Effect of Saffron Extract on the Hepatotoxicity Induced by Copper Nanoparticles in Male Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
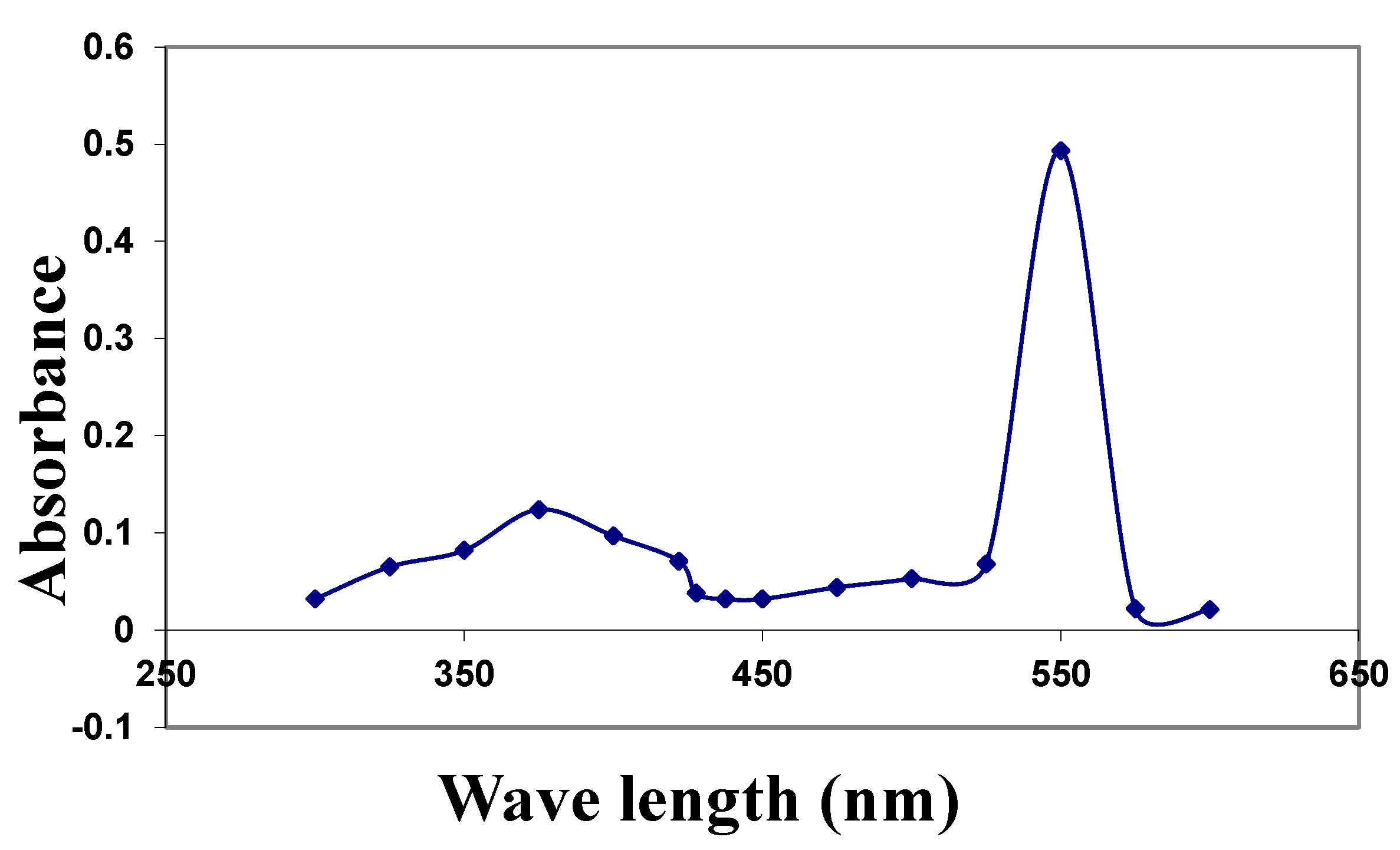
2.1. Characterization of the CuNPs and Zeta Potential
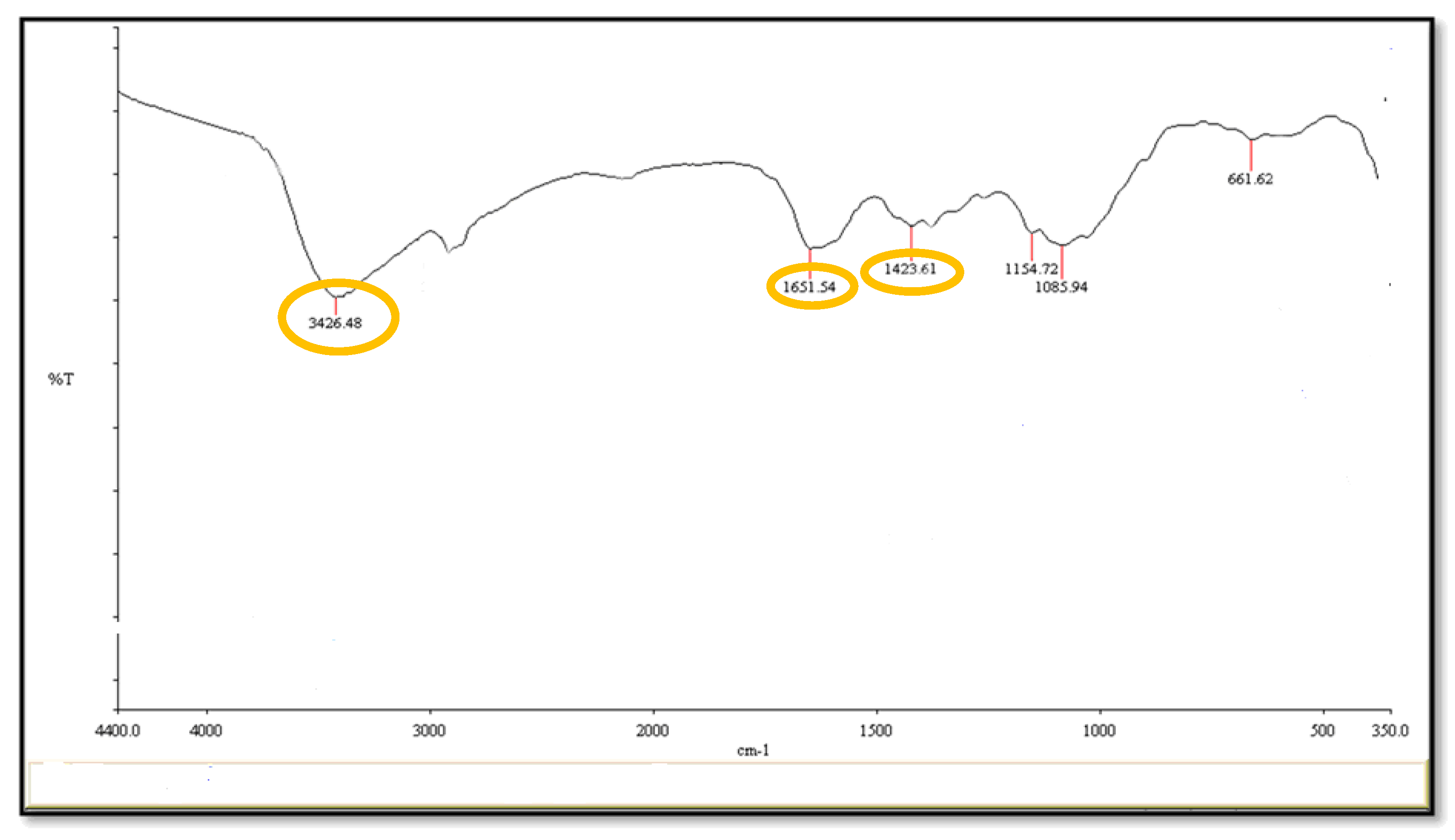
2.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-I) and Morphology of CuNPs Using the Electron Microscope (EM)
2.3. External Signs, Body Weight and Mortality
2.4. Enzymes Markers in Serum of Mice
2.5. Oxidative Stress and Total Antioxidant
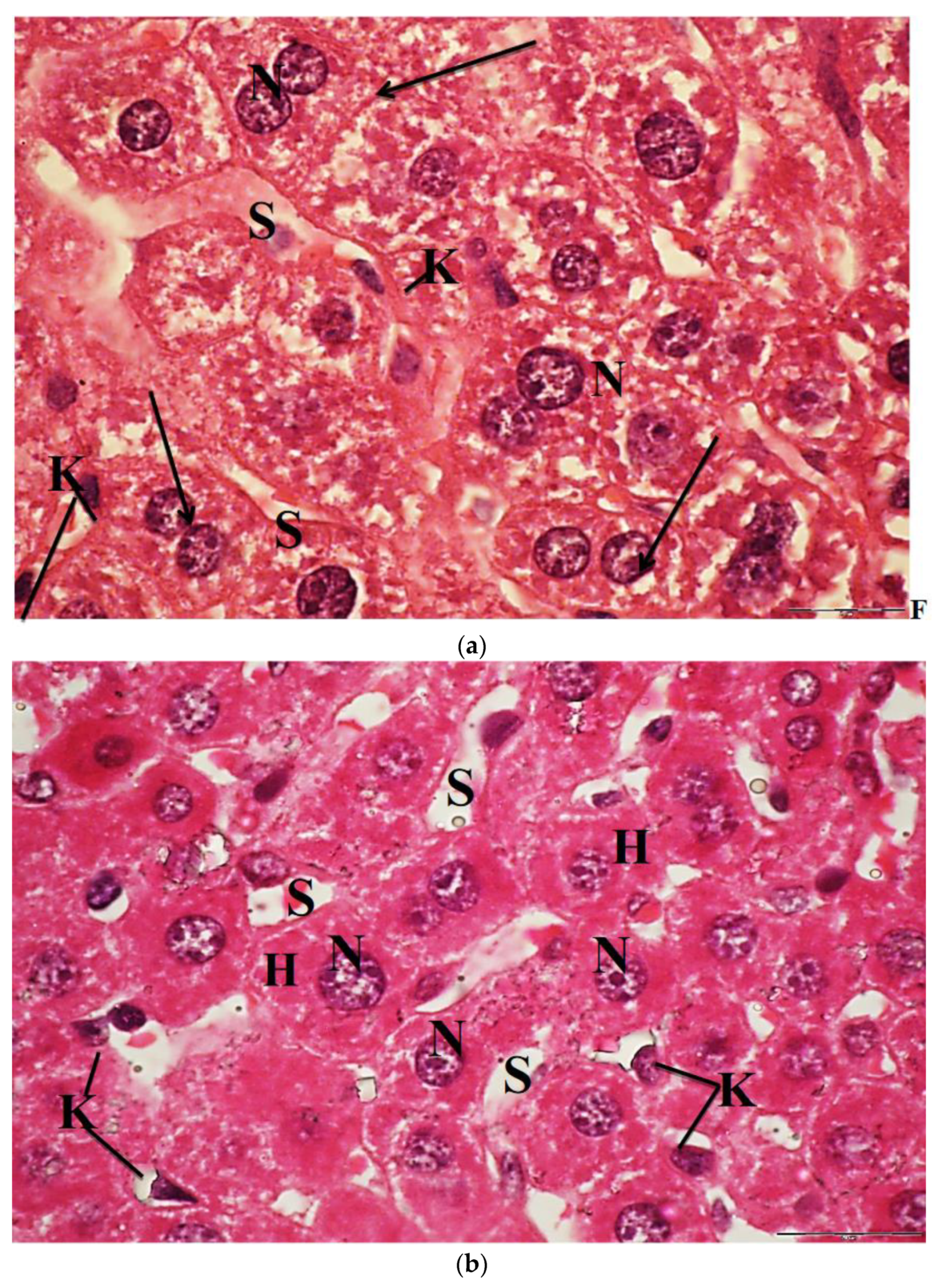
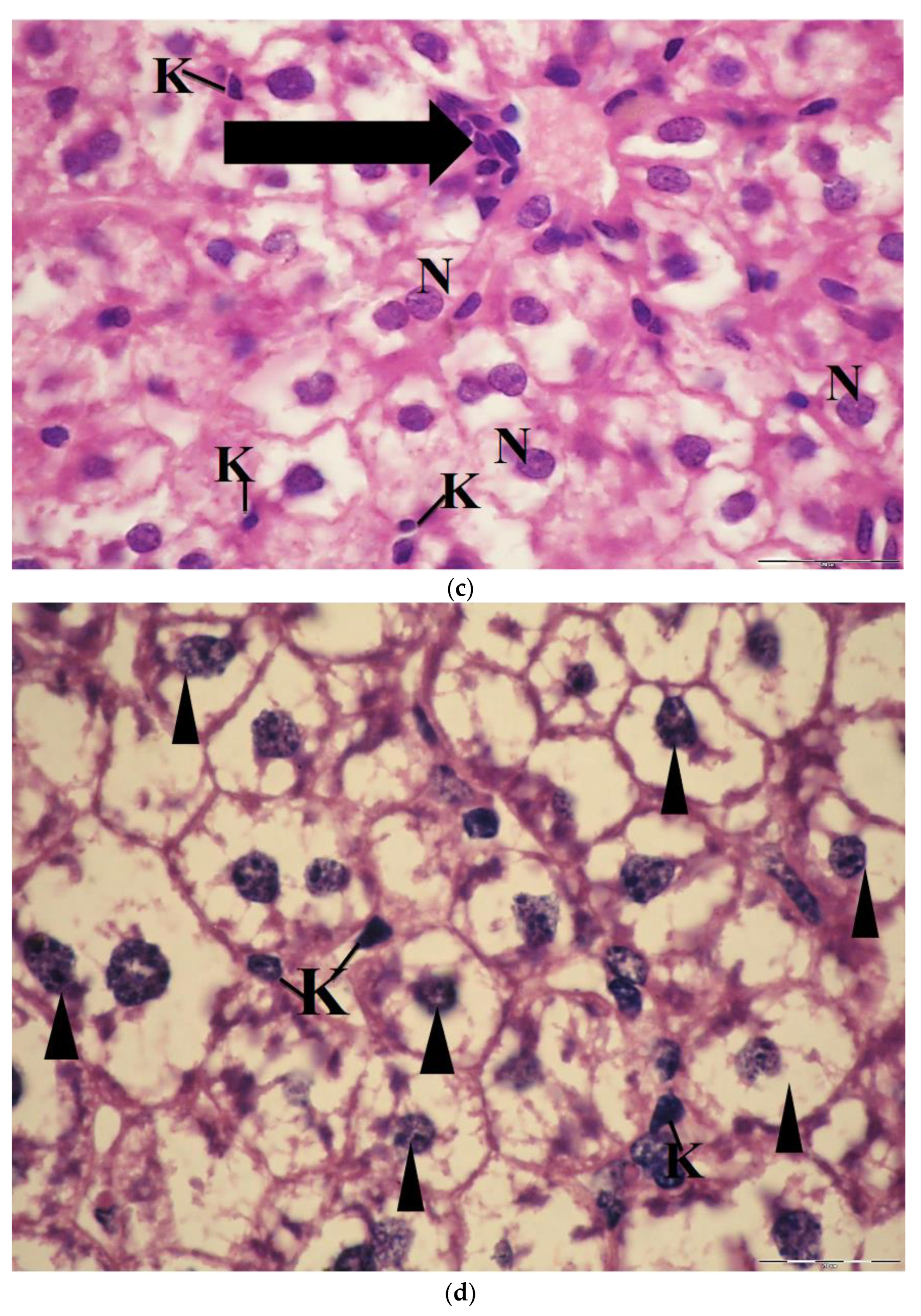
2.6. Light Microscopic Observations
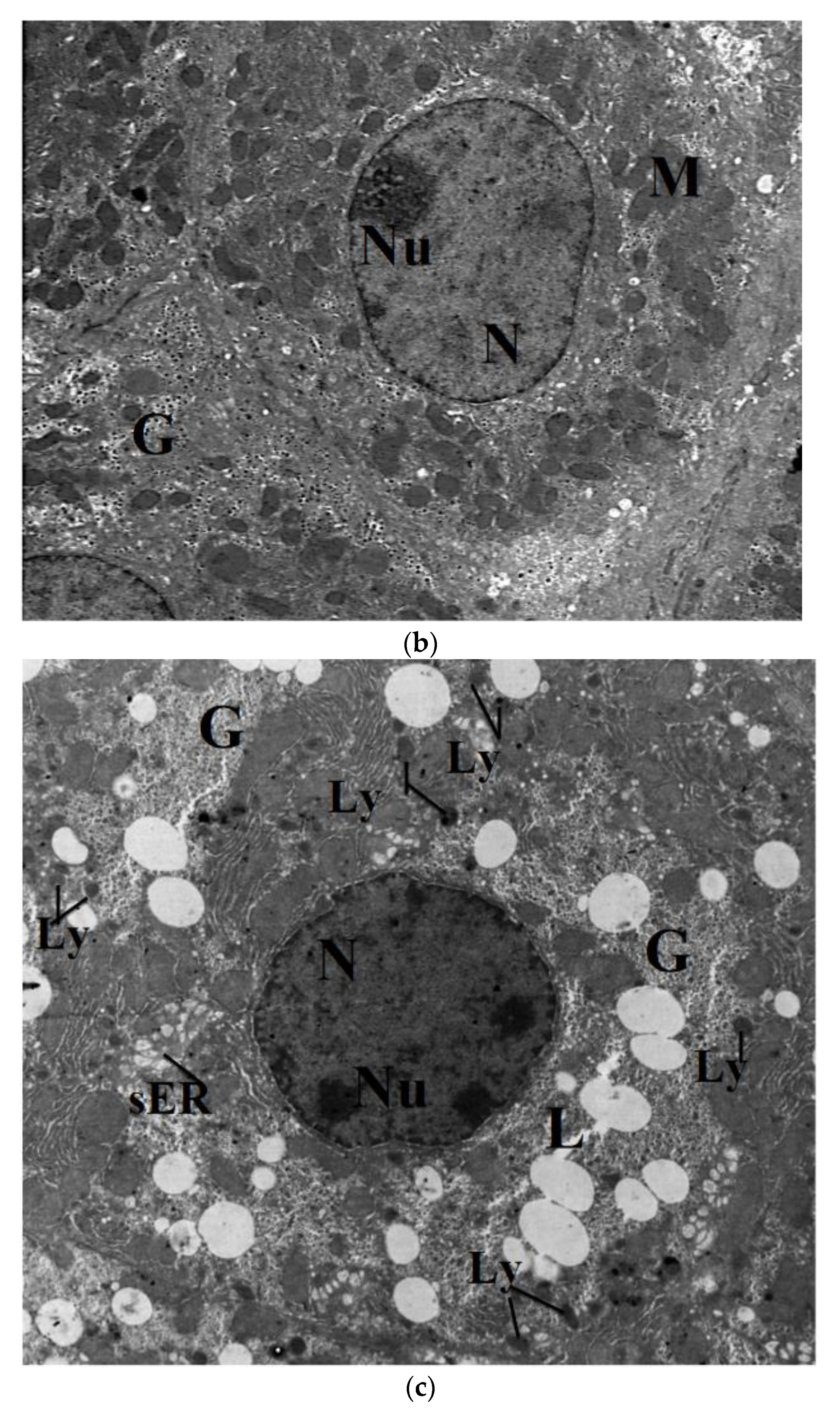
2.7. Transmission Electron Microscope
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles
4.3. Preparation of Ethanolic Saffron Extract
4.4. Animal Design and Care
4.5. Toxicological Assessment of CuNPs
4.6. Characterization of CuNPs
4.6.1. Ultraviolet–Visible Absorption Spectroscopy (UV-Vis)
4.6.2. Particle Size Analysis and Zeta Potential
4.6.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT- IR)
4.6.4. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) for Nanoparticles
4.7. Body Weight and Biochemical Parameters
4.8. Qualitative DNA Fragmentation Assay Using Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
4.9. Light Microscopic Investigation
4.10. Transmission Electron Microscopic Study
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Shamsadin-Azad, Z.; Taher, M.A.; Cheraghi, S.; Karimi-Maleh, H. A nanostructure voltammetric platform amplified with ionic liquid for determination of tert-butylhydroxyanisole in the presence kojic acid. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 1781–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-maleh, H.; Cellat, K.; Arıkan, K.; Şavk, A. Palladium-Nickel nanoparticles decorated on Functionalized-MWCNT for high precision non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 250, 123042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, F.; Sannakki, B.; Mandke, M.V.; Pathan, H.M. Copper nanoparticles: Synthesis methods and its light harvesting performance. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 144, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, V.V.; Siwale, R.; Singh, A.K.; Mody, H.R. Introduction to metallic nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, X.; Qin, B.; Xing, D.; Guo, Y.; Fan, R. Investigation of the Mending Effect and Mechanism of Copper Nano-Particles on a Tribologically Stressed Surface. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, N.; DiTaranto, N.; Torsi, L.; Picca, R.A.; Sabbatini, L.; Valentini, A.; Novello, L.; Tantillo, G.; Bleve-Zacheo, T.; Zambonin, P.G. Analytical characterization of bioactive fluoropolymer ultra-thin coatings modified by copper nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 381, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, E. Manufactured Nanomaterials (Fullerenes, C60) Induce Oxidative Stress in the Brain of Juvenile Largemouth Bass. Environ. Health Perspect 2004, 112, 1058–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.-H.; Shen, C.-C.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Huang, S.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Kao, C.-C.; Liao, J.-W.; Kang, J.-J. Organ biodistribution, clearance, and genotoxicity of orally administered zinc oxide nanoparticles in mice. Nanotoxicology 2011, 6, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Liu, J.; Li, N.; Wang, J.; Duan, Y.; Yan, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Hong, F. Oxidative stress in the brain of mice caused by translocated nanoparticulate TiO2 delivered to the abdominal cavity. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, M.; Mak, N.K.; Chen, F.; Jiang, Y. Triphenyltin induced growth inhibition and antioxidative responses in the green microalga Scenedesmus quadricauda. Ecotoxicology 2010, 20, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhardi, C.M.; Diniz, Y.S.; Faine, L.A.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Burneiko, R.C.; Ribas, B.O.; Novelli, E.L. Toxicity of copper intake: Lipid profile, oxidative stress and susceptibility to renal dysfunction. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 2053–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorn, P.Z.; Hermann, H.D.; Max, L.; Heide, S.; Barabara, K.G.; Hartmut, D. Epidemiological investigation on chronic copper toxicity to children exposed via the public drinking water supply. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 302, 127–144. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Meng, H.; Xing, G.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, G.; Wang, T.; Yuan, H.; Ye, C.; Zhao, F.; et al. Acute toxicological effects of copper nanoparticles in vivo. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 163, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, R.; Wu, C.; Yang, B.; Ma, H.; Shi, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Liao, M. Integrated metabolomic analysis of the nano-sized copper particle-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats: A rapid in vivo screening method for nanotoxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 232, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Adamcakova-Dodd, A.; O’Shaughnessy, P.T.; Grassian, V.H.; Thorne, P.S. Effects of copper nanoparticle exposure on host defense in a murine pulmonary infection model. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bakunin, V.N.; Suslov, A.Y.; Kuzmina, G.N.; Parenago, O.P.; Topchiev, A.V. Synthesis and application of inorganic nanoparticles as lubricant. Components. J. Nanopart. Res. 2004, 2, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Chen, Z.; Xing, G.; Yuan, H.; Chen, C.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y. Ultrahigh reactivity provokes nanotoxicity: Explanation of oral toxicity of nano-copper particles. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 175, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doudi, M.; Setorki, M. Acute effect of nano-copper on liver tissue and function in rats. J. Nanomed. 2014, 1, 331–338. [Google Scholar]
- Cholewińska, E.; Ognik, K.; Fotschki, B.; Zduńczyk, Z.; Juśkiewicz, J. Comparison of the effect of dietary copper nanoparticles and one copper (II) salt on the copper biodistribution and gastrointestinal and hepatic morphology and function in a rat model. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 48, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFeudis, F.V.; Papadopoulos, V.; Drieu, K. Ginkgo biloba extracts and cancer: A research area in its infancy. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 17, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frik, B.; Wink, W.M. Medicinal Plants of the World, 3rd ed.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2003; pp. 1–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari, S.I.; Manzoor, M.; Dhar, M. A comprehensive review of the pharmacological potential of Crocus sativus and its bioactive apocarotenoids. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 98, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.-Z.; Wen, X.-D.; Shoyama, Y.; Yuan, C.-S. Role of saffron and its constituents on cancer chemoprevention. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.; Sarwat, M.; Khan, T.H. Mechanism behind the anti-tumor potential of saffron (Crocus sativus L.): The molecular perspective. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 115, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarghandian, S.; Borji, A.; Farahmand, S.K.; Afshari, R.; Davoodi, S. Crocus sativus L. (Saffron) Stigma Aqueous Extract Induces Apoptosis in Alveolar Human Lung Cancer Cells through Caspase-Dependent Pathways Activation. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 417928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colapietro, A.; Mancini, A.; D’Alessandro, A.M.; Festuccia, C. Crocetin and Crocin from Saffron in Cancer Chemotherapy and Chemoprevention. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarpoor, V.; Karimabad, M.N.; Mahmoodi, M.; Mirzaei, M.R. The saffron effects on expression pattern of critical self-renewal genes in adenocarcinoma tumor cell line (AGS). Gene Rep. 2020, 19, 100629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Du, G.H. Saffron: A potential immunological adjuvant in anti-tumor therapy. Chin. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, 304–305. [Google Scholar]
- Khorasanchi, Z.; Shafiee, M.; Kermanshahi, F.; Khazaei, M.; Ryzhikov, M.; Parizadeh, M.R.; Kermanshahi, B.; Ferns, G.A.; Avan, A.; Hassanian, S.M. Crocus sativus a natural food coloring and flavoring has potent anti-tumor properties. Phytomedicine 2018, 43, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezici, S. Comparative anticancer activity analysis of saffron extracts and a principle component, crocetin for prevention and treatment of human malignancies. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 5435–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festuccia, C.; Mancini, A.; Gravina, G.L.; Scarsella, L.; Lloréns, S.; Alonso, G.L.; Tatone, C.; Di Cesare, E.; Jannini, E.A.; Lenzi, A.; et al. Antitumor Effects of Saffron-Derived Carotenoids in Prostate Cancer Cell Models. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 135048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathaie, S.Z.; Miri, H.; Mohagheghi, M.-A.; Dizaji, M.M.; Shahbazfar, A.-A.; Hasanzadeh, H. Saffron Aqueous Extract Inhibits the Chemically-induced Gastric Cancer Progression in the Wistar Albino Rat. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2013, 16, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makhlouf, H.; Diab-Assaf, M.; Alghabsha, M.; Mona, T.; Ramez, C.; Antoine, S.M. In vitro antiproliferative activity of saffron extracts against human acute lymphoblastic T-cell human leukemia. Indian J. Tradit. Knowled. 2016, 15, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Shakeri, M.; Tayer, A.H.; Shakeri, H.; Jahromi, A.S.; Moradzadeh, M.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M. Toxicity of Saffron Extracts on Cancer and Normal Cells: A Review Article. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 1867–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, S.; Roshanravan, N. Saffron; An updated review on biological properties with special focus on cardiovascular effects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarghandian, S.; Asadi-Samani, M.; Farkhondeh, T.; Bahmani, M. Assessment the effect of saffron ethanolic extract (Crocus sativus L.) on oxidative damages in aged male rat liver. Pharm. Lett. 2016, 8, 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Khazdair, M.R.; Boskabady, M.H.; Hosseini, M.; Rezaee, R.; Tsatsakis, A.M. The effects of Crocus sativus (saffron) and its constituents on nervous system: A review. Avicenna J. Phytomed 2015, 5, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zilaee, M.; Hosseini, S.A.; Jafarirad, S.; Abolnezhadian, F.; Cheraghian, B.; Namjoyan, F.; Ghadiri, A. An evaluation of the effects of saffron supplementation on the asthma clinical symptoms and asthma severity in patients with mild and moderate persistent allergic asthma: A double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kermani, T.; Zebarjadi, M.; Mehrad-Majd, H.; Mirhafez, S.-R.; Shemshian, M.; Ghasemi, F.; Mohammadzadeh, E.; Mousavi, S.H.; Norouzy, A.; Moghiman, T.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Crocus sativus on Serum Cytokine Levels in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo- Controlled Trial. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 12, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boskabady, M.-H.; Gholamnezhad, Z.; Khazdair, M.-R.; Tavakol-Afshari, J. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Saffron and Its Derivatives; Elsevier Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 405–421. [Google Scholar]
- Broadhead, G.K.; Grigg, J.R.; McCluskey, P.; Hong, T.; Schlub, T.E.; Chang, A.A. Saffron therapy for the treatment of mild/moderate age-related macular degeneration: A randomized clinical trial. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 257, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, M.; Wang, Y.; Xue, L.; Qunji, K.; Wu, X. Synthesis of Highly Stable Dispersion of Nanosized Copper Particles Using L-Ascorbic Acid. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Tripathy, N.; Son, H.; Ha, K.; Jeong, H.; Hahn, Y. A comprehensive in vitro and in vivo study of metal nanoparticles toxicity. J. Mater. Chem. 2013, 1, 2985–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaskill, C.L.; Miller, L.M.; Mattoon, J.S.; Hoffmann, W.E.; Burton, S.A.; Gelens, H.C.J.; Ihle, S.L.; Miller, J.B.; Shaw, D.H.; Cribb, A.E. Liver Histopathology and Liver and Serum Alanine Aminotransferase and Alkaline Phosphatase Activities in Epileptic Dogs Receiving Phenobarbital. Veter Pathol. 2005, 42, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.H.; Ji, J.H.; Park, J.D.; Yoon, J.U.; Kim, D.S.; Jeon, K.S.; Song, M.Y.; Jeong, J.; Han, B.S.; Han, J.H.; et al. Subchronic Inhalation Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 108, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.H. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2010, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, E.; Khorsandi, L.; Orazizadeh, M.; Jozi, Z. Dose-dependent hepatotoxicity effects of zinc nanoparticles. J. Nanomed. 2015, 2, 273–282. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, R.; Mo, Y.; Feng, L.; Chien, S.; Tollerud, D.J.; Zhang, Q. DNA Damage Caused by Metal Nanoparticles: Involvement of Oxidative Stress and Activation of ATM. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simkó, M.; Mattsson, M.-O. Risks from accidental exposures to engineered nanoparticles and neurological health effects: A critical review. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Salmi, F.A.; Hamza, R.Z.; El-Shenawy, N.S.; Al-Salmi, F.A. The Interaction of Zinc Oxide/Green Tea Extract Complex Nanoparticles and its Effect on Monosodium Glutamate Toxicity in Liver of Rats. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotto, D.; Maria, L.S.; Valentini, J.; Paniz, C.; Schmitt, G.; Garcia, S.C.; Pomblum, V.J.; Rocha, J.B.T.; Farina, M. Importance of the lipid peroxidation biomarkers and methodological aspects FOR malondialdehyde quantification. Química Nova 2009, 32, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sengottuvelan, M.; Senthilkumar, R.; Nalini, N. Modulatory influence of dietary resveratrol during different phases of 1,2-dimethylhydrazine induced mucosal lipid-peroxidation, antioxidant status, and aberrant crypt foci development in rat colon carcinogenesis. Biochim. Bioph. Acta 2006, 1760, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaapen, A.M.; Borm, P.J.; Albrecht, C.; Schins, R.P. Inhaled particles and lung cancer. Part A: Mechanisms. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thannickal, V.J.; Fanburg, B.L. Reactive oxygen species in cell signaling. Am. J. Physiol. 2000, 279, 1005–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fahmy, B.; Cormier, S.A. Copper oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in airway epithelial cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2009, 23, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranjbar, A.; Ataie, Z.; Khajavi, F.; Ghasemi, H. Effects of silver nanoparticle on oxidative stress biomarkers in rat. J. Nanomed. 2013, 1, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Lee, I.K.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.; Choi, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Hyun, J.W. Silver nanoparticles induce oxidative cell damage in human liver cells through inhibition of reduced glutathione and induction of mitochondria-involved apoptosis. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 201, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anlin, M.A.; Tieyong, W.U.; Enyu, D. Prevention and treatment of saffron on experimental alcoholic and CCI4 liver injury in Westar rats. Chin. J. Integ. Trad. Western Med. Liver Dis. 2000, 1, 6–19. [Google Scholar]
- Mohajeri, D.; Doustar, Y.; Rezaei, A.; Mesgari-Abbasi, M. Hepatoprotective effect of ethanolic extract of Crocus sativus L. (Saffron) stigma in comparison with silymarin against rifampin induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Zahedan J. Res. Med. Sci. 2011, 12, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Mohajeri, D.; Doustar, Y. Protective effect of ethanolic extract of Crocus sativus L. (Saffron) stigma against Cisplatin induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Med. Sci. J. 2012, 21, 251–261. [Google Scholar]
- Sardari, R.R.; Zarchi, S.R.; Talebi, A. Toxicological effects of silver nanoparticles in rats. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 6, 5587–5593. [Google Scholar]
- Iranshahi, M.; Khoshangosht, M.; Mohammadkhani, Z.; Karimi, G. Protective effects of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of saffron stigma and petal on liver toxicity induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice. Pharmacology 2011, 1, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Sadeghnia, H.R.; Ziaee, T.; Danaee, A. Protective effect of aqueous saffron extract (Crocus sativus L.) and crocin, its active constituent, on renal ischemia-reperfusion-induced oxidative damage in rats. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 8, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Yosry, A.O.; Seham, A.I. Effect of aqueous saffron extract on sodium valproate-induced histological and histochemical alterations in liver of albino rats. J. Adv. Res. 2014, 2, 735–745. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.-Q.; Liu, J.-X.; Wang, J.-N.; Xu, L. Effects of crocin on reperfusion-induced oxidative/nitrative injury to cerebral microvessels after global cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2007, 1138, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Duan, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, N.; Yan, J.; Ruan, J.; Wang, H.; et al. The Acute Liver Injury in Mice Caused by Nano-Anatase TiO2. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johar, D.; Roth, J.C.; Bay, G.H.; Walker, J.; Kroczak, T.J.; Los, M. Inflammatory response, reactive oxygen species, programmed (necrotic-like and apoptotic) cell death and cancer. Rocz. Akad. Med. Bialymst. 2004, 49, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Nikalje, S.B.; Muley, D.V.; Angadi, S.M. Histopathological changes in liver of freshwater major carp, Labeo rohita after acute and chronic exposure to textile mill effluent. Bioscan 2012, 7, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Colegio, O.R.; Van Itallie, C.; Rahner, C.; Anderson, J.M. Claudin extracellular domains determine paracellular charge selectivity and resistance but not tight junction fibril architecture. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2003, 284, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waisberg, M.; Joseph, P.; Hale, B.; Beyersmann, D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicology 2003, 192, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Mikecz, A.V. Formation of nucleoplasmic protein aggregates impairs nuclear function in response to SiO2 nanoparticles. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 305, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopotko, D.O.; Lukianova-Hleb, E.Y.; Oraevsky, A.O. Clusterization of nanoparticles during their interaction with living cells. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boya, P.; Andreau, K.; Poncet, D.; Zamzami, N.; Perfettini, J.-L.; Metivier, D.; Ojcius, D.M.; Jaattela, M.; Kroemer, G. Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization Induces Cell Death in a Mitochondrion-dependent Fashion. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Liong, M.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Cationic Polystyrene Nanosphere Toxicity Depends on Cell-Specific Endocytic and Mitochondrial Injury Pathways. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevenod, F. Nephrotoxicity and the proximal tubule. Insights from cadmium. Nephr. Physiol. 2003, 93, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, S.; Crowley, C.; Smaihi, M.; Bonfils, C.; Erlanger, B.F.; Seta, P. Cellular localization of a water-soluble fullerene derivative. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 294, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sioutas, C.; Cho, A.; Schmitz, D.; Misra, C.; Sempf, J.; Wang, M.; Oberley, T.; Froines, J.; Nel, A. Ultrafine particulate pollutants induce oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Environ. Health Perspect 2003, 111, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ChevilIe, N.F. Ultrastructural Pathology: An Introduction to Interpretation, 1st ed.; The Iowa State University Press: Ames, Iowa, 1994; pp. 67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, N.C. Kupffer cells and liver metastasis. Optimization and limitation of activation of tumoricidal activity. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1989, 8, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Jain, A.; Devra, V. Experimental investigation on the synthesis of copper nanoparticles by chemical reduction method. Intern. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 973–983. [Google Scholar]
- Katsumoto, F.; Miyazaki, K.; Nakayama, F. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in hepatocytes by kupffer cells after partial hepatectomy. Hepatology 1989, 9, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callery, M.P.; Mangino, M.J.; Wayne, F.M. Kupffer cell prostaglandin-E2 production is amplified during hepatic regeneration. Hepatology 1991, 14, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, H.; Choi, J. p38 MAPK activation, DNA damage cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis as mechanisms of toxicity of silver nanoparticles in Jurkat T cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8337–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawen, A. Apoptosis? an introduction. BioEssays 2003, 25, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, G.R.; Loureiro, A.P.; Marques, S.A.; Miyamoto, S.; Yamaguchi, L.F.; Onuki, J.; Almeida, E.A.; Garcia, C.C.; Barbosa, L.F.; Medeiros, M.H.; et al. Oxidative and alkylating damage in DNA. Mutat. Res. 2003, 544, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Brant, J.; Hotze, M.; Sempf, J.; Oberley, T.; Sioutas, C.; Yeh, J.I.; Wiesner, M.R.; Nel, A.E. Comparison of the Abilities of Ambient and Manufactured Nanoparticles To Induce Cellular Toxicity According to an Oxidative Stress Paradigm. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1794–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, H.A.; Swanson, J. Toxicity of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles in Mammalian Cells. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2006, 41, 2699–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premkumar, K.; Abraham, S.K.; Santhiya, S.T.; Ramesh, A. Protective effects of saffron on genotoxins-induced oxidative stress in Swiss albino mice. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, A.; Soliman, G.; Mahmoud, S.S.; Nofal, S.M.; Abdel-Rahman, R.F. Evaluation of the safety and antioxidant activities of Crocus sativus and Propolis ethanolic extracts. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2012, 16, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botsoglou, N.A.; Fletouris, D.J.; Papageorgiou, G.E.; Vassilopoulos, V.N.; Mantis, A.J.; Trakatellis, A.G. Rapid, Sensitive, and Specific Thiobarbituric Acid Method for Measuring Lipid Peroxidation in Animal Tissue, Food, and Feedstuff Samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koracevic, D.; Koracevic, G.; Djordjevic, V.; Andrejevic, S.; Cosic, V. Method for the measurement of antioxidant activity in human fluids. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 54, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reitman, S.; Frankel, S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum level of glutamate- oxaloacetate and pyrovate transaminases. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1957, 28, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.D.; Halsall, H.B.; Pesce, A.J.; Heineman, W.R. Determination of serum alkaline phosphatase activity by electrochemical detection with flow injection analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 1993, 346, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.A.; Dykes, D.D.; Polesky, H.F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Gamble, M. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 6th ed.; Elsevier Churchill Livingstone: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008; pp. 601–641. [Google Scholar]
- Bozzola, J.J.; Russell, L.D. Electron Microscope, 2nd ed.; Jones and Bartlett Publishers: Sudbury, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]










| Experimental Groups | No. of Mice | No. of Dead Mice | % of Mortality | Mean of Body Weight (g) | The Mean Change in Body Weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | |||||
| Control | 10 | 0 | - | 22.3 ± 2.081 | 28.34 ± 1.15 | 27.09 ± 7.16 |
| 60 mg/kg bw ethanolic saffron extract | 10 | 0 | - | 24.33 ± 1.15 | 30.6 ± 1.54 | 26.02 ± 2.06 |
| 100 mg/kg bw CuNPs | 10 | 1 | 10 | 23.01 ± 1.32 | 28.66 ± 1.5 | 24.78 ± 7.2 |
| 250 mg/kg CuNPs | 10 | 3 | 30 | 22.66 ± 2.5 | 26.66 ± 1.5 | 18.24 ± 9.02 a |
| 100 mg/kg bw CuNPs + 60 mg/kg ethanolic saffron extract | 10 | 0 | - | 23.67 ± 1.15 | 29.66 ± 0.57 | 25.62 ± 8.33 |
| 250 mg/kg bw CuNPs + 60 mg/kg ethanolic saffron extract | 10 | 1 | 10 | 22.66 ± 2.3 | 28 ± 1.73 | 23.88 ± 5.2 |
| Experimental Animals | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzymes Activity (U/mL) | Control | 60 mg/kg ESE | 100 mg/kg bw CuNP | 250 mg/kg bw CuNP | 100 mg/kg CuNP + 60 mg/kg bw ESE | 250 mg/kg CuNP + 60 mg/kg bw ESE |
| AST | 60.18 ± 2.03 | 50.3 ± 2.4 | 68.84 ± 5.6 a | 80.55 ± 4.6 a | 51.66 ± 4.3 b | 53.35 ± 1.8 c |
| ALT | 68.44 ± 12.9 | 60.81 ± 5.1 | 79.08 ± 2.2 a | 90.38 ± 9.01 a | 60.3 ± 5.80 b | 61.95 ± 7.2 c |
| ALP | 134.46 ± 2.4 | 122.52 ± 2.07 | 139.56 ± 15.7 a | 146.6 ± 0.4 a | 120.56 ± 3.7 b | 128.17 ± 8.3 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Attia, A.A.; Ramdan, H.S.; Al-Eisa, R.A.; Adle Fadle, B.O.A.; El-Shenawy, N.S. Effect of Saffron Extract on the Hepatotoxicity Induced by Copper Nanoparticles in Male Mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 3045. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26103045
Attia AA, Ramdan HS, Al-Eisa RA, Adle Fadle BOA, El-Shenawy NS. Effect of Saffron Extract on the Hepatotoxicity Induced by Copper Nanoparticles in Male Mice. Molecules. 2021; 26(10):3045. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26103045
Chicago/Turabian StyleAttia, Azza A., Heba S. Ramdan, Rasha A. Al-Eisa, Bassant O. A. Adle Fadle, and Nahla S. El-Shenawy. 2021. "Effect of Saffron Extract on the Hepatotoxicity Induced by Copper Nanoparticles in Male Mice" Molecules 26, no. 10: 3045. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26103045
APA StyleAttia, A. A., Ramdan, H. S., Al-Eisa, R. A., Adle Fadle, B. O. A., & El-Shenawy, N. S. (2021). Effect of Saffron Extract on the Hepatotoxicity Induced by Copper Nanoparticles in Male Mice. Molecules, 26(10), 3045. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26103045







