Bioactive Electrospun Fibers of Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Incorporating α-Tocopherol for Food Packaging Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of PCL/α-Tocopherol Solutions
2.3. Rheology of PCL/α-Tocopherol Solutions
2.4. Electrospinning
2.5. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.7. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.8. Water Contact Angle Measurements (WCA)
2.9. DPPH Antioxidant Assay
2.10. ABTS Antioxidant Assay
2.11. Migration Study of α-Tocopherol from PCL/αT Electrospun Fiber Coatings
3. Results and Discussion
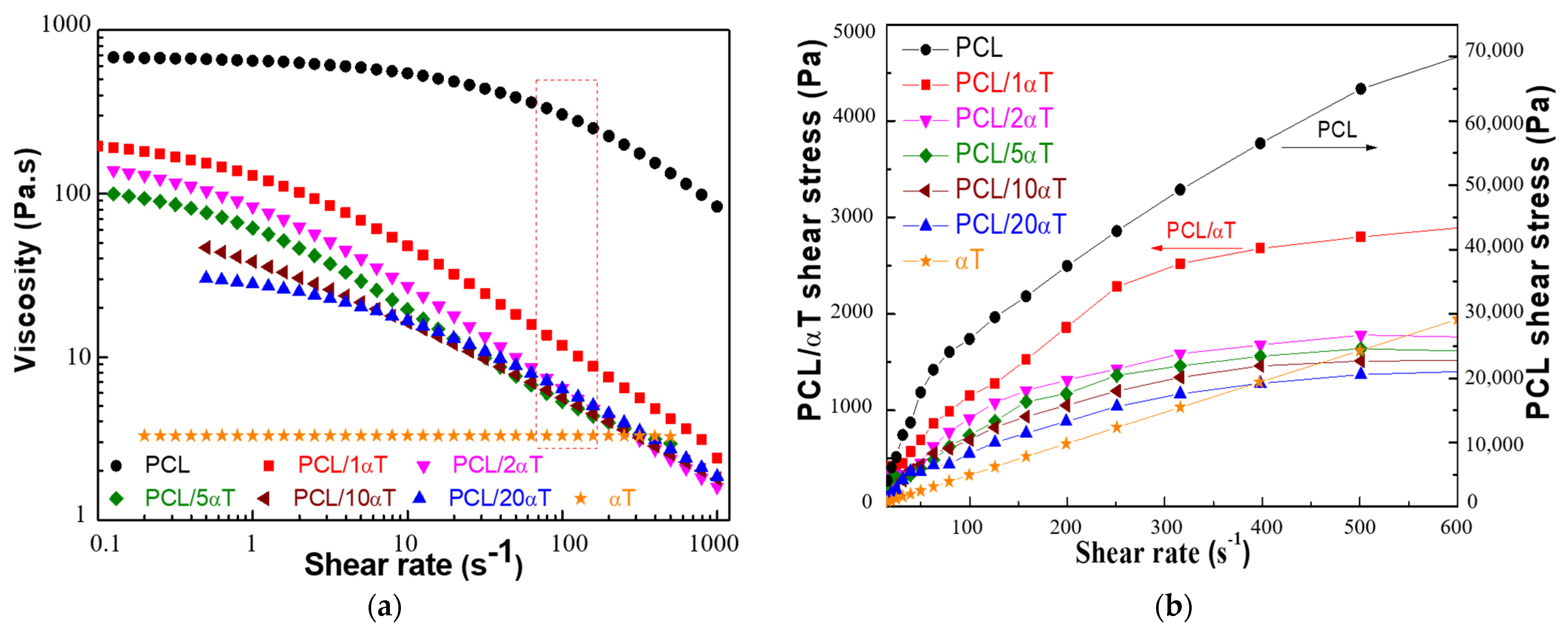
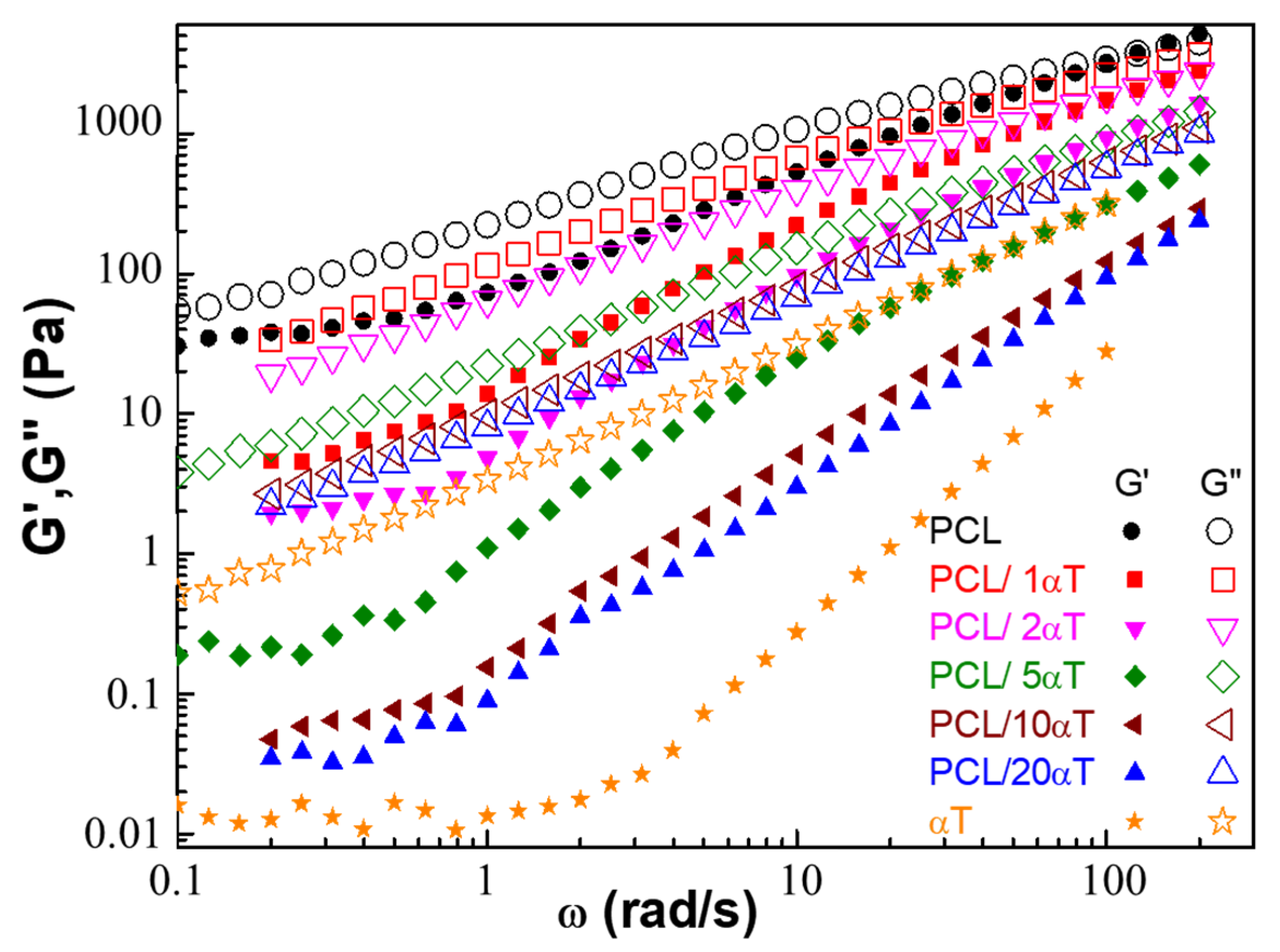
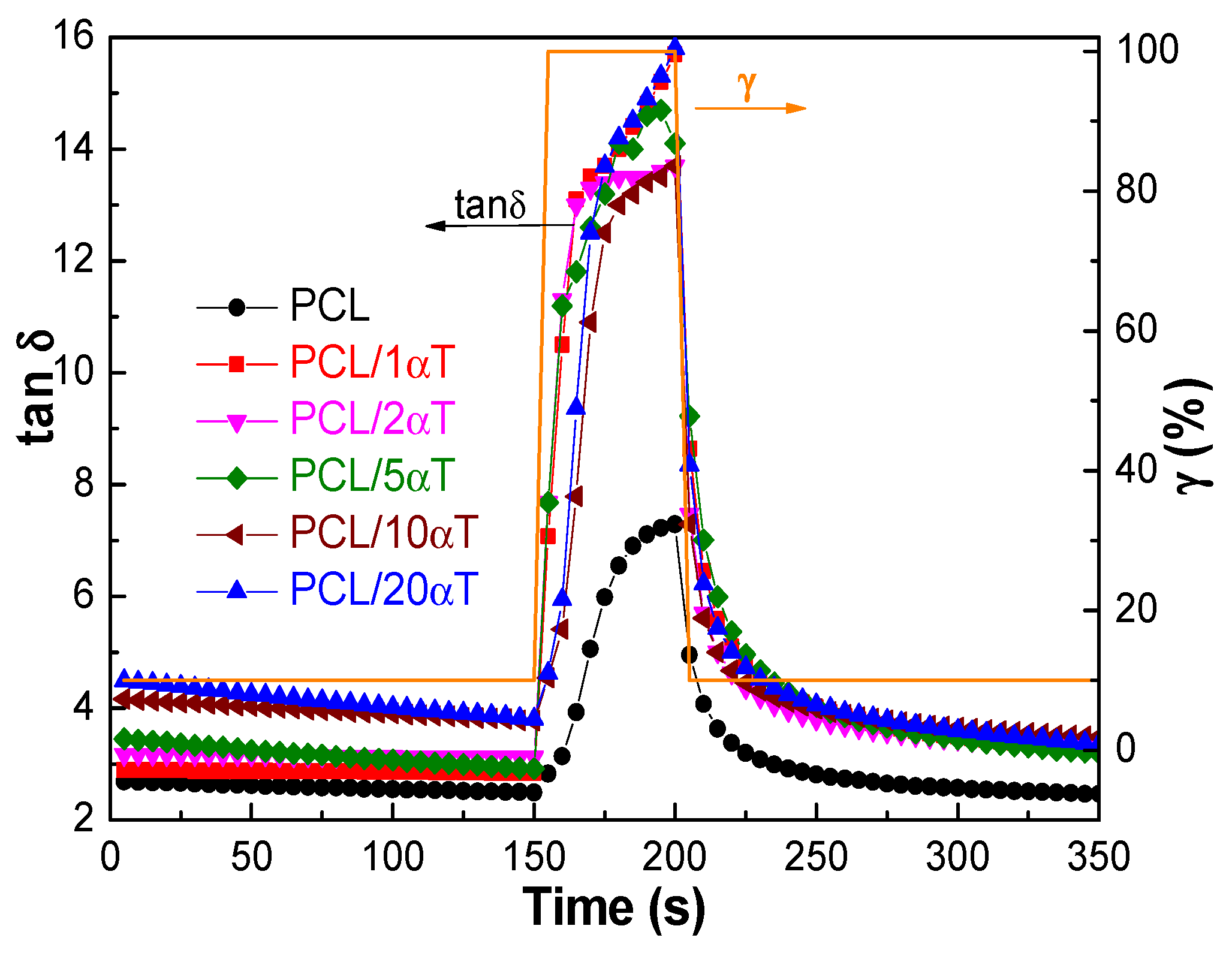
3.1. Rheological Behavior of PCL/α-Tocopherol Solutions
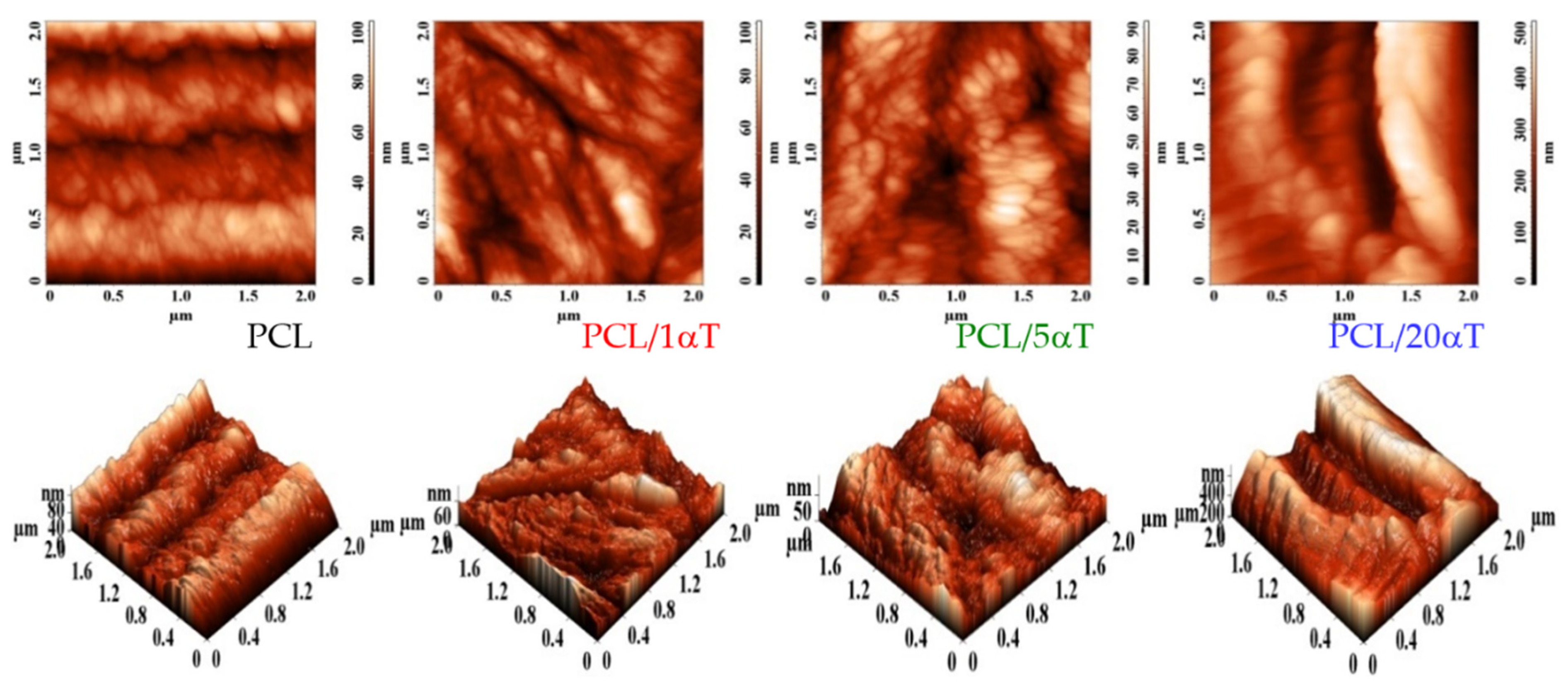
3.2. Characterization of PCL/α-Tocopherol Electrospun Fibers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Yildirim, S.; Röcker, B.; Pettersen, M.K.; Nilsen-Nygaard, J.; Ayhan, Z.; Rutkaite, R.; Radusin, T.; Suminska, P.; Marcos, B.; Coma, V. Active packaging applications for food. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilela, C.; Kurek, M.; Hayouka, Z.; Röcker, B.; Yildirim, S.; Antunes, M.D.C.; Nilsen-Nygaard, J.; Pettersen, M.K.; Freire, C.S.R. A concise guide to active agents for active food packaging. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 80, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, C.; Duraccio, D.; Cimmino, S. Food packaging based on polymer nanomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1766–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sid, S.; Mor, R.S.; Kishore, A.; Sharanagat, V.S. Bio-sourced polymers as alternatives to conventional food packaging materials: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 115, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoleru, E.; Irimia, A.; Butnaru, E. Bio-Based Bioplastics in Active Food Packaging. In Bioplastics for Sustainable Development; Kuddus, M.R., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2021; Chapter 14; pp. 347–379. [Google Scholar]
- Butnaru, E.; Stoleru, E.; Irimia, A. Synthetic Bioplastics in Active Food Packaging. In Bioplastics for Sustainable Development; Kuddus, M.R., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2021; Chapter 15; pp. 381–398. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, A.; Neogi, S. Oxygen scavengers for food packaging applications: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, B.; Wu, S.; Siddiqui, M.W. Incorporating essential oils or compounds derived thereof into edible coatings: Effect on quality and shelf life of fresh/fresh-cut produce. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, C.; Sivertsvik, M.; Mitelut, A.C.; Brebu, M.A.; Stoleru, E.; Rosnes, J.T.; Tanase, E.E.; Khan, W.; Pamfil, D.; Cornea, C.P.; et al. Comparative analysis of the composition and active property evaluation of certain essential oils to assess their potential applications in active food packaging. Materials 2017, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoleru, E.; Dumitriu, R.P.; Brebu, M.; Vasile, C.; Enache, A. Development of bioactive polymeric materials by incorporation of essential/vegetal oils into biopolymer matrices. Proceedings 2021, 69, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Göksen, G.; José Fabra, M.; Pérez-Cataluña, A.; Ibrahim Ekiz, H.; Sanchez, G.; López-Rubio, A. Biodegradable active food packaging structures based on hybrid cross-linked electrospun polyvinyl alcohol fibers containing essential oils and their application in the preservation of chicken breast fillets. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 27, 100613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-González, M.; Corral-González, A.; Felix, M.; Romero, A.A.; Martin-Alfonso, J.E. Developing active poly(vinyl alcohol)-based membranes with encapsulated antimicrobial enzymes via electrospinning for food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Fang, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Huang, Z. Lysozyme-based composite membranes and their potential application for active packaging. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, C.; Stoleru, E.; Darie-Nita, R.N.; Dumitriu, R.P.; Pamfil, D.; Tartau, L. Biocompatible materials based on plasticized poly(lactic acid), chitosan and rosemary ethanolic extract I. Effect of chitosan on the properties of plasticized poly(lactic acid) Materials. Polymers 2019, 11, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoleru, E.; Munteanu, S.B.; Dumitriu, R.P.; Coroaba, A.; Drobota, M.; Fras Zemljic, L.; Pricope, G.M.; Vasile, C. Polyethylene materials with multifunctional surface properties by electrospraying chitosan/vitamin E formulation destined to biomedical and food packaging applications. Iran. Polym. J. 2016, 25, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, L. Effect of α-tocopherol antioxidant on rheological and physicochemical properties of chitosan/zein edible films. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 118, 108799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, J.; Ćirković, J.; Radojković, A.; Mutavdžić, D.; Tanasijević, G.; Joksimović, C.; Bakić, G.; Branković, G.; Branković, Z. Chitosan and pectin-based films and coatings with active components for application in antimicrobial food packaging. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 158, 106349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, G.R.; Mohan, S.D.; Davis, F.J.; Ahn, K.; Al-Azab, M.; El Hadi, A.; Elliott, D.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y.; Nagarajan, A.; Nazhipkyzy, M. Structure development in electrospun fibres. In Electrospinning: Principles, Practice and Possibilities, 1st ed.; Mitchell, G.R., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2015; Chapter 8; pp. 136–171. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, M.D.; Mitchell, G.R.; Mohan, S.D.; Olley, R.H. Development of orientation during electrospinning of fibres of poly(ε-caprolactone). Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vong, M.; Diaz Sanchez, F.J.; Keirouz, A.; Nuansing, W.; Radacsi, N. Ultrafast fabrication of nanofiber-based 3D macrostructures by 3D electrospinning. Mater. Des. 2021, 208, 109916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luraghi, A.; Peri, F.; Moroni, L. Electrospinning for drug delivery applications: A review. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. Antioxidant, antibacterial and antifungal electrospun nanofibers for food packaging applications. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, F.; Bahrami, A.; Esfanjani, A.F.; Hosseini, H.; McClements, D.J.; Williams, L. Electrospun antimicrobial materials: Advanced packaging materials for food applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamabadi, H.; Assadpour, E.; Tabarestani, H.S.; Falsafi, S.R.; Jafari, S.M. Electrospinning approach for nanoencapsulation of bioactive compounds; recent advances and innovations. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 100, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, E.; Franco, P.; Campardelli, R.; De Marco, I.; Perego, P. Zein electrospun fibers purification and vanillin impregnation in a one-step supercritical process to produce safe active packaging. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, Z.; Ipek, S.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Antioxidant electrospun zein nanofibrous web encapsulating quercetin/cyclodextrin inclusion complex. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jovanska, L.; Chiu, C.-H.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Chiang, W.-D.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Wang, R. Development of a PCL-PEO double network colorimetric pH sensor using electrospun fibers containing Hibiscus rosa sinensis extract and silver nanoparticles for food monitoring. Food Chem. 2021, 368, 130813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, S.; Hirai, T.; Matsubara, M.; Yoshida, H.; Beniya, A. Dynamic viscosity recovery of electrospinning solution for stabilizing elongated ultrafine polymer nanofiber by TEMPO-CNF. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-My Le, A.; Tran, N.M.-P.; Phan, T.B.; Tran, P.A.; Tran, L.D.; Nguyen, T.H. Poloxamer additive as luminal surface modification to modulate wettability and bioactivities of small-diameter polyurethane/polycaprolactone electrospun hollow tube for vascular prosthesis applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 101771. [Google Scholar]
- El Fawal, G.; Hong, H.; Mo, X.; Wang, H. Fabrication of scaffold based on gelatin and polycaprolactone (PCL) for wound dressing application. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Ali, A. Development and characterization of biodegradable antimicrobial packaging films based on polycaprolactone, starch and pomegranate rind hybrids. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2018, 18, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Yipeng, Z.; Zhang, H. Electrospun chitosan/ polycaprolactone nanofibers containing chlorogenic acid-loaded halloysite nanotube for active food packaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, A.; Velásquez, E.; Pina, C.; José Galotto, M.; López de Dicastillo, C. Designing active mats based on cellulose acetate/polycaprolactone core/ shell structures with different release kinetics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiuk, I.; Wilczura-Wachnik, H.; Myśliński, A. α-Tocopherol/AOT/alkane/water system. Calorimetric studies. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 131, 2885–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Union. Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 of 14 January 2011 on Plastic Materials and Articles Intended to Come into Contact with Food. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, 12, 2–89. [Google Scholar]
- Dumitriu, R.P.; Stoica, I.; Vasilescu, D.S.; Cazacu, G.; Vasile, C. Alginate/lignosulfonate blends with photoprotective and antioxidant properties for active packaging applications. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darie-Niţa, R.N.; Vasile, C.; Stoleru, E.; Pamfil, D.; Zaharescu, T.; Tarţau, L.; Tudorachi, N.; Brebu, M.A.; Pricope, G.M.; Dumitriu, R.P.; et al. Evaluation of the rosemary extract effect on the properties of polylactic acid-based materials. Materials 2018, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoleru, E.; Dumitriu, R.P.; Munteanu, B.S.; Zaharescu, T.; Tanase, E.E.; Mitelut, A.; Ailiesei, G.L.; Vasile, C. Novel procedure to enhance PLA surface properties by chitosan irreversible immobilization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 367, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitriu, R.P.; Mitchell, G.R.; Davis, F.J.; Vasile, C. Functionalized coatings by electrospinning for anti-oxidant food packaging. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 12, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, S.M.; Montanheiro Noronha, C.; Gonçalves da Rosa, C.; Gustavo Sganzerla, W.; Casagrande Bellettini, I.; Ramos Nunes, M.; Cleber Bertoldi, F.; Manique Barreto, P.L. PVA antioxidant nanocomposite films functionalized with alpha-tocopherol loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 581, 123793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei-Mohkam, A.; Garavand, F.; Dehnad, D.; Keramat, J.; Nasirpour, A. Optimisation, antioxidant attributes, stability and release behaviour of carboxymethyl cellulose films incorporated with nanoencapsulated vitamin E. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 134, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrany, E.A.; Desobry, S. Partition coeffcients in food/packaging systems: A review. Food Addit. Contam. 2004, 21, 1186–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wang, Z.-W.; Bai, Y.-H. Determination of the partition and diffusion coefficients of five chemical additives from polyethylene terephthalate material in contact with food simulants. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 21, 100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graessley, W.W. Polymer chain dimensions and the dependence of viscoelastic properties on concentration, molecular weight and solvent power. Polymers 1980, 21, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNair, O.D.; Brent, D.P.; Sparks, B.J.; Patton, D.L.; Savin, D.A. Sequential thiol click reactions: Formation of ternary thiourethane/thiol-ene networks with enhanced thermal and mechanical properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6088–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Peng, C.; Narayanan, A.; Kaur, S.; Xu, Y.; Weiss, R.A.; Joy, A. Opposing effects of side-chain flexibility and hydrogen bonding on the thermal, mechanical, and rheological properties of supramolecularly cross-linked polyesters. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 9294–9305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazani, S.; Karimi, M. Investigating the influence of temperature on electrospinning of polycaprolactone solutions. e-Polymers 2014, 14, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, J.; Uyama, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Inoue, Y. Hydrogen-bonding interaction and miscibility between poly(ε-caprolactone) and enzymatically polymerized novel polyphenols. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 2898–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rošic, R.; Pelipenko, J.; Kocbek, P.; Baumgartner, S.; Bešter-Rogač, M.; Kristl, J. The role of rheology of polymer solutions in predicting nanofiber formation by electrospinning. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukemper, R.; Becker, T.; Jekle, M. Surface energy of food contact materials and its relation to wheat dough adhesion. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 1142–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashud Alam, A.K.M.; Ewaldz, E.; Xiang, C.; Qu, W.; Bai, X. Tunable wettability of biodegradable multilayer sandwich-structured electrospun nanofibrous membranes. Polymers 2020, 12, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvate, S.; Dixit, P.; Chattopadhyay, S. Superhydrophobic surfaces: Insights from theory and experiment. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 1323–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Xia, M. Chitosan and procyanidin composite films with high antioxidant activity and pH responsivity for cheese packaging. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dintcheva, N.T.; Arrigo, R.; Gambarotti, C.; Carroccio, S.; Filippone, G.; Cicogna, F.; Guenzi, M. α-Tocopherol-induced radical scavenging activity in carbon nanotubes for thermo-oxidation resistant ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene-based nanocomposites. Carbon 2014, 74, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.T.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Vicente, A.A. Influence of α-tocopherol on physicochemical properties of chitosan-based films. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Platzer, M.; Kiese, S.; Herfellner, T.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Miesbauer, O.; Eisner, P. Common trends and differences in antioxidant activity analysis of phenolic substances using single electron transfer based assays. Molecules 2021, 26, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Gagaoua, M.; Barba, F.J.; Zhang, W.; Lorenzo, J.M. A Comprehensive review on lipid oxidation in meat and meat products. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Otero-Pazos, P.; Sendón, R.; Blanco-Fernandez, B.; Blanco-Dorado, S.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Concheiro, A.; Angulo, I.; Paseiro-Losada, P.; Rodríguez-Bernaldo de Quirós, A. Preparation of antioxidant active films based on chitosan: Diffusivity study of a-tocopherol into food simulants. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samsudin, H.; Auras, R.; Mishra, D.; Dolan, K.; Burgess, G.; Rubino, M.; Selke, S.; Soto-Valdez, H. Migration of antioxidants from polylactic acid films: A parameter estimation approach and an overview of the current mass transfer models. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, L. Combined antioxidant and sensory effects of active chitosan/zein film containing α-tocopherol on Agaricus bisporus. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



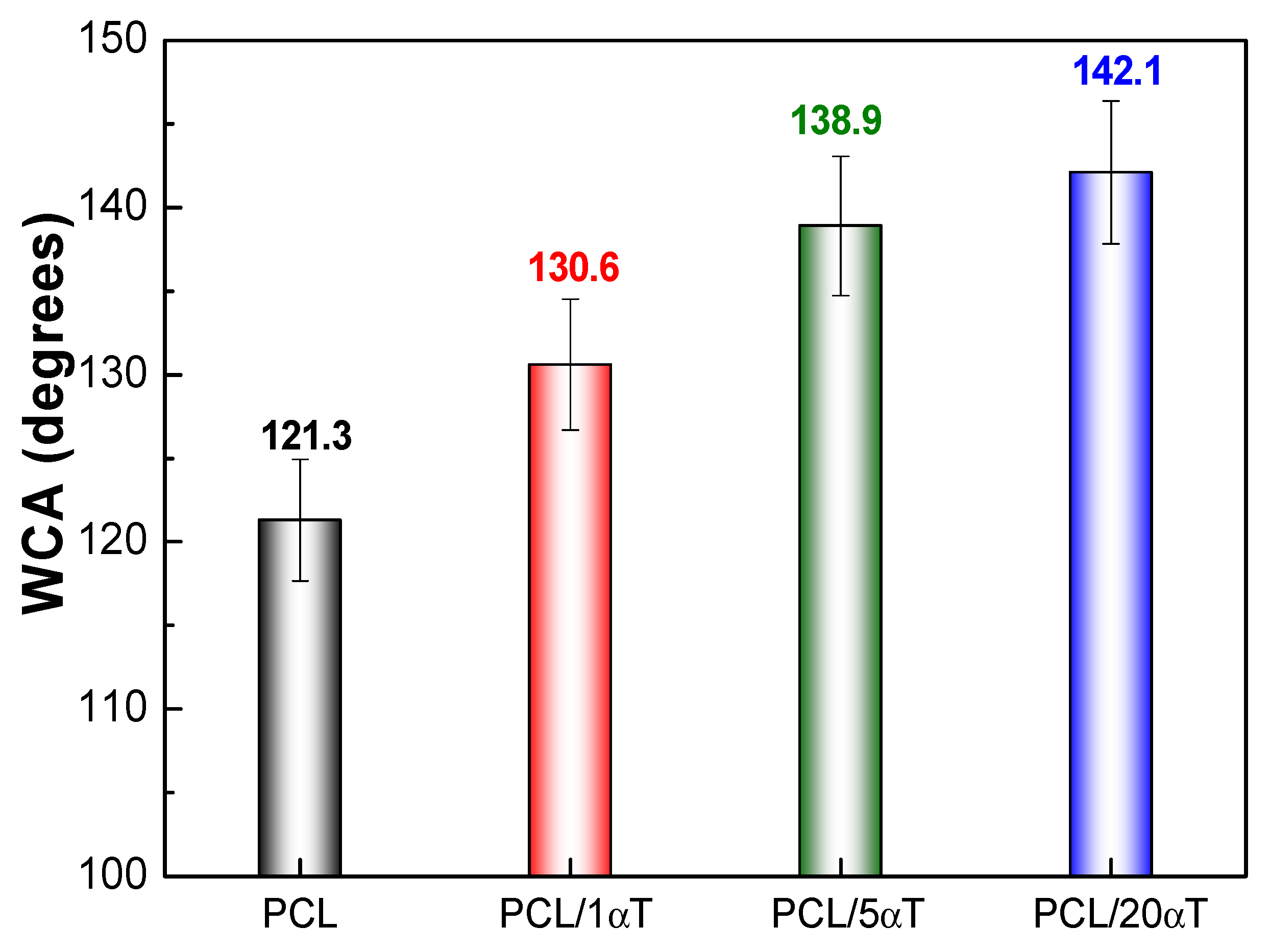


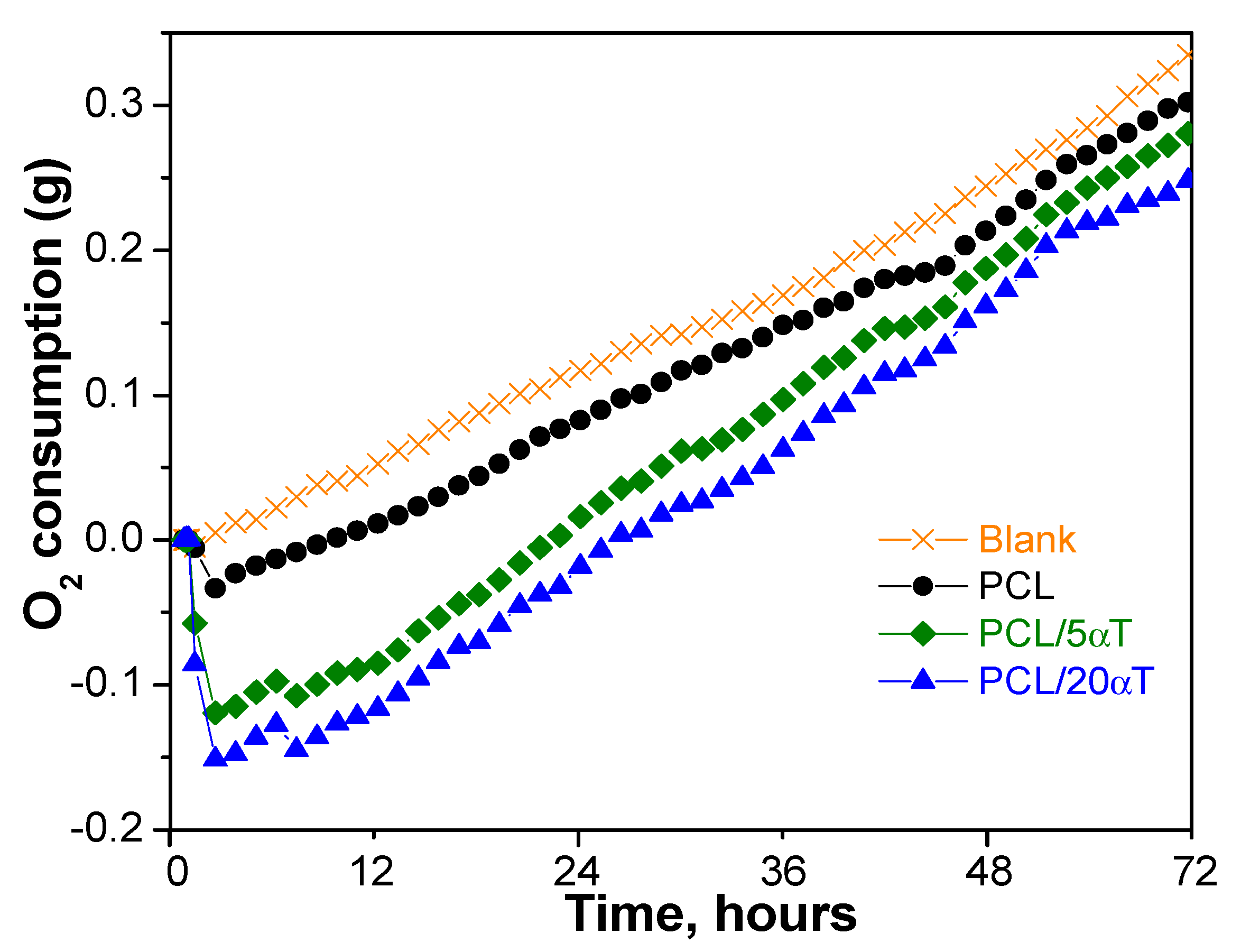
| Sample | αT Migration, % | Kp | C (mg/kg Food Sim) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCL/1αT | 29.89 | 2.345 | 2.89 |
| PCL/5αT | 20.14 | 3.965 | 9.09 |
| PCL/20αT | 16.70 | 4.988 | 26.22 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dumitriu, R.P.; Stoleru, E.; Mitchell, G.R.; Vasile, C.; Brebu, M. Bioactive Electrospun Fibers of Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Incorporating α-Tocopherol for Food Packaging Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185498
Dumitriu RP, Stoleru E, Mitchell GR, Vasile C, Brebu M. Bioactive Electrospun Fibers of Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Incorporating α-Tocopherol for Food Packaging Applications. Molecules. 2021; 26(18):5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185498
Chicago/Turabian StyleDumitriu, Raluca P., Elena Stoleru, Geoffrey R. Mitchell, Cornelia Vasile, and Mihai Brebu. 2021. "Bioactive Electrospun Fibers of Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Incorporating α-Tocopherol for Food Packaging Applications" Molecules 26, no. 18: 5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185498
APA StyleDumitriu, R. P., Stoleru, E., Mitchell, G. R., Vasile, C., & Brebu, M. (2021). Bioactive Electrospun Fibers of Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Incorporating α-Tocopherol for Food Packaging Applications. Molecules, 26(18), 5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185498







