Abstract
Previous studies have indicated widespread insecticide resistance in malaria vector populations from Cameroon. However, the intensity of this resistance and underlying mechanisms are poorly known. Therefore, we conducted three cross-sectional resistance surveys between April 2018 and October 2019, using the revised World Health Organization protocol, which includes resistance incidences and intensity assessments. Field-collected Anopheles gambiae s.l. populations from Nkolondom, Nkolbisson and Ekié vegetable farms in the city of Yaoundé were tested with deltamethrin, permethrin, alpha-cypermethrin and etofenprox, using 1× insecticide diagnostic concentrations for resistance incidence, then 5× and 10× concentrations for resistance intensity. Subsamples were analyzed for species identification and the detection of resistance-associated molecular markers using TaqMan® qPCR assays. In Nkolbisson, both An. coluzzii (96%) and An. gambiae s.s. (4%) were found together, whereas only An. gambiae s.s. was present in Nkolondom, and only An. coluzzii was present in Ekié. All three populations were resistant to the four insecticides (<75% mortality rates―MR1×), with intensity generally fluctuating over the time between mod-erate (<98%―MR5×; ≥98%―MR10×) and high (76–97%―MR10×). The kdr L995F, L995S, and N1570Y, and the Ace-1 G280S-resistant alleles were found in An. gambiae from Nkolondom, at 73%, 1%, 16% and 13% frequencies, respectively, whereas only the kdr L995F was found in An. gambiae s.s. from Nkolbisson at a 50% frequency. In An. coluzzii from Nkolbisson and Ekié, we detected only the kdr L995F allele at 65% and 60% frequencies, respectively. Furthermore, expression levels of Cyp6m2, Cyp9k1, and Gste2 metabolic genes were highly upregulated (over fivefold) in Nkolondom and Nkolbisson. Pyrethroid and etofenprox-based vector control interventions may be jeopardized in the prospected areas, due to high resistance intensity, with multiple mechanisms in An. gambiae s.s. and An. coluzzii.
1. Background
The intensification of core vector control interventions with long-lasting insecticidal nets (LLINs) and indoor residual spraying (IRS), associated with the improved diagnosis and treatment of cases has resulted in substantial reductions in the global malaria incidence between 2000 and 2015 [1,2]. Indeed, an estimated 663 million clinical cases were averted during this fifteen-year period, with 68%, 22% and 10% contributions by LLINs, artemisinin combination therapies (ACTs) and IRS, respectively [1]. However, between 2015 and 2019, the decline in malaria incidence stalled to less than 2%, compared to 27% between 2000 and 2015 [2]. In 2019, the number of cases was globally estimated at 229 million in 87 endemic countries. At the same time, the rapid expansion of insecticide resistance in the most efficient Anopheles vectors of Plasmodium parasites jeopardizes the interventions’ effectiveness. Indeed, insecticide resistance of Anopheles populations to at least one insecticide class has been reported in 73 malaria-endemic countries [2]. In 28 countries, malaria vector populations are resistant to the four main insecticide classes used in public health control (i.e., carbamates, organochlorides, organophosphates and pyrethroids) [2]; of particular concern is the resistance to pyrethroid insecticides, because all World Health Organization (WHO) prequalified LLINs contain at least one pyrethroid [3].
Mosquito populations displaying resistance to public health insecticides are very common in areas with agricultural cultivations [4,5,6,7] and in locations with intensive insecticide-based vector control interventions [8,9], presumably due to the high selective pressure imposed by the insecticides deployed. In addition, the accumulation of waste and other pollutants generated through human activities in the environment around mosquito breeding sites tends to increase the selection of mosquito resistance to insecticides [10].
In Cameroon, malaria prevention largely relies on the use of LLINs [11]. During the last decade, over 20 million LLINs were freely distributed to the general population through several nationwide campaigns, which resulted in 77% of the population owning at least one treated net, and 58% of the population using LLINs regularly [11,12]. As a result of these efforts, the prevalence of malaria in the general population decreased from 41% to 24% between 2000 and 2015, and the related mortality decreased by 54% (i.e., from about 13,000 to 6000) [11,12]. Alternative measures, such as IRS and larviciding, are still in the pilot phase [12].
Despite the LLIN campaigns, Cameroon remained one of the 11 countries accounting for 70% of the global burden of malaria in 2019 [2]. The factors leading to high malaria burden despite the interventions are poorly known. Meanwhile, the country is committed to a high-burden/high-impact approach. Regarding the insecticide susceptibility of the malaria vectors, studies conducted during the last 20 years on the major malaria vector species in Cameroon, including An. gambiae s.s., An. coluzzii and An. arabiensis, have shown that pyrethroid resistance has rapidly increased since its first report in 2003 [13,14,15]. The primary mechanisms conferring pyrethroid resistance in An. gambiae s.s. and An. coluzzii are target-site point mutations in the para voltage-gated sodium channel gene, including the knockdown resistance (kdr) L995F/S (formerly known as L1014F/S) and N1570Y (formerly known as N1575Y) mutations [14,15,16,17]. In addition, the increased expression of cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (P450) CYP6P3, CYP6M2, and CYP6P4, and glutathione S-transferase (GST) GST1-6 has been associated with pyrethroid resistance [18,19]. Furthermore, the acetylcholinesterase mutation Ace-1 G280S (formerly known as Ace-1 G119S) that confers resistance to carbamates and organophosphates has been detected in the same mosquito species in Cameroon [18,19,20].
A previous study attempting to assess the intensity of deltamethrin resistance in An. gambiae s.l. from Pitoa in North Cameroon using dose-response assays revealed a more than 500-fold resistance ratio compared to the An. gambiae s.s. Kisumu insecticide-susceptible reference strain [21]. Furthermore, exposing these mosquitoes to a 10× deltamethrin diagnostic concentration (0.5%) displayed a moderate level of resistance according to WHO classifications [21]. Similarly, a longitudinal study based on the WHO insecticide susceptibility assay conducted over 5 years from 2011 to 2015 confirmed the rapid expansion of deltamethrin resistance in An. gambiae s.l. populations from the North region of Cameroon, especially in urban settings and agricultural areas [17]. All these findings highlight the variability and complexity shaping insecticide resistance patterns in An. gambiae s.s., An. coluzzii and An. arabiensis populations from Cameroon. However, data on the intensity of insecticide resistance in various ecological settings in Cameroon and its potential operational significance are very limited. Therefore, in-depth investigations of insecticide resistance are essential for identification of the areas where alternative or complementary vector control interventions are urgently needed on top of LLINs, e.g., scaling up IRS or larviciding.
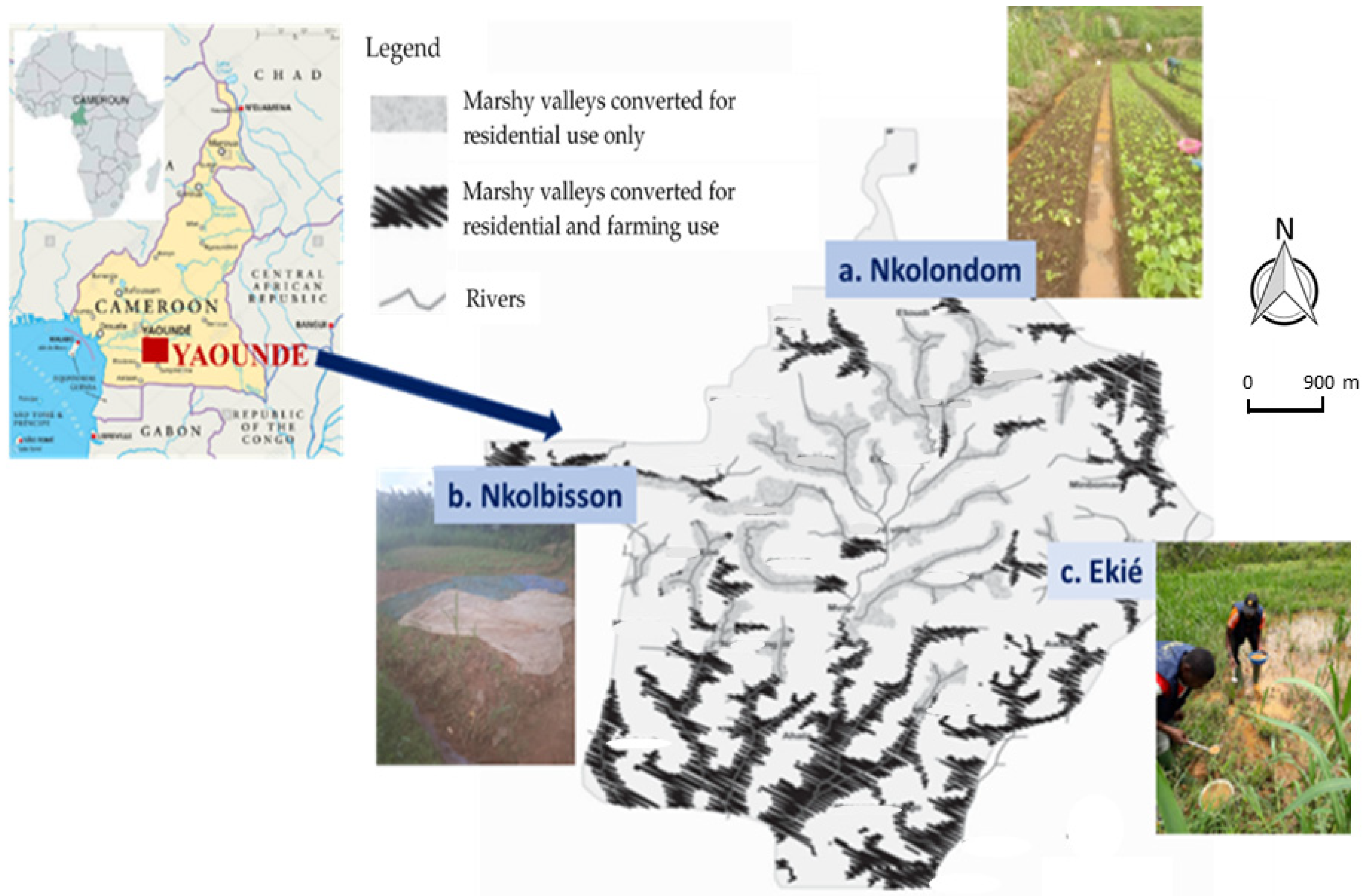
The aim of the current study was to assess the dynamics of pyrethroid resistance in terms of incidence and intensity in An. gambiae s.l. populations from three vegetable farming areas in the city of Yaoundé, namely, Nkolondom, Nkolbisson and Ekié (Figure 1). The second objective was to assess the susceptibility of pyrethroid resistant An. gambiae s.l. populations to etofenprox, as a potential active ingredient for LLINs and IRS in pyrethroid resistance areas. We sampled mosquito larvae from the field in three cross-sectional surveys between April 2018 and October 2019, reared them until adult stage in the laboratory, assessed the insecticide resistance incidence and intensity using WHO insecticide susceptibility bioassays, and then we used molecular assays to identify the underlying resistance mechanisms. The study was conducted during the short rainy season (April–May 2018), the main dry season (December 2018–January 2019) and the main rainy season (September–October 2019).
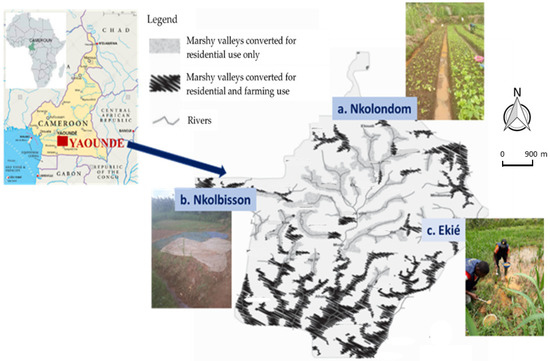
Figure 1.
Map of Yaoundé in Cameroon showing the marshy valleys with typical mosquito breeding sites in Nkolondom, Nkolbisson and Ekié, where immature Anopheles gambiae s.l. stages were collected (a large drain channel in Nkolondom; stream-bed pool in Nkolbisson; swamp in Ekié). (Adapted from [22]).
2. Results
2.1. Species Composition
In April–May 2018, 50 adult mosquito specimens from each study site emerging from field-collected larvae and morphologically identified as belonging to the An. gambiae complex were further identified to species level, using TaqMan® qPCR assays. In addition, 50 specimens from an An. gambiae s.s. insecticide-susceptible laboratory colony (the Kisumu strain) were included as a control in the analysis. Overall, two sibling species, An. gambiae s.s. and An. coluzzii, were identified. Both species were found in Nkolbisson, with a predominance of An. coluzzii (96%), whereas in Nkolondom and Ekié, all specimens were An. gambiae s.s. and An. coluzzii, respectively (Table 1). Mosquito samples of the Kisumu strain were confirmed as An. gambiae s.s.

Table 1.
Frequencies of kdr L995F/S and N1570Y and Ace-1 G280S resistance alleles among Anopheles gambiae s.s. and An. coluzzii populations from Nkolondom, Nkolbisson and Ekié, Cameroon, in April 2018.
2.2. Trends of Insecticide Resistance in Anopheles gambiae s.l. Populations
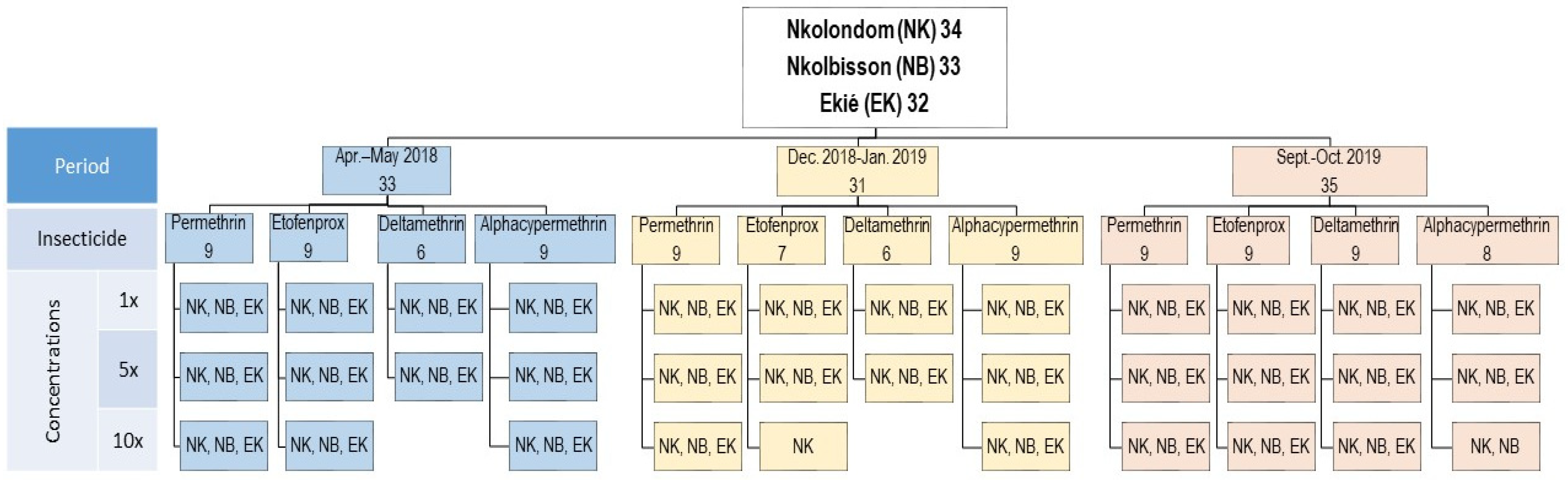
A total of 9582 An. gambiae s.l. specimens from Ekié (n = 3156), Nkolbisson (n = 3215) and Nkolondom (n = 3211) were used for insecticide susceptibility testing. The bioassays also included 456 adult females of the Kisumu An. gambiae s.s. reference susceptible colony as a negative control. Overall, 111 bioassays were performed during three consecutive surveys in April–May 2018, December 2018–January 2019 and September–October 2019. These included 99 susceptibility tests with field-collected An. gambiae s.l. specimens and 12 tests with the Kisumu reference colony. For each study site, 32–34 tests were carried out (Figure 2). These included:
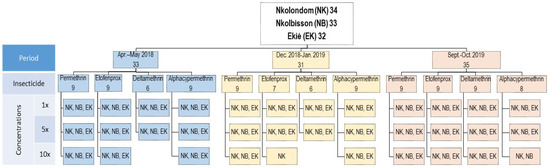
Figure 2.
Study design showing resistance incidence and resistance intensity assays carried out with field-collected Anoheles gambiae s.l. samples throughout the two-year study period (2018–2019). (Apr.–May 2018: April–May 2018; Dec. 2018–Jan. 2019: December 2018–January 2019; Sept.–Oct. 2019: September–October 2019).
Twelve susceptibility tests using insecticide diagnostic concentrations (1× DCs) (i.e., 0.05% deltamethrin, 0.05% alpha-cypermethrin, 0.75% permethrin and 0.5% etofenprox);
Twelve insecticide resistance intensity tests using four 5× DC (i.e., 0.25% deltamethrin, 0.25% alpha-cypermethrin, 3.75% permethrin and 2.5% etofenprox);
Finally, 8–10 insecticide resistance intensity tests using 10× DC (i.e., 0.5% deltamethrin, 0.5% alpha-cypermethrin, 7.5% permethrin and 5% etofenprox), depending on the availability of mosquitoes.
2.2.1. Resistance Frequencies
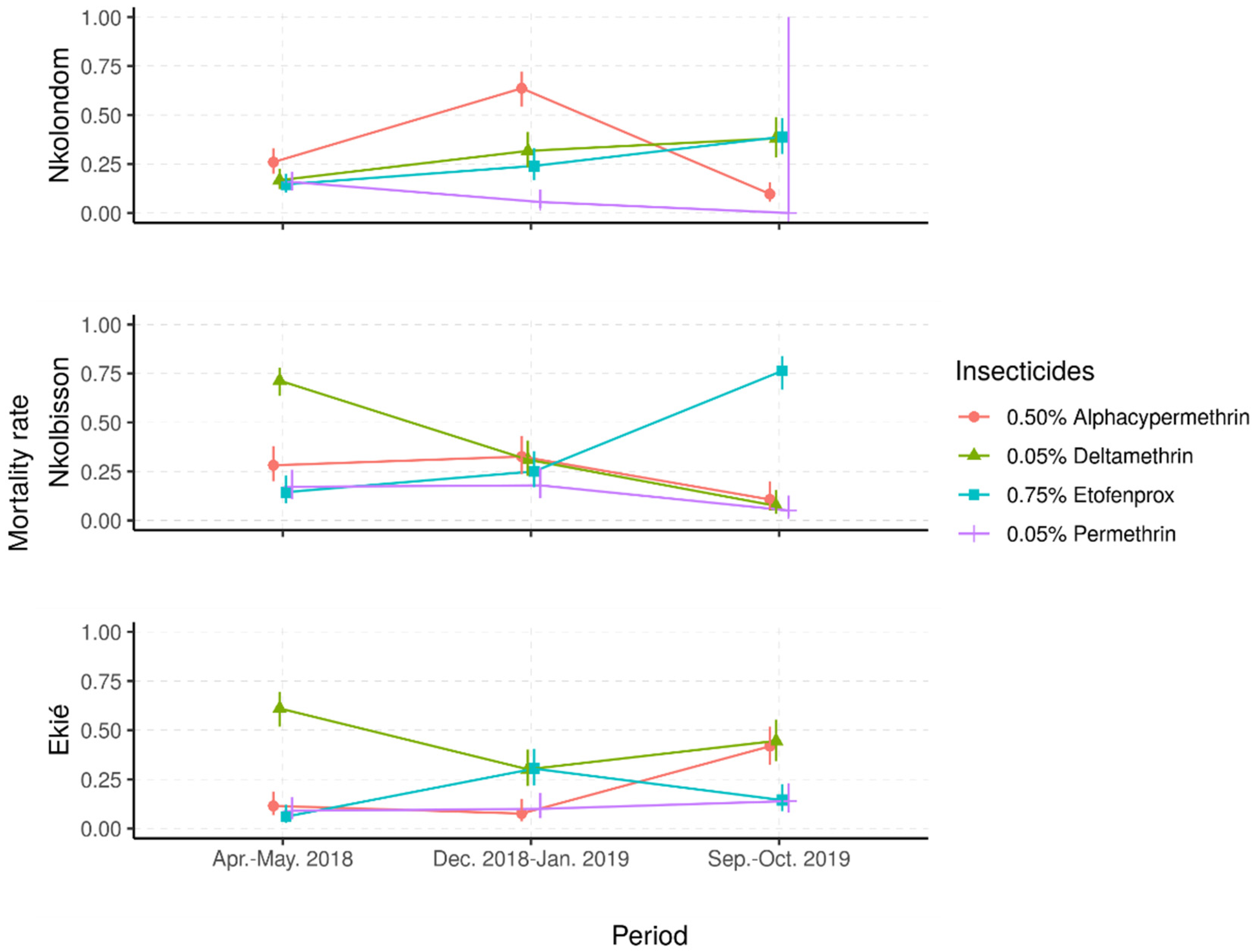
Mortality rates in the controls, exposed to silicone-oil-impregnated paper only, were below 5%, whereas the mortality rates for the Kisumu colony against all insecticides were consistently above 98% (Table 2). In contrast, across the three study sites, the field populations showed resistance to all four insecticides tested (Figure 3). The lowest mortality rates were recorded with permethrin (mostly less than 20%), whereas the three other insecticides induced variable mortality rates ranging from 25% to 75%, suggesting temporal or season fluctuations of insecticide resistance.

Table 2.
Patterns of resistance frequency versus resistance intensity among Anopheles gambiae s.l. populations from Nkolondom, Nkolbisson and Ekié during the three surveys.
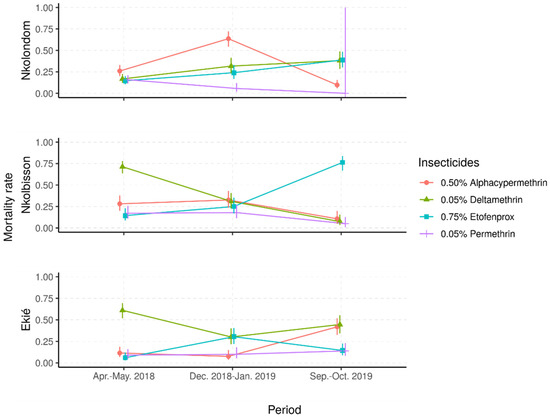
Figure 3.
Predicted mortality rates and their 95% confidence intervals from a mixed-effects logistic regression model of field Anopheles gambiae s.l. samples following exposure to four insecticide diagnostic concentrations. (Apr.–May 2018: April–May 2018; Dec. 2018–Jan. 2019: December 2018–January 2019; Sept.–Oct. 2019: September–October 2019).
Depending on the study site, different patterns of time-based variations of mortality rates were observed. In samples from Nkolondom, the mortality rates to deltamethrin and etofenprox gradually increased, from less than 20% in April–May 2018 to around 40% in September–October 2019, suggesting a temporal decrease in resistance frequency to these insecticides. In contrast, the mortality to permethrin decreased from 20% to less than 5% in the same period, suggesting an increase in resistance frequency to this insecticide. However, the mortality to alpha-cypermethrin was higher during the dry season in December 2018 (70%) compared with the two rainy seasons (around 10%), suggesting very important fluctuations of alpha-cypermethrin resistance frequency from one season to another.
In An. gambiae s.l. samples from Nkolbisson, the mortality rates to deltamethrin gradually decreased, from 70% in April–May 2018 to less than 15% in September–October 2019, suggesting a progressive increase in resistance frequencies over the time. However, the mortality rates to permethrin and alpha-cypermethrin fluctuated between 15% and 30% in April–May 2018 and December 2018–January 2019; then, they decreased to less than 10% in September–October 2019, suggesting a deferred increase in resistance frequencies to these insecticides. In contrast, the mortality to etofenprox increased from 20% to 75% over time, suggesting a decrease in etofenprox resistance frequency.
In An. gambiae s.l. samples from Ekié, seasonal variations of resistance frequencies were observed for deltamethrin and etofenprox. Indeed, the lowest mortality to deltamethrin was recorded during the dry season (≈30%) and the highest (≈70%) during the rainy seasons. An opposite propensity was seen with etofenprox, against which mosquito mortality was significantly higher during the dry season (≈30%) compared with the rainy seasons (<20%) (p < 0.05%). For permethrin and alpha-cypermethrin, mosquito mortality rates were mostly less than 20%, although a significant increase was seen with alpha-cypermethrin in October 2019 (40%) (p < 0.05%).
2.2.2. Status and Dynamics of Resistance Intensity
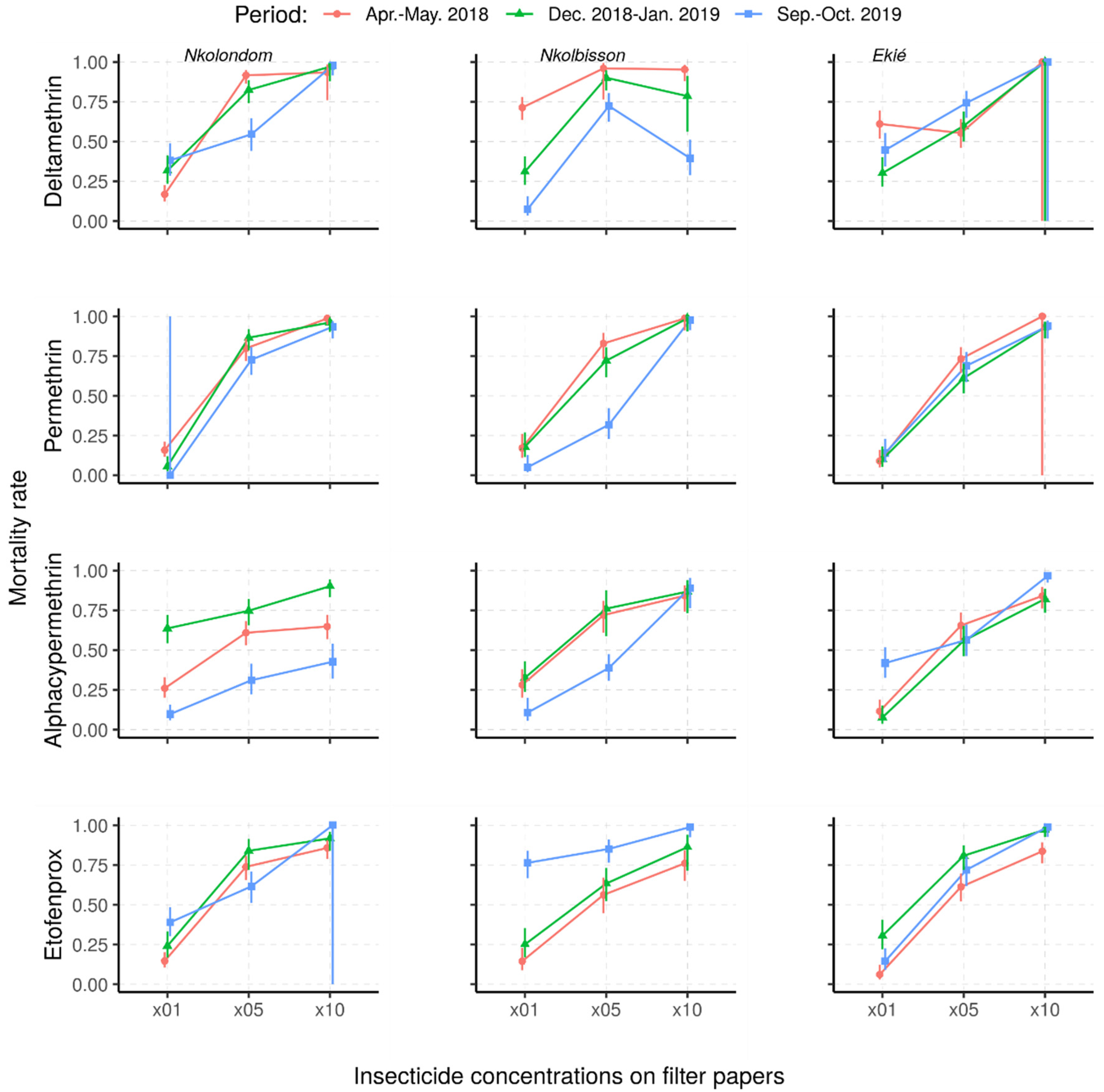
The mortality rates of An. gambiae s.l. from Nkolondom, Nkolbisson and Ekié resulting from resistance intensity tests are provided in Figure 4. Against the 5× DCs, fewer than 95% of the mosquitoes were killed, irrespective of the survey period or the study site, indicating that the intensity of resistance in surveyed mosquito populations was either moderate or high. Indeed, the use of 10× DC confirmed moderate or high resistance in An. gambiae s.l. from the three study sites, depending on the survey period and the insecticide.
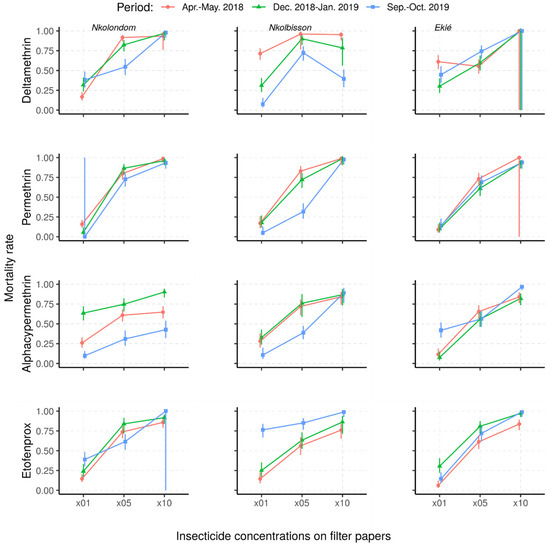
Figure 4.
Predicted mortality rates and their 95% confidence intervals of field-collected Anopheles gambiae s.l. samples from a mixed-effects logistic regression model following exposure to 1×, 5× and 10× insecticide concentrations (Apr.–May 2018: April–May 2018; Dec. 2018–Jan. 2019: December 2018–January 2019; Sept.–Oct. 2019: September–October 2019).
Overall, the resistance intensity was moderate (<98% MR5×; ≥98% MR10) in 11 of the 36 assays and high (45–97% MR10×) in 25 of the assays. Considering the wide range of mortality rates indicating high resistance intensity (according to the WHO criteria), we further classified high resistance intensity into three levels: level 1 (75–97% mortality rate―HL1), level 2 (50–74% mortality rate―HL2) and level 3 (<50% mortality rate―HL3) (Table 2). According to this further classification, the high resistance intensity was mostly at HL1 (in 21/25 tested samples, 84%), with only four cases at HL2 and HL3 (4/25 tested samples, 16%). Both HL2 and HL3 resistance intensity to deltamethrin were recorded in mosquito samples from Nkolbisson, as well as those from Nkolondom to alpha-cypermethrin.
Depending on study sites and insecticides used, changes in resistance intensity were observed. The intensity of deltamethrin resistance stalled at HL1 in Nkolondom and at moderate level (MD) in Ekié, whereas it progressively increased from HL1 in April–May 2018 to HL2 (50–75% mortality rates) in December 2018–January 2019 and HL3 (<50% mortality rates) in September–October 2019 for mosquito samples from Nkolbisson.
With permethrin, the intensity of resistance changed in the three mosquito populations during the December 2018–January 2019 study period, either from MD to HL1 or vice versa. With alpha-cypermethrin, the intensity of resistance stalled at HL1 in mosquito samples from Nkolbisson, whereas it progressively increased from HL1 in April–May 2018, to HL2 (50–75% mortality rates) in December 2018–January 2019 and HL3 (<50% mortality rates) in September–October 2019 for mosquito samples from Nkolondom.
However, the intensity of resistance to alpha-cypermethrin in mosquito samples from Ekié decreased from HL1 in December 2018–January 2019 to MD in September–October 2019. Additionally, at the same period, the intensity resistance to etofenprox was minimized in the three study mosquito populations, from HL1 to MD.
2.2.3. Relationship between the Frequency and the Intensity of Insecticide Resistance
A broad analysis of the mortality rates of An. gambiae s.l. samples post-exposure to 1× DC and 10× DC (Table 2) revealed a wide variation in mortality rates to the 1× DC, falling under the threshold of confirmed resistance. However, the corresponding resistance intensity to 10× DC was mostly either MD or HL1, except for a few cases of HL2 and HL3 recorded in Nkolbisson and Nkolondom in September–October 2019 (<40% mortality rates to 10× deltamethrin and alpha-cypermethrin DC, respectively). The HL3 resistance intensity to 10× DC was associated with mortality rates of less than 5% to 1× DC. However, for the MD, HL1 and HL2 resistance intensities, the counter mortality rates post-exposure to the 1× DC varied widely, from 0.0% to 75%.
2.3. Molecular Markers of Insecticide Resistance
Overall, there was a site-to-site variation in the allelic frequencies of resistance molecular markers (Table 1 and Table 3).

Table 3.
Differential expression of metabolic and cuticular resistance genes among the Nkolondom and Nkolbisson mosquito populations as compared with the Kisumu susceptible strain in April 2018.
In the An. gambiae s.s. population from Nkolondom, the kdr L995F allele was recorded in the highest frequency (72.0%). Interestingly, the kdr L995S allele was also found, although at a heterozygote state with L995F in only one mosquito specimen (1.00% allelic frequency). Nkolondom was also the only area where the kdr N1570Y allele was recorded (at a frequency of 16.0%). The Ace-1 G280S allele was also found at a 13.0% frequency.
In Nkolbisson, the kdr L995F allele was present at a frequency of 50.0% in An. gambiae s.s. and 65.0% in An. coluzzii. Neither mutant kdr L995S, N1570Y nor Ace-1 G280S alleles were recorded in either An. gambiae or An. coluzzii.
In the An. coluzzii population from Ekié, the kdr L995F allele was found at a 60.0% frequency, whereas no mutant kdr L995S, N1570Y or Ace-1 G280S were detected.
The gene expression analysis of genes putatively implicated in insecticide resistance measured in the Nkolondom and Nkolbisson An. gambiae s.l. populations showed that the following genes were upregulated compared to the susceptible Kisumu laboratory colony: Cyp6m2, Cyp9k1, Cyp6p4, Cyp6z1, Gste2 and Cyp4g16 (Table 3). The genes with the highest fold changes (>5-fold) in the Nkolondom population were the P450s Cyp6m2 (17.1-fold) and Cyp9k1 (6.0- fold) and the GST Gste2 (12.8-fold). Cyp6m2 and Cyp9k1 were also among the most upregulated genes in the Nkolbisson population together with Cyp6p4 (6.2-fold) and Gste2 (52.0-fold).
3. Discussion
In this study, a stepwise assessment of insecticide resistance in An. gambiae s.l. populations from three urban areas in Yaoundé provided evidence for moderate- to high-intensity resistance to pyrethroids and etofenprox. The selected study sites consisted of two vegetable farming areas, Ekié and Nkolbisson, where insecticide resistance has not yet been assessed, and a third farming area, Nkolondom, serving as a positive control, where insecticide resistance has previously been extensively investigated, including its underlying resistance mechanisms [6,16,19,23,24]. Mosquito species identification revealed the presence of both An. gambiae s.s. and An. coluzzii, with variable compositions between study sites.
The distribution of An. gambiae s.s. and An. coluzzii observed in the three study areas is in agreement with previous studies [23,24,25,26], confirming the ubiquity of both species in various ecological settings in Yaoundé. The differences in species composition may be due to temporal shifts in species, owing to biotic interactions occurring at the larval, adult or both stages, such as competition, predation and parasitism [27,28], or by selection pressure resulting from the use of chemical insecticides in both agriculture and public health [23,29].
The susceptibility tests conducted with the 1× DC confirmed pyrethroid resistance in the Nkolondom An. gambiae s.s. population, and in the Nkolbisson and Ekié An. coluzzii populations. In addition, etofenprox resistance has been observed in both species for the first time and across all three study sites. Etofenprox is a non-ester pyrethroid (pseudo-pyrethroid); this insecticide has been recommended by the WHO as an alternative for indoor residual spraying operations [30] and the treatment of bed nets [3] against malaria vectors because it exhibits lower toxicity to non-target organisms. This active ingredient may be deployed in areas where malaria vectors are susceptible, in order to overcome pyrethroid resistance [31]. However, the development of etofenprox resistance alongside resistance to the ester pyrethroids in An. gambiae s.s. and An. coluzzii populations from the three study sites emphasizes the need for other alternative vector-control measures in Yaoundé. Moreover, further investigations, including identification of the underlying mechanisms, are required to assess the geographic distribution of etofenprox resistance in the other parts of Cameroon.
The bioassays carried out with 5× DC and 10× DC revealed a mosaic pattern in terms of the intensity of insecticide resistance, in both An. gambiae s.s. and An. coluzzii, over the 18-month monitoring period, with many fluctuations from moderate to high intensity, and vice versa. In a few cases, the resistance intensity remained as moderate or high over the study period. These patterns might be driven by seasonal changes affecting the expression of insecticide resistance genes in one way or another, or an outcome of stochastic variations between bioassays. Either way, none of the studied populations were neither susceptible to pyrethroids and etofenprox, nor did they exhibit a low resistance intensity, highlighting the extent of the insecticide resistance problem in the Yaoundé urban and peri-urban areas.
Improper use of insecticides in agriculture and public health has been recognized as a major factor leading to the selection of insecticide resistance in malaria vectors, with substantial temporal variations as a function of treatment cycles and seasonality [4,5,6,7,8,9]. Considering the likely selection pressure, which is continuously imposed on the malaria vector populations due to heavy use of insecticides in market gardening areas [32], the observed resistance pattern does not come as a surprise. Indeed, swamps in Yaoundé are subject to urban agriculture permanently operating throughout the year with intensive and improper use of chemical insecticides [24]. Previous studies revealed that agricultural pesticides and mainly insecticide applications are commonly utilized in Nkolondom and Nkolbisson, although the farmers do not receive specific training on pesticide management [32]. Indeed, insecticides of different classes, including pyrethroids (cypermethrin, deltamethrin, and lambdacyhalothrin), carbamates (carbofuran), organophosphates (Dimethoate, Diazinon, and Pyriforce® (chlorpyrifos ethyl)), and organochlorines (Endosulfan), are frequently used by farmers to fight against crop pests in vegetable farms in Yaoundé [32]. In addition, LLINs and other insecticide-based tools are commonly used for malaria prevention and personal protection against mosquito bites in households [33].
A broad analysis of resistance intensity versus resistance frequency showed that a high resistance frequency, as revealed from the substantial decline in mosquito mortality to 1× DC, may not systematically reflect a significant increase in the intensity of resistance obtained from tests with 10× DC. Therefore, the current study clearly demonstrates the added value of resistance intensity assessments in the monitoring of vector resistance to insecticides. We presumed that the mosquito samples falling within the range 0% to 98% mortality rates to 10× DC, indicating high resistance intensity according the WHO criteria [34], may also undergo different levels of high resistance intensity over the time. Therefore, we further classified high resistance into three levels, i.e., level 1 (75–98% mortality rate―HL1), level 2 (50–74% mortality rate―HL2) and level 3 (<50% mortality rate―HL3). This additional classification could be used to follow up the evolution of high resistance intensity in field mosquito populations. Furthermore, based on this supplementary classification, it appears that the HL3 resistance intensity recorded with deltamethrin in Nkolbisson and alpha-cypermethrin in Nkolondom is comparable with that reported in An. gambiae s.l. from Kolokopé cotton cultivation areas in Togo, with less than 40% mortality at the 10× DC [35]. In the southern and central regions of Mali, high-intensity resistance was reported in 16 An. gambiae s.l. populations, fluctuating between HL1 and HL3 over the test period from 2016 to 2018 [36]. Conversely, in Zambia, Ethiopia, and Nigeria, there was an increase in resistance intensity from moderate to high, or from susceptible to low resistance intensity over the monitoring period [37,38]. However, the variability in the intensity of insecticide resistance observed in An. gambiae s.s. and An. coluzzii populations from Yaoundé may reflect the situation in several areas of Cameroon, whether resistance has already been reported there or not.
The patterns of resistance intensity reported in this study may result from the simultaneous presence of multiple resistance mechanisms, including target-site and metabolic resistance. We hypothesize that multiple insecticide mechanisms in both An. gambiae s.s. and An. coluzzii species may have driven the variations of pyrethroid and etofenprox resistance intensity in the surveyed populations, due to the level of selection pressure. Almost half of the analyzed specimens were homozygous-resistant at the kdr L995F locus (L995F/L995F), contrary to one L995F/S hybrid in a single An. gambiae s.s. individual. In addition to the kdr L995F and L995S alleles, the kdr N1570Y, also called “super kdr”, was found in Nkolondom (frequency = 16.0%). The presence of the N1570Y mutation in Nkolondom is in line with Bamou et al. (recorded frequency = 9.46%) [18]; however, there was a higher allelic frequency in the present study. Combined with the L995F mutation, the N1570Y mutation may reinforce the intensity of An. gambiae s.s. resistance to pyrethroids in the study area. The G280S mutation conferring resistance to organophosphates and carbamates was also found in Nkolondom (frequency = 13.0%), confirming previous reports (recorded frequency = 21.78%) [18,39]. Neither N1570Y mutations nor G280S mutations were present in the other two study sites (i.e., Nkolbisson and Ekié). The multiplicity of target-site resistance mutations in An. gambiae s.s. from Nkolondom is consistent with previous reports, whereas the presence of the kdr L1014F at 60–65% frequencies in Nkolbisson and Ekié is documented here for the first time. In addition, the expression analysis of genes implicated in metabolic resistance, performed in the Nkolondom and Nkolbisson mosquito populations, showed that the P450 genes Cyp6m2 and Cyp9k1 were highly upregulated, above fivefold in both populations. Both genes have recently been reported to be upregulated in An. gambiae s.l. populations from Cameroon [18]. It has previously been shown that Cyp9k1 is implicated in the metabolism of the alpha-cyano pyrethroid deltamethrin and Cyp6m2 in the metabolism of alpha- and non-alpha-pyrethroids [40,41]. Gste2, which confers resistance to DDT [42], was also found to be highly upregulated in Nkolondom and Nkolbisson.
The current study provides valuable data for the evidence-based selection of areas where additional vector-control measures are urgently needed to sustain the ongoing interventions with LLNs.
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Study Sites
The study was conducted in three vegetable farming areas located in Nkolondom (3°57′18″ N, 11°29′36″ E), Nkolbisson (3°52′46″ N, 11°25′55″ E) and Ekié (3°49′38″ N, 11°31′53″ E), in the north, west and east of Yaoundé, respectively: Yaoundé is the capital city of Cameroon (Figure 1). Nkolbisson is located 8 km from Nkolondom and 13 km from Ekié, whereas the distance between Ekié and Nkolondom is 16 km. Yaoundé lies at 760 m altitude; the average annual temperature is 23.8 °C, with 1628.3 mm average annual rainfall and an annual average 83.0% relative humidity. The climate is characterized by two wet and two dry seasons [43]. The rains mostly fall from March to November, with two peaks in May (219.7 mm) and October (296.1 mm) and a relative breakdown between July and August (short dry season) when precipitation does not exceed 120 mm per month. The main dry season lasts for 3 months, from December to February; the rainfall at that time is less than 50 mm per month. The hydrographic network is very diverse, but consists mostly of streams, rivers, and ponds.
The three study sites are subject to vegetable farming activities due to the presence of swamps (Figure 1). The number of farmers in these districts has increased rapidly since the 2000s, as one of the consequences of the rapid urbanization associated with high demand for food. At least 85% of the population living in these marshlands are involved in agriculture. The food production is diverse, including leafy vegetables, condiments, floriculture, and other food crops highly valued by city dwellers, which are grown year-round [44]. The crop production is intensive and associated with a wide use of chemical fertilizers as well as pesticides [30,44]. More than 70% of farmers treat their crops with at least two chemicals per treatment cycle [28,44]. The puddles created between the cultivated ridges are suitable breeding sites for Anopheles mosquitoes, vectors of Plasmodium parasites. The mosquito species breeding here belong to the An. gambiae species complex and An. funestus group. The estimated annual entomological inoculation rates are high, reaching up to 92 infective bites/person/year (ib/m/y) [45]. The transmission is perennial; malaria infections are essentially due to Plasmodium falciparum, with few P. malariae cases reported [11,46]. The annual Plasmodium parasite prevalence in the general populations of these areas ranges from 25% to 55% (unpublished data).
4.2. Mosquito Collection, Rearing and Processing
Mosquito collections were conducted in April–May 2018 during the short rainy season, in December 2018–January 2019 during the main dry season, and September–October 2019, during the main rainy season. In each study site, all open water bodies in and around the vegetable farms, including large drain channels, puddles, stream-bed pools, and swamps (Figure 1) were inspected across a total area of ≈ 1–2 km2. Anopheles larvae and pupae were collected from their breeding sites using the dipping method [47]. Collected mosquito larvae were transported to the Malaria Research Laboratory of Organisation de Coordination pour la lutte contre les Endémies en Afrique Centrale (OCEAC) and reared in the insectary until adult emergence at 27 ± 3 °C, 60–80% relative humidity, and a 12:12 light-dark cycle. Upon emergence, female An. gambiae s.l. were identified using morphological identification keys [48,49]. Three- to five-day-old unfed females of An. gambiae s.l. were used for insecticide susceptibility and resistance intensity tests, as well as for molecular analysis.
4.3. Insecticide Susceptibility Assays
Insecticide resistance was assessed using the standard WHO susceptibility test procedures for adult mosquitoes [34]. Tests were performed under ambient room temperature (24–27 °C) and a relative humidity of 70–80%, using discriminating concentrations (DCs) of insecticides on filter paper. The test DCs and insecticides included three ester pyrethroids, i.e., 0.05% deltamethrin, 0.75% permethrin and 0.05% alpha-cypermethrin, and the non-ester pyrethroid 0.5% etofenprox. Insecticide-impregnated filter papers were supplied by the Vector Control Research Unit (VCRU) of the Universiti Sains of Malaysia. One bioassay included four replicates of 20–25 female mosquitoes from field-collected larvae per insecticide. A total of 3492 mosquitoes were used for these tests, including 1192 from Ekié, 1200 from Nkolondom and 1100 from Nkolbisson (Table 4). One to two tubes of 20–25 mosquitoes were exposed to silicone-oil-impregnated paper and served as controls. After a one-hour exposure, mosquitoes were transferred to holding tubes and provided with a cotton pad soaked in 10% sugar solution for feeding.

Table 4.
Number of mosquitoes used for insecticide susceptibility and resistance intensity testing.
The number of mosquitoes knocked down during exposure to insecticide-impregnated papers was recorded at five-minute intervals, and mortality was determined 24 h post-exposure. Tests were also performed with three- to five-day-old unfed females of the insecticide-susceptible An. gambiae s.s. Kisumu laboratory colony.
4.4. Resistance Intensity Assays
Once the resistance status was determined using the DCs, intensity bioassays with 5× and 10× DCs for alpha-cypermethrin, deltamethrin, permethrin and etofenprox were performed according to the standard WHO bioassay method as described above [34]. All insecticides combined, 3534 and 2556 An. gambiae s.l. mosquitoes were used for intensity tests with 5× and 10× DCs, respectively (Table 4).
The filter papers impregnated with 5× DCs and 10× DCs (Table 2) were also supplied by the VCRU. Results were interpreted following the WHO criteria for insecticide resistance intensity [35]. Mosquito specimens were then stored in RNAlater® (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States) at −20 °C for further molecular analysis.
4.5. Molecular Assays
A subset of 50 An. gambiae s.l. specimens per study site, used as controls during the susceptibility and resistance intensity bioassays conducted in April 2018, were randomly selected and used for species identification, kdr L995F, L995S, and N1570Y, and Ace-1 G280S genotyping. These analyses were carried out at the molecular biology laboratory of the Centre Suisse de Recherches Scientifiques en Côte d’Ivoire (CSRS) in Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire. Genomic DNA was extracted from individual mosquitoes using a magnetic beads-based protocol (MagnaMedics Diagnostics GmbH, Aachem, Germany, Cat. No. MD01017), following [50], and stored at −20 °C until used for the TaqMan® reverse-transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) assays. The lysate was diluted 10× in PCR-grade water and used for the RT-qPCR SNP TaqMan® assays (Eurofins Genomics, Ebersberg, Germany). Species identification and detection of insecticide resistance mutations were performed on the CFX96 Bio-Rad Real-Time PCR system (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc, Hercules, CA, USA) using a one-step RT-PCR master mix supplied by FTD (Fast-track diagnostics, Luxembourg) in a total reaction volume of 10 µL [50,51,52,53,54].
Another subset of 50 randomly selected An. gambiae s.l. specimens per study site also collected in April–May 2018 was used for metabolic and cuticular resistance gene expression analysis at the OCEAC laboratory of medical entomology. Expression levels of Cyp6p3, Cyp6m2, Cyp9k1, Cyp6p4, Cyp6z1, Cyp6p1, and Cyp4g16 were measured relative to a housekeeping gene encoding the ribosomal protein S7 (RPS7) in field-collected specimens and compared to expression levels of the same detox genes in the susceptible Kisumu colony using triplex assays with the direct RT-qPCR approach: 1:200 diluted lysates without RNA extraction [55]. Briefly, 10 mosquitoes were homogenized in 100 µL of RTL lysis buffer (QIAGEN, Cat. No. 79216) using a battery-powered tissue grinder and a plastic pestle in a 1.5 mL micro centrifuge tube. The lysate was diluted using RNase-free water (1:200), and 10 µL was directly added to “ready-to-go” lyophilized pellets presented in Vontas and Mavridis, 2019 [56]. The runs were performed in a QuantStudio™ 5 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems™, Waltham, MA, USA) with the following thermal cycle parameters: 50 °C for 15 min, 95 °C for 3 min, and 40 cycles of 95 °C for 3 s and 60 °C for 30 s. Samples were amplified in at least two technical replicates, using three biological replicates for gene expression analysis for each population. QuantStudioTM Design & Analysis Software v1.5.2 (Applied Biosystems™, Waltham, MA, USA) was used for the calculation of Ct values for each reaction, which were then used to calculate fold-changes according to the Pfaffl method [57].
Assays were designed and performed in the framework of the interdisciplinary research project DMC-MALVEC (https://dmc-malvec.eu, accessed on 8 September 2021). The list of probes and primers used for molecular analysis is provided in Table 5.

Table 5.
List of probes and primers used for molecular analysis.
4.6. Data Analysis
The resistance status was classified according to the WHO criteria [34]. Mortality rates below 90% indicate resistance, whereas those above 98% indicate susceptibility. Mortality rates between 90% and 98% indicate possible resistance to be confirmed. For assessment of the resistance intensity, the following WHO interpretation criteria [34] were used:
Mortality rates of 98–100% at 5× DC indicate a low resistance intensity;
Mortality rates less than 98% at 5× DC indicate a moderate to high resistance intensity, and 98–100% mortality rates at 10× DC confirm a moderate resistance intensity;
Mortality rates of less than 98% at 10× DC indicate a high resistance intensity.
The trends of mortality rates as an indicator of resistance status or resistance intensity were analyzed using the R statistical software (R Core Team 2021, version 4.1.1) [58] via RStudio. Packages dplyr, ggplot2 were used for data description and generating graphs of mortality rates of tested An. gambiae s.l. samples [59], whereas lme4 and lmerTest were used for modelling the resulting profile of insecticide resistance [60,61].
We considered logistic regression with the logit link function to model mortality as an outcome. In the experiments performed, the mosquitoes were grouped in tubes. Therefore, we first confronted the baseline classical logistic model with the mixed-effects model in which the randomized variable was the tube. For this, we performed the log-likelihood ratio test. The test was significant at the 5% level, with a p-value ≈ 0 < 1% (statistic , degrees of freedom = 1). Therefore, the mortality data were modeled using mixed-effects logistic regression. Thus, the remaining mortality analyses were based on the mixed-effects logistic regression model in which the randomized variable was the tube. The fixed effects were the insecticide and mosquito collection period.
Statistical analyses were carried out using the statistical software R via RStudio. In particular, the following packages were used: dplyr, ggplot2 for data description and generating graphs, whereas lme4 and lmerTest were used for modelling mortality.
5. Conclusions
This study provides evidence of moderate to high levels of resistance intensity to ester pyrethroids and the non-ester pyrethroid etofenprox in vegetable farming areas in Yaoundé, Cameroon. Therefore, the effectiveness of LLIN treated with ester and non-ester pyrethroids may be compromised in these areas. Additionally, IRS with etofenprox is not a good alternative for the replacement of LLINs in these areas. Further investigations are needed to assess the geographic distribution of the high resistance intensity, and the underlying mechanisms in other areas in Cameroon.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.E., P.N. and M.P.; Methodology, M.P., W.E.E., S.M., L.R.M., P.K.N.E., A.T.N., K.L.N. and J.C.T.; software, W.T.; Formal Analysis, M.P., P.N., K.M., N.C.W., P.F.K., J.E. and W.T.; Data Curation, L.R.M., W.E.E., S.M., K.L.N., P.K.N.E., A.T.N.; Writing―Original Draft Preparation, P.N., M.P. and J.E.; Resources, K.M., N.C.W., P.F.K., M.C., P.M., P.A.-A.; Project Administration, P.N., P.A.-A. and J.E.; Supervision, J.E.; Funding Acquisition, J.V., J.E., P.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was funded by the European Union Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (688207-DMC-MALVEC).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study protocol was approved by the Cameroon National Ethics Committee (N°2020/07/1573/L/CNERSH/SP) and by the Ministry of Public Health (N°D30-633/AAR/MINSANTE/SG/DROS/NDG/). We also obtained the administrative authorizations from the respective district officers of the districts of Yaoundé I, IV and VII.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during the current study are included in this published article.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all the residents of Ekié, Nkolondom and Nkolbisson who agreed to participate in this study and gave permission to enter their compounds for mosquito larvae collection. We would also like to thank the insectary team that reared the Kisumu An. gambiae s.s. colony.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of mosquitoes used for susceptibility tests and molecular analysis are available from the authors.
Abbreviations
| ACTs | Artemisinin combination therapies |
| CSRS | Centre Suisse de Recherches Scientifique en Côte d’Ivoire |
| DC | Diagnostic concentrations |
| HL1 | High level 1 |
| HL2 | High level 2 |
| HL3 | High level 3 |
| IRS | Indoor residual spraying |
| Kdr | Knockdown resistance |
| LLINs | Long-lasting insecticidal nets |
| MR | Mortality rates |
| RR | Resistant homozygote |
| RS | Heterozygotes |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse-transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| SS | Susceptible homozygote |
| VCRU | Vector Control Research Unit |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Bhatt, S.; Weiss, D.J.; Cameron, E.; Bisanzio, D.; Mappin, B.; Dalrymple, U.; Battle, K.; Moyes, C.; Henry, A.; Eckhoff, P.A.; et al. The effect of malaria control on Plasmodium falciparum in Africa between 2000 and 2015. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 526, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2020: 20 Years of Global Progress and Challenges. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240015791 (accessed on 29 July 2021).
- World Health Organization. Pre-Qualification Team: Pre-Qualified Vector Control Products. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/pq-vector-control/prequalified-lists/VCP_PQ-List_26August2020.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- Diabate, A.; Baldet, T.; Chandre, F.; Akoobeto, M.; Guiguemde, T.R.; Darriet, F.; Brengues, C.; Guillet, P.; Hemingway, J.; Small, G.J.; et al. The role of agricultural use of insecticides in resistance to pyrethroids in Anopheles gambiae s.l. in Burkina Faso. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 67, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadouleton, A.; Martin, T.; Padonou, G.; Chandre, F.; Asidi, A.; Djogbenou, L.; Dabire, R.; Aikpon, R.; Boko, M.; Glitho, I.; et al. Cotton pest management practices and the selection of pyrethroid resistance in Anopheles gambiae populations in northern Benin. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talom, A.D.; Tchuinkam, T.; Zeukeng, F.; Demano, M.L.; Kuate, A.F.; Lehman, G.L.; Djouaka, R. Susceptibility of Anopheles gambiae s.l. to pyrethroid insecticides in vegetable farms in the city of Yaoundé, Cameroon. J. Entomol. Zool Stud. 2020, 8, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar]
- Mouhamadou, C.S.; de Souza, S.S.; Fodjo, B.K.; Zoh, M.G.; Bli, N.K.; Koudou, B.G. Evidence of insecticide resistance selection in wild Anopheles coluzzii mosquitoes due to agricultural pesticide use. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogdon, W.G.; McAllister, J.C. Insecticide resistance and vector control. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1998, 4, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbel, V.; N’Guessan, R. Distribution, Mechanisms, Impact and Management of Insecticide Resistance in Malaria Vectors: A Pragmatic Review. In Anopheles Mosquitoes―New Insights into Malaria Vectors; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Tene Fossog, B.; Ndo, C.; Menze Djantio, B.; Zebaze Togouet, S.; Awono-Ambene, P.; Costantini, C.; Wondji, C.S.; Ranson, H. Anopheles gambiae distribution and insecticide resistance in the cities of Douala and Yaoundé (Cameroon): Influence of urban agriculture and pollution. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ministère de la Santé. Programme National de Lutte Contre le Paludisme au Cameroun. Plan Stratégique National de Lutte Contre le Paludisme, 2020–2024. Available online: file:///C:/Users/josye/AppData/Local/Temp/PlanstrategiquenationalPaludisme2020–2024.pdf (accessed on 29 July 2021).
- Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Ndo, C.; Njiokou, F.; Bigoga, J.; Awono-Ambene, P.; Etang, J.; Ekobo, A.S.; Wondji, C.S. Review of malaria situation in Cameroon: Technical viewpoint on challenges and prospects for disease elimination. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Etang, J.; Manga, L.; Chandre, F.; Guillet, P.; Fondjo, E.; Mimpfoundi, R.; Toto, J.C.; Fontenille, D. Insecticide susceptibility status of Anopheles gambiae s.l. (Diptera: Culicidae) in the Republic of Cameroon. J. Med. Entomol. 2003, 40, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etang, J.; Chouaibou, M.; Ndjemai, H.; Chandre, F.; Morlais, I.; Fondjo, E.; Simard, F.; Brengues, C.; Nwane, P. First report of knockdown mutations in the malaria Anopheles gambiae from Cameroon. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 74, 795–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Sonhafouo-Chiana, N.; Ngadjeu, C.S.; Doumbe-Belisse, P.; Talipouo, A.; Djamouko-Djonkam, L.; Kopya, E.; Bamou, R.; Awono-Ambene, P.; Wondji, C.S. Review of the evolution of insecticide resistance in main malaria vectors in Cameroon from 1990 to 2017. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwane, P.; Etang, J.; Chouaïbou, M.; Toto, J.C.; Mimpfoundi, R.; Simard, F. Kdr-based insecticide resistance in Anopheles gambiae s.s. populations in Cameroon: Spread of the L1014F and L1014S mutations. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mandeng, S.E.; Awono-Ambene, H.P.; Bigoga, J.D.; Ekoko, W.E.; Binyang, J.; Piameu, M.; Mbakop, L.R.; Fesuh, B.N.; Mvondo, N.; Tabue, N.; et al. Spatial and temporal development of deltamethrin resistance in malaria vectors of the Anopheles gambiae complex from North Cameroon. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bamou, R.; Sonhafouo-Chiana, N.; Mavridis, K.; Tchuinkam, T.; Wondji, C.S.; Vontas, J.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C. Status of Insecticide Resistance and Its Mechanisms in Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles coluzzii Populations from Forest Settings in South Cameroon. Genes 2019, 10, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Etang, J.; Manga, L.; Toto, J.C.; Guillet, P.; Fondjo, E.; Chandre, F. Spectrum of metabolic-based resistance to DDT and pyrethroids in Anopheles gambiae s.l. populations from Cameroon. J. Vector Ecol. 2007, 32, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elanga-Ndille, E.; Nouage, L.; Ndo, C.; Binyang, A.; Assatse, T.; Nguiffo-Nguete, D.; Djonabaye, D.; Irwing, H.; Tene-Fossog, B.; Wondji, C.S. The G119S Acetylcholinesterase (Ace-1) Target Site Mutation Confers Carbamate Resistance in the Major Malaria Vector Anopheles gambiae from Cameroon: A Challenge for the Coming IRS Implementation. Genes 2019, 10, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Etang, J.; Pennetier, C.; Piameu, M.; Bouraima, A.; Chandre, F.; Awono-Ambene, P.; Coosemans, M.; Corbel, V. When intensity of deltamethrin resistance in Anopheles gambiae s.l. leads to loss of Long-Lasting Insecticidal Nets bio-efficacy: A case study in north Cameroon. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguendo Yongsi, H.B.; Ntetu Lutumba, A.; Bryant, R.C.; Ojuku, T.; Thora, H.M. Uncontrolled Draining of Rainwater and Health. Consequences in Yaoundé―Cameroon. Acta Univ. 2009, 19, 20–30. [Google Scholar]
- Nwane, P.; Etang, J.; Chouaïbou, M.; Toto, J.C.; Koffi, A.; Mimpfoundi, R.; Simard, F. Multiple insecticide resistance mechanisms in Anopheles gambiae s.l. populations from Cameroon, Central Africa. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fouet, C.; Ashu, A.F.; Ambadiang, M.M.; Tchapga, W.; Wondji, C.S.; Kamdem, C. Resistance of Anopheles gambiae to the new insecticide clothianidin associated with unrestricted use of agricultural neonicotinoids in Yaoundé, Cameroon. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamou, R.; Mbakop, L.R.; Kopya, E.; Ndo, C.; Awono-Ambene, P.; Tchuinkam, T.; Rono, M.K.; Mwangangi, J.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C. Changes in malaria vector bionomics and transmission patterns in the equatorial forest region of Cameroon between 2000 and 2017. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamouko-Djonkam, L.; Mounchili-Ndam, S.; Kala-Chouakeu, N.; Nana-Ndjangwo, S.; Kopya, E.; Sonhafouo-Chiana, N.; Talipouo, A.; Ngadjeu, C.S.; Doumbe-Belisse, P.; Bamou, R.; et al. Spatial distribution of Anopheles gambiae sensu lato larvae in the urban environment of Yaoundé, Cameroon. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diabaté, A.; Dabire, R.K.; Millogo, N.; Lehmann, T. Evaluating the Effect of Postmating Isolation Between Molecular Forms of Anopheles gambiae (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2007, 44, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimonneau, G.; Bouyer, J.; Morand, S.; Besansky, N.J.; Diabate, A.; Simard, F. A behavioral mechanism underlying ecological divergence in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Behav. Ecol. 2010, 21, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nwane, P.; Etang, J.; Chouaibou, M.; Toto, J.C.; Kerah-Hinzoumbé, C.; Mimpfoundi, R.; Awono-Ambene, H.P.; Simard, F. Trends in DDT and pyrethroid resistance in Anopheles gambiae s.s. populations from urban and agro-industrial settings in southern Cameroon. BMC Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. World Health Organization Recommended Insecticides for Indoor Residual Spraying against Malaria Vectors. 2015. Available online: https://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/vector_ecology/vector-control/Insecticides (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Chanda, E.; Alister Kandyata, A.; Javan Chanda, J.; Phiri, F.N.; Muzia, L.; Kamuliwo, M. The Efficacy of Vectron 20 WP, Etofenprox, for Indoor Residual Spraying in Areas of High Vector Resistance to Pyrethroids and Organochlorines in Zambia. ISRN Prev. Med. 2013, 2013, 371934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mfopou, Y.C.M.; Traore, M.; Kenmogne, P.P.N.; Aboubakar, A.; Manguele, G.S.F.; Maboune, S.A.T.; Ndam, J.R.N.; Gnankambary, Z.; Nacro, H.B. Structure of Vegetables Farming and Farmer’s Perception of Soil and Water Degradation in Two Peri urban Areas in Yaounde Cameroon. Open J. Soil Sci. 2017, 7, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talipouo, A.; Ngadjeu, C.S.; Patricia Doumbe-Belisse, P.; Landre Djamouko-Djonkam, L.; Sonhafouo-Chiana, N.; Edmond Kopya, E.; Bamou, R.; Awono-Ambene, P.; Woromogo, S.; Kekeunou, S.; et al. Malaria prevention in the city of Yaoundé: Knowledge and practices of urban dwellers. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Test Procedures: For Insecticide Resistance Monitoring in Malaria Vector Mosquitoes; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; 56p, Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/250677/9789241511575-eng.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Ahadji-Dabla, K.M.; Chabi, J.; Apetogbo, G.Y.; Hadi, M.P.; Ketoh, G.K. Pyrethroid Resistance Intensity of Anopheles gambiae sensu lato (Diptera: Culicidae) from Phase II Hut Trial Station in Kolokope, Eastern Plateau Togo: A Potential Site to Assess the Next Generation of Long-Lasting Insecticidal Nets. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovi, A.; Keita, C.; Sinaba, Y.; Dicko, A.; Traore, I.; Cisse, M.B.; Koita, O.; Dengela, D.O.; Flatley, C.; Bankineza, E.; et al. Anopheles gambiae (s.l.) exhibit high intensity pyrethroid resistance throughout Southern and Central Mali (2016–2018): PBO or next generation LLINs may provide greater control. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awolola, T.S.; Adeogun, A.; Olakiigbe, A.K.; Oyeniyi, T.; Olukosi, Y.A.; Okoh, H.; Arowolo, T.; Akila, J.; Oduola, A.; Amajoh, C.N. Pyrethroids resistance intensity and resistance mechanisms in Anopheles gambiae from malaria vector surveillance sites in Nigeria. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Insecticide Resistance in Malaria Vectors: 2010–2016; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/igo (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Elanga-Ndille, E.; Binyang, A.; Ndo, C.; Assatse, T.; Nouage, L.; Tchouakui, M.; Tene-Fossog, B.; Kekeunou, S.; Wondji, C.S. Entomological indicators of malaria transmission and insecticide resistance profile of Anopheles gambiae at the early phase of irrigated rice farming in the forest area of central Cameroon. Wellcome Open Res. 2020, 5, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, B.J.; Bibby, J.; Pignatelli, P.; Muangnoicharoen, S.; O’Neill, P.M.; Lian, L.Y.; Muller, P.; Nikou, D.; Steven, A.; Hemingway, J.; et al. Cytochrome P450 6M2 from the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae metabolizes pyrethroids: Sequential metabolism of deltamethrin revealed. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vontas, J.; Katsavou, E.; Mavridis, K. Cytochrome P450-based metabolic insecticide resistance in Anopheles and Aedes mosquito vectors: Muddying the waters. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 170, 104666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranson, H.; Jensen, B.; Wang, X.; Prapanthadara, L.; Hemingway, J.; Collins, F.H. Genetic mapping of two loci affecting DDT resistance in the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Insect Mol. Biol. 2000, 9, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaounde, Climate Yaounde, Temperatures Yaounde, Weather Averages. Available online: http://www.yaounde.climatemps.com/ (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Nguegang, P.A. L’agriculture Urbaine et périurbaine à Yaoundé: Analyse Multifonctionnelle d’une activité Montante en économie de survie. Ph.D. Thesis, Sciences Agronomiques et Ingénierie Biologique, Université libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium, 2008. Available online: file:///C:/Users/josye/AppData/Local/Temp/TheseNguegangProsper.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Doumbe-Belisse, P.; Ngadjeu, C.S.; Sonhafouo-Chiana, N.; Talipouo, A.; Djamouko-Djonkam, L.; Kopya, E.; Bamou, R.; Toto, J.C.; Mounchili, S.; Tabue, R.; et al. High malaria transmission sustained by Anopheles gambiae s.l. occurring both indoors and outdoors in the city of Yaoundé, Cameroon. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Kolk, M.; Etti Tebo, A.; Nimpaye, H.; Ngo Ndombol, D.; Sauerwein, R.; Eling, W. Transmission of Plasmodium falciparum in urban Yaoundé Cameroon is seasonal and age-dependent. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 97, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumsden, W.H.R.; Service, M.W. Mosquito Ecology. Field Sampling Methods. J. Appl. Ecol. 1977, 14, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, M.T.; Coetzee, M. A supplement to the Anophelinae of Africa South of the Sahara. Publ. Afr. Inst. Med. Res. 1987, 55, 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Gillies, M.T.; De Meillon, B. The Anophelinae of Africa South of the Sahara (Ethiopian Zoogeographical Region.); Publications of the South African Institute for Medical Research: Johannesburg, South Africa, 1968; pp. 1–343. [Google Scholar]
- Mavridis, K.; Wipf, N.; Müller, P.; Traoré, M.M.; Muller, G.; Vontas, J. Detection and Monitoring of Insecticide Resistance Mutations in Anopheles gambiae: Individual vs. Pooled Specimens. Genes 2018, 9, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bass, C.; Williamson, M.S.; Field, L.M. Development of a multiplex real-time PCR assay for identification of members of the Anopheles gambiae species complex. Acta Trop. 2008, 107, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, M.J.; Liyanapathirana, M.; Agossa, F.R.; Weetman, D.; Ranson, H.; Donnelly, M.J.; Wilding, C.S. Footprints of positive selection associated with a mutation (N1575Y) in the voltage-gated sodium channel of Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6614–6619. [Google Scholar]
- Bass, C.; Nikou, D.; Donnelly, M.J.; Williamson, M.S.; Ranson, H.; Ball, A.; Vontas, J.; Field, L.M. Detection of knockdown resistance (kdr) mutations in Anopheles gambiae: A comparison of two new high-throughput assays with existing methods. Malar. J. 2007, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bass, C.; Nikou, D.; Vontas, J.; Williamson, M.S.; Field, L.M. Development of high-throughput real-time PCR assays for the identification of insensitive acetylcholinesterase (ace-1R) in Anopheles gambiae. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 96, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavridis, K.; Wipf, N.; Medves, S.; Erquiaga, I.; Müller, P.; Vontas, J. Rapid multiplex gene expression assays for monitoring metabolic resistance in the major malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vontas, J.; Mavridis, K. Vector population monitoring tools for insecticide resistance management: Myth or fact? Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 161, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Horgan, G.W.; Dempfle, L. Relative Expression Software Tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H. lmerTest package: Tests in linear mixed effects models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickham, H.; Navarro, D.; Pedersen, T.L. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).