Hypoxia/Brain Ischemia and Its Protective Effect against Apoptotic Cell Death. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10388–10393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honjo, Y.; Ayaki, T.; Tomiyama, T.; Horibe, T.; Ito, H.; Mori, H.; Takahashi, R.; Kawakami, K. Decreased levels of PDI and P5 in oligodendrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathology 2017, 37, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Lipton, S.A. Redox modulation by S-nitrosylation contributes to protein misfolding, mitochondrial dynamics, and neuronal synaptic damage in neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zai, A.; Rudd, M.A.; Scribner, A.W.; Loscalzo, J. Cell-surface protein disulfide isomerase catalyzes transnitrosation and regulates intracellular transfer of nitric oxide. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, N.; Root, P.; Jiang, X.M.; Hogg, P.J.; Mutus, B. Mechanism of transfer of NO from extracellular S-nitrosothiols into the cytosol by cell-surface protein disulfide isomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9539–9544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uehara, T.; Nakamura, T.; Yao, D.; Shi, Z.Q.; Lipton, S.A. S-Nitrosylated protein-disulphide isomerase links protein misfolding to neurodegeneration. Nature 2006, 441, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obukuro, K.; Nobunaga, M.; Takigawa, M.; Morioka, H.; Hisatsune, A.; Isohama, Y.; Shimokawa, H.; Tsutsui, M.; Katsuki, H. Nitric oxide mediates selective degeneration of hypothalamic orexin neurons through dysfunction of protein disulfide isomerase. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 12557–12568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Oguro, A.; Yagi, E.; Mitani, A.; Kudoh, S.N.; Imaoka, S. Bisphenol A and rotenone induce S-nitrosylation of protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) and inhibit neurite outgrowth of primary cultured cells of the rat hippocampus and PC12 cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 45, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, B.; Rodighiero, C.; Lencer, W.I.; Rapoport, T.A. Protein disulfide isomerase acts as a redox-dependent chaperone to unfold cholera toxin. Cell 2001, 104, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubin, P.; Guyette, J.; Taylor, M.; O’Donnell, M.; Herndon, L.; Burress, H.; Riad, A.; Tatulian, S.A.; Teter, K. Protein disulfide isomerase does not act as an unfoldase in the disassembly of cholera toxin. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20181320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, J.; Gao, J.; Liang, Z.; Yang, D. PDI-Regulated Disulfide Bond Formation in Protein Folding and Biomolecular Assembly. Molecules 2021, 26, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010171
Fu J, Gao J, Liang Z, Yang D. PDI-Regulated Disulfide Bond Formation in Protein Folding and Biomolecular Assembly. Molecules. 2021; 26(1):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010171
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Jiahui, Jihui Gao, Zhongxin Liang, and Dong Yang. 2021. "PDI-Regulated Disulfide Bond Formation in Protein Folding and Biomolecular Assembly" Molecules 26, no. 1: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010171
APA StyleFu, J., Gao, J., Liang, Z., & Yang, D. (2021). PDI-Regulated Disulfide Bond Formation in Protein Folding and Biomolecular Assembly. Molecules, 26(1), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010171






