Regiospecific Positioning of Palmitic Acid in Triacylglycerol Structure of Enzymatically Modified Lipids Affects Physicochemical and In Vitro Digestion Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Acylglycerol Composition
2.2. Fatty Acids Composition
2.3. Triacylglycerol Composition
2.4. Melting Points
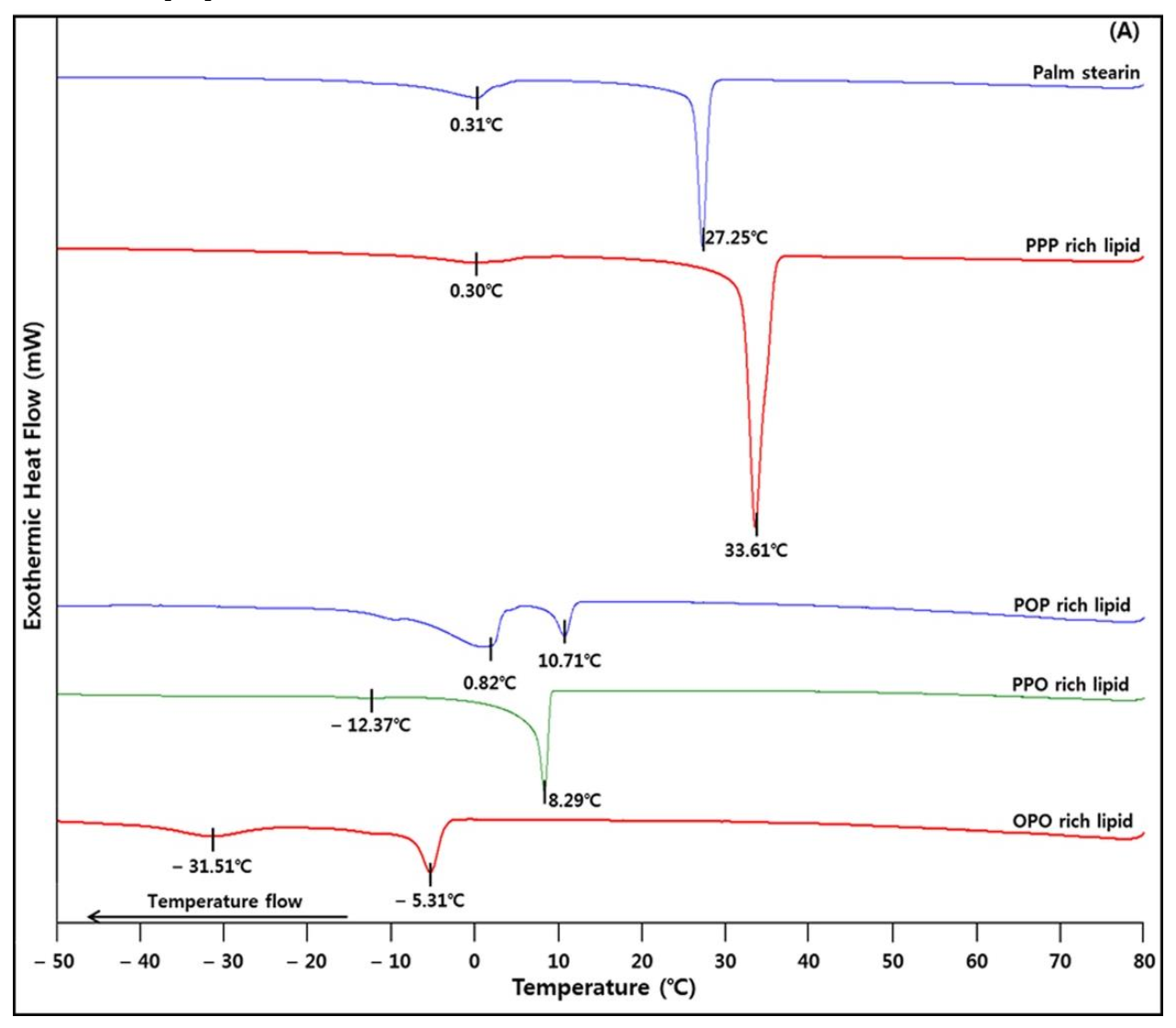
2.5. Crystallization and Melting Properties
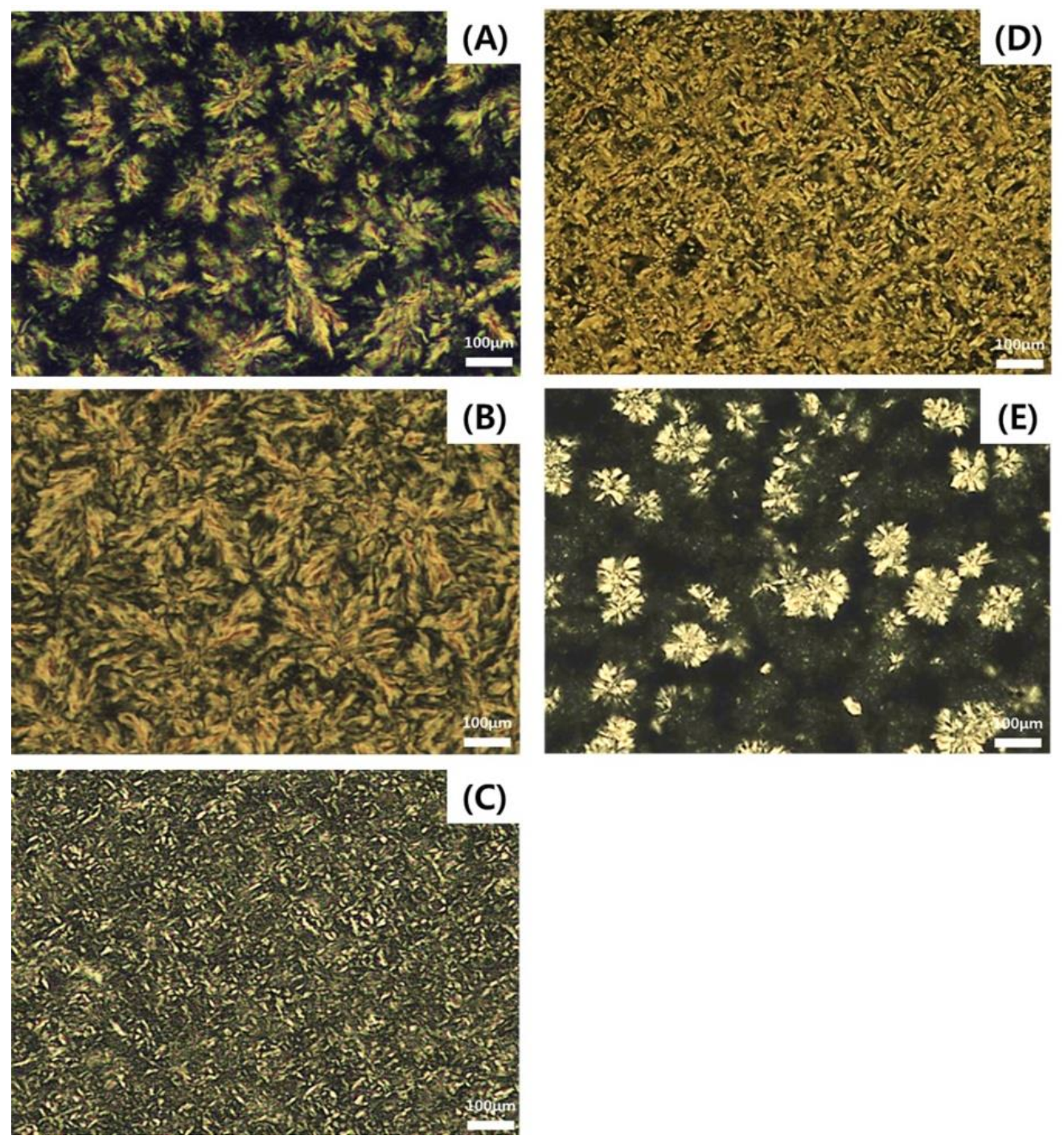
2.6. Crystal Morphology
2.7. Free Fatty Acids (FFAs) Released by the Hydrolyzed Lipids during In Vitro Multi-Step Digestion
2.8. Acylglycerol Composition of the Hydrolyzed Lipids during the In Vitro Multi-Step Digestion Model
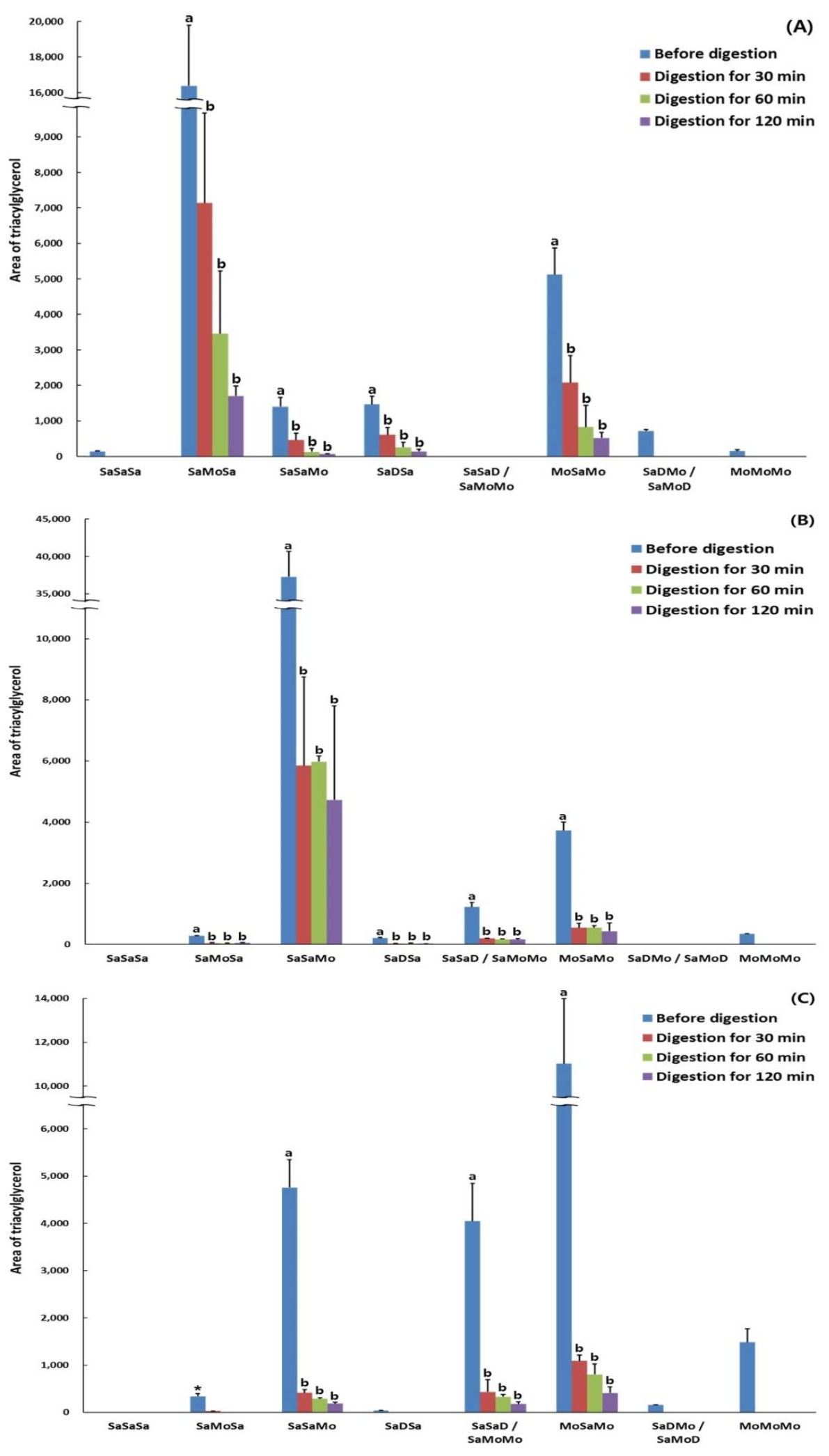
2.9. Triacylglycerol Compositions of the Hydrolyzed Lipids during In Vitro Multi-Step Digestion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
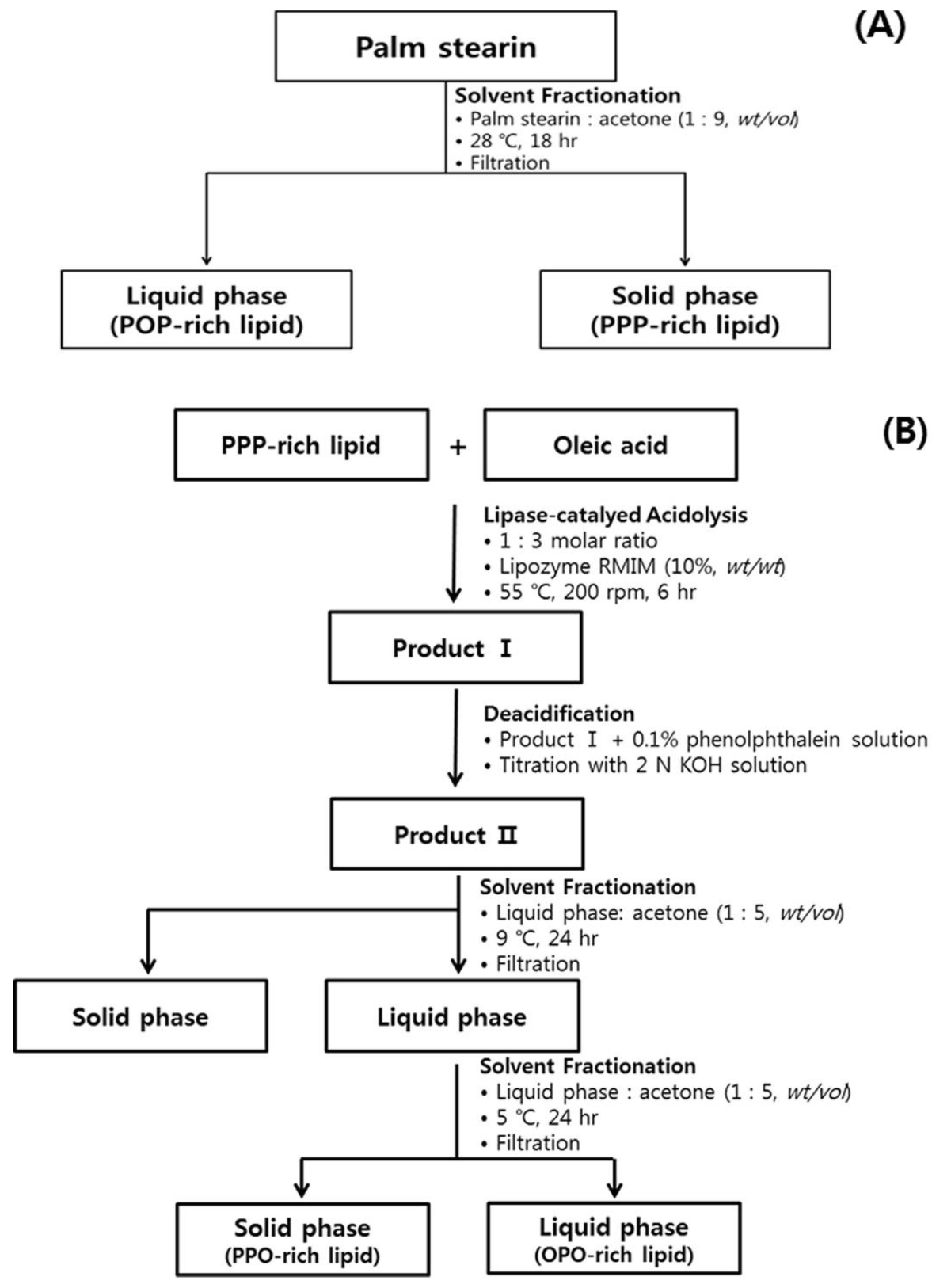
3.2. Production of PPP-Rich and POP-Rich Lipids
3.3. Production of PPO-Rich and OPO-Rich Lipids
3.4. Analysis of Acylglycerol Composition with 1H-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
3.5. Analysis of TAG Composition with Silver Ion-High Performance Liquid Chromatography (Ag-HPLC)
3.6. Analysis of Fatty Acid Composition
3.7. Analysis of Melting and Crystallization Properties with Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.8. Crystal Morphology by Polarized Light Microscopy
3.9. In Vitro Multi-Step Digestion Model
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Baker, M.R.; Bouzidi, L.; Garti, N.; Narine, S.S. Multi-length-scale elucidation of kinetic and symmetry effects on the behavior of stearic and oleic TAG. Ⅱ: OSO and SOO. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marikkar, J.M.N.; Yanty, N.A.M.; Paciculli, M.; Miskandar, M.S.; Chiavaro, E. Composition and thermal properties of quaternary mixtures of palm oil: Palm stearin: Soybean oil: Cocoa butter. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2018, 30, 740–751. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, T.; Qi, C.; Dai, X.; Xia, Y.; Sun, C.; Sun, J.; Yu, R.; Zhou, Q.; Jin, Q.; Wei, W.; et al. Triacylglyerol composition of breast milk during different lactation stages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2272–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyano, T.; Hachlya, I. Phase behavior of mixed systems of SOS and OSO. J. Phys. Chem. 1992, 96, 10514–10520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minato, A.; Ueno, S.; Yano, J.; Smith, K.; Seto, H.; Amemiya, Y.; Sato, K. Thermal and structural properties of sn-1,3-dipalmitoyl-2-oleoylglycerol and sn-1,3-dioleoyl-2-palmitoylglycerol binary mixtures examined with synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction. JAOCS 1997, 74, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanan, A.; Darling, B.; Bouzidi, L.; Narine, S.S. Mitigating crystallization of saturated FAMES (FA methyl esters) in biodiesel. 3. The binary phase behavior of 1,3-dioleoyl-2-palmitoyl glycerol-methyl palmitate—A multi-length scale structural elucidation of mechanism responsible for inhibiting FAME crystallization. Energy 2015, 86, 500–513. [Google Scholar]
- Boodhoo, M.V.; Bouzidi, L.; Narine, S.S. The binary phase behavior of 1,3-dipalmitoyl-2-stearoyl-sn-glycerol and 1,2-dipalmitoyl-3-stearoyl-sn-glycerol. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2009, 160, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Akoh, C.C.; Himmelsbach, D.S.; Lee, K.T. Preparation of interesterified plastic fats from fats and oils free of trans fatty acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4039–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, M.C.; Genot, C.; Gayet, C.; Lopez, C.; Fin, F.; Joffre, F.; Vendeuvre, J.L.; Bouvier, J.; Chardigny, J.M.; Raynal-Ljutovac, K.; et al. Multiscale structures of lipids in foods as parameters affecting FA bioavailability and lipid metabolism. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 354–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karupaiah, T.; Sundram, K. Effects of stereospecific positioning of FAs in triacylglycerol structures in native and randomized fats: A review of their nutritional implications. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, B.R.; Lee, J.H. In vitro and in vivo digestibility of soybean, fish, and microalgal oils, and their influences on fatty acid distribution in tissue lipid of mice. Molecules 2020, 25, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoe, S.; Yamamura, J.; Matsuyama, H.; Hase, M.; Shiota, M.; Miura, S. The positional distribution of dioleoyl-palmitoyl glycerol influences lymph chylomicron transport, composition and size in rats. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Son, J.M.; Akoh, C.C.; Kim, M.R.; Lee, K.T. Optimized synthesis of 1,3-dioleoyl-2-palmitoylglycerol-rich triacylglycerol via interesterification catalyzed by a lipase from Thermomyces Ianuginosus. New Biotechnol. 2010, 27, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.M.; Lee, J.H.; Xue, C.L.; Hong, S.T.; Lee, K.T. Optimization of lipase-catalyzed interesterification for production of human milk fat substitutes by response surface methodology. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 43, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, C.; Xu, W.; Miu, Z.; Jin, Q.; Wnag, X. Enzymatic synthesis of structured triacylglycerols rich in 1,3-dioeloyl-2-palmitoylglycerol and 1-oleoyl-2-palmitoyl-3-linoleoylglycerol in a solvent free system. LWT 2020, 118, 108798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.K.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, K.T. Synthesis of cocoa butter alternative from coconut oil fraction and palm oil fractions by lipase-catalyzed interesterification. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 39, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, X.; Feng, F. Synthesis of structured lipid 1,3-dioleoyl-2-palmitoylglycerol in both solvent and solvent-free system. LWT 2015, 60, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.J.; Na, B.R.; Lee, J.H. Hydrolytic properties of algae oil and DAG-rich algae oil using pH-stat and multi-step in vitro digestion models. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 47, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.M.; Lee, K.T. Comparison of hydrolysis from in vitro digestion using symmetric triacylglycerol compounds by enzymatic interesterification. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 43, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Li, Y. Review of in vitro digestion models for rapid screening of emulsion-based systems. Food Funct. 2010, 1, 32–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sams, L.; Paume, J.; Giallo, J.; Carrière, F. Relevant pH and lipase for in vitro models of gastric digestion. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Sallancet, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carrière, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A standardized static in vitro digestion method suitable for food—An international concensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Balance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Choi, E.O.; Oh, C.H.; Song, Y.O.; Jung, M.W.; Hong, S.T.; Jang, P.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.J. FOOD LIPIDS, 1st ed.; SOOHAKSA: Seoul, Korea, 2015; pp. 365–370. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, S.D.; Buddhi, D. Accelerated thermal cycle test of acetamide, stearic acid and paraffin wax for solar thermal latent heat storage applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2002, 43, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, R.L.; Young, R.J. Effect of micelle formation on the absorption of neutral fat and fatty acids by the chicken. J. Nutr. 1975, 105, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Callejo, R.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; O’Hagan, D. The difluoromethylene (CF2) group in aliphatic chains: Synthesis and conformational preference of palmitic acids and nonadecane containing CF2 groups. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoyama, M. Structure and phase characterization of triacylglycerols by raman spectroscopy. Bull NARO Inst. Livest. Grassl. Sci. 2012, 12, 19–68. [Google Scholar]
- Gwie, G.G.; Griffiths, R.J.; Cooney, D.T.; Johns, M.L.; Wilson, D.I. Microstructures formed by spray freezing of food fats. JAOCS 2006, 83, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, W.; Moore, J.H. The digestibility coefficients of myristic, palmitic and stearic acids in the diet of sheep. J. Dairy. Res. 1968, 35, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, M.D.; Uriatre, P.S. Study by 1H NMR spectroscopy of the evolution of extra virgin olive oil composition submitted to frying temperature in an industrial fryer for a prolonged period of time. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.E. Standardization of chemical shifts of TMS and solvent signals in NMR solvents. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2006, 44, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, P.; Barnes, T.J.; Boyd, B.J.; Prestidge, C.A. Porous nanostructure controls kinetics, disposition and self-assembly structure of lipid digestion products. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 78385–78395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieva-Echvarría, B.; Goicoechea, E.; Manzanos, M.J.; Guillén, M.D. Usefulness of 1H-NMR in assessing the extent of lipid digestion. Food Chem. 2015, 179, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Rubio, A.S.; Sopelana, P.; Guillén, M.D. Influence of minor components on lipid bioaccessibility and oxidation durting in vitro digestion of soybean oil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 4793–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, L.; Sasaki, E.; Yasunami, H.; Nomiyama, S.; Nakayama, M.; Sugano, M.; Imaizumi, K.; Yazawa, K. Digestion and lymphatic transport of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids given in the form of triacylglycerol, free acid and ethyl ester in rat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1259, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momchilava, S.M.; Nikolova-Damyanova, B.M. Advances in silver ion chromatography for the analysis of fatty acids and triacylglycerols-2001 to 2011. Anal. Sci. 2012, 28, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.S.; Shin, J.A.; Lee, K.T. Enzymatic reaction model for the production of symmetrical lipid moelcules using the response surface methodology. Korean J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 56, 265–282. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, H.; Lee, J.H. Optimization of omega-3 enriched-diacylglycerol production by enzymatic esterification using a response surface methodology. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOCS. Official Method and Recommended Practices, 6th ed.; American Oil Chemists’ Society: Champaign, IL, USA, 2009; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Versantvoort, C.H.M.; Oomen, A.G.; de Kamp, E.V.; Rompelberg, C.J.M.; Sips, A.J.A.M. Applicability of an in vitro digestion model in assessing the bioaccessibility of mycotoxins from food. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.D.; Sassene, P.; Kleberg, K.; Bakala-N’Goma, J.C.; Calderone, M.; Jannin, V.; Igonin, A.; Partheil, A.; Marchaud, D.; Jule, E.; et al. Toward the establishment of standardized in vitro tests for lipid-based formulations, part 1: Method parameterization and comparison of in vitro digestion profiles across a range of representative formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 3360–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncoso, E.; Aguilera, J.M.; McClements, D.J. Influence of particle size on the in vitro digestibility of protein-coated lipid nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 382, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Acylglycerol (mmol%) | Palm Stearin | PPP-Rich Lipid | POP-Rich Lipid | PPO-Rich Lipid | OPO-Rich Lipid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triacylglycerol (TAG) | 96.9 ± 0.0 d(1) | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 93.4 ± 0.0 e | 99.1 ± 0.0 c | 99.3 ± 0.0 b |
| Diacylglycerol (DAG) | 3.1 ± 0.0 b | 0.0 ± 0.0 d | 6.3 ± 0.1 a | 0.7 ± 0.0 c | 0.7 ± 0.0 c |
| 1,3-DAG | 1.3 ± 0.0 b | 0.0 ± 0.0 d | 3.1 ± 0.1 a | 0.4 ± 0.0 c | 0.3 ± 0.0 c |
| 1,2-DAG | 1.9 ± 0.0 b | 0.0 ± 0.0 d | 3.3 ± 0.1 a | 0.3 ± 0.0 c | 0.3 ± 0.0 c |
| Monoacylglycerol (MAG) | - (2) | - | 0.3 ± 0.0 a | 0.2 ± 0.0 b | 0.1 ± 0.0 c |
| 1-MAG | - | - | 0.1 ± 0.0 b | 0.2 ± 0.0 a | 0.0 ± 0.0 c |
| 2-MAG | - | - | 0.1 ± 0.0 a | 0.0 ± 0.0 b | 0.1 ± 0.0 b |
| Fatty Acid (% of Total Fatty Acids) | Palm Stearin | PPP-Rich Lipid | POP-Rich Lipid | PPO-Rich Lipid | OPO-Rich Lipid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C14:0 | 1.1 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 0.0 | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 0.7 ± 0.0 |
| C16:0 | 63.4 ± 0.2 b(1) | 79.4 ± 0.0 a | 46.5 ± 0.0 d | 46.9 ± 0.0 c | 30.2 ± 0.1 e |
| C18:0 | 4.8 ± 0.0 b | 5.0 ± 0.0 a | 4.5 ± 0.0 c | 3.7 ± 0.0 d | 2.5 ± 0.1 e |
| C18:1t | 0.1 ± 0.0 | - (2) | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.7 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 |
| C18:1n-9c | 24.9 ± 0.2 d | 11.6 ± 0.0 e | 38.9 ± 0.0 c | 45.3 ± 0.0 b | 60.9 ± 0.2 a |
| C18:1n-7c | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 0.6 ± 0.0 | - | - |
| C18:2n-6c | 5.1 ± 0.0 b | 2.1 ± 0.0 e | 8.2 ± 0.0 a | 2.8 ± 0.0 d | 4.6 ± 0.1 c |
| C20:0 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.0 |
| SFA (3) | 69.6 ± 0.2 b | 86.0 ± 0.0 a | 52.2 ± 0.0 c | 51.2 ± 0.0 d | 33.5 ± 0.2 e |
| USFA (3) | 30.4 ± 0.2 d | 14.0 ± 0.0 e | 47.8 ± 0.0 c | 48.8 ± 0.0 b | 66.5 ± 0.2 a |
| MUFA (3) | 25.3 ± 0.2 d | 11.9 ± 0.0 e | 39.6 ± 0.0 c | 46.0 ± 0.0 b | 61.9 ± 0.3 a |
| Slip melting point (°C) | 55.6 ± 0.4 b | 59.5 ± 0.7 a | 27.3 ± 0.4 c | 26.5 ± 0.0 c | 15.0 ± 0.0 d |
| Complete melting point (°C) | 57.0 ± 0.0 b | 61.5 ± 0.0 a | 29.5 ± 0.7 c | 27.5 ± 0.0 d | 18.5 ± 0.7 e |
| Fatty Acid (% of Total Fatty Acids) | Palm Stearin | PPP-Rich Lipid | POP-Rich Lipid | PPO-Rich Lipid | OPO-Rich Lipid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sn-2 position | |||||
| C16:0 | 45.6 ± 1.6 d(1) | 73.4 ± 0.3 b | 14.3 ± 0.1 e | 81.2 ± 2.1 a | 60.3 ± 0.7 c |
| C18:0 | 2.8 ± 0.8 ab | 4.3 ± 1.5 a | 1.3 ± 0.0 b | 2.2 ± 0.3 b | 3.1 ± 0.0 ab |
| C18:1n-9c | 42.5 ± 1.8 b | 19.9 ± 0.2 d | 67.9 ± 0.1 a | 13.0 ± 1.0 e | 31.8 ± 0.1 c |
| C18:2n-6c | 9.1 ± 0.6 b | 2.3 ± 0.9 d | 16.5 ± 0.0 a | 3.6 ± 0.8 cd | 4.8 ± 0.8 c |
| SFA (2) | 48.4 ± 2.4 d | 77.8 ± 1.2 b | 15.7 ± 0.1 e | 83.4 ± 1.8 a | 63.4 ± 0.7 c |
| USFA (2) | 51.6 ± 2.4 b | 22.2 ± 1.2 d | 84.3 ± 0.1 a | 16.6 ± 1.8 e | 36.6 ± 0.7 c |
| MUFA (2) | 42.5 ± 1.8 b | 19.9 ± 0.2 d | 67.9 ± 0.1 a | 13.0 ± 1.0 e | 31.8 ± 0.1 c |
| sn-1,3 position | |||||
| C14:0 | 1.6 ± 0.0 | 1.9 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 0.0 | 0.8 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 |
| C16:0 | 72.3 ± 0.4 b | 82.3 ± 0.2 a | 62.5 ± 0.0 c | 29.7 ± 1.1 d | 15.2 ± 0.6 e |
| C18:0 | 5.8 ± 0.5 a | 5.4 ± 0.7 ab | 6.1 ± 0.0 a | 4.5 ± 0.2 b | 2.2 ± 0.1 c |
| C18:1t | 0.1 ± 0.0 | - (3) | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 1.1 ± 0.0 | 1.5 ± 0.1 |
| C18:1n-9c | 16.0 ± 0.6 d | 7.5 ± 0.1 e | 24.3 ± 0.0 c | 61.4 ± 0.5 b | 75.4 ± 0.3 a |
| C18:1n-7c | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | - | - |
| C18:2n-6c | 3.0 ± 0.3 b | 2.0 ± 0.5 c | 4.1 ± 0.0 a | 2.3 ± 0.4 bc | 4.5 ± 0.3 a |
| C20:0 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.0 |
| SFA (2) | 80.2 ± 0.9 b | 90.1 ± 0.6 a | 70.4 ± 0.0 c | 35.2 ± 0.9 d | 18.6 ± 0.7 e |
| USFA (2) | 19.8 ± 0.9 d | 9.9 ± 0.6 e | 29.6 ± 0.0 c | 64.8 ± 0.9 b | 81.4 ± 0.7 a |
| MUFA (2) | 16.8 ± 0.6 d | 7.8 ± 0.1 e | 25.4 ± 0.0 c | 62.5 ± 0.5 b | 76.9 ± 0.3 a |
| Triacylglycerol (1) (% of Total Triayclglyerol) | Palm Stearin | PPP-Rich Lipid | POP-Rich Lipid | PPO-Rich Lipid | OPO-Rich Lipid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SaSaSa (PPP) | 38.0 ± 0.2 b(2) | 81.2 ± 1.1 a | 0.6 ± 0.0 c | - (3) | - |
| SaMoSa (POP) | 42.4 ± 0.3 b | 15.1 ± 0.8 c | 64.4 ± 1.4 a | 0.7 ± 0.1 d | 1.6 ± 0.1 d |
| SaSaMo (PPO) | 3.8 ± 0.2 c | 1.2 ± 0.1 d | 5.5 ± 0.0 c | 86.5 ± 0.2 a | 22.0 ± 2.0 b |
| SaDSa (PLP) | 3.2 ± 0.1b | 0.8 ± 0.1 c | 5.8 ± 0.2 a | 0.5 ± 0.0 d | 0.2 ± 0.0 e |
| SaSaD/SaMoMo (PPL/POO) | - | - | - | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 18.6 ± 0.4 *(4) |
| MoSaMo (OPO) | 10.8 ± 0.3 c | 1.9 ± 0.1 d | 20.3 ± 0.9 b | 8.7 ± 0.1 c | 50.2 ± 2.7 a |
| SaDMo/SaMoD (PLO/POL) | 1.5 ± 0.1 b | - | 2.9 ± 0.4 a | - | 0.7 ± 0.1 c |
| MoMoMo (OOO) | 0.3 ± 0.0 d | - | 0.6 ± 0.0 c | 0.8 ± 0.1b | 6.8 ± 0.1 a |
| Acylglycerol (μmol) | POP-Rich Lipid | PPO-Rich Lipid | OPO-Rich Lipid | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Digestion | In Vitro Digestion | Before Digestion | In Vitro Digestion | Before Digestion | In Vitro Digestion | ||||
| 60 min | 120 min | 60 min | 120 min | 60 min | 120 min | ||||
| Triacylglycerol (TAG) | 810.76 ± 12.27 a(1) (100%) (2) | 158.33 ± 6.17 b (19.53%) | 97.89 ± 1.80 c (12.10%) | 848.12 ± 58.08 a (100%) | 130.04 ± 1.23 b (15.33%) | 101.04 ± 1.80 b (11.91%) | 727.01 ± 31.00 a (100%) | 100.73 ± 0.38 b (13.86%) | 74.20 ± 3.38 b (10.21%) |
| Diacylglycerol (DAG) | 54.96 ± 1.52 b (100%) | 68.97 ± 3.69 a (125.49%) | 32.51 ± 4.06 c (59.15%) | 6.12 ± 1.72 b (100%) | 54.49 ± 5.80 a (890.36%) | 45.07 ± 2.79 a (736.44%) | 4.79 ± 0.14 c (100%) | 40.62 ± 0.93 a (848.02%) | 15.24 ± 2.65 b (318.16%) |
| 1,3-DAG | 26.55 ± 1.66 a | 15.67 ± 1.86 b | 8.52 ± 0.02 c | 3.57 ± 0.46 b | 12.87 ± 1.68 a | 12.22 ± 0.26 a | 2.48 ± 0.05 b | 12.21 ± 0.32 a | 3.25 ± 0.42 b |
| 1,2-DAG | 28.41 ± 0.14 b | 53.30 ± 1.83 a | 22.99 ± 4.03 b | 2.56 ± 0.23 b | 41.63 ± 4.12 a | 32.85 ± 3.06 a | 2.31 ± 0.18 c | 28.41 ± 0.61 a | 11.99 ± 2.22 b |
| Monoacylglycerol (MAG) | 2.30 ± 0.26 a (100%) | 2.43 ± 0.22 a (105.65%) | 3.21 ± 0.86 a (139.57%) | 1.58 ± 0.01 b (100%) | 4.20 ± 0.81 a (265.82%) | 2.86 ± 0.34 ab (181.01%) | 0.58 ± 0.08 b (100%) | 5.82 ± 1.79 a (1003.45%) | 3.84 ± 0.11 ab (662.07%) |
| 1-MAG | 1.08 ± 0.03 a | 1.36 ± 0.18 a | 1.85 ± 0.50 a | 1.25 ± 0.06 b | 2.65 ± 0.67 a | 1.68 ± 0.05 ab | 0.15 ± 0.01 b | 3.64 ± 1.27 a | 1.87 ± 0.29 ab |
| 2-MAG | 1.22 ± 0.22 a | 1.07 ± 0.05 a | 1.37 ± 0.36 a | 0.33 ± 0.05 b | 1.55 ± 0.14 a | 1.18 ± 0.29 a | 0.43 ± 0.07 b | 2.18 ± 0.52 a | 1.97 ± 0.18 a |
| Triacylglycerol (1) (Area of Total Triacylglycerol) | POP-Rich Lipid | PPO-Rich Lipid | OPO-Rich Lipid | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Digestion | In Vitro Digestion | Before Digestion | In Vitro Digestion | Before Digestion | In vitro Digestion | |||||||
| 30 min | 60 min | 120 min | 30 min | 60 min | 120 min | 30 min | 60 min | 120 min | ||||
| SaSaSa (PPP) | 140 ± 18 (2) | - (3) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SaMoSa (POP) | 16493 ± 3410 a(4) (100%) (5) | 7180 ± 2538 b (43.53%) | 3458 ± 1772 b (20.97%) | 1705 ± 278 b (10.34%) | 284 ± 4 a (100%) | 43 ± 16 b (15.14%) | 40 ± 9 b (14.08%) | 54 ± 9 b (19.01%) | 339 ± 55 *(6) (100%) | 28 ± 1 (8.26%) | - | - |
| SaSaMo (PPO) | 1403 ± 261 a (100%) | 457 ± 196 b (32.57%) | 132 ± 97 b (9.41%) | 69 ± 11 b (4.92%) | 37079 ± 3403 a (100%) | 5855 ± 2899 b (15.79%) | 5977 ± 188 b (16.12%) | 4730 ± 3071 b (12.76%) | 4756 ± 594 a (100%) | 416 ± 70 b (8.75%) | 289 ± 23 b (6.08%) | 187 ± 28 b (3.93%) |
| SaDSa (PLP) | 1468 ± 222 a (100%) | 610 ± 202 b (41.55%) | 258 ± 141 b (17.57%) | 142 ± 59 b (9.67%) | 211 ± 18 a (100%) | 29 ± 3 b (13.74%) | 36 ± 9 b (17.06%) | 27 ± 3 b (12.80%) | 37 ± 7 | - | - | - |
| SaSaD/SaMoMo (PPL/POO) | - | - | - | - | 1226 ± 145 a (100%) | 195 ± 17 b (15.91%) | 169 ± 15 b (13.78%) | 160 ± 37 b (11.70%) | 4047 ± 800 a (100%) | 432 ± 263 b (10.67%) | 332 ± 48 b (8.20%) | 178 ± 43 b (4.40%) |
| MoSaMo (OPO) | 5172 ± 741 a (100%) | 2077 ± 763 b (40.16%) | 830 ± 610 b (16.05%) | 523 ± 155 b (10.11%) | 3728 ± 278 a (100%) | 550 ± 136 b (14.75%) | 548 ± 68 b (14.70%) | 436 ± 262 b (11.70%) | 11,019 ± 2963 a (100%) | 1088 ± 124 b (9.87%) | 803 ± 222 b (7.29%) | 411 ± 124 b (3.73%) |
| SaDMo/SaMoD (PLO/POL) | 720 ± 42 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 155 ± 6 | - | - | - |
| MoMoMo (OOO) | 149 ± 37 | - | - | - | 347 ± 4 | - | - | - | 1482 ± 291 | - | - | - |
| Unknown | - | 3457 ± 1027 a | 5244 ± 578 a | 6898 ± 1633 a | - | 1004 ± 429 b | 2606 ± 216 ab | 4444 ± 1215 a | - | 1148 ± 86 b | 1955 ± 287 ab | 4564 ± 1601 a |
| FFA (7) | - | 4678 ± 368 b | 5515 ± 1139 b | 8486 ± 255 a | - | 11,154 ± 3465 a | 12,298 ± 714 a | 15,923 ± 688 a | - | 18,293 ± 2863 b | 26,264 ± 4074 ab | 30,650 ± 4044 a |
| Saliva Juice | Gastric Juice | Duodenal Juice | Bile Juice | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inorganic solution | 1 mL KCl (89.6 g/L) | 1.57 mL NaCl (175.3 g/L) | 4 mL NaCl (175.3 g/L) | 3 mL NaCl (175.3 g/L) |
| 1 mL KSCN (20 g/L) | 0.3 mL NaH2PO4 (88.8 g/L) | 4 mL NaHCO3 (84.7 g/L) | 6.83 mL NaHCO3 (84.7 g/L) | |
| 1 mL NaH2PO4 (88.8 g/L) | 0.92 mL KCl (89.6 g/L) | 1 mL KH2PO4 (8 g/L) | 0.42 mL KCl (89.6 g/L) | |
| 0.17 mL NaCl (175.3 g/L) | 1.8 mL CaCl2·2H2O (22.2 g/L) | 0.63 mL KCl (89.6 g/L) | 1 mL CaCl2·2H2O (22.2 g/L) | |
| 2 mL NaHCO3 (84.7 g/L) | 1 mL NH4Cl (30.6 g/L) | 1 mL MgCl2 (5 g/L) | 15 μL HCl (440.3 g/L) | |
| 0.65 mL HCl (440.3 g/L) | 0.9 mL CaCl2·2H2O (22.2 g/L) | |||
| 18 μL HCl (440.3 g/L) | ||||
| Organic solution | 1 mL Glucose (65 g/L) | |||
| 0.8 mL Urea (25 g/L) | 1 mL Glucuronic acid (2 g/L) | 0.4 mL Urea (25 g/L) | 1 mL Urea (25 g/L) | |
| 0.34 mL Urea (25 g/L) | ||||
| 1 mL Glucosamine (33 g/L) | ||||
| Supplementation to the solution | α-amylase 29 mg | BSA 0.1 g | BSA 0.1 g | BSA 0.18 g |
| Uric acid 1.5 mg | Pepsin 0.25 g | Pancreatin 0.9 g | Bile salt 3 g | |
| Mucin 2.5 mg | Mucin 0.3 g | Lipase 0.15 g | ||
| pH | 6.8 ± 0.2 (2) | 1.3 ± 0.02 | 8.1 ± 0.2 | 8.2 ± 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, H.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Regiospecific Positioning of Palmitic Acid in Triacylglycerol Structure of Enzymatically Modified Lipids Affects Physicochemical and In Vitro Digestion Properties. Molecules 2021, 26, 4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134015
Chang H-J, Lee J-H. Regiospecific Positioning of Palmitic Acid in Triacylglycerol Structure of Enzymatically Modified Lipids Affects Physicochemical and In Vitro Digestion Properties. Molecules. 2021; 26(13):4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134015
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Hyeon-Jun, and Jeung-Hee Lee. 2021. "Regiospecific Positioning of Palmitic Acid in Triacylglycerol Structure of Enzymatically Modified Lipids Affects Physicochemical and In Vitro Digestion Properties" Molecules 26, no. 13: 4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134015
APA StyleChang, H.-J., & Lee, J.-H. (2021). Regiospecific Positioning of Palmitic Acid in Triacylglycerol Structure of Enzymatically Modified Lipids Affects Physicochemical and In Vitro Digestion Properties. Molecules, 26(13), 4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134015





