WE-ASCA: The Weighted-Effect ASCA for Analyzing Unbalanced Multifactorial Designs—A Raman Spectra-Based Example
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. A Comparison between Analyses of Multifactorial Design Using ASCA, ASCA+ and WE-ASCA
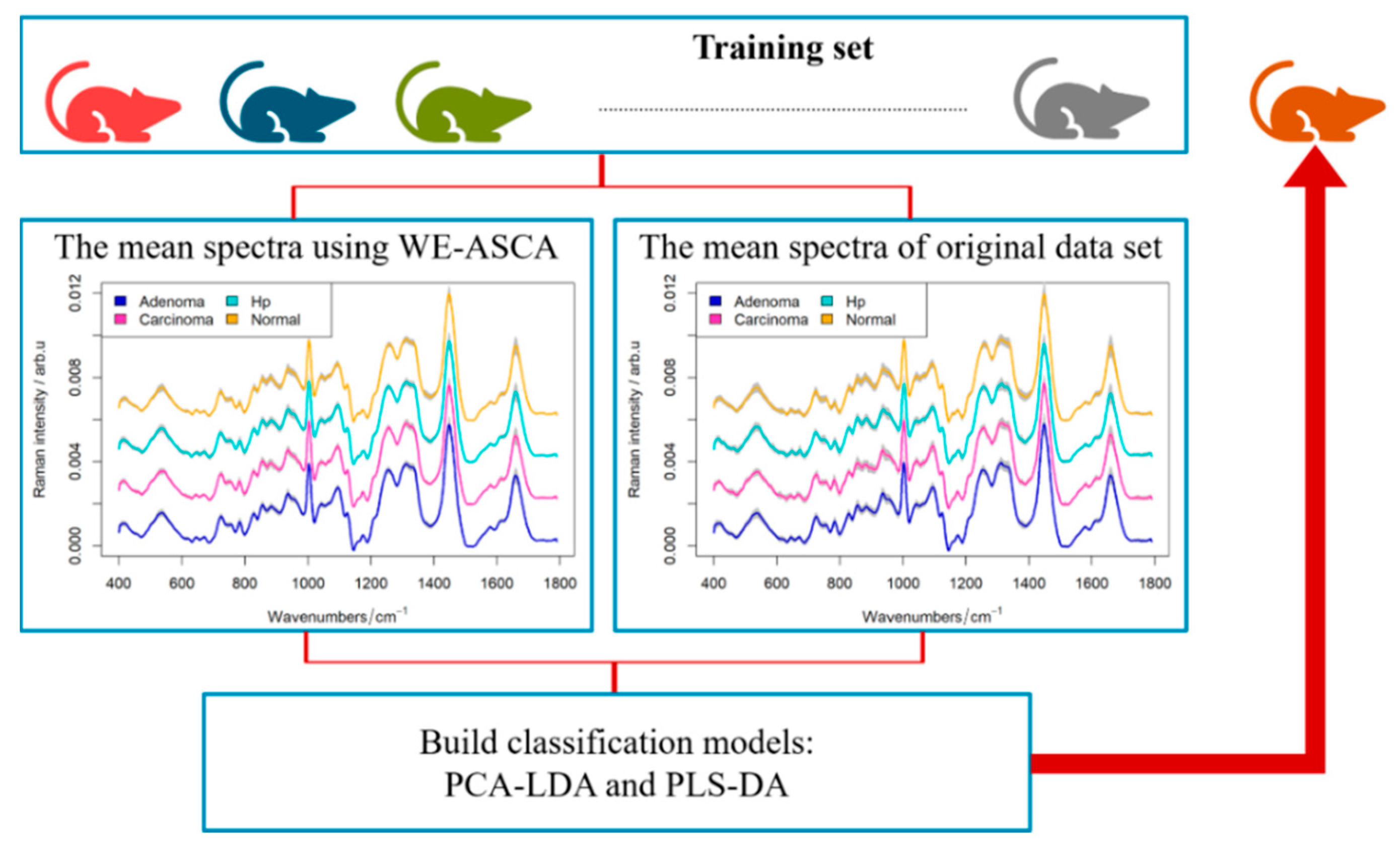
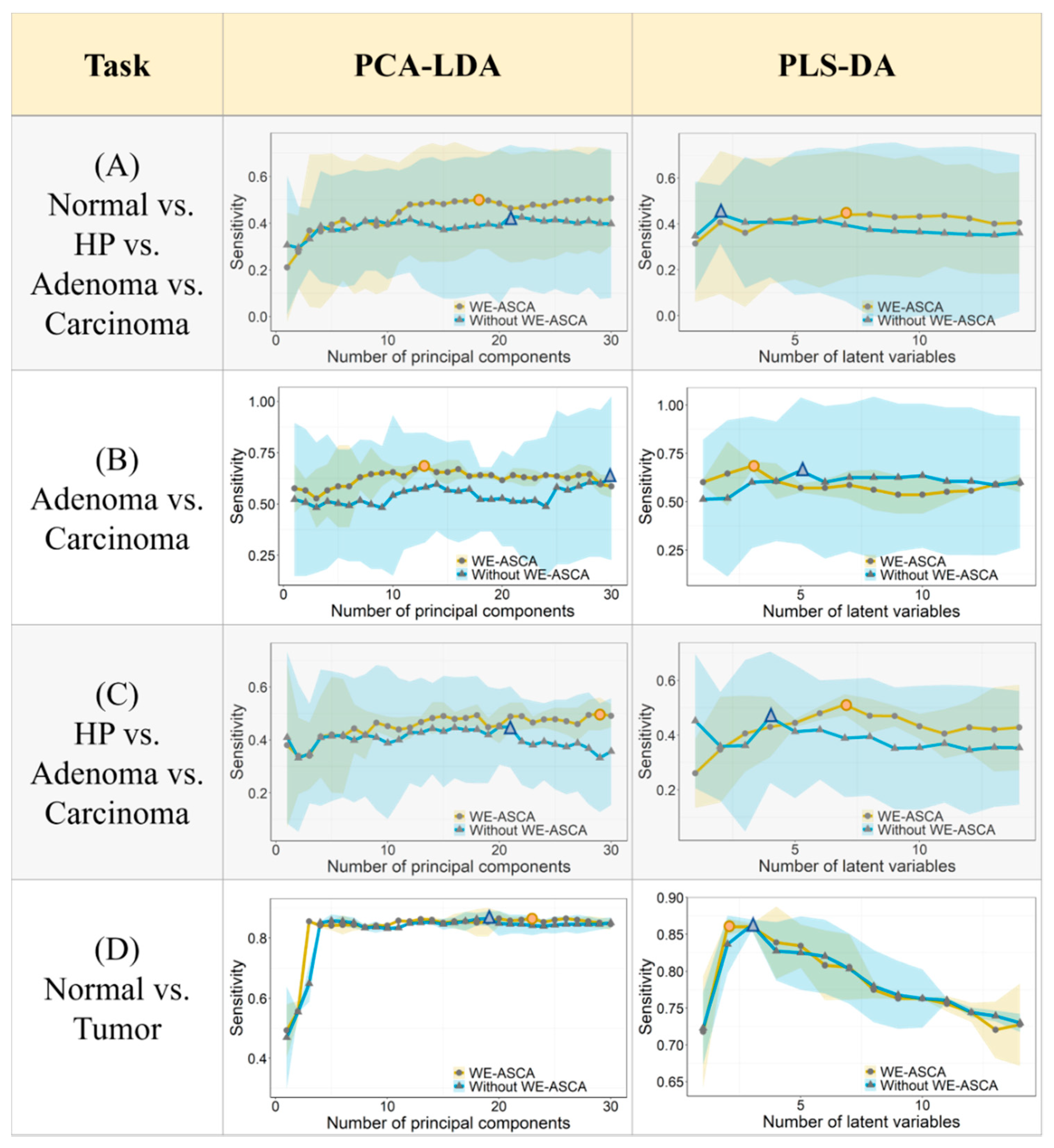
2.2. A WE-ASCA as Preprocessing Technique in Classification Models
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. ASCA for Crossed Balanced Design
4.2. General Linear Models and ASCA+
4.3. Weighted-Effect ASCA (WE-ASCA)
4.4. The Percentage of Variance
4.5. Permutation Tests
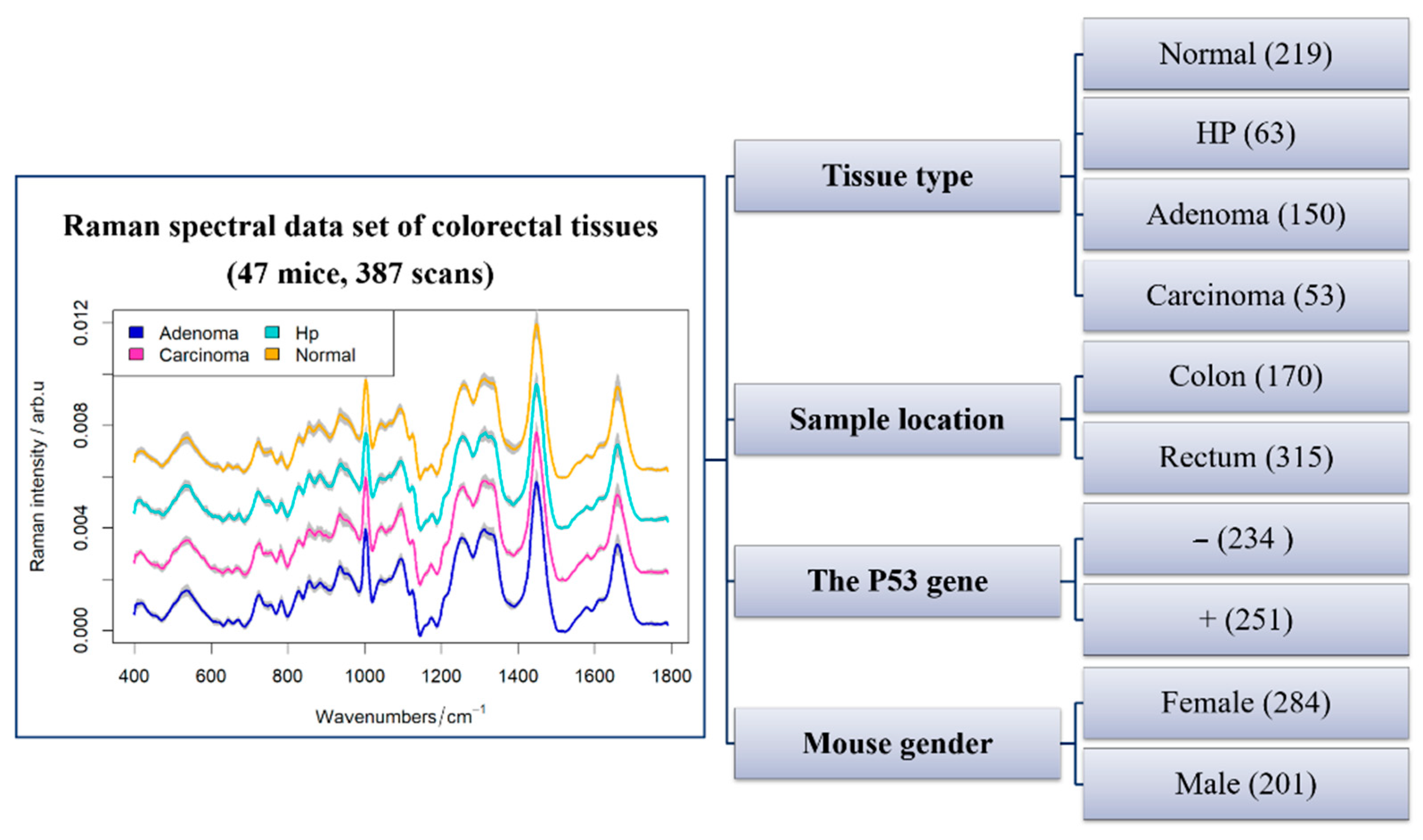
4.6. Data and Software
- Raman spectra of colon cancer in a mice model: https://zenodo.org/deposit/3975464
- Weighted-effect ASCA (WE-ASCA) codes: https://zenodo.org/deposit/3975471
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sampford, R.M.; Cochran, W.G. Sampling Techniques. Biometrics 1978, 34, 332–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.M.F.; Sugden, R.A. Sampling and Assignment Mechanisms in Experiments, Surveys and Observational Studies, Correspondent Paper. Int. Stat. Rev. 1988, 56, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, D.M.; Hunter, W.G. Experimental Design: Review and Comment. Technometrics 1984, 26, 71–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, B.J. Statistical Principles of Experimental Design; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1962; Volume 3, pp. 381–385. [Google Scholar]
- Mead, R.; Curnow, R.N.; Hasted, A.M. Statistical Methods in Agriculture and Experimental Biology, 3rd ed.; Chapman and Hall, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 1–472. [Google Scholar]
- Durakovic, B. Design of experiments application, concepts, examples: State of the art. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2017, 5, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St»hle, L.; Wold, S. Analysis of variance (ANOVA). Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1989, 6, 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, R. Analysis of Variance and Generalized Linear Models. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences; Smelser, N.J., Baltes, P.B., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 473–480. [Google Scholar]
- Mardia, K.V.; Kent, J.T.; Bibby, J.M. Multivariate Analysis; Academic Press: London, UK, 1979; Volume 37. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, H.M. Multivariate Analysis of Quality. An Introduction. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratchell, N. Multivariate response surface modelling by principal components analysis. J. Chemom. 1989, 3, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.J.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; van der Greef, J.; Timmerman, M.E.; Westerhuis, J.; Smilde, A.K. ASCA: Analysis of multivariate data obtained from an experimental design. J. Chemom. 2005, 19, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilde, A.K.; Jansen, J.J.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Lamers, R.-J.A.N.; van der Greef, J.; Timmerman, M.E. ANOVA-simultaneous component analysis (ASCA): A new tool for analyzing designed metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3043–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.; ter Braak, C. Permutation tests for multi-factorial analysis of variance. J. Stat. Comp. Simul. 2003, 73, 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinetto, C.; Engel, J.; Jansen, J.J. ANOVA simultaneous component analysis: A tutorial review. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2020, 6, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, M.E.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Smilde, A.K.; Ceulemans, E. Scaling in ANOVA-simultaneous component analysis. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, M.; Féraud, B.; Govaerts, B. ASCA+ and APCA+: Extensions of ASCA and APCA in the analysis of unbalanced multifactorial designs. J. Chemom. 2017, 31, e2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, H.; Thyregod, P. Introduction to General and Generalized LInear Models; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuis, R.; Grotenhuis, M.; Pelzer, B. Weighted Effect Coding for Observational Data with wec. R. J. 2017, 9, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- te Grotenhuis, M.; Pelzer, B.; Eisinga, R.; Niuwenhuis, R.; Schimdt-Catran, A.; Konig, R. A novel method for modelling interaction between categorical variables. Int. J. Public Health 2017, 62, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogler, N.; Bocklitz, T.; Salah, F.S.; Schmidt, C.; Bräuer, R.; Cui, T.; Mireskandari, M.; Greten, F.R.; Schimidt, M.; Stallmach, A.; et al. Systematic evaluation of the biological variance within the Raman based colorectal tissue diagnostics. J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwanenburg, G.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Jansen, J.J.; Smilde, A.K. ANOVA–principal component analysis and ANOVA–simultaneous component analysis: A comparison. J. Chemom. 2011, 25, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilde, A.K.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Westerhuis, J.A. The geometry of ASCA. J. Chemom. 2008, 22, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neter, J.; Wasserman, W.; Kutner, M. Applied Linear Statistical Models, 4th ed.; Irwin: Chicago, IL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, R.G.; Mitchell-Olds, T. Anova for Unbalanced Data: An Overview. Ecology 1993, 74, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langsrud, Ø. ANOVA for unbalanced data: Use Type II instead of Type III sums of squares. Stat. Comput. 2003, 13, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
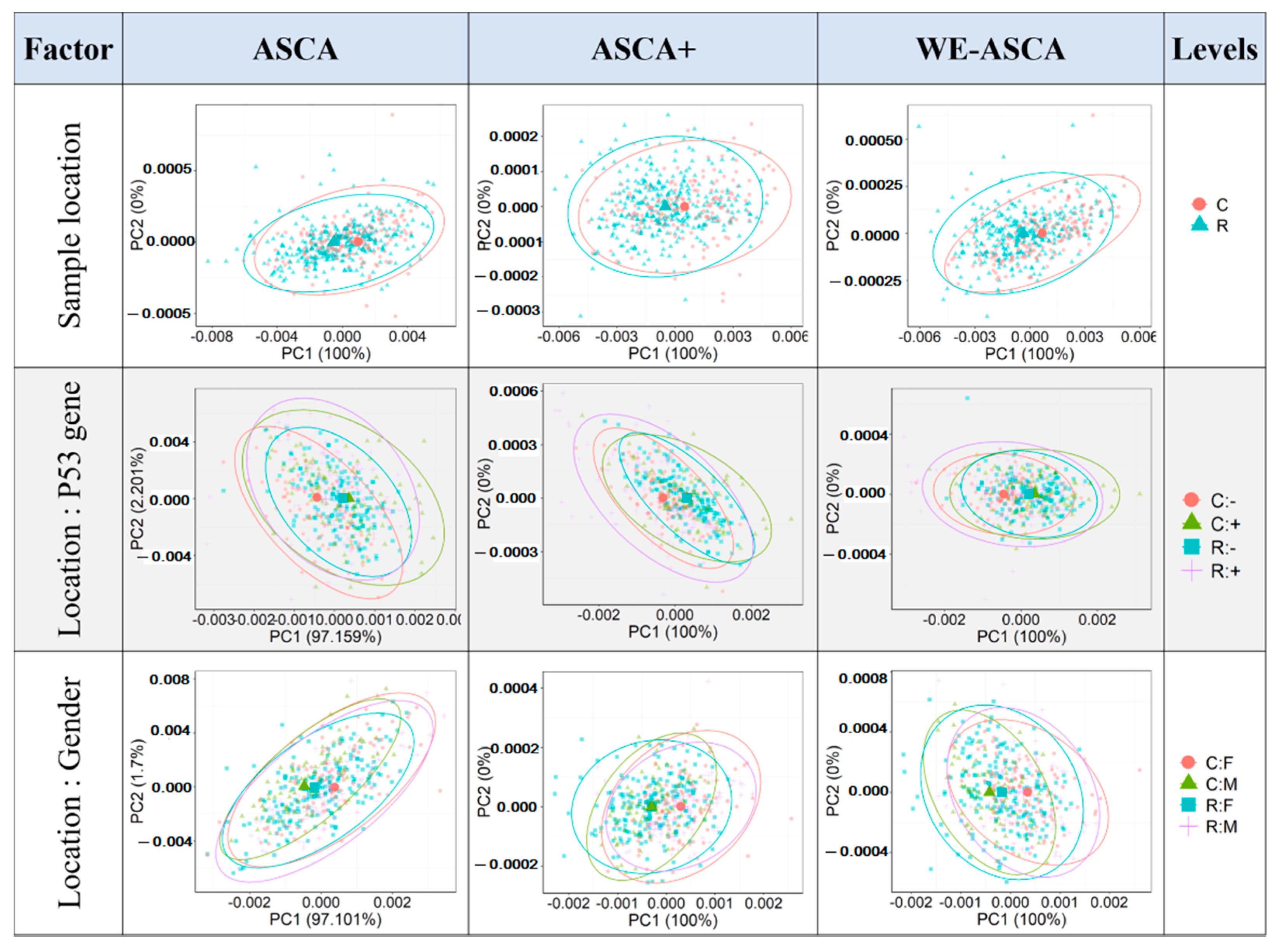
| Effect | Individual | Location | P53 Gene | Gender | Location: P53 | Location: Gender | P53: Gender | Residuals | Sum (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASCA | 37.96 | 1.47 | 1.07 | 1.03 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.94 | 65.06 | 108.62 |
| ASCA+ | 33.00 | 0.53 | 0 | 0 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0 | 59.38 | 93.3 |
| WE-ASCA | 33.94 | 0.61 | 0 | 0 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0 | 61.07 | 96.01 |
| Effect | All Data | Individuals | Location | Location: P53 | Location: Gender | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASCA | PC1 (%) | 42.52 | 36.44 | 100 | 97.16 | 97.10 |
| PC2 (%) | 15.20 | 17.74 | 0 | 2.20 | 1.7 | |
| ASCA+ | PC1 (%) | 42.52 | 38.78 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| PC2 (%) | 15.20 | 17.40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| WE-ASCA | PC1 (%) | 42.52 | 35.49 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| PC2 (%) | 15.20 | 18.19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Effect | Individuals | Location | Location: P53 | Location: Gender | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASCA+ | 0.000 | 0.034 | 0.399 | 0.453 | |
| WE-ASCA | 0.000 | 0.021 | 0.383 | 0.424 | |
| Possible Combinations | Factors | Interaction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 1 | |||||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | |||
| Model | Type III Sum Squares | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean model | ||
| Two-factor cross design | ||
| Without the effect of | ||
| Without the effect of | ||
| Without the effect of | ||
Sample Availability: Not available. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, N.; Jansen, J.; van den Doel, A.; Tinnevelt, G.H.; Bocklitz, T. WE-ASCA: The Weighted-Effect ASCA for Analyzing Unbalanced Multifactorial Designs—A Raman Spectra-Based Example. Molecules 2021, 26, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010066
Ali N, Jansen J, van den Doel A, Tinnevelt GH, Bocklitz T. WE-ASCA: The Weighted-Effect ASCA for Analyzing Unbalanced Multifactorial Designs—A Raman Spectra-Based Example. Molecules. 2021; 26(1):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010066
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Nairveen, Jeroen Jansen, André van den Doel, Gerjen Herman Tinnevelt, and Thomas Bocklitz. 2021. "WE-ASCA: The Weighted-Effect ASCA for Analyzing Unbalanced Multifactorial Designs—A Raman Spectra-Based Example" Molecules 26, no. 1: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010066
APA StyleAli, N., Jansen, J., van den Doel, A., Tinnevelt, G. H., & Bocklitz, T. (2021). WE-ASCA: The Weighted-Effect ASCA for Analyzing Unbalanced Multifactorial Designs—A Raman Spectra-Based Example. Molecules, 26(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010066








