Smartphone-Assisted Colorimetric Detection of Glutathione and Glutathione Reductase Activity in Human Serum and Mouse Liver Using Hemin/G-Quadruplex DNAzyme
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Principle of the Colorimetric Sensing Strategy
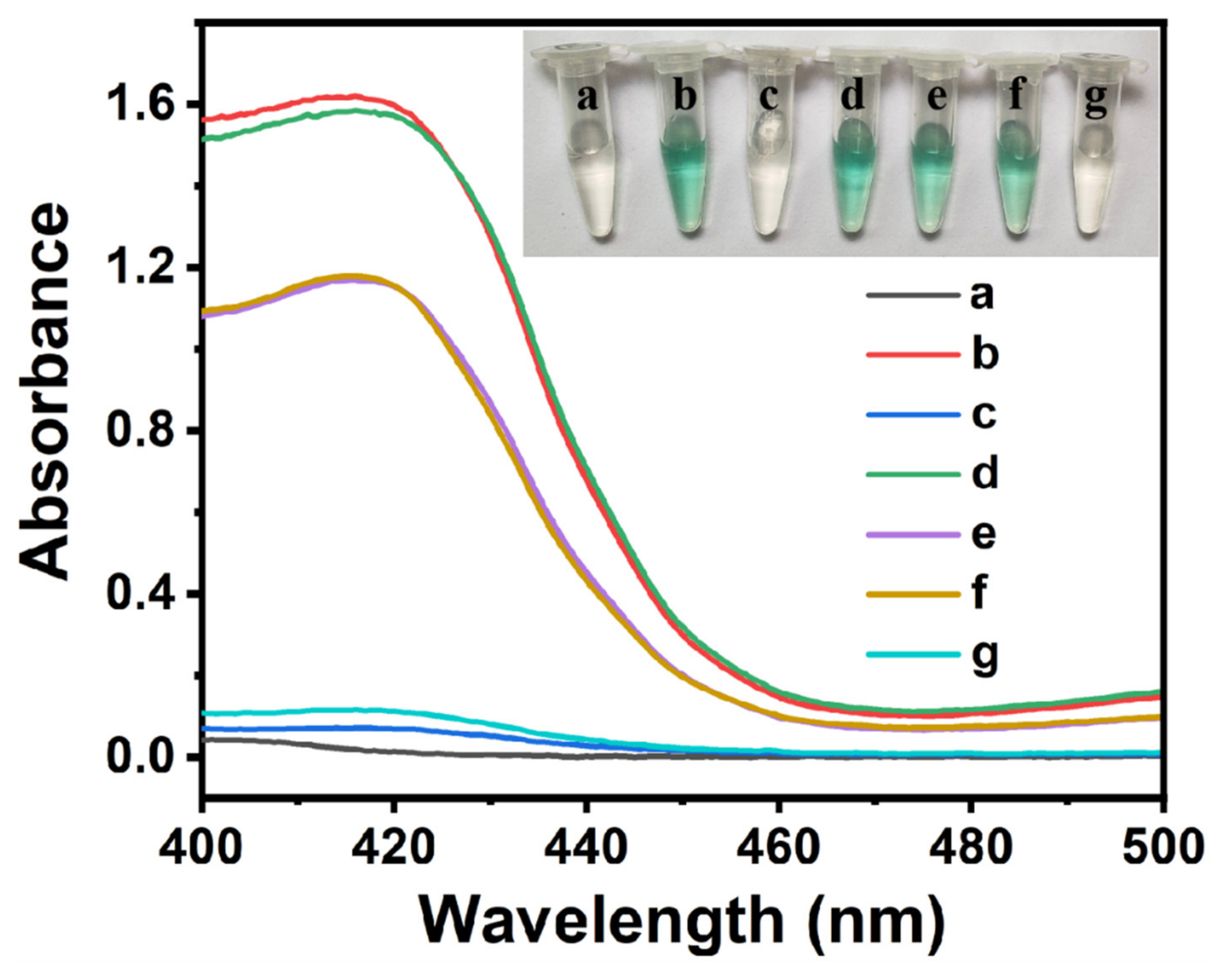
2.2. Feasibility of the Colorimetric Sensing Strategy
2.3. Optimization of the Experimental Conditions
2.4. Analytical Performance
2.5. Real Samples Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
3.3. Colorimetric Detection of GSH and GR
3.4. Selectivity of the Proposed Method
3.5. Determination of GSH and GR in Human Serum and Mouse Liver
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Meister, A.; Anderson, M.E. Glutathione. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1983, 52, 711–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Zhang, T.; Lv, S.; Jin, Q. Fluorescence turn-on assay for glutathione reductase activity based on a conjugated polyelectrolyte with multiple carboxylate groups. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 10901–10907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, D.M.; Tew, K.D.; Tapiero, H. The importance of glutathione in human disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2003, 57, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Li, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Xi, Z. A highly sensitive fluorescence probe for fast thiol-quantification assay of glutathione reductase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4034–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, B.S.; Orselli, S.M.; Rex, T.S. The redox couple between glutathione and ascorbic acid: A chemical and physiological perspective. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1994, 17, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovatta, I.; Tennant, R.S.; Helton, R.; Marr, R.A.; Singer, O.; Redwine, J.M.; Ellison, J.A.; Schadt, E.E.; Verna, I.M.; Lochart, D.J.; et al. Glyoxalase 1 and glutathione reductase regulate anxiety in inbred mouse strains. Nature 2005, 438, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.P.; Marinho, C.; Sequeira, R.; Apelt, N.; Laires, M.J.; Falcao, L.M.; Nogueira, J.B.; Bicho, M. Age related hypertension can be explained by a decrease in methemoglobin reductase and glutathione reductase activity. J. Hypertens. 2008, 26, S111. [Google Scholar]
- Manimaran, A.; Sarkar, S.N.; Sankar, P. Influence of repeated preexposure to arsenic on acetaminophen-induced oxidative stress in liver of male rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.F.; Zhang, C.; Song, J.; Ji, X.J.; Wang, W. Cytidine-gold nanoclusters as peroxidase mimetic for colorimetric detection of glutathione (GSH), glutathione disulfide (GSSG) and glutathione reductase (GR). Spectrochim. Acta A 2021, 250, 119316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, R.M.; Ma, L.; Han, X.; Ma, C.L.; Qu, F.L.; Xia, L. Hg2+-mediated stabilization of G-triplex based molecular beacon for label free fluorescence detection of Hg2+, reduced glutathione, and glutathione reductase activity. Spectrochim. Acta A 2020, 228, 117855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, X.E.; Sun, J.; Zhu, S.; Lei, C.; Li, R.; Gong, P.; Ling, B.; Wang, R.; Wang, H. Probing glutathione reductase activity with graphene quantum dots and gold nanoparticles system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 263, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Su, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Fang, D.; Wang, X. Unexpected thiols triggering photoluminescent enhancement of cytidine stabilized au nanoclusters for sensitive assays of glutathione reductase and its inhibitors screening. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4766–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Ning, G.; Chu, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. A sensitive and simple impedance sensing strategy for glutathione and glutathione reductase activity detection. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 74, 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Tietze, F. Enzymic method for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione. Anal. Biochem. 1969, 27, 502–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.; Kode, A.; Biswas, S.K. Assay for quantitative determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide levels using enzymatic recycling method. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 1, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wei, W.; Qu, X. Colorimetric biosensing using smart materials. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4215–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.; Sharon, E.; Teller, C.; Henning, A.; Tzfati, Y.; Willner, I. DNAzyme-like activity of hemin-telomeric G-quadruplexes for the optical analysis of telomerase and its inhibitors. ChemBioChem 2010, 11, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.M.; Niu, F.N.; Yu, A.M.; Lai, G.S. Proximity binding-triggered assembly of two MNAzymes for catalyzed release of G-quadruplex DNAzymes and an ultrasensitive homogeneous bioassay of platelet-derived growth factor. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.N.; Guo, R.; Wei, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhao, X.Y.; Xu, Z.R. Sensitive multicolor visual detection of telomerase activity based on catalytic hairpin assembly and etching of Au nanorods. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 122, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.M.; Zou, L.; Luo, Y.W.; Ling, L.S. Ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of circulating tumor DNA using hybridization chain reaction and the pivot of triplex DNA. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.R.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zheng, F.Q.; Wang, S.X.; Zhang, D.H.; Wang, J.L. A portable system for on-site quantification of formaldehyde in air based on G-quadruplex halves coupled with A smartphone reader. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, E.; Ravan, H.; Mohammadi, A.; Pourghadamyari, H. Colorimetric detection of miRNA-21 by DNAzyme-coupled branched DNA constructs. Talanta 2020, 216, 120913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Yang, L.; Chu, S.Y.; Liu, B.H.; Zhang, Q.K.; Zou, L.M.; Yu, S.M.; Jiang, C.L. Semiquantitative visual detection of lead ions with a smartphone via a colorimetric paper-based analytical device. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 9292–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.J.; Ma, X.H.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Miao, L.J.; Zhou, Z.W.; Shen, Z.Y.; Wu, A.G. High-performance colorimetric detection of thiosulfate by using silver nanoparticles for smartphone-based analysis. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.K.; Tseng, W.B.; Wu, M.J.; Alagarsamy, A.S.K.K.; Tseng, W.L.; Lin, P.C. Polyadenosine-based fluorescent probe for reversible pH sensing based on protonated adenine-adenine base pairs: Applications to sensing of enzyme substrate system and enzymatic logic gates. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, Y.; Bothra, S.; Kumar, R.; Sahoo, S.K. Smartphone-assisted colorimetric detection of Cr3+ using vitamin B6 cofactor functionalized gold nanoparticles and its applications in real sample analyses. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 6892–6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, C.L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Ding, F.; Zou, P.; Wang, X.X.; Zhao, Q.B.; Rao, H.B. Ultrathin films of a metal-organic framework prepared from 2-methylimidazole, manganese(II) and cobalt(II) with strong oxidase-mimicking activity for colorimetric determination of glutathione and glutathione reductase activity. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delides, A.; Spooner, R.J.; Goldberg, D.M.; Neal, F.E. An optimized semi-automatic rate method for serum glutathione reductase activity and its application to patients with malignant disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 1976, 29, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Analyte | Added | Found | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSH (µM) | 0 | 2.26 ± 0.13 | – | 5.93 |
| 0.5 | 2.99 ± 0.07 | 108.54 | 2.22 | |
| 2 | 4.39 ± 0.34 | 103.12 | 7.66 | |
| 25 | 26.92 ± 0.39 | 98.77 | 1.45 | |
| GR (mU/mL) | 0 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | – | 8.05 |
| 0.05 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 108.86 | 9.27 | |
| 0.2 | 0.40 ± 0.04 | 108.46 | 8.79 | |
| 2 | 2.26 ± 0.13 | 104.02 | 5.90 |
| Analyte | Added | Found | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSH 2 (nmol/g) | 0 | 89.87 ± 8.41 | – | 9.36 |
| 30 | 117.88 ± 0.96 | 98.34 | 0.82 | |
| 120 | 220.95 ± 15.71 | 105.28 | 7.11 | |
| 600 | 663.37 ± 48.04 | 96.16 | 7.24 | |
| GR 3 (U/g) | 0 | 3.48 ± 0.25 | – | 7.29 |
| 0.6 | 4.12 ± 0.22 | 100.98 | 5.42 | |
| 3 | 6.67 ± 0.52 | 102.94 | 7.81 | |
| 15 | 19.08 ± 1.35 | 103.21 | 7.07 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, Y.; Li, M.; Liao, X.; Zou, L. Smartphone-Assisted Colorimetric Detection of Glutathione and Glutathione Reductase Activity in Human Serum and Mouse Liver Using Hemin/G-Quadruplex DNAzyme. Molecules 2021, 26, 5016. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165016
Lai Y, Li M, Liao X, Zou L. Smartphone-Assisted Colorimetric Detection of Glutathione and Glutathione Reductase Activity in Human Serum and Mouse Liver Using Hemin/G-Quadruplex DNAzyme. Molecules. 2021; 26(16):5016. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165016
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Yufen, Mengyan Li, Xiaofei Liao, and Li Zou. 2021. "Smartphone-Assisted Colorimetric Detection of Glutathione and Glutathione Reductase Activity in Human Serum and Mouse Liver Using Hemin/G-Quadruplex DNAzyme" Molecules 26, no. 16: 5016. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165016
APA StyleLai, Y., Li, M., Liao, X., & Zou, L. (2021). Smartphone-Assisted Colorimetric Detection of Glutathione and Glutathione Reductase Activity in Human Serum and Mouse Liver Using Hemin/G-Quadruplex DNAzyme. Molecules, 26(16), 5016. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165016






