Systematic Review on Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Antibacterial Activities: Application and Theoretical Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Step 1: Formulating the Problem
2.2. Step 2: Literature Searches for Research Syntheses
2.3. Step 3: Data Extraction
2.4. Step 4: Evaluate the Quality of Primary Data and Research Synthesis
2.5. Step 5: Meta-Analyzing and Integrating Their Outcomes of the Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included Studies
3.2. Silver Nanoparticles Reduction through Plant Extract as Reducing Agents
3.3. Synthesis
3.4. Size in Relation with Antibacterial Activity
4. Discussion
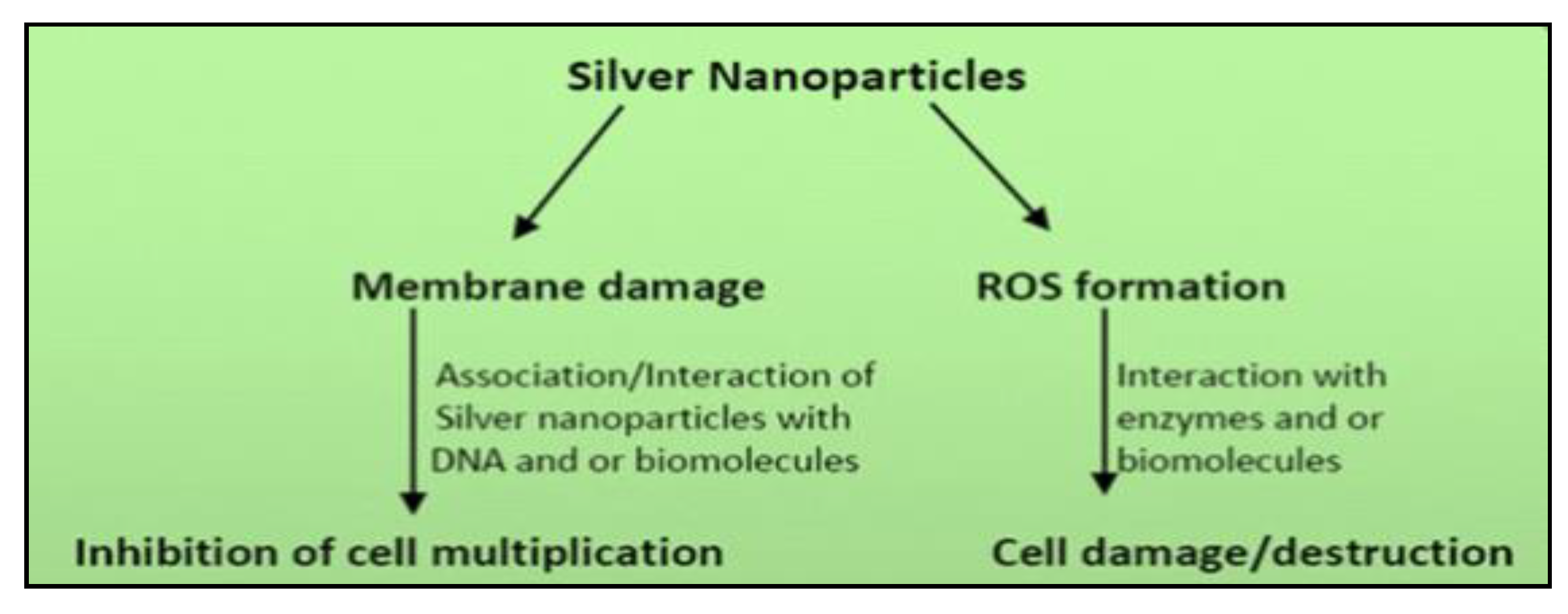
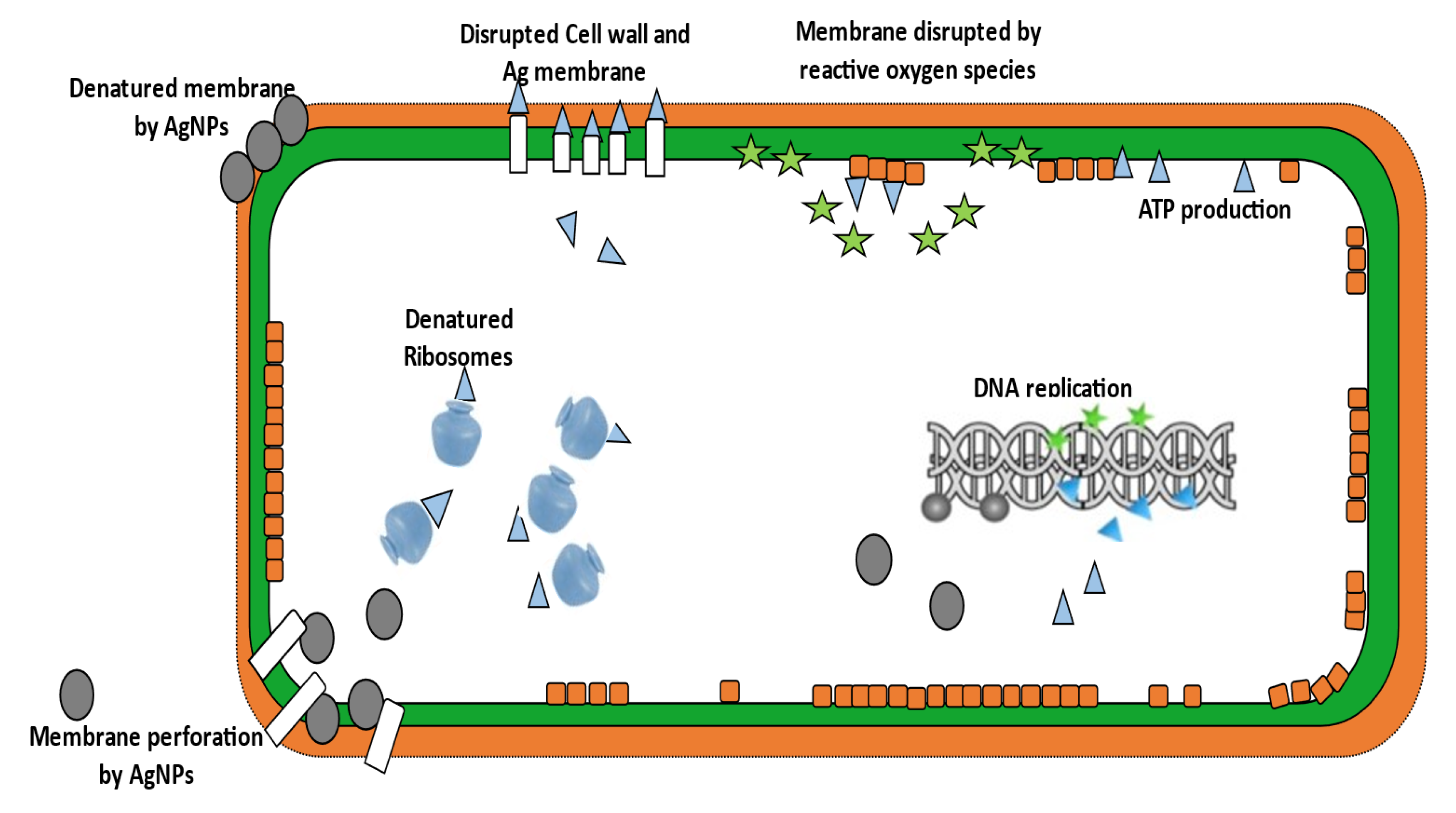
4.1. Ag-NPs Application and Mechanism of Action
4.2. ROS-Based Antibacterial Effects of Silver Ions
4.3. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
4.4. Ag-NPs Application
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rao, M.L.; Savithramma, N. Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Svensonia Hyderabadensis leaf extract and evaluation of their antimicrobial efficacy. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2011, 3, 1117. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Jun, B.H. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis and application for nanomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yousaf, H.; Mehmood, A.; Ahmad, K.S.; Raffi, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications as an alternative antibacterial and antioxidant agent. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dastjerdi, R.; Montazer, M. A review on the application of inorganic nano-structured materials in the modification of textiles: Focus on anti-microbial properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.V. Photophysical, photochemical and photocatalytic aspects of metal nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 7729–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Rycenga, M.; Skrabalak, S.E.; Wiley, B.; Xia, Y. Chemical synthesis of novel plasmonic nanoparticles. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2009, 60, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiriou, G.A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Antibacterial activity of nanosilver ions and particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Su, S.; He, Y.; Huang, Q.; Hu, W.; Li, D.; Fan, C.; Lee, S.T. Long-term antimicrobial effect of silicon nanowires decorated with silver nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Saraswathi, A.; Indi, S.S.; Hoti, S.L.; Vasan, H.N. Ag@ AgI, core@ shell structure in agarose matrix as hybrid: Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8550–8561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Z.M.; Zhang, Q.B.; Puppala, H.L.; Colvin, V.L.; Alvarez, P.J. Negligible particle-specific antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4271–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterisation, Properties, Applications, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Science 2002, 298, 2176–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiley, B.; Sun, Y.; Mayers, B.; Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of metal nanostructures: The case of silver. Chem. A Eur. J. 2005, 11, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El-Nour, K.M.; Eftaiha, A.A.; Al-Warthan, A.; Ammar, R.A. Synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 2010, 3, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, L. A facile method to prepare size-tunable silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial mechanism. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Gu, X.; He, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, L. Synthesis of silver nanoparticle-decorated hydroxyapatite (HA@ Ag) poriferous nanocomposites and the study of their antibacterial activities. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 41722–41730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang, C.Y.; et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Jin, W.; Qasim, A.M.; Gao, A.; Peng, X.; Li, W.; Feng, H.; Chu, P.K. Antibacterial effects of titanium embedded with silver nanoparticles based on electron-transfer-induced reactive oxygen species. Biomaterials 2017, 124, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ouay, B.; Stellacci, F. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: A surface science insight. Nano Today 2015, 10, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, S.; Liu, L.; Li, L. Flexible antibacterial film based on conjugated polyelectrolyte/silver nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 9051–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, M.; Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Ullah, A.A.; Hossain, K.F.; Banik, S.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. A systematic review on silver nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity: Physicochemical properties and perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröfel, A.; Kratošová, G.; Šafařík, I.; Šafaříková, M.; Raška, I.; Shor, L.M. Applications of biosynthesized metallic nanoparticles—A review. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4023–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.K.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharissova, O.V.; Dias, H.R.; Kharisov, B.I.; Pérez, B.O.; Pérez, V.M. The greener synthesis of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumel, A.M.; Surayya, M.M.; Yaro, M.N.; Waziri, I.Z.; Amina, A.A. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its synergistic antimicrobial potency: An overview. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 6, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- SivaKumar, T.; Rathimeena, T.; Thangapandian, V.; Shankar, T. Silver nanoparticles synthesis of Mentha arvensis extracts and evaluation of antioxidant properties. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 1, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Prabu, H.J.; Johnson, I. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized from plant leaf extract of Cycas circinalis, Ficus amplissima, Commelina benghalensis and Lippia nodiflora leaves. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 443–449. [Google Scholar]
- Arokiyaraj, S.; Arasu, M.V.; Vincent, S.; Prakash, N.U.; Choi, S.H.; Oh, Y.K.; Choi, K.C.; Kim, K.H. Rapid green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Chrysanthemum indicum L and its antibacterial and cytotoxic effects: An in vitro study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murugan, K.; Senthilkumar, B.; Senbagam, D.; Al-Sohaibani, S. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Acacia leucophloea extract and their antibacterial activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2431. [Google Scholar]
- Gurunathan, S.; Raman, J.; Abd Malek, S.N.; John, P.A.; Vikineswary, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ganoderma neo-japonicum Imazeki: A potential cytotoxic agent against breast cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4399. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, H.; Koenka, A.C. The overview of reviews: Unique challenges and opportunities when research syntheses are the principal elements of new integrative scholarship. Am. Psychol. 2012, 67, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shea, B.J.; Grimshaw, J.M.; Wells, G.A.; Boers, M.; Andersson, N.; Hamel, C.; Porter, A.C.; Tugwell, P.; Moher, D.; Bouter, L.M. Development of AMSTAR: A measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2007, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pieper, D.; Mathes, T.; Eikermann, M. Impact of choice of quality appraisal tool for systematic reviews in overviews. J. Evid. Based Med. 2014, 7, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costas, R.; Bordons, M. Do age and professional rank influence the order of authorship in scientific publications? Some evidence from a micro-level perspective. Scientometrics 2011, 88, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun’an Qing, L.C.; Li, R.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y. Potential antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic implants by advanced modification technologies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Gautam, P.K.; Verma, A.; Singh, V.; Shivapriya, P.M.; Shivalkar, S.; Sahoo, A.K.; Samanta, S.K. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles as effective alternatives to treat antibiotics resistant bacterial infections: A review. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 25, e00427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.O.; Janjua-Sharif, F.N.; Ali, H.; Ahmed, F. Systematic reviews explained: AMSTAR-how to tell the good from the bad and the ugly. Oral Health Dent. Manag. 2013, 12, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.U.; Anjum, S.I.; Ansari, M.J.; Khan, M.H.; Kamal, S.; Rahman, K.; Shoaib, M.; Man, S.; Khan, A.J.; Khan, S.U.; et al. Antimicrobial potentials of medicinal plant’s extract and their derived silver nanoparticles: A focus on honey bee pathogen. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1815–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Ashraf, N.; Ashraf, T.; Zhou, R.B.; Yin, D.C. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles (MNPs) by plants and microbes: Their cellular uptake, biocompatibility, and biomedical applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 2913–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Singh, L.; Mishra, S. Biosynthetic silver nanoparticles-current trends and future scope: An overview. IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2019, 14, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.; Bulut, O.; Some, S.; Mandal, A.K.; Yilmaz, M.D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Biomolecule-nanoparticle organizations targeting antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2673–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Mahmoudi-Gom Yek, S.; Motahharifar, N.; Ghafori Gorab, M. Recent developments in the plant-mediated green synthesis of Ag-based nanoparticles for environmental and catalytic applications. Chem. Rec. 2019, 19, 2436–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Rizvi, R.; Mahmood, I. Biofabrication of silver nanoparticles from various plant extracts: Blessing to nanotechnology. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 99, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, P.; Ali, N.; Rahman, L.; Ali, M.; Shinwari, Z.K. Antimicrobial activities of biologically synthesized metal nanoparticles: An insight into the mechanism of action. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 24, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Some, S.; Sen, I.K.; Mandal, A.; Aslan, T.; Ustun, Y.; Yilmaz, E.Ş.; Katı, A.; Demirbas, A.; Mandal, A.K.; Ocsoy, I. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their versatile antimicrobial properties. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 6, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimirad, S.; Ajalloueian, F.; Ghorbanpour, M. Synthesis and therapeutic potential of silver nanomaterials derived from plant extracts. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 260–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shafey, A.M. Green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles from plant leaf extracts and their applications: A review. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 304–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Houreld, N.N.; Kroukamp, E.M.; Abrahamse, H. Cellular imaging and bactericidal mechanism of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles against human pathogenic bacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 178, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, A.; Naomi, R.; Utami, N.D.; Mohammad, A.W.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mustafa, N.; Fauzi, M.B. The potential of silver nanoparticles for antiviral and antibacterial applications: A mechanism of action. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, Z.; Nemmar, A. Health impact of silver nanoparticles: A review of the biodistribution and toxicity following various routes of exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, I.X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, I.S.; Mei, M.L.; Li, Q.; Chu, C.H. The antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and its application in dentistry. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, S.; Munir, S.; Zeb, N.; Ullah, A.; Khan, B.; Ali, J.; Bilal, M.; Omer, M.; Alamzeb, M.; Salman, S.M.; et al. Green nanotechnology: A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles—An ecofriendly approach. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Escárcega-González, C.E.; Garza-Cervantes, J.A.; Vazquez-Rodríguez, A.; Montelongo-Peralta, L.Z.; Treviño-Gonzalez, M.T.; Castro, E.D.; Saucedo-Salazar, E.M.; Morales, R.C.; Soto, D.R.; González, F.T.; et al. In vivo antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles produced via a green chemistry synthesis using Acacia rigidula as a reducing and capping agent. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagar, N.; Devra, V. Green synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica leaves. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 213, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, O.V.; Mikhailova, E.O. Elemental silver nanoparticles: Biosynthesis and bio applications. Materials 2019, 12, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamelian, M.; Zangeneh, M.M.; Amisama, A.; Varmira, K.; Veisi, H. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Thymus kotschyanus extract and evaluation of their antioxidant, antibacterial and cytotoxic effects. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, H.; Zafar, A.; Rasheed, M.N.; Ali, Z.; Mehmood, K.; Mazher, A.; Hasan, M.; Mahmood, N. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Fagonia cretica and their antimicrobial activities. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haqq, S.M.; Pandey, H.I.; Gerard, M.A.; Chattree, A.M. Bio-fabrication of silver nanoparticles using Chrysanthemum coronarium flower extract and It’s in vitro antibacterial activity. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2018, 10, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, N.M.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Timmiati, S.N. Green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles via plant extracts: An overview. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 112004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aragao, A.P.; de Oliveira, T.M.; Quelemes, P.V.; Perfeito, M.L.; Araujo, M.C.; Santiago, J.D.; Cardoso, V.S.; Quaresma, P.; de Almeida, J.R.; da Silva, D.A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the seaweed Gracilaria birdiae and their antibacterial activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 4182–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasnain, M.S.; Javed, M.N.; Alam, M.S.; Rishishwar, P.; Rishishwar, S.; Ali, S.; Nayak, A.K.; Beg, S. Purple heart plant leaves extract-mediated silver nanoparticle synthesis: Optimization by Box-Behnken design. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, C.A.; Kumar, V.G.; Dhas, T.S.; Karthick, V.; Govindaraju, K.; Joselin, J.M.; Baalamurugan, J. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles (biosynthesis): A short review on recent advances. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 27, 101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Lee, Y.I.; Shim, I.K.; Jun, B.H.; Cho, H.J.; Joung, J.W. Large-scale synthesis of polymer-stabilized silver nanoparticles. In Solid State Phenomena; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Freienbach, Switzerland, 2007; Volume 124, pp. 1189–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, M.A.; Kanwal, Z.; Rauf, A.; Sabri, A.N.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Size-and shape-dependent antibacterial studies of silver nanoparticles synthesized by wet chemical routes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, H.; Du, J.; Singh, P.; Yi, T.H. Ecofriendly synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by Euphrasia officinalis leaf extract and its biomedical applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patil, S.; Chandrasekaran, R. Biogenic nanoparticles: A comprehensive perspective in synthesis, characterization, application and its challenges. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2020, 18, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibrov, P.; Dzioba, J.; Gosink, K.K.; Häse, C.C. Chemiosmotic mechanism of antimicrobial activity of Ag+ in Vibrio cholerae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2668–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reidy, B.; Haase, A.; Luch, A.; Dawson, K.A.; Lynch, I. Mechanisms of silver nanoparticle release, transformation and toxicity: A critical review of current knowledge and recommendations for future studies and applications. Materials 2013, 6, 2295–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bragg, P.D.; Rainnie, D.J. The effect of silver ions on the respiratory chain of Escherichia coli. Can. J. Microbiol. 1974, 20, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holt, K.B.; Bard, A.J. Interaction of silver (I) ions with the respiratory chain of Escherichia coli: An electrochemical and scanning electrochemical microscopy study of the antimicrobial mechanism of micromolar Ag+. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 13214–13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klueh, U.; Wagner, V.; Kelly, S.; Johnson, A.; Bryers, J.D. Efficacy of silver-coated fabric to prevent bacterial colonization and subsequent device-based biofilm formation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2000, 53, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, M.; Hara, K.; Kudo, J. Bactericidal actions of a silver ion solution on Escherichia coli, studied by energy-filtering transmission electron microscopy and proteomic analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 7589–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, W.K.; Koo, H.C.; Kim, K.W.; Shin, S.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.H. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of the silver ion in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Carballo, G.; Higueras, L.; Gavara, R.; Hernández-Muñoz, P. Silver ions release from antibacterial chitosan films containing in situ generated silver nanoparticles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Husen, A.; Rao, R.A. A review on biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biocidal properties. J. Nanobiotechnology 2018, 16, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Zheng, J. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: Structural effects. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapat, R.A.; Chaubal, T.V.; Joshi, C.P.; Bapat, P.R.; Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; Gorain, B.; Kesharwani, P. An overview of application of silver nanoparticles for biomaterials in dentistry. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 881–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorrami, S.; Zarrabi, A.; Khaleghi, M.; Danaei, M.; Mozafari, M.R. Selective cytotoxicity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles against the MCF-7 tumor cell line and their enhanced antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramkumar, V.S.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Sivagurunathan, P.; Saratale, G.D.; Dung, T.N.; Kannapiran, E. Biofabrication and characterization of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of seaweed Enteromorpha compressa and its biomedical properties. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Nakazato, G.; Seabra, A.B. Antimicrobial activity of biogenic silver nanoparticles, and silver chloride nanoparticles: An overview and comments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6555–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, S.; Pastar, I.; Drakulich, S.; Dikici, E.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Deo, S.; Daunert, S. Nanotechnology-driven therapeutic interventions in wound healing: Potential uses and applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naraginti, S.; Kumari, P.L.; Das, R.K.; Sivakumar, A.; Patil, S.H.; Andhalkar, V.V. Amelioration of excision wounds by topical application of green synthesized, formulated silver and gold nanoparticles in albino Wistar rats. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, D.; Chatterjee, S. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using guava (Psidium guajava) leaf extract and its antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahsan, A.; Farooq, M.A.; Ahsan Bajwa, A.; Parveen, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Parthenium hysterophorus: Optimization, characterization and in vitro therapeutic evaluation. Molecules 2020, 25, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelere, I.A.; Lateef, A.; Aboyeji, D.O.; Abdulsalam, R.; Adabara, N.U.; Bala, J.D. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Extract of Buchholzia Coriacea (Wonderful Kola) Seeds and Their Antimicrobial Activities. Ann. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 18, 671–679. [Google Scholar]
- Saratale, R.G.; Benelli, G.; Kumar, G.; Kim, D.S.; Saratale, G.D. Bio-fabrication of silver nanoparticles using the leaf extract of an ancient herbal medicine, dandelion (Taraxacum officinale), evaluation of their antioxidant, anticancer potential, and antimicrobial activity against phytopathogens. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10392–10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakkala, J.R.; Mata, R.; Gupta, A.K.; Sadras, S.R. Biological activities of green silver nanoparticles synthesized with Acorous calamus rhizome extract. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 85, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Lu, C.; Tang, M.; Yang, Z.; Jia, W.; Ma, Y.; Jia, P.; Pei, D.; Wang, H. Nanotoxicity of silver nanoparticles on HEK293T cells: A combined study using biomechanical and biological techniques. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6770–6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franci, G.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S.; Palomba, L.; Rai, M.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 8856–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.; Kim, Y.J.; Singh, H.; Wang, C.; Hwang, K.H.; Farh, M.E.; Yang, D.C. Biosynthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial applications of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 2567. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelghany, T.M.; Al-Rajhi, A.M.; Al Abboud, M.A.; Alawlaqi, M.M.; Magdah, A.G.; Helmy, E.A.; Mabrouk, A.S. Recent advances in green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications: About future directions. A review. BioNanoScience 2018, 8, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, Y.K.; Panda, S.K.; Bastia, A.K.; Mohanta, T.K. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Protium serratum and investigation of their potential impacts on food safety and control. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, P.; Mehta, A.; Kachhwaha, S.; Kothari, S.L. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2013, 5, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Gaikar, V.G.; Sen, D.; Mazumder, S.; Pandita, N.S. Phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using walnut (Juglans regia) bark with characterization of the antibacterial activity against Streptococcus mutans. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 690–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.S.; Kokate, M.R.; Kolekar, S.S. Bioinspired synthesis of highly stabilized silver nanoparticles using Ocimum tenuiflorum leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 91, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.; Bairwa, V.K.; Kachhwaha, S.; Kothari, S.L. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using callus extract of Capsicum annuum L. and their activity against microorganisms. Int. J. Nanotechnol. Appl. 2014, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Krutyakov, Y.A.; Kudrinskiy, A.A.; Olenin, A.Y.; Lisichkin, G.V. Synthesis and properties of silver nanoparticles: Advances and prospects. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2008, 77, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhai, A. Preparation of microsized silver crystals with different morphologies by a wet-chemical method. Rare Met. 2010, 29, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintelu, S.A.; Olugbeko, S.C.; Folorunso, F.A.; Oyebamiji, A.K.; Folorunso, A.S. Characterization and pharmacological efficacy of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized using the bark extract of Garcinia kola. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 2876019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Quality Assessment Tool AMSTAR | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | Score | |
| 1 | Khan et al. 2018 [39] | 1 | CA | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| 2 | Ahmed et al.2019 [40] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| 3 | Mishra et al. 2019 [41] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| 4 | Roy et al. 2019 [42] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| 5 | Nasrollahzadeh et al. 2019 [43] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| 6 | Zafar et al. 2019 [44] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| 7 | Nisar et al. 2019 [45] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| 8 | Some et al. 2018 [46] | 1 | 0 | 1 | CA | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| 9 | Fahimirad et al. 2019 [47] | 1 | 0 | 1 | CA | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| 10 | ElShafey 2020 [48] | 1 | 0 | 1 | CA | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| 11 | Kumar et al. 2018 [49] | 1 | 0 | 1 | CA | 0 | 1 | NA | 0 | NA | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| 12 | Singh et al. 2020 [37] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| 13 | Salleh et al. 2020 [50] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| 14 | Yun’an Qing et al. 2018 [36] | 1 | CA | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | CA | 1 | 6 |
| 15 | Ferdous 2020 [51] | 1 | CA | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| 16 | Yin et al. 2020 [52] | 1 | CA | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| 17 | Ahmad et al. 2019 [53] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| 18 | Gumel et al. 2019 [25] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | CA | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| 19 | Escárcega-González et al. 2018 [54] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| 20 | Nagar et al. 2018 [55] | 1 | CA | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 0 | 1 | 5 |
| 21 | Mikhailov et al. 2018 [56] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 0 | NA | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| 22 | Hamelian et al 2018 [57] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 0 | 1 | 4 |
| 23 | Zulfiqar et al. 2018 [58] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | NA | 0 | NA | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| 24 | Haqq 2018 [59] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | NA | 0 | NA | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| 25 | Ishak et al. 2019 [60] | 1 | 0 | CA | 0 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| 26 | de Aragao et al. 2019 [61] | 1 | 0 | CA | 0 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| 27 | Hasnain Met al. 2019 [62] | 1 | 0 | CA | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| 28 | Das et al. 2020 [63] | 1 | 0 | CA | 1 | 0 | 1 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| S. No | Eligibility Item |
|---|---|
| 1. | Provided with the prior design. |
| 2. | Extraction of data and selection of duplicate study is made. |
| 3. | Literature has been searched comprehensively. |
| 4. | The publication has passed the inclusion criteria. |
| 5. | An index of articles (with inclusion and/or exclusion) is given. |
| 6. | Features of included articles are provided. |
| 7. | The scientific quality of the included studies was evaluated before documenting. |
| 8. | The scientific quality of the included studies was used to formulate conclusions. |
| 9. | Appropriate methods were used to combine the studies’ findings. |
| 10. | The likelihood of publication bias was assessed. |
| 11. | The conflict of interest was stated. |
| Author | Year | Objective of Study | Summary Finding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yun’an Qing et al. [36] | 2018 |
|
|
| Ferdous [51] | 2020 |
|
|
| Yin et al. [52] | 2020 |
|
|
| Ahmad et al. [53] | 2019 |
|
|
| Hamelian et al. [57] | 2018 |
|
|
| Gumel et al. [26] | 2019 |
|
|
| Escárcega-González et al. [54] | 2018 |
|
|
| Nagar et al. [55] | 2018 |
|
|
| Ahmad et al. [40] | 2019 |
|
|
| Mishra et al. [41] | 2019 |
|
|
| Mikhailov et al. [56] | 2018 |
|
|
| Roy et al. [42] | 2019 |
|
|
| Zulfiqar et al. [58] | 2019 |
|
|
| Nasrollahzadeh et al. [43] | 2019 |
|
|
| Zafar et al. [44] | 2019 |
|
|
| Nisar et al. [45] | 2019 |
|
|
| Some et al. [46] | 2019 |
|
|
| Haqq et al. [59] | 2018 |
|
|
| Ishak et al. 2019 [60] | 2019 |
|
|
| El Shafey [48] | 2020 |
|
|
| de Aragao et al. [61] | 2019 |
|
|
| Hasnain et al. 2019 [62] | 2019 |
|
|
| Khan et al. [39] | 2018 |
|
|
| Kumar et al. [49] | 2019 |
|
|
| Fahimirad et al. [47] |
|
| |
| Singh et al. [36] | 2020 |
|
|
| Das et al. [63] | 2020 |
|
|
| Salleh et al. [50] | 2020 |
|
|
| Plant | Used Component for the Synthesis | Size (nm) | Shape | Bacterial Impact | Bio-Functionalizing Compounds | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thymus kotschyanus | Extract | 50–60 | Spherical | Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus | Protein | [58] |
| Juglans regia (Bark) | Leaf | 15–30 | Cubic and smooth | Streptococcus mutans | Flavonoids | [63] |
| Seaweed ulva flexuosa | Extract | 42–83 | Spherical | Antibacterial action against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus | Protein | [44] |
| Acacia rigidula | Extract | 8–60 | Spherical | Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, P. aeruginosa | Phenol compound | [45] |
| Azadirachta indica | Leaf | 48 | Cubic | E. coli | Protein | [46] |
| Ocimum tenuiflorum | Extract | 25–40 | Linear | E. coli and B. subtilis | Flavonoids | [47] |
| Elephantopus scaber | Extract | 37 | Spherical | B. subtilis, L. lactis, P. aeruginosa, A. penicillioides | Proteins | [50] |
| Fagonia cretica | Extract | 16 | Spherical | Proteus vulgaris, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae | Hydroxyl and secondary amines | [51] |
| Carica papaya (Papaya) | Leaf | 60–80 | Spherical | Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus | Proteins | [52] |
| Argemone mexicana | Leaf | 30 | Cubic | E. coli and B. subtilis | Leaf proteins and metabolites | [53] |
| Datura stramonium | Leaf | 15–20 | Spherical | Streptococcus mutans | Flavonoids, terpenoids | [54] |
| Cola nitida pod | Extract | 12–80 | Cubic | E. coli, P. aeruginosa and Klebsiella | Protein | [52] |
| Taraxacum officinale | Leaf | 15 | Cubic and hexagonal | Xanthomonas axonopodis and P. syringae | Flavonoids, terpenoids, and triterpenes | [26] |
| Rosa indica | Leaf | 1–100 | spherical | P. aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis | Polyphenol | [55] |
| Phoenix dactylifera | 15–40 | Cubic | E. coli | Polyphenols, lipids, and fatty acids | [53] | |
| Mangosteen | Extract | 30 | Spherical | E. coli and S. aureus | Flavonoids | [58] |
| Rheum palmatum root | Extract | 121 | Cubic | S. aureus and P. aeruginosa | Flavonoids, terpenoids | [64] |
| Prunus japonica | Extract | 26 | Spherical | Proteus vulgaris | Protein | [59] |
| Boerhaaviadiffusa | 25 | F. ranchiophilum | Phenol | [60] | ||
| Banana peel | Extract | 23.7 | Cubic | E. coli, P. aeruginosa | Lips and fatty acids | [61] |
| Aloe vera | leaf | 15.2 | Cubic | S. aureus | Protein | [62] |
| Pelargonium graveolens (Geranium) | Leaves | 16–40 | Spherical | E. coli, P. aeruginosa | Flavonoids | [63] |
| Sargassum wightii | Extract | 68.04 | Cubic | S. aureus and P. aeruginosa | Protein | [26] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qamer, S.; Romli, M.H.; Che-Hamzah, F.; Misni, N.; Joseph, N.M.S.; AL-Haj, N.A.; Amin-Nordin, S. Systematic Review on Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Antibacterial Activities: Application and Theoretical Perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 5057. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165057
Qamer S, Romli MH, Che-Hamzah F, Misni N, Joseph NMS, AL-Haj NA, Amin-Nordin S. Systematic Review on Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Antibacterial Activities: Application and Theoretical Perspectives. Molecules. 2021; 26(16):5057. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165057
Chicago/Turabian StyleQamer, Shafqat, Muhammad Hibatullah Romli, Fahrudin Che-Hamzah, Norashiqin Misni, Narcisse M. S. Joseph, Nagi A. AL-Haj, and Syafinaz Amin-Nordin. 2021. "Systematic Review on Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Antibacterial Activities: Application and Theoretical Perspectives" Molecules 26, no. 16: 5057. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165057
APA StyleQamer, S., Romli, M. H., Che-Hamzah, F., Misni, N., Joseph, N. M. S., AL-Haj, N. A., & Amin-Nordin, S. (2021). Systematic Review on Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Antibacterial Activities: Application and Theoretical Perspectives. Molecules, 26(16), 5057. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165057






