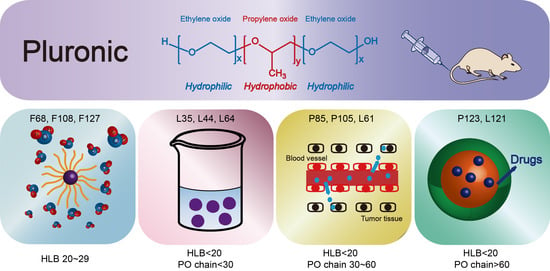
Polymeric Drug Delivery System Based on Pluronics for Cancer Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
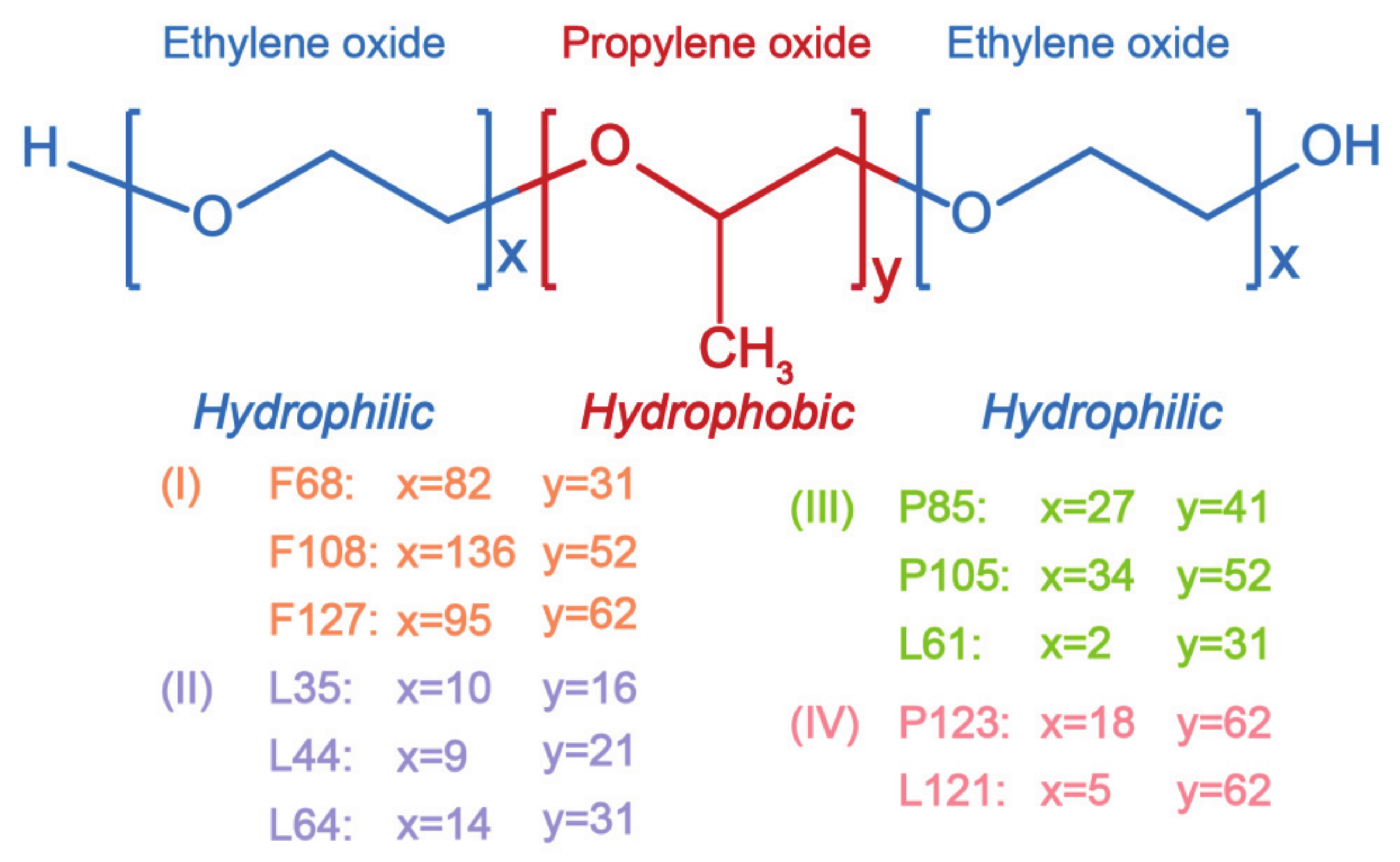
2. Pluronic Classification
2.1. HLB (Hydrophile-Lipophile Balance) 20–29 Hydrophilic Pluronics
2.2. Pluronic with HLB <20 and PO Chain <30
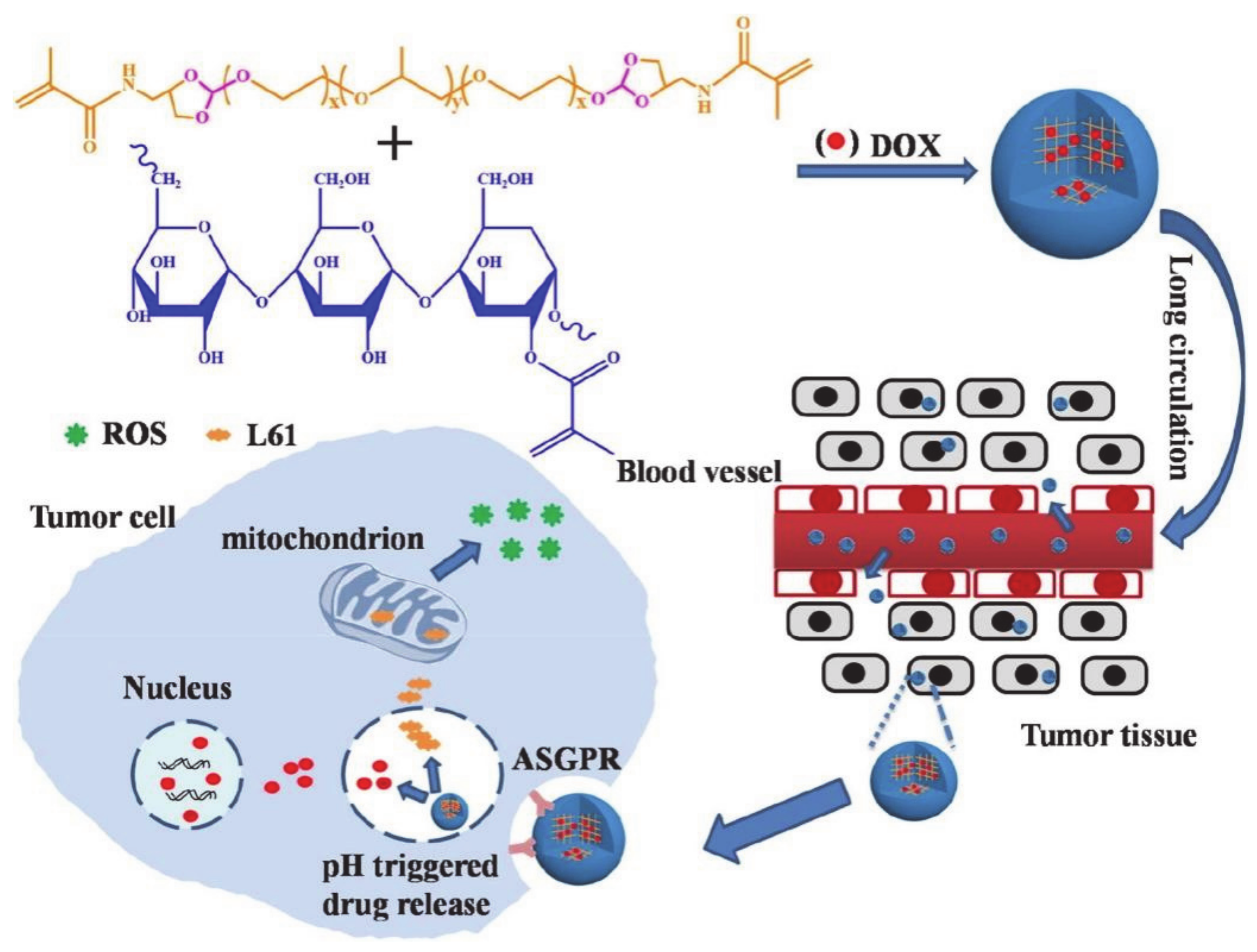
2.3. Pluronics with HLB < 20 and PO Chain 30–60
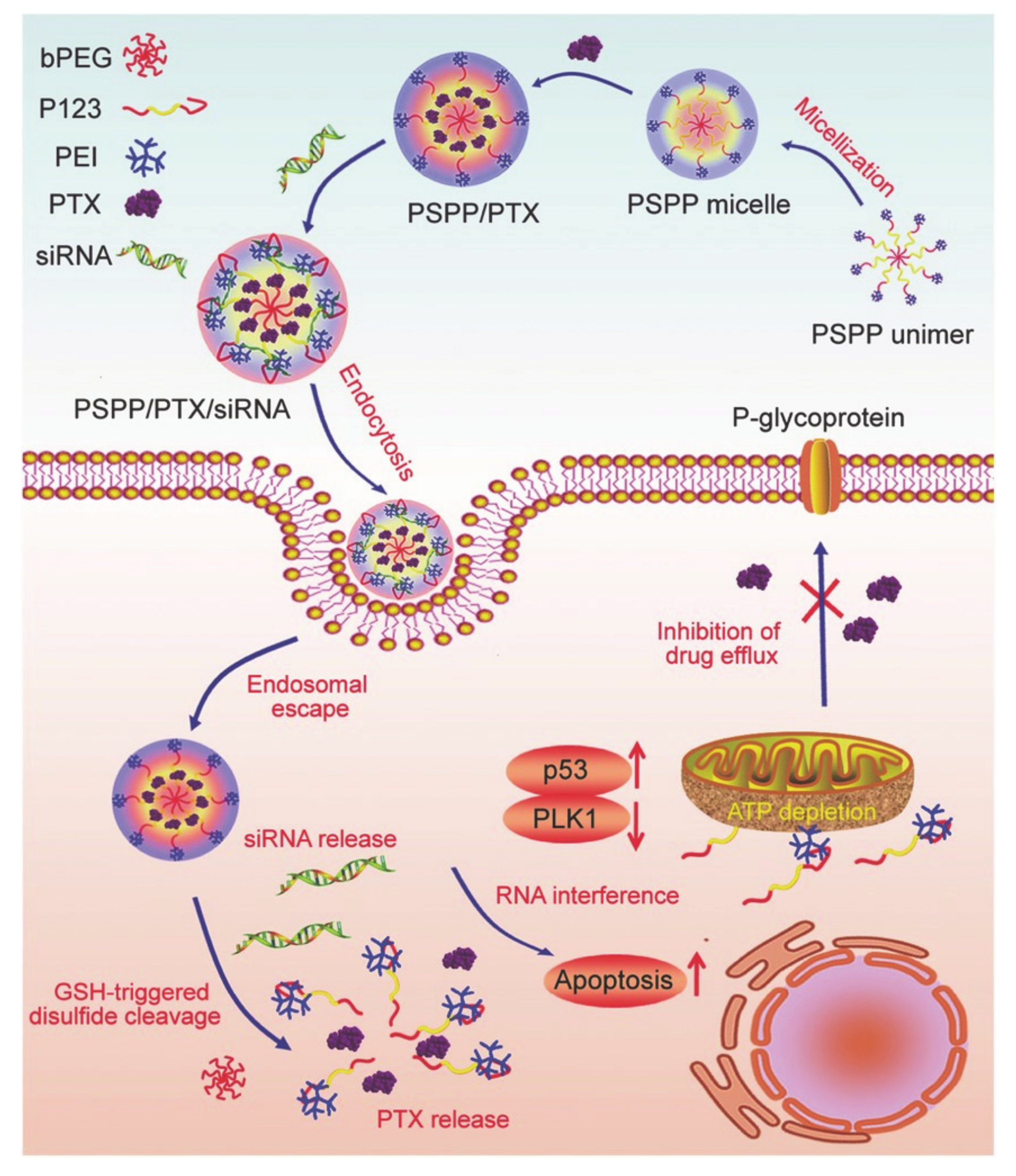
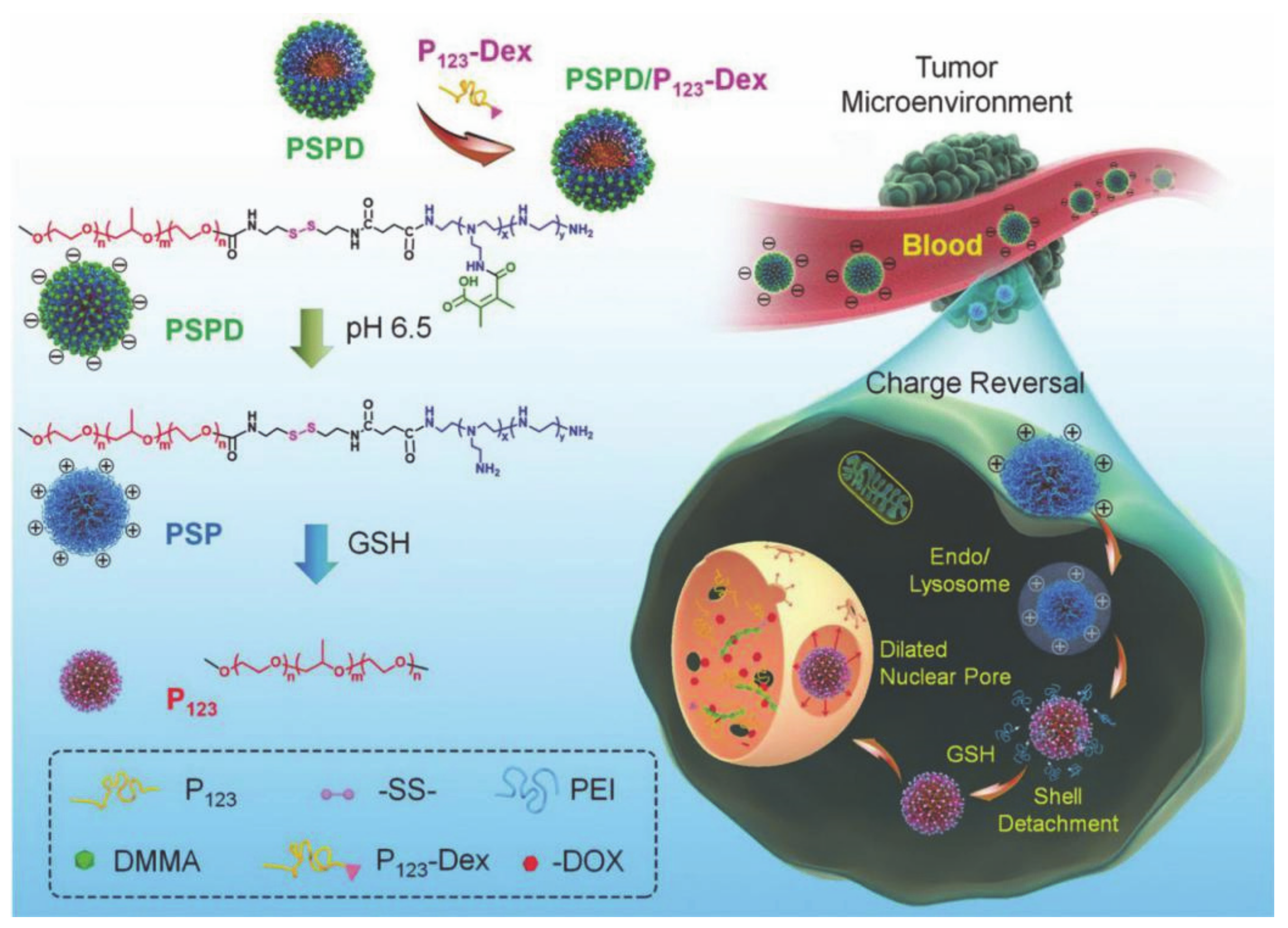
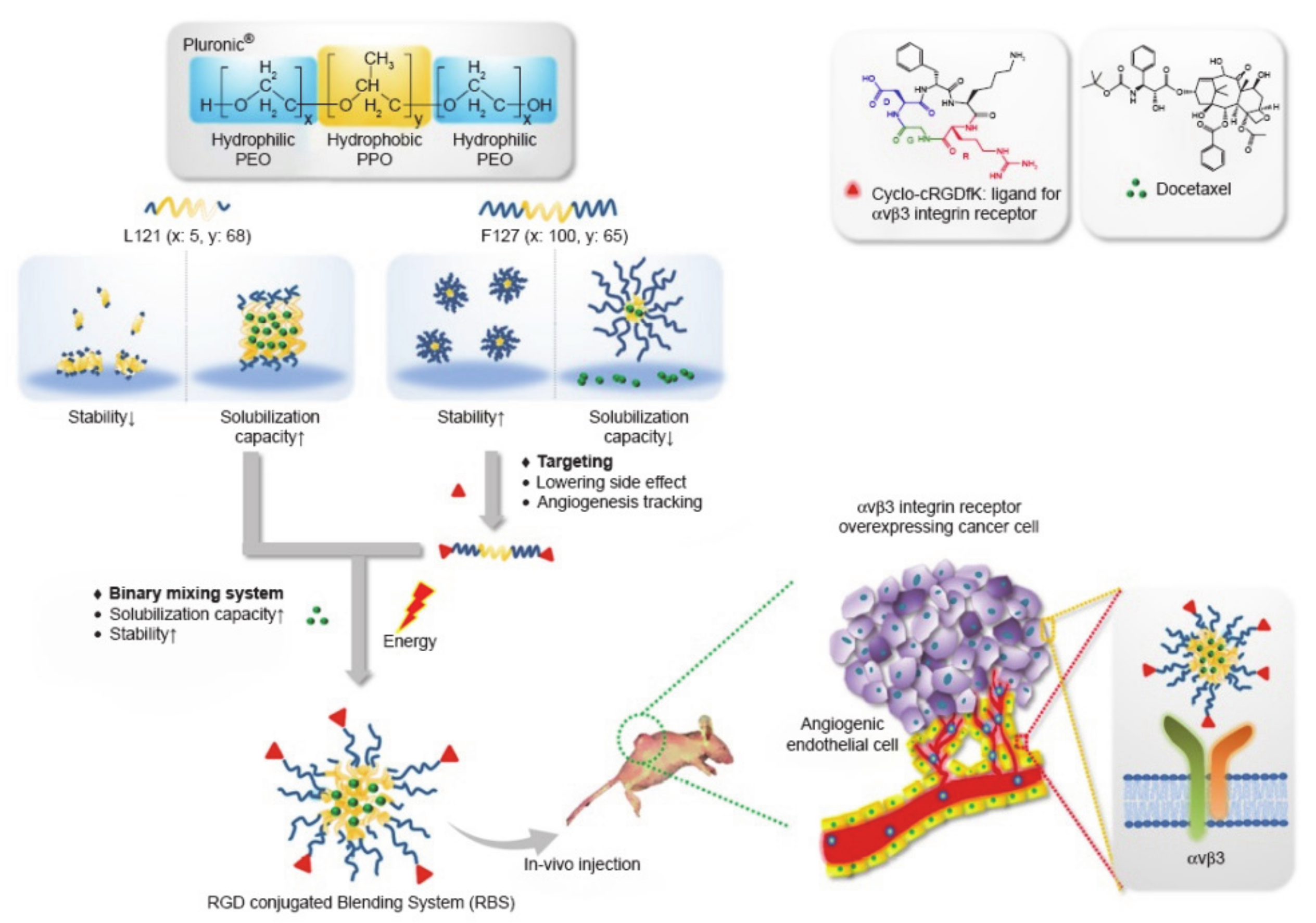
2.4. Pluronics with HLB < 20 and PO Chain > 60
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, B.; Huang, Z.; Shi, Q.; Middha, E.; Xu, S.; Li, L.; Wu, M.; Jiang, J.; Hu, Q.; Fu, Z.; et al. Organic Small Molecule Based Photothermal Agents with Molecular Rotors for Malignant Breast Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 30, 1907093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.; Qiang, Z.; Chu, M.; Shi, D.; Ren, J. Polymeric Drug Delivery System with Actively Targeted Cell Penetration and Nuclear Targeting for Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.A.; Andrews, K.S.; Brooks, D.; Fedewa, S.A.; Manassaram-Baptiste, D.; Saslow, D.; Brawley, O.W.; Wender, R.C. Cancer screening in the United States, 2017: A review of current American Cancer Society guidelines and current issues in cancer screening. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashin, P.; Mahteme, H.; Spång, N.; Syk, I.; Frödin, J.; Torkzad, M.; Glimelius, B.; Graf, W. Cytoreductive surgery and intraperitoneal chemotherapy versus systemic chemotherapy for colorectal peritoneal metastases: A randomised trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 53, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruysscher, D.; Niedermann, G.; Burnet, N.; Siva, S.; Lee, A.W.M.; Hegi-Johnson, F. Radiotherapy toxicity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-S.; Li, X.-Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, P.; Li, X.; Augusto, O.A.; Qin, Z.-K.; Liu, Z.-W.; Li, Y.-H.; Han, H.; et al. Radiotherapy plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone in penile cancer patients with extracapsular nodal extension after inguinal lymph node surgery: A multi-institutional study. World J. Urol. 2020, 39, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, H.; Zhen, M.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, L.; Shu, C.; Wang, C. Biocompatible [60]/[70] Fullerenols: Potent Defense against Oxidative Injury Induced by Reduplicative Chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35539–35547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Tumor-Specific Chemotherapy by Nanomedicine-Enabled Differential Stress Sensitization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9693–9701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, X.; Yu, J.; Fan, Y.; He, T.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Qiu, H.; Yin, S. Amphiphilic Rhomboidal Organoplatinum(II) Metallacycles with Encapsulated Doxorubicin for Synergistic Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 8061–8068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.R.; Nojoomi, A.; Mozafari, M.; Dubnika, A.; Inayathullah, M.; Rajadas, J. Nanomaterials engineering for drug delivery: A hybridization approach. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3995–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, V.; Jaleh, V.; Mohsen, M. Pulmonary Delivery of Triptorelin Loaded in Pluronic Based Nanomicelles in Rat Model. Curr. Drug Del. 2018, 15, 630–640. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzi, P.; Amini, M.; Mottaghitalab, F.; Mirzazadeh Tekie, F.S.; Dinarvand, R.; Mirzaie, Z.H.; Atyabi, F. Design and fabrication of dual-targeted delivery system based on gemcitabine-conjugated human serum albumin nanoparticles. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2020, 96, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, M.; Jung, S.; Kwon, K.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; Kwon, I.; Tae, G. Co-delivery of therapeutic protein and cata-lase-mimic nanoparticle using a biocompatible nanocarrier for enhanced therapeutic effect. J. Control. Release 2019, 309, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Guo, H.; Edman, M.; Hamm-Alvarez, S.F. Application of advances in endocytosis and membrane trafficking to drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 157, 118–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, X.; Wang, M.; Liu, K. Tumor microenvironment-induced structure changing drug/gene delivery system for overcoming delivery-associated challenges. J. Control. Release 2020, 323, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, N.; Sulfikkarali, N.; RajendraPrasad, N.; Karthikeyan, S. Enhanced anticancer activity of naringenin-loaded nanoparticles in human cervical (HeLa) cancer cells. Biomed. Prev. Nutr. 2011, 1, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: A review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Dong, H. Engineering of a novel pluronic F127/graphene nanohybrid for pH responsive drug delivery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2011, 100, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Wang, X.; Nie, S.; Chen, Z.; Shin, D.M. Therapeutic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery in Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, G.; Kaplan, D.L.; Wang, X. Control of silk microsphere formation using polyethylene glycol (PEG). Acta Biomater. 2016, 39, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Cai, H.; Liu, J.; Cui, B.; Wang, L.; Yin, L.; Zhou, J.; Huo, M. Biological evaluation of PEG modified nanosuspensions based on human serum albumin for tumor targeted delivery of paclitaxel. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 83, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, Y. Recent development of brush polymers via polymerization of poly(ethylene glycol)-based macromonomers. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 2212–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Maltzahn, G.; Park, J.-H.; Agrawal, A.; Bandaru, N.K.; Das, S.K.; Sailor, M.J.; Bhatia, S.N. Computationally Guided Photothermal Tumor Therapy Using Long-Circulating Gold Nanorod Antennas. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romberg, B.; Hennink, W.E.; Storm, G. Sheddable Coatings for Long-Circulating Nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 2007, 25, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmo, A.C.; Zhang, M.; Kumar, S.; Vogus, D.R.; Menegatti, S.; Helgeson, M.E.; Mitragotri, S. Elasticity of Nanoparticles Influences Their Blood Circulation, Phagocytosis, Endocytosis, and Targeting. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3169–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrault, S.D.; Walkey, C.; Jennings, T.; Fischer, H.C.; Chan, W.C.W. Mediating Tumor Targeting Efficiency of Nanoparticles Through Design. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1909–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, W.; Fromen, C.A.; Lopez-Cazares, G.; Eniola-Adefeso, O. PEGylation of model drug carriers enhances phagocytosis by primary human neutrophils. Acta Biomater. 2018, 79, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, D.; Liu, C.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Su, Y.; Zhao, L.; Meng, F.; Luo, J. Biodegradable pH-sensitive polyurethane mi-celles with different polyethylene glycol (PEG) locations for anti-cancer drug carrier applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 97684–97693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Wu, F.; Liao, C.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, S. Terminal Acetylated/Acrylated Poly(ethylene glycol) Fabricated Drug Carriers: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1956–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Liu, X.; Wei, J.J.; Wang, S.; Bin Xu, B.; Long, D.; Chen, F. T-Nb2O5 nanoparticle enabled pseudocapacitance with fast Li-ion intercalation. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 14165–14170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arranja, A.; Denkova, A.G.; Morawska, K.; Waton, G.; van Vlierberghe, S.; Dubruel, P.; Schosseler, F.; Mendes, E. Interactions of Pluronic nanocarriers with 2D and 3D cell cultures: Effects of PEO block length and aggregation state. J. Control. Release 2016, 224, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pragatheeswaran, A.M.; Chen, S.B. Effect of Chain Length of PEO on the Gelation and Micellization of the Pluronic F127 Copolymer Aqueous System. Langmuir 2013, 29, 9694–9701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.-C.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Gau, C.-S. Interfacial properties of Pluronics and the interactions between Pluronics and choles-terol/DPPC mixed monolayers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 322, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, B.; Barick, K.C.; Verma, G.; Aswal, V.K.; Freilich, I.; Danino, D.; Singh, B.G.; Priyadarsini, K.I.; Hassan, P.A. PEG coated vesicles from mixtures of Pluronic P123 and l-α-phosphatidylcholine: Structure, rheology and curcumin encapsulation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 26821–26832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; del Rosario, L.S.; Demirdirek, B.; Bae, A.; Uhrich, K.E. Comparison of PEG chain length and density on amphiphilic macromolecular nanocarriers: Self-assembled and unimolecular micelles. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nostrum, C.F. Polymeric micelles to deliver photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 2004, 56, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.G.; Cho, S.-H.; Lee, H.; Cha, M.H.; Park, K.; Jeong, B.; Han, D.K. Thermoreversible Radial Growth of Micellar Assembly for Hydrogel Formation Using Zwitterionic Oligopeptide Copolymer. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 2269–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrakova, E.V.; Kabanov, A.V. Pluronic block copolymers: Evolution of drug delivery concept from inert nanocarriers to biological response modifiers. J. Control. Release 2008, 130, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, B.; Tucker, J.D.; Lu, P.; Lu, Q. Poly(ester amine) constructed from polyethylenimine and pluronic for gene delivery in vitro and in vivo. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3224–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, B.; Lu, P.; Cloer, C.; Tucker, J.D.; Lu, Q. Polyethylenimine-modified Pluronics (PCMs) Improve Morpholino Oligomer Delivery in Cell Culture and Dystrophic mdx Mice. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.L.; Lavasanifar, A.; Kwon, G.S. Amphiphilic block copolymers for drug delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 92, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jing, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zang, X.; Qiao, M.; Zhao, X.; Hu, H.; Chen, D. Intracellular release of PluronicL64 unimers into MCF-7/ADR cells to overcome multidrug resistance by surface-modified PAMAM. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3970–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sha, X.; Han, L.; Fang, X. Poly(caprolactone)-modified Pluronic P105 micelles for reversal of paclitaxcel-resistance in SKOV-3 tumors. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 4741–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yuan, S.; Hao, J.; Fang, X. Mechanism of inhibition of P-glycoprotein mediated efflux by Pluronic P123/F127 block copolymers: Relationship between copolymer concentration and inhibitory activity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 83, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakhova, D.Y.; Rapoport, N.Y.; Batrakova, E.V.; Timoshin, A.A.; Li, S.; Nicholls, D.; Alakhov, V.Y.; Kabanov, A.V. Differential metabolic responses to pluronic in MDR and non-MDR cells: A novel pathway for chemosensitization of drug resistant cancers. J. Control. Release 2010, 142, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Li, Y. Nanohybrid systems of non-ionic surfactant inserting liposomes loading paclitaxel for reversal of multidrug resistance. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 422, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Lv, X.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, R. Pluronic micelles with suppressing doxorubicin efflux and detoxifica-tion for efficiently reversing breast cancer resistance. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 146, 105275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, J.; Hu, H.; Zhao, X.; Qiao, M. Reversing multidrug resistance by intracellular delivery of Pluronic® P85 unimers. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 9602–9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.-Y.; Zhang, W.-M. Recent progress in drug delivery of pluronic P123: Pharmaceutical perspectives. J. Drug Target. 2017, 25, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, R. Development and optimization of pluronic® F127 and HPMC based thermosensitive gel for the skin delivery of metoprolol succinate. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Bindokas, V.P.; Skinner, M.; Emrick, T.; Marks, J.D. Mitochondrial mechanisms of neuronal rescue by F-68, a hydrophilic Pluronic block co-polymer, following acute substrate deprivation. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 109, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xia, T.; Duch, M.C.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Sun, B.; Lin, S.; Meng, H.; Liao, Y.-P.; et al. Pluronic F108 Coating De-creases the Lung Fibrosis Potential of Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes by Reducing Lysosomal Injury. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3050–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Chong, J.Y.; Shi, L.; Wang, R. PTFE-assisted immobilization of Pluronic F127 in PVDF hollow fiber membranes with enhanced hydrophilicity through nonsolvent-thermally induced phase separation method. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.M.; Carbone, P. Amphiphilic copolymers change the nature of the ordered-to-disordered phase transition of lipid membranes from discontinuous to continuous. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 13746–13757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiano, R.; de la Cruz, J. Ribosomal protein L35 is required for 27SB pre-rRNA processing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 5177–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naskar, B.; Ghosh, S.; Moulik, S.P. Interaction of normal and reverse pluronics (L44 and 10R5) and their mixtures with ani-onic surfactant sodium N-dodecanoylsarcosinate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 414, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Li, K.; Liu, M.; Hu, X.; Xu, M.; Yan, R.; Zhao, S. P85 regulates neuronal migration through affecting neuronal morphology during mouse corticogenesis. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 372, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Jia, X.; Wang, Y. Optimization and evaluation of Oridonin-loaded Soluplus ®-Pluronic P105 mixed micelles for oral administration. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 518, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Shi, H.; Qiao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, W.; Dong, L.; Xie, F.; Zhao, C.; Kang, L. pH-sensitive micelles for the intracellular co-delivery of curcumin and Pluronic L61 unimers for synergistic reversal effect of multidrug resistance. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.-F.; Chen, C.-N.; Chen, M.-C.; Lai, C.-H.; Liang, H.-F.; Sung, H.-W. Shell-crosslinked Pluronic L121 micelles as a drug delivery vehicle. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezaveh, S.; Samanta, S.; De Nicola, A.; Milano, G.; Roccatano, D. Understanding the Interaction of Block Copolymers with DMPC Lipid Bilayer Using Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 14333–14345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V.P. Structure and design of polymeric surfactant-based drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2001, 73, 137–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitto-Barry, A.; Barry, N.P.E. Pluronic® block-copolymers in medicine: From chemical and biological versatility to rationalisation and clinical advances. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 3291–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.B.; dos Santos, R.S.; da Silva, M.B.; Braga, G.; Cook, M.T.; Bruschi, M.L. Interaction between mucoadhesive cellulose derivatives and Pluronic F127: Investigation on the micelle structure and mucoadhesive performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 119, 111643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Ding, L.; Yao, H.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. A Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) Fenton Nanoagent-Enabled Nanocatalytic Cancer Therapy in Synergy with Autophagy Inhibition. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1907152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
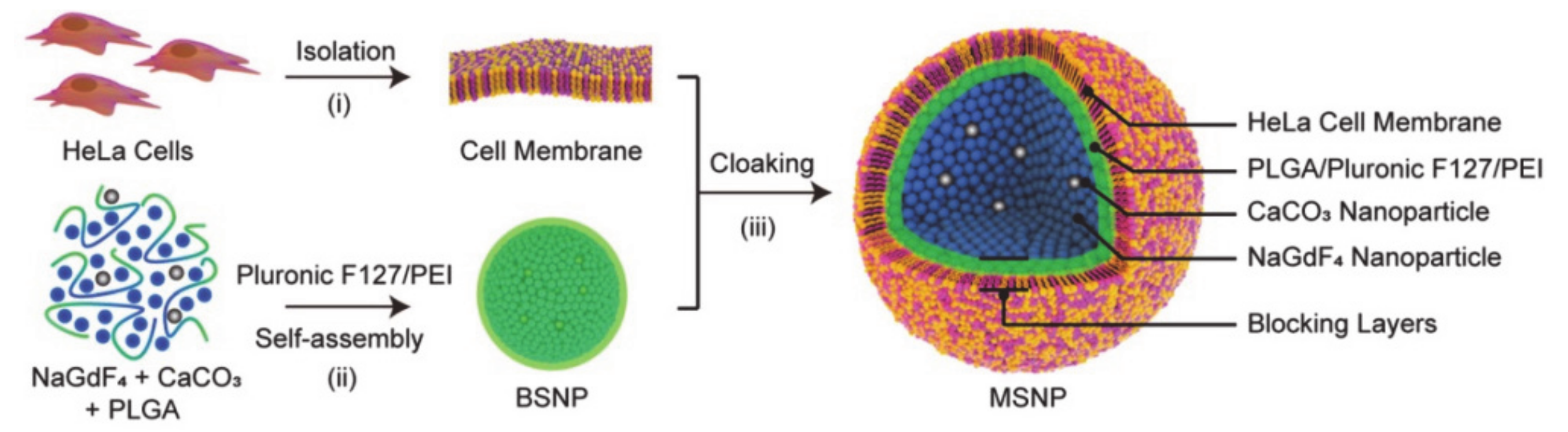
- Yi, Z.; Luo, Z.; Barth, N.D.; Meng, X.; Liu, H.; Bu, W.; All, A.; Vendrell, M.; Liu, X. In Vivo Tumor Visualization through MRI Off-On Switching of NaGdF4–CaCO3 Nanoconjugates. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
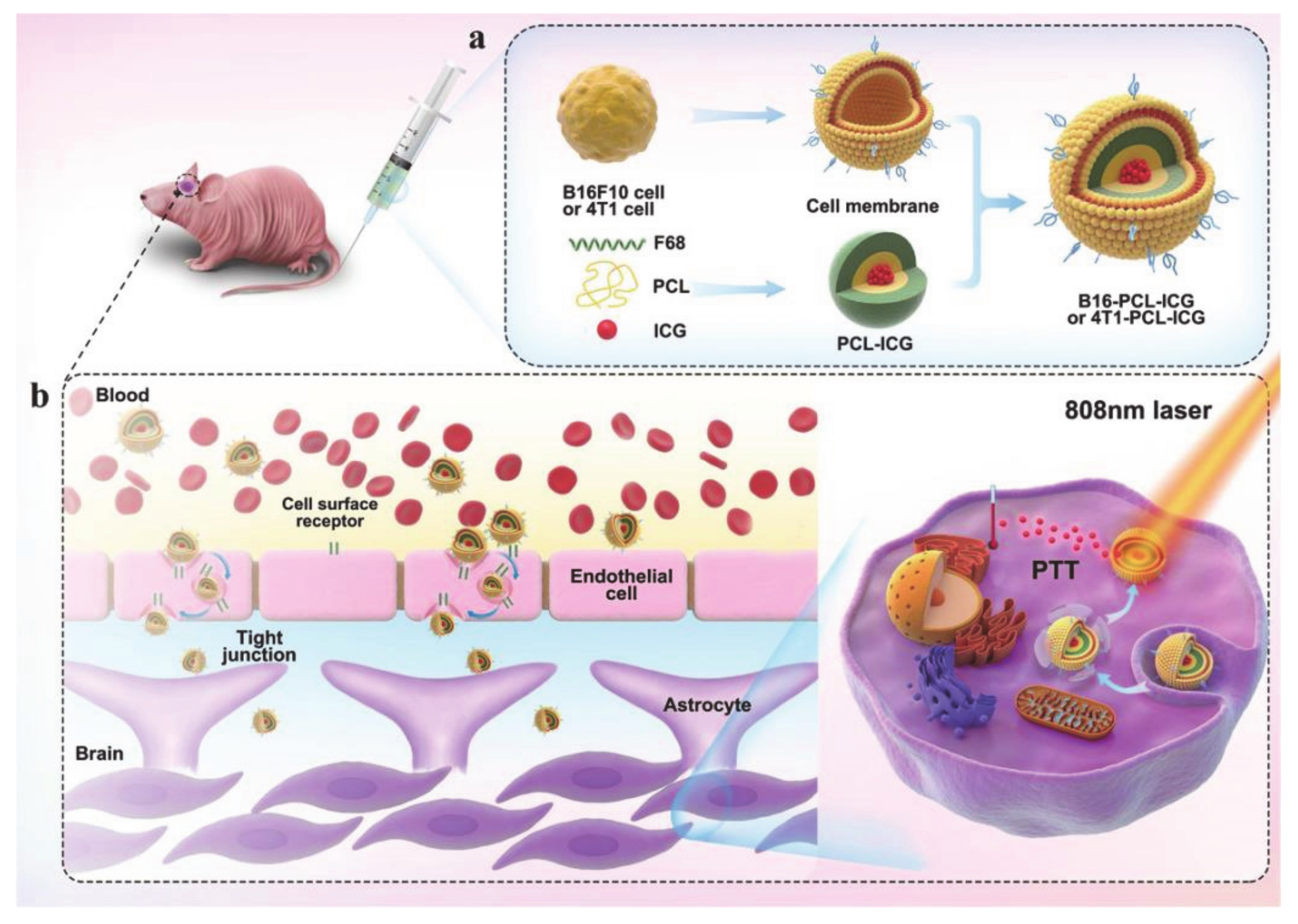
- Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z. Camouflaging Nanoparticles with Brain Metastatic Tumor Cell Membranes: A New Strategy to Traverse Blood–Brain Barrier for Imaging and Therapy of Brain Tumors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
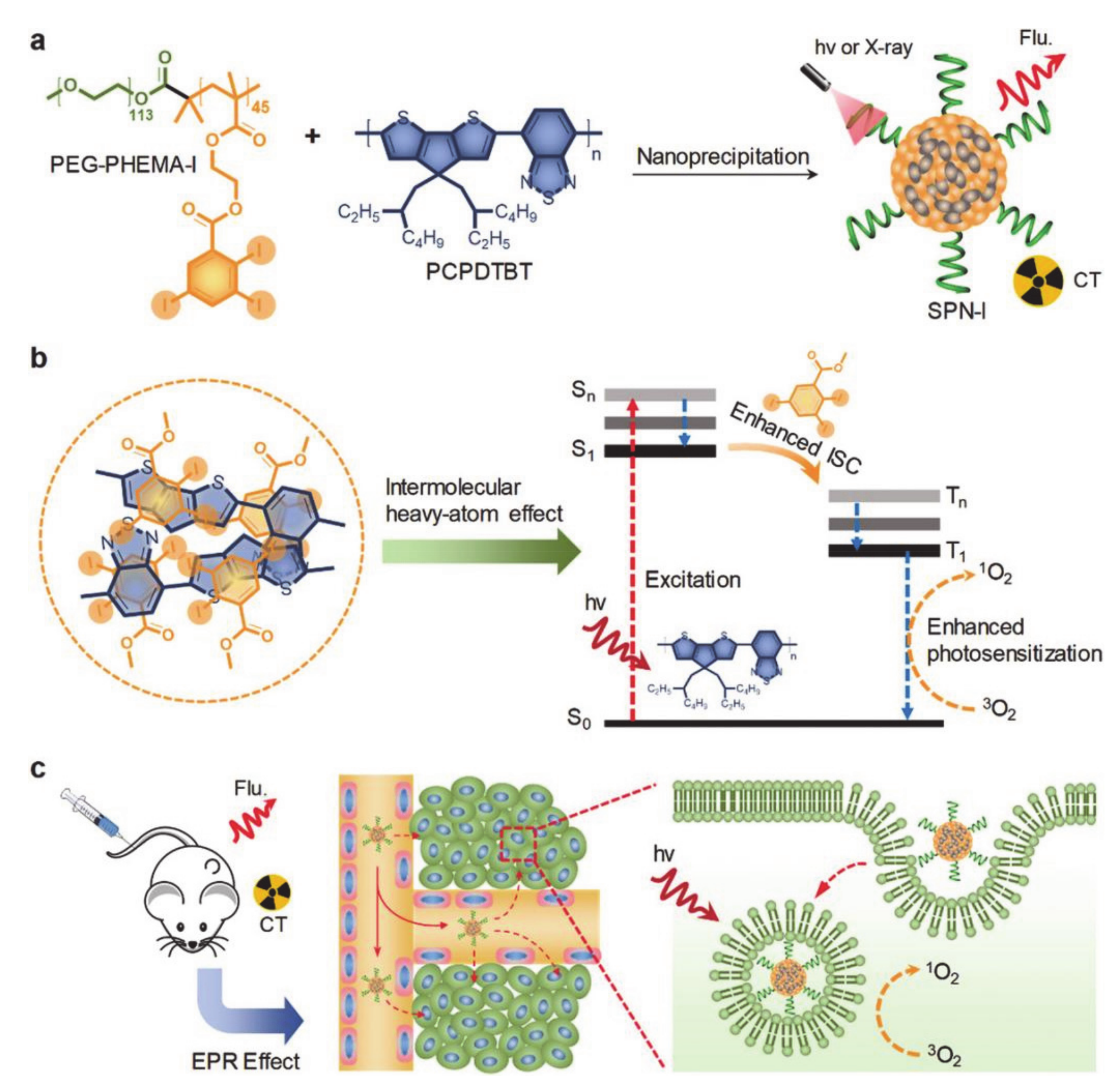
- Zhou, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, X.; Li, R.; Xie, C.; Fan, Q. Iodine-Rich Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticles for CT/Fluorescence Dual-Modal Imaging-Guided Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy. Small 2020, 16, e1905641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
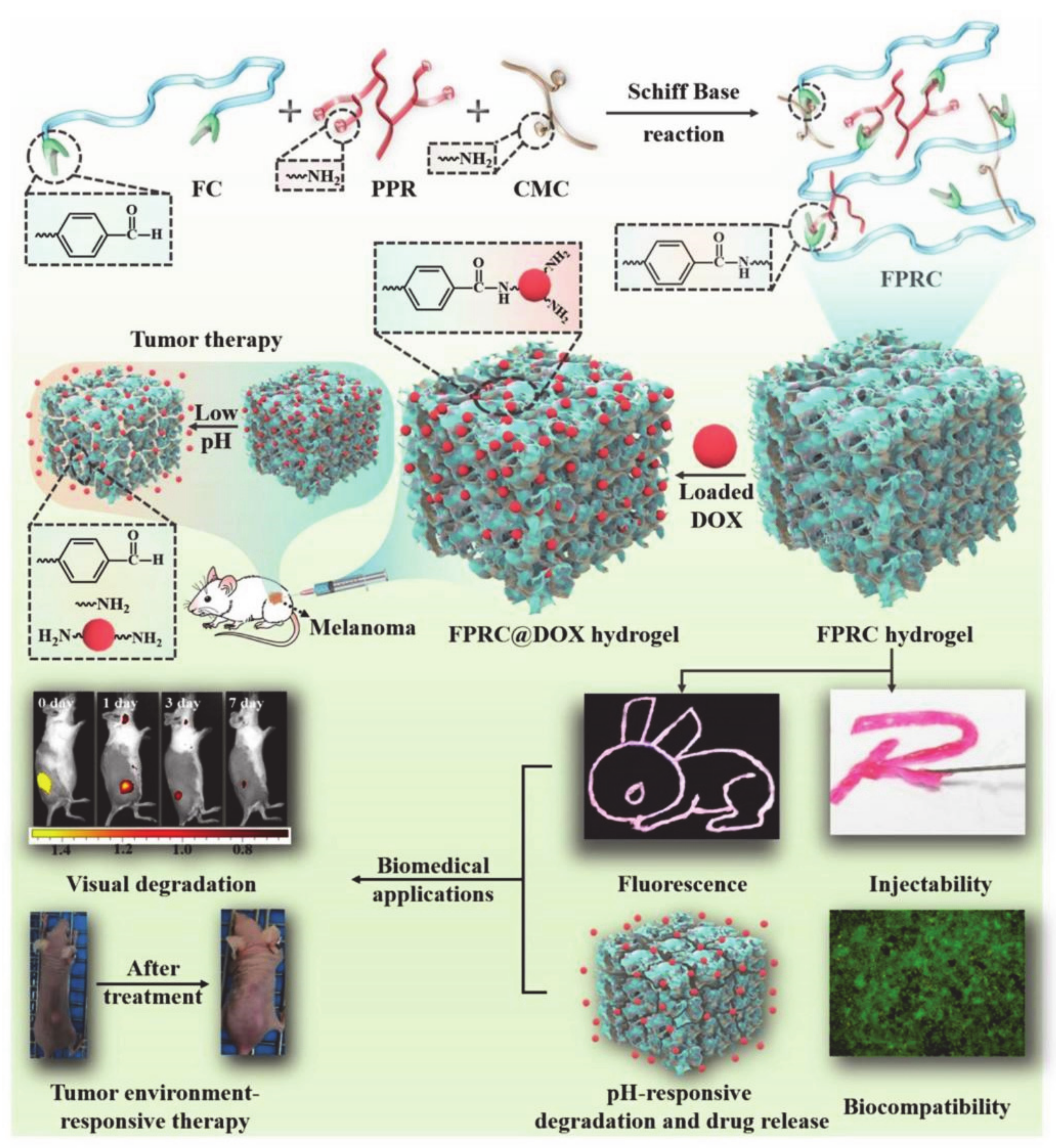
- Wang, M.; Chen, M.; Niu, W.; Winston, D.D.; Cheng, W.; Lei, B. Injectable biodegradation-visual self-healing citrate hydro-gel with high tissue penetration for microenvironment-responsive degradation and local tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2020, 261, 120301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Guo, R.; Deng, L.; Dong, A.; Zhang, J. Facile Fabrication of Redox-Responsive Covalent Organic Framework Nanocarriers for Efficiently Loading and Delivering Doxorubicin. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, e1900570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Huang, L.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Ding, L.; Liu, L.; Dong, Y.; Wang, W.; Duan, Y. Highly biocompatible thermosensitive nanocomposite gel for combined therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma via the enhancement of mitochondria related apoptosis. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 21, 102062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
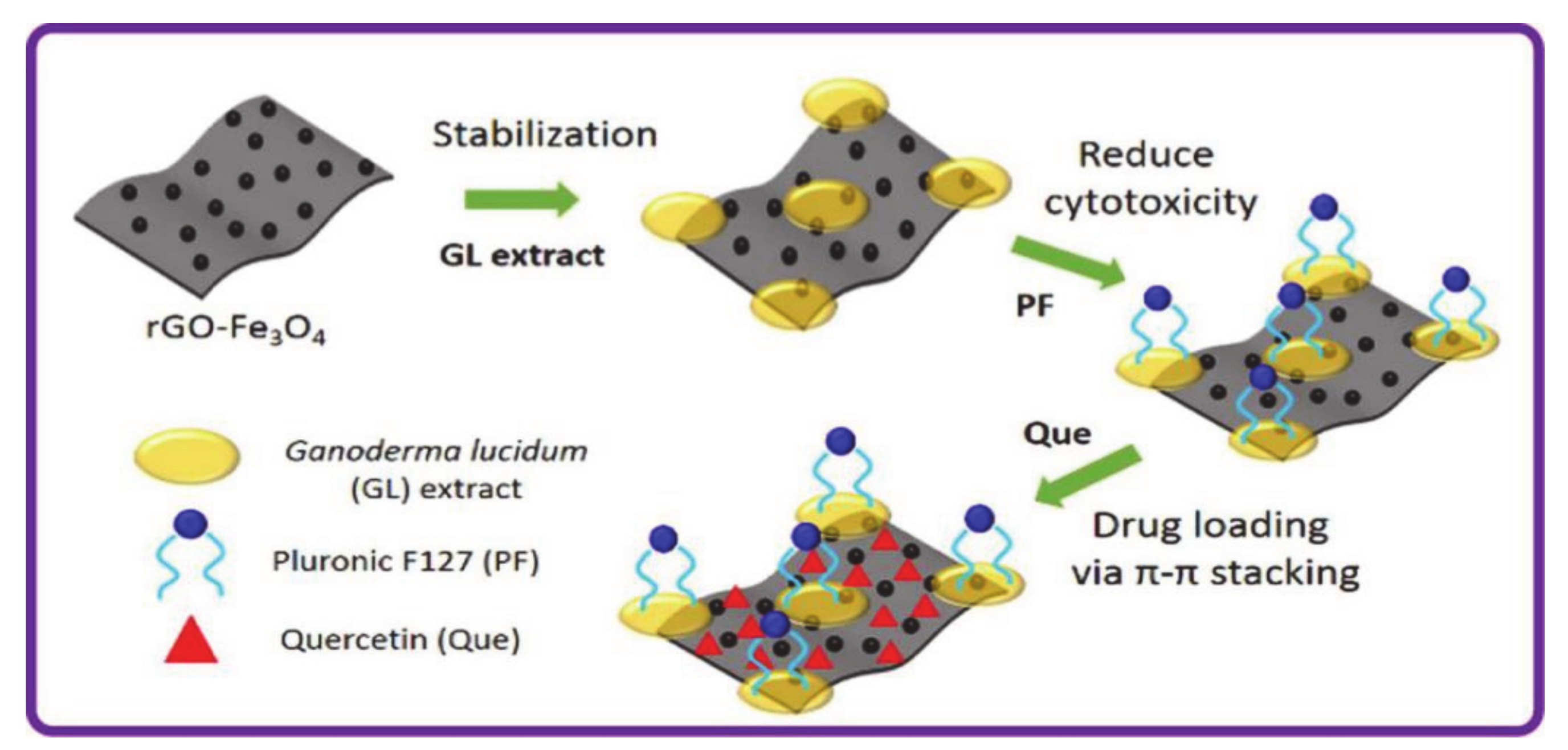
- Lee, X.J.; Lim, H.N.; Gowthaman, N.S.K.; Rahman, M.B.A.; Che Abdullah, C.A.; Muthoosamy, K. In situ surface functionalization of superparamagnetic reduced graphene oxide—Fe3O4 nanocomposite via Ganoderma lucidum extract for targeted cancer therapy application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 512, 145738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, N.I.; Stroeve, P.; Tringe, J.W.; Faller, R. Understanding the Interaction of Pluronics L61 and L64 with a DOPC Lipid Bilayer: An Atomistic Molecular Dynamics Study. Langmuir 2016, 32, 10026–10033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
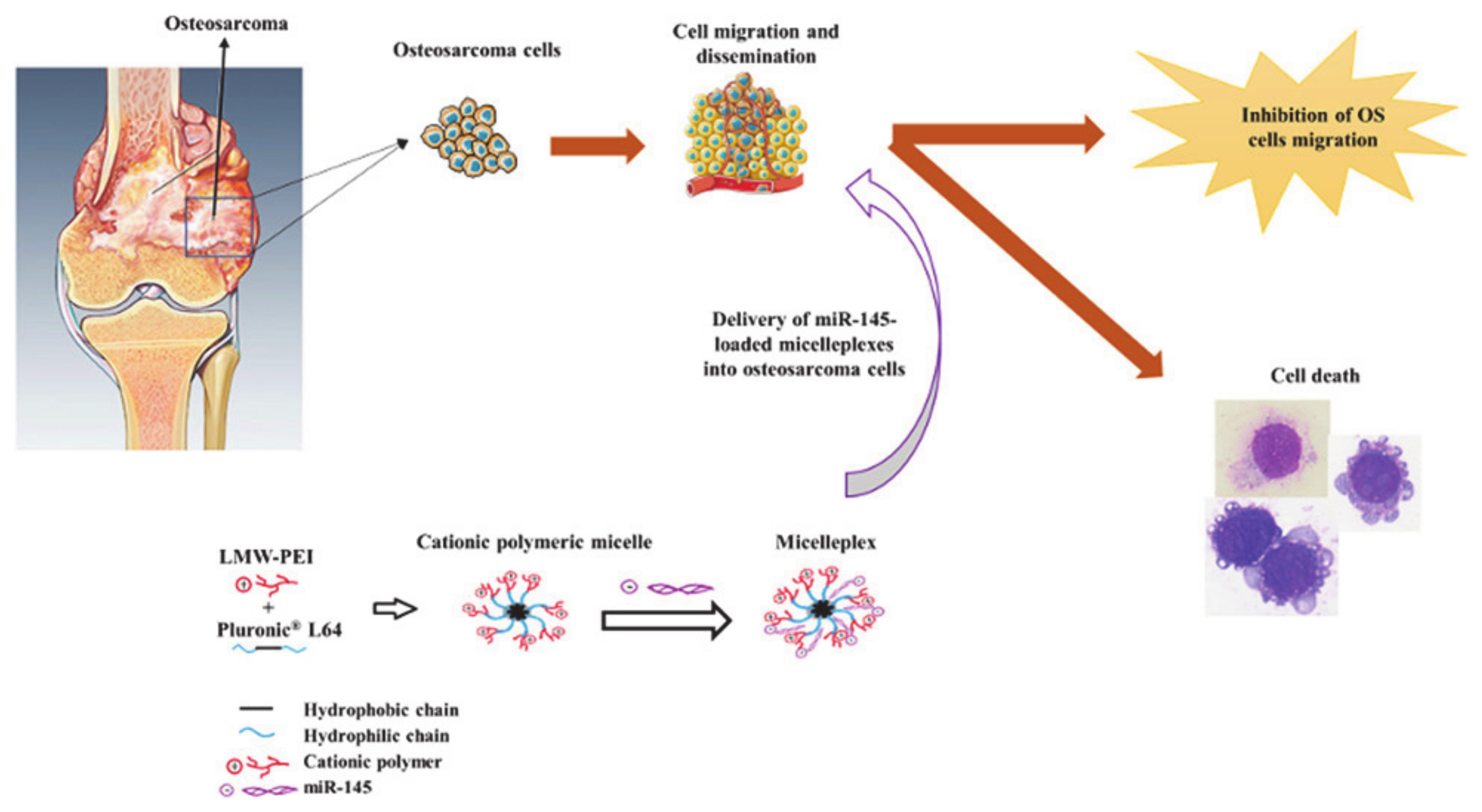
- Magalhães, M.; Almeida, M.; Tavares-da-Silva, E.; Roleira, F.M.F.; Varela, C.; Jorge, J.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Carvalho, R.A.; Veiga, F.; Santos, A.C.; et al. miR-145-loaded micelleplexes as a novel therapeutic strategy to inhibit proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 123, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Han, F.; Tang, J.Z.; Gao, R.; Wang, G. The proper strategy to compress and protect plasmid DNA in the Pluronic L64-electropulse system for enhanced intramuscular gene delivery. Regen. Biomater. 2019, 6, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
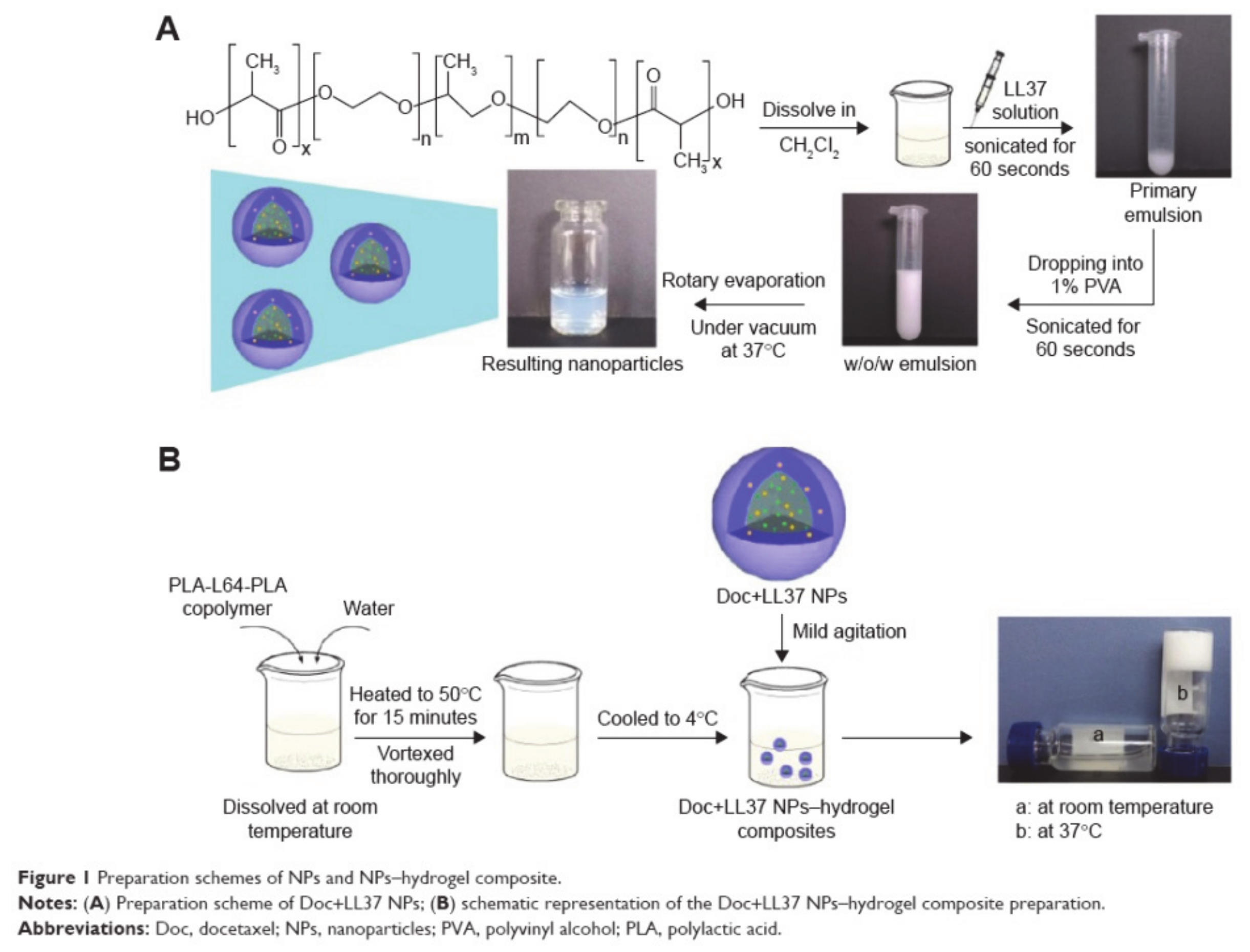
- Li, X.; Fan, R.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Tong, A.; Shi, J.; Xiang, M.; Zhou, L.; Guo, G. In situ gel-forming dual drug delivery system for synergistic combination therapy of colorectal peritoneal carcinomatosis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 101494–101506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Tong, A.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Mei, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; You, C.; Guo, G. Enhanced antitumor effects by docetaxel/LL37-loaded thermosensitive hydrogel nanoparticles in peritoneal carcinomatosis of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 7291–7305. [Google Scholar]
- Alakhov, V.Y.; Moskaleva, E.Y.; Batrakova, E.V.; Kabanov, A.V. Hypersensitization of Multidrug Resistant Human Ovarian Carcinoma Cells by Pluronic P85 Block Copolymer. Bioconjug. Chem. 1996, 7, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambaux, M.-F.; Faivre-Fiorina, B.; Bonneaux, F.; Marchal, S.; Merlin, J.-L.; Dellacherie, E.; Labrude, P.; Vigneron, C. Involvement of neutrophilic granulocytes in the uptake of biodegradable non-stealth and stealth nanoparticles in guinea pig. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
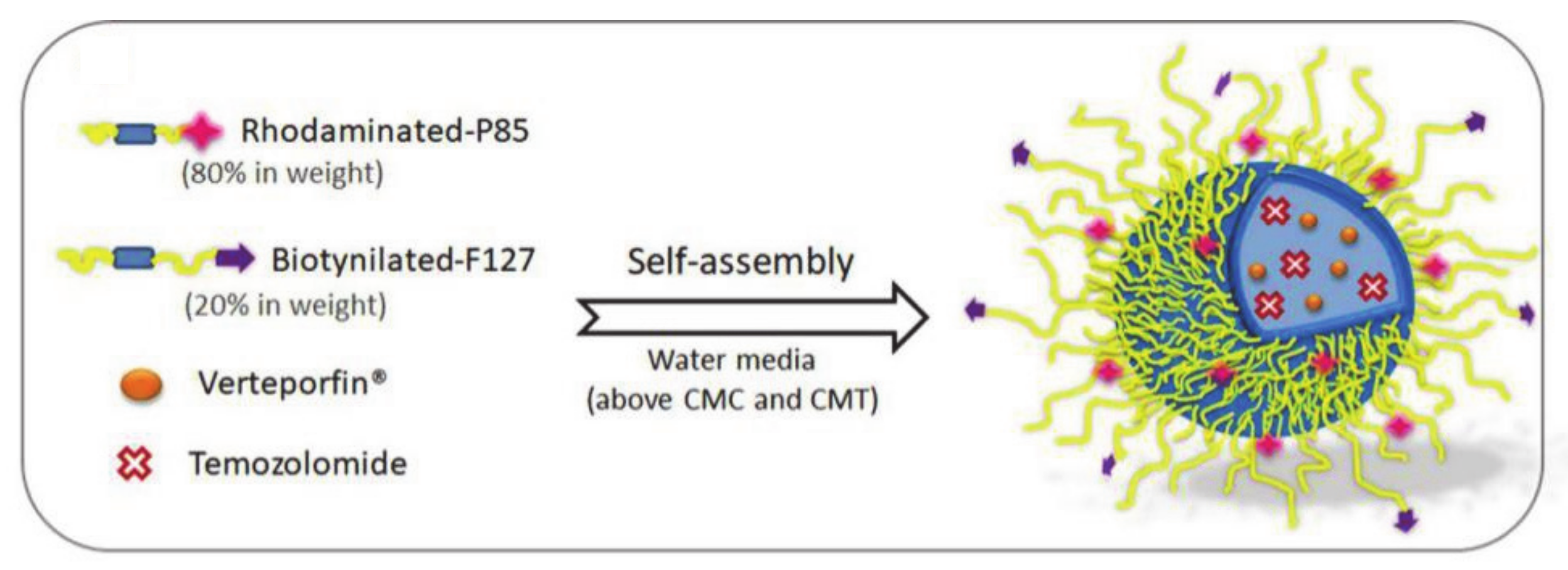
- Pellosi, D.S.; Paula, L.B.; de Melo, M.T.; Tedesco, A.C. Targeted and Synergic Glioblastoma Treatment: Multifunctional Nanoparticles Delivering Verteporfin as Adjuvant Therapy for Temozolomide Chemotherapy. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1009–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Wang, L.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y. Dual-targeting nanocarrier based on glucose and folic acid functionalized pluronic P105 polymeric micelles for enhanced brain distribution. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
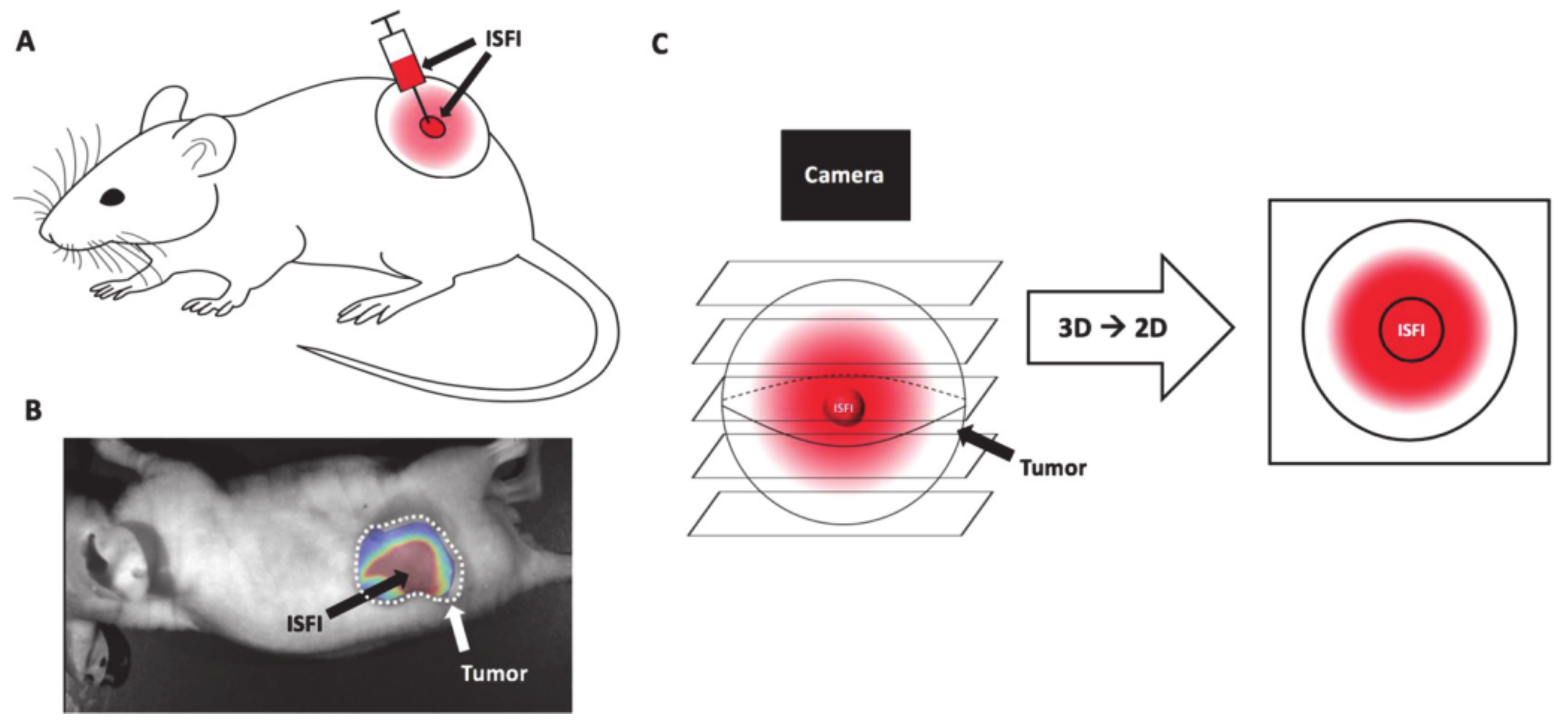
- Jeganathan, S.; Budziszewski, E.; Hernandez, C.; Dhingra, A.; Exner, A.A. Improving Treatment Efficacy of In Situ Forming Implants via Concurrent Delivery of Chemotherapeutic and Chemosensitizer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lv, X.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, R. pH-sensitive and pluronic-modified pullulan nanogels for greatly improved antitumor in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, J.D.; Husseini, G.; Rapoport, N.; Pitt, W.G. Stabilization of Pluronic P-105 Micelles with an Interpenetrating Network of N,N-Diethylacrylamide. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 9306–9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, R. Solubilization of hydrocarbons and resulting aggregate shape transitions in aqueous solutions of Pluronic® (PEO–PPO–PEO) block copolymers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 1999, 16, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, D.; Shen, Y.; Tang, G.; Ping, Y. Redox-Activatable ATP-Depleting Micelles with Dual Modulation Characteristics for Multidrug-Resistant Cancer Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Bai, H.; Shen, J.; Chen, X.; Ping, Y.; Tang, G. A Cooperative Dimensional Strategy for Enhanced Nucleus-Targeted Delivery of Anticancer Drugs. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Moon, J.; Sim, T.; Hoang, N.H.; Won, W.R.; Lee, E.S.; Youn, Y.S.; Choi, H.G.; Oh, K.; Oh, K.T. Cyclic RGD-conjugated Pluronic® blending system for active, targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 4627–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Pellosi, D.S.; Pagliara, V.; Milone, M.R.; Pucci, B.; Caetano, W.; Hioka, N.; Budillon, A.; Ungaro, F.; Russo, G.; et al. Biotin-targeted Pluronic ® P123/F127 mixed micelles delivering niclosamide: A repositioning strategy to treat drug-resistant lung cancer cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
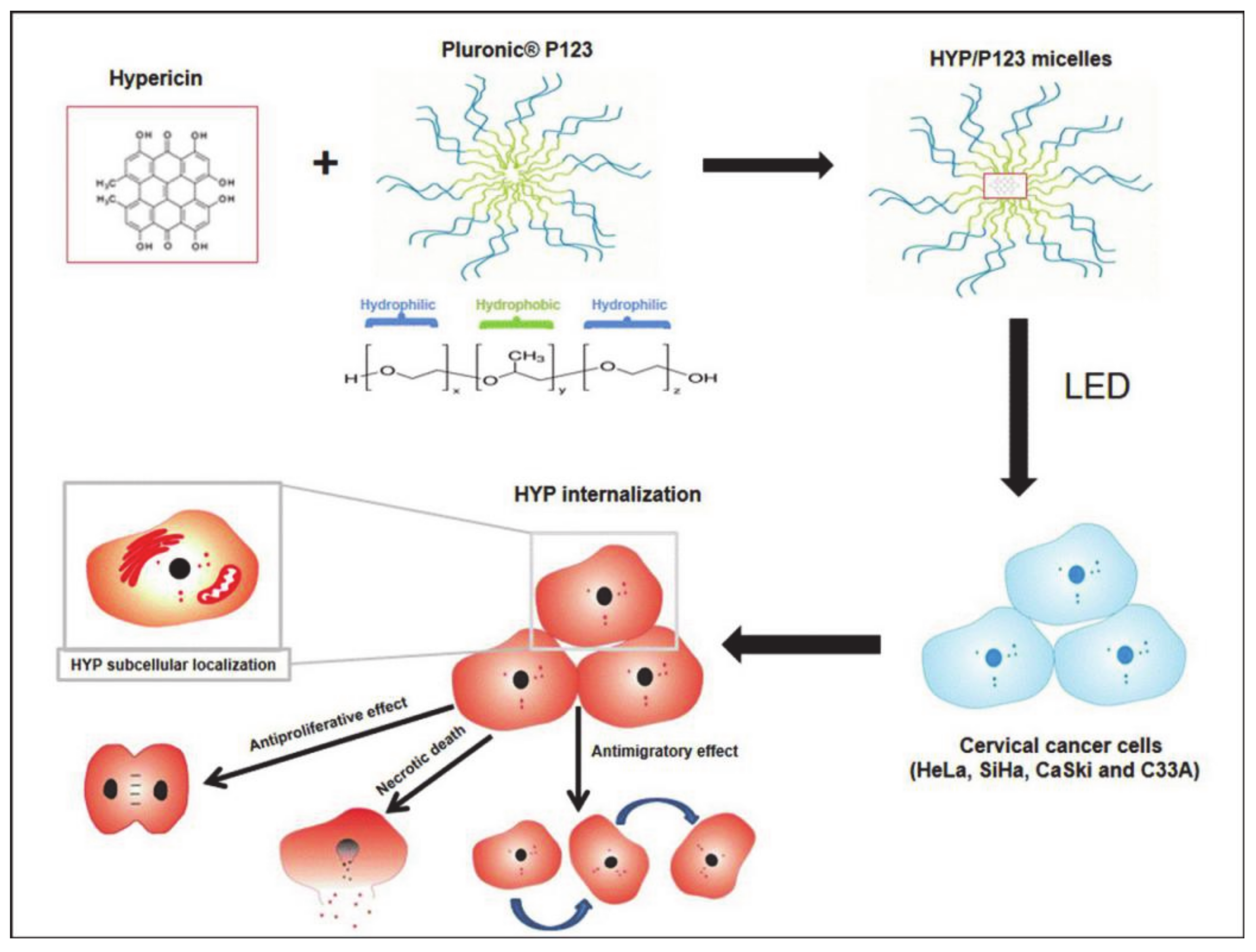
- Damke, G.M.Z.F.; Damke, E.; de Souza Bonfim-Mendonça, P.; Ratti, B.A.; de Freitas Meirelles, L.E.; da Silva, V.R.S.; Gon-Çalves, R.S.; César, G.B.; de Oliveira Silva, S.; Caetano, W.; et al. Selective photodynamic effects on cervical cancer cells provided by P123 Pluronic®-based nanoparticles modulating hypericin delivery. Life Sci. 2020, 255, 117858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
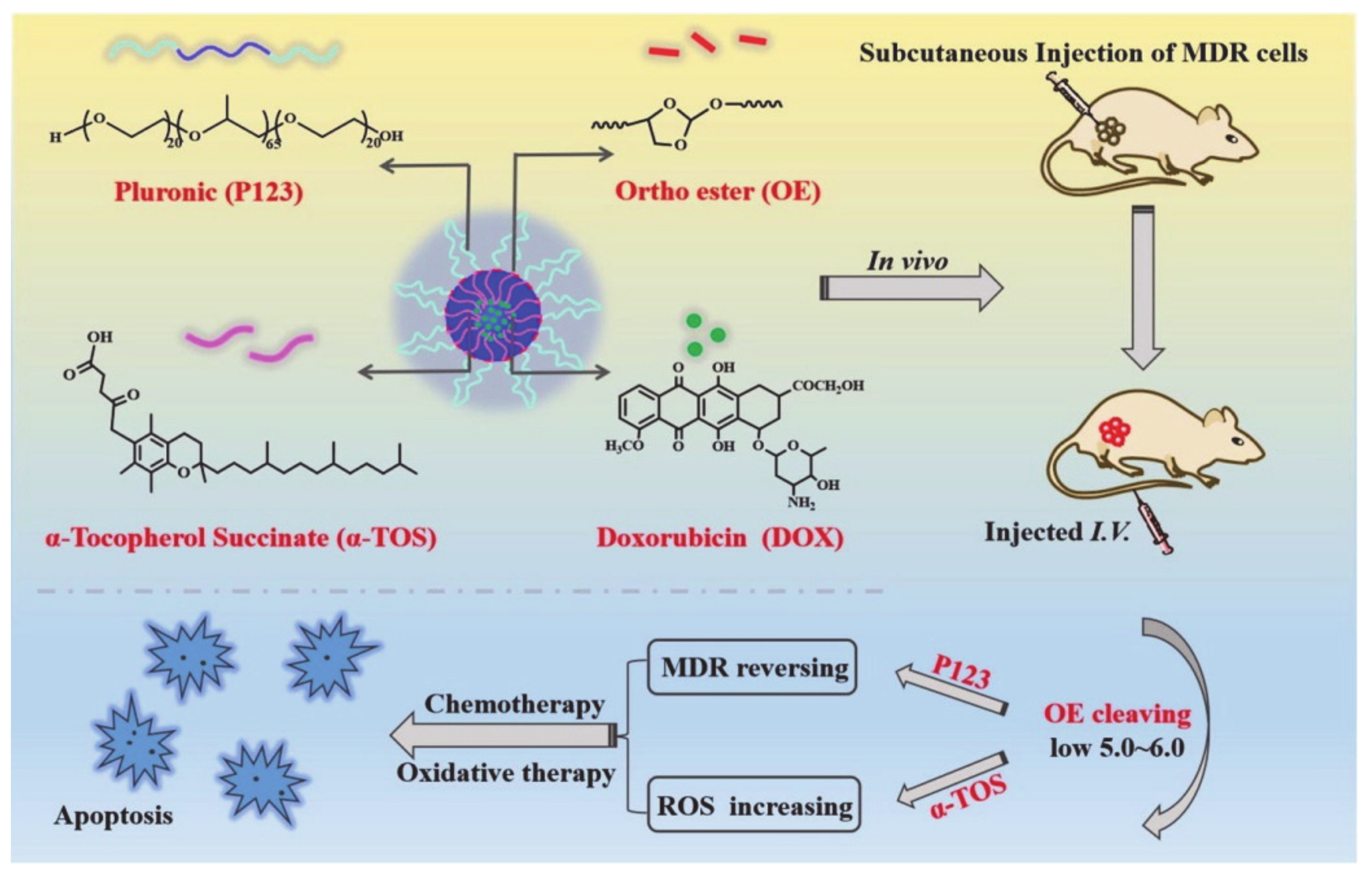
- Cheng, X.; Zeng, X.; Zheng, Y.; Fang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, R. pH-sensitive pluronic micelles combined with oxidative stress amplification for enhancing multidrug resistance breast cancer therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 565, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.; Qiu, H.; Yin, S.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Polymeric Drug Delivery System Based on Pluronics for Cancer Treatment. Molecules 2021, 26, 3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123610
Yu J, Qiu H, Yin S, Wang H, Li Y. Polymeric Drug Delivery System Based on Pluronics for Cancer Treatment. Molecules. 2021; 26(12):3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123610
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Jialin, Huayu Qiu, Shouchun Yin, Hebin Wang, and Yang Li. 2021. "Polymeric Drug Delivery System Based on Pluronics for Cancer Treatment" Molecules 26, no. 12: 3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123610
APA StyleYu, J., Qiu, H., Yin, S., Wang, H., & Li, Y. (2021). Polymeric Drug Delivery System Based on Pluronics for Cancer Treatment. Molecules, 26(12), 3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123610