SR-17018 Stimulates Atypical µ-Opioid Receptor Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation
Abstract
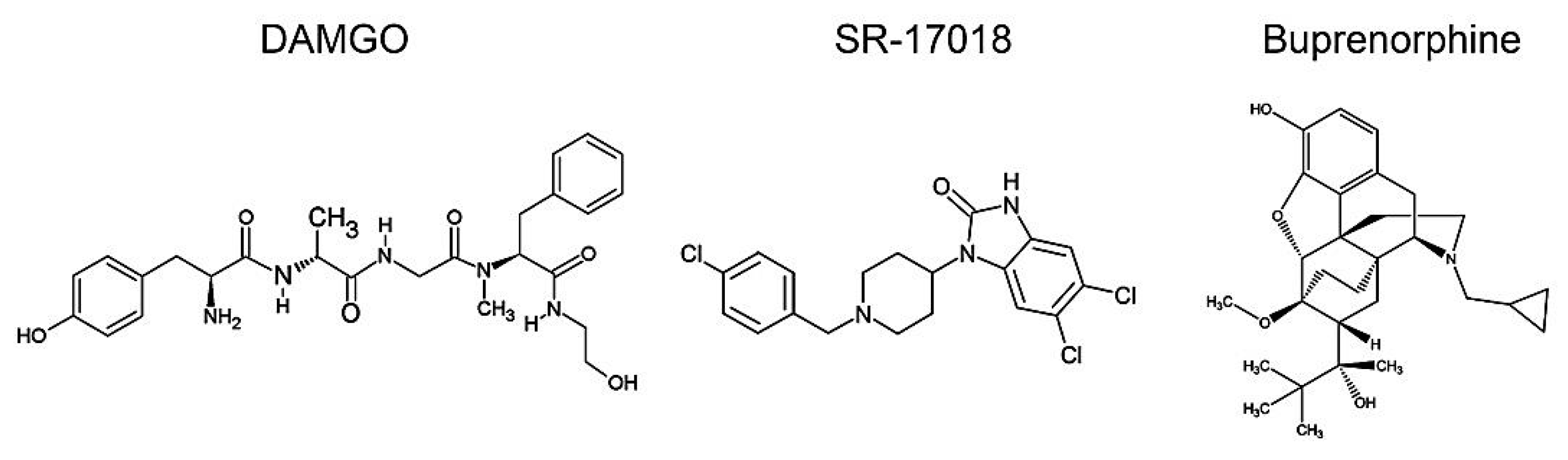
:1. Introduction
2. Results
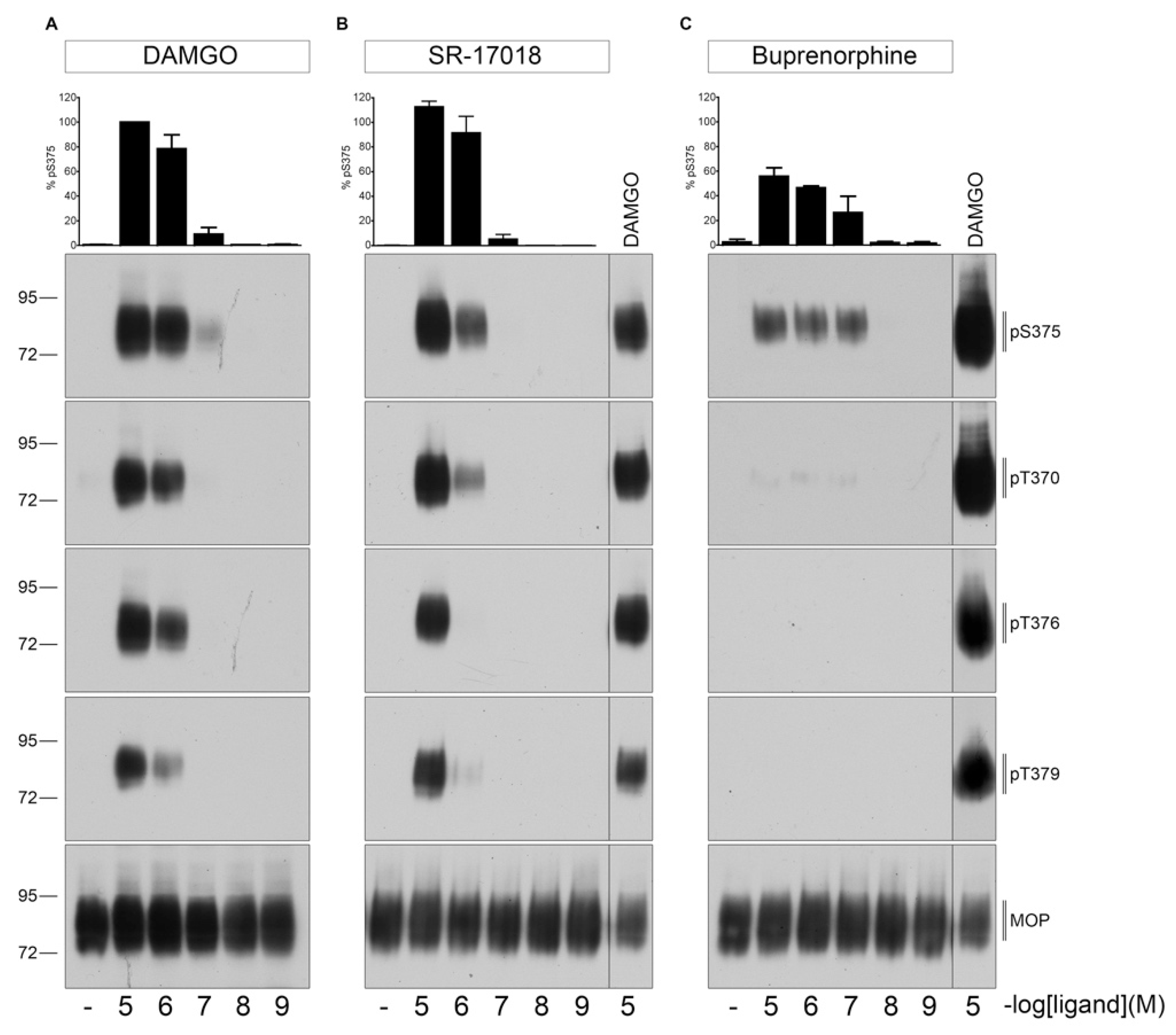
2.1. Agonist-Induced Dose-Dependent MOP Phosphorylation
2.2. Agonist-Induced Time-Dependent MOP Phosphorylation
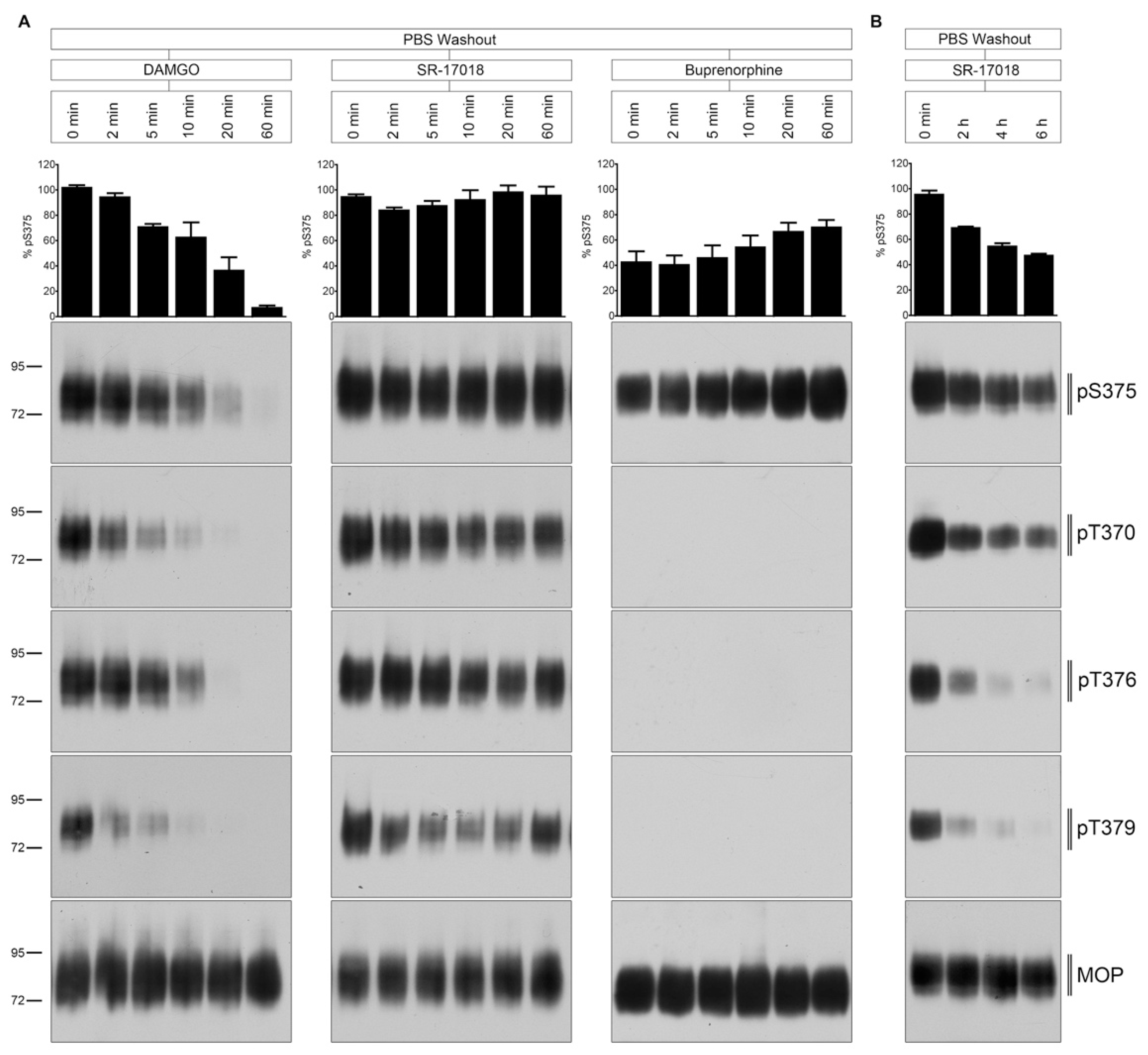
2.3. PBS Buffer Washout of Agonist-Induced Phosphorylation
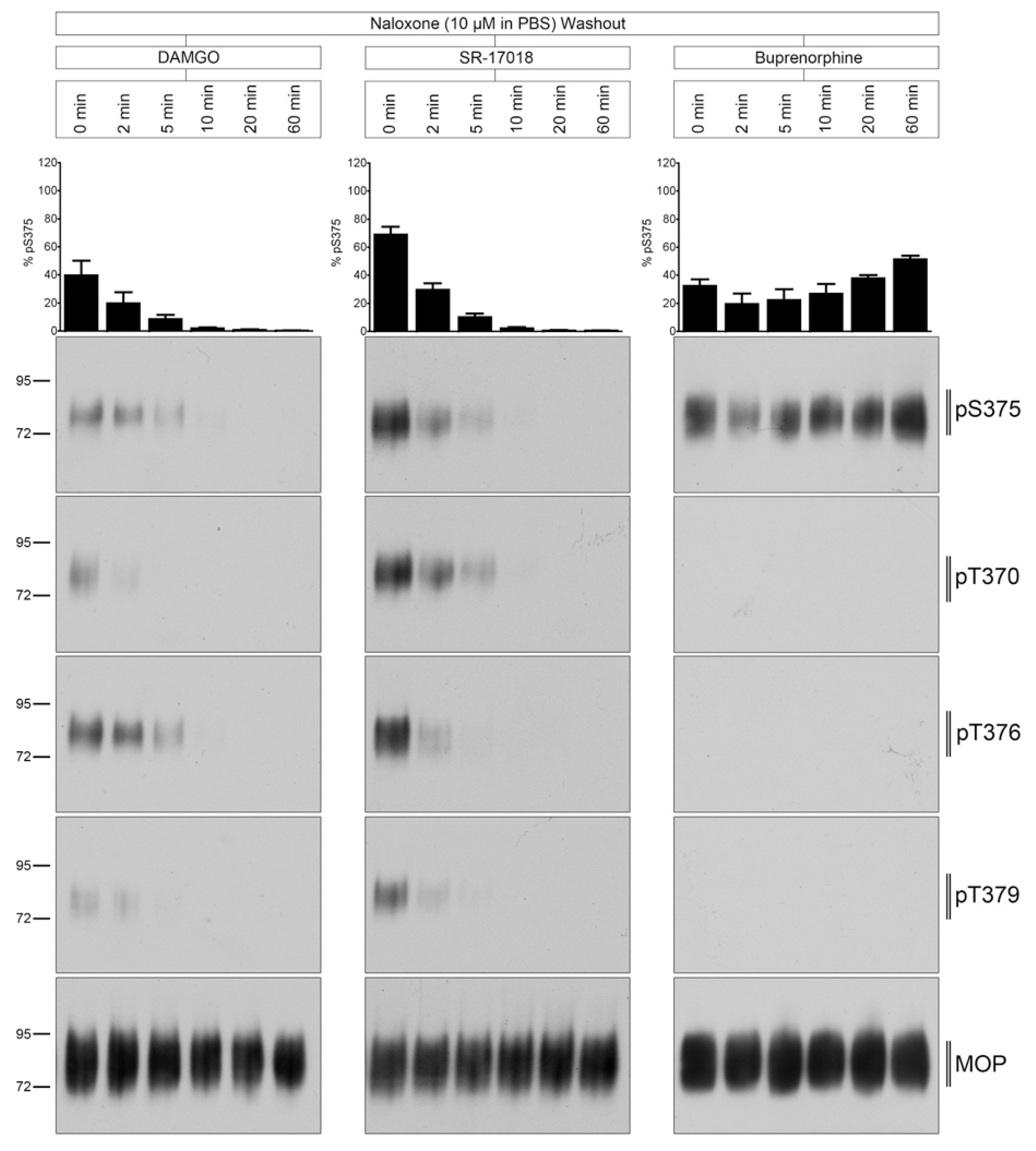
2.4. Naloxone Washout of Agonist-Induced Phosphorylation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.3. Western Blot Assay
4.4. Immunocytochemistry
4.5. Data Availability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Koob, G.F. Neurobiological substrates for the dark side of compulsivity in addiction. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56 (Suppl. 1), 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, J.T.; Ingram, S.L.; Henderson, G.; Chavkin, C.; von Zastrow, M.; Schulz, S.; Koch, T.; Evans, C.J.; Christie, M.J. Regulation of mu-opioid receptors: Desensitization, phosphorylation, internalization, and tolerance. Pharm. Rev. 2013, 65, 223–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmid, C.L.; Kennedy, N.M.; Ross, N.C.; Lovell, K.M.; Yue, Z.; Morgenweck, J.; Cameron, M.D.; Bannister, T.D.; Bohn, L.M. Bias factor and therapeutic window correlate to predict safer opioid analgesics. Cell 2017, 171, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillis, A.; Gondin, A.B.; Kliewer, A.; Sanchez, J.; Lim, H.D.; Alamein, C.; Manandhar, P.; Santiago, M.; Fritzwanker, S.; Schmiedel, F.; et al. Low intrinsic efficacy for g protein activation can explain the improved side effect profiles of new opioid agonists. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, e3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grim, T.W.; Schmid, C.L.; Stahl, E.L.; Pantouli, F.; Ho, J.H.; Acevedo-Canabal, A.; Kennedy, N.M.; Cameron, M.D.; Bannister, T.D.; Bohn, L.M. A G protein signaling-biased agonist at the mu-opioid receptor reverses morphine tolerance while preventing morphine withdrawal. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, J.; Rivero, G.; Baptist, M.; Llorente, J.; Al-Sabah, S.; Krasel, C.; Dewey, W.L.; Bailey, C.P.; Rosethorne, E.M.; Charlton, S.J.; et al. Mu-opioid receptors: Correlation of agonist efficacy for signalling with ability to activate internalization. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 78, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pergolizzi, J.; Aloisi, A.M.; Dahan, A.; Filitz, J.; Langford, R.; Likar, R.; Mercadante, S.; Morlion, B.; Raffa, R.B.; Sabatowski, R.; et al. Current knowledge of buprenorphine and its unique pharmacological profile. Pain Pract. 2010, 10, 428–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutfy, K.; Eitan, S.; Bryant, C.D.; Yang, Y.C.; Saliminejad, N.; Walwyn, W.; Kieffer, B.L.; Takeshima, H.; Carroll, F.I.; Maidment, N.T.; et al. Buprenorphine-induced antinociception is mediated by mu-opioid receptors and compromised by concomitant activation of opioid receptor-like receptors. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10331–10337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Just, S.; Illing, S.; Trester-Zedlitz, M.; Lau, E.K.; Kotowski, S.J.; Miess, E.; Mann, A.; Doll, C.; Trinidad, J.C.; Burlingame, A.L.; et al. Differentiation of opioid drug effects by hierarchical multi-site phosphorylation. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 83, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miess, E.; Gondin, A.B.; Yousuf, A.; Steinborn, R.; Mosslein, N.; Yang, Y.; Goldner, M.; Ruland, J.G.; Bunemann, M.; Krasel, C.; et al. Multisite phosphorylation is required for sustained interaction with grks and arrestins during rapid mu-opioid receptor desensitization. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaas9609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doll, C.; Poll, F.; Peuker, K.; Loktev, A.; Gluck, L.; Schulz, S. Deciphering micro-opioid receptor phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in hek293 cells. Br. J. Pharm. 2012, 167, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, M.F.; Wrobel, T.M.; Marcher-Rorsted, E.; Pedersen, D.S.; Moller, T.C.; Gabriele, F.; Pedersen, H.; Matosiuk, D.; Foster, S.R.; Bouvier, M.; et al. Biased agonism of clinically approved mu-opioid receptor agonists and trv130 is not controlled by binding and signaling kinetics. Neuropharmacology 2020, 166, 107718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, M.A.; Kim, P.S. Buprenorphine for chronic pain: A systemic review. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2018, 22, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, A.; Miess, E.; Sianati, S.; Du, Y.P.; Schulz, S.; Christie, M.J. Role of phosphorylation sites in desensitization of micro-opioid receptor. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 88, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pfeiffer, M.; Koch, T.; Schroder, H.; Laugsch, M.; Hollt, V.; Schulz, S. Heterodimerization of somatostatin and opioid receptors cross-modulates phosphorylation, internalization, and desensitization. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 19762–19772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fritzwanker, S.; Schulz, S.; Kliewer, A. SR-17018 Stimulates Atypical µ-Opioid Receptor Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation. Molecules 2021, 26, 4509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154509
Fritzwanker S, Schulz S, Kliewer A. SR-17018 Stimulates Atypical µ-Opioid Receptor Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation. Molecules. 2021; 26(15):4509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154509
Chicago/Turabian StyleFritzwanker, Sebastian, Stefan Schulz, and Andrea Kliewer. 2021. "SR-17018 Stimulates Atypical µ-Opioid Receptor Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation" Molecules 26, no. 15: 4509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154509
APA StyleFritzwanker, S., Schulz, S., & Kliewer, A. (2021). SR-17018 Stimulates Atypical µ-Opioid Receptor Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation. Molecules, 26(15), 4509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154509





