Application of Optimal Control Theory to Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Formulation of the Control Problem
2.1. The Model System
2.2. The Rotating Wave Approximation
3. Optimal Control Theory
3.1. A Short Introduction to Optimal Control Theory
3.2. Optimal Gradient-Based Algorithm
- Choose guess fields and .
- Propagate forward the state of every ion k and compute .
- Propagate backward the adjoint state of the system from Equation (8).
- Compute the corrections and to the control fields, , where is a small positive constant.
- Define the new control fields .
- Truncate the new control fields and to satisfy the constraint :
- Go to Step 2 until a given accuracy is reached.
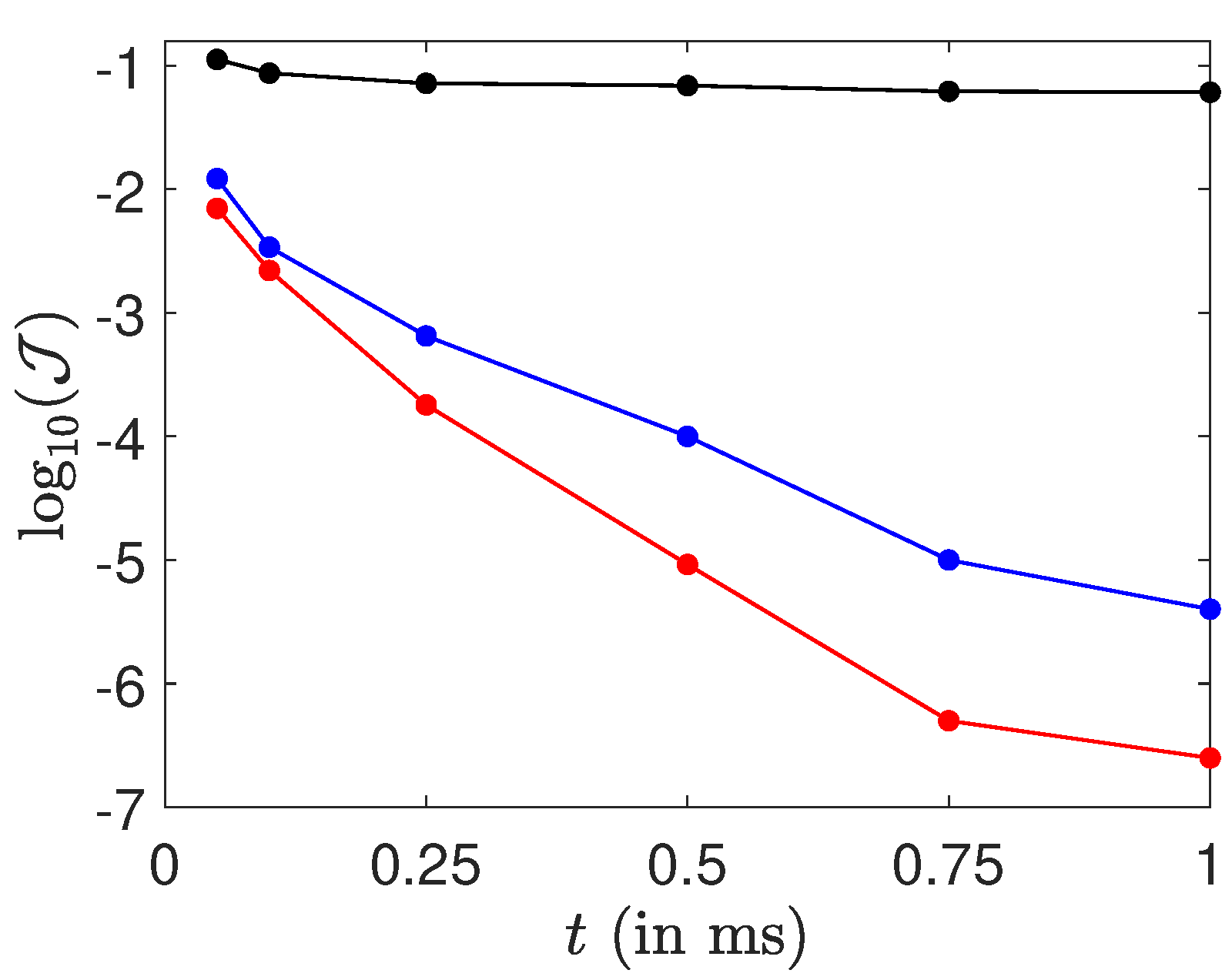
4. Numerical Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OCT | Optimal Control Theory |
| LQOCT | Linear Quadratic Optimal Control Theory |
| ICR | Ion Cyclotron Resonance |
| PMP | Pontryagin Maximum Principle |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| RWA | Rotating Wave Approximation |
Appendix A. The Rotating Wave Approximation
Appendix B. Adiabatic Excitation of ICR Process

Appendix C. Excitation by the SWIFT Approach
Appendix D. Application of LQOCT to ICR
References
- Bryson, A.E.; Ho, Y.-C. Applied Optimal Control; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bressan, A.; Piccoli, B. Introduction to the Mathematical Theory of Control; American Institute of Mathematical Sciences: Springfield, MO, USA, 2007; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Glaser, S.J.; Boscain, U.; Calarco, T.; Koch, C.; Kockenberger, K.; Kosloff, R.; Kuprov, I.; Luy, B.; Schirmer, S.; Schulte-Herbrüggen, T.; et al. Training Schrödinger’s cat: Quantum optimal control. Eur. Phys. J. D 2015, 69, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schättler, H.; Ledzewicz, U. Geometric Optimal Control: Theory, Methods and Examples; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Brif, C.; Chakrabarti, R.; Rabitz, H. Control of quantum phenomena: Past, present and future. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 075008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daems, D.; Ruschhaupt, A.; Sugny, D.; Guérin, S. Robust Quantum Control by a Single-Shot Shaped Pulse. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 050404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Damme, L.; Schraft, D.; Genov, G.; Sugny, D.; Halfmann, T.; Guérin, S. Robust NOT-gate by single-shot shaped pulses: Demonstration by rephasing of atomic coherences. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 022309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, L.; Ansel, Q.; Glaser, S.; Sugny, D. Robust optimal control of two-level quantum systems. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 063403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontryagin, L.S.; Boltyanskii, V.G.; Gamkrelidze, R.V.; Mishechenko, E.F. The Mathematical Theory of Optimal Processes; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Liberzon, D. Calculus of Variations and Optimal Control Theory; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnard, B.; Sugny, D. Optimal Control in Space and Quantum Dynamics; AIMS Applied Mathematics: Springfield, MO, USA, 2012; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Jurdjevic, V. Geometric Control Theory; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Boscain, U.; Sigalotti, M.; Sugny, D. Introduction to the Foundations of Quantum Optimal Control Theory. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2010.09368. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.S.; Khaneja, N. Ensemble control of Bloch equations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2009, 54, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozbar, K.; Ehni, S.; Skinner, T.E.; Glaser, S.J.; Luy, B. Exploring the limits of broadband 90 and 180 universal rotation pulses. J. Magn. Reson. 2012, 225, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Kozbar, K.; Skinner, T.E.; Khaneja, N.; Glaser, S.J.; Luy, B. Exploring the limits of broadband excitation and inversion: II. Rf-power optimized pulses. J. Magn. Reson. 2008, 194, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Kozbar, K.; Skinner, T.E.; Khaneja, N.; Glaser, S.J.; Luy, B. Exploring the limits of broadband excitation and inversion pulses. J. Magn. Reson. 2004, 170, 236. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, C.P.; Lemeshko, M.; Sugny, D. Quantum control of molecular rotation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2019, 91, 035005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, M.H. Spin Dynamics: Basics of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, R.R.; Bodenhausen, G.; Wokaun, A. Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in One and Two Dimensions; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Mareci, T.H.; Scott, K.W.; Andrew, E.R. Selective inversion radiofrequency pulses by optimal control. J. Magn. Reson. 1986, 70, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conolly, S.; Nashimura, D.; Macovski, A. Optimal Control Solutions to the Magnetic Resonance Selective Excitation Problem. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 1986, 5, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Zur, Y. Design of adiabatic selective pulses using optimal control theory. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 36, 401409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, N.C.; Kehlet, C.; Glaser, S.J.; Khaneja, N. Optimal control methods in NMR spectroscopy. In Encyclopedia of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance; Harris, R.K., Wasylishen, R.L., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lapert, M.; Zhang, Y.; Braun, M.; Glaser, S.J.; Sugny, D. Singular Extremals for the Time-Optimal Control of Dissipative Spin 1/2 Particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 083001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, M.A.; King, K.F.; Zhou, X.J. Handbook of MRI Pulse Sequences; Elsevier Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lapert, M.; Zhang, Y.; Janich, M.; Glaser, S.J.; Sugny, D. Exploring the Physical Limits of Saturation Contrast in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinding, M.S.; Maximov, I.I.; Tosner, Z.; Nielsen, N.C. Fast numerical design of spatial-selective RF pulses in MRI using Krotov and quasi-Newton based optimal control methods. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 054203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximov, I.I.; Vinding, M.S.; Desmond, H.; Nielsen, N.C.; Shah, N.J. Real-time 2D spatially selective MRI experiments: Comparative analysis of optimal control design methods. J. Magn. Reson. 2015, 254, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaneja, N.; Reiss, T.; Kehlet, C.; Schulte-Herbrüggen, T.; Glaser, S.J. Optimal control of coupled spin dynamics: Design of NMR pulse sequences by gradient ascent algorithms. J. Magn. Reson. 2005, 172, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comisarow, M.B.; Marshall, A.G. Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1974, 25, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comisarow, M.B.; Marshall, A.G. Frequency-sweep Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1974, 26, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.G.; Hendrickson, C.L.; Jackson, G.S. Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry: A primer. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 1998, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, E.N.; Heeren, R.M.A.; Popov, A.M.; Pozdneev, A.V.; Chingin, K.S. Realistic modeling of ion cloud motion in a Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance cell by use of a particle-in-cell approach. Rapid Comm. Mass Spect. 2007, 21, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, A.A.; Pelupessy, P.; Rolando, C.; Bodenhausen, G. Theory for spiralling ions for 2D FT-ICR and comparison with precessing magnetization vectors in 2D NMR. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 9167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfandler, P.; Bodenhausen, G.; Rapin, J.; Houriet, R.; Gaumann, T. Two-dimensional ion cyclotron resonance mass spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1987, 138, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Agthoven, M.A.; Delsuc, M.-A.; Bodenhausen, G.; Rolando, C. Towards analytically useful two-dimensional Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Agthoven, M.A.; Chiron, L.; Coutouly, M.-A.; Sehgal, A.A.; Pelupessy, P.; Delsuc, M.-A.; Rolando, C. Optimization of the discrete pulse sequence for two-dimensional FT-ICR mass spectrometry using infrared multiphoton dissociation. Int. J. Mass Spec. 2014, 370, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Agthoven, M.A.; Delsuc, M.-A.; Rolando, C. Two-dimensional FT-ICR/MS with IRMPD as fragmentation mode. Int. J. Mass Spec. 2011, 306, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Bouclon, J.; Chiron, L.; Witt, M.; Delsuc, M.-A.; Rolando, C. Nonuniform Sampling Acquisition of Two-Dimensional Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry for Increased Mass Resolution of Tandem Mass Spectrometry Precursor Ions. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Agthoven, M.A.; Lam, Y.P.Y.; O’Connor, P.B.; Rolando, C.; Delsuc, M.-A. Two dimensional mass spectrometry: New perspectives for tandem mass spectrometry. Eur. Biophys. J. 2019, 48, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.G.; Lin, W.T.-C.; Ricca, T.L. Tailored excitation for Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S. Linear response theory of ion excitation for Fourier transform mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1991, 2, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guan, S.; Marshall, A.G. Stored waveform inverse Fourier transform ion excitation in trapped-ion mass spectrometry: Theory and applications. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Process. 1996, 157, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockett, R.W. Finite Dimensional Linear Systems; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnans, F.; Rouchon, P. Commande et Optimisation de Systemes Dynamiques; Ecole Polytechnique: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.-S. Ensemble control of finite-dimensional time-varying linear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2011, 56, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-S. Control of Inhomogeneous Ensemble. Ph.D. Thesis, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Martikyan, V.; Guéry-Odelin, D.; Sugny, D. Comparison between optimal control and shortcut to adiabaticity protocols in a linear control system. Phys. Rev. A 2020, 101, 013423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martikyan, V.; Devra, A.; Guéry-Odelin, D.; Glaser, S.J.; Sugny, D. Robust control of an ensemble of springs: Application to ion cyclotron resonance and two-level quantum systems. Phys. Rev. A 2020, 102, 053104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-S.; Ruths, J.; Glaser, S.J. Exact broadband excitation of two-level systems by mapping spins to springs. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, M.A.; Mueller, L. Nonresonant effects of frequency-selectives pulses. J. Magn. Reson. 1992, 99, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, L.; Bodenhausen, G. Phase shifts induced by transient Bloch-Siegert effects in NMR. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1990, 168, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shahriar, M.S.; Pradhan, P.; Morzinski, J. Driver-phase-correlated fluctuations in the rotation of a strongly driven quantum bit. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 69, 032308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werschnik, J.; Gross, E.K.U. Quantum optimal control theory. J. Phys. B 2007, 40, R175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapert, M.; Tehini, R.; Turinici, G.; Sugny, D. Monotonically convergent optimal control theory of quantum systems with spectral constraints on the control field. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 79, 063411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borneman, T.W.; Cory, D.G. Bandwidth-Limited Con-trol and Ringdown Suppression in High-Q Resonators. J. Magn. Reson. 2012, 225, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hincks, I.N.; Granade, C.E.; Borneman, T.W.; Cory, D.G. Controlling Quantum Devices with Nonlinear Hard-ware. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2015, 4, 024012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, W.; Haas, H.; Chen, A.Q.; Jeon, N.; Lauhon, L.J.; Cory, D.G.; Budakian, R. High-Resolution Nanoscale Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. X 2018, 8, 011030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzoi, F.; Gambetta, J.M.; Merkel, S.T.; Wilhelm, F.K. Optimal control methods for rapidly time-varyingHamiltonians. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 84, 022307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spindler, P.E.; Zhang, Y.; Endeward, B.; Gershernzon, N.; Skinner, T.E.; Glaser, S.J.; Prisner, T.F. Shaped optimalcontrol pulses for increased excitation bandwidth in EPR. J. Magn. Reson. 2012, 218, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, A.; Julsgaard, B.; Rippe, L.; Ying, Y.; Kröll, S.; Fisher, R.; Glaser, S.J. Extracting High Fidelity Quantum Computer Hardware from Random Systems. Phys. Scr. T 2009, 137, 014009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spindler, P.E.; Schöps, P.; Kallies, W.; Glaser, S.J.; Prisner, T.F. Perspectives of Shaped Pulses for EPR Spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 2017, 280, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershenzon, N.I.; Skinner, T.E.; Brutscher, B.; Khaneja, N.; Nimbalkar, M.; Luy, B.; Glaser, S.J. Linear phase slope in pulse design: Application to coherence transfer. J. Magn. Reson. 2008, 192, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershenzon, N.I.; Kobzar, K.; Luy, B.; Glaser, S.J.; Skinner, T.E. Optimal control design of excitation pulses that accommodate relaxation. J. Magn. Reson. 2007, 188, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, C.-C.; Ho, T.-S.H.; Rabitz, H. Monotonic convergent quantum optimal control method with exact equality constraints on the optimized control fields. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 053418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Sample Availability: Not available. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martikyan, V.; Beluffi, C.; Glaser, S.J.; Delsuc, M.-A.; Sugny, D. Application of Optimal Control Theory to Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance. Molecules 2021, 26, 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102860
Martikyan V, Beluffi C, Glaser SJ, Delsuc M-A, Sugny D. Application of Optimal Control Theory to Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance. Molecules. 2021; 26(10):2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102860
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartikyan, Vardan, Camille Beluffi, Steffen J. Glaser, Marc-André Delsuc, and Dominique Sugny. 2021. "Application of Optimal Control Theory to Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance" Molecules 26, no. 10: 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102860
APA StyleMartikyan, V., Beluffi, C., Glaser, S. J., Delsuc, M.-A., & Sugny, D. (2021). Application of Optimal Control Theory to Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance. Molecules, 26(10), 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102860





