Design of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Containing Cymbopogon martinii (Palmarosa) Essential Oil against Aspergillus nomius
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical Analysis of Palmarosa Essential Oil by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
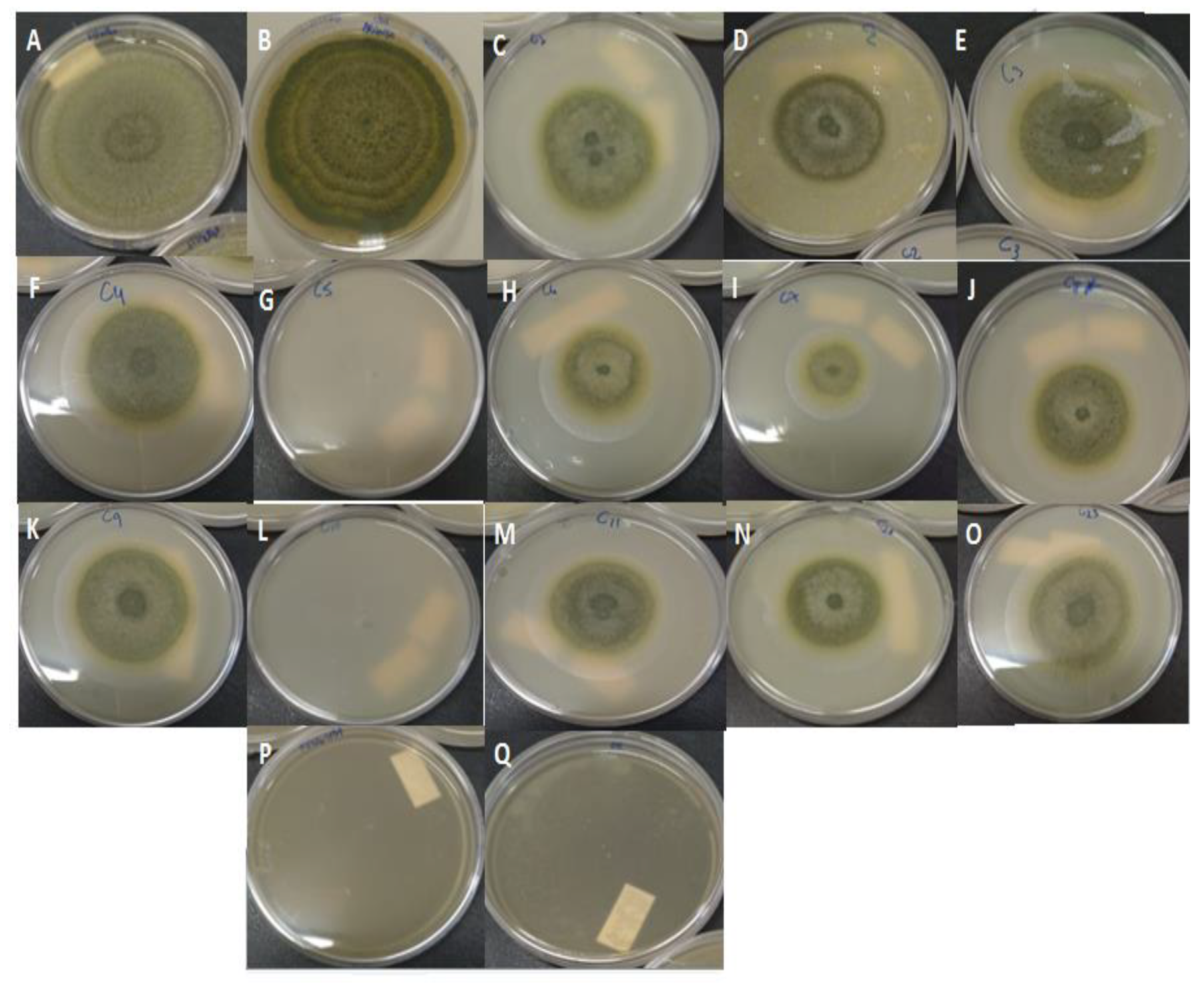
2.2. Antifungal Activity of Non-Encapsulated Palmarosa Essential Oil
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Size, Polydispersity Index (PDI), and Zeta Potential (ζ-Potential)
2.5. Entrapment Efficiency (EE) and PEO Content (PEOC)
2.6. Characterization of the Optimized Formulations (OFs) of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Containing Palmarosa Essential Oil
2.7. Stability Study
2.8. Fourier Transform Raman Spectroscopy (FT-Raman)
2.9. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Chemical Analysis of Palmarosa Essential Oil
3.3. Development of a GC-MS Method for Quantification of Geraniol in the Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Containing Palmarosa Essential Oil
3.4. Antifungal Activity
3.4.1. Determination of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Fungicidal Concentration (MFC) of Palmarosa Essential Oil
3.4.2. Inhibition of Mycelial Growth (IMG)
3.5. NLC Development Based on the Design of Experiments (DoE)
3.6. Size, Polydispersity Index, and Zeta Potential
3.7. Entrapment Efficiency (EE) and PEO Content (PEOC)
3.8. In Situ Test with Brazil Nuts
3.9. Stability Study
3.10. Fourier Transform Raman Spectroscopy (FT-Raman)
3.11. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- MAPA: Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. Agrostat: Exportação Importação. 2020. Available online: http://indicadores.agricultura.gov.br/agrostat/index.htm (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- EC. European Commission 2003. Commission Decision 2003/493/EC of 4 July 2003 Imposing Special Conditions on the Import of Brazil Nuts in Shell, Originating in or Consigned from Brazil; Official Journal of the European Union. OJL 168, 5 July 2003; pp. 33–38. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32003D0493&from=en (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- Tonini, H.; Lopes, C.E.V.; Borges, R.A.; Kaminski, P.E.; Alves, M.S.; Fagundes, P.R.O. Fenologia, estrutura e produção de sementes em castanhais nativos de Roraima e características socioeconômicas dos extrativistas. Bol. Do Mus. Para. Emílio Goeldi. Ciências Nat. 2014, 9, 399–414. [Google Scholar]
- Santana, A.C.; Santana, L.; Santana, A.L.; Martins, C.M. Valoração e sustentabilidade da castanha-do-brasil na Amazônia. Rev. de Ciências Agrárias 2017, 60, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, F.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Coelho, C. The still underestimated problem of fungal diseases worldwide. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drenth, A.; Guest, D.I. Fungal and oomycete diseases of tropical tree fruit crops. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2016, 54, 373–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniwaki, M.H.; Frisvad, J.C.; Ferranti, L.S.; Ferranti, L.S.; Lopes, A.S.; Larsen, T.O.; Fungaro, M.H.F.; Iamanka, B.T. Biodiversity of mycobiota throughout the Brazil nut supply chain: From rainforest to consumer. Food Microbiol. 2017, 61, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.G.; Mack, B.M.; Beltz, S.B. Genomic sequence of the aflatoxigenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus nomius. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer). Chemical Agents and Related Occupations; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 225–248. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro, F.; Augusto, L.G.S.; Rigotto, R.M.; Friedrich, K.; Búrigo, A.C. Dossiê ABRASCO: Um Alerta Sobre os Impactos dos Agrotóxicos na Saúde; EPSJV: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; Expressão Popular: São Paulo, Brazil, 2015; ISBN 978-85-9876-880-9. [Google Scholar]
- Giordani, I.A.; Busatta, E.; Bonfim, E.; Oliveira Filho, L.C.I.; Baretta, D.; Baretta, C.R.D.M. Effect of toxicity in Folsomia candida by the use of fungicide and insecticide in subtropical soil. Braz. J. Environ. Sci. (Online) 2021, 56, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.A.; Ahmad, I. In vitro antifungal, anti-elastase and anti-keratinase activity of essential oils of Cinnamomum-, Syzygium- and Cymbopogon-species against Aspergillus fumigatus and Trichophyton rubrum. Phytomedicine 2011, 19, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, V.; Gunasekaran, C.; Christy, I.K.; Dharmaraj, J.; Chinnaraj, P.; Paul, C.A. Toxicity, antifeedant and biochemical efficacy of Mentha piperita L. essential oil and their major constituents against stored grain pest. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 156, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakaraparthi, P.S.; Srinivas, K.V.N.S.; Kumar, J.K.; Kumar, A.N.; Rajput, D.K.; Anubala, S. Changes in the essential oil content and composition of palmarosa (Cymbopogon martinii) harvested at different stages and short intervals in two different seasons. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 69, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalagatur, N.K.; Nirmal Ghosh, O.S.; Sundararaj, N.; Mudili, V. Antifungal activity of chitosan nanoparticles encapsulated with Cymbopogon martinii essential oil on plant pathogenic fungi Fusarium graminearum. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xavier, A.L.S.; Silva França, K.R.; Cardoso, T.A.L. Efeito do óleo essencial de palmarosa (Cymbopogon martinii) sobre fungos fitopatogênicos em sementes de soja. Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, e4529108660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamarta, S.; Aldavero, A.C.; Rojo, M. Antibacterial Properties of Cymbopogon martinii essential Oil against Bacillus subtillis food industry pathogen. Proceedings 2020, 66, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jummes, B.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Rosa, C.G. Noronha, C.M.; Nunes, M.R.; Bertoldi, F.C.; Barreto, P.L.M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial poly-ε-caprolactone nanoparticles loaded with Cymbopogon martinii essential oil. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 23, 101499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, M.; Pouramin, S.; Adinepour, F.; Haghani, S.; Jafari, S.M. Chitosan nanoparticles loaded with clove essential oil: Characterization, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahedikia, N.; Garavand, F.; Tajeddin, B.; Cacciotti, I.; Jafari, S.M.; Omidi, T.; Zahedi, Z. Biodegradable zein film composites reinforced with chitosan nanoparticles and cinnamon essential oil: Physical, mechanical, structural and antimicrobial attributes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 177, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katouzian, I.; Esfanjani, A.F.; Jafari, S.M.; Akhavan, S. Formulation and application of a new generation of lipid nano-carriers for the food bioactive ingredients. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Mozafari, M.R.; Mohebbi, M. Nanoencapsulation of food ingredients using lipid based delivery systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 23, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Shegokar, R.; Keck, C.M. 20 years of lipid nanoparticles (SLN and NLC): Present state of development and industrial applications. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2011, 8, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodrati, M.; Farahpour, M.R.; Hamishehkar, H. Encapsulation of Peppermint essential oil in nanostructured lipid carriers: In-vitro antibacterial activity and accelerative effect on infected wound healing. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 564, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahr, F.K.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H.; Kafil, H.S. Food grade nanostructured lipid carrier for cardamom essential oil: Preparation, characterization and antimicrobial activity. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashiri, S.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Ayaseh, A.; Dehghannya, J.; Ehsani, A.; Ozyurt, H. Essential oil-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: The effects of liquid lipid type on the physicochemical properties in beverage models. Food Biosci. 2020, 35, 100526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outuki, P.M.; Kleinubing, S.A.; Hoscheid, J.; Montanha, M.C.; Silva, E.A.; Couto, R.O.; Kimura, E.; Cardoso, M.L.C. The incorporation of Pterodon pubescens fruit oil into optimized nanostructured lipid carriers improves its effectiveness in colorectal cancer. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 123, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokarizadeh, M.; Kafil, H.S.; Ghanbarzadeh, S.; Alizadeh, A.; Hamishehkar, H. Improvement of citral antimicrobial activity by incorporation into nanostructured lipid carriers: A potential application in food stuffs as a natural preservative. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 409. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, M.A.; Sahoo, D.; Singh, T.B.; Rajashekar, Y. Antifungal activity and volatile organic compounds analysis of essential oils from Cymbopogon species using solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 3, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyal, P.; Murray, B.L.; McFeeters, R.L.; Setzer, W.N. Essential oil characterization of Thymus vulgaris from various geographical locations. Foods 2016, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.N.; Reddy, C.S.; Muralidharan, K. Efficacy of certain agrochemicals on Aspergillus spp. and subsequent aflatoxin production in rice. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2009, 93, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, P.; Bricchi, E.; Zeppilli, N.; Dimitriu, L.; Rondolini, M.; Angeles, G.; Venanzoni, R. Screening of the antifungal activity of essential oils against human and plant pathogenic filamentous fungi. Flora Mediterr. 2019, 29, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Filho, J.G.; Silva, G.C.; Egea, M.B.; Azeredo, H.M.C.; Ferreira, M.D. Essential Oils as Natural Fungicides to Control Rhizopus stolonifer-Induced Spoiled of Strawberries. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 13244–13251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomfim, N.S.; Kohiyama, C.Y.; Nakasugi, L.P.; Nerilo, S.B.; Mossini, S.A.G.; Romoli, J.C.Z.; Mikcha, J.M.G.; Abreu Filho, B.A.; Machinski, M., Jr. Antifungal and antiaflatoxigenic activity of rosemary essential oil (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) against Aspergillus flavus. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2020, 37, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Wu, H.; Shi, F.; Wang, H.; Chen, K.; Feng, J.; Jia, W. Antifungal activity screening for mint and thyme essential oils against Rhizopus stolonifer and their application in postharvest preservation of strawberry and peach fruits. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamjidi, F.; Shahedi, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Nasirpour, A. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC): A potential delivery system for bioactive food molecules. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 19, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Pan, W. Characterization and evaluation of nanostructured lipid carrier as a vehicle for oral delivery of etoposide. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 43, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrea, E.; Ott, C.; Meghea, A. New approaches on the synthesis of effective nanostructured lipid carriers. Rev. Chim. 2014, 65, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, P.; Kumar, G.A. Nanosuspension technology: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 2, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Chetoni, P.; Burgalassi, S.; Monti, D.; Tampucci, S.; Tullio, V.; Cuffini, A.M.; Spagnolo, R.; Zara, G.P.; Cavalli, R. Solid lipid nanoparticles as promising tool for intraocular tobramycin delivery: Pharmacokinetic studies on rabbits. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 109, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Eldridge, R.; Palombo, E.; Harding, I. Optimisation and Stability Assessment of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles using Particle Size and Zeta Potential. J. Phys. Sci. 2014, 25, 59–75. [Google Scholar]
- Heurtault, B.; Saulnier, P.; Pech, B.; Proust, J.E.; Benoit, J.P. Physico-chemical stability of colloidal lipid particles. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4283–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzar, M.K.; Piruzifard, M.K.; Hamishehkar, H.; Pirsa, S. Cocoa butter and cocoa butter substitute as a lipid carrier of Cuminum cyminum L. essential oil; physicochemical properties, physical stability and controlled release study. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 314, 113638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manea, A.M.; Vasile, B.S.; Meghea, A. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of green tea extract loaded into nanostructured lipid carriers. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2014, 17, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, G.B.; Patil, N.D.; Deshmukh, P.K.; Patil, P.O.; Bari, S.B. Nanostructured lipid carriers as a potential vehicle for Carvedilol delivery: Application of factorial design approach. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, A.C.; Marques, E.B.P.; Leimann, F.V.; Gonçalves, O.H.; Ineu, R.P.; Araújo, P.H.H.; Oliveira, D.; Sayer, C. Encapsulation of clove oil in nanostructured lipid carriers from natural waxes: Preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation of the cholinesterase enzymes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 583, 123879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Feng, P.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y. An improved interfacial coacervation technique to fabricate biodegradable nanocapsules of an aqueous peptide solution from polylactide and its block copolymers with poly (ethylene glycol). Colloid Polym. Sci. 2001, 279, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, B.; Arpicco, S.; Rocco, F.; Marsaud, V.; Renoir, J.M.; Cattel, L.; Couvreur, P. Encapsulation of gemcitabine lipophilic derivatives into polycyanoacrylate nanospheres and nanocapsules. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 344, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Huertas, C.E.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Polymer-based nanocapsules for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 385, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donsì, F.; Ferrari, G. Essential oil nanoemulsions as antimicrobial agents in food. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 233, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribes, S.; Fuentes, A.; Talens, P.; Barat, J.M.; Ferrari, G.; Donsì, F. Influence of emulsifier type on the antifungal activity of cinnamon leaf, lemon and bergamot oil nanoemulsions against Aspergillus niger. Food Control 2017, 73, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, L.N.; Breitkreitz, M.C.; Guilherme, V.A.; da Silva, G.H.; Couto, V.M.; Castro, S.R.; Paula, B.O.; Machado, D.; Paula, E. Natural lipids-based NLC containing lidocaine: From pre-formulation to in vivo studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jores, K.; Haberland, A.; Wartewig, S.; Mäder, K.; Mehnert, W. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and oil-loaded SLN studied by spectrofluorometry and Raman spectroscopy. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, P. Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy. In Dean’s Analytical Chemistry Handbook, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bresson, S.; Rousseau, D.; Ghosh, S.; El Marssi, M.; Faivre, V. Raman spectroscopy of the polymorphic forms and liquid state of cocoa butter. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2011, 113, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saupe, A.; Gordon, K.C.; Rades, T. Structural investigations on nanoemulsions, solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers by cryo-field emission scanning electron microscopy and Raman spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 314, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeten, V.; Hourant, P.; Morales, M.T.; Aparicio, R. Oil and fat classification by FTRaman spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2638–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlina, D.; Novita, M.; Anwar, M.T.; Kusumo, H.; Sato, H. Raman Spectra of Polyethylene Glycol/Cellulose Acetate Butyrate Biopolymer Blend. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; p. 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsutake, H.; Ribeiro, L.N.; Silva, G.H.R.; Castro, S.R.; Paula, E.; Poppi, R.J.; Breitkreitz, M.C. Evaluation of miscibility and polymorphism of synthetic and natural lipids for nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) formulations by Raman mapping and multivariate curve resolution (MCR). Eur. J. Lipid Sci. 2019, 135, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, H.; Baranska, M. Identification and quantification of valuable plant substances by IR and Raman spectroscopya. Vib. Spectrosc. 2007, 43, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentzsch, P.V.; Ramos, L.A.; Ciobotă, V. Handheld Raman spectroscopy for the distinction of essential oils used in the cosmetics industry. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skoog, D.A.; West, D.M.; Holler, F.J.; Crouch, S.R. Fundamentos de Química Analítica, 8th ed.; Thomson: São Paulo, Brasil, 2006; ISBN 8522104360. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry, 4th ed.; Allured Pub. Corp.: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007; ISBN 1932633219. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Singh, V.K.; Dwivedy, A.K.; Chaudhari, A.K.; Dubey, N.K. Nanostructured Pimpinella anisum essential oil as novel green food preservative against fungal infestation, aflatoxin B1 contamination and deterioration of nutritional qualities. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Ban, X.; Zeng, H.; He, J.; Huang, B.; Wang, Y. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of essential oil from Cicuta virosa L. var. latisecta Celak. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 145, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Severino, P.; Santana, M.H.A.; Pinho, S.C. Nanopartículas de lipídios sólidos: Métodos clássicos de produção laboratorial. Química Nova 2011, 34, 1762–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Fang, C.L.; Liu, C.H.; Su, Y.H. Lipid nanoparticles as vehicles for topical psoralen delivery: Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) versus nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussi, S.V.; Silva, R.C.; Oliveira, M.C.; Lucci, C.M.; Azevedo, R.B.; Ferreira, L.A.M. New approach to improve encapsulation and antitumor activity of doxorubicin loaded in solid lipid nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas-Silva, O.; Venâncio, A. Brazil nuts: Benefits and risks associated with contamination by fungi and mycotoxins. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.S.S.; Freitas-Silva, O.; Castro, I.M.; Teixeira, A.; Marques-da-Silva, S.H.; Sales-Moraes, A.C.S.; Abreu, L.F.; Sousa, C.L. Efficacy of sodium hypochlorite and peracetic acid against Aspergillus nomius in Brazil nuts. Food Microbiol. 2020, 90, 103449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Peak | Compound | RIcalc | Relative Area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NI | 905 | 0.03 |
| 2 | NI | 1041 | 0.04 |
| 3 | NI | 1051 | 0.04 |
| 4 | β-myrcene | 1088 | 0.25 |
| 5 | NI | 1128 | 0.07 |
| 6 | Trans-β-Ocimene | 1134 | 0.30 |
| 7 | Cis-β-Ocimene | 1145 | 1.14 |
| 8 | Linalool | 1199 | 3.01 |
| 9 | Geraniol | 1354 | 80.37 |
| 10 | Citral | 1368 | 0.60 |
| 11 | NI | 1397 | 0.11 |
| 12 | Geraniol ester | 1477 | 10.85 |
| 13 | Caryophyllene | 1517 | 2.08 |
| 14 | Neryl acetate | 1847 | 0.92 |
| 15 | Geranyl propionate | 2042 | 0.18 |
| Total amount of identified compounds | 99.70 | ||
| Monoterpene hydrocarbons | 1.69 | ||
| Oxygenated monoterpene | 94.83 | ||
| Sesquiterpene hydrocarbons | 2.08 | ||
| Others | 1.10 | ||
| Not identified | 0.29 | ||
| NLC Formulations | Size (nm) | PDI | ζ-Potential (mV) | EE (%) | PEOC (mg g−1 of NLC) | IMG (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 236.3 ± 5.7 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | −35.9 ± 2.7 | 98.7 ± 2.8 | 2.71 ± 0.08 | 43.8 ± 1.4 |
| F2 | 210.4 ± 3.5 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | −33.2 ± 0.7 | 89.5 ± 1.8 | 2.22 ± 0.04 | 44.7 ± 1.9 |
| F3 | 269.1 ± 8.7 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | −36.9 ± 0.2 | 82.8 ± 1.3 | 1.83 ± 0.03 | 29.7 ± 2.2 |
| F4 | 290.8 ± 3.0 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | −33.4 ± 0.8 | 78.5 ± 1.0 | 1.49 ± 0.02 | 26.9 ± 1.0 |
| F5 | 231.2 ± 5.8 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | −35.4 ± 1.0 | 90.7 ± 0.8 | 2.84 ± 0.03 | 98.8 ± 0.0 |
| F6 | 214.9 ± 2.4 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | −25.2 ± 0.5 | 86.7 ± 4.3 | 2.43 ± 0.12 | 50.6 ± 6.5 |
| F7 | 173.8 ± 2.3 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | −36.9 ± 1.3 | 76.1 ± 1.7 | 2.31 ± 0.05 | 60.5 ± 4.4 |
| F8 | 221.4 ± 16.2 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | −32.4 ± 0.7 | 86.2 ± 0.4 | 2.14 ± 0.01 | 44.2 ± 2.4 |
| F9 | 193.6 ± 2.5 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | −31.2 ± 0.5 | 99.9 ± 1.3 | 1.87 ± 0.03 | 24.7 ± 4.3 |
| F10 | 226.5 ± 6.1 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | −41.8 ± 1.0 | 95.9 ± 6.7 | 3.01 ± 0.21 | 98.8 ± 0.0 |
| F11 | 198.9 ± 5.6 | 0.18 ± 0.02 | −34.6 ± 1.4 | 89.5 ± 3.4 | 2.13 ± 0.08 | 45.5 ± 2.4 |
| F12 | 263.2 ± 51.2 | 0.21 ± 0.07 | −37.1 ± 1.0 | 96.9 ± 2.2 | 2.66 ± 0.06 | 45.1 ± 5.2 |
| F13 | 191.6 ± 6.9 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | −25.3 ± 1.1 | 73.6 ± 1.1 | 1.37 ± 0.02 | 31.2 ± 1.7 |
| Formulation | Amount (%, w/w) | Proportion (w/w) | Pseudocomponents | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X1 | X2 | X3 | X1 | X2 | X3 | |
| OF1 | 3.897 | 1.247 | 0.606 | 0.678 | 0.217 | 0.105 | 0.330 | 0.552 | 0.118 |
| OF4 | 3.833 | 1.258 | 0.659 | 0.667 | 0.219 | 0.115 | 0.259 | 0.564 | 0.177 |
| OF12 | 3.858 | 1.254 | 0.638 | 0.671 | 0.218 | 0.111 | 0.287 | 0.560 | 0.153 |
| NLC Formulation | Size (nm) | PDI | ζ-Potential (mV) | EE (%) | PEOC (mg g−1 of NLC) | IMG (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OF1 | 112.0 ± 1.6 | 0.16 ± 0.001 | −34.6 ± 2.2 | 101.7 ± 0.9 | 3.17 ± 0.03 | 97.3 ± 1.3 |
| OF4 | 178.6 ± 2.7 | 0.27 ± 0.008 | −32.7 ± 0.1 | 100.2 ± 0.8 | 3.15 ± 0.03 | 100 |
| OF12 | 143.3 ± 0.8 | 0.18 ± 0.003 | −29.1 ± 0.7 | 102.7 ± 2.4 | 3.22 ± 0.07 | 100 |
| Time | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 Hours | 30 Days | 60 Days | 90 Days | ||
| OF1 | Size (nm) | 112.1 ± 1.6 b | 125.9 ± 3.2 a | 118.3 ± 0.1 c | 123.2 ± 1.1 b |
| PDI | 0.16 ± 0.001 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 b | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 0.18 ± 0.02 a,b | |
| ζ-potential (mV) | −34.6 ± 2.2 a | −31.8 ± 1.4 a,b | −30.8 ± 0.8 b | −31.8 ± 0.5 a,b | |
| EE (%) | 101.7 ± 0.9 b | 101.6 ± 0.5 a,b | 100.3 ± 1.6 a,b | 99.2 ± 0.3 a | |
| PEOC * | 3.17 ± 0.03 b | 3.17 ± 0.02 a,b | 3.13 ± 0.05 a,b | 3.09 ± 0.01 a | |
| pH | 6.35 ± 0.04 a | 6.42 ± 0.04 a | 6.38 ± 0.02 a | 6.42 ± 0.03 a | |
| IMG (%) | 97.29 b | 100 a | 100 a | 100 a | |
| OF4 | Size (nm) | 178.6 ± 2.7 c | 121.2 ± 2.1 a,b | 119.9 ± 1.0 a | 125.2 ± 1.3 b |
| PDI | 0.27 ± 0.01 b | 0.19 ± 0.02 a | 0.16 ± 0.03 a | 0.18 ± 0,01 a | |
| ζ-potential (mV) | −32.7 ± 0.1 a | −27.6 ± 1.1 c | −29.8 ± 1.2 b | −33.4 ± 0.2 a | |
| EE (%) | 100.3 ± 0.8 a | 100.9 ± 3.3 a | 100.4 ± 1.2 a | 100.1 ± 1.1 a | |
| PEOC * | 3.15±0.03 a | 3.18 ± 0.10 a | 3.16 ± 0.04 a | 3.15 ± 0.03 a | |
| pH | 6.42 ± 0.03 a | 6.34 ± 0.05 a | 6.41 ± 0.04 a | 6.42 ± 0.01 a | |
| IMG (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| OF12 | Size (nm) | 143.4 ± 0.8 b | 138.8 ± 2.3 a,b | 137.8 ± 1.3 a | 137.6 ± 2.4 a |
| PDI | 0.18 ± 0.00 a | 0.17 ± 0.02 a | 0.17 ± 0.01 a | 0.18 ± 0.00 a | |
| ζ-potential (mV) | −29.1 ± 0.7 a | −27.4 ± 0.1 a | −29.1 ± 1.6 a | −26.9 ± 0.5 a | |
| EE (%) | 102.7 ± 2.4 a | 101.4 ± 3.4 a | 102.9 ± 1.7 a | 102.5 ± 2.6 a | |
| PEOC * | 3.22 ± 0.07 a | 3.18 ± 0.11 a | 3.23 ± 0.05 a | 3.21 ± 0.08 a | |
| pH | 6.31 ± 0.03 a | 6.38 ± 0.03 a | 6.35 ± 0.03 a | 6.37 ± 0.05 a | |
| IMG (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| Formulations | Amount (%, w/w) | Proportions (w/w) | Pseudocomponents | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X1 | X2 | X3 | X1 | X2 | X3 | |
| F1 | 4.150 | 1.100 | 0.500 | 0.722 | 0.191 | 0.087 | 0.611 | 0.389 | 0.000 |
| F2 | 4.017 | 0.992 | 0.742 | 0.699 | 0.172 | 0.129 | 0.463 | 0.269 | 0.269 |
| F3 | 4.233 | 0.883 | 0.633 | 0.736 | 0.154 | 0.110 | 0.704 | 0.148 | 0.148 |
| F4 | 4.450 | 0.767 | 0.533 | 0.774 | 0.133 | 0.093 | 0.944 | 0.019 | 0.037 |
| F5 | 3.867 | 1.250 | 0.633 | 0.672 | 0.217 | 0.110 | 0.296 | 0.556 | 0.148 |
| F6 | 3.808 | 1.121 | 0.821 | 0.662 | 0.195 | 0.143 | 0.231 | 0.412 | 0.356 |
| F7 | 3.600 | 1.217 | 0.933 | 0.626 | 0.212 | 0.162 | 0.000 | 0.519 | 0.481 |
| F8 | 4.017 | 0.992 | 0.742 | 0.699 | 0.172 | 0.129 | 0.463 | 0.269 | 0.269 |
| F9 | 4.150 | 0.750 | 0.850 | 0.722 | 0.130 | 0.148 | 0.611 | 0.000 | 0.389 |
| F10 | 3.867 | 1.250 | 0.633 | 0.672 | 0.217 | 0.110 | 0.296 | 0.556 | 0.148 |
| F11 | 3.800 | 0.950 | 1.000 | 0.661 | 0.165 | 0.174 | 0.222 | 0.222 | 0.556 |
| F12 | 4.150 | 1.100 | 0.500 | 0.722 | 0.191 | 0.087 | 0.611 | 0.389 | 0.000 |
| F13 | 4.000 | 0.750 | 1.000 | 0.696 | 0.130 | 0.174 | 0.444 | 0.000 | 0.556 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uchida, D.T.; Siqueira, G.F.; dos Reis, E.M.; Hegeto, F.L.; Medina Neto, A.; Reis, A.V.; Bruschi, M.L.; Villa Nova, M.; Machinski Júnior, M. Design of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Containing Cymbopogon martinii (Palmarosa) Essential Oil against Aspergillus nomius. Molecules 2021, 26, 4825. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164825
Uchida DT, Siqueira GF, dos Reis EM, Hegeto FL, Medina Neto A, Reis AV, Bruschi ML, Villa Nova M, Machinski Júnior M. Design of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Containing Cymbopogon martinii (Palmarosa) Essential Oil against Aspergillus nomius. Molecules. 2021; 26(16):4825. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164825
Chicago/Turabian StyleUchida, Denise Tiemi, Gabriella Ferreira Siqueira, Edson Marques dos Reis, Fábio Luis Hegeto, Antonio Medina Neto, Adriano Valim Reis, Marcos Luciano Bruschi, Mônica Villa Nova, and Miguel Machinski Júnior. 2021. "Design of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Containing Cymbopogon martinii (Palmarosa) Essential Oil against Aspergillus nomius" Molecules 26, no. 16: 4825. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164825
APA StyleUchida, D. T., Siqueira, G. F., dos Reis, E. M., Hegeto, F. L., Medina Neto, A., Reis, A. V., Bruschi, M. L., Villa Nova, M., & Machinski Júnior, M. (2021). Design of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Containing Cymbopogon martinii (Palmarosa) Essential Oil against Aspergillus nomius. Molecules, 26(16), 4825. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164825







