Microspheres Used in Liver Radioembolization: From Conception to Clinical Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preparations and Labeling (Sir-Spheres®, Therasphere®, QuiremSpheres®)
3. Radionuclide Properties and Clinical Applications
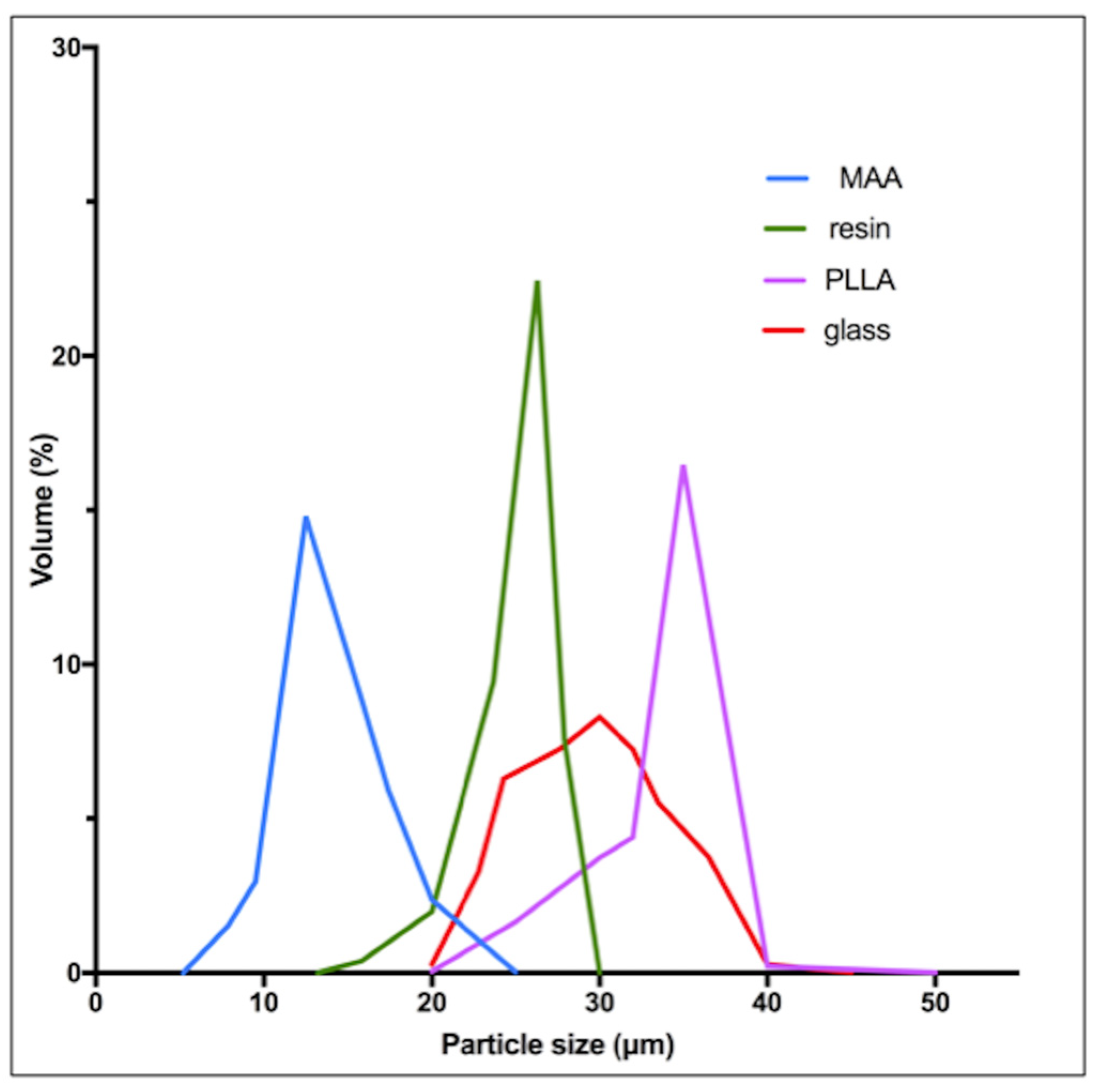
4. Radioactive Microspheres Properties
5. Impact at a Microscopic Level-Microdosimetry
6. Impact at a Macroscopic Level-Clinical Effects
7. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewandowski, R.J.; Salem, R. Yttrium-90 radioembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma and metastatic disease to the liver. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2006, 23, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giammarile, F.; Bodei, L.; Chiesa, C.; Flux, G.; Forrer, F.; Kraeber-Bodere, F.; Brans, B.; Lambert, B.; Konijnenberg, M.; Borson-Chazot, F.; et al. EANM procedure guideline for the treatment of liver cancer and liver metastases with intra-arterial radioactive compounds. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.S.; Nutting, C.; Coldwell, D.; Gaiser, J.; Drachenberg, C. Pathologic response and microdosimetry of 90Y microspheres in man: Review of four explanted whole livers. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2004, 60, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A. Radioembolization of hepatic tumors. J. Gastrointest. Oncol 2014, 5, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, B.; Bacher, K.; Defreyne, L. Rhenium-188 based radiopharmaceuticals for treatment of liver tumours. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 53, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaba, R.C. Planning Arteriography for Yttrium-90 Microsphere Radioembolization. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 32, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gnesin, S.; Canetti, L.; Adib, S.; Cherbuin, N.; Silva Monteiro, M.; Bize, P.; Denys, A.; Prior, J.O.; Baechler, S.; Boubaker, A. Partition Model-Based 99mTc-MAA SPECT/CT Predictive Dosimetry Compared with 90Y TOF PET/CT Posttreatment Dosimetry in Radioembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Quantitative Agreement Comparison. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1672–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braat, A.; Prince, J.F.; van Rooij, R.; Bruijnen, R.C.G.; van den Bosch, M.; Lam, M. Safety analysis of holmium-166 microsphere scout dose imaging during radioembolisation work-up: A cohort study. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gray, B.N. Polymer Based Radionuclide Containing Particulate Material. Patent No. WO2002034300A1, 2 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Westcott, M.A.; Coldwell, D.M.; Liu, D.M.; Zikria, J.F. The development, commercialization, and clinical context of yttrium-90 radiolabeled resin and glass microspheres. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 1, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SIR-Spheres. Instructions For Use; SIRTeX Medical Limited: Sydney, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Day, D.; Ehrhardt, G. Glass Microspheres. U.S. Patent 4,789,501, 6 December 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Therasphere, Products Pecifications. Available online: https://www.bostonscientific.com/en-US/products/cancer-therapies/therasphere-y90-glass-microspheres.html (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Nijsen, J.; van Steenbergen, M.; Kooijman, H.; Talsma, H.; Kroon-Batenburg, L.; van de Weert, M.; van Rijk, P.; de Witte, A.; Schip, A.V.H.; Hennink, W. Characterization of poly(l-lactic acid) microspheres loaded with holmium acetylacetonate. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 3073–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijsen, J.F.; Zonnenberg, B.A.; Woittiez, J.R.; Rook, D.W.; Swildens-van Woudenberg, I.A.; van Rijk, P.P.; van het Schip, A.D. Holmium-166 poly lactic acid microspheres applicable for intra-arterial radionuclide therapy of hepatic malignancies: Effects of preparation and neutron activation techniques. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 26, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielhuis, S.; Nijsen, J.; de Roos, R.; Krijger, G.; van Rijk, P.; Hennink, W.; Schip, A.V.H. Production of GMP-grade radioactive holmium loaded poly(l-lactic acid) microspheres for clinical application. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 311, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arranja, A.; Hennink, W.; Chassagne, C.; Denkova, A.; Nijsen, J. Preparation and characterization of inorganic radioactive holmium-166 microspheres for internal radionuclide therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 106, 110244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QuiremSpheres. Instruction for Use. Available online: https://www.quirem.com/quiremspheres/ (accessed on 5 October 2020).
- Murthy, R.; Kamat, P.; Nuñez, R.; Salem, R. Radioembolization of Yttrium-90 Microspheres for Hepatic Malignancy. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 25, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klaassen, N.J.M.; Arntz, M.J.; Gil Arranja, A.; Roosen, J.; Nijsen, J.F.W. The various therapeutic applications of the medical isotope holmium-166: A narrative review. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2019, 4, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, M.; Li, C. Synthetic nanoparticles for delivery of radioisotopes and radiosensitizers in cancer therapy. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brans, B.; Bodei, L.; Giammarile, F.; Linden, O.; Luster, M.; Oyen, W.J.G.; Tennvall, J. Clinical radionuclide therapy dosimetry: The quest for the "Holy Gray". Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 34, 772–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sofou, S. Radionuclide carriers for targeting of cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Ao, E.C.I.; Lambert, B.; Brans, B.; Vandenberghe, S.; Mok, G.S.P. Quantitative Imaging for Targeted Radionuclide Therapy Dosimetry—Technical Review. Theranostics 2017, 7, 4551–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lhommel, R.; van Elmbt, L.; Goffette, P.; Van den Eynde, M.; Jamar, F.; Pauwels, S.; Walrand, S. Feasibility of 90Y TOF PET-based dosimetry in liver metastasis therapy using SIR-Spheres. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.H.; Steinberg, J.D.; Tay, Y.S.; Lim, G.K.; Yan, J.; Townsend, D.W.; Takano, A.; Burgmans, M.C.; Irani, F.G.; Teo, T.K.; et al. Post-radioembolization yttrium-90 PET/CT—Part 1: Diagnostic reporting. EJNMMI Res. 2013, 3, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elschot, M.; Vermolen, B.J.; Lam, M.G.; de Keizer, B.; van den Bosch, M.A.; de Jong, H.W. Quantitative comparison of PET and Bremsstrahlung SPECT for imaging the in vivo yttrium-90 microsphere distribution after liver radioembolization. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seevinck, P.R.; van de Maat, G.H.; de Wit, T.C.; Vente, M.A.; Nijsen, J.F.; Bakker, C.J. Magnetic resonance imaging-based radiation-absorbed dose estimation of 166Ho microspheres in liver radioembolization. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, e437–e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vente, M.A.; Nijsen, J.F.; de Wit, T.C.; Seppenwoolde, J.H.; Krijger, G.C.; Seevinck, P.R.; Huisman, A.; Zonnenberg, B.A.; van den Ingh, T.S.; van het Schip, A.D. Clinical effects of transcatheter hepatic arterial embolization with holmium-166 poly (L-lactic acid) microspheres in healthy pigs. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bakker, R.C.; de Roos, R.; Ververs, F.T.; Lam, M.G.; van der Lee, M.K.; Zonnenberg, B.A.; Krijger, G.C. Blood and urine analyses after radioembolization of liver malignancies with [166Ho]Ho-acetylacetonate-poly(l-lactic acid) microspheres. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2019, 71, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bult, W. Holmium Microparticles for Intratumoral Radioablation. Ph.D. Thesis, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, T.; Virmani, S.; Neidt, T.M.; Szolc-Kowalska, B.; Sato, K.T.; Ryu, R.K.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Gates, V.L.; Woloschak, G.E.; Salem, R.; et al. MR tracking of iron-labeled glass radioembolization microspheres during transcatheter delivery to rabbit VX2 liver tumors: Feasibility study. Radiology 2008, 249, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garin, E.; Rolland, Y.; Boucher, E. Pre-therapeutic dosimetry evaluation and selective internal radiation therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma using yttrium-90-loaded microspheres. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 1055–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smits, M.L.; Nijsen, J.F.; van den Bosch, M.A.; Lam, M.G.; Vente, M.A.; Huijbregts, J.E.; van het Schip, A.D.; Elschot, M.; Bult, W.; de Jong, H.W.; et al. Holmium-166 radioembolization for the treatment of patients with liver metastases: Design of the phase I HEPAR trial. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bastiaannet, R.; Kappadath, S.C.; Kunnen, B.; Braat, A.; Lam, M.; de Jong, H. The physics of radioembolization. EJNMMI Phys. 2018, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, T.; Hill, J.; Fahrbach, T.; Collins, Z. Differences in Radiation Activity Between Glass and Resin 90Y Microspheres in Treating Unresectable Hepatic Cancer. Health Phys. 2017, 112, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, R.; Antonana, J.; Aramburu, J.; Ezponda, A.; Prieto, E.; Andonegui, A.; Ortega, J.; Vivas, I.; Sancho, L.; Sangro, B.; et al. A proof-of-concept study of the in-vivo validation of a computational fluid dynamics model of personalized radioembolization. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walrand, S.; Hesse, M.; Chiesa, C.; Lhommel, R.; Jamar, F. The low hepatic toxicity per Gray of 90Y glass microspheres is linked to their transport in the arterial tree favoring a nonuniform trapping as observed in posttherapy PET imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasciak, A.S.; Abiola, G.; Liddell, R.P.; Crookston, N.; Besharati, S.; Donahue, D.; Thompson, R.E.; Frey, E.; Anders, R.A.; Dreher, M.R.; et al. The number of microspheres in Y90 radioembolization directly affects normal tissue radiation exposure. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogberg, J.; Rizell, M.; Hultborn, R.; Svensson, J.; Henrikson, O.; Molne, J.; Gjertsson, P.; Bernhardt, P. Increased absorbed liver dose in Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT) correlates with increased sphere-cluster frequency and absorbed dose inhomogeneity. EJNMMI Phys. 2015, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hogberg, J.; Rizell, M.; Hultborn, R.; Svensson, J.; Henrikson, O.; Molne, J.; Gjertsson, P.; Bernhardt, P. Heterogeneity of microsphere distribution in resected liver and tumour tissue following selective intrahepatic radiotherapy. EJNMMI Res. 2014, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caine, M.; McCafferty, M.S.; McGhee, S.; Garcia, P.; Mullett, W.M.; Zhang, X.; Hill, M.; Dreher, M.R.; Lewis, A.L. Impact of Yttrium-90 Microsphere Density, Flow Dynamics, and Administration Technique on Spatial Distribution: Analysis Using an In Vitro Model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 260–268.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jernigan, S.R.; Osborne, J.A.; Mirek, C.J.; Buckner, G. Selective internal radiation therapy: Quantifying distal penetration and distribution of resin and glass microspheres in a surrogate arterial model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasciak, A.S.; Bourgeois, A.C.; Bradley, Y.C. A Microdosimetric Analysis of Absorbed Dose to Tumor as a Function of Number of Microspheres per Unit Volume in 90Y Radioembolization. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riaz, A.; Awais, R.; Salem, R. Side effects of yttrium-90 radioembolization. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilbao, J.I.; de Martino, A.; de Luis, E.; Diaz-Dorronsoro, L.; Alonso-Burgos, A.; Martinez de la Cuesta, A.; Sangro, B.; Garcia de Jalon, J.A. Biocompatibility, inflammatory response, and recannalization characteristics of nonradioactive resin microspheres: Histological findings. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 32, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braat, A.J.; Smits, M.L.; Braat, M.N.; van den Hoven, A.F.; Prince, J.F.; de Jong, H.W.; van den Bosch, M.A.; Lam, M.G. 90Y Hepatic Radioembolization: An Update on Current Practice and Recent Developments. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gil-Alzugaray, B.; Chopitea, A.; Inarrairaegui, M.; Bilbao, J.I.; Rodriguez-Fraile, M.; Rodriguez, J.; Benito, A.; Dominguez, I.; D’Avola, D.; Herrero, J.I.; et al. Prognostic factors and prevention of radioembolization-induced liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koay, E.J.; Owen, D.; Das, P. Radiation-Induced Liver Disease and Modern Radiotherapy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 28, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremonesi, M.; Ferrari, M.; Bartolomei, M.; Orsi, F.; Bonomo, G.; Arico, D.; Mallia, A.; De Cicco, C.; Pedroli, G.; Paganelli, G. Radioembolisation with 90Y-microspheres: Dosimetric and radiobiological investigation for multi-cycle treatment. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strigari, L.; Sciuto, R.; Rea, S.; Carpanese, L.; Pizzi, G.; Soriani, A.; Iaccarino, G.; Benassi, M.; Ettorre, G.M.; Maini, C.L. Efficacy and toxicity related to treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with 90Y-SIR spheres: Radiobiologic considerations. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiesa, C.; Mira, M.; Bhoori, S.; Bormolini, G.; Maccauro, M.; Spreafico, C.; Cascella, T.; Cavallo, A.; De Nile, M.C.; Mazzaglia, S.; et al. Radioembolization of hepatocarcinoma with 90Y glass microspheres: Treatment optimization using the dose-toxicity relationship. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 3018–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, J.F.; van den Bosch, M.; Nijsen, J.F.W.; Smits, M.L.J.; van den Hoven, A.F.; Nikolakopoulos, S.; Wessels, F.J.; Bruijnen, R.C.G.; Braat, M.; Zonnenberg, B.A.; et al. Efficacy of Radioembolization with 166Ho-Microspheres in Salvage Patients with Liver Metastases: A Phase 2 Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smits, M.L.; Nijsen, J.F.; van den Bosch, M.A.; Lam, M.G.; Vente, M.A.; Mali, W.P.; van Het Schip, A.D.; Zonnenberg, B.A. Holmium-166 radioembolisation in patients with unresectable, chemorefractory liver metastases (HEPAR trial): A phase 1, dose-escalation study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Maat, G.H.; Seevinck, P.R.; Elschot, M.; Smits, M.L.; de Leeuw, H.; van Het Schip, A.D.; Vente, M.A.; Zonnenberg, B.A.; de Jong, H.W.; Lam, M.G.; et al. MRI-based biodistribution assessment of holmium-166 poly(L-lactic acid) microspheres after radioembolisation. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crookston, N.R.; Fung, G.S.K.; Frey, E.C. Development of a Customizable Hepatic Arterial Tree and Particle Transport Model for Use in Treatment Planning. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2019, 3, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walrand, S.; Hesse, M.; Jamar, F.; Lhommel, R. A hepatic dose-toxicity model opening the way toward individualized radioembolization planning. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, L.C.; Hoban, P.W. Treatment plan comparison using equivalent uniform biologically effective dose (EUBED). Phys. Med. Biol. 2000, 45, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Abadie, P.; Hesse, M.; Jamar, F.; Lhommel, R.; Walrand, S. 90Y TOF-PET based EUD reunifies patient survival prediction in resin and glass microspheres radioembolization of HCC tumours. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 245010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallini, J.R.; Gabr, A.; Thorlund, K.; Balijepalli, C.; Ayres, D.; Kanters, S.; Ebrahim, S.; Mills, E.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Salem, R. Comparison of the Adverse Event Profile of TheraSphere((R)) with SIR-Spheres((R)) for the Treatment of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 40, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsultan, A.A.; Braat, A.; Smits, M.L.J.; Barentsz, M.W.; Bastiaannet, R.; Bruijnen, R.C.G.; de Keizer, B.; de Jong, H.; Lam, M.; Maccauro, M.; et al. Current Status and Future Direction of Hepatic Radioembolisation. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 33, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.; Banerjee, S.; Louie, J.D.; Abdelmaksoud, M.H.K.; Iagaru, A.H.; Ennen, R.E.; Sze, D.Y. Root cause analysis of gastroduodenal ulceration after yttrium-90 radioembolization. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 36, 1536–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinders, M.T.M.; Smits, M.L.J.; van Roekel, C.; Braat, A. Holmium-166 Microsphere Radioembolization of Hepatic Malignancies. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 49, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piana, P.M.; Bar, V.; Doyle, L.; Anne, R.; Sato, T.; Eschelman, D.J.; McCann, J.W.; Gonsalves, C.F.; Brown, D.B. Early arterial stasis during resin-based yttrium-90 radioembolization: Incidence and preliminary outcomes. HPB 2014, 16, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, K.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Bui, J.T.; Omary, R.; Hunter, R.D.; Kulik, L.; Mulcahy, M.; Liu, D.; Chrisman, H.; Resnick, S.; et al. Treatment of unresectable primary and metastatic liver cancer with yttrium-90 microspheres (TheraSphere): Assessment of hepatic arterial embolization. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2006, 29, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padia, S.A.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Johnson, G.E.; Sze, D.Y.; Ward, T.J.; Gaba, R.C.; Baerlocher, M.O.; Gates, V.L.; Riaz, A.; Brown, D.B.; et al. Radioembolization of Hepatic Malignancies: Background, Quality Improvement Guidelines, and Future Directions. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biederman, D.M.; Titano, J.J.; Tabori, N.E.; Pierobon, E.S.; Alshebeeb, K.; Schwartz, M.; Facciuto, M.E.; Gunasekaran, G.; Florman, S.; Fischman, A.M.; et al. Outcomes of Radioembolization in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Invasion: Resin versus Glass Microspheres. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Gucht, A.; Jreige, M.; Denys, A.; Blanc-Durand, P.; Boubaker, A.; Pomoni, A.; Mitsakis, P.; Silva-Monteiro, M.; Gnesin, S.; Lalonde, M.N.; et al. Resin Versus Glass Microspheres for 90Y Transarterial Radioembolization: Comparing Survival in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Pretreatment Partition Model Dosimetry. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Radosa, C.G.; Radosa, J.C.; Grosche-Schlee, S.; Zophel, K.; Plodeck, V.; Kuhn, J.P.; Kotzerke, J.; Hoffmann, R.T. Holmium-166 Radioembolization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Feasibility and Safety of a New Treatment Option in Clinical Practice. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, A.S.; Ball, D.; Cohen, S.J.; Cohn, M.; Coldwell, D.M.; Drooz, A.; Ehrenwald, E.; Kanani, S.; Rose, S.C.; Nutting, C.W.; et al. Multicenter evaluation of the safety and efficacy of radioembolization in patients with unresectable colorectal liver metastases selected as candidates for 90Y resin microspheres. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2015, 6, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, R.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Prudhomme, T.; Ehrenwald, E.; Baigorri, B.; Critchfield, J.; Kallini, J.; Gabr, A.; Gorodetski, B.; Geschwind, J.F.; et al. 90Y Radioembolization of Colorectal Hepatic Metastases Using Glass Microspheres: Safety and Survival Outcomes from a 531-Patient Multicenter Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenbaum, C.E.; Verkooijen, H.M.; Lam, M.G.; Smits, M.L.; Koopman, M.; van Seeters, T.; Vermoolen, M.A.; van den Bosch, M.A. Radioembolization for treatment of salvage patients with colorectal cancer liver metastases: A systematic review. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 1890–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, A.L.; Dieudonne, A.; Ronot, M.; Sanchez, M.; Pereira, H.; Chatellier, G.; Garin, E.; Castera, L.; Lebtahi, R.; Vilgrain, V.; et al. Relationship of Tumor Radiation-absorbed Dose to Survival and Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Transarterial Radioembolization with 90Y in the SARAH Study. Radiology 2020, 296, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garin, E.; Lenoir, L.; Edeline, J.; Laffont, S.; Mesbah, H.; Poree, P.; Sulpice, L.; Boudjema, K.; Mesbah, M.; Guillygomarc’h, A.; et al. Boosted selective internal radiation therapy with 90Y-loaded glass microspheres (B-SIRT) for hepatocellular carcinoma patients: A new personalized promising concept. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garin, E.; Tselikas, L.; Guiu, B.; Chalaye, J.; Edeline, J.; de Baere, T.; Assenat, E.; Tacher, V.; Robert, C.; Terroir-Cassou-Mounat, M.; et al. Personalised versus standard dosimetry approach of selective internal radiation therapy in patients with locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (DOSISPHERE-01): A randomised, multicentre, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hoven, A.F.; Rosenbaum, C.E.; Elias, S.G.; de Jong, H.W.; Koopman, M.; Verkooijen, H.M.; Alavi, A.; van den Bosch, M.A.; Lam, M.G. Insights into the Dose-Response Relationship of Radioembolization with Resin 90Y-Microspheres: A Prospective Cohort Study in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willowson, K.P.; Hayes, A.R.; Chan, D.L.H.; Tapner, M.; Bernard, E.J.; Maher, R.; Pavlakis, N.; Clarke, S.J.; Bailey, D.L. Clinical and imaging-based prognostic factors in radioembolisation of liver metastases from colorectal cancer: A retrospective exploratory analysis. EJNMMI Res. 2017, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alsultan, A.A.; van Roekel, C.; Barentsz, M.W.; Smits, M.L.J.; Kunnen, B.; Koopman, M.; Bruijnen, R.C.G.; de Keizer, B.; Lam, M. Dose-response and dose-toxicity relationships for yttrium-90 glass radioembolization in patients with colorectal cancer liver metastases. J. Nucl. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Roekel, C.; Bastiaannet, R.; Smits, M.L.J.; Bruijnen, R.C.; Braat, A.; de Jong, H.; Elias, S.G.; Lam, M. Dose-Effect Relationships of 166Ho Radioembolization in Colorectal Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Abadie, P.; Walrand, S.; Hesse, M.; Annet, L.; Borbath, I.; Van den Eynde, M.; Lhommel, R.; Jamar, F. Prediction of tumor response and patient outcome after radioembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma using 90Y-PET-computed tomography dosimetry. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levillain, H.; Bagni, O.; Deroose, C.M.; Dieudonne, A.; Gnesin, S.; Grosser, O.S.; Kappadath, S.C.; Kennedy, A.; Kokabi, N.; Liu, D.M.; et al. International recommendations for personalised selective internal radiation therapy of primary and metastatic liver diseases with yttrium-90 resin microspheres. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, C.; Maccauro, M. 166Ho microsphere scout dose for more accurate radioembolization treatment planning. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smits, M.L.J.; Dassen, M.G.; Prince, J.F.; Braat, A.; Beijst, C.; Bruijnen, R.C.G.; de Jong, H.; Lam, M. The superior predictive value of 166Ho-scout compared with (99m)Tc-macroaggregated albumin prior to 166Ho-microspheres radioembolization in patients with liver metastases. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Floridi, C.; Radaelli, A.; Abi-Jaoudeh, N.; Grass, M.; Lin, M.; Chiaradia, M.; Geschwind, J.F.; Kobeiter, H.; Squillaci, E.; Maleux, G.; et al. C-arm cone-beam computed tomography in interventional oncology: Technical aspects and clinical applications. Radiol. Med. 2014, 119, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, T.K.; Omary, R.A.; Gates, V.; Mounajjed, T.; Larson, A.C.; Barakat, O.; Sato, K.T.; Mulcahy, M.; Gordon, S.; Lewandowski, R.J.; et al. The effect of catheter-directed CT angiography on yttrium-90 radioembolization treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2005, 16, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Abadie, P.W.S.; Goffette, P.; Amini, N.; Van Maanen, A.; Lhommel, R.; Jamar, F. Antireflux catheter improves tumor targeting in liver radioembolization with resin microspheres. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Walrand, S.; Hesse, M.; d’Abadie, P.; Jamar, F. Hepatic Arterial Buffer Response in Liver Radioembolization and Potential Use for Improved Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, P.H.A.; Ajithkumar, T.; Harris, M.; Croagh, D.; Aghmesheh, M.; Nagrial, A.; Nguyen, N.; Nikfarjam, M.; Wilson, N.; Kenny, D.; et al. O-1 PanCO: Updated results of an open-label, single-arm pilot study of OncoSil P-32 microparticles in unresectable locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma (LAPC) with gemcitabine + nab-paclitaxel or FOLFIRINOX chemotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Labeled Microspheres | Half-Life | Beta Emission (E. Max) | Range of Beta Radiation | Other Emissions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yttrium-90 (90Y) | Resin or glass | 2.7 days | 2.28 MeV | Mean: 2.5 mm (Max: 11 mm) | Positron (32 × 10−6) |
| Holmium-166 (166Ho) | Poly (L-Lactic acid) | 1.1 day | 1.77 MeV (49%), 1.86 MeV (50%) | Mean: 2.5 mm (Max: 8.7 mm) | Gamma (6.7%) |
| Microspheres | Diameter (Mean) | Density | Approximative Number of Micro-Spheres Per GBq * | Activity Per Microsphere |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90Y-Resin | 32 μm | 1.6 g/mL | 13 × 106 | 50 Bq |
| 90Y-Glass | 25 μm | 3.3 g/mL | 0.4 × 106 | 2500 Bq |
| 166Ho-PLLA | 30 μm | 1.4 g/mL | 10 × 106 | 450 Bq |
| Types | Usual Recommended Method for Activity Planning |
|---|---|
| 90Y-Resin (BSA method) | (BSA: the body surface area in m2) |
| 90Y-Glass (mono-compartmental method) | (Dosetarget liver: 80–150 Gy) |
| 166Ho-PLLA (mono-compartmental method) | (Dosewhole liver: 60 Gy) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
d’Abadie, P.; Hesse, M.; Louppe, A.; Lhommel, R.; Walrand, S.; Jamar, F. Microspheres Used in Liver Radioembolization: From Conception to Clinical Effects. Molecules 2021, 26, 3966. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133966
d’Abadie P, Hesse M, Louppe A, Lhommel R, Walrand S, Jamar F. Microspheres Used in Liver Radioembolization: From Conception to Clinical Effects. Molecules. 2021; 26(13):3966. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133966
Chicago/Turabian Styled’Abadie, Philippe, Michel Hesse, Amandine Louppe, Renaud Lhommel, Stephan Walrand, and Francois Jamar. 2021. "Microspheres Used in Liver Radioembolization: From Conception to Clinical Effects" Molecules 26, no. 13: 3966. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133966
APA Styled’Abadie, P., Hesse, M., Louppe, A., Lhommel, R., Walrand, S., & Jamar, F. (2021). Microspheres Used in Liver Radioembolization: From Conception to Clinical Effects. Molecules, 26(13), 3966. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133966






