Effect of pH and Pea Protein: Xanthan Gum Ratio on Emulsions with High Oil Content and High Internal Phase Emulsion Formation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
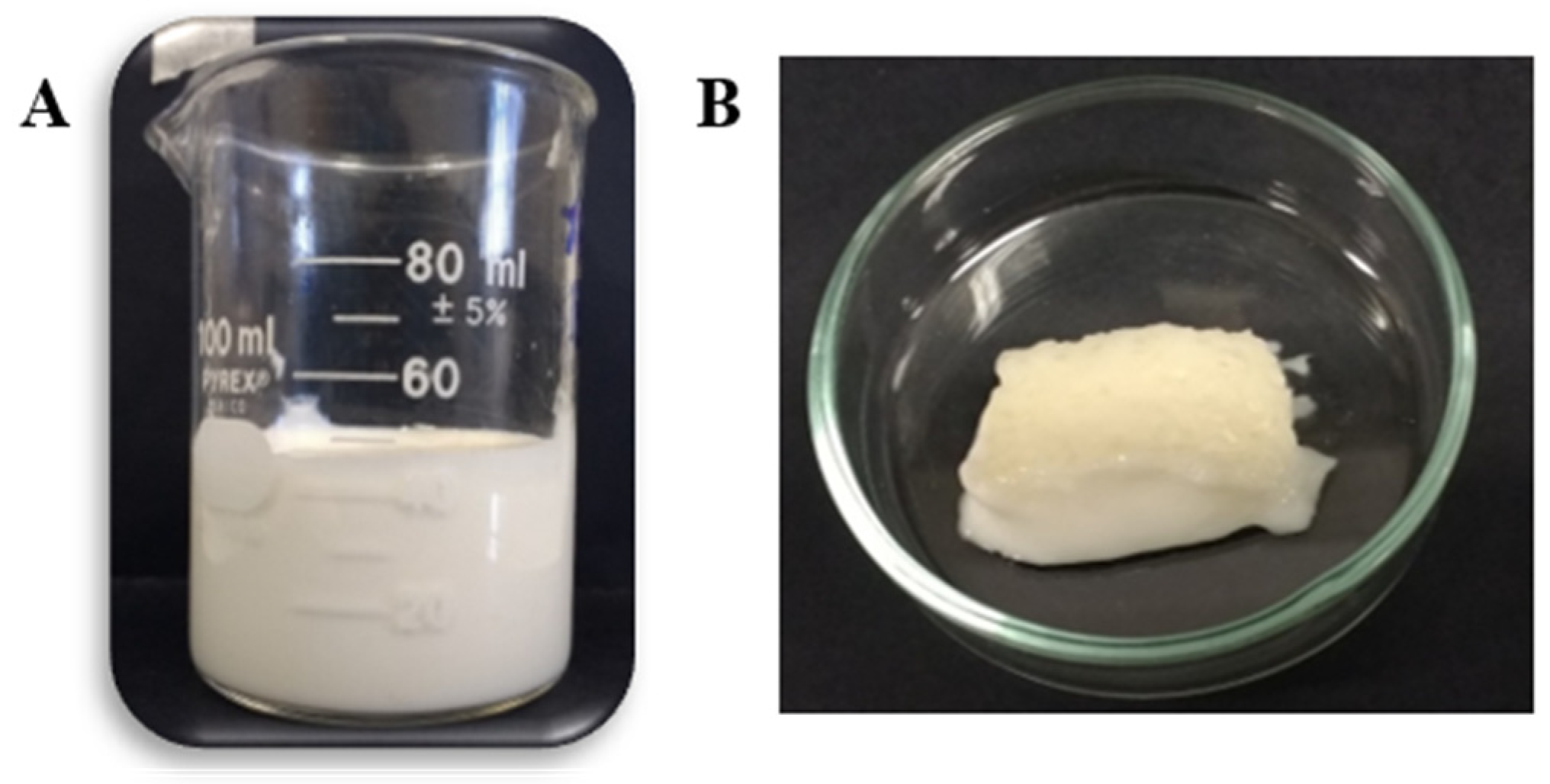
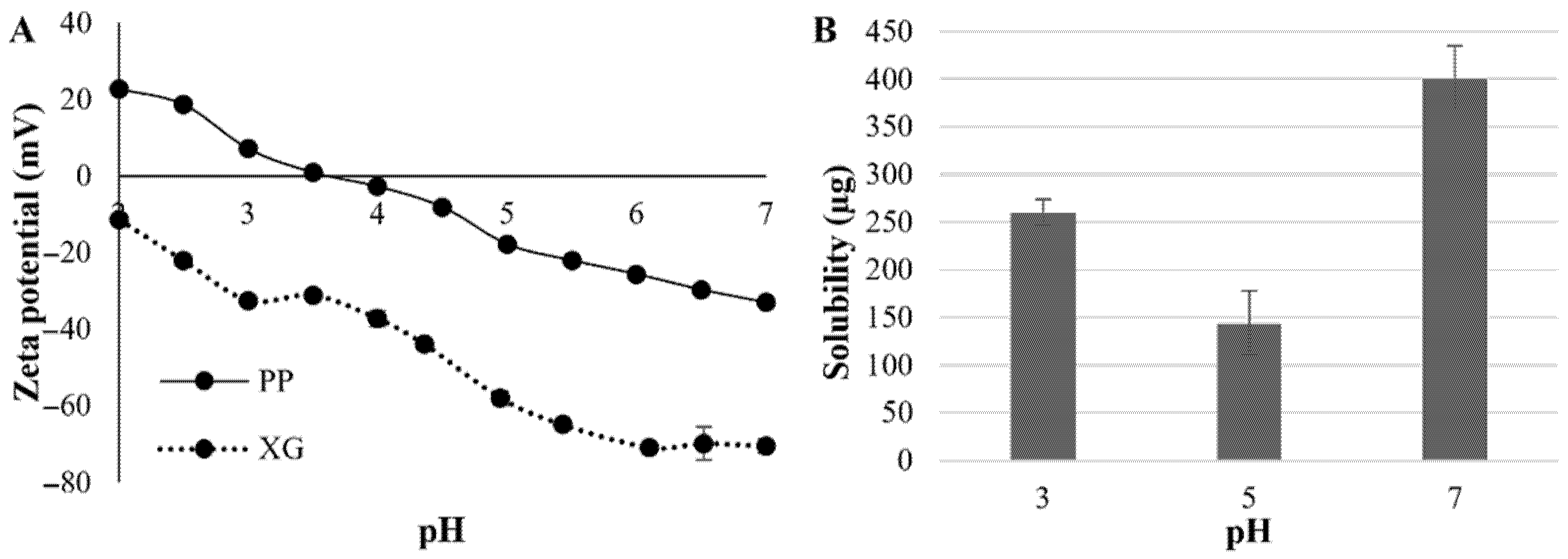
2.1. Hydrocolloids and Pea Protein: Xanthan Gum Electrostatic Complexes’ Characterization
2.2. Macrostructure and Water Loss
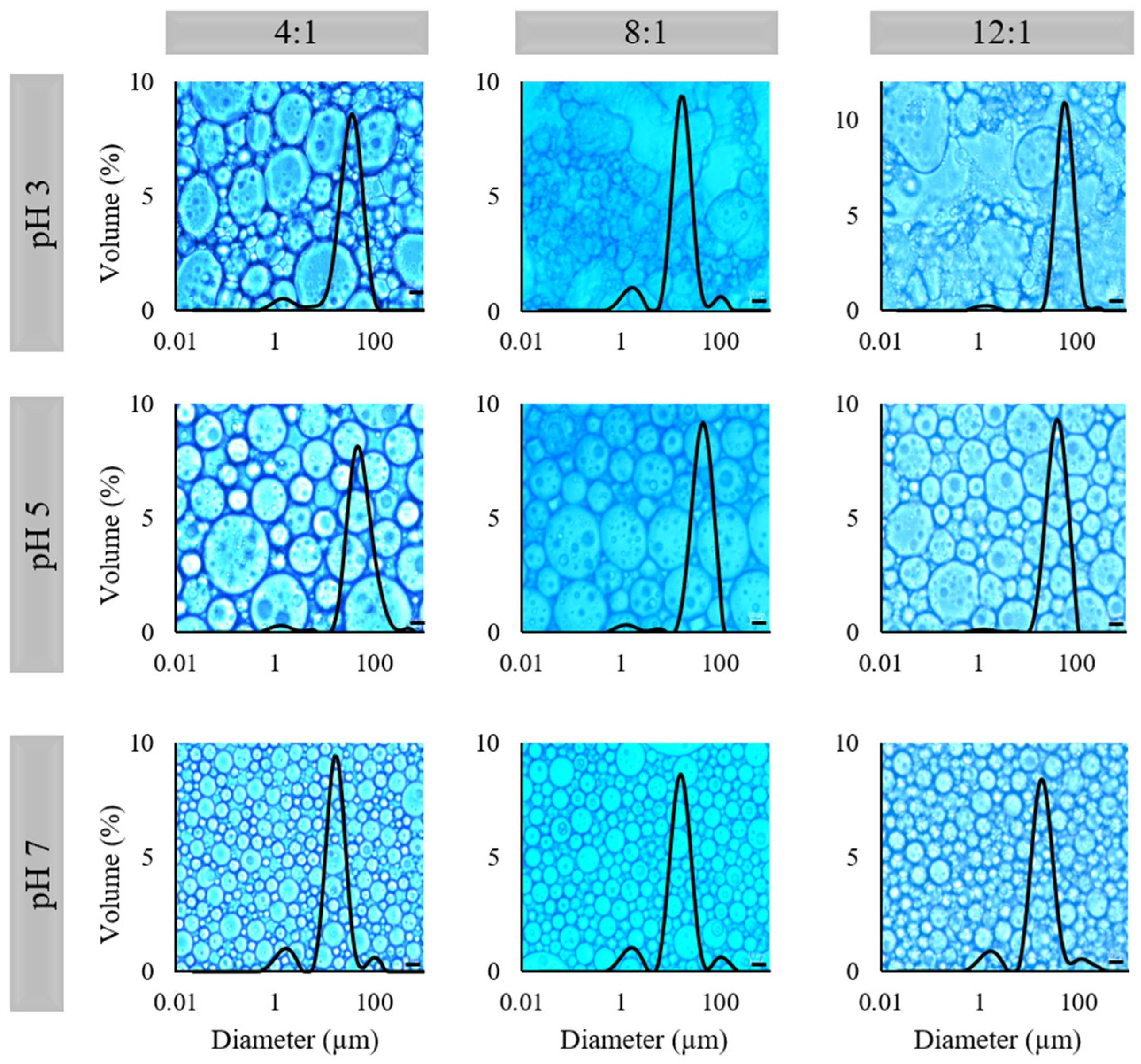
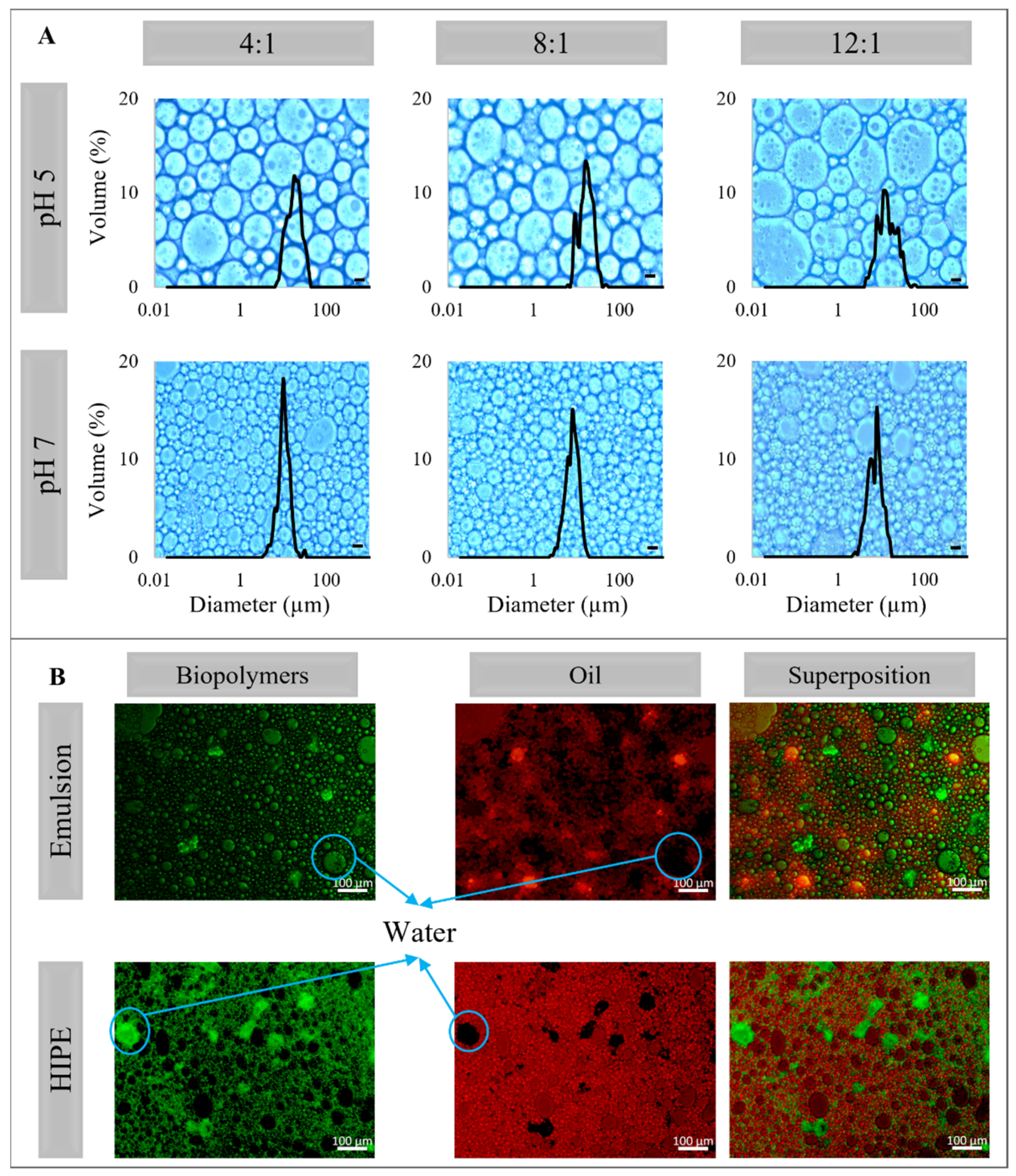
2.3. Microstructure and Droplet Size
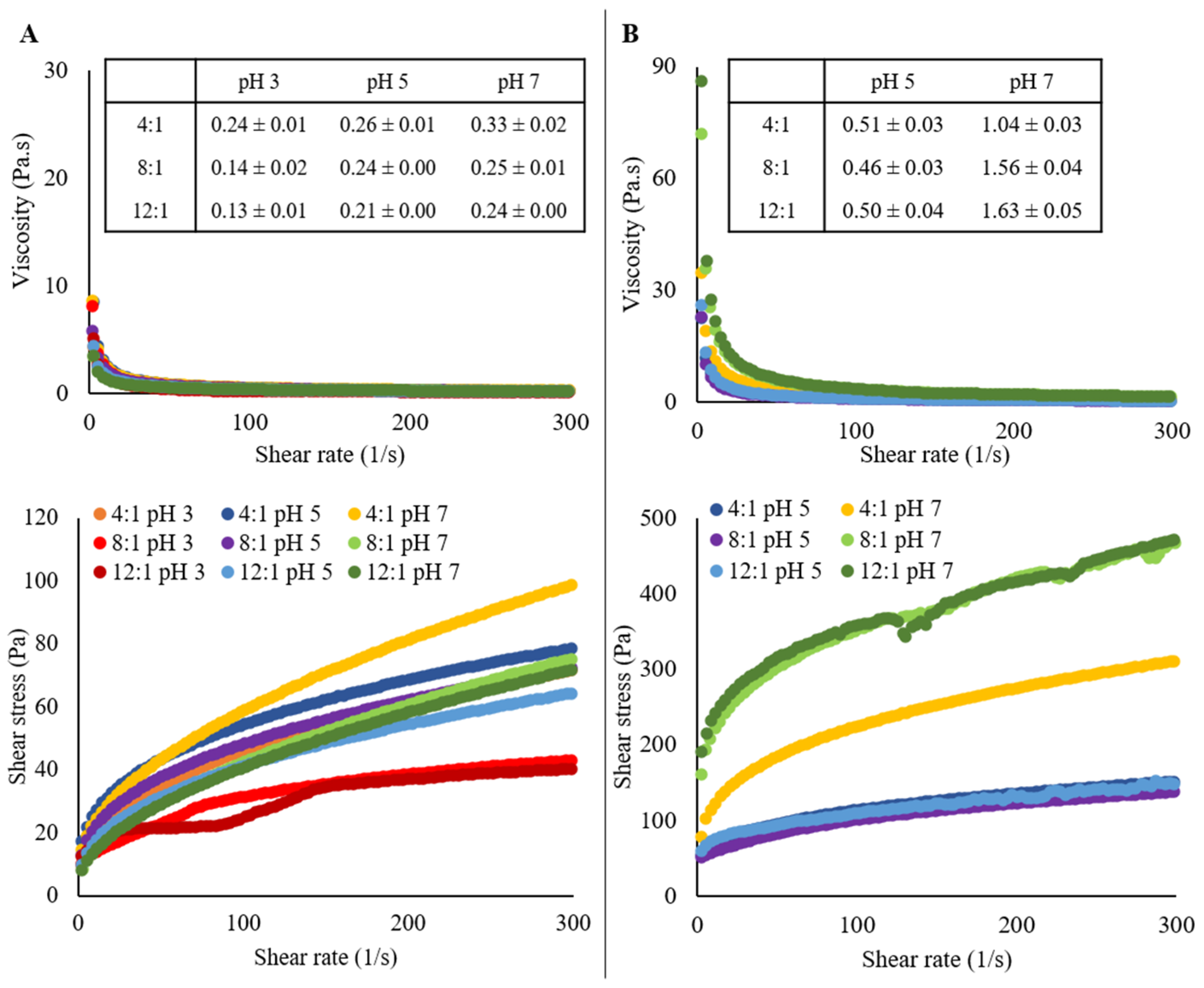
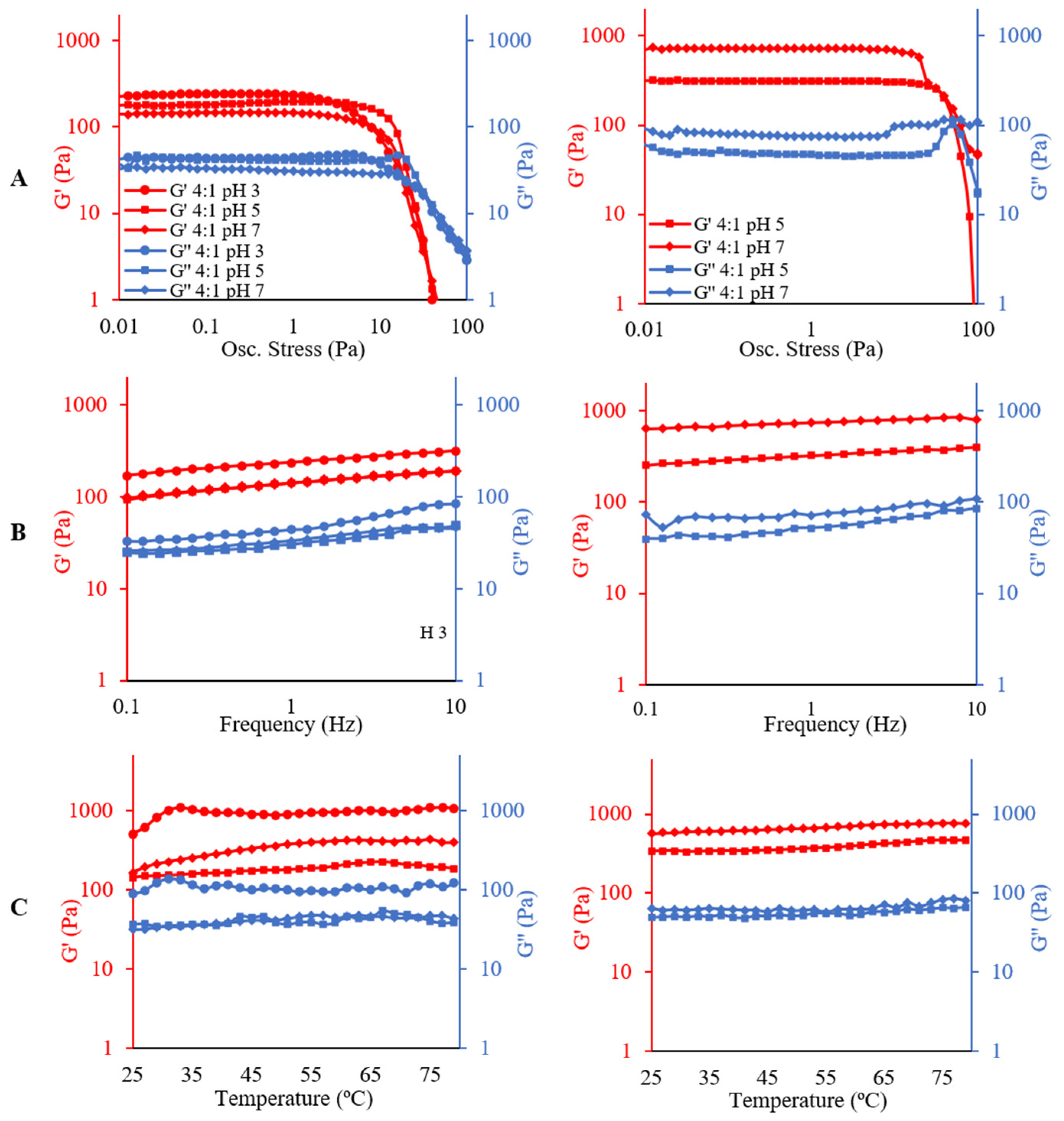
2.4. Rheological Analysis
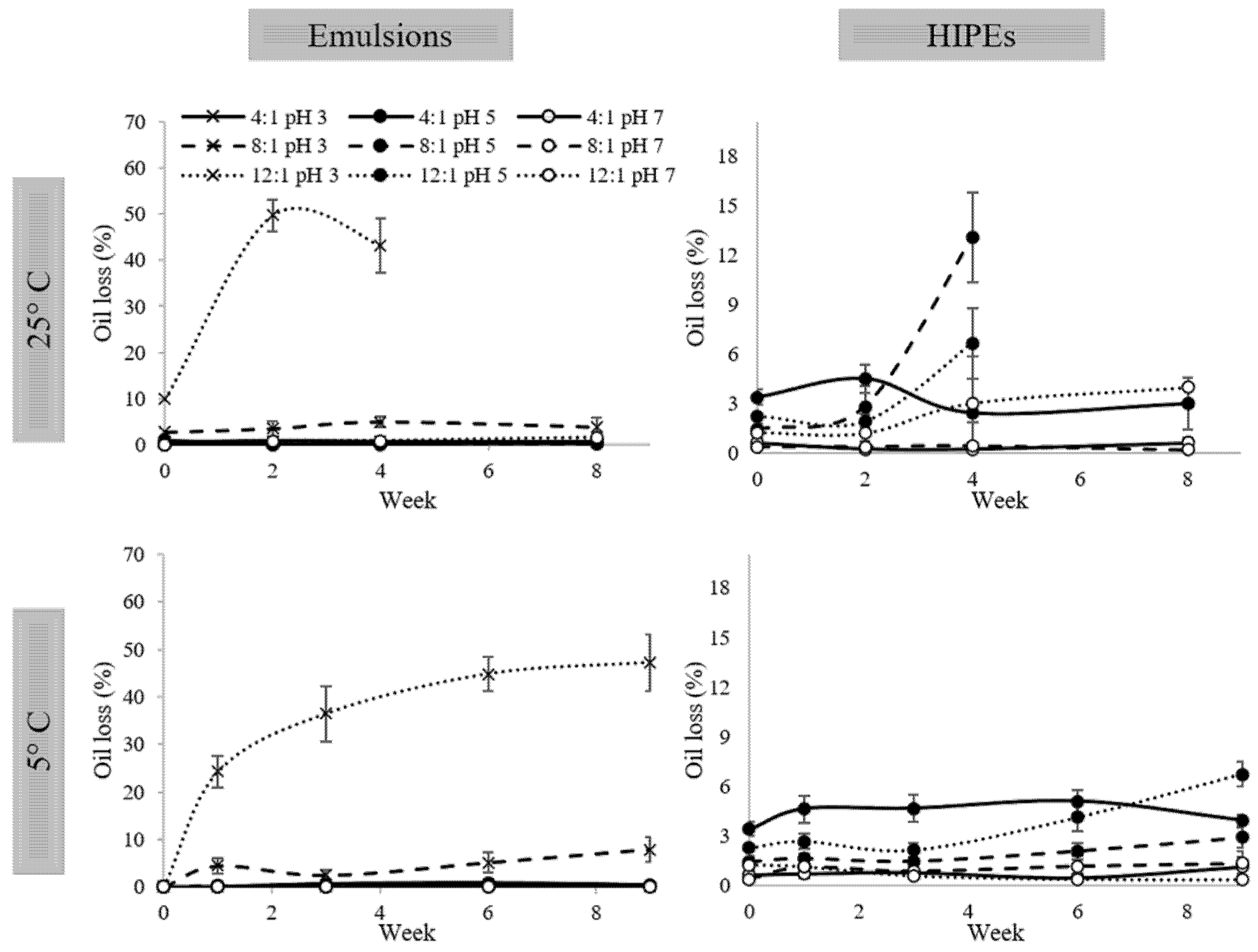
2.5. Oil Release
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Material
3.2. Protein Solubility
3.3. Zeta Potential of Polymers
3.4. Emulsion Preparation
3.5. High Internal Phase Emulsion (HIPE) Preparation
3.6. Emulsions and HIPEs Characterization
3.6.1. Microstructure
3.6.2. Droplet Size
3.6.3. Rheological Assays
3.6.4. Oil Loss Determination
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Appendix A
References
- Ferro, A.C.; Okuro, P.K.; Badan, A.P.; Cunha, R.L. Role of the oil on glyceryl monostearate based oleogels. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, E.; Sahari, M.A.; Barzegar, M.; Gavlighi, H.A. Novel oleogel formulation based on amaranth oil: Physicochemical characterization. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1986–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Said dos Santos, R.; Rosseto, H.C.; Bassi da Silva, J.; Vecchi, C.F.; Caetano, W.; Bruschi, M.L. The effect of carbomer 934P and different vegetable oils on physical stability, mechanical and rheological properties of emulsion-based systems containing propolis. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 307, 112969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Lan, Y.; Cui, L.; Monono, E.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Formation, characterization, and potential food application of rice bran wax oleogels: Expeller-pressed corn germ oil versus refined corn oil. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De de Vries, A.; Gomez, Y.L.; Van Der Linden, E.; Scholten, E. The effect of oil type on network formation by protein aggregates into oleogels. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 11803–11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nephomnyshy, I.; Rosen-Kligvasser, J.; Davidovich-Pinhas, M. The development of a direct approach to formulate high oil content zein-based emulsion gels using moderate temperatures. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, W.; Sun, Q.Q.; Vermeir, L.; Dewettinck, K.; Patel, A.R.; Van der Meeren, P. pH and protein to polysaccharide ratio control the structural properties and viscoelastic network of HIPE-templated biopolymeric oleogels. Food Struct. 2019, 21, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, A.; Yu, W.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Xue, J.; Guo, Y. Structuring oil-in-water emulsion by forming egg yolk/alginate complexes: Their potential application in fabricating low-fat mayonnaise-like emulsion gels and redispersible solid emulsions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandagi, P.M.; Pandey, P.; Gadad, A.P.; Mastiholimath, V.S. Formulation and evaluation of microemulsion based luliconazole gel for topical delivery. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2020, 54, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satapathy, M.; Quereshi, D.; Hanh Nguyen, T.T.; Pani, D.; Mohanty, B.; Anis, A.; Maji, S.; Kim, D.; Sarkar, P.; Pal, K. Preparation and characterization of cocoa butter and whey protein isolate based emulgels for pharmaceutical and probiotics delivery applications. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.W.; Fu, S.Y.; Hou, J.J.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.M.; Yang, X.Q. Zein based oil-in-glycerol emulgels enriched with β-carotene as margarine alternatives. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utrilla, M.C.; García Ruiz, A.; Soriano, A. Effect of partial replacement of pork meat with an olive oil organogel on the physicochemical and sensory quality of dry-ripened venison sausages. Meat Sci. 2014, 97, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Lu, W.; Kelly, A.L.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, B.; Miao, S. Interactions of vegetable proteins with other polymers: Structure-function relationships and applications in the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagoner, T.; Vardhanabhuti, B.; Foegeding, E.A. Designing whey protein–polysaccharide particles for colloidal stabilit. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemmer, K.J.; Waldner, L.; Stone, A.; Low, N.H.; Nickerson, M.T. Complex coacervation of pea protein isolate and alginate polysaccharides. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ochoa, F.; Santos, V.E.; Casas, J.A.; Gómez, E. Xanthan gum: Production, recovery, and properties. Biotechnol. Adv. 2000, 18, 549–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wei, T.; Wei, Z.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Influence of soybean soluble polysaccharides and beet pectin on the physicochemical properties of lactoferrin-coated orange oil emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corstens, M.N.; Osorio Caltenco, L.A.; de Vries, R.; Schroën, K.; Berton-Carabin, C.C. Interfacial behaviour of biopolymer multilayers: Influence of in vitro digestive conditions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 153, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzey, D.; McClements, D.J. Formation, stability and properties of multilayer emulsions for application in the food industry. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavernier, I.; Patel, A.R.; Van der Meeren, P.; Dewettinck, K. Emulsion-templated liquid oil structuring with soy protein and soy protein: K-carrageenan complexes. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 65, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, W.; Van der Meeren, P.; Wijaya, C.H.; Patel, A.R. High internal phase emulsions stabilized solely by whey protein isolate-low methoxyl pectin complexes: Effect of pH and polymer concentration. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.P.; Zhang, H.H.; Huang, G.Q.; Xiao, J.X. Whey protein isolate—Low methoxyl pectin coacervates as a high internal phase Pickering emulsion stabilizer. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 42, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Gan, C.; Wen, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wu, X. Development of pea protein and high methoxyl pectin colloidal particles stabilized high internal phase pickering emulsions for β-carotene protection and delivery. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; McClements, D.J.; Zhu, Y.; Zou, L.; Zhou, W.; Liu, W. Fabrication of OSA starch/chitosan polysaccharide-based high internal phase emulsion via altering interfacial behaviors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10937–10946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Gu, L.; Su, Y.; Chang, C.; Dong, S.; Tang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Formation of egg yolk-modified starch complex and its stabilization effect on high internal phase emulsions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez-Erazo, E.M.; Bosqui, K.; Rabelo, R.S.; Kurozawa, L.E.; Hubinger, M.D. High internal phase emulsions (HIPE) using pea protein and different polysaccharides as stabilizers. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Natale, G.; Virgilio, N.; Heuzey, M.C. Synergistic gelation of gelatin B with xanthan gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.; Xanthakis, E.; Langton, M.; Menzel, C.; Vilaplana, F.; Johansson, D.P.; Lopez-Sanchez, P. Mixed legume systems of pea protein and unrefined lentil fraction: Textural properties and microstructure. LWT 2021, 144, 111212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, B.; Shi, A.; Wang, Q.; Binks, B.P. High-internal-phase pickering emulsions stabilized solely by peanut-protein-isolate microgel particles with multiple potential applications. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9274–9278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.Z.; Peng, X.-Q.; Tang, C.-H. Edible pickering high internal phase emulsions stabilized by soy glycinin: Improvement of emulsification performance and pickering stabilization by glycation with soy polysaccharide. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; McClements, D.J. Theoretical stability maps for guiding preparation of emulsions stabilized by protein-polysaccharide interfacial complexes. Langmuir 2009, 25, 6649–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Gu, Y.; Xia, S.; Huang, Q. High internal phase pickering emulsions stabilized by pea protein isolate-high methoxyl pectin-EGCG complex: Interfacial properties and microstructure. Food Chem. 2021, 350, 129251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.; Costa, A.L.R.; de Assis Perrechil, F.; da Cunha, R.L. Role of the phases composition on the incorporation of gallic acid in O/W and W/O emulsions. J. Food Eng. 2016, 168, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yousefi, A.R.; Razavi, S.M.A. Dynamic rheological properties of wheat starch gels as affected by chemical modification and concentration. Starch-Stärke 2015, 67, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffe, J.F. Rheological Methods in Food Process Engineering, 2nd ed.; Freeman Press: East Lansing, MI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.H.; Ross-Murphy, S.B. Structural and mechanical properties of biopolymer gels. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1987, 83, 57–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Sui, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mao, Z.; Xu, H. Cellulose-rich oleogels prepared with an emulsion-templated approach. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Qi, K.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Effects of thickening agents on the formation and properties of edible oleogels based on hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Qi, K.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Macro-micro structure characterization and molecular properties of emulsion-templated polysaccharide oleogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Dumlu, P.; Vermeir, L.; Lewille, B.; Lesaffer, A.; Dewettinck, K. Rheological characterization of gel-in-oil-in-gel type structured emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 46, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, A.R.; Rajarethinem, P.S.; Cludts, N.; Lewille, B.; De Vos, W.H.; Lesaffer, A.; Dewettinck, K. Biopolymer-based structuring of liquid oil into soft solids and oleogels using water-continuous emulsions as templates. Langmuir 2015, 31, 2065–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.N.; Zhou, F.Z.; Yang, T.; Yin, S.W.; Tang, C.H.; Yang, X.Q. Fabrication and characterization of Pickering High Internal Phase Emulsions (HIPEs) stabilized by chitosan-caseinophosphopeptides nanocomplexes as oral delivery vehicles. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye bindin. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saout, C.; Quéré, C.; Donval, A.; Paulet, Y.M.; Samain, J.F. An experimental study of the combined effects of temperature and photoperiod on reproductive physiology of Pecten maximus from the bay of brest (France). Aquaculture 1999, 172, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
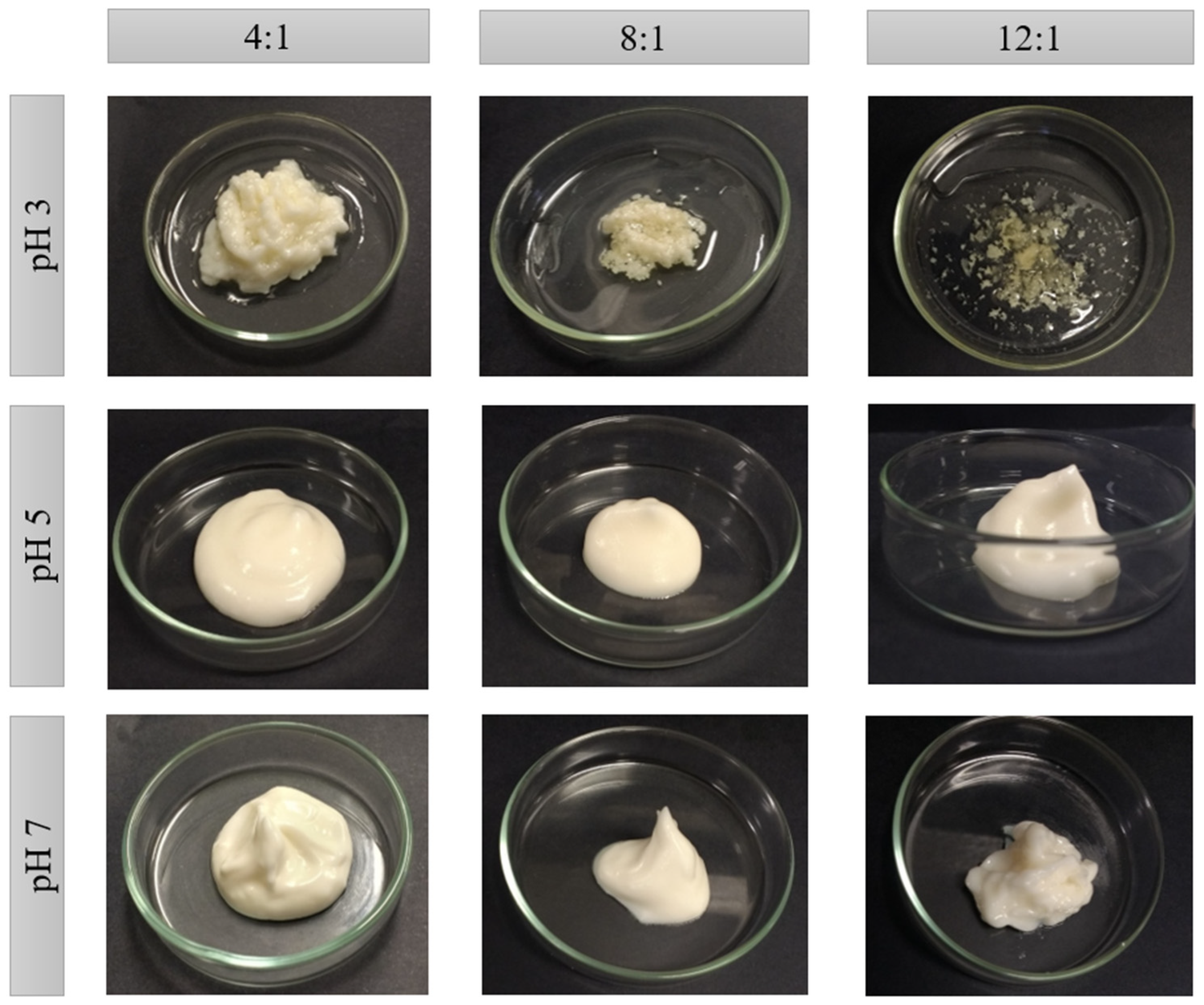
| Ratio | pH | Mass Loss (g) | Total Mass (g) | Water | Oil | PP + XG | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g | % | g | % | g | % | ||||
| 4:1 | 3 | 33.33 ± 0.59 Ab | 66.67 | 5.87 | 8.80 | 60.00 | 90.00 | 0.80 | 1.20 |
| 5 | 17.38 ± 0.80 Cc | 82.62 | 21.82 | 26.41 | 60.00 | 72.62 | 0.80 | 0.97 | |
| 7 | 22.38 ± 0.36 Bc | 77.62 | 16.82 | 21.67 | 60.00 | 77.30 | 0.80 | 1.03 | |
| 8:1 | 3 | 37.28 ± 0.40 Aa | 62.72 | 1.92 | 3.06 | 60.00 | 95.66 | 0.80 | 1.28 |
| 5 | 23.17 ± 1.76 Cb | 76.83 | 16.03 | 20.86 | 60.00 | 78.09 | 0.80 | 1.04 | |
| 7 | 29.83 ± 1.05 Bb | 70.17 | 9.37 | 13.35 | 60.00 | 85.51 | 0.80 | 1.14 | |
| 12:1 | 3 | 37.96 ± 1.87 Aa | 62.04 | 1.24 | 2.00 | 60.00 | 96.71 | 0.80 | 1.29 |
| 5 | 26.38 ± 1.03 Ca | 73.62 | 12.82 | 17.41 | 60.00 | 81.50 | 0.80 | 1.09 | |
| 7 | 31.26 ± 0.90 Ba | 68.74 | 7.94 | 11.55 | 60.00 | 87.29 | 0.80 | 1.16 | |
| Emulsions | HIPEs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratio | pH | D[4,3] (µm) | Mo (µm) | Span | D[4,3] (µm) * | D[Th] (µm) | Mo (µm) * | Span * |
| 4:1 | 3.0 | 34.28 ± 0.89 Bc | 36.29 ± 1.77 Bb | 1.42 ± 0.04 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| 5.0 | 51.79 ± 7.20 Aa | 43.96 ± 1.99 Aab | 1.51 ± 0.23 | 27.16 | 20.38 ± 6.22 | 22.44 | 1.05 | |
| 7.0 | 19.17 ± 0.65 Cb | 16.21 ± 0.79 Cb | 1.57 ± 0.11 | 16.33 | 11.46 ± 2.83 | 10.02 | 0.80 | |
| 8:1 | 3.0 | 51.95 ± 2.16 Ab | 55.35 ± 2.50 Aa | 1.24 ± 0.05 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| 5.0 | 43.61 ± 1.9 Ab | 45.68 ± 2.23 Ba | 1.21 ± 0.08 | 25.38 | 18.99 ± 5.39 | 15.88 | 0.91 | |
| 7.0 | 18.75 ± 0.52 Bb | 15.60 ± 0.71 Cb | 1.71 ± 0.04 | 10.86 | 8.74 ± 2.30 | 7.96 | 0.89 | |
| 12:1 | 3.0 | 59.56 ± 1.42 Ca | 57.51 ± 2.81 Aa | 1.17 ± 0.08 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| 5.0 | 40.60 ± 1.19 Bb | 41.53 ± 2.51 Bb | 1.28 ± 0.06 | 31.25 | 16.60 ± 6.81 | 12.62 | 1.48 | |
| 7.0 | 23.16 ± 1.04 Aa | 18.55 ± 1.12 Ca | 1.61 ± 0.13 | 10.71 | 8.00 ± 2.42 | 7.86 | 1.01 | |
| PP:XG | pH | G′LVR (Pa) | G″LVR (Pa) | OSL (Pa) | Tan δLVR | FPs (Pa) | FPG (Pa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emulsions | 4:1 | 3 | 236 ± 4 Ab | 43 ± 1 Aa | 0.71 ± 0.08 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 22.52 ± 2.58 | 22 ± 1 |
| 5 | 185 ± 6 Ba | 41 ± 2 Aa | 3.57 ± 0.41 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 17.90 ± 2.05 | 38 ± 4 | ||
| 7 | 144 ± 2 Ca | 32 ± 1 Ba | 1.79 ± 0.20 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 17.90 ± 2.05 | 21 ± 4 | ||
| 8:1 | 3 | 253 ± 2 Aa | 40 ± 2 Aa | 2.17 ± 0.23 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 62.99 ± 0.03 | 24 ± 1 | |
| 5 | 140 ± 1 Bb | 31 ± 2 Bb | 1.86 ± 0.18 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 14.22 ± 1.63 | 23 ± 6 | ||
| 7 | 98 ± 2 Cc | 31 ± 2 Ba | 0.71 ± 0.08 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 7.94 ± 0.00 | 21 ± 1 | ||
| 12:1 | 3 | 253 ± 2 Aa | 38 ± 1 Aa | 2.72 ± 0.28 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 50.10 ± 0.01 | 26 ± 3 | |
| 5 | 128 ± 1 Bc | 26 ± 1 Bc | 1.42 ± 0.16 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 17.89 ± 2.05 | 33 ± 9 | ||
| 7 | 113 ± 2 Cb | 22 ± 1 Cb | 0.90 ± 0.20 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 9.99 ± 0.01 | 20 ± 1 | ||
| HIPEs | 4:1 | 5 | 311 ± 2 Bc | 48 ± 2 | 5.66 ± 0.65 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 50.11 ± 0.01 | 108 ± 6 |
| 7 | 726 ± 4 Ac | 79 ± 4 | 2.25 ± 0.26 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 60.65 ± 5.15 | 107 ± 8 | ||
| 8:1 | 5 | 323 ± 1 Ba | 54 ± 3 | 3.57 ± 0.41 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 56.60 ± 6.49 | 78 ± 6 | |
| 7 | 1183 ± 3 Aa | 105 ± 6 | 11.29 ± 1.29 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | -- | -- | ||
| 12:1 | 5 | 319 ± 1 Bb | 43 ± 1 | 4.50 ± 0.51 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 86.28 ± 9.14 | 76 ± 3 | |
| 7 | 1035 ± 3 Ab | 90 ± 6 | 14.22 ± 1.63 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | -- | -- |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vélez-Erazo, E.M.; Bosqui, K.; Rabelo, R.S.; Hubinger, M.D. Effect of pH and Pea Protein: Xanthan Gum Ratio on Emulsions with High Oil Content and High Internal Phase Emulsion Formation. Molecules 2021, 26, 5646. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185646
Vélez-Erazo EM, Bosqui K, Rabelo RS, Hubinger MD. Effect of pH and Pea Protein: Xanthan Gum Ratio on Emulsions with High Oil Content and High Internal Phase Emulsion Formation. Molecules. 2021; 26(18):5646. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185646
Chicago/Turabian StyleVélez-Erazo, Eliana Marcela, Karina Bosqui, Renata S. Rabelo, and Miriam Dupas Hubinger. 2021. "Effect of pH and Pea Protein: Xanthan Gum Ratio on Emulsions with High Oil Content and High Internal Phase Emulsion Formation" Molecules 26, no. 18: 5646. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185646
APA StyleVélez-Erazo, E. M., Bosqui, K., Rabelo, R. S., & Hubinger, M. D. (2021). Effect of pH and Pea Protein: Xanthan Gum Ratio on Emulsions with High Oil Content and High Internal Phase Emulsion Formation. Molecules, 26(18), 5646. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185646







