Influence of Drug Load on the Printability and Solid-State Properties of 3D-Printed Naproxen-Based Amorphous Solid Dispersion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
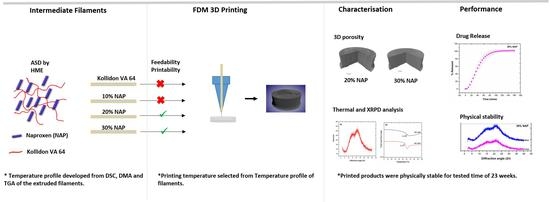
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Development of Filaments by Hot-Melt Extrusion
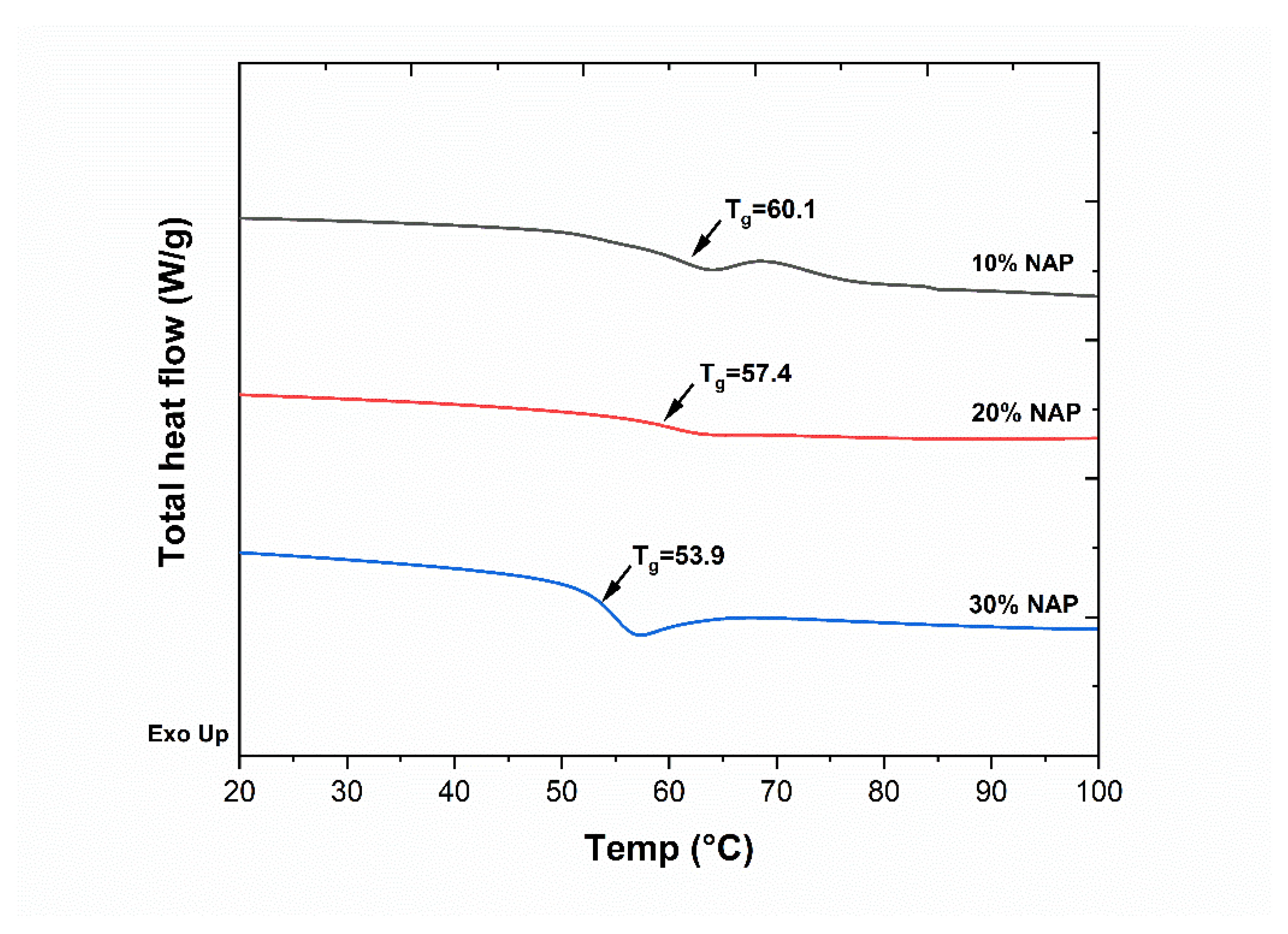
2.2. Characterisation of Filaments
2.3. Selection of Printing Parameters
2.4. 3D Printing
2.5. Characterisation of Printed Dosage Form with XµCT
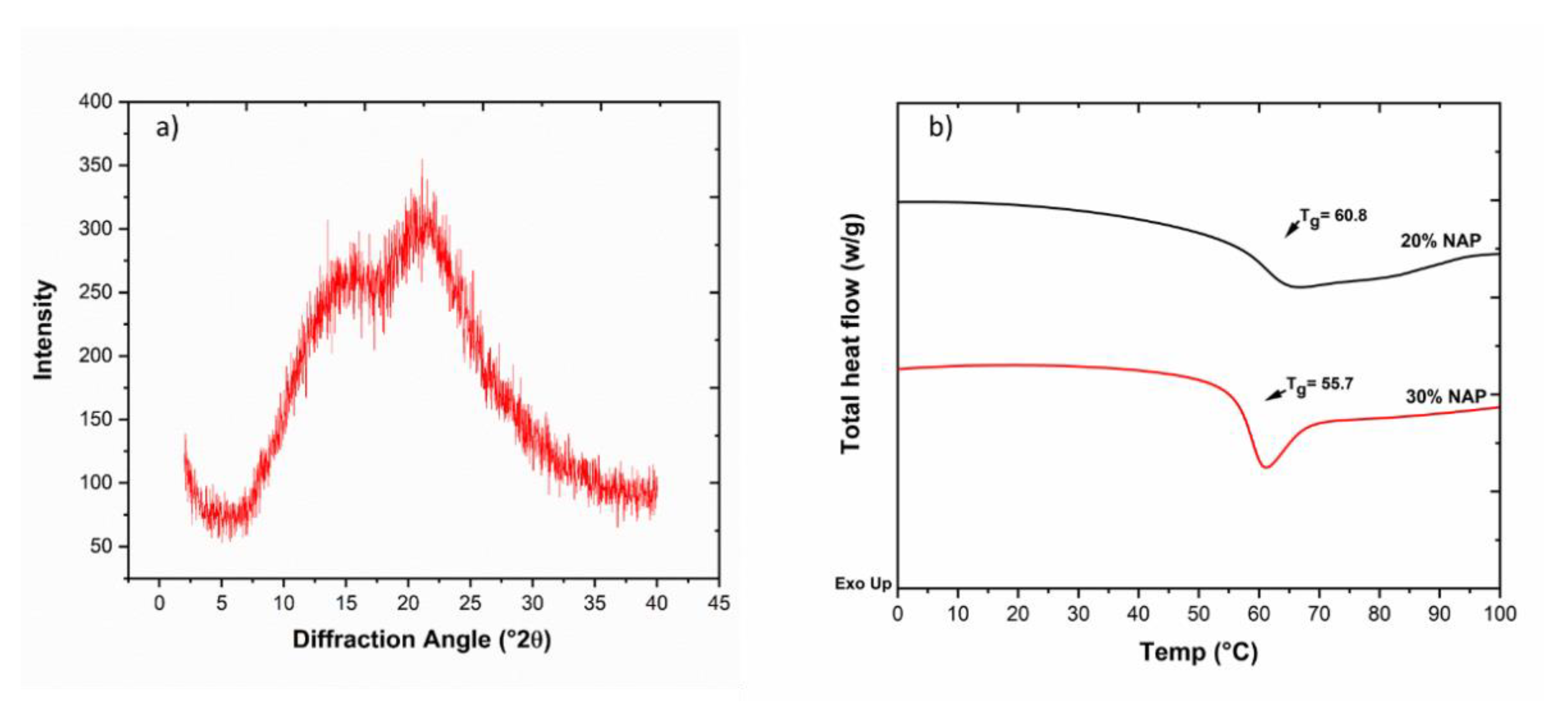
2.6. Solid-State Properties of the Printed Dosage Form
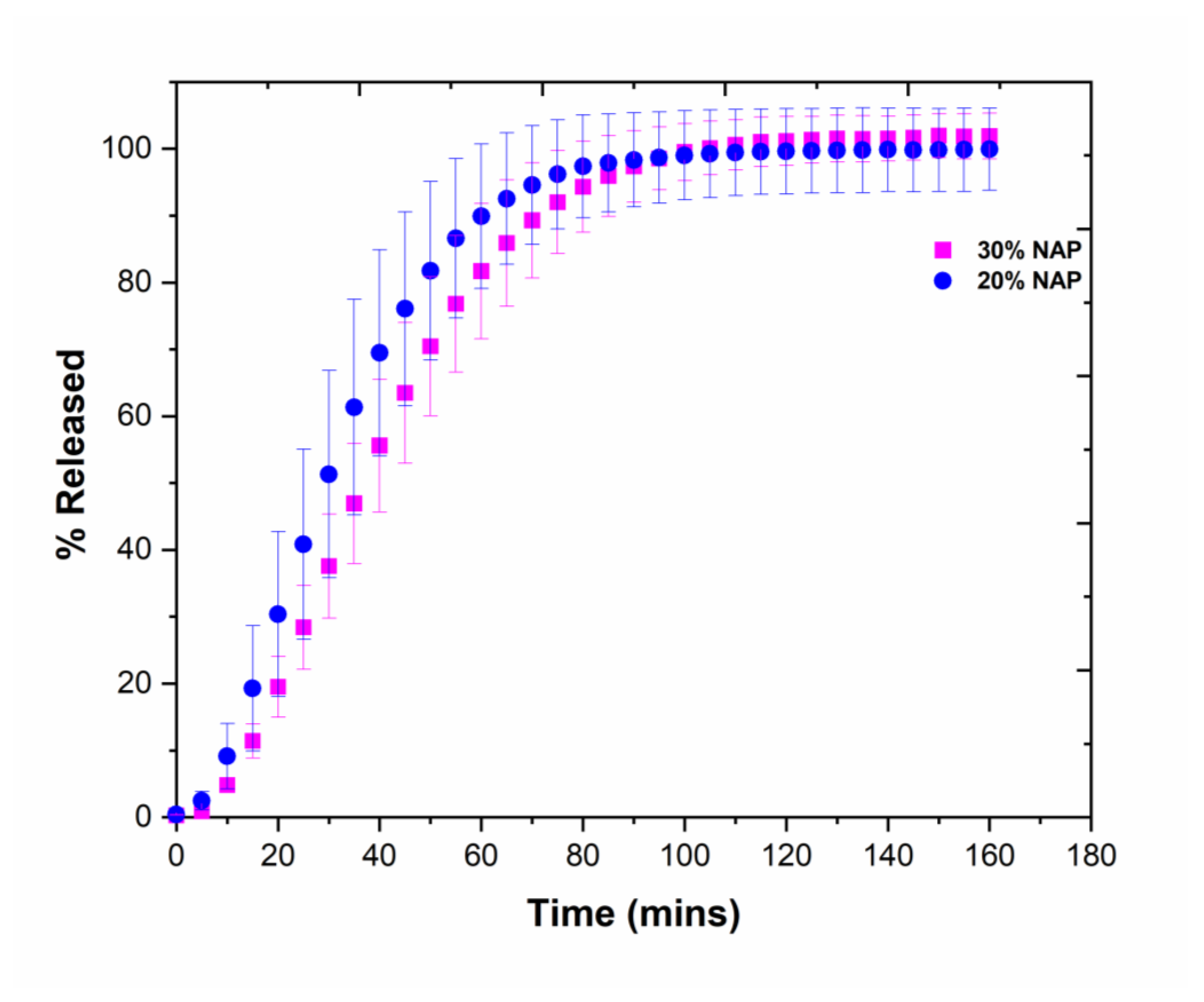
2.7. Drug Release
2.8. Physical Stability of Printed Tablets
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Hot-Melt Extrusion
3.3. 3D Printing
3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
3.6. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
3.7. X-ray Powder Diffraction
3.8. X-ray Computer Tomography
3.9. Physical Stability
3.10. Drug Release
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Collins, F.S.; Varmus, H. A New Initiative on Precision Medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- NHS England; Medical Directorate; Medicines, Diagnostics and Personalised Medicine Unit; Graham, E. Improving Outcomes Through Personalised Medicine; NHS England: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- FORUM Academy of Medical Sciences. Stratified, Personalised or P4 Medicine: A New Direction for Placing the Patient at the Centre of Healthcare and Health Education. 2015. Available online: https://acmedsci.ac.uk/viewFile/564091e072d41.pdf (accessed on 26 July 2021).
- Yan, Q.; Dong, H.; Su, J.; Han, J.; Song, B.; Wei, Q.; Shi, Y. A Review of 3D Printing Technology for Medical Applications. Engineering 2018, 4, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goole, J.; Amighi, K. 3D printing in pharmaceutics: A new tool for designing customized drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 499, 376–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, B.N.; A Gold, S. A review of melt extrusion additive manufacturing processes: II. Materials, dimensional accuracy, and surface roughness. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2015, 21, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhnan, M.A.; Okwuosa, T.C.; Sadia, M.; Wan, K.-W.; Ahmed, W.; Arafat, B. Emergence of 3D Printed Dosage Forms: Opportunities and Challenges. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 1817–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.K.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Nokhodchi, A. Advanced Pharmaceutical Applications of Hot-Melt Extrusion Coupled with Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) 3D Printing for Personalised Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandari, S.; Nyavanandi, D.; Dumpa, N.; Repka, M.A. Coupling hot melt extrusion and fused deposition modeling: Critical properties for successful performance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 172, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scoutaris, N.; Ross, S.; Douroumis, D. 3D Printed “Starmix” Drug Loaded Dosage Forms for Paediatric Applications. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyanes, A.; Allahham, N.; Trenfield, S.J.; Stoyanov, E.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Direct powder extrusion 3D printing: Fabrication of drug products using a novel single-step process. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Faham, A.; Clas, S.-D.; Boyd, B.; Jannin, V.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Zhao, H.; Lecommandoux, S.; Evans, J.C.; Allen, C.; et al. Lipids and polymers in pharmaceutical technology: Lifelong companions. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 558, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rams-Baron, M.; Jachowicz, R.; Boldyreva, E.; Zhou, D.; Jamróz, W.; Paluch, M. Physical Instability: A Key Problem of Amorphous Drugs; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 107–157. [Google Scholar]
- Rades, T.; Gordon, K.C.; Graeser, K.; Hassan, A. A Molecular Structure, Properties, and States of Matter. In Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy, 22nd ed.; Felton, L.A., Ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2013; Volume 77, pp. 117–206. [Google Scholar]
- Bellantone, R.A. Fundamentals of Amorphous Systems: Thermodynamic Aspects. In Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Theory and Practice; Shah, N., Sandhu, H., Choi, D.S., Chokshi, H., Malick, A.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvı’l, B. Solid Forms of Pharmaceutical Molecules. In Glassy, Amorphous and Nano-Crystalline Materials; Šesták, J.J., Hubík, P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen, R.; Priemel, P.A.; Surwase, S.; Graeser, K.; Strachan, C.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Theoretical Considerations in Developing Amorphous Solid Dispersions. In Amorphous Solid Dispersions; Shah, N., Sandhu, H., Choi, D.S., Chokshi, H., Malick, A.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, 2014; pp. 35–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissi, E.O.; Grohganz, H.; Löbmann, K.; Ruggiero, M.T.; Zeitler, J.A.; Rades, T. Glass-Transition Temperature of the β-Relaxation as the Major Predictive Parameter for Recrystallization of Neat Amorphous Drugs. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 2803–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaka, S.R.K.; Bommana, M.M.; Desai, D.; Djordjevic, J.; Phuapradit, W.; Shah, N. Excipients for Amorphous Solid Dispersions. In Advances in Delivery Science and Technology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 123–161. [Google Scholar]
- Dengale, S.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T.; Löbmann, K. Recent advances in co-amorphous drug formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghel, S.; Cathcart, H.; O’Reilly, N.J. Polymeric Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A Review of Amorphization, Crystallization, Stabilization, Solid-State Characterization, and Aqueous Solubilization of Biopharmaceutical Classification System Class II Drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knopp, M.M.; Olesen, N.E.; Holm, P.; Löbmann, K.; Holm, R.; Langguth, P.; Rades, T. Evaluation of Drug–Polymer Solubility Curves Through Formal Statistical Analysis: Comparison of Preparation Techniques. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, D.E.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Zhou, D.; Gao, Y.; Taylor, L.S. Understanding the Behavior of Amorphous Pharmaceutical Systems during Dissolution. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Taylor, L.; Edgar, K.J. The role of polymers in oral bioavailability enhancement; a review. Polymer 2015, 77, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandhu, H.; Shah, N.; Chokshi, H.; Malick, A. Overview of Amorphous Solid Dispersion Technologies. In Advances in Delivery Science and Technology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 91–122. [Google Scholar]
- Crowley, M.M.; Zhang, F.; Repka, M.A.; Thumma, S.; Upadhye, S.B.; Battu, S.K.; McGinity, J.W.; Martin, C. Pharmaceutical Applications of Hot-Melt Extrusion: Part I. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2007, 33, 909–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, H.; Tiwari, R.V.; Repka, M.A. Hot-Melt Extrusion: From Theory to Application in Pharmaceutical Formulation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trenfield, S.J.; Awad, A.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. 3D Printing Pharmaceuticals: Drug Development to Frontline Care. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Trenfield, S.J.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Reshaping drug development using 3D printing. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norman, J.; Madurawe, R.D.; Moore, C.M.; Khan, M.; Khairuzzaman, A. A new chapter in pharmaceutical manufacturing: 3D-printed drug products. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 108, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aho, J.; Bøtker, J.P.; Genina, N.; Edinger, M.; Arnfast, L.; Rantanen, J. Roadmap to 3D-Printed Oral Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms: Feedstock Filament Properties and Characterization for Fused Deposition Modeling. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borandeh, S.; van Bochove, B.; Teotia, A.; Seppälä, J. Polymeric drug delivery systems by additive manufacturing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 173, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane-Viaño, I.; Januskaite, P.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Basit, A.W.; Goyanes, A. Semi-solid extrusion 3D printing in drug delivery and biomedicine: Personalised solutions for healthcare challenges. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 367–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollamaram, G.; Croker, D.M.; Walker, G.; Goyanes, A.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. Low temperature fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing of thermolabile drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 545, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Öblom, H.; Zhang, J.; Pimparade, M.; Speer, I.; Preis, M.; Repka, M.; Sandler, N. 3D-Printed Isoniazid Tablets for the Treatment and Prevention of Tuberculosis—Personalized Dosing and Drug Release. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khaled, S.A.; Alexander, M.; Wildman, R.; Wallace, M.J.; Sharpe, S.; Yoo, J.; Roberts, C.J. 3D extrusion printing of high drug loading immediate release paracetamol tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 538, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolter, K.; Karl, M.; Gryczke, A.; Ludwigshafen am Rhein, B. Hot-Melt Extrusion with BASF Pharma Polymers: Ex-Trusion Compendium; BASF: Ludwigshafen, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, F. Reactive Melt Extrusion to Improve the Dissolution Performance and Physical Stability of Naproxen Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 658–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, V.R.; Lou, X.; Osterling, D.J.; Stolarik, D.F.; Jenkins, G.J.; Nichols, B.L.B.; Dong, Y.; Edgar, K.J.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Taylor, L.S. Amorphous solid dispersions of enzalutamide and novel polysaccharide derivatives: Investigation of relationships between polymer structure and performance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbadawi, M.; Castro, B.M.; Gavins, F.K.; Ong, J.J.; Gaisford, S.; Pérez, G.; Basit, A.W.; Cabalar, P.; Goyanes, A. M3DISEEN: A novel machine learning approach for predicting the 3D printability of medicines. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 590, 119837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, C.; Quodbach, J. Formulation development and process analysis of drug-loaded filaments manufactured via hot-melt extrusion for 3D-printing of medicines. Pharm. Dev. Techno. 2018, 23, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markl, D.; Zeitler, J.A.; Rasch, C.; Michaelsen, M.H.; Müllertz, A.; Rantanen, J.; Rades, T.; Bøtker, J. Analysis of 3D Prints by X-ray Computed Microtomography and Terahertz Pulsed Imaging. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 1037–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markl, D.; Zeitler, J.A. A Review of Disintegration Mechanisms and Measurement Techniques. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 890–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markl, D.; Strobel, A.; Schlossnikl, R.; Boetker, J.; Bawuah, P.; Ridgway, C.; Rantanen, J.; Rades, T.; Gane, P.; Peiponen, K.-E.; et al. Characterisation of pore structures of pharmaceutical tablets: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 538, 188–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Nasereddin, J.; McDonagh, T.; von Zeppelin, D.; Gleadall, A.; Alqahtani, F.; Bibb, R.; Belton, P.; Qi, S. Effects of porosity on drug release kinetics of swellable and erodible porous pharmaceutical solid dosage forms fabricated by hot melt droplet deposition 3D printing. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 120626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vynckier, A.-K.; De Beer, T.; Monteyne, T.; Voorspoels, J.; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. Enteric protection of naproxen in a fixed-dose combination product produced by hot-melt co-extrusion. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 491, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blaabjerg, L.I.; Lindenberg, E.; Löbmann, K.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Glass Forming Ability of Amorphous Drugs Investigated by Continuous Cooling and Isothermal Transformation. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3318–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaabjerg, L.I.; Lindenberg, E.; Rades, T.; Grohganz, H.; Löbmann, K. Influence of preparation pathway on the glass forming ability. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 521, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryanarayanan, R.; Rastogi, S. X-Ray Powder Diffractometry. In Encyclopedia of Pharmaceutical Technology, 3rd ed.; Swarbrick, J., Ed.; Informa Healthcare: London, UK, 2007; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Surana, R.; Suryanarayanan, R. Quantitation of crystallinity in substantially amorphous pharmaceuticals and study of crystallization kinetics by X-ray powder diffractometry. Powder Diffr. 2000, 15, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, M.M.; Gannon, N.; Porsch, I.; Rask, M.B.; Olesen, N.E.; Langguth, P.; Holm, R.; Rades, T. A Promising New Method to Estimate Drug-Polymer Solubility at Room Temperature. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2621–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



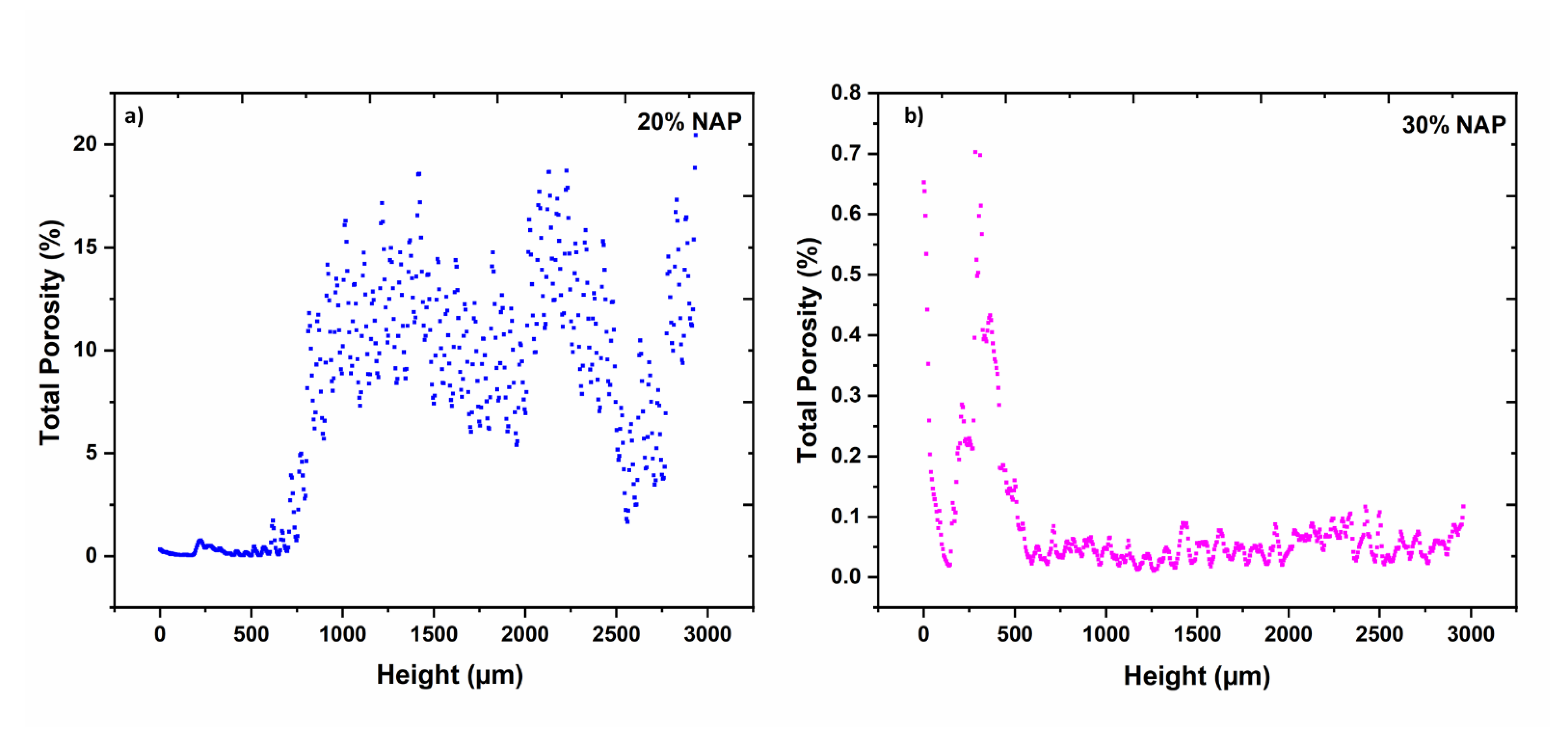

| Parameter | Unit | 20% NAP | 30% NAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Height of tablet 1 | mm | 3.11 | 3.17 |
| Mean diameter 1 | mm | 8.06 | 8.46 |
| Open porosity 1 | % | 6.67 | 0.02 |
| Closed porosity 1 | % | 1.12 | 0.07 |
| Total porosity | % | 7.79 | 0.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kissi, E.O.; Nilsson, R.; Nogueira, L.P.; Larsson, A.; Tho, I. Influence of Drug Load on the Printability and Solid-State Properties of 3D-Printed Naproxen-Based Amorphous Solid Dispersion. Molecules 2021, 26, 4492. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154492
Kissi EO, Nilsson R, Nogueira LP, Larsson A, Tho I. Influence of Drug Load on the Printability and Solid-State Properties of 3D-Printed Naproxen-Based Amorphous Solid Dispersion. Molecules. 2021; 26(15):4492. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154492
Chicago/Turabian StyleKissi, Eric Ofosu, Robin Nilsson, Liebert Parreiras Nogueira, Anette Larsson, and Ingunn Tho. 2021. "Influence of Drug Load on the Printability and Solid-State Properties of 3D-Printed Naproxen-Based Amorphous Solid Dispersion" Molecules 26, no. 15: 4492. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154492
APA StyleKissi, E. O., Nilsson, R., Nogueira, L. P., Larsson, A., & Tho, I. (2021). Influence of Drug Load on the Printability and Solid-State Properties of 3D-Printed Naproxen-Based Amorphous Solid Dispersion. Molecules, 26(15), 4492. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154492