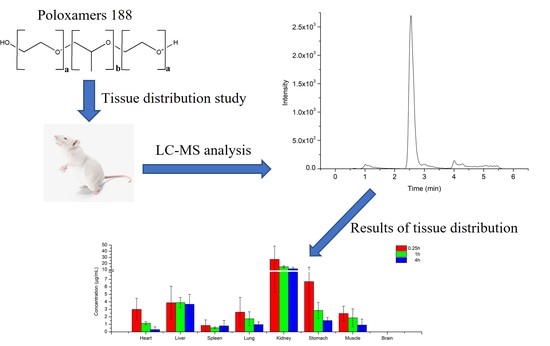
Tissue Distribution Study of Poloxamer188 in Rats by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole Time of Flight/Mass Spectrometry with MSALL-Based Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
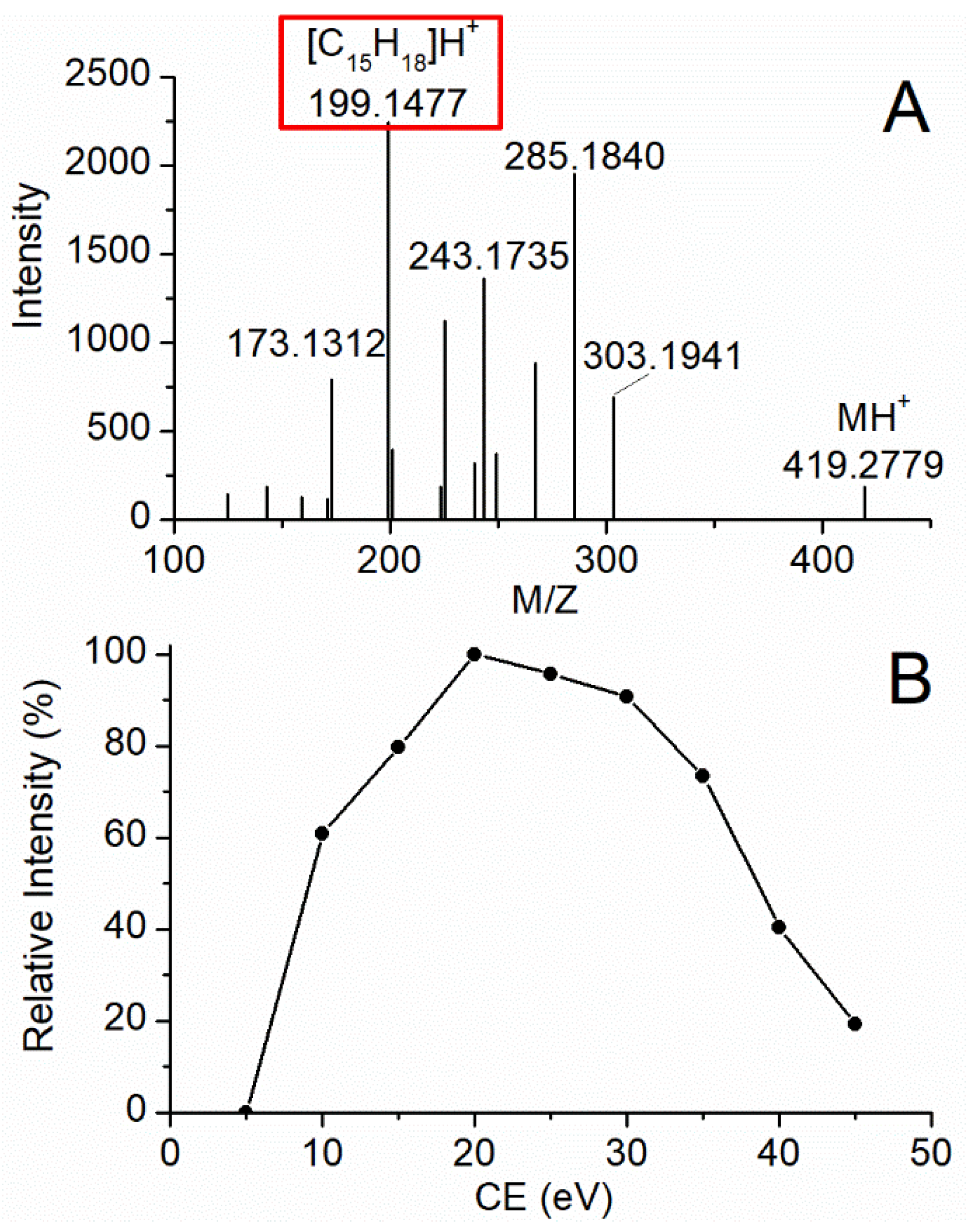
2.1. Optimization of MS Conditions
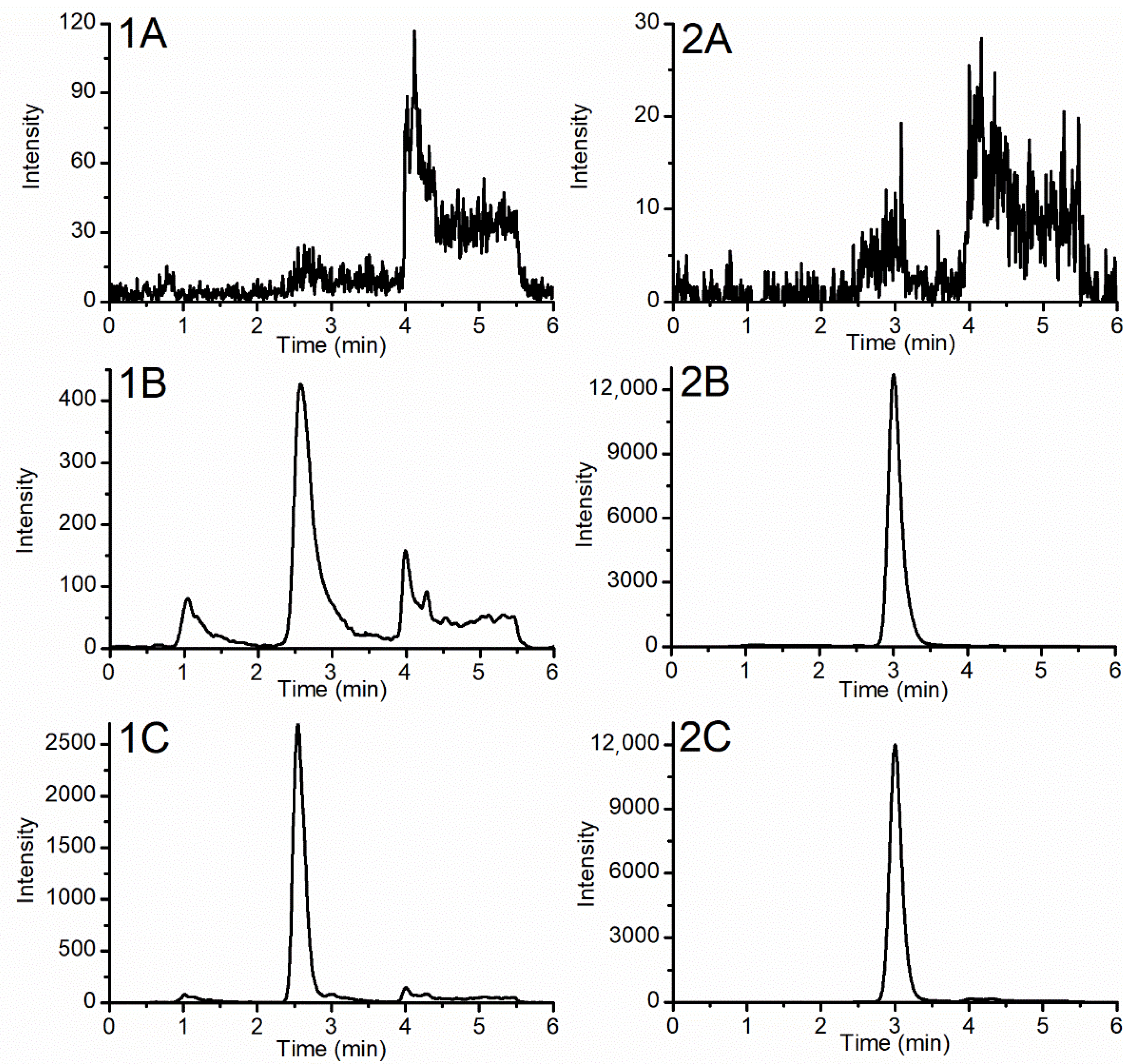
2.2. Chromatography Development
2.3. Assay Validation
2.4. Tissue Distribution
3. Materials and Methords
3.1. Chemical Reagents and Materials
3.2. Sample Preparations
3.3. UPLC-Q-TOF/MS Conditions
3.4. Data Processing
3.5. Assay Validation
3.6. Tissue Distribution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| PL188 | poloxamer188 |
| PPO | poly propylene oxide |
| PEO | poly ethylene oxide |
| MRM | multiple reaction monitoring |
| Q-TOF/MS | Quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometer |
| CE | collision energy |
| DP | declustering potential |
| IS | internal standard |
| LLOQ | lower limit of quantitation |
| QC | quality control |
| LOD | limit of detection |
| ULOQ | upper limit of quantitation |
| UHPLC | ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography |
References
- Jung, Y.W.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.Y.; Koo, E.J.; Oh, K.S.; Yuk, S.H. Pluronic-Based Core/Shell Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Diagnosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 3488–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodratti, A.M.; Alexandridis, P. Formulation of Poloxamers for Drug Delivery. J. Func. Biom. 2018, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Alexandridis, P. Physicochemical aspects of drug delivery and release from polymer-based colloids. Curr. Opin. Colloid. In. 2000, 5, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkari, A.C.S.; Papini, J.Z.B.; Garcia, G.K.; Franco, M.; Cavalcanti, L.P.; Gasperini, A.; Alkschbirs, M.I.; Yokaichyia, F.; de Paula, E.; Tófoli, G.R.; et al. Poloxamer 407/188 binary thermosensitive hydrogels as delivery systems for infiltrative local anesthesia: Physico-chemical characterization and pharmacological evaluation. Mat. Sci. Eng. C Mater. 2016, 68, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandridis, P. Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis, Morphology Control, and Stabilization Facilitated by Functional Polymers. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharwat, T. Viscoelastic properties of sterically stabilised emulsions and their stability. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 692–708. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, H.; Amaral, M.H.; Lobão, P.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Applications of poloxamers in ophthalmic pharmaceutical formulations: An overview. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dun, J.; Osei-Yeboah, F.; Boulas, P.; Lin, Y.; Sun, C.C. A systematic evaluation of poloxamers as tablet lubricants. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 576, 118994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audrey, S.; Amanda, C.; Sona, J.; Eduardo, C.; Ricardo, F.; Ricardo, S.; Rogéria, N.; Silvio, D. Application of Poloxamers for the Development of Drug Delivery System to Treat Leishmaniasis: A Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2020, 22, 296–309. [Google Scholar]
- Tingting, Z.; Shiqi, C.; Haibo, D.; Quanjin, L.; Gang, S.; Juchun, L.; Wei, Z.; Guangneng, P.; Zhijun, Z.; Hualin, F. Novel glucosamine-loaded thermosensitive hydrogels based on poloxamers for osteoarthritis therapy by intra-articular injection. Mat. Sci. Eng. C Mater. 2021, 118, 111352. [Google Scholar]
- Grindel, J.M.; Jaworski, T.; Emanuele, R.M.; Culbreth, P. Pharmacokinetics of a novel surface-active agent, purified poloxamer 188, in rat, rabbit, dog and man. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2002, 23, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grindel, J.M.; Jaworski, T.; Piraner, O.; Emanuele, R.M.; Balasubramanian, M. Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion of a Novel Surface-Active Agent, Purified Poloxamer 188, in Rats, Dogs, and Humans. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 1936–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Thompson, M.J.; Wang, Q.; Tsai, E.W. Quantitation of poloxamers in pharmaceutical formulations using size exclusion chromatography and colorimetric methods. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2004, 35, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.H.; Zhou, C.; Khor, H.K.; Qiu, J. Direct determination of residual Pluronic F-68 in in-process samples from monoclonal antibody preparations by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschen, C.A.; Klemm, D.; Graf, T.; Kopf, R.; Pinto, C.; Müller, C.; Bell, C.H.; Pfaff, J. Simultaneous quantification of polysorbate 20 and poloxamer 188 in biopharmaceutical formulations using evaporative light scattering detection. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 192, 113640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, D.L.; Ranglová, K.; Hájek, J.; Hrouzek, P. Quantification of methionine and selenomethionine in biological samples using multiple reaction monitoring high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (MRM-HPLC-MS/MS). J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1084, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Ferreira, C.R.; Virequ, A.A.; Cooks, R.G. Multiple reaction monitoring profiling (MRM profiling): Small molecule exploratory analysis guided by chemical functionality. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2021, 235, 105048. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Su, C.; Ren, T.; Meng, X.; Shi, M.; Fawcett, J.P.; Zhang, M.; Hu, W.; Gu, J. MSAll strategy for comprehensive quantitative analysis of PEGylated-doxorubicin, PEG and doxorubicin by LC-high resolution q-q-TOF mass spectrometry coupled with all window acquisition of all fragment ion spectra. Analyst 2017, 142, 4279–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Meng, X.; Cheng, L.; Su, C.; Sun, Y.; Sun, L.; Tang, Z.; Fawcett, J.P.; Yang, Y.; Gu, J. Development and Application of an MSALL-Based Approach for the Quantitative Analysis of Linear Polyethylene Glycols in Rat Plasma by Liquid Chromatography Triple-Quadrupole/Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5193–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhong, L.; Yin, Y. Development of data-independent acquisition workflows for metabolomic analysis on a quadrupole-orbitrap platform. Talanta 2017, 164, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, Z.-J. Advancing untargeted metabolomics using data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry technology. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 4349–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, M.; Cordewener, J.H.; de Groot, J.C.; Smeekens, S.; America, A.H.; Hanson, J. Dynamic protein composition of Arabidopsis thaliana cytosolic ribosomes in response to sucrose feeding as revealed by label free MSE proteomics. Proteomics 2012, 12, 1024–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, G.H.M.F.; Guest, P.C.; Martins-de-Souza, D. LC-MSE, Multiplex MS/MS, Ion Mobility, and Label-Free Quantitation in Clinical Proteomics. Meth. Mol. Biol. 2017, 1546, 57–73. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation. Rockville (MD): 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/bioanalytical-method-validation-guidance-industry (accessed on 16 September 2021).


| Concentration (μg/mL) | Intraday | Interday | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (RE, %) | Precision (RSD, %) | Accuracy (RE, %) | Precision (RSD, %) | |
| 0.1 | 9.7 | 6.8 | 12.5 | 10.9 |
| 0.3 | 8.3 | 5.4 | 7.6 | 12.1 |
| 1.5 | −1.1 | 7.2 | 2.2 | 9.3 |
| 8 | −6.9 | 8.1 | −8.4 | 6.7 |
| Concentration (μg/mL) | Matrix Effect | Extraction Recovery | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD (%) | RSD (%) | Mean ± SD (%) | RSD (%) | |
| 0.3 | 93.0 ± 5.4 | 5.8 | 85.7 ± 6.1 | 7.1 |
| 1.5 | 88.6 ± 7.3 | 8.2 | 75.2 ± 9.2 | 12.2 |
| 8 | 89.2 ± 6.5 | 7.3 | 73.9 ± 3.8 | 5.1 |
| Concentration (μg/mL) | Before Process (4 h, RT) | After Process (4 h, RT) | Auto-Sampler (8 h, 15 °C) | Three Freeze-Thaw Cycles (−20 °C to RT) | Long-Term (−80 °C, 30 days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE (%) | RE (%) | RE (%) | RE (%) | RE (%) | |
| 0.3 | −3.6 | 1.2 | 2.8 | −4.4 | −6.7 |
| 1.5 | −3.1 | −8.5 | −5 | −6.2 | −9.6 |
| 8 | −10.2 | −7.7 | −11.3 | −10.9 | −13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lin, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, H.; Feng, B. Tissue Distribution Study of Poloxamer188 in Rats by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole Time of Flight/Mass Spectrometry with MSALL-Based Approach. Molecules 2021, 26, 5644. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185644
Feng Y, Li L, Li Y, Zhou X, Lin X, Cui Y, Zhu H, Feng B. Tissue Distribution Study of Poloxamer188 in Rats by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole Time of Flight/Mass Spectrometry with MSALL-Based Approach. Molecules. 2021; 26(18):5644. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185644
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yixuan, Lele Li, Yuxuan Li, Xinxin Zhou, Xiaoying Lin, Yue Cui, Heyun Zhu, and Bo Feng. 2021. "Tissue Distribution Study of Poloxamer188 in Rats by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole Time of Flight/Mass Spectrometry with MSALL-Based Approach" Molecules 26, no. 18: 5644. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185644
APA StyleFeng, Y., Li, L., Li, Y., Zhou, X., Lin, X., Cui, Y., Zhu, H., & Feng, B. (2021). Tissue Distribution Study of Poloxamer188 in Rats by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole Time of Flight/Mass Spectrometry with MSALL-Based Approach. Molecules, 26(18), 5644. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185644