Generation of a Hetero Spin Complex from Iron(II) Iodide with Redox Active Acenaphthene-1,2-Diimine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization
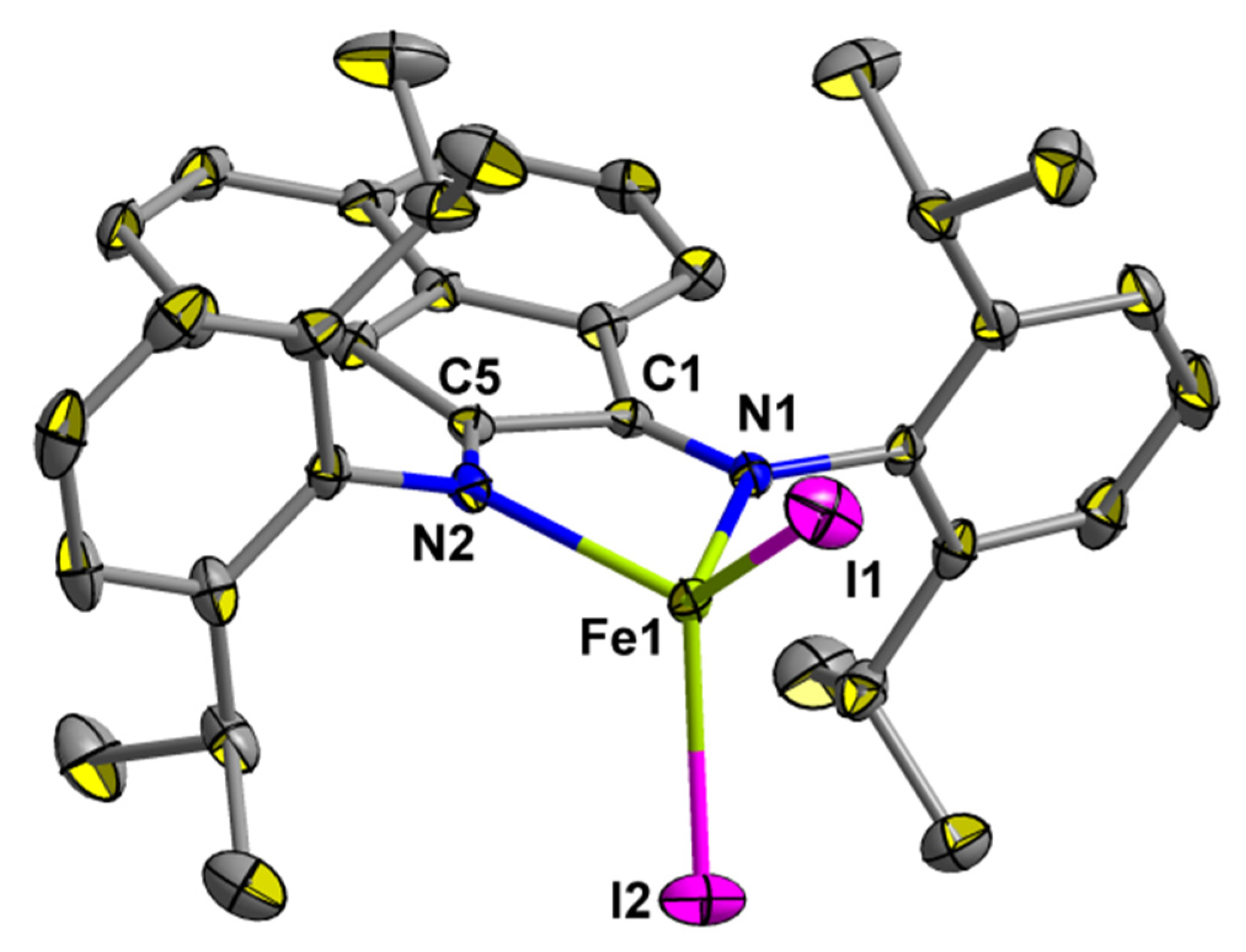
2.2. Molecular Structure
2.3. UV–VIS Spectra and Calculations
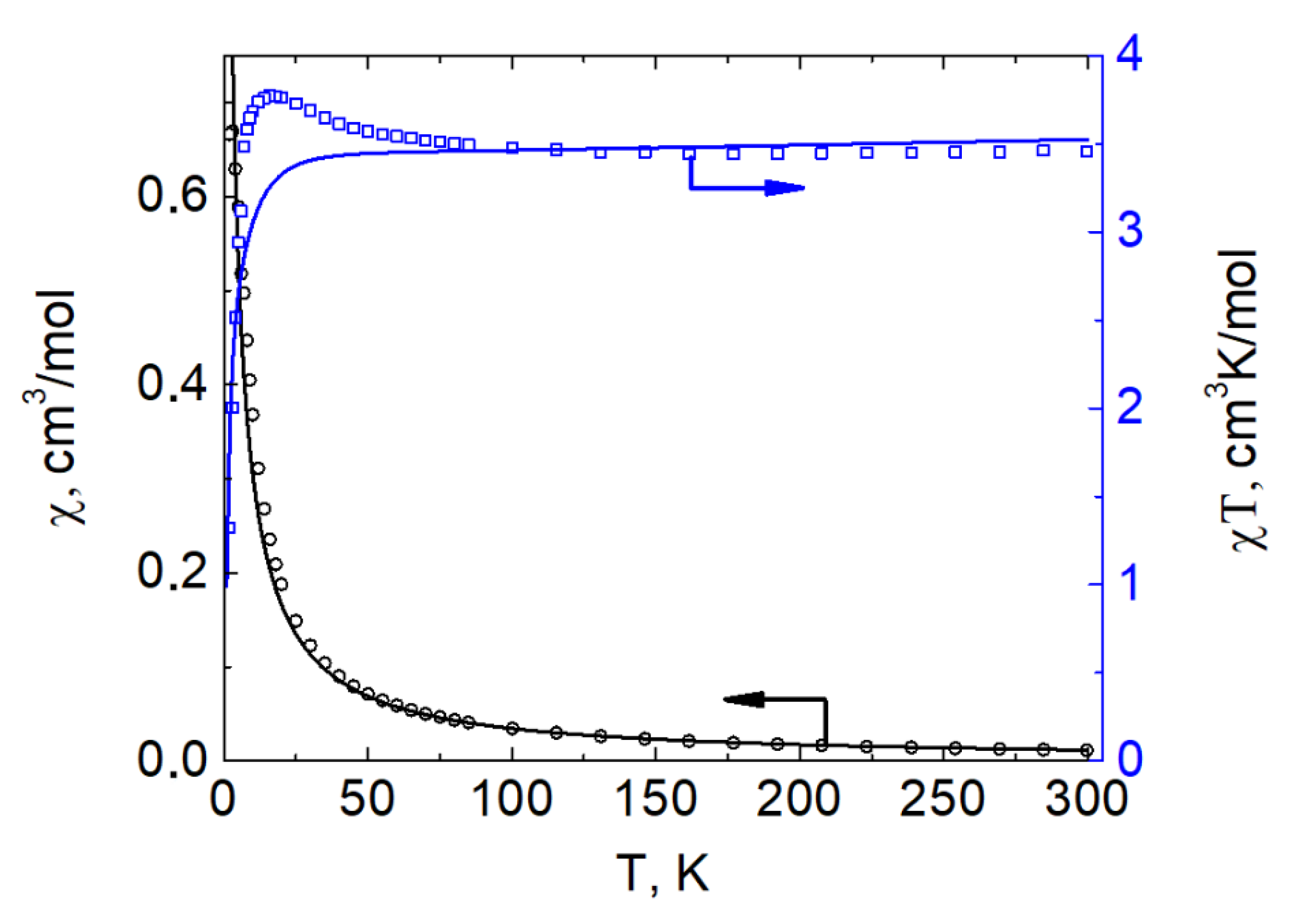
2.4. Solid State Magnetic Properties and Calculations
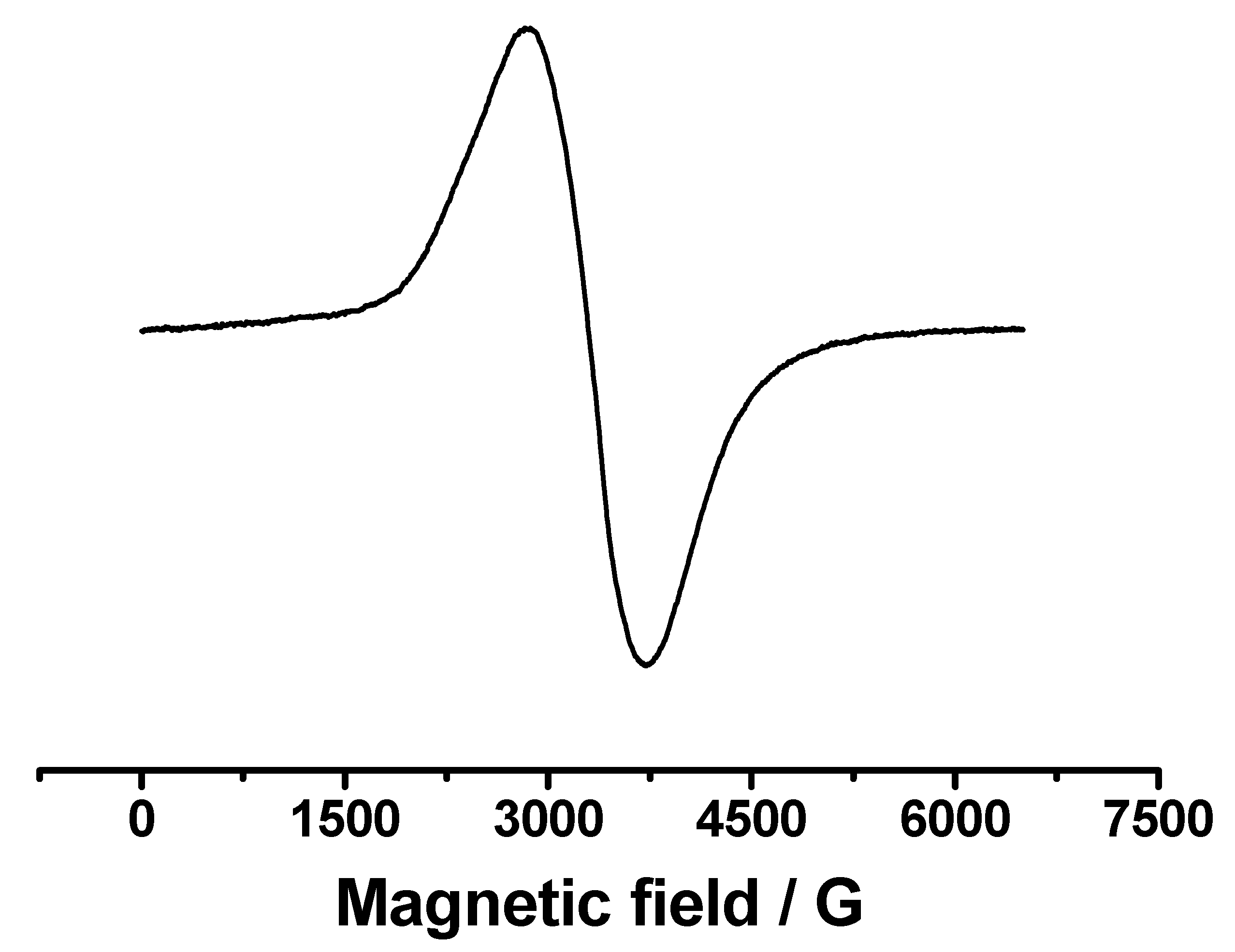
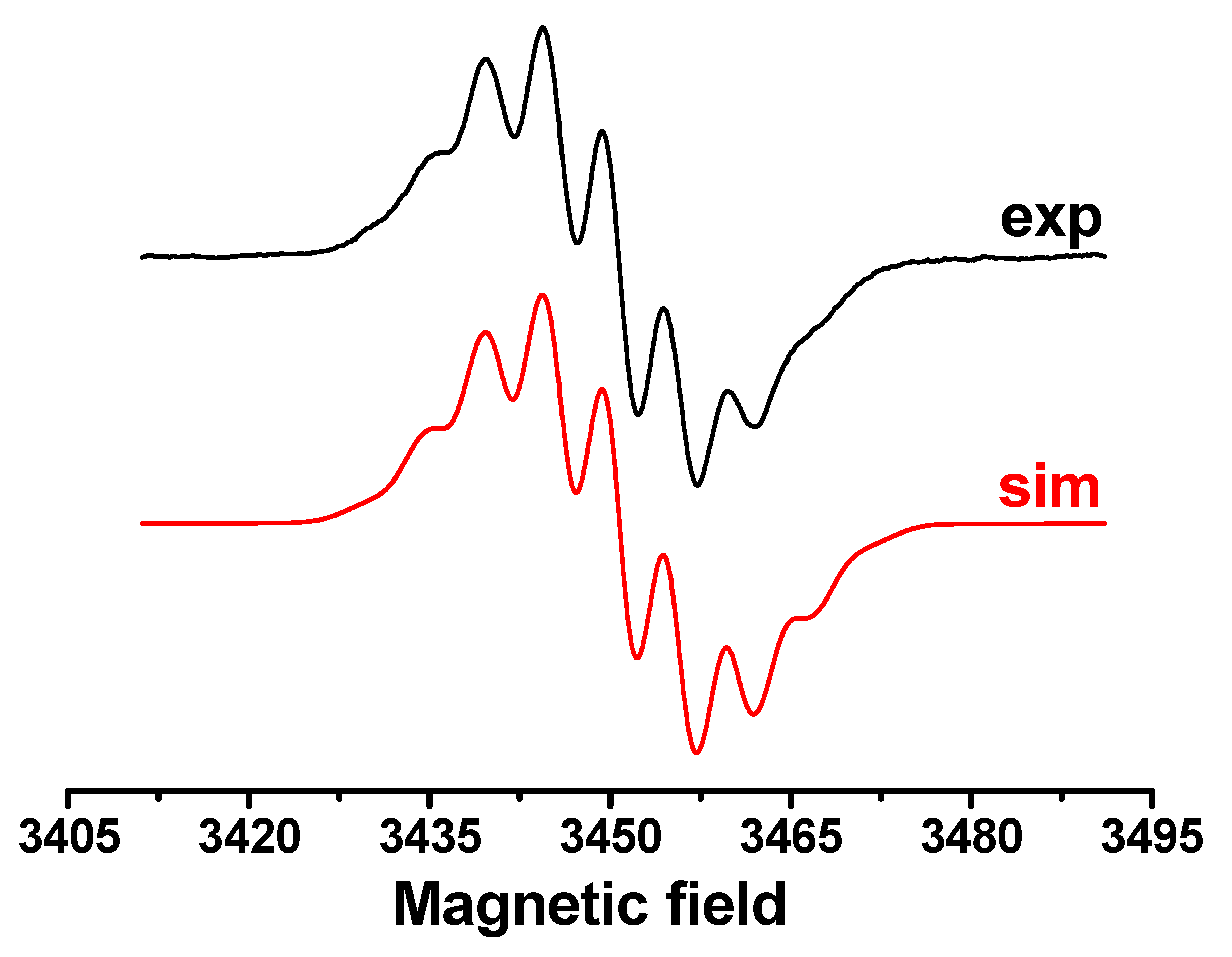
2.5. Cyclic Voltammetry and EPR Spectroscopy
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Remarks
3.2. Synthesis of [(dpp-BIAN)FeIII2]·CH3CN (1·CH3CN)
3.3. Details of Quantum Chemical Calculations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sato, O. Dynamic molecular crystals with switchable physical properties. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessoli, R.; Gatteschi, D.; Caneschi, A.; Novak, M.A. Magnetic bistability in a metal-ion cluster. Nature 1993, 365, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layfield, R.A. Organometallic Single-Molecule Magnets. Organometallics 2014, 33, 1084–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, G.A.; Murrie, M. 3d single-ion magnets. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2135–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demir, S.; Jeon, I.-R.; Long, J.R.; Harris, T.D. Radical ligand-containing single-molecule magnets. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 289, 149–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frost, J.M.; Harriman, K.L.M.; Murugesu, M. The rise of 3-d single-ion magnets in molecular magnetism: Towards materials from molecules? Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2470–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sessoli, R. Toward the Quantum Computer: Magnetic Molecules Back in the Race. ACS Cent. Sci. 2015, 1, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornia, A.; Seneor, P. The molecular way. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czap, G.; Wagner, P.J.; Xue, F.; Gu, L.; Li, J.; Yao, J.; Wu, R.; Ho, W. Probing and imaging spin interactions with a magnetic single-molecule sensor. Science 2019, 364, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komeda, T.; Katoh, K.; Yamashita, M. Single Molecule Magnet for Quantum Information Process’: Life Innovation. In Molecular Technology; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2019; pp. 263–304. [Google Scholar]
- Gaita-Ariño, A.; Luis, F.; Hill, S.; Coronado, E. Molecular spins for quantum computation. Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, M.; Akhtar, M.N.; Tong, M.-L. Recent advance in heterometallic nanomagnets based on TMxLn4−x cubane subunits. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 387, 129–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, G.; Gatteschi, D.; Hendrickson, D.N.; Sessoli, R. Single-molecule magnets. MRS Bull. 2000, 25, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatteschi, D.; Sessoli, R.; Cornia, A. Single-molecule magnets based on iron(III) oxo clusters. Chem. Commun. 2000, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrie, M. Cobalt(II) single-molecule magnets. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harman, W.H.; Harris, T.D.; Freedman, D.E.; Fong, H.; Chang, A.; Rinehart, J.D.; Ozarowski, A.; Sougrati, M.T.; Grandjean, F.; Long, G.J.; et al. Slow Magnetic Relaxation in a Family of Trigonal Pyramidal Iron(II) Pyrrolide Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18115–18126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, M.; Zadrozny, J.M.; Long, J.R.; Neese, F. A theoretical analysis of chemical bonding, vibronic coupling, and magnetic anisotropy in linear iron(II) complexes with single-molecule magnet behavior. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Coca, S.; Cremades, E.; Aliaga-Alcalde, N.; Ruiz, E. Huge Magnetic Anisotropy in a Trigonal-Pyramidal Nickel(II) Complex. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 676–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Álvarez, A.; Vallejo, J.; Pardo, E.; Julve, M.; Lloret, F.; Krzystek, J.; Armentano, D.; Wernsdorfer, W.; Cano, J. Field-Induced Slow Magnetic Relaxation in a Mononuclear Manganese(III)–Porphyrin Complex. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 17299–17307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, F.; Ohtani, R.; Nakamura, M.; Lindoy, L.F.; Hayami, S. Slow Magnetic Relaxation Triggered by a Structural Phase Transition in Long-Chain-Alkylated Cobalt(II) Single-Ion Magnets. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 7409–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, M.K.; Nyvang, A.; Walsh, J.P.S.; Bunting, P.C.; Long, J.R.; Neese, F.; Atanasov, M.; Genoni, A.; Overgaard, J. Insights into Single-Molecule-Magnet Behavior from the Experimental Electron Density of Linear Two-Coordinate Iron Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 3211–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, D.E.; Harman, W.H.; Harris, T.D.; Long, G.J.; Chang, C.J.; Long, J.R. Slow Magnetic Relaxation in a High-Spin Iron(II) Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1224–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadrozny, J.M.; Atanasov, M.; Bryan, A.M.; Lin, C.-Y.; Rekken, B.D.; Power, P.P.; Neese, F.; Long, J.R. Slow magnetization dynamics in a series of two-coordinate iron(II) complexes. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.-X.; Chen, X.-X.; Xiang, J.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Jia, L.-H.; Wang, B.-W.; Cheng, S.-C.; Zhou, X.; Leung, C.-F.; Gao, S. Slow Magnetic Relaxation in a Series of Mononuclear 8-Coordinate Fe(II) and Co(II) Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 3761–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Hickey, A.K.; Pink, M.; Telser, J.; Tierney, D.L.; Amoza, M.; Rouzieres, M.; Ozumerzifon, T.J.; Hoffert, W.A.; Shores, M.P.; et al. Magnetization Slow Dynamics in Ferrocenium Complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, K.; Cosquer, G.; Sugisaki, K.; Matsuoka, H.; Sato, K.; Breedlove, B.K.; Yamashita, M. Isostructural M(II) complexes (M = Mn, Fe, Co) with field-induced slow magnetic relaxation for Mn and Co complexes. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 12023–12030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Koten, G.; Vrieze, K. 1,4-Diaza-1,3-Butadiene (α-Diimine) Ligands: Their Coordination Modes and the Reactivity of Their Metal Complexes; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 21, pp. 151–239. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, M.; Seibel, M.; Kelm, H.; Demeshko, S.; Meyer, F.; Krüger, H.-J. How Does a Coordinated Radical Ligand Affect the Spin Crossover Properties in an Octahedral Iron(II) Complex? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 5988–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khusniyarov, M.M.; Weyhermueller, T.; Bill, E.; Wieghardt, K. Tuning the Oxidation Level, the Spin State, and the Degree of Electron Delocalization in Homo- and Heteroleptic Bis(α-diimine)iron Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1208–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.; Miesel, D.; Hildebrandt, A.; Ragaini, F.; Schaarschmidt, D.; Jacobi von Wangelin, A. Synthesis and Catalysis of Redox-Active Bis(imino)acenaphthene (BIAN) Iron Complexes. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 3203–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekesa, F.S.; Arias-Ugarte, R.; Kong, L.; Sumner, Z.; McGovern, G.P.; Findlater, M. Iron-Catalyzed Hydrosilylation of Aldehydes and Ketones under Solvent-Free Conditions. Organometallics 2015, 34, 5051–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supej, M.J.; Volkov, A.; Darko, L.; West, R.A.; Darmon, J.M.; Schulz, C.E.; Wheeler, K.A.; Hoyt, H.M. Aryl-substituted BIAN complexes of iron dibromide: Synthesis, X-ray and electronic structure, and catalytic hydrosilylation activity. Polyhedron 2016, 114, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Zhu, F.; Bu, D.; Lei, H. Ferrous complexes supported by sterically encumbered asymmetric bis(arylimino)acenaphthene (BIAN) ligands: Synthesis, characterization and screening for catalytic hydrosilylation of carbonyl compounds. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15321–15329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaefer, B.A.; Margulieux, G.W.; Tiedemann, M.A.; Small, B.L.; Chirik, P.J. Synthesis and Electronic Structure of Iron Borate Betaine Complexes as a Route to Single-Component Iron Ethylene Oligomerization and Polymerization Catalysts. Organometallics 2015, 34, 5615–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, R.K.; Shaver, M.P.; Gibson, V.C.; White, A.J.P. α-Diimine, Diamine, and Diphosphine Iron Catalysts for the Controlled Radical Polymerization of Styrene and Acrylate Monomers. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 7441–7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.-H.; Shih, W.-C.; Tsai, F.-T.; Tsai, M.-L.; Ching, W.-M.; Hsieh, H.-H.; Liaw, W.-F. Electrocatalytic Water Reduction Beginning with a {Fe(NO)2}10-Reduced Dinitrosyliron Complex: Identification of Nitrogen-Doped FeOx(OH)y as a Real Heterogeneous Catalyst. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 14715–14726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, J.; Frühauf, H.-W.; Smeets, W.J.J.; Spek, A.L. Comparing structures and reactivity in analogous Fe and Ru complexes. (iPr-DAB)Fe(CO)2I2 and (iPr-DAB)FeI2: A perfectly reversible CO-carrier system. (R-DAB = N,N′-R2-1,4-diaza-1,3-butadiene). Inorg. Chim. Acta 1999, 291, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Child, C.R.; Kealey, S.; Jones, H.; Miller, P.W.; White, A.J.P.; Gee, A.D.; Long, N.J. Binding and photodissociation of CO in iron(II) complexes for application in positron emission tomography (PET) radiolabelling. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 6210–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedushkin, I.L.; Skatova, A.A.; Khvoinova, N.M.; Lukoyanov, A.N.; Fukin, G.K.; Ketkov, S.Y.; Maslov, M.O.; Bogomyakov, A.S.; Makarov, V.M. New high-spin iron complexes based on bis(imino)acenaphthenes (BIAN): Synthesis, structure, and magnetic properties. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2013, 62, 2122–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, M.R.; Dunbar, K.R. Ligands effects on the magnetic anisotropy of tetrahedral cobalt complexes. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12266–12269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yambulatov, D.S.; Nikolaevskii, S.A.; Kiskin, M.A.; Magdesieva, T.V.; Levitskiy, O.A.; Korchagin, D.V.; Efimov, N.N.; Vasil’ev, P.N.; Goloveshkin, A.S.; Sidorov, A.A.; et al. Complexes of Cobalt(II) Iodide with Pyridine and Redox Active 1,2-Bis(arylimino)acenaphthene: Synthesis, Structure, Electrochemical, and Single Ion Magnet Properties. Molecules 2020, 25, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedushkin, I.L.; Skatova, A.A.; Chudakova, V.A.; Fukin, G.K. Four-Step Reduction of dpp-bian with Sodium Metal: Crystal Structures of the Sodium Salts of the Mono-, Di-, Tri- and Tetraanions of dpp-bian. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3294–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulovicova, A.; El-Ayaan, U.; Shibayama, K.; Morita, T.; Fukuda, Y. Mixed-Ligand Copper(II) Complexes with the Rigid Bidentate Bis(N-arylimino)acenaphthene Ligand: Synthesis, Spectroscopic-, and X-ray Structural Characterization. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 2001, 2641–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedushkin, I.L.; Yambulatov, D.S.; Skatova, A.A.; Baranov, E.V.; Demeshko, S.; Bogomyakov, A.S.; Ovcharenko, V.I.; Zueva, E.M. Ytterbium and Europium Complexes of Redox-Active Ligands: Searching for Redox Isomerism. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 9825–9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ayaan, U.; Paulovicova, A.; Yamada, S.; Fukuda, Y. The Crystal Structure of Bis[N-(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)imino] Acenaphthene and Studies of its Copper(I) and Copper(II) Complexes. J. Coord. Chem. 2003, 56, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bill, E.; Bothe, E.; Chaudhuri, P.; Chlopek, K.; Herebian, D.; Kokatam, S.; Ray, K.; Weyhermüller, T.; Neese, F.; Wieghardt, K. Molecular and electronic structure of four- and five-coordinate cobalt complexes containing two o-phenylenediamine- or two o-aminophenol-type ligands at various oxidation levels: An experimental, density functional, and correlated ab initio study. Chem. A Eur. J. 2004, 11, 204–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaevskii, S.A.; Kiskin, M.A.; Starikov, A.G.; Efimov, N.N.; Bogomyakov, A.S.; Minin, V.V.; Ugolkova, E.A.; Nikitin, O.M.; Magdesieva, T.V.; Sidorov, A.A.; et al. Atmospheric Oxygen Influence on the Chemical Transformations of 4,5-Dimethyl-1,2-Phenylenediamine in the Reactions with Copper(II) Pivalate. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2019, 45, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yambulatov, D.S.; Skatova, A.A.; Cherkasov, A.V.; Fedushkin, I.L. Addition of phenylacetylene and camphor to the complex [(dpp-bian)Eu(dme)2] (dpp-bian is the 1,2-bis[(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)imino]acenaphthene dianion). Russ. Chem. Bull. 2017, 66, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skatova, A.A.; Yambulatov, D.S.; Fedyushkin, I.L.; Baranov, E.V. Europium and Ytterbium Complexes with the Redox Active Acenaphthene-1,2-Diimine Ligand. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2018, 44, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedushkin, I.L.; Skatova, A.A.; Yambulatov, D.S.; Cherkasov, A.V.; Demeshko, S.V. Europium complexes with 1,2-bis(arylimino)acenaphthenes: A search for redox isomers. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2015, 64, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klementyeva, S.V.; Starikova, A.A.; Abramov, P.A. Reactions of [(dpp-Bian)Ln(dme)2] (Ln=Eu, Yb) with some oxidants. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2018, 92, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.; Zysman-Colman, E. Synthesis, UV–Vis and CV properties of a structurally related series of bis(Arylimino)acenaphthenes (Ar-BIANs). J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2013, 26, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viganò, M.; Ferretti, F.; Caselli, A.; Ragaini, F.; Rossi, M.; Mussini, P.; Macchi, P. Easy Entry into Reduced Ar-BIANH2 Compounds: A New Class of Quinone/Hydroquinone-Type Redox-Active Couples with an Easily Tunable Potential. Chem. A Eur. J. 2014, 20, 14451–14464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khrizanforova, V.V.; Morozov, V.I.; Khrizanforov, M.N.; Lukoyanov, A.N.; Kataeva, O.N.; Fedushkin, I.L.; Budnikova, Y.H. Iron complexes of BIANs: Redox trends and electrocatalysis of hydrogen evolution. Polyhedron 2018, 154, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrizanforov, M.N.; Arkhipova, D.M.; Shekurov, R.P.; Gerasimova, T.P.; Ermolaev, V.V.; Islamov, D.R.; Miluykov, V.A.; Kataeva, O.N.; Khrizanforova, V.V.; Sinyashin, O.G.; et al. Novel paste electrodes based on phosphonium salt room temperature ionic liquids for studying the redox properties of insoluble compounds. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 19, 2883–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukoyanov, A.N.; Ulivanova, E.A.; Razborov, D.A.; Khrizanforova, V.V.; Budnikova, Y.H.; Makarov, S.G.; Rumyantcev, R.V.; Ketkov, S.Y.; Fedushkin, I.L. One-Electron Reduction of 2-Mono(2,6-diisopropylphenylimino)acenaphthene-1-one (dpp-mian). Chem. A Eur. J. 2019, 25, 3858–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubelka, P. New Contributions to the Optics of Intensely Light-Scattering Materials. Part, I.J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1948, 38, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SMART (Control) and SAINT (Integration) Software; Version 5.0; Bruker AXS, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1997.
- Krause, L.; Herbst-Irmer, R.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Stalke, D. Comparison of silver and molybdenum microfocus X-ray sources for single-crystal structure determination. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheldrick, G. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dreuw, A.; Head-Gordon, M. Single-Reference ab Initio Methods for the Calculation of Excited States of Large Molecules. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 4009–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Neese, F. Double-hybrid density functional theory for excited electronic states of molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 154116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, B.O.; Taylor, P.R.; Sigbahn, P.E.M. A complete active space SCF method (CASSCF) using a density matrix formulated super-CI approach. Chem. Phys. 1980, 48, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, C.; Cimiraglia, R.; Malrieu, J.-P. n-electron valence state perturbation theory: A spinless formulation and an efficient implementation of the strongly contracted and of the partially contracted variants. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 9138–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.A. Relativistic electronic-structure calculations employing a two-component no-pair formalism with external-field projection operators. Phys. Rev. A 1986, 33, 3742–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douglas, M.; Kroll, N.M. Quantum electrodynamical corrections to the fine structure of helium. Ann. Phys. 1974, 82, 89–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazis, D.A.; Chen, X.-Y.; Landis, C.R.; Neese, F. All-Electron Scalar Relativistic Basis Sets for Third-Row Transition Metal Atoms. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunning, T.H.; Botch, B.H.; Harrison, J.F. On the orbital description of the 4s3dn+1 states of the transition metal atoms. J. Chem. Phys. 1980, 72, 3419–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganyushin, D.; Neese, F. A fully variational spin-orbit coupled complete active space self-consistent field approach: Application to electron paramagnetic resonance g-tensors. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 104113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurice, R.; Bastardis, R.; Graaf, C.d.; Suaud, N.; Mallah, T.; Guihéry, N. Universal Theoretical Approach to Extract Anisotropic Spin Hamiltonians. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2009, 5, 2977–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neese, F. Software update: The ORCA program system, version 4.0. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2018, 8, e1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| 1·CH3CN | ||
| Formula | C38H43FeI2N3 | |
| Mr (g mol−1) | 851.40 | |
| T (K) | 100 | 280 |
| Crystal system | Orthorhombic | |
| Space group | Pbca | |
| a (Å) | 19.400(2) | 19.568(4) |
| b (Å) | 19.303(3) | 19.309(5) |
| c (Å) | 19.581(2) | 19.824(3) |
| V (Å3) | 7333.0(18) | 7490(3) |
| Z | 8 | |
| ρcalc,(g cm−3) | 1.542 | 1.510 |
| μ (mm−1) | 2.124 | 2.080 |
| F(000) | 3392 | 3392 |
| Crystal size, (mm) | 0.12 × 0.12 × 0.04 | |
| θmin/θmax (°) | 2.08/28.28 | 2.06/26.37 |
| Index ranges | −25 ≤ h ≤ 25 | −24 ≤ h ≤ 24 |
| −25 ≤ k ≤ 25 | −24 ≤ k ≤ 24 | |
| −26 ≤ l ≤ 26 | −24 ≤ l ≤ 24 | |
| Reflections collected | 75400 | 66864 |
| Independent reflections | 7386 | 4922 |
| Rint | 0.0847 | 0.1118 |
| Tmin/Tmax | 0.6758/0.7461 | 0.6599/0.7461 |
| GOF on F2 | 1.100 | 1.047 |
| Final R indices (I > 2σ(I)) | R1 = 0.0475, wR2 = 0.0792 | R1 = 0.0690, wR2 = 0.1363 |
| R indices (all data) | R1 = 0.0654, wR2 = 0.0847 | R1 = 0.1167, wR2 = 0.1568 |
| Largest diffraction peak/hole (e Å−3) (dmin/dmax) | −0.863/0.732 | −0.885/0.685 |
| Temperature/Parameter | 100 K | 280 K |
|---|---|---|
| C (1)−C (5) | 1.506 (5) | 1.504 (8) |
| N (1)−C (1) | 1.288 (4) | 1.294 (7) |
| N (2)−C (5) | 1.284 (4) | 1.285 (7) |
| Fe (1)−N (1) | 2.128 (3) | 2.124 (5) |
| Fe (1)−N (2) | 2.139 (3) | 2.139 (5) |
| Fe (1)−I (1) | 2.5654 (6) | 2.5542 (10) |
| Fe (1)−I (2) | 2.5683 (6) | 2.5556 (11) |
| I(1) − Fe(1) − I(2) | 113.44 (2) | 112.79 (4) |
| N(1) − Fe(1) − N(2) | 78.48 (11) | 78.27 (17) |
| Fe…Femin | 9.747 (2) | 9.755 (4) |
| Compound | Solvent | Reduction | Oxidation |
|---|---|---|---|
| [(dpp-BIAN)FeIII2] | CH3CN | −0.95/- −2.00/- | −0.21/−0.31 0.02/−0.13 0.33/0.21 |
| CH2Cl2 | −0.82/−0.71 −1.67/- | 0.05/−0.10 0.33/0.21 | |
| Solid | −0.82/−0.76 −1.69/- | 0.05/−0.03 0.35/0.27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yambulatov, D.S.; Nikolaevskii, S.A.; Kiskin, M.A.; Kholin, K.V.; Khrizanforov, M.N.; Budnikova, Y.G.; Babeshkin, K.A.; Efimov, N.N.; Goloveshkin, A.S.; Imshennik, V.K.; et al. Generation of a Hetero Spin Complex from Iron(II) Iodide with Redox Active Acenaphthene-1,2-Diimine. Molecules 2021, 26, 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102998
Yambulatov DS, Nikolaevskii SA, Kiskin MA, Kholin KV, Khrizanforov MN, Budnikova YG, Babeshkin KA, Efimov NN, Goloveshkin AS, Imshennik VK, et al. Generation of a Hetero Spin Complex from Iron(II) Iodide with Redox Active Acenaphthene-1,2-Diimine. Molecules. 2021; 26(10):2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102998
Chicago/Turabian StyleYambulatov, Dmitriy S., Stanislav A. Nikolaevskii, Mikhail A. Kiskin, Kirill V. Kholin, Mikhail N. Khrizanforov, Yulia G. Budnikova, Konstantin A. Babeshkin, Nikolay N. Efimov, Alexander S. Goloveshkin, Vladimir K. Imshennik, and et al. 2021. "Generation of a Hetero Spin Complex from Iron(II) Iodide with Redox Active Acenaphthene-1,2-Diimine" Molecules 26, no. 10: 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102998
APA StyleYambulatov, D. S., Nikolaevskii, S. A., Kiskin, M. A., Kholin, K. V., Khrizanforov, M. N., Budnikova, Y. G., Babeshkin, K. A., Efimov, N. N., Goloveshkin, A. S., Imshennik, V. K., Maksimov, Y. V., Kadilenko, E. M., Gritsan, N. P., & Eremenko, I. L. (2021). Generation of a Hetero Spin Complex from Iron(II) Iodide with Redox Active Acenaphthene-1,2-Diimine. Molecules, 26(10), 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102998









